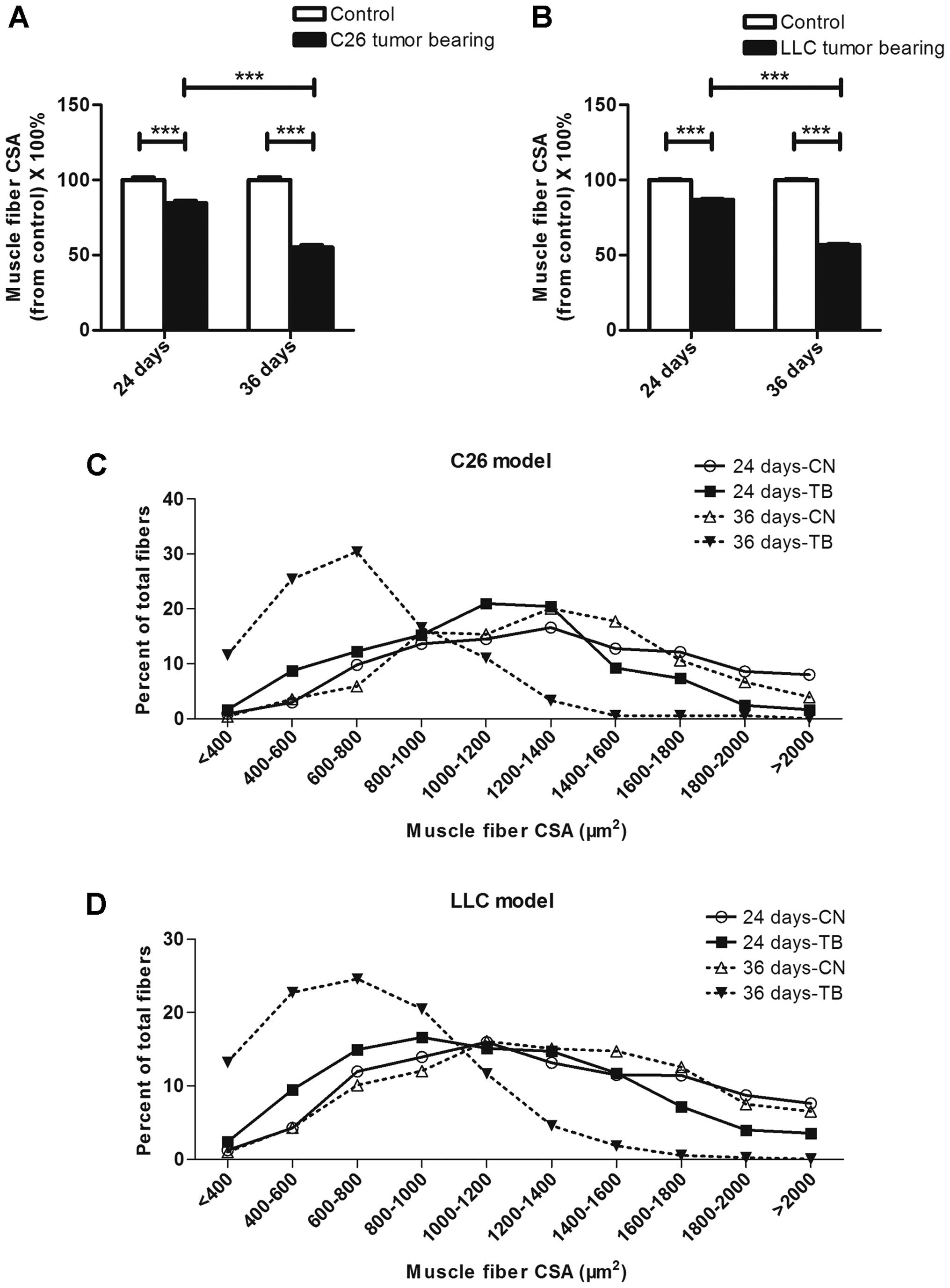
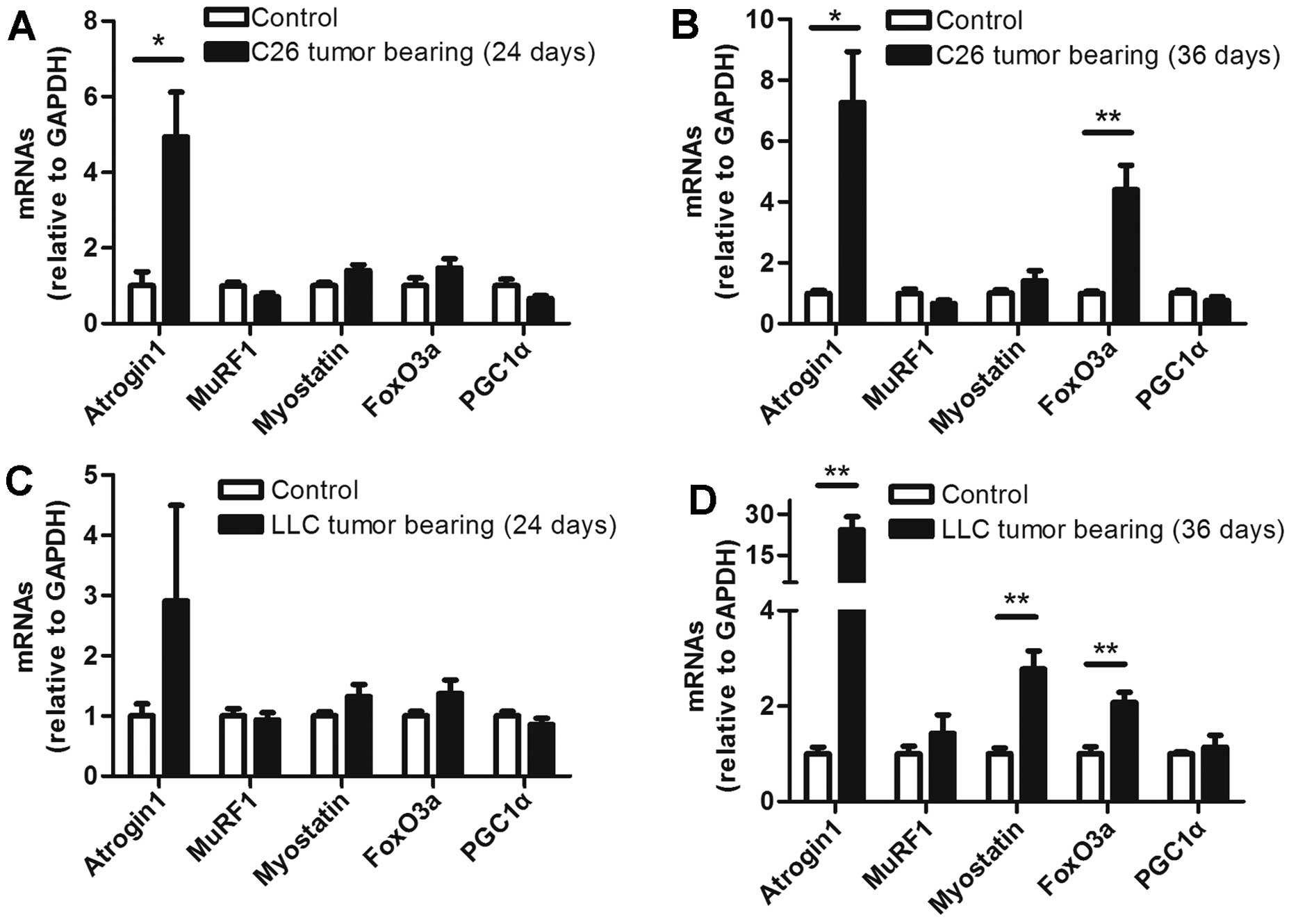
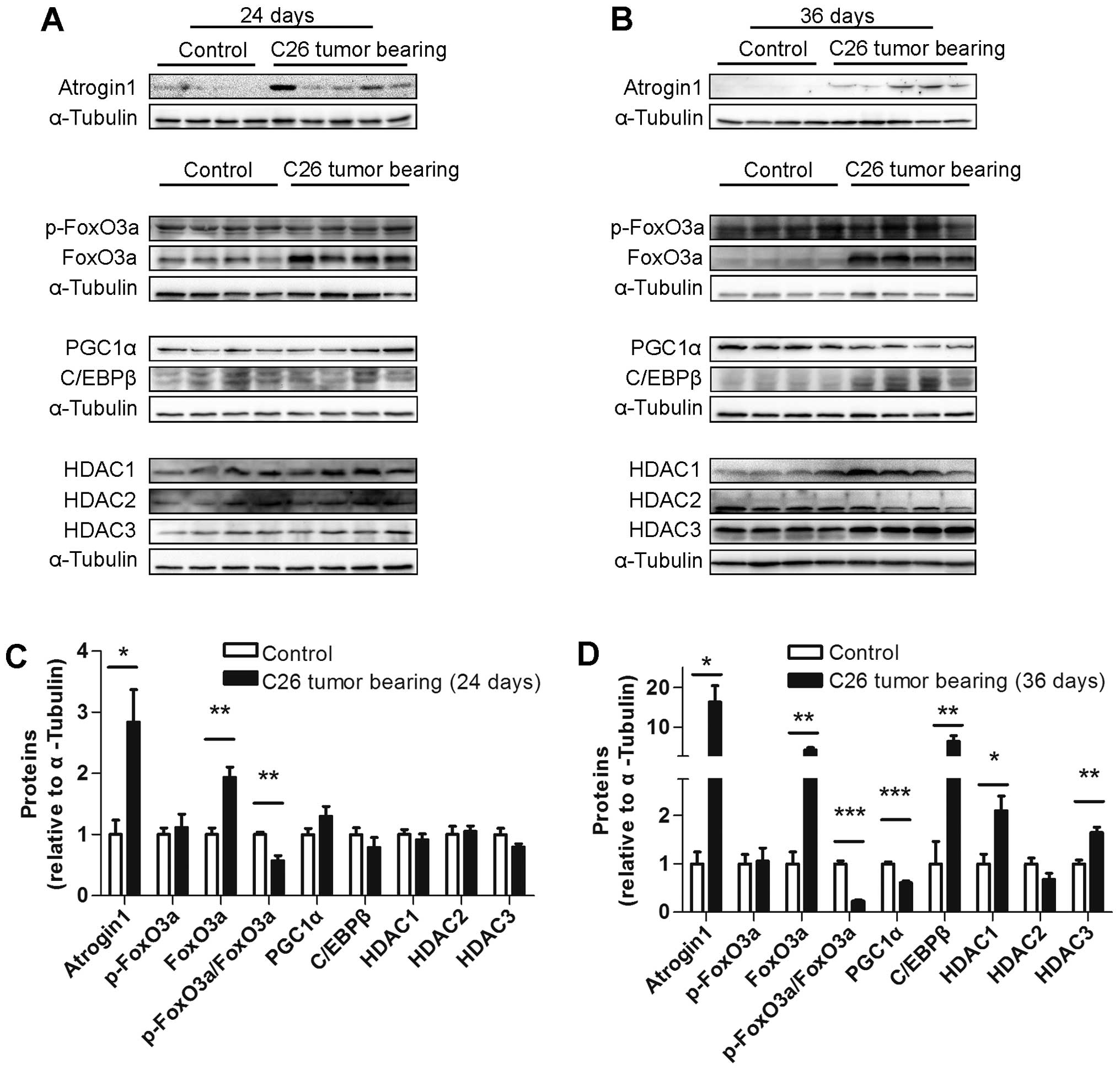
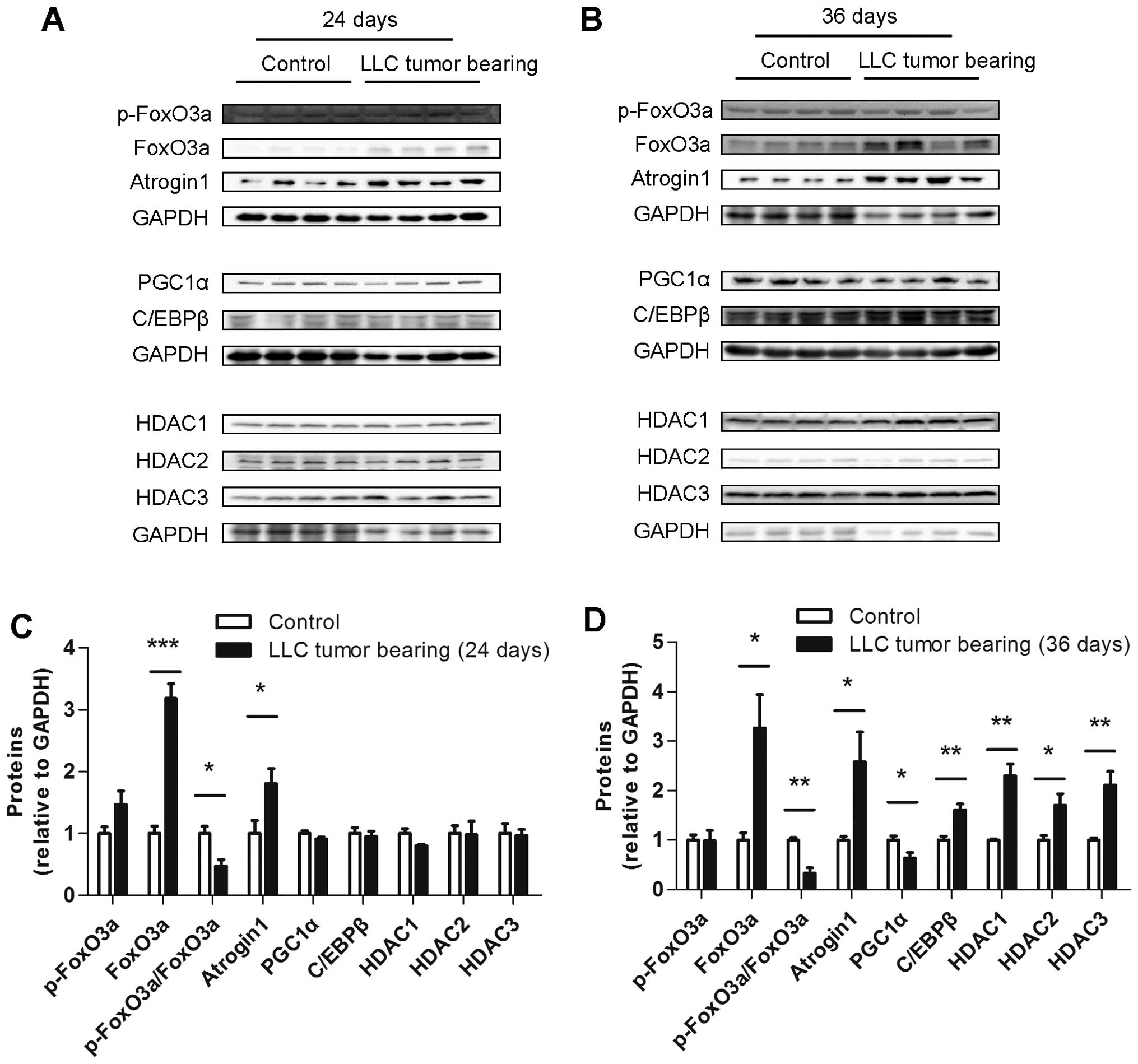
|
1
|
Argilés JM, Busquets S, Stemmler B and
López-Soriano FJ: Cancer cachexia: Understanding the molecular
basis. Nat Rev Cancer. 14:754–762. 2014. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
2
|
Li B, Wan L, Li Y, Yu Q, Chen P, Gan R,
Yang Q, Han Y and Guo C: Baicalin, a component of Scutellaria
baicalensis, alleviates anorexia and inhibits skeletal muscle
atrophy in experimental cancer cachexia. Tumour Biol.
35:12415–12425. 2014. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
3
|
Talbert EE, Metzger GA, He WA and
Guttridge DC: Modeling human cancer cachexia in colon 26
tumor-bearing adult mice. J Cachexia Sarcopenia Muscle. 5:321–328.
2014. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
4
|
Cai D, Frantz JD, Tawa NE Jr, Melendez PA,
Oh BC, Lidov HG, Hasselgren PO, Frontera WR, Lee J, Glass DJ, et
al: IKKbeta/NF-kappaB activation causes severe muscle wasting in
mice. Cell. 119:285–298. 2004. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
5
|
Acharyya S, Ladner KJ, Nelsen LL, Damrauer
J, Reiser PJ, Swoap S and Guttridge DC: Cancer cachexia is
regulated by selective targeting of skeletal muscle gene products.
J Clin Invest. 114:370–378. 2004. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
6
|
Bonetto A, Aydogdu T, Jin X, Zhang Z, Zhan
R, Puzis L, Koniaris LG and Zimmers TA: JAK/STAT3 pathway
inhibition blocks skeletal muscle wasting downstream of IL-6 and in
experimental cancer cachexia. Am J Physiol Endocrinol Metab.
303:E410–E421. 2012. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
7
|
Ham DJ, Murphy KT, Chee A, Lynch GS and
Koopman R: Glycine administration attenuates skeletal muscle
wasting in a mouse model of cancer cachexia. Clin Nutr. 33:448–458.
2014. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
8
|
Bonetto A, Aydogdu T, Kunzevitzky N,
Guttridge DC, Khuri S, Koniaris LG and Zimmers TA: STAT3 activation
in skeletal muscle links muscle wasting and the acute phase
response in cancer cachexia. PLoS One. 6:e225382011. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
9
|
Murphy KT, Chee A, Trieu J, Naim T and
Lynch GS: Importance of functional and metabolic impairments in the
characterization of the C-26 murine model of cancer cachexia. Dis
Model Mech. 5:533–545. 2012. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
10
|
Zhang G, Jin B and Li YP: C/EBPβ mediates
tumour-induced ubiquitin ligase atrogin1/MAFbx upregulation and
muscle wasting. EMBO J. 30:4323–4335. 2011. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
11
|
Busquets S, Toledo M, Orpí M, Massa D,
Porta M, Capdevila E, Padilla N, Frailis V, López-Soriano FJ, Han
HQ, et al: Myostatin blockage using actRIIB antagonism in mice
bearing the Lewis lung carcinoma results in the improvement of
muscle wasting and physical performance. J Cachexia Sarcopenia
Muscle. 3:37–43. 2012. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
12
|
Ruas JL, White JP, Rao RR, Kleiner S,
Brannan KT, Harrison BC, Greene NP, Wu J, Estall JL, Irving BA, et
al: A PGC-1α isoform induced by resistance training regulates
skeletal muscle hypertrophy. Cell. 151:1319–1331. 2012. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
13
|
Reed SA, Sandesara PB, Senf SM and Judge
AR: Inhibition of FoxO transcriptional activity prevents muscle
fiber atrophy during cachexia and induces hypertrophy. FASEB J.
26:987–1000. 2012. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
14
|
Puppa MJ, Gao S, Narsale AA and Carson JA:
Skeletal muscle glycoprotein 130s role in Lewis lung
carcinoma-induced cachexia. FASEB J. 28:998–1009. 2014. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
15
|
He SS, Wu QJ, Gong CY, Luo ST, Zhang S, Li
M, Lu L, Wei YQ and Yang L: Enhanced efficacy of combination
therapy with adeno-associated virus-delivered pigment
epithelium-derived factor and cisplatin in a mouse model of Lewis
lung carcinoma. Mol Med Rep. 9:2069–2076. 2014.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
16
|
Wang H, Lai YJ, Chan YL, Li TL and Wu CJ:
Epigallocatechin-3-gallate effectively attenuates skeletal muscle
atrophy caused by cancer cachexia. Cancer Lett. 305:40–49. 2011.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
17
|
Fearon KC, Glass DJ and Guttridge DC:
Cancer cachexia: Mediators, signaling, and metabolic pathways. Cell
Metab. 16:153–166. 2012. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
18
|
Johns N, Stephens NA and Fearon KC: Muscle
wasting in cancer. Int J Biochem Cell Biol. 45:2215–2229. 2013.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
19
|
McPherron AC, Lawler AM and Lee SJ:
Regulation of skeletal muscle mass in mice by a new TGF-beta
superfamily member. Nature. 387:83–90. 1997. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
20
|
Padrão AI, Oliveira P, Vitorino R, Colaço
B, Pires MJ, Márquez M, Castellanos E, Neuparth MJ, Teixeira C,
Costa C, et al: Bladder cancer-induced skeletal muscle wasting:
Disclosing the role of mitochondria plasticity. Int J Biochem Cell
Biol. 45:1399–1409. 2013. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
21
|
Padrão AI, Moreira-Gonçalves D, Oliveira
PA, Teixeira C, Faustino-Rocha AI, Helguero L, Vitorino R, Santos
LL, Amado F, Duarte JA, et al: Endurance training prevents TWEAK
but not myostatin-mediated cardiac remodelling in cancer cachexia.
Arch Biochem Biophys. 567:13–21. 2015. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
22
|
Gallot YS, Durieux AC, Castells J,
Desgeorges MM, Vernus B, Plantureux L, Rémond D, Jahnke VE, Lefai
E, Dardevet D, et al: Myostatin gene inactivation prevents skeletal
muscle wasting in cancer. Cancer Res. 74:7344–7356. 2014.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
23
|
Han HQ, Zhou X, Mitch WE and Goldberg AL:
Myostatin/activin pathway antagonism: Molecular basis and
therapeutic potential. Int J Biochem Cell Biol. 45:2333–2347. 2013.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
24
|
Zhou X, Wang JL, Lu J, Song Y, Kwak KS,
Jiao Q, Rosenfeld R, Chen Q, Boone T, Simonet WS, et al: Reversal
of cancer cachexia and muscle wasting by ActRIIB antagonism leads
to prolonged survival. Cell. 142:531–543. 2010. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
25
|
Lokireddy S, Wijesoma IW, Bonala S, Wei M,
Sze SK, McFarlane C, Kambadur R and Sharma M: Myostatin is a novel
tumoral factor that induces cancer cachexia. Biochem J. 446:23–36.
2012. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
26
|
Ramaswamy S, Nakamura N, Sansal I,
Bergeron L and Sellers WR: A novel mechanism of gene regulation and
tumor suppression by the transcription factor FKHR. Cancer Cell.
2:81–91. 2002. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
27
|
Sandri M, Sandri C, Gilbert A, Skurk C,
Calabria E, Picard A, Walsh K, Schiaffino S, Lecker SH and Goldberg
AL: Foxo transcription factors induce the atrophy-related ubiquitin
ligase atrogin-1 and cause skeletal muscle atrophy. Cell.
117:399–412. 2004. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
28
|
Bodine SC, Latres E, Baumhueter S, Lai VK,
Nunez L, Clarke BA, Poueymirou WT, Panaro FJ, Na E, Dharmarajan K,
et al: Identification of ubiquitin ligases required for skeletal
muscle atrophy. Science. 294:1704–1708. 2001. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
29
|
Gomes MD, Lecker SH, Jagoe RT, Navon A and
Goldberg AL: Atrogin-1, a muscle-specific F-box protein highly
expressed during muscle atrophy. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA.
98:14440–14445. 2001. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
30
|
Cohen S, Nathan JA and Goldberg AL: Muscle
wasting in disease: Molecular mechanisms and promising therapies.
Nat Rev Drug Discov. 14:58–74. 2015. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
31
|
Wang DT, Yang YJ, Huang RH, Zhang ZH and
Lin X: Myostatin activates the ubiquitin-proteasome and
autophagy-lysosome systems contributing to muscle wasting in
chronic kidney disease. Oxid Med Cell Longev. 2015:6849652015.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
32
|
Attaix D, Ventadour S, Codran A, Béchet D,
Taillandier D and Combaret L: The ubiquitin-proteasome system and
skeletal muscle wasting. Essays Biochem. 41:173–186. 2005.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
33
|
Taillandier D, Combaret L, Pouch MN,
Samuels SE, Béchet D and Attaix D: The role of
ubiquitin-proteasome-dependent proteolysis in the remodelling of
skeletal muscle. Proc Nutr Soc. 63:357–361. 2004. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
34
|
Lokireddy S, Wijesoma IW, Sze SK,
McFarlane C, Kambadur R and Sharma M: Identification of
atrogin-1-targeted proteins during the myostatin-induced skeletal
muscle wasting. Am J Physiol Cell Physiol. 303:C512–C529. 2012.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
35
|
Sandri M, Lin J, Handschin C, Yang W,
Arany ZP, Lecker SH, Goldberg AL and Spiegelman BM: PGC-1alpha
protects skeletal muscle from atrophy by suppressing FoxO3 action
and atrophy-specific gene transcription. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA.
103:16260–16265. 2006. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
36
|
Esterbauer H, Oberkofler H, Krempler F and
Patsch W: Human peroxisome proliferator activated receptor gamma
coactivator 1 (PPARGC1) gene: cDNA sequence, genomic organization,
chromosomal localization, and tissue expression. Genomics.
62:98–102. 1999. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
37
|
Puigserver P: Tissue-specific regulation
of metabolic pathways through the transcriptional coactivator
PGC1-alpha. Int J Obes. 29:(Suppl 1). S5–S9. 2005. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
38
|
Brault JJ, Jespersen JG and Goldberg AL:
Peroxisome proliferator-activated receptor gamma coactivator 1alpha
or 1beta overexpression inhibits muscle protein degradation,
induction of ubiquitin ligases, and disuse atrophy. J Biol Chem.
285:19460–19471. 2010. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
39
|
Cannavino J, Brocca L, Sandri M,
Bottinelli R and Pellegrino MA: PGC1-α over-expression prevents
metabolic alterations and soleus muscle atrophy in hindlimb
unloaded mice. J Physiol. 592:4575–4589. 2014. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
40
|
Wenz T, Rossi SG, Rotundo RL, Spiegelman
BM and Moraes CT: Increased muscle PGC-1alpha expression protects
from sarcopenia and metabolic disease during aging. Proc Natl Acad
Sci USA. 106:20405–20410. 2009. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
41
|
Ramji DP and Foka P:
CCAAT/enhancer-binding proteins: Structure, function and
regulation. Biochem J. 365:561–575. 2002. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
42
|
Allen DL, Bandstra ER, Harrison BC, Thorng
S, Stodieck LS, Kostenuik PJ, Morony S, Lacey DL, Hammond TG,
Leinwand LL, et al: Effects of spaceflight on murine skeletal
muscle gene expression. J Appl Physiol (1985). 106:582–595. 2009.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
43
|
Penner G, Gang G, Sun X, Wray C and
Hasselgren PO: C/EBP DNA-binding activity is upregulated by a
glucocorticoid-dependent mechanism in septic muscle. Am J Physiol
Regul Integr Comp Physiol. 282:R439–R444. 2002. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
44
|
Zhang G and Li YP: p38β MAPK upregulates
atrogin1/MAFbx by specific phosphorylation of C/EBPβ. Skelet
Muscle. 2:202012. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
45
|
McKinsey TA, Zhang CL and Olson EN:
Control of muscle development by dueling HATs and HDACs. Curr Opin
Genet Dev. 11:497–504. 2001. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
46
|
Alamdari N, Aversa Z, Castillero E and
Hasselgren PO: Acetylation and deacetylation - novel factors in
muscle wasting. Metabolism. 62:1–11. 2013. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
47
|
Yang H, Wei W, Menconi M and Hasselgren
PO: Dexamethasone-induced protein degradation in cultured myotubes
is p300/HAT dependent. Am J Physiol Regul Integr Comp Physiol.
292:R337–R334. 2007. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
48
|
Demos-Davies KM, Ferguson BS, Cavasin MA,
Mahaffey JH, Williams SM, Spiltoir JI, Schuetze KB, Horn TR, Chen
B, Ferrara C, et al: HDAC6 contributes to pathological responses of
heart and skeletal muscle to chronic angiotensin-II signaling. Am J
Physiol Heart Circ Physiol. 307:H252–H258. 2014. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
49
|
Beharry AW, Sandesara PB, Roberts BM,
Ferreira LF, Senf SM and Judge AR: HDAC1 activates FoxO and is both
sufficient and required for skeletal muscle atrophy. J Cell Sci.
127:1441–1453. 2014. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
50
|
Greco S, De Simone M, Colussi C,
Zaccagnini G, Fasanaro P, Pescatori M, Cardani R, Perbellini R,
Isaia E, Sale P, et al: Common micro-RNA signature in skeletal
muscle damage and regeneration induced by Duchenne muscular
dystrophy and acute ischemia. FASEB J. 23:3335–3346. 2009.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
51
|
Guess MG, Barthel KK, Harrison BC and
Leinwand LA: miR-30 family microRNAs regulate myogenic
differentiation and provide negative feedback on the microRNA
pathway. PLoS One. 10:e01182292015. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
52
|
Cavallo F, Calogero RA and Forni G: Are
oncoantigens suitable targets for anti-tumour therapy? Nat Rev
Cancer. 7:707–713. 2007. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
53
|
Das SK, Eder S, Schauer S, Diwoky C,
Temmel H, Guertl B, Gorkiewicz G, Tamilarasan KP, Kumari P, Trauner
M, et al: Adipose triglyceride lipase contributes to
cancer-associated cachexia. Science. 333:233–238. 2011. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
54
|
Kliewer KL, Ke JY, Tian M, Cole RM,
Andridge RR and Belury MA: Adipose tissue lipolysis and energy
metabolism in early cancer cachexia in mice. Cancer Biol Ther.
2014.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
55
|
Minetti GC, Colussi C, Adami R, Serra C,
Mozzetta C, Parente V, Fortuni S, Straino S, Sampaolesi M, Di
Padova M, et al: Functional and morphological recovery of
dystrophic muscles in mice treated with deacetylase inhibitors. Nat
Med. 12:1147–1150. 2006. View
Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
56
|
Moresi V, Williams AH, Meadows E, Flynn
JM, Potthoff MJ, McAnally J, Shelton JM, Backs J, Klein WH,
Richardson JA, et al: Myogenin and class II HDACs control
neurogenic muscle atrophy by inducing E3 ubiquitin ligases. Cell.
143:35–45. 2010. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|