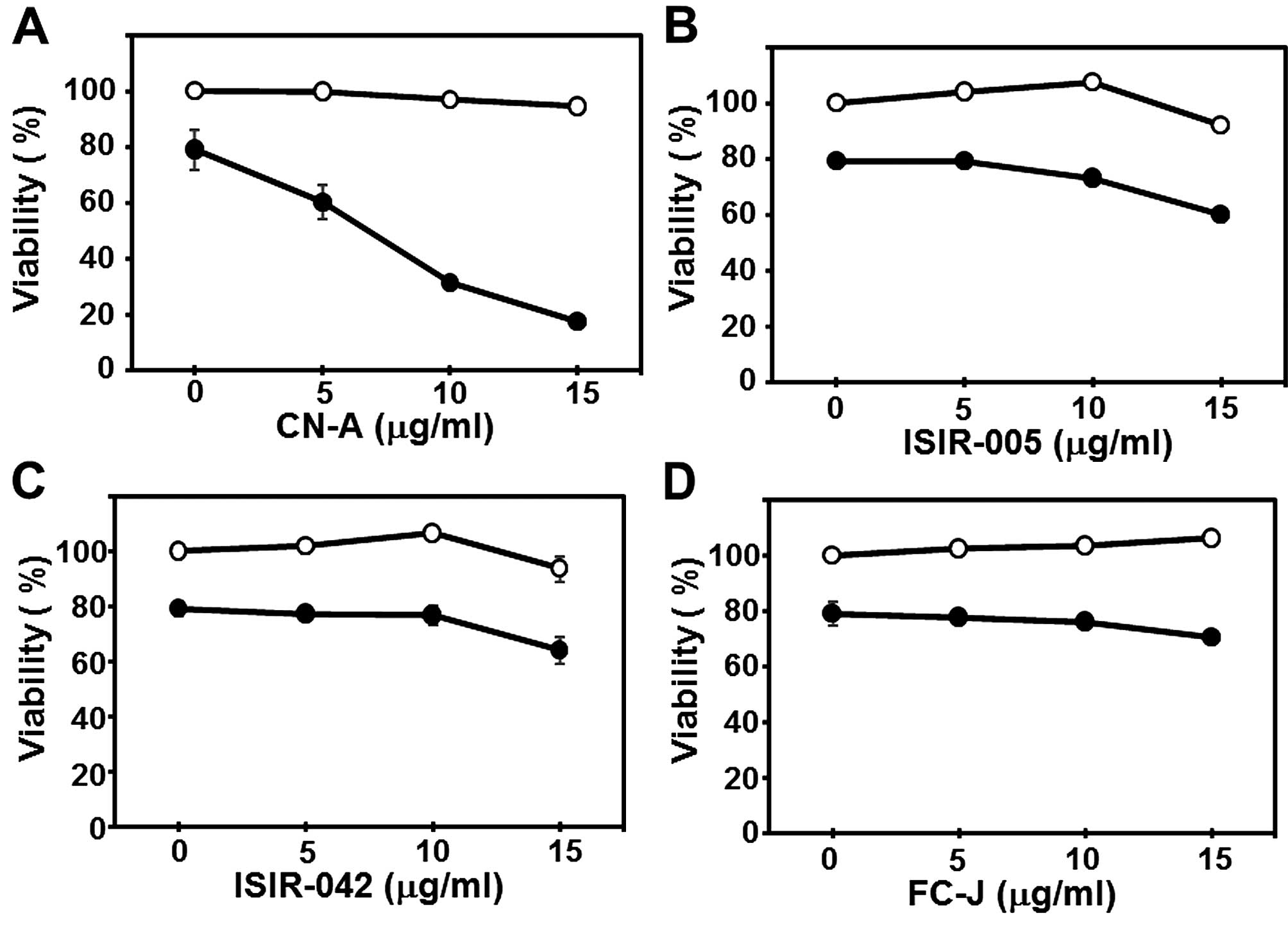
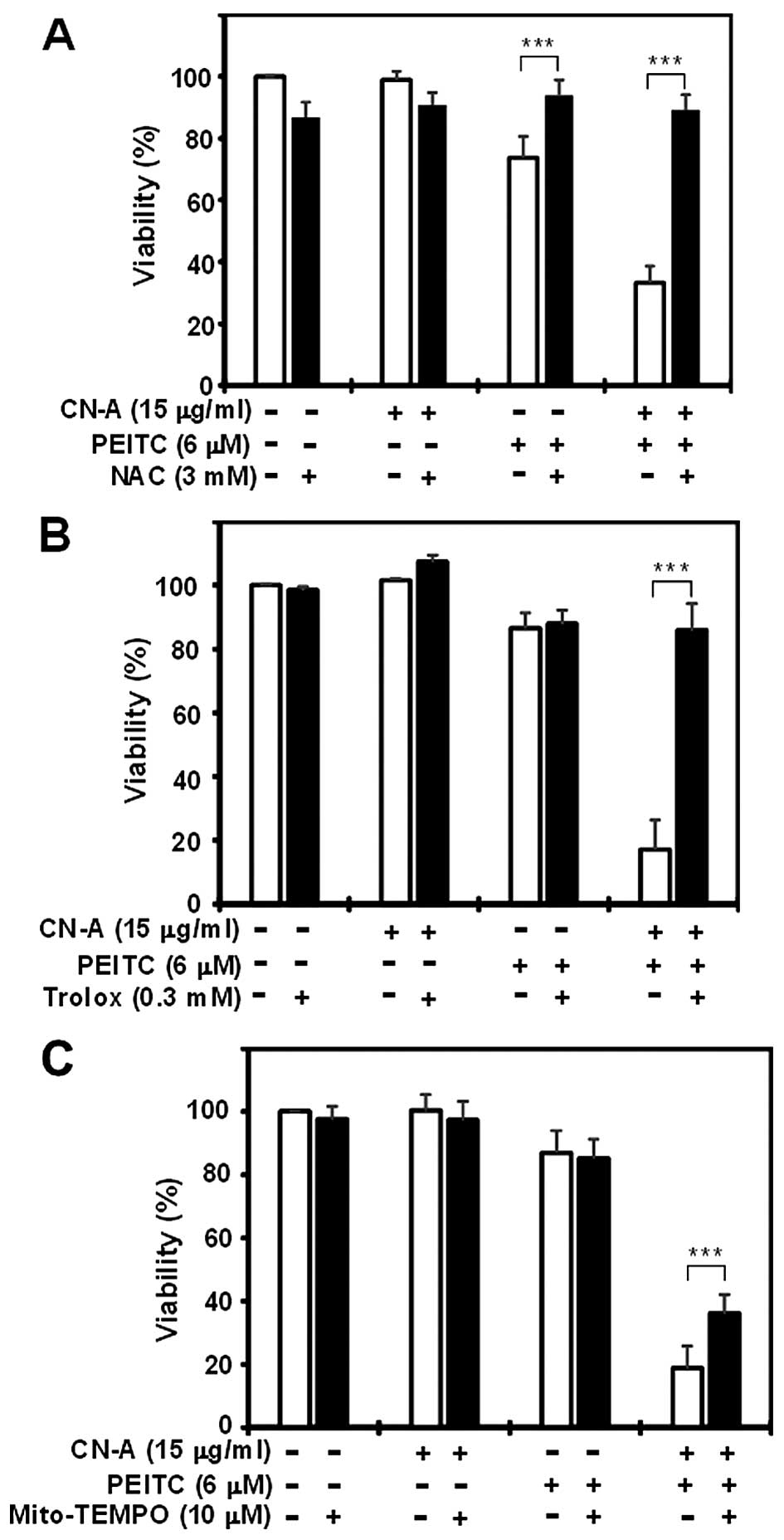
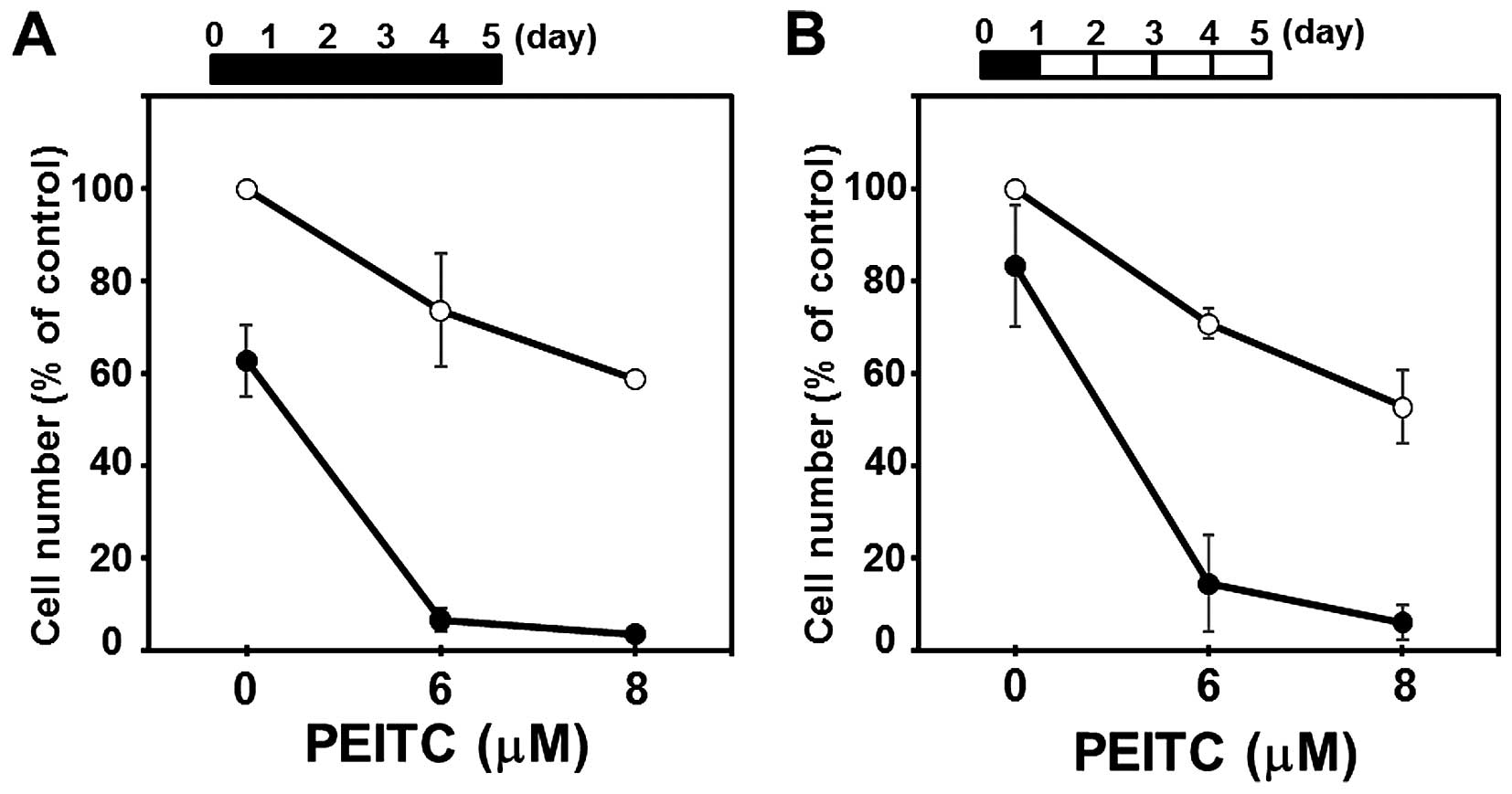
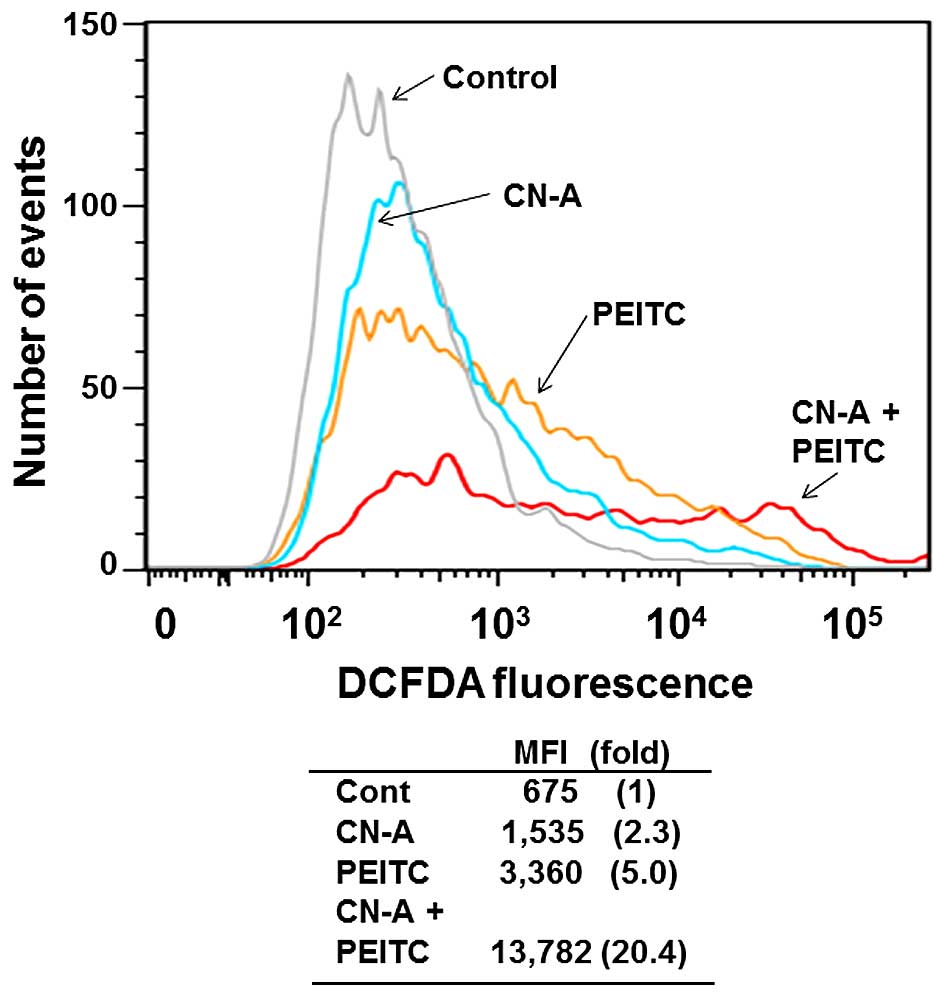
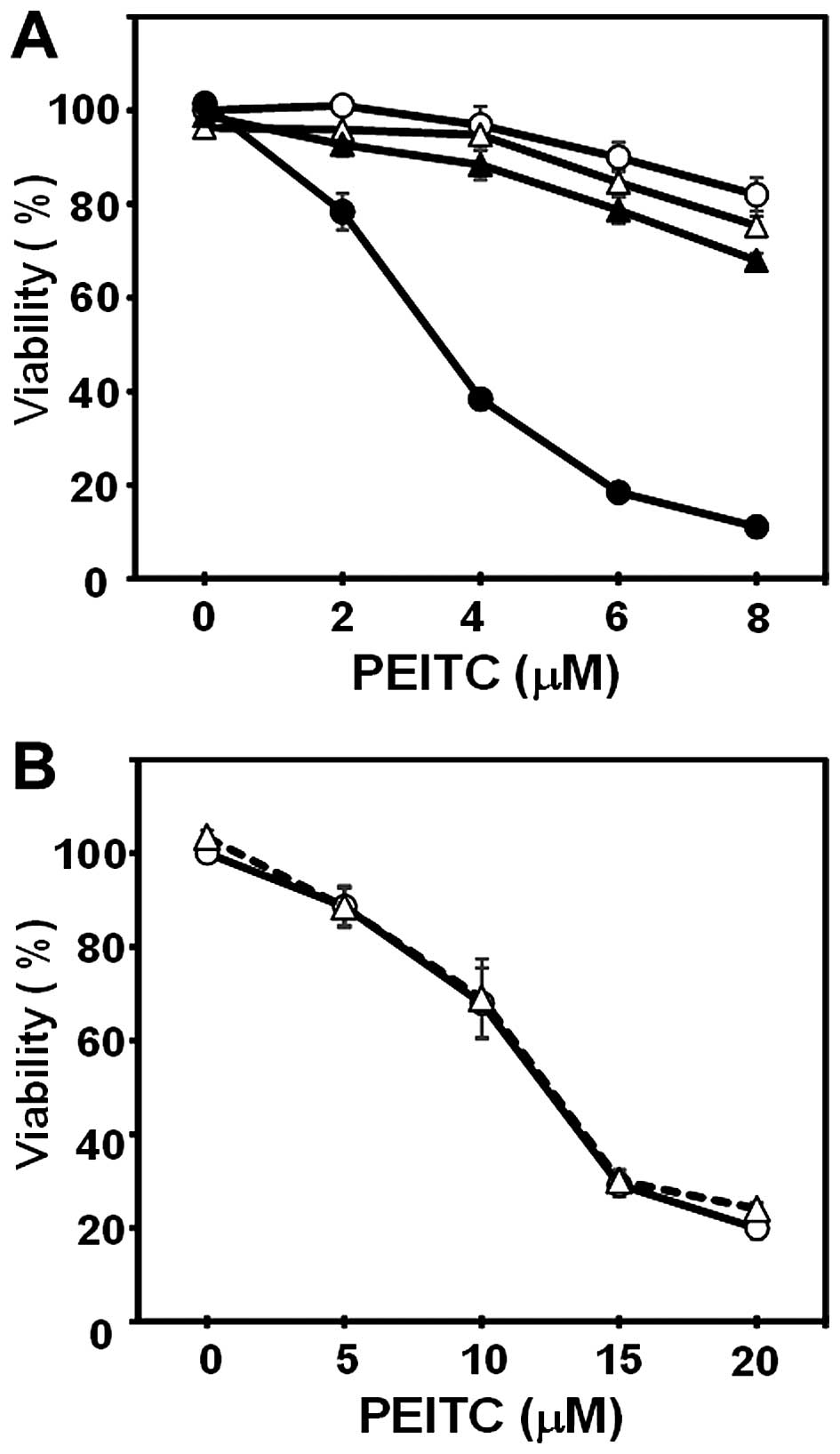
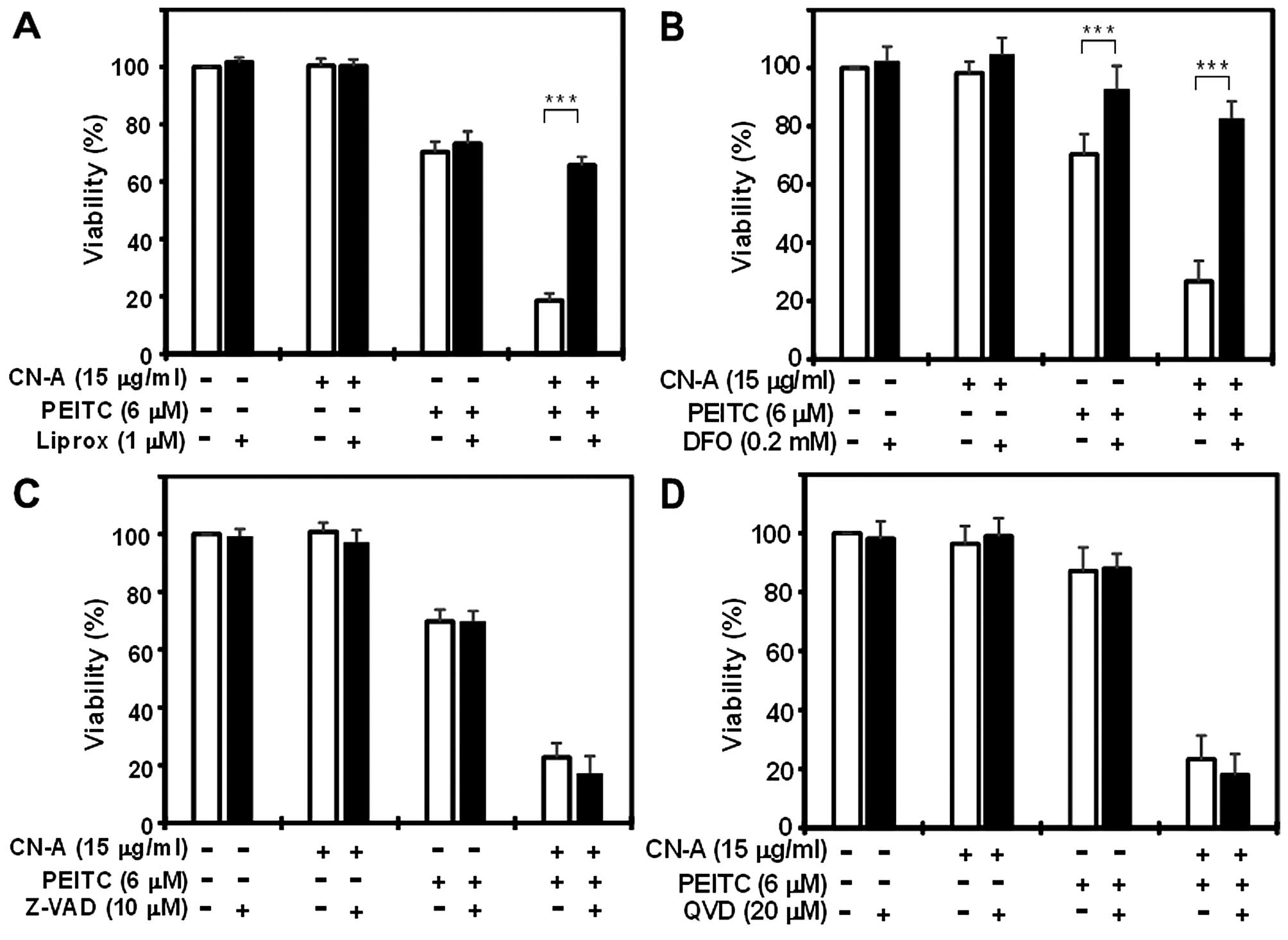
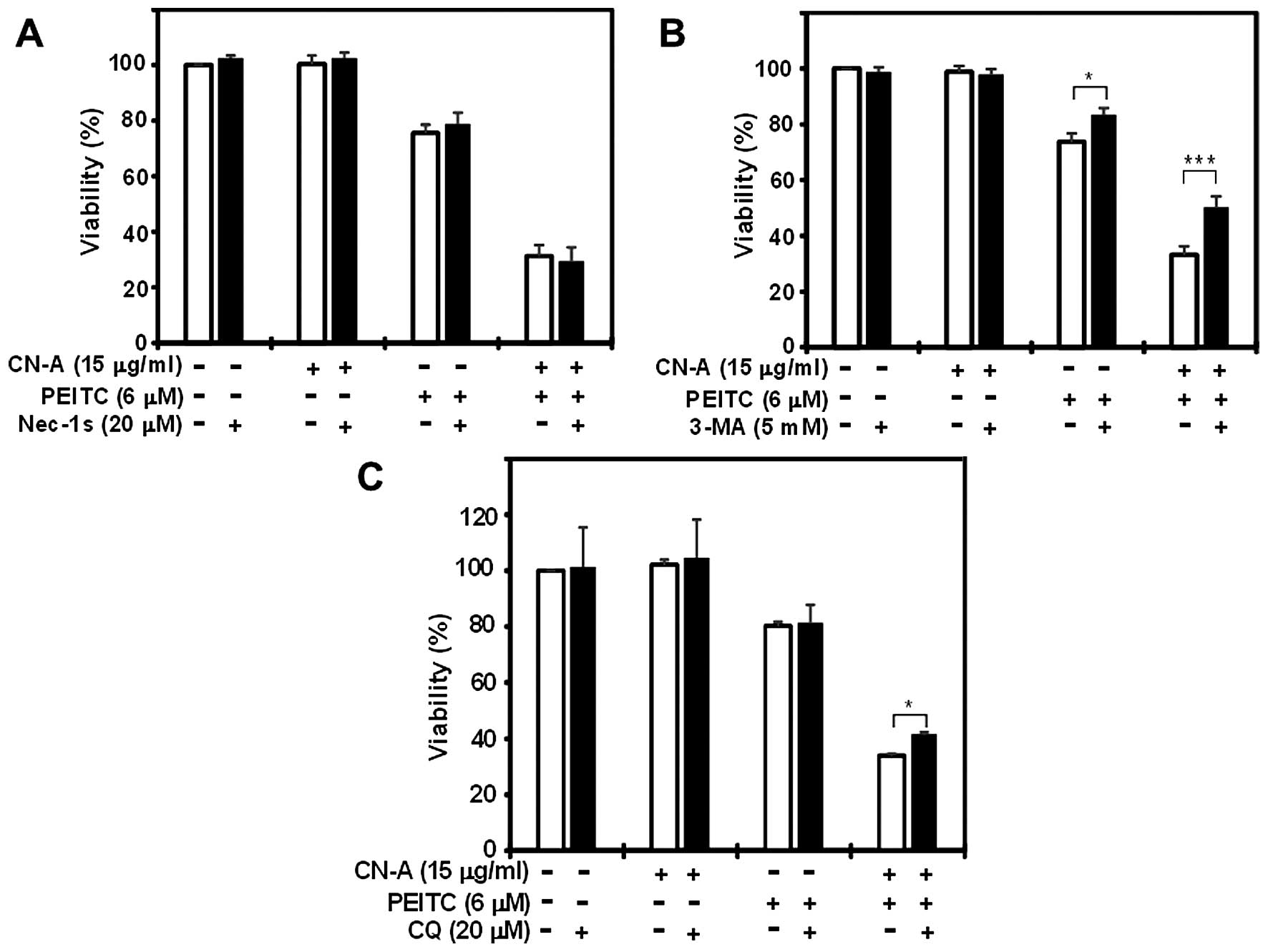
|
1
|
Siegel R, Ma J, Zou Z and Jemal A: Cancer
statistics, 2014. CA Cancer J Clin. 64:9–29. 2014. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
2
|
Hidalgo M: Pancreatic cancer. N Engl J
Med. 362:1605–1617. 2010. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
3
|
Burris HA III, Moore MJ, Andersen J, Green
MR, Rothenberg ML, Modiano MR, Cripps MC, Portenoy RK, Storniolo
AM, Tarassoff P, et al: Improvements in survival and clinical
benefit with gemcitabine as first-line therapy for patients with
advanced pancreas cancer: A randomized trial. J Clin Oncol.
15:2403–2413. 1997.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
4
|
Kroep JR, Pinedo HM, van Groeningen CJ and
Peters GJ: Experimental drugs and drug combinations in pancreatic
cancer. Ann Oncol. 10(Suppl 4): S234–S238. 1999. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
5
|
Jakstaite A, Maziukiene A, Silkuniene G,
Kmieliute K, Gulbinas A and Dambrauskas Z: HuR mediated
post-transcriptional regulation as a new potential adjuvant
therapeutic target in chemotherapy for pancreatic cancer. World J
Gastroenterol. 21:13004–13019. 2015. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
6
|
Guilford JM and Pezzuto JM: Natural
products as inhibitors of carcinogenesis. Expert Opin Investig
Drugs. 17:1341–1352. 2008. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
7
|
Higdon JV, Delage B, Williams DE and
Dashwood RH: Cruciferous vegetables and human cancer risk:
Epidemiologic evidence and mechanistic basis. Pharmacol Res.
55:224–236. 2007. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
8
|
Tang L, Zirpoli GR, Guru K, Moysich KB,
Zhang Y, Ambrosone CB and McCann SE: Intake of cruciferous
vegetables modifies bladder cancer survival. Cancer Epidemiol
Biomarkers Prev. 19:1806–1811. 2010. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
9
|
Gupta P, Wright SE, Kim SH and Srivastava
SK: Phenethyl isothiocyanate: A comprehensive review of anti-cancer
mechanisms. Biochim Biophys Acta. 1846:405–424. 2014.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
10
|
Satyan KS, Swamy N, Dizon DS, Singh R,
Granai CO and Brard L: Phenethyl isothiocyanate (PEITC) inhibits
growth of ovarian cancer cells by inducing apoptosis: Role of
caspase and MAPK activation. Gynecol Oncol. 103:261–270. 2006.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
11
|
Wu X, Zhou QH and Xu K: Are
isothiocyanates potential anticancer drugs? Acta Pharmacol Sin.
30:501–512. 2009. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
12
|
Hong YH, Uddin MH, Jo U, Kim B, Song J,
Suh DH, Kim HS and Song YS: ROS accumulation by PEITC selectively
kills ovarian cancer cells via UPR-mediated apoptosis. Front Oncol.
5:1672015. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
13
|
Trachootham D, Zhou Y, Zhang H, Demizu Y,
Chen Z, Pelicano H, Chiao PJ, Achanta G, Arlinghaus RB, Liu J, et
al: Selective killing of oncogenically transformed cells through a
ROS-mediated mechanism by beta-phenylethyl isothiocyanate. Cancer
Cell. 10:241–252. 2006. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
14
|
Xiao D, Powolny AA, Moura MB, Kelley EE,
Bommareddy A, Kim SH, Hahm ER, Normolle D, Van Houten B and Singh
SV: Phenethyl isothiocyanate inhibits oxidative phosphorylation to
trigger reactive oxygen species-mediated death of human prostate
cancer cells. J Biol Chem. 285:26558–26569. 2010. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
15
|
Shaw AT, Winslow MM, Magendantz M, Ouyang
C, Dowdle J, Subramanian A, Lewis TA, Maglathin RL, Tolliday N and
Jacks T: Selective killing of K-ras mutant cancer cells by small
molecule inducers of oxidative stress. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA.
108:8773–8778. 2011. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
16
|
Yang WS and Stockwell BR: Synthetic lethal
screening identifies compounds activating iron-dependent,
nonapoptotic cell death in oncogenic-RAS-harboring cancer cells.
Chem Biol. 15:234–245. 2008. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
17
|
Dixon SJ, Lemberg KM, Lamprecht MR, Skouta
R, Zaitsev EM, Gleason CE, Patel DN, Bauer AJ, Cantley AM, Yang WS,
et al: Ferroptosis: An iron-dependent form of nonapoptotic cell
death. Cell. 149:1060–1072. 2012. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
18
|
Yang WS and Stockwell BR: Ferroptosis:
Death by lipid peroxidation. Trends Cell Biol. 26:165–176. 2016.
View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
19
|
Sassa T, Tojyo T and Munakata K: Isolation
of a new plant growth substance with cytokinin-like activity.
Nature. 227:3791970. View
Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
20
|
Asahi K, Honma Y, Hazeki K, Sassa T,
Kubohara Y, Sakurai A and Takahashi N: Cotylenin A, a plant-growth
regulator, induces the differentiation in murine and human myeloid
leukemia cells. Biochem Biophys Res Commun. 238:758–763. 1997.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
21
|
Yamamoto-Yamaguchi Y, Yamada K, Ishii Y,
Asahi KI, Tomoyasu S and Honma Y: Induction of the monocytic
differentiation of myeloid leukaemia cells by cotylenin A, a plant
growth regulator. Br J Haematol. 112:697–705. 2001. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
22
|
Yamada K, Honma Y, Asahi KI, Sassa T, Hino
KI and Tomoyasu S: Differentiation of human acute myeloid leukaemia
cells in primary culture in response to cotylenin A, a plant growth
regulator. Br J Haematol. 114:814–821. 2001. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
23
|
Honma Y: Cotylenin A - a plant growth
regulator as a differentiation-inducing agent against myeloid
leukemia. Leuk Lymphoma. 43:1169–1178. 2002. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
24
|
Kasukabe T, Okabe-Kado J, Kato N, Honma Y
and Kumakura S: Cotylenin A and arsenic trioxide cooperatively
suppress cell proliferation and cell invasion activity in human
breast cancer cells. Int J Oncol. 46:841–848. 2015.
|
|
25
|
Kawakami K, Hattori M, Inoue T, Maruyama
Y, Ohkanda J, Kato N, Tongu M, Yamada T, Akimoto M, Takenaga K, et
al: A novel fusicoccin derivative preferentially targets hypoxic
tumor cells and inhibits tumor growth in xenografts. Anticancer
Agents Med Chem. 12:791–800. 2012. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
26
|
Kasukabe T, Okabe-Kado J, Kato N, Sassa T
and Honma Y: Effects of combined treatment with rapamycin and
cotylenin A, a novel differentiation-inducing agent, on human
breast carcinoma MCF-7 cells and xenografts. Breast Cancer Res.
7:R1097–R1110. 2005. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
27
|
Kasukabe T, Okabe-Kado J, Haranosono Y,
Kato N and Honma Y: Inhibition of rapamycin-induced Akt
phosphorylation by cotylenin A correlates with their synergistic
growth inhibition of cancer cells. Int J Oncol. 42:767–775.
2013.
|
|
28
|
Miyake T, Honma Y, Urano T, Kato N and
Suzumiya J: Combined treatment with tamoxifen and a fusicoccin
derivative (ISIR-042) to overcome resistance to therapy and to
enhance the antitumor activity of 5-fluorouracil and gemcitabine in
pancreatic cancer cells. Int J Oncol. 47:315–324. 2015.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
29
|
Friedmann Angeli JP, Schneider M, Proneth
B, Tyurina YY, Tyurin VA, Hammond VJ, Herbach N, Aichler M, Walch
A, Eggenhofer E, et al: Inactivation of the ferroptosis regulator
Gpx4 triggers acute renal failure in mice. Nat Cell Biol.
16:1180–1191. 2014. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
30
|
Xargay-Torrent S, López-Guerra M,
Montraveta A, Saborit-Villarroya I, Rosich L, Navarro A,
Pérez-Galán P, Roué G, Campo E and Colomer D: Sorafenib inhibits
cell migration and stroma-mediated bortezomib resistance by
interfering B-cell receptor signaling and protein translation in
mantle cell lymphoma. Clin Cancer Res. 19:586–597. 2013. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
31
|
Takahashi N, Duprez L, Grootjans S,
Cauwels A, Nerinckx W, DuHadaway JB, Goossens V, Roelandt R, Van
Hauwermeiren F, Libert C, et al: Necrostatin-1 analogues: Critical
issues on the specificity, activity and in vivo use in experimental
disease models. Cell Death Dis. 3:e4372012. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
32
|
Carew JS, Nawrocki ST, Giles FJ and
Cleveland JL: Targeting autophagy: A novel anticancer strategy with
therapeutic implications for imatinib resistance. Biologics.
2:201–204. 2008.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
33
|
Keum YS, Jeong WS and Kong AN:
Chemoprevention by isothiocyanates and their underlying molecular
signaling mechanisms. Mutat Res. 555:191–202. 2004. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
34
|
Chen YR, Wang W, Kong AN and Tan TH:
Molecular mechanisms of c-Jun N-terminal kinase-mediated apoptosis
induced by anticarcinogenic isothiocyanates. J Biol Chem.
273:1769–1775. 1998. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
35
|
Yang YM, Conaway CC, Chiao JW, Wang CX,
Amin S, Whysner J, Dai W, Reinhardt J and Chung FL: Inhibition of
benzo(a)pyrene-induced lung tumorigenesis in A/J mice by dietary
N-acetylcysteine conjugates of benzyl and phenethyl isothiocyanates
during the postinitiation phase is associated with activation of
mitogen-activated protein kinases and p53 activity and induction of
apoptosis. Cancer Res. 62:2–7. 2002.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
36
|
Jutooru I, Guthrie AS, Chadalapaka G,
Pathi S, Kim K, Burghardt R, Jin UH and Safe S: Mechanism of action
of phenethylisothiocyanate and other reactive oxygen
species-inducing anticancer agents. Mol Cell Biol. 34:2382–2395.
2014. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
37
|
Kasukabe T, Okabe-Kado J and Honma Y:
Cotylenin A, a new differentiation inducer, and rapamycin
cooperatively inhibit growth of cancer cells through induction of
cyclin G2. Cancer Sci. 99:1693–1698. 2008. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
38
|
Mujumdar N, Mackenzie TN, Dudeja V, Chugh
R, Antonoff MB, Borja-Cacho D, Sangwan V, Dawra R, Vickers SM and
Saluja AK: Triptolide induces cell death in pancreatic cancer cells
by apoptotic and autophagic pathways. Gastroenterology.
139:598–608. 2010. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|