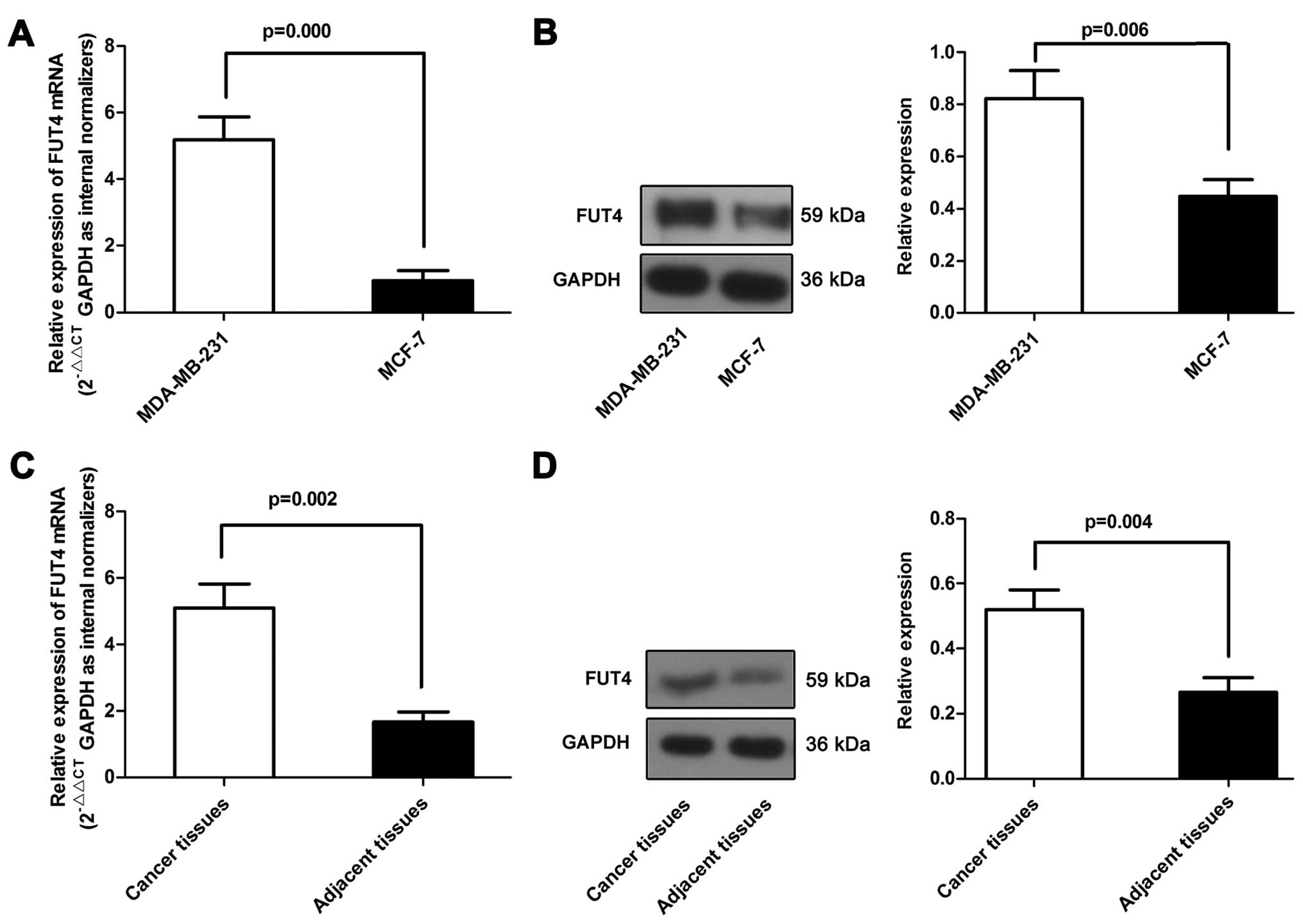
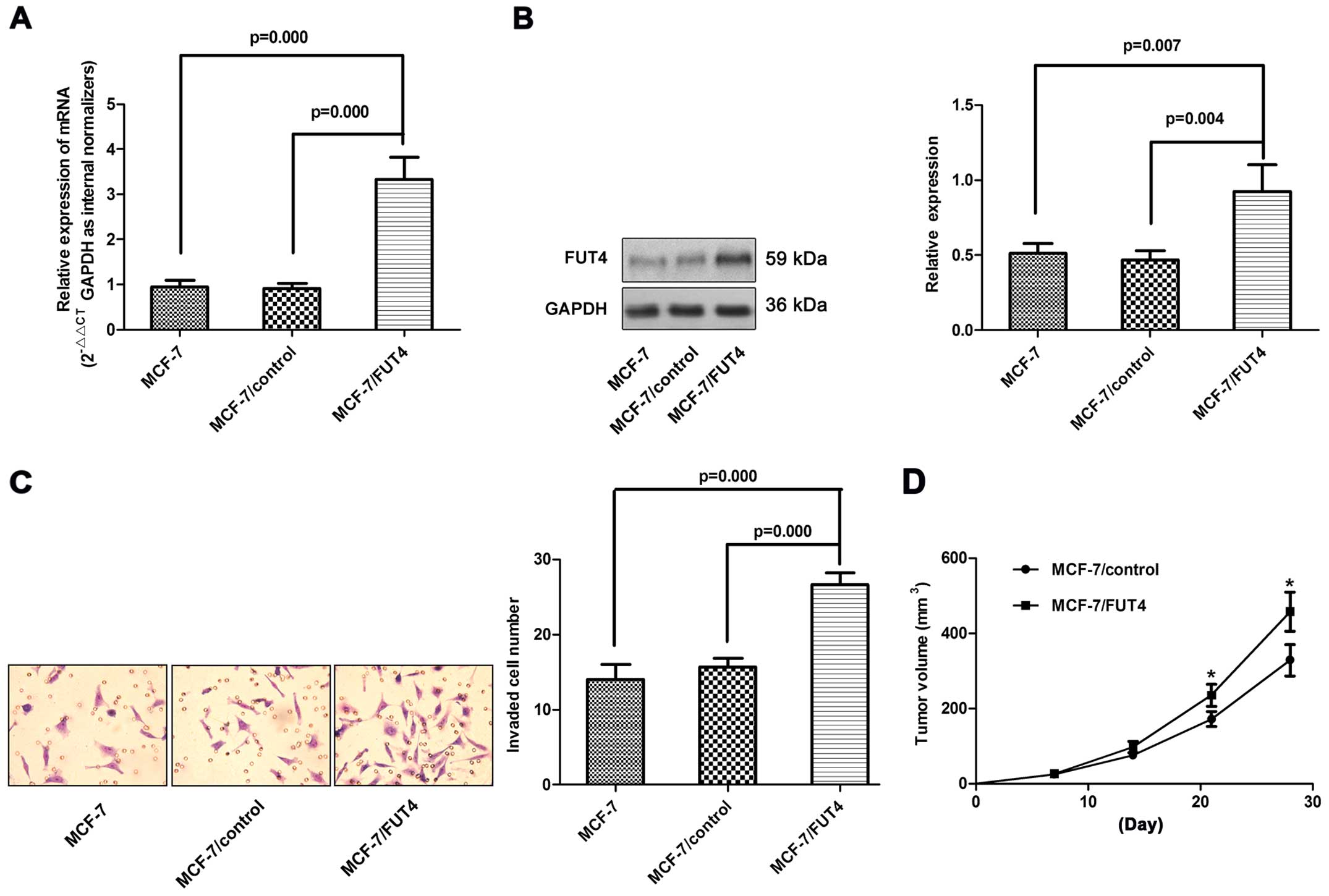
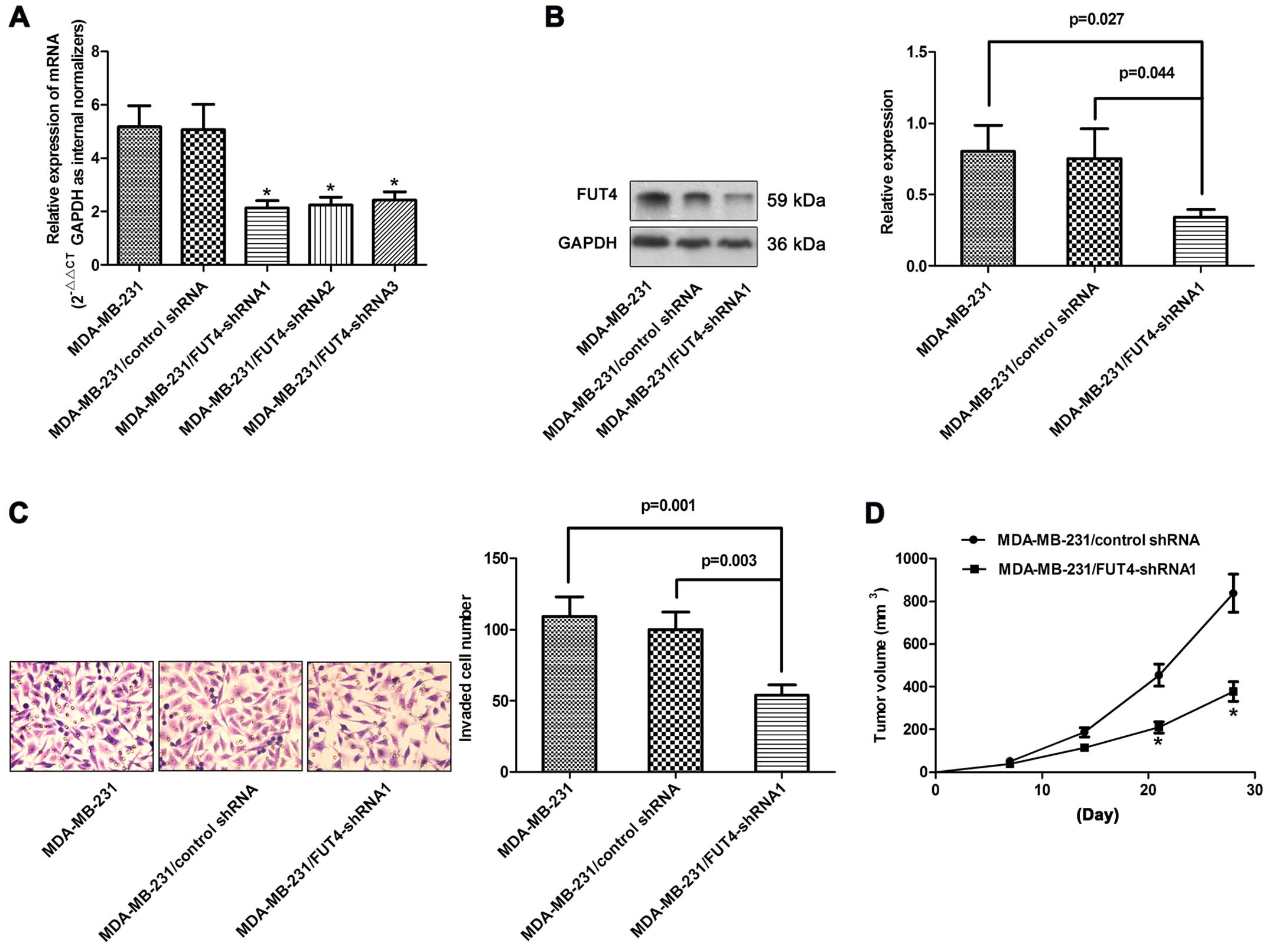
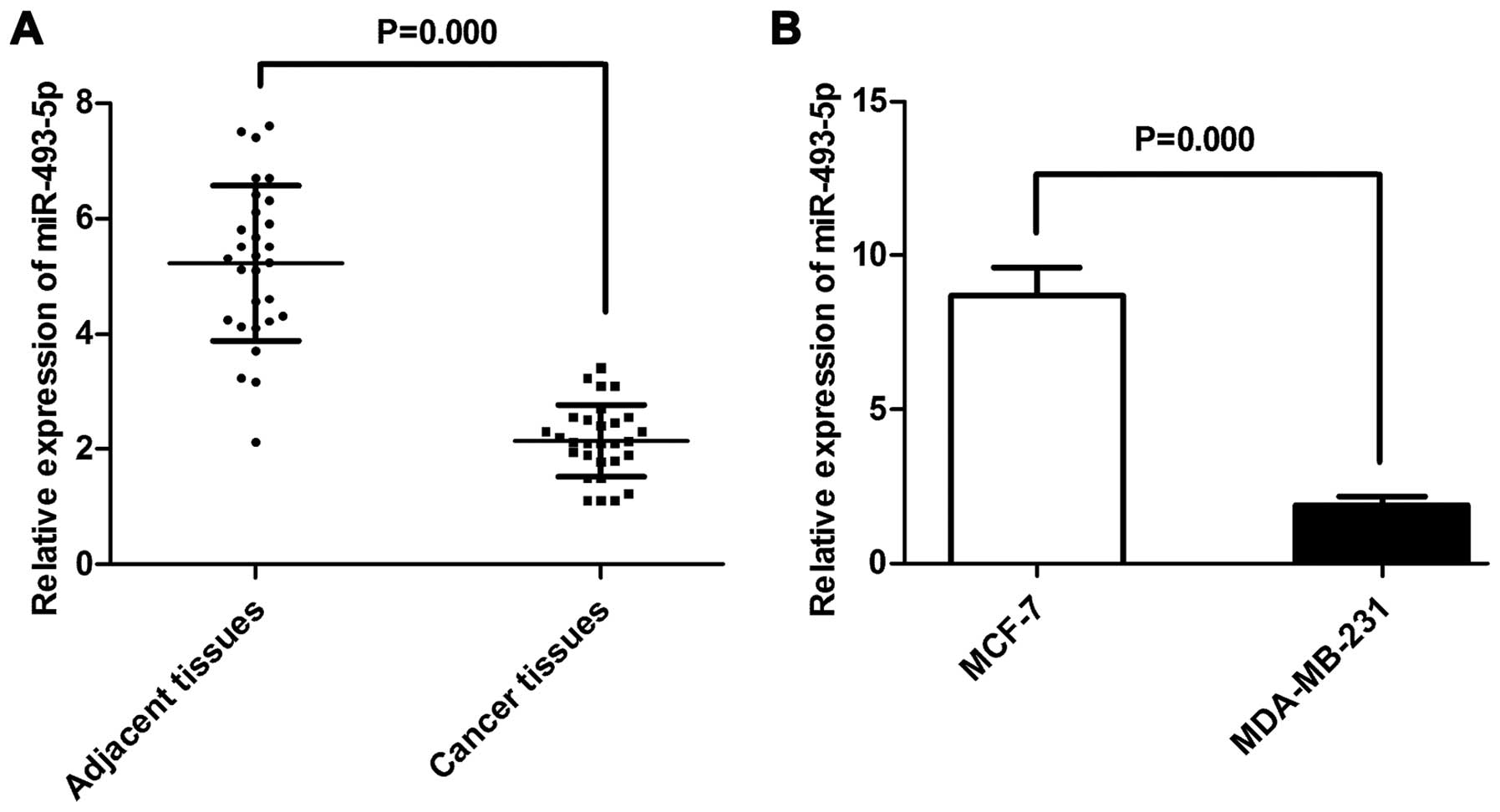
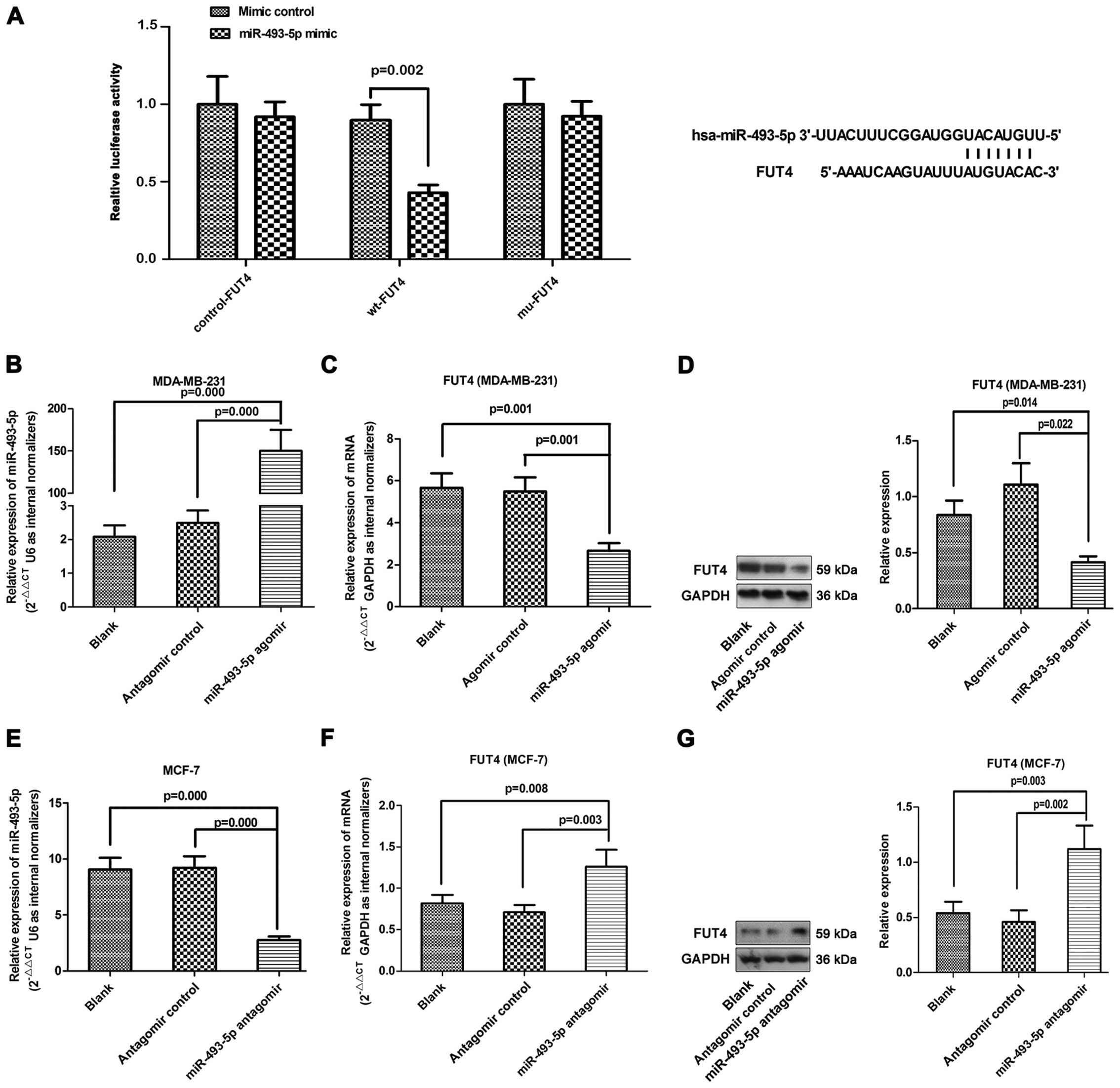
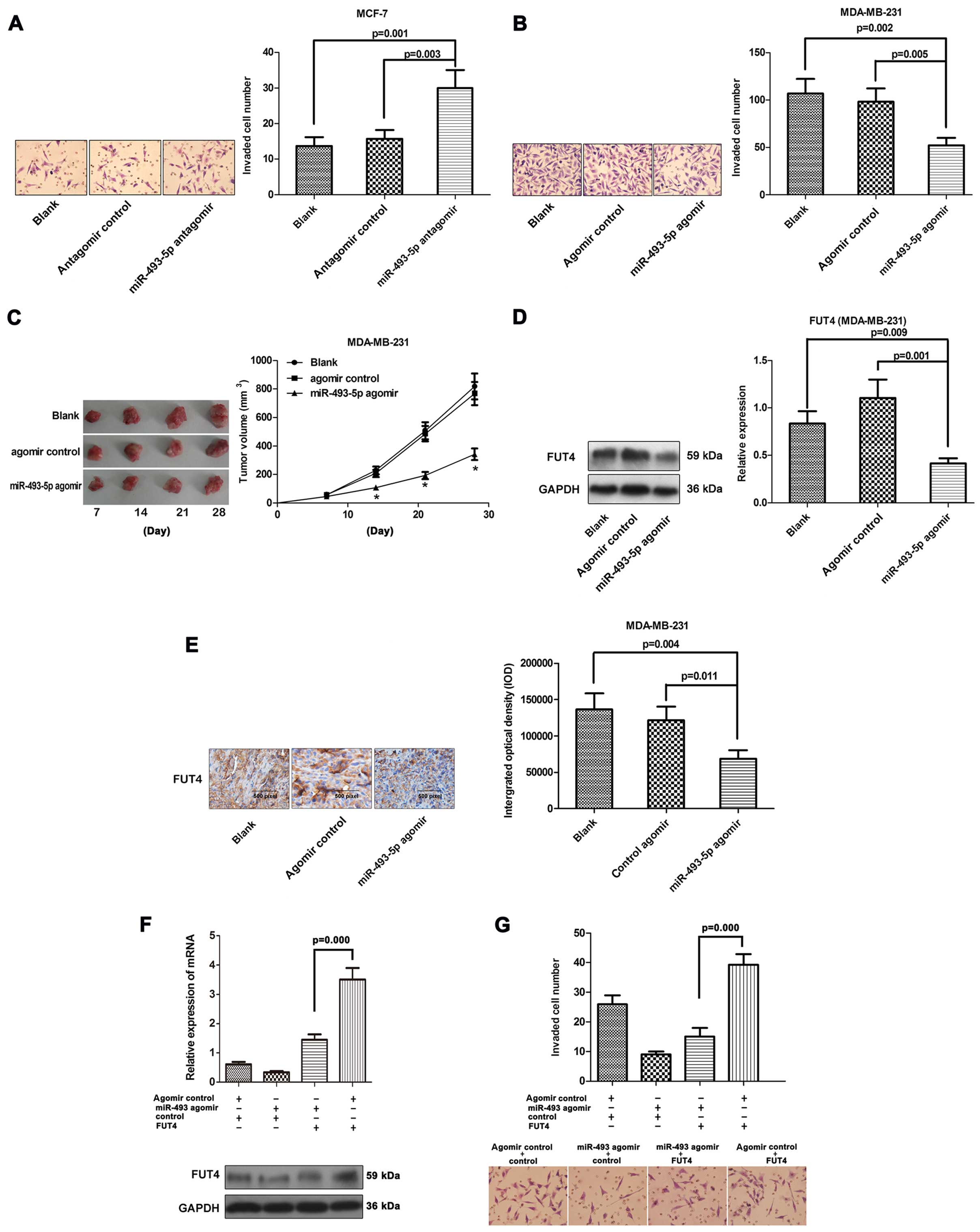
|
1
|
Jemal A, Siegel R, Ward E, Murray T, Xu J
and Thun MJ: Cancer statistics, 2007. CA Cancer J Clin. 57:43–66.
2007. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
2
|
He D, Wang C, Cao L, Zhou J, Huang J and
Fang H: Epidemic trend of female breast cancer incidence in Min
Hang District, Shanghai. China Cancer. 13:108–110. 2010.
|
|
3
|
Stellrecht CM, Vangapandu HV, Le XF, Mao W
and Shentu S: ATP directed agent, 8-chloro-adenosine, induces AMP
activated protein kinase activity, leading to autophagic cell death
in breast cancer cells. J Hematol Oncol. 7:232014. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
4
|
Apweiler R, Hermjakob H and Sharon N: On
the frequency of protein glycosylation, as deduced from analysis of
the SWISS-PROT database. Biochim Biophys Acta. 1473:4–8. 1999.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
5
|
Spiro RG: Protein glycosylation: Nature,
distribution, enzymatic formation, and disease implications of
glycopeptide bonds. Glycobiology. 12:43R–56R. 2002. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
6
|
Desiderio V, Papagerakis P, Tirino V,
Zheng L, Matossian M, Prince ME, Paino F, Mele L, Papaccio F,
Montella R, et al: Increased fucosylation has a pivotal role in
invasive and metastatic properties of head and neck cancer stem
cells. Oncotarget. 6:71–84. 2015.
|
|
7
|
Wang QY, Guo P, Duan LL, Shen ZH and Chen
HL: α-1,3-Fucosyltransferase-VII stimulates the growth of
hepatocarcinoma cells via the cyclin-dependent kinase inhibitor
p27Kip1. Cell Mol Life Sci. 62:171–178. 2005. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
8
|
Hiller KM, Mayben JP, Bendt KM, Manousos
GA, Senger K, Cameron HS and Weston BW: Transfection of alpha(1,3)
fucosyltransferase antisense sequences impairs the proliferative
and tumorigenic ability of human colon carcinoma cells. Mol
Carcinog. 27:280–288. 2000. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
9
|
Sanchez-Mejias A and Tay Y: Competing
endogenous RNA networks: Tying the essential knots for cancer
biology and therapeutics. J Hematol Oncol. 8:302015. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
10
|
Thomson DW, Bracken CP and Goodall GJ:
Experimental strategies for microRNA target identification. Nucleic
Acids Res. 39:6845–6853. 2011. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
11
|
Calin GA and Croce CM: MicroRNA-cancer
connection: The beginning of a new tale. Cancer Res. 66:7390–7394.
2006. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
12
|
Croce CM: miRNAs in the spotlight:
Understanding cancer gene dependency. Nat Med. 17:935–936. 2011.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
13
|
Hurst DR, Edmonds MD, Scott GK, Benz CC,
Vaidya KS and Welch DR: Breast cancer metastasis suppressor 1
up-regulates miR-146, which suppresses breast cancer metastasis.
Cancer Res. 69:1279–1283. 2009. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
14
|
Liu S, Goldstein RH, Scepansky EM and
Rosenblatt M: Inhibition of rho-associated kinase signaling
prevents breast cancer metastasis to human bone. Cancer Res.
69:8742–8751. 2009. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
15
|
Phua YW, Nguyen A, Roden DL, Elsworth B,
Deng N, Nikolic I, Yang J, Mcfarland A, Russell R, Kaplan W, et al:
MicroRNA profiling of the pubertal mouse mammary gland identifies
miR-184 as a candidate breast tumour suppressor gene. Breast Cancer
Res. 17:832015. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
16
|
Lattová E, Tomanek B, Bartusik D and
Perreault H: N-glycomic changes in human breast carcinoma MCF-7 and
T-lymphoblastoid cells after treatment with herceptin and
herceptin/Lipoplex. J Proteome Res. 9:1533–1540. 2010. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
17
|
Shu H, Zhang S, Kang X, Li S, Qin X, Sun
C, Lu H and Liu Y: Protein expression and fucosylated glycans of
the serum haptoglobin-β subunit in hepatitis B virus-based liver
diseases. Acta Biochim Biophys Sin. 43:528–534. 2011. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
18
|
Mejías-Luque R, López-Ferrer A, Garrido M,
Fabra A and de Bolós C: Changes in the invasive and metastatic
capacities of HT-29/M3 cells induced by the expression of
fucosyltransferase 1. Cancer Sci. 98:1000–1005. 2007. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
19
|
Vasseur JA, Goetz JA, Alley WR Jr and
Novotny MV: Smoking and lung cancer-induced changes in
N-glycosylation of blood serum proteins. Glycobiology.
22:1684–1708. 2012. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
20
|
Julien S, Ivetic A, Grigoriadis A, QiZe D,
Burford B, Sproviero D, Picco G, Gillett C, Papp SL, Schaffer L, et
al: Selectin ligand sialyl-Lewis x antigen drives metastasis of
hormone-dependent breast cancers. Cancer Res. 71:7683–7693. 2011.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
21
|
Yan X, Lin Y, Liu S, Aziz F, Yan Q and
Fucosyltransferase IV: (FUT4) as an effective biomarker for the
diagnosis of breast cancer. Biomed Pharmacother. 70:299–304. 2015.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
22
|
Weston BW, Hiller KM, Mayben JP, Manousos
GA, Bendt KM, Liu R and Cusack JC Jr: Expression of human
alpha(1,3)fucosyltransferase antisense sequences inhibits
selectin-mediated adhesion and liver metastasis of colon carcinoma
cells. Cancer Res. 59:2127–2135. 1999.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
23
|
Palumberi D, Aldi S, Ermini L, Ziche M,
Finetti F, Donnini S and Rosati F: RNA-mediated gene silencing of
FUT1 and FUT2 influences expression and activities of bovine and
human fucosylated nucleolin and inhibits cell adhesion and
proliferation. J Cell Biochem. 111:229–238. 2010. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
24
|
Guo Q, Guo B, Wang Y, Wu J, Jiang W, Zhao
S, Qiao S and Wu Y: Functional analysis of
α1,3/4-fucosyltransferase VI in human hepatocellular carcinoma
cells. Biochem Biophys Res Commun. 417:311–317. 2012. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
25
|
Lim LP, Lau NC, Garrett-Engele P, Grimson
A, Schelter JM, Castle J, Bartel DP, Linsley PS and Johnson JM:
Microarray analysis shows that some microRNAs downregulate large
numbers of target mRNAs. Nature. 433:769–773. 2005. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
26
|
Naidu S, Magee P and Garofalo M:
MiRNA-based therapeutic intervention of cancer. J Hematol Oncol.
8:682015. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
27
|
Voorhoeve PM, le Sage C, Schrier M, Gillis
AJ, Stoop H, Nagel R, Liu YP, van Duijse J, Drost J, Griekspoor A,
et al: A genetic screen implicates miRNA-372 and miRNA-373 as
oncogenes in testicular germ cell tumors. Cell. 124:1169–1181.
2006. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
28
|
Ma L, Teruya-Feldstein J and Weinberg RA:
Tumour invasion and metastasis initiated by microRNA-10b in breast
cancer. Nature. 449:682–688. 2007. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
29
|
Tavazoie SF, Alarcón C, Oskarsson T, Padua
D, Wang Q, Bos PD, Gerald WL and Massagué J: Endogenous human
microRNAs that suppress breast cancer metastasis. Nature.
451:147–152. 2008. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
30
|
Kahai S, Lee SC, Lee DY, Yang J, Li M,
Wang CH, Jiang Z, Zhang Y, Peng C and Yang BB: MicroRNA miR-378
regulates nephronectin expression modulating osteoblast
differentiation by targeting GalNT-7. PLoS One. 4:e75352009.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
31
|
Serino G, Sallustio F, Cox SN, Pesce F and
Schena FP: Abnormal miR-148b expression promotes aberrant
glycosylation of IgA1 in IgA nephropathy. J Am Soc Nephrol.
23:814–824. 2012. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
32
|
Minami A, Shimono Y, Mizutani K, Nobutani
K, Momose K, Azuma T and Takai Y: Reduction of the ST6
β-galactosamide α-2,6-sialyltransferase 1 (ST6GAL1)-catalyzed
sialylation of nectin-like molecule 2/cell adhesion molecule 1 and
enhancement of ErbB2/ErbB3 signaling by microRNA-199a. J Biol Chem.
288:11845–11853. 2013. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
33
|
Okamoto K, Ishiguro T, Midorikawa Y, Ohata
H, Izumiya M, Tsuchiya N, Sato A, Sakai H and Nakagama H: miR-493
induction during carcinogenesis blocks metastatic settlement of
colon cancer cells in liver. EMBO J. 31:1752–1763. 2012. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
34
|
Gu Y, Cheng Y, Song Y, Zhang Z, Deng M,
Wang C, Zheng G and He Z: MicroRNA-493 suppresses tumor growth,
invasion and metastasis of lung cancer by regulating E2F1. PLoS
One. 9:e1026022014. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
35
|
Ueno K, Hirata H, Majid S, Yamamura S,
Shahryari V, Tabatabai ZL, Hinoda Y and Dahiya R: Tumor suppressor
microRNA-493 decreases cell motility and migration ability in human
bladder cancer cells by downregulating RhoC and FZD4. Mol Cancer
Ther. 11:244–253. 2012. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
36
|
Lehmann U, Streichert T, Otto B, Albat C,
Hasemeier B, Christgen H, Schipper E, Hille U, Kreipe HH and Länger
F: Identification of differentially expressed microRNAs in human
male breast cancer. BMC Cancer. 10:1092010. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
37
|
Cascione L, Gasparini P, Lovat F, Carasi
S, Pulvirenti A, Ferro A, Alder H, He G, Vecchione A, Croce CM, et
al: Integrated microRNA and mRNA signatures associated with
survival in triple negative breast cancer. PLoS One. 8:e559102013.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|