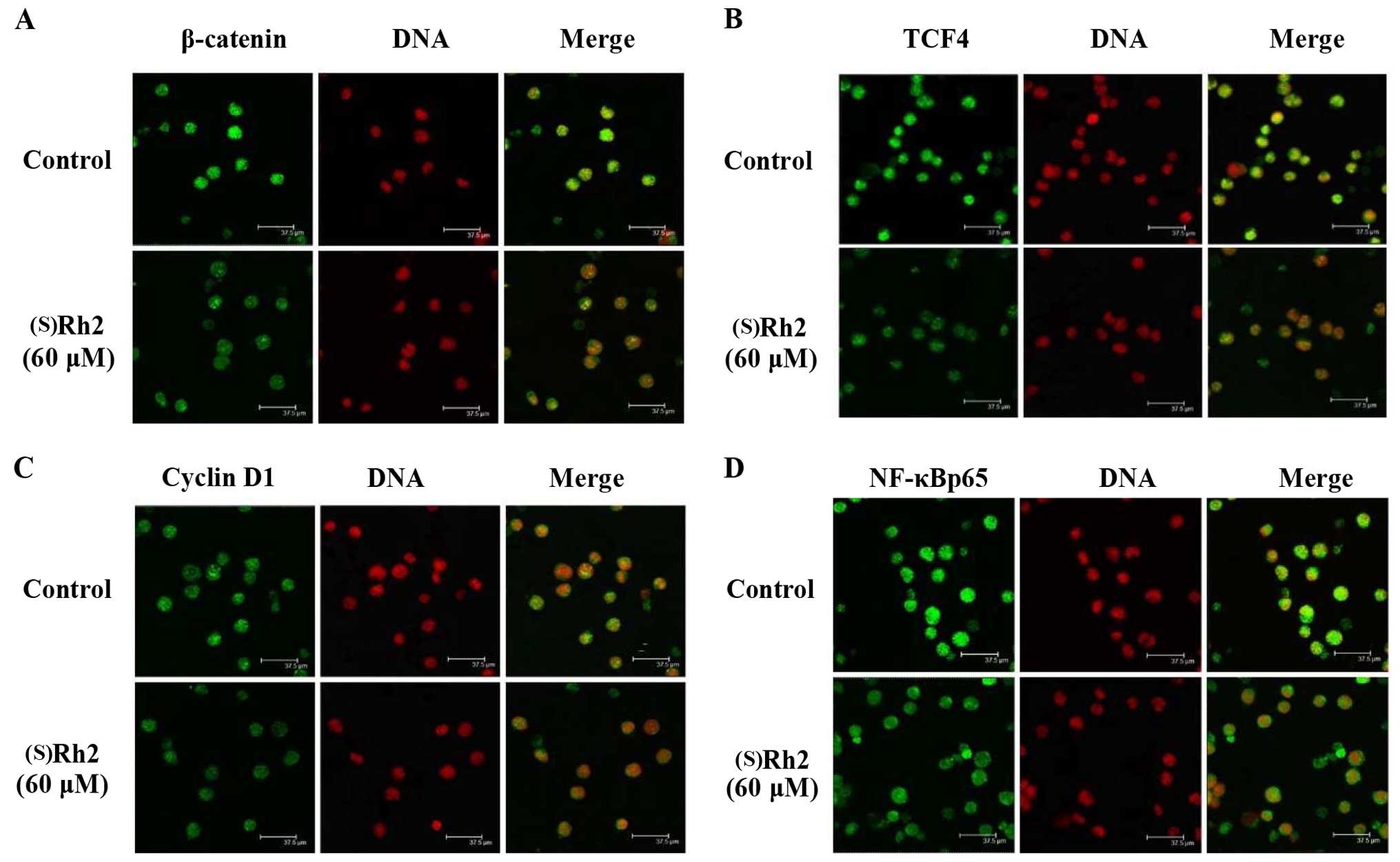
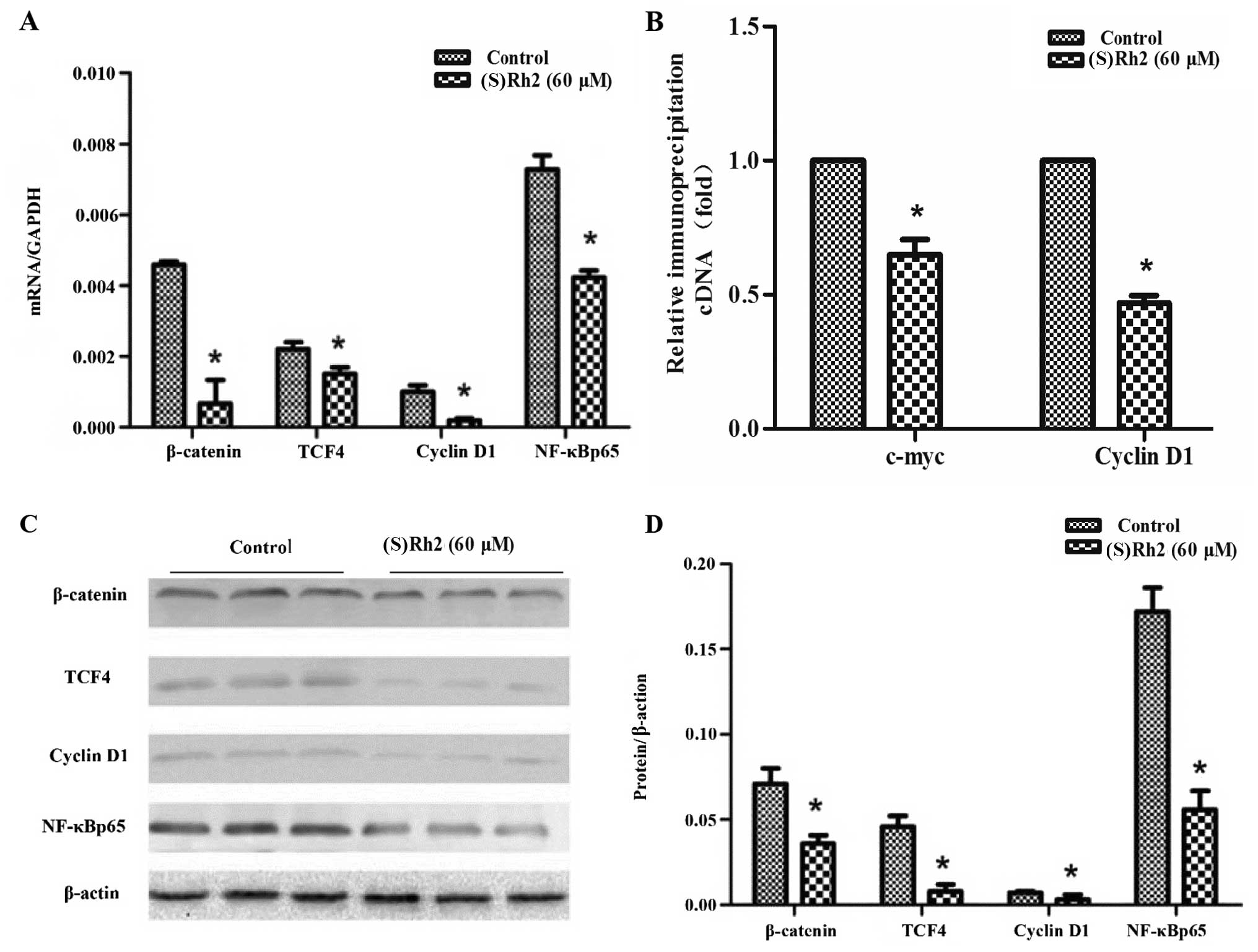
|
1
|
Pui C-H, Robison LL and Look AT: Acute
lymphoblastic leukaemia. Lancet. 371:1030–1043. 2008. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
2
|
Jia WD, Sun HC, Zhang JB, Xu Y, Qian YB,
Pang JZ, Wang L, Qin LX, Liu YK and Tang ZY: A novel peptide that
selectively binds highly metastatic hepatocellular carcinoma cell
surface is related to invasion and metastasis. Cancer Lett.
247:234–242. 2007. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
3
|
Wang S, Wu X, Tan M, Gong J, Tan W, Bian
B, Chen M and Wang Y: Fighting fire with fire: poisonous Chinese
herbal medicine for cancer therapy. J Ethnopharmacol. 140:33–45.
2012. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
4
|
Kitaoka F, Kakiuchi N, Long C, Itoga M,
Mitsue A, Mouri C and Mikage M: Molecular characterization of
akebia plants and the derived traditional herbal medicine. Biol
Pharm Bull. 32:665–670. 2009. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
5
|
Xia T, Wang JC, Xu W, Xu LH, Lao CH, Ye QX
and Fang JP: 20S-ginsenoside Rh2 induces apoptosis in human
leukaemia Reh cells through mitochondrial signaling pathways. Biol
Pharm Bull. 37:248–254. 2014. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
6
|
Toh DF, Patel DN, Chan EC, Teo A, Neo SY
and Koh HL: Anti-proliferative effects of raw and steamed extracts
of Panax notoginseng and its ginsenoside constituents on human
liver cancer cells. Chin Med. 6:42011. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
7
|
Shergis JL, Zhang AL, Zhou W and Xue CC:
Panax ginseng in randomised controlled trials: a systematic review.
Phytother Res. 27:949–965. 2013. View
Article : Google Scholar
|
|
8
|
Lee HS, Kim MR, Park Y, Park HJ, Chang UJ,
Kim SY and Suh HJ: Fermenting red ginseng enhances its safety and
efficacy as a novel skin care anti-aging ingredient: in vitro and
animal study. J Med Food. 15:1015–1023. 2012. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
9
|
Wang JWLR, Wang YP, et al: The role of
total saponins of panax ginseng in vitro induced CD34 hematopoietic
stem/progenitor cell proliferation. Chin J Anat. 29:430–432.
2006.
|
|
10
|
Zhang C, Yu H and Hou J: Effects of 20 (S)
-ginsenoside Rh2 and 20 (R)-ginsenoside Rh2 on proliferation and
apoptosis of human lung adenocarcinoma A549 cells. Zhongguo Zhong
Yao Za Zhi. 36:1670–1674. 2011.In Chinese. PubMed/NCBI
|
|
11
|
Shi Q, Li J, Feng Z, Zhao L, Luo L, You Z,
Li D, Xia J, Zuo G and Chen D: Effect of ginsenoside Rh2 on the
migratory ability of HepG2 liver carcinoma cells: recruiting
histone deacetylase and inhibiting activator protein 1
transcription factors. Mol Med Rep. 10:1779–1785. 2014.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
12
|
Guo XX, Li Y, Sun C, Jiang D, Lin YJ, Jin
FX, Lee SK and Jin YH: p53-dependent Fas expression is critical for
ginsenoside Rh2 triggered caspase-8 activation in HeLa cells.
Protein Cell. 5:224–234. 2014. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
13
|
Yang JH, Han SJ, Ryu JH, Jang IS and Kim
DH: Ginsenoside Rh2 ameliorates scopolamine-induced learning
deficit in mice. Biol Pharm Bull. 32:1710–1715. 2009. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
14
|
Bae EA, Han MJ, Shin YW and Kim DH:
Inhibitory effects of Korean red ginseng and its genuine
constituents ginsenosides Rg3, Rf, and Rh2 in mouse passive
cutaneous anaphylaxis reaction and contact dermatitis models. Biol
Pharm Bull. 29:1862–1867. 2006. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
15
|
Nam MH, Kim SI, Liu JR, Yang DC, Lim YP,
Kwon KH, Yoo JS and Park YM: Proteomic analysis of Korean ginseng
(Panax ginseng C.A. Meyer). J Chromatogr B Analyt Technol Biomed
Life Sci. 815:147–155. 2005. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
16
|
Kitts DD, Popovich DG and Hu C:
Characterizing the mechanism for ginsenoside-induced cytotoxicity
in cultured leukemia (THP-1) cells. Can J Physiol Pharmacol.
85:1173–1183. 2007. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
17
|
Dunn IF and Black PM: The neurosurgeon as
local oncologist: cellular and molecular neurosurgery in malignant
glioma therapy. Neurosurgery. 52:1411–1422. 2003. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
18
|
Wu N, Wu GC, Hu R, Li M and Feng H:
Ginsenoside Rh2 inhibits glioma cell proliferation by targeting
microRNA-128. Acta Pharmacol Sin. 32:345–353. 2011. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
19
|
Qu X, Qu S, Yu X, Xu H, Chen Y, Ma X and
Sui D: Pseudo-G-Rh2 induces mitochondrial-mediated apoptosis in
SGC-7901 human gastric cancer cells. Oncol Rep. 26:1441–1446.
2011.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
20
|
Kim MJ, Yun H, Kim DH, Kang I, Choe W, Kim
SS and Ha J: AMP-activated protein kinase determines apoptotic
sensitivity of cancer cells to ginsenoside-Rh2. J Ginseng Res.
38:16–21. 2014. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
21
|
Cadigan KM and Nusse R: Wnt signaling: a
common theme in animal development. Genes Dev. 11:3286–3305. 1997.
View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
22
|
Neppl RL and Wang DZ: The myriad essential
roles of microRNAs in cardiovascular homeostasis and disease. Genes
Dis. 1:18–39. 2014. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
23
|
Polakis P: Drugging Wnt signalling in
cancer. EMBO J. 31:2737–2746. 2012. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
24
|
Lu D, Zhao Y, Tawatao R, Cottam HB, Sen M,
Leoni LM, Kipps TJ, Corr M and Carson DA: Activation of the Wnt
signaling pathway in chronic lymphocytic leukemia. Proc Natl Acad
Sci USA. 101:3118–3123. 2004. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
25
|
Lu D, Liu JX, Endo T, Zhou H, Yao S,
Willert K, Schmidt-Wolf IG, Kipps TJ and Carson DA: Ethacrynic acid
exhibits selective toxicity to chronic lymphocytic leukemia cells
by inhibition of the Wnt/beta-catenin pathway. PLoS One.
4:e82942009. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
26
|
Wang W, Wang H, Rayburn ER, Zhao Y, Hill
DL and Zhang R: 20(S)-25-methoxyl-dammarane-3beta, 12beta,
20-triol, a novel natural product for prostate cancer therapy:
activity in vitro and in vivo and mechanisms of action. Br J
Cancer. 98:792–802. 2008. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
27
|
Nag SA, Qin JJ, Wang W, Wang MH, Wang H
and Zhang R: Ginsenosides as anticancer agents: in vitro and in
vivo activities, structure-activity relationships, and molecular
mechanisms of action. Front Pharmacol. 3:252012. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
28
|
Takahashi-Yanaga F and Sasaguri T: The
Wnt/beta-catenin signaling pathway as a target in drug discovery. J
Pharmacol Sci. 104:293–302. 2007. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
29
|
Mai YJ, Qiu LG, Li ZJ, Yu Z, Li CH, Wang
YF, Wang GR and Li Q: The expression of beta-catenin and its
significance in leukemia cells. Zhonghua Xue Ye Xue Za Zhi.
28:541–544. 2007.In Chinese. PubMed/NCBI
|
|
30
|
Saldanha G, Ghura V, Potter L and Fletcher
A: Nuclear beta-catenin in basal cell carcinoma correlates with
increased proliferation. Br J Dermatol. 151:157–164. 2004.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
31
|
Minke KS, Staib P, Puetter A, Gehrke I,
Gandhirajan RK, Schlösser A, Schmitt EK, Hallek M and Kreuzer KA:
Small molecule inhibitors of WNT signaling effectively induce
apoptosis in acute myeloid leukemia cells. Eur J Haematol.
82:165–175. 2009. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
32
|
in't Hout FE, van der Reijden BA,
Monteferrario D, Jansen JH and Huls G: High expression of
transcription factor 4 (TCF4) is an independent adverse prognostic
factor in acute myeloid leukemia that could guide treatment
decisions. Haematologica. 99:e257–e259. 2014. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
33
|
Chang HR, Cheng TL, Liu TZ, Hu HS, Hsu LS,
Tseng WC, Chen CH and Tsao DA: Genetic and cellular
characterizations of human TCF4 with microsatellite instability in
colon cancer and leukemia cell lines. Cancer Lett. 233:165–171.
2006. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
34
|
Tian W, Xu Y, Han X, Duggineni S, Han X,
Huang Z and An J: Development of a novel fluorescence
polarization-based assay for studying the β-catenin/Tcf4
interaction. J Biomol Screen. 17:530–534. 2012. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
35
|
Cadigan KM: Wnt-beta-catenin signaling.
Curr Biol. 18:R943–R947. 2008. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
36
|
Lento W, Congdon K, Voermans C, Kritzik M
and Reya T: Wnt signaling in normal and malignant hematopoiesis.
Cold Spring Harb Perspect Biol. 5:pii: a008011. 2013. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
37
|
Dai WB, Ren ZP, Chen WL, Du J, Shi Z and
Tang DY: Expression and significance of APC, beta-catenin, C-myc,
and cyclin D1 proteins in colorectal carcinoma. Ai Zheng. 26:963–6.
2007.In Chinese. PubMed/NCBI
|
|
38
|
Baek SH, Kioussi C, Briata P, Wang D,
Nguyen HD, Ohgi KA, Glass CK, Wynshaw-Boris A, Rose DW and
Rosenfeld MG: Regulated subset of G1 growth-control genes in
response to derepression by the Wnt pathway. Proc Natl Acad Sci
USA. 100:3245–3250. 2003. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
39
|
He TC, Sparks AB, Rago C, Hermeking H,
Zawel L, da Costa LT, Morin PJ, Vogelstein B and Kinzler KW:
Identification of c-MYC as a target of the APC pathway. Science.
281:1509–1512. 1998. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
40
|
Gandhirajan RK, Poll-Wolbeck SJ, Gehrke I
and Kreuzer KA: Wnt/β-catenin/LEF-1 signaling in chronic
lymphocytic leukemia (CLL): a target for current and potential
therapeutic options. Curr Cancer Drug Targets. 10:716–727. 2010.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
41
|
Tung JN, Chiang CC, Tsai YY, Chou YY, Yeh
KT, Lee H and Cheng YW: CyclinD1 protein expressed in pterygia is
associated with β-catenin protein localization. Mol Vis.
16:2733–2738. 2010.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
42
|
Wang YX, Zhang JH and Gu ZW: Beta-catenin
and cyclin D1 mRNA levels in newly diagnosed patients with acute
myeloid leukemia and their significance. Zhongguo Shi Yan Xue Ye
Xue Za Zhi. 17:304–308. 2009.In Chinese. PubMed/NCBI
|
|
43
|
Fabre C, Carvalho G, Tasdemir E, Braun T,
Adès L, Grosjean J, Boehrer S, Métivier D, Souquère S, Pierron G,
et al: NF-kappaB inhibition sensitizes to starvation-induced cell
death in high-risk myelodysplastic syndrome and acute myeloid
leukemia. Oncogene. 26:4071–4083. 2007. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
44
|
Frelin C, Imbert V, Griessinger E, Peyron
AC, Rochet N, Philip P, Dageville C, Sirvent A, Hummelsberger M,
Bérard E, et al: Targeting NF-kappaB activation via pharmacologic
inhibition of IKK2-induced apoptosis of human acute myeloid
leukemia cells. Blood. 105:804–811. 2005. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
45
|
Li K, Hu C, Mei C, Ren Z, Vera JC, Zhuang
Z, Jin J and Tong H: Sequential combination of decitabine and
idarubicin synergistically enhances anti-leukemia effect followed
by demethylating Wnt pathway inhibitor promoters and downregulating
Wnt pathway nuclear target. J Transl Med. 12:1672014. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
46
|
Chun KS and Surh YJ: Signal transduction
pathways regulating cyclooxygenase-2 expression: potential
molecular targets for chemoprevention. Biochem Pharmacol.
68:1089–1100. 2004. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
47
|
Yeh CT1, Yao CJ, Yan JL, Chuang SE, Lee
LM, Chen CM, Yeh CF, Li CH and Lai GM: Apoptotic cell death and
inhibition of Wnt/beta-catenin signaling pathway in human colon
cancer cells by an active fraction (hs7) from Taiwanofungus
camphoratus. Evid Based Complement Alternat Med. 2011:7502302011.
View Article : Google Scholar
|