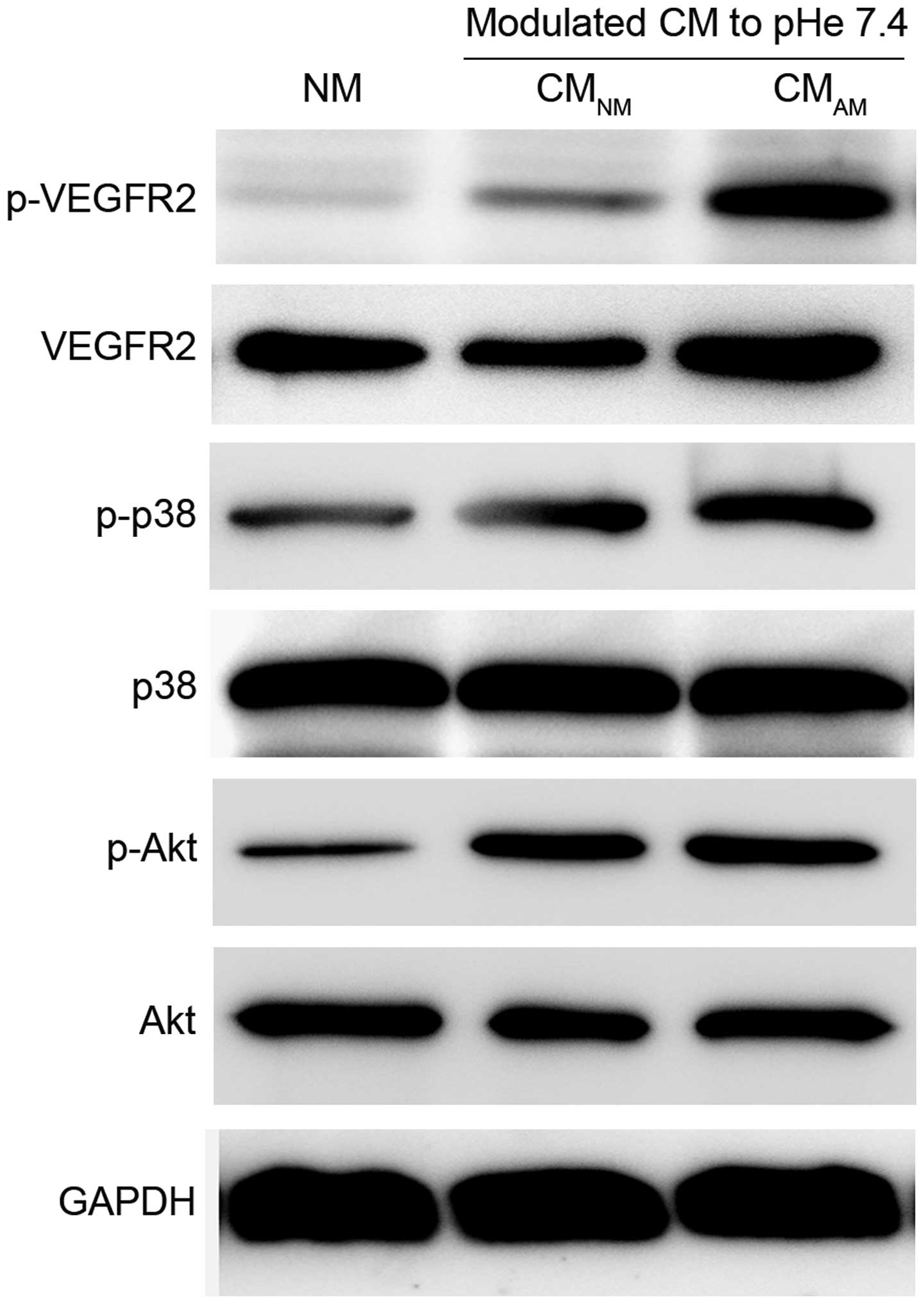
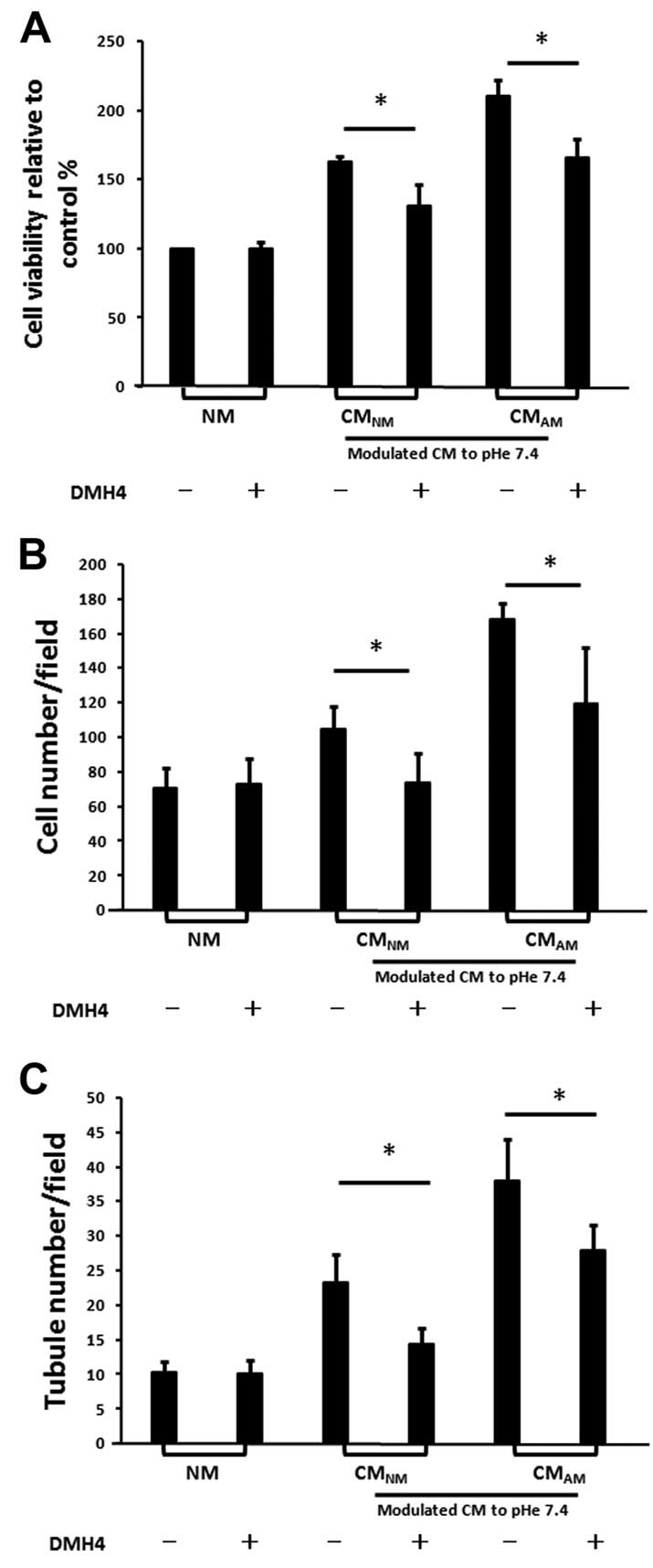
|
1
|
Piccioli A, Maccauro G, Spinelli MS,
Biagini R and Rossi B: Bone metastases of unknown origin:
Epidemiology and principles of management. J Orthop Traumatol.
16:81–86. 2015. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
2
|
Doctor SM, Tsao CK, Godbold JH, Galsky MD
and Oh WK: Is prostate cancer changing?: Evolving patterns of
metastatic castration-resistant prostate cancer. Cancer.
120:833–839. 2014. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
3
|
Polyak K, Haviv I and Campbell IG:
Co-evolution of tumor cells and their microenvironment. Trends
Genet. 25:30–38. 2009. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
4
|
Gribben J, Rosenwald A, Gascoyne R and
Lenz G: Targeting the microenvironment. Leuk Lymphoma. 51(Suppl 1):
S34–S40. 2010. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
5
|
Whipple CA: Tumor talk: understanding the
conversation between the tumor and its microenvironment. Cancer
Cell Microenviron. 2:e7732015.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
6
|
Chiche J, Brahimi-Horn MC and Pouysségur
J: Tumour hypoxia induces a metabolic shift causing acidosis: A
common feature in cancer. J Cell Mol Med. 14:771–794. 2010.
View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
7
|
Gillies RJ, Robey I and Gatenby RA: Causes
and consequences of increased glucose metabolism of cancers. J Nucl
Med. 49(Suppl 2): 24S–42S. 2008. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
8
|
Pastorekova S, Zatovicova M and Pastorek
J: Cancer-associated carbonic anhydrases and their inhibition. Curr
Pharm Des. 14:685–698. 2008. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
9
|
Vaupel P, Kallinowski F and Okunieff P:
Blood flow, oxygen and nutrient supply, and metabolic
microenvironment of human tumors: A review. Cancer Res.
49:6449–6465. 1989.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
10
|
Riemann A, Schneider B, Gündel D, Stock C,
Gekle M and Thews O: Acidosis promotes metastasis formation by
enhancing tumor cell motility. Adv Exp Med Biol. 876:215–220. 2016.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
11
|
Song J, Ge Z, Yang X, Luo Q, Wang C, You
H, Ge T, Deng Y, Lin H, Cui Y, et al: Hepatic stellate cells
activated by acidic tumor microenvironment promote the metastasis
of hepatocellular carcinoma via osteopontin. Cancer Lett.
356:713–720. 2015. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
12
|
Gerweck LE, Vijayappa S and Kozin S: Tumor
pH controls the in vivo efficacy of weak acid and base
chemotherapeutics. Mol Cancer Ther. 5:1275–1279. 2006. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
13
|
Li X, Wu JB, Li Q, Shigemura K, Chung LW
and Huang WC: SREBP-2 promotes stem cell-like properties and
metastasis by transcriptional activation of c-Myc in prostate
cancer. Oncotarget. 7:12869–12884. 2016.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
14
|
Hjelmeland AB, Wu Q, Heddleston JM,
Choudhary GS, MacSwords J, Lathia JD, McLendon R, Lindner D, Sloan
A and Rich JN: Acidic stress promotes a glioma stem cell phenotype.
Cell Death Differ. 18:829–840. 2011. View Article : Google Scholar :
|
|
15
|
Rofstad EK, Mathiesen B, Kindem K and
Galappathi K: Acidic extracellular pH promotes experimental
metastasis of human melanoma cells in athymic nude mice. Cancer
Res. 66:6699–6707. 2006. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
16
|
Matsubara T, Diresta GR, Kakunaga S, Li D
and Healey JH: Additive influence of extracellular pH, oxygen
tension, and pressure on invasiveness and survival of human
osteosarcoma cells. Front Oncol. 3:1992013. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
17
|
Hidalgo M and Eckhardt SG: Development of
matrix metalloproteinase inhibitors in cancer therapy. J Natl
Cancer Inst. 93:178–193. 2001. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
18
|
Cardillo MR, Di Silverio F and Gentile V:
Quantitative immunohistochemical and in situ hybridization analysis
of metalloproteinases in prostate cancer. Anticancer Res.
26:973–982. 2006.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
19
|
Pallares J, Rojo F, Iriarte J, Morote J,
Armadans LI and de Torres I: Study of microvessel density and the
expression of the angiogenic factors VEGF, bFGF and the receptors
Flt-1 and FLK-1 in benign, premalignant and malignant prostate
tissues. Histol Histopathol. 21:857–865. 2006.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
20
|
Wegiel B, Bjartell A, Tuomela J, Dizeyi N,
Tinzl M, Helczynski L, Nilsson E, Otterbein LE, Härkönen P and
Persson JL: Multiple cellular mechanisms related to cyclin A1 in
prostate cancer invasion and metastasis. J Natl Cancer Inst.
100:1022–1036. 2008. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
21
|
Shang B, Cao Z and Zhou Q: Progress in
tumor vascular normalization for anticancer therapy: Challenges and
perspectives. Front Med. 6:67–78. 2012. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
22
|
De Palma M and Naldini L: Role of
haematopoietic cells and endothelial progenitors in tumour
angiogenesis. Biochim Biophys Acta. 1766:159–166. 2006.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
23
|
Nolan DJ, Ciarrocchi A, Mellick AS, Jaggi
JS, Bambino K, Gupta S, Heikamp E, McDevitt MR, Scheinberg DA,
Benezra R, et al: Bone marrow-derived endothelial progenitor cells
are a major determinant of nascent tumor neovascularization. Genes
Dev. 21:1546–1558. 2007. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
24
|
Li B, Sharpe EE, Maupin AB, Teleron AA,
Pyle AL, Carmeliet P and Young PP: VEGF and PlGF promote adult
vasculogenesis by enhancing EPC recruitment and vessel formation at
the site of tumor neovascularization. FASEB J. 20:1495–1497. 2006.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
25
|
Lee SH, Jeong D, Han YS and Baek MJ:
Pivotal role of vascular endothelial growth factor pathway in tumor
angiogenesis. Ann Surg Treat Res. 89:1–8. 2015. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
26
|
Huang S, Guo W, Tang Y, Ren D, Zou X and
Peng X: miR-143 and miR-145 inhibit stem cell characteristics of
PC-3 prostate cancer cells. Oncol Rep. 28:1831–1837.
2012.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
27
|
Huang S, He P, Peng X, Li J, Xu D and Tang
Y: Pristimerin inhibits prostate cancer bone metastasis by
targeting PC-3 stem cell characteristics and VEGF-induced
vasculogenesis of BM-EPCs. Cell Physiol Biochem. 37:253–268. 2015.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
28
|
Folkins C, Shaked Y, Man S, Tang T, Lee
CR, Zhu Z, Hoffman RM and Kerbel RS: Glioma tumor stem-like cells
promote tumor angiogenesis and vasculogenesis via vascular
endothelial growth factor and stromal-derived factor 1. Cancer Res.
69:7243–7251. 2009. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
29
|
Shuman Moss LA, Jensen-Taubman S and
Stetler-Stevenson WG: Matrix metalloproteinases: Changing roles in
tumor progression and metastasis. Am J Pathol. 181:1895–1899. 2012.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
30
|
Aalinkeel R, Nair BB, Reynolds JL, Sykes
DE, Mahajan SD, Chadha KC and Schwartz SA: Overexpression of MMP-9
contributes to invasiveness of prostate cancer cell line LNCaP.
Immunol Invest. 40:447–464. 2011. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
31
|
Wang Q, Diao X, Sun J and Chen Z:
Regulation of VEGF, MMP-9 and metastasis by CXCR4 in a prostate
cancer cell line. Cell Biol Int. 35:897–904. 2011. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
32
|
Kowshik J, Giri H, Kishore TK, Kesavan R,
Vankudavath RN, Reddy GB, Dixit M and Nagini S: Ellagic acid
inhibits VEGF/VEGFR2, PI3K/Akt and MAPK signaling cascades in the
hamster cheek pouch carcinogenesis model. Anticancer Agents Med
Chem. 14:1249–1260. 2014. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
33
|
Koch S and Claesson-Welsh L: Signal
transduction by vascular endothelial growth factor receptors. Cold
Spring Harb Perspect Med. 2:a0065022012. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
34
|
Tang Y, Huang B, Sun L, Peng X, Chen X and
Zou X: Ginkgolide B promotes proliferation and functional
activities of bone marrow-derived endothelial progenitor cells:
Involvement of Akt/eNOS and MAPK/p38 signaling pathways. Eur Cell
Mater. 21:459–469. 2011.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
35
|
D'Amico L, Patanè S, Grange C, Bussolati
B, Isella C, Fontani L, Godio L, Cilli M, D'Amelio P, Isaia G, et
al: Primary breast cancer stem-like cells metastasise to bone,
switch phenotype and acquire a bone tropism signature. Br J Cancer.
108:2525–2536. 2013. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
36
|
Balic M, Lin H, Young L, Hawes D, Giuliano
A, McNamara G, Datar RH and Cote RJ: Most early disseminated cancer
cells detected in bone marrow of breast cancer patients have a
putative breast cancer stem cell phenotype. Clin Cancer Res.
12:5615–5621. 2006. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
37
|
Li H and Tang DG: Prostate cancer stem
cells and their potential roles in metastasis. J Surg Oncol.
103:558–562. 2011. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
38
|
Monteiro J and Fodde R: Cancer stemness
and metastasis: Therapeutic consequences and perspectives. Eur J
Cancer. 46:1198–1203. 2010. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
39
|
Michl M, Heinemann V, Jung A, Engel J,
Kirchner T and Neumann J: Expression of cancer stem cell markers in
metastatic colorectal cancer correlates with liver metastasis, but
not with metastasis to the central nervous system. Pathol Res
Pract. 211:601–609. 2015. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
40
|
Purcell WT, Rudek MA and Hidalgo M:
Development of matrix metalloproteinase inhibitors in cancer
therapy. Hematol Oncol Clin North Am. 16:1189–1227. 2002.
View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
41
|
Hadler-Olsen E, Winberg JO and
Uhlin-Hansen L: Matrix metalloproteinases in cancer: Their value as
diagnostic and prognostic markers and therapeutic targets. Tumour
Biol. 34:2041–2051. 2013. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
42
|
Yang JS, Lin CW, Su SC and Yang SF:
Pharmacodynamic considerations in the use of matrix
metalloproteinase inhibitors in cancer treatment. Expert Opin Drug
Metab Toxicol. 12:191–200. 2016. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
43
|
Gao L, Fang YQ, Zhang TY, Ge B, Tang RJ,
Huang JF, Jiang LM and Tan N: Acidic extracellular microenvironment
promotes the invasion and cathepsin B secretion of PC-3 cells. Int
J Clin Exp Med. 8:7367–7373. 2015.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
44
|
Buckley JJ and Jessen JR: Matrix
metalloproteinase function in non-mammalian model organisms. Front
Biosci. 7:168–183. 2015. View
Article : Google Scholar
|
|
45
|
Zhang X, Huang S, Guo J, Zhou L, You L,
Zhang T and Zhao Y: Insights into the distinct roles of MMP-11 in
tumor biology and future therapeutics (Review). Int J Oncol.
48:1783–1793. 2016.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
46
|
Gao D, Nolan D, McDonnell K, Vahdat L,
Benezra R, Altorki N and Mittal V: Bone marrow-derived endothelial
progenitor cells contribute to the angiogenic switch in tumor
growth and metastatic progression. Biochim Biophys Acta.
1796:33–40. 2009.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
47
|
Moschetta M, Mishima Y, Sahin I, Manier S,
Glavey S, Vacca A, Roccaro AM and Ghobrial IM: Role of endothelial
progenitor cells in cancer progression. Biochim Biophys Acta.
1846:26–39. 2014.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
48
|
Carmeliet P: Angiogenesis in life, disease
and medicine. Nature. 438:932–936. 2005. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
49
|
Hoffmann BR, Wagner JR, Prisco AR, Janiak
A and Greene AS: Vascular endothelial growth factor-A signaling in
bone marrow-derived endothelial progenitor cells exposed to hypoxic
stress. Physiol Genomics. 45:1021–1034. 2013. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
50
|
Farace F, Gross-Goupil M, Tournay E,
Taylor M, Vimond N, Jacques N, Billiot F, Mauguen A, Hill C and
Escudier B: Levels of circulating CD45 (dim)CD34 (+)VEGFR2 (+)
progenitor cells correlate with outcome in metastatic renal cell
carcinoma patients treated with tyrosine kinase inhibitors. Br J
Cancer. 104:1144–1150. 2011. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|