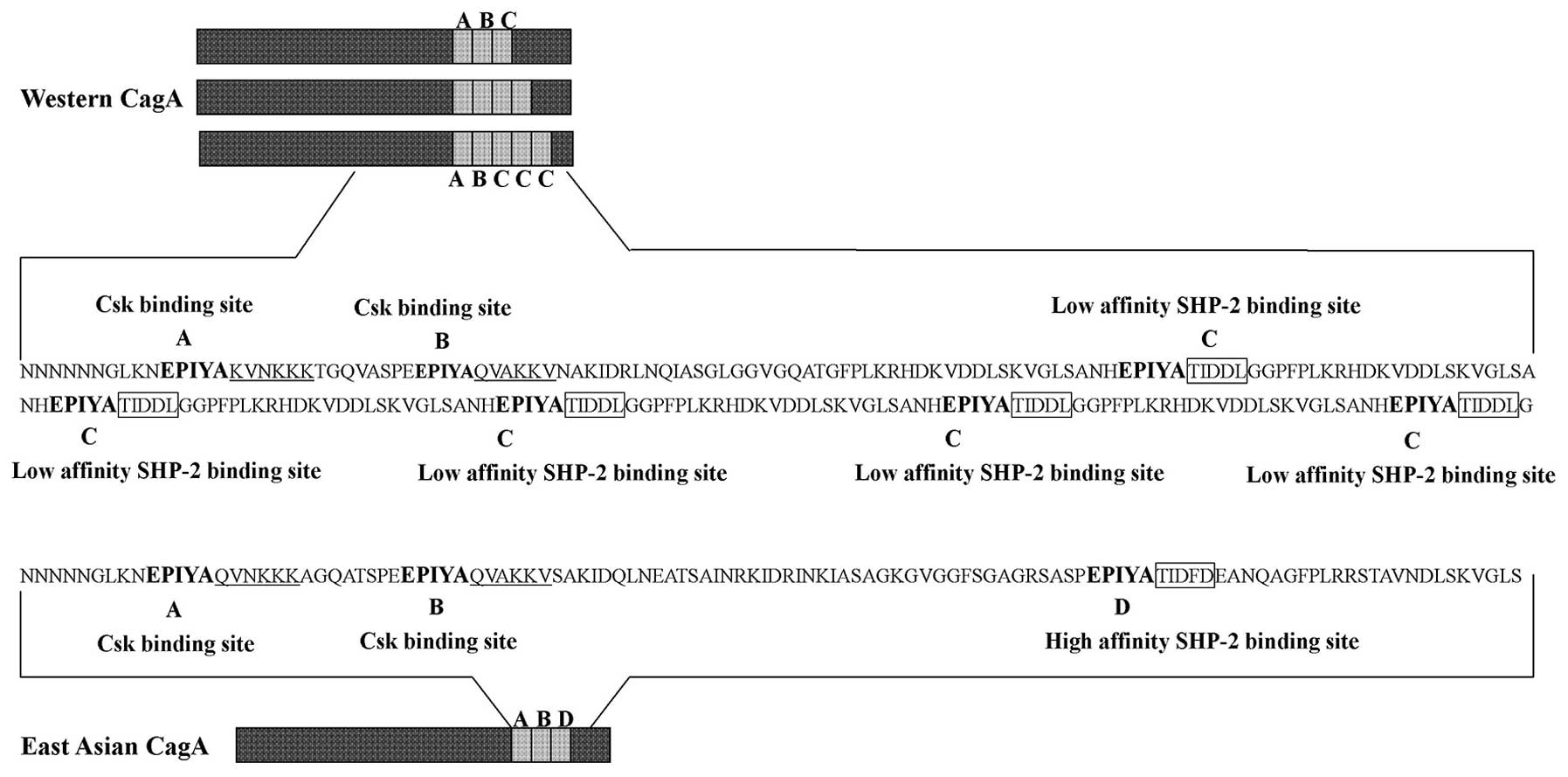
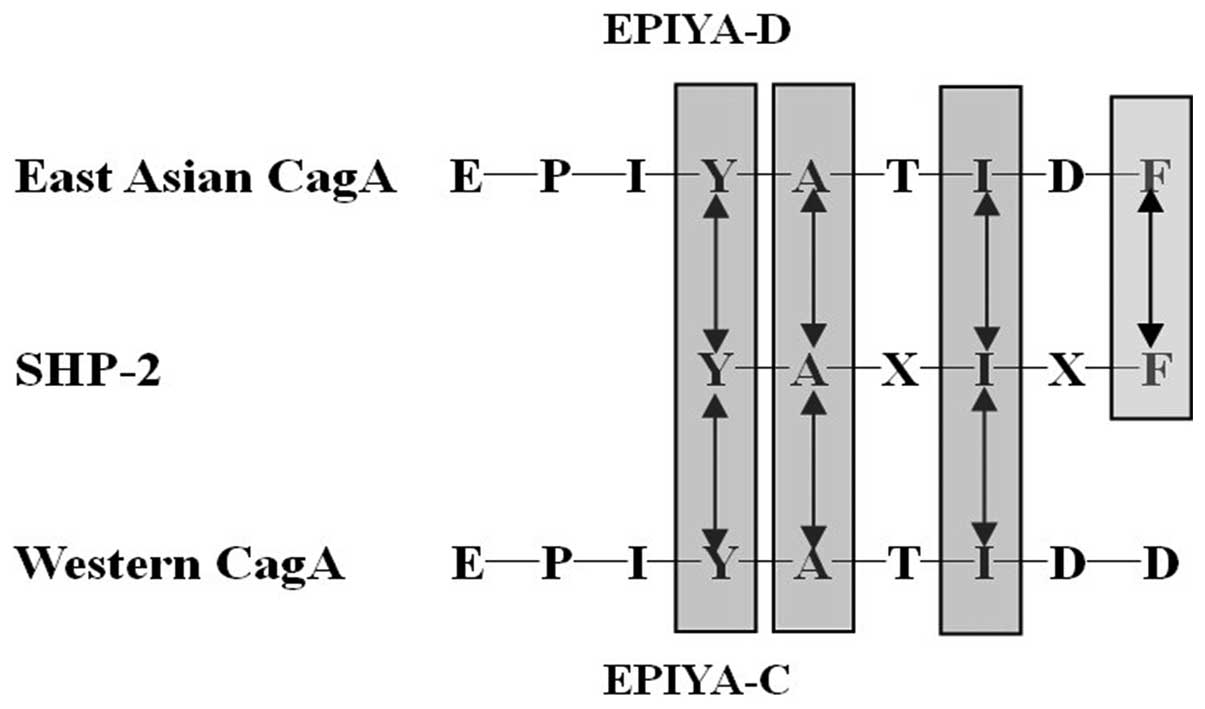
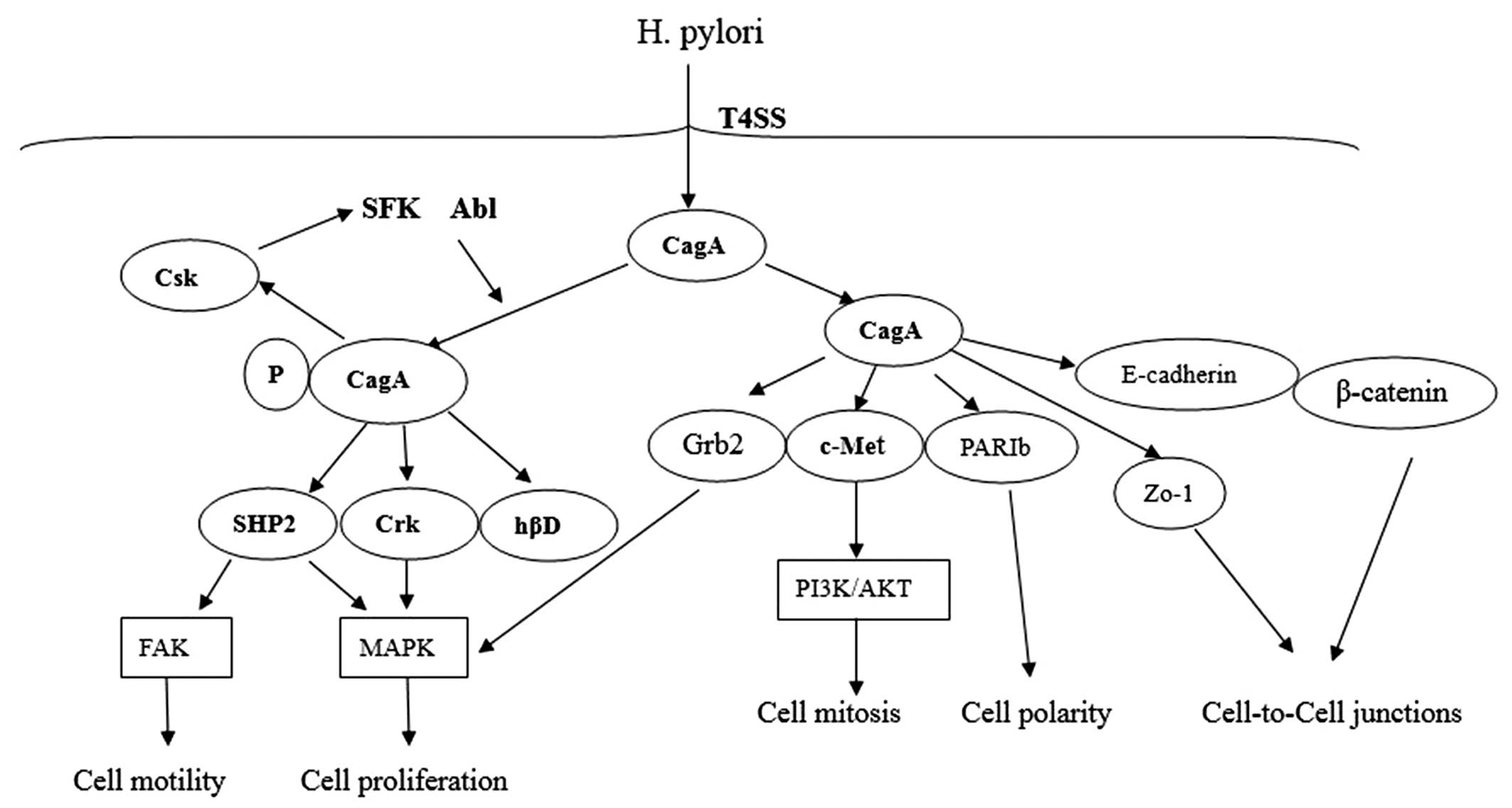
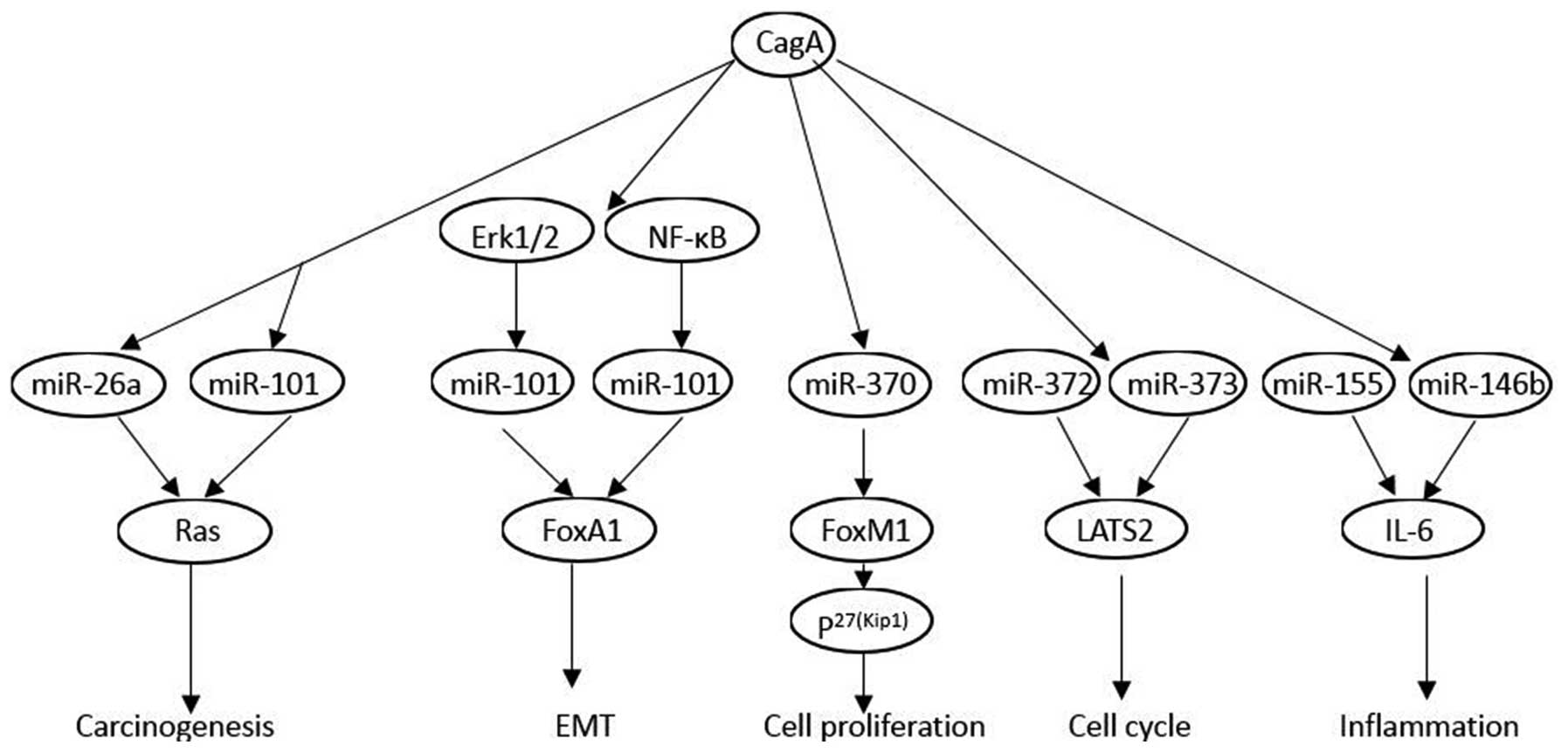
|
1
|
Pacchiani N, Censini S, Buti L and Covacci
A: Echoes of a distant past: The cag pathogenicity island of
Helicobacter pylori. Cold Spring Harb Perspect Med. 3:a0103552013.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
2
|
Cavaleiro-Pinto M, Peleteiro B, Lunet N
and Barros H: Helicobacter pylori infection and gastric cardia
cancer: Systematic review and meta-analysis. Cancer Causes Control.
22:375–387. 2011. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
3
|
Akopyants NS, Clifton SW, Kersulyte D,
Crabtree JE, Youree BE, Reece CA, Bukanov NO, Drazek ES, Roe BA and
Berg DE: Analyses of the cag pathogenicity island of Helicobacter
pylori. Mol Microbiol. 28:37–53. 1998. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
4
|
Censini S, Lange C, Xiang Z, Crabtree JE,
Ghiara P, Borodovsky M, Rappuoli R and Covacci A: cag, a
pathogenicity island of Helicobacter pylori, encodes type
I-specific and disease-associated virulence factors. Proc Natl Acad
Sci USA. 93:14648–14653. 1996. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
5
|
Yamaoka Y: Helicobacter pylori typing as a
tool for tracking human migration. Clin Microbiol Infect.
15:829–834. 2009. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
6
|
Lai CH, Perng CL, Lan KH and Lin HJ:
Association of IS605 and cag-PAI of Helicobacter pylori isolated
from patients with gastrointestinal diseases in Taiwan.
Gastroenterol Res Pract. 2013:3562172013. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
7
|
Torres J, Perez-Perez GI, Leal-Herrera Y
and Munoz O: Infection with CagA+ Helicobacter pylori
strains as a possible predictor of risk in the development of
gastric adenocarcinoma in Mexico. Int J Cancer. 78:298–300. 1998.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
8
|
Batista SA, Rocha GA, Rocha AM, Saraiva
IE, Cabral MM, Oliveira RC and Queiroz DM: Higher number of
Helicobacter pylori CagA EPIYA C phosphorylation sites increases
the risk of gastric cancer, but not duodenal ulcer. BMC Microbiol.
11:612011. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
9
|
Franco AT, Johnston E, Krishna U, Yamaoka
Y, Israel DA, Nagy TA, Wroblewski LE, Piazuelo MB, Correa P and
Peek RM Jr: Regulation of gastric carcinogenesis by Helicobacter
pylori virulence factors. Cancer Res. 68:379–387. 2008. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
10
|
Ohnishi N, Yuasa H, Tanaka S, Sawa H,
Miura M, Matsui A, Higashi H, Musashi M, Iwabuchi K, Suzuki M, et
al: Transgenic expression of Helicobacter pylori CagA induces
gastrointestinal and hematopoietic neoplasms in mouse. Proc Natl
Acad Sci USA. 105:1003–1008. 2008. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
11
|
Backert S, Tegtmeyer N and Fischer W:
Composition, structure and function of the Helicobacter pylori cag
pathogenicity island encoded type IV secretion system. Future
Microbiol. 10:955–965. 2015. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
12
|
Tegtmeyer N, Hartig R, Delahay RM, Rohde
M, Brandt S, Conradi J, Takahashi S, Smolka AJ, Sewald N and
Backert S: A small fibronectin-mimicking protein from bacteria
induces cell spreading and focal adhesion formation. J Biol Chem.
285:23515–23526. 2010. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
13
|
Murata-Kamiya N, Kikuchi K, Hayashi T,
Higashi H and Hatakeyama M: Helicobacter pylori exploits host
membrane phosphatidylserine for delivery, localization, and
pathophysiological action of the CagA oncoprotein. Cell Host
Microbe. 7:399–411. 2010. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
14
|
Fischer W: Assembly and molecular mode of
action of the Helicobacter pylori Cag type IV secretion apparatus.
FEBS J. 278:1203–1212. 2011. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
15
|
Gopal GJ, Pal J, Kumar A and Mukhopadhyay
G: C-terminal domain of CagX is responsible for its interaction
with CagT protein of Helicobacter pylori type IV secretion system.
Biochem Biophys Res Commun. 456:98–103. 2015. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
16
|
Shariq M, Kumar N, Kumari R, Kumar A,
Subbarao N and Mukhopadhyay G: Biochemical analysis of CagE: A
VirB4 homologue of Helicobacter pylori Cag-T4SS. PLoS One.
10:e01426062015. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
17
|
Odenbreit S, Püls J, Sedlmaier B, Gerland
E, Fischer W and Haas R: Translocation of Helicobacter pylori CagA
into gastric epithelial cells by type IV secretion. Science.
287:1497–1500. 2000. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
18
|
Schindele F, Weiss E, Haas R and Fischer
W: Quantitative analysis of CagA type IV secretion by Helicobacter
pylori reveals substrate recognition and translocation
requirements. Mol Microbiol. 100:188–203. 2016. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
19
|
Stein M, Bagnoli F, Halenbeck R, Rappuoli
R, Fantl WJ and Covacci A: c-Src/Lyn kinases activate Helicobacter
pylori CagA through tyrosine phosphorylation of the EPIYA motifs.
Mol Microbiol. 43:971–980. 2002. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
20
|
Tegtmeyer N and Backert S: Role of Abl and
Src family kinases in actin-cytoskeletal rearrangements induced by
the Helicobacter pylori CagA protein. Eur J Cell Biol. 90:880–890.
2011. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
21
|
Tammer I, Brandt S, Hartig R, König W and
Backert S: Activation of Abl by Helicobacter pylori: A novel kinase
for CagA and crucial mediator of host cell scattering.
Gastroenterology. 132:1309–1319. 2007. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
22
|
Zhu Y-L, Zheng S, Du Q, Qian K-D and Fang
P-C: Characterization of CagA variable region of Helicobacter
pylori isolates from Chinese patients. World J Gastroenterol.
11:880–884. 2005. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
23
|
Vaziri F, Peerayeh SN, Alebouyeh M,
Maghsoudi N, Azimzadeh P, Siadat SD and Zali MR: Novel effects of
Helicobacter pylori CagA on key genes of gastric cancer signal
transduction: A comparative transfection study. Pathog Dis.
73:ftu0212015. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
24
|
Zhang XS, Tegtmeyer N, Traube L, Jindal S,
Perez-Perez G, Sticht H, Backert S and Blaser MJ: A specific A/T
polymorphism in Western tyrosine phosphorylation B-motifs regulates
Helicobacter pylori CagA epithelial cell interactions. PLoS Pathog.
11:e10046212015. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
25
|
Ferreira RM, Machado JC, Leite M, Carneiro
F and Figueiredo C: The number of Helicobacter pylori CagA EPIYA C
tyrosine phosphorylation motifs influences the pattern of gastritis
and the development of gastric carcinoma. Histopathology.
60:992–998. 2012. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
26
|
Higashi H, Tsutsumi R, Fujita A, Yamazaki
S, Asaka M, Azuma T and Hatakeyama M: Biological activity of the
Helicobacter pylori virulence factor CagA is determined by
variation in the tyrosine phosphorylation sites. Proc Natl Acad Sci
USA. 99:14428–14433. 2002. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
27
|
Monstein H-J, Karlsson A, Ryberg A and
Borch K: Application of PCR amplicon sequencing using a single
primer pair in PCR amplification to assess variations in
Helicobacter pylori CagA EPIYA tyrosine phosphorylation motifs. BMC
Res Notes. 3:352010. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
28
|
De Souza D, Fabri LJ, Nash A, Hilton DJ,
Nicola NA and Baca M: SH2 domains from suppressor of cytokine
signaling-3 and protein tyrosine phosphatase SHP-2 have similar
binding specificities. Biochemistry. 41:9229–9236. 2002. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
29
|
Mueller D, Tegtmeyer N, Brandt S, Yamaoka
Y, De Poire E, Sgouras D, Wessler S, Torres J, Smolka A and Backert
S: c-Src and c-Abl kinases control hierarchic phosphorylation and
function of the CagA effector protein in Western and East Asian
Helicobacter pylori strains. J Clin Invest. 122:1553–1566. 2012.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
30
|
Ren S, Higashi H, Lu H, Azuma T and
Hatakeyama M: Structural basis and functional consequence of
Helicobacter pylori CagA multimerization in cells. J Biol Chem.
281:32344–32352. 2006. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
31
|
Yamazaki S, Yamakawa A, Ito Y, Ohtani M,
Higashi H, Hatakeyama M and Azuma T: The CagA protein of
Helicobacter pylori is translocated into epithelial cells and binds
to SHP-2 in human gastric mucosa. J Infect Dis. 187:334–337. 2003.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
32
|
Montagner A, Yart A, Dance M, Perret B,
Salles JP and Raynal P: A novel role for Gab1 and SHP2 in epidermal
growth factor-induced Ras activation. J Biol Chem. 280:5350–5360.
2005. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
33
|
Higashi H, Nakaya A, Tsutsumi R, Yokoyama
K, Fujii Y, Ishikawa S, Higuchi M, Takahashi A, Kurashima Y,
Teishikata Y, et al: Helicobacter pylori CagA induces
Ras-independent morphogenetic response through SHP-2 recruitment
and activation. J Biol Chem. 279:17205–17216. 2004. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
34
|
Tsutsumi R, Takahashi A, Azuma T, Higashi
H and Hatakeyama M: Focal adhesion kinase is a substrate and
downstream effector of SHP-2 complexed with Helicobacter pylori
CagA. Mol Cell Biol. 26:261–276. 2006. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
35
|
Tsutsumi R, Higashi H, Higuchi M, Okada M
and Hatakeyama M: Attenuation of Helicobacter pylori CagA × SHP-2
signaling by interaction between CagA and C-terminal Src kinase. J
Biol Chem. 278:3664–3670. 2003. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
36
|
Suzuki M, Mimuro H, Suzuki T, Park M,
Yamamoto T and Sasakawa C: Interaction of CagA with Crk plays an
important role in Helicobacter pylori-induced loss of gastric
epithelial cell adhesion. J Exp Med. 202:1235–1247. 2005.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
37
|
Bauer B, Pang E, Holland C, Kessler M,
Bartfeld S and Meyer TF: The Helicobacter pylori virulence effector
CagA abrogates human β-defensin 3 expression via inactivation of
EGFR signaling. Cell Host Microbe. 11:576–586. 2012. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
38
|
Patel SR, Smith K, Letley DP, Cook KW,
Memon AA, Ingram RJ, Staples E, Backert S, Zaitoun AM, Atherton JC,
et al: Helicobacter pylori downregulates expression of human
β-defensin 1 in the gastric mucosa in a type IV secretion-dependent
fashion. Cell Microbiol. 15:2080–2092. 2013. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
39
|
Churin Y, Al-Ghoul L, Kepp O, Meyer TF,
Birchmeier W and Naumann M: Helicobacter pylori CagA protein
targets the c-Met receptor and enhances the motogenic response. J
Cell Biol. 161:249–255. 2003. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
40
|
Suzuki M, Mimuro H, Kiga K, Fukumatsu M,
Ishijima N, Morikawa H, Nagai S, Koyasu S, Gilman RH, Kersulyte D,
et al: Helicobacter pylori CagA phosphorylation-independent
function in epithelial proliferation and inflammation. Cell Host
Microbe. 5:23–34. 2009. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
41
|
Mimuro H, Suzuki T, Tanaka J, Asahi M,
Haas R and Sasakawa C: Grb2 is a key mediator of Helicobacter
pylori CagA protein activities. Mol Cell. 10:745–755. 2002.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
42
|
Amieva MR, Vogelmann R, Covacci A,
Tompkins LS, Nelson WJ and Falkow S: Disruption of the epithelial
apical-junctional complex by Helicobacter pylori CagA. Science.
300:1430–1434. 2003. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
43
|
Murata-Kamiya N, Kurashima Y, Teishikata
Y, Yamahashi Y, Saito Y, Higashi H, Aburatani H, Akiyama T, Peek RM
Jr, Azuma T, et al: Helicobacter pylori CagA interacts with
E-cadherin and deregulates the β-catenin signal that promotes
intestinal transdifferentiation in gastric epithelial cells.
Oncogene. 26:4617–4626. 2007. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
44
|
Neal JT, Peterson TS, Kent ML and
Guillemin K: H. pylori virulence factor CagA increases intestinal
cell proliferation by Wnt pathway activation in a transgenic
zebrafish model. Dis Model Mech. 6:802–810. 2013. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
45
|
Oliveira MJ, Costa AM, Costa AC, Ferreira
RM, Sampaio P, Machado JC, Seruca R, Mareel M and Figueiredo C:
CagA associates with c-Met, E-cadherin, and p120-catenin in a
multiproteic complex that suppresses Helicobacter pylori-induced
cell-invasive phenotype. J Infect Dis. 200:745–755. 2009.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
46
|
Kurashima Y, Murata-Kamiya N, Kikuchi K,
Higashi H, Azuma T, Kondo S and Hatakeyama M: Deregulation of
beta-catenin signal by Helicobacter pylori CagA requires the
CagA-multimerization sequence. Int J Cancer. 122:823–831. 2008.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
47
|
Saadat I, Higashi H, Obuse C, Umeda M,
Murata-Kamiya N, Saito Y, Lu H, Ohnishi N, Azuma T, Suzuki A, et
al: Helicobacter pylori CagA targets PAR1/MARK kinase to disrupt
epithelial cell polarity. Nature. 447:330–333. 2007. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
48
|
Goldstein B and Macara IG: The PAR
proteins: Fundamental players in animal cell polarization. Dev
Cell. 13:609–622. 2007. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
49
|
Suzuki A and Ohno S: The PAR-aPKC system:
Lessons in polarity. J Cell Sci. 119:979–987. 2006. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
50
|
Lu HS, Saito Y, Umeda M, Murata-Kamiya N,
Zhang HM, Higashi H and Hatakeyama M: Structural and functional
diversity in the PAR1b/MARK2-binding region of Helicobacter pylori
CagA. Cancer Sci. 99:2004–2011. 2008.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
51
|
Lu H, Murata-Kamiya N, Saito Y and
Hatakeyama M: Role of partitioning-defective 1/microtubule
affinity-regulating kinases in the morphogenetic activity of
Helicobacter pylori CagA. J Biol Chem. 284:23024–23036. 2009.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
52
|
Zeaiter Z, Cohen D, Müsch A, Bagnoli F,
Covacci A and Stein M: Analysis of detergent-resistant membranes of
Helicobacter pylori infected gastric adenocarcinoma cells reveals a
role for MARK2/Par1b in CagA-mediated disruption of cellular
polarity. Cell Microbiol. 10:781–794. 2008. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
53
|
Yamahashi Y and Hatakeyama M: PAR1b takes
the stage in the morphogenetic and motogenetic activity of
Helicobacter pylori CagA oncoprotein. Cell Adhes Migr. 7:11–18.
2013. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
54
|
Suzuki N, Murata-Kamiya N, Yanagiya K,
Suda W, Hattori M, Kanda H, Bingo A, Fujii Y, Maeda S, Koike K, et
al: Mutual reinforcement of inflammation and carcinogenesis by the
Helicobacter pylori CagA oncoprotein. Sci Rep. 5:100242015.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
55
|
Mishra JP, Cohen D, Zamperone A, Nesic D,
Muesch A and Stein M: CagA of Helicobacter pylori interacts with
and inhibits the serine-threonine kinase PRK2. Cell Microbiol.
17:1670–1682. 2015. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
56
|
Sandoval J and Esteller M: Cancer
epigenomics: Beyond genomics. Curr Opin Genet Dev. 22:50–55. 2012.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
57
|
Verma M: The role of epigenomics in the
study of cancer biomarkers and in the development of diagnostic
tools. Adv Exp Med Biol. 867:59–80. 2015. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
58
|
Hernando-Herraez I, Garcia-Perez R, Sharp
AJ and Marques-Bonet T: DNA methylation: Insights into human
evolution. PLoS Genet. 11:e10056612015. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
59
|
Maekita T, Nakazawa K, Mihara M, Nakajima
T, Yanaoka K, Iguchi M, Arii K, Kaneda A, Tsukamoto T, Tatematsu M,
et al: High levels of aberrant DNA methylation in Helicobacter
pylori-infected gastric mucosae and its possible association with
gastric cancer risk. Clin Cancer Res. 12:989–995. 2006. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
60
|
Yoshida T, Kato J, Maekita T, Yamashita S,
Enomoto S, Ando T, Niwa T, Deguchi H, Ueda K, Inoue I, et al:
Altered mucosal DNA methylation in parallel with highly active
Helicobacter pylori-related gastritis. Gastric Cancer. 16:488–497.
2013. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
61
|
Tomita H, Takaishi S, Menheniott TR, Yang
X, Shibata W, Jin G, Betz KS, Kawakami K, Minamoto T and Tomasetto
C: Inhibition of gastric carcinogenesis by the hormone gastrin is
mediated by suppression of TFF1 epigenetic silencing.
Gastroenterology. 140:879–891. 2011. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
62
|
Guo XB, Guo L, Zhi QM, Ji J, Jiang JL,
Zhang RJ, Zhang JN, Zhang J, Chen XH, Cai Q, et al: Helicobacter
pylori induces promoter hypermethylation and downregulates gene
expression of IRX1 transcription factor on human gastric mucosa. J
Gastroenterol Hepatol. 26:1685–1690. 2011. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
63
|
Hayashi Y, Tsujii M, Wang J, Kondo J,
Akasaka T, Jin Y, Li W, Nakamura T, Nishida T, Iijima H, et al:
CagA mediates epigenetic regulation to attenuate let-7 expression
in Helicobacter pylori-related carcinogenesis. Gut. 62:1536–1546.
2013. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
64
|
Zhang YW, Eom SY, Yim DH, Song YJ, Yun HY,
Park JS, Youn SJ, Kim BS, Kim YD and Kim H: Evaluation of the
relationship between dietary factors, CagA-positive Helicobacter
pylori infection, and RUNX3 promoter hypermethylation in gastric
cancer tissue. World J Gastroenterol. 19:1778–1787. 2013.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
65
|
He L and Hannon GJ: MicroRNAs: Small RNAs
with a big role in gene regulation. Nat Rev Genet. 5:522–531. 2004.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
66
|
Xiao C and Rajewsky K: MicroRNA control in
the immune system: Basic principles. Cell. 136:26–36. 2009.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
67
|
Libânio D, Dinis-Ribeiro M and
Pimentel-Nunes P: Helicobacter pylori and microRNAs: Relation with
innate immunity and progression of preneoplastic conditions. World
J Clin Oncol. 6:111–132. 2015. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
68
|
Noto JM and Peek RM: The role of microRNAs
in Helicobacter pylori pathogenesis and gastric carcinogenesis.
Front Cell Infect Microbiol. 1:212012. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
69
|
Matsushima K, Isomoto H, Inoue N, Nakayama
T, Hayashi T, Nakayama M, Nakao K, Hirayama T and Kohno S: MicroRNA
signatures in Helicobacter pylori-infected gastric mucosa. Int J
Cancer. 128:361–370. 2011. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
70
|
Zhu Y, Jiang Q, Lou X, Ji X, Wen Z, Wu J,
Tao H, Jiang T, He W, Wang C, et al: MicroRNAs up-regulated by CagA
of Helicobacter pylori induce intestinal metaplasia of gastric
epithelial cells. PLoS One. 7:e351472012. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
71
|
Feng Y, Wang L, Zeng J, Shen L, Liang X,
Yu H, Liu S, Liu Z, Sun Y, Li W, et al: FoxM1 is overexpressed in
Helicobacter pylori-induced gastric carcinogenesis and is
negatively regulated by miR-370. Mol Cancer Res. 11:834–844. 2013.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
72
|
Li N, Tang B, Zhu ED, Li BS, Zhuang Y, Yu
S, Lu DS, Zou QM, Xiao B and Mao XH: Increased miR-222 in H.
pylori-associated gastric cancer correlated with tumor progression
by promoting cancer cell proliferation and targeting RECK. FEBS
Lett. 586:722–728. 2012. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
73
|
Belair C, Baud J, Chabas S, Sharma CM,
Vogel J, Staedel C and Darfeuille F: Helicobacter pylori interferes
with an embryonic stem cell micro RNA cluster to block cell cycle
progression. Silence. 2:72011. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
74
|
Cheng SF, Li L and Wang LM: miR-155 and
miR-146b negatively regulates IL6 in Helicobacter pylori
(cagA+) infected gastroduodenal ulcer. Eur Rev Med
Pharmacol Sci. 19:607–613. 2015.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
75
|
Harr JC, Gonzalez-Sandoval A and Gasser
SM: Histones and histone modifications in perinuclear chromatin
anchoring: From yeast to man. EMBO Rep. 17:139–155. 2016.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
76
|
Schones DE, Cui K, Cuddapah S, Roh TY,
Barski A, Wang Z, Wei G and Zhao K: Dynamic regulation of
nucleosome positioning in the human genome. Cell. 132:887–898.
2008. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
77
|
Xia G, Schneider-Stock R, Diestel A,
Habold C, Krueger S, Roessner A, Naumann M and Lendeckel U:
Helicobacter pylori regulates p21 (WAF1) by histone H4 acetylation.
Biochem Biophys Res Commun. 369:526–531. 2008. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
78
|
Fehri LF, Rechner C, Janssen S, Mak TN,
Holland C, Bartfeld S, Brüggemann H and Meyer TF: Helicobacter
pylori-induced modification of the histone H3 phosphorylation
status in gastric epithelial cells reflects its impact on cell
cycle regulation. Epigenetics. 4:577–586. 2009. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
79
|
Liang X, Zeng J, Wang L, Shen L, Li S, Ma
L, Ci X, Yu J, Jia M, Sun Y, et al: Histone demethylase RBP2
induced by Helicobactor pylori CagA participates in the malignant
transformation of gastric epithelial cells. Oncotarget.
5:5798–5807. 2014. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|