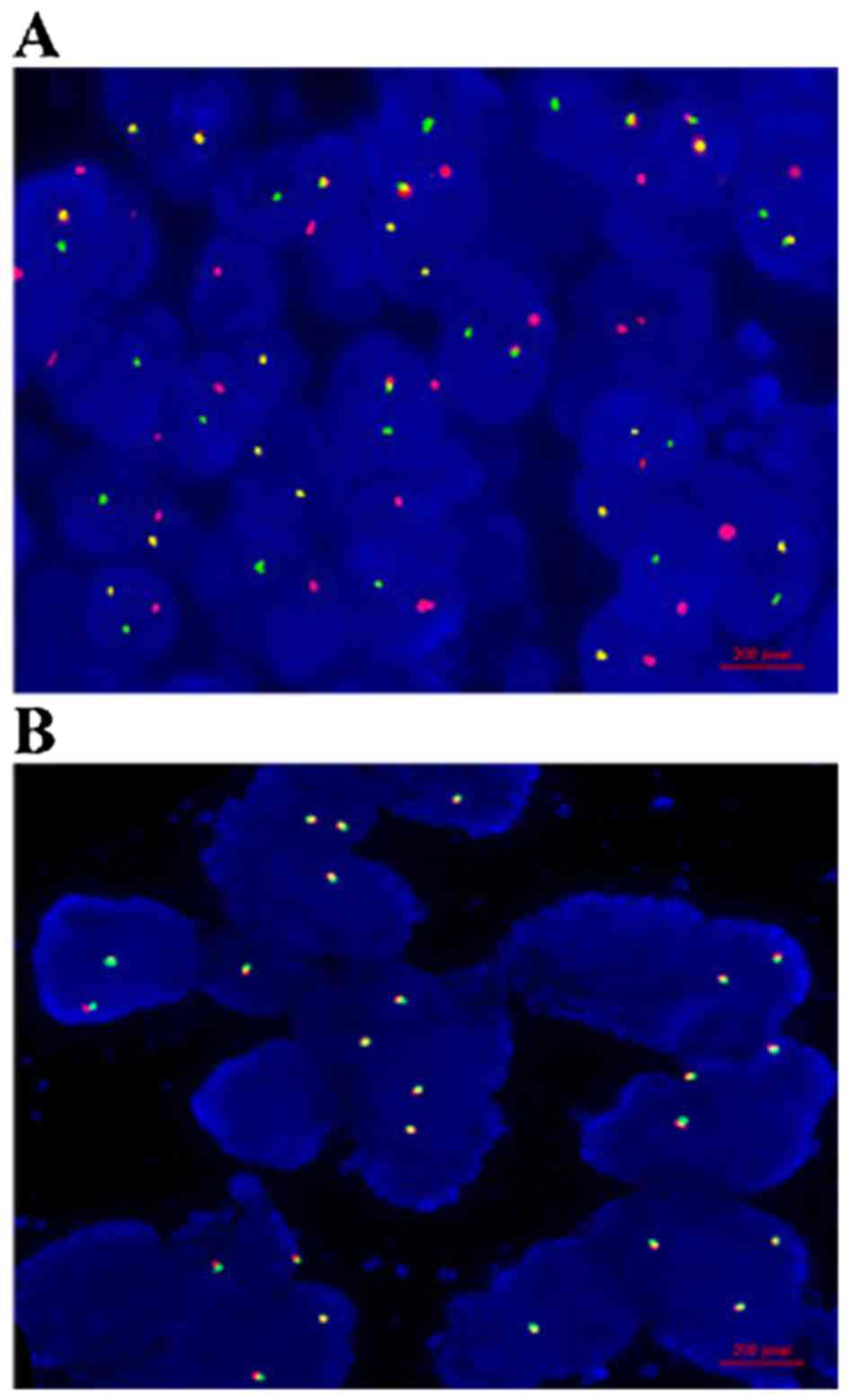
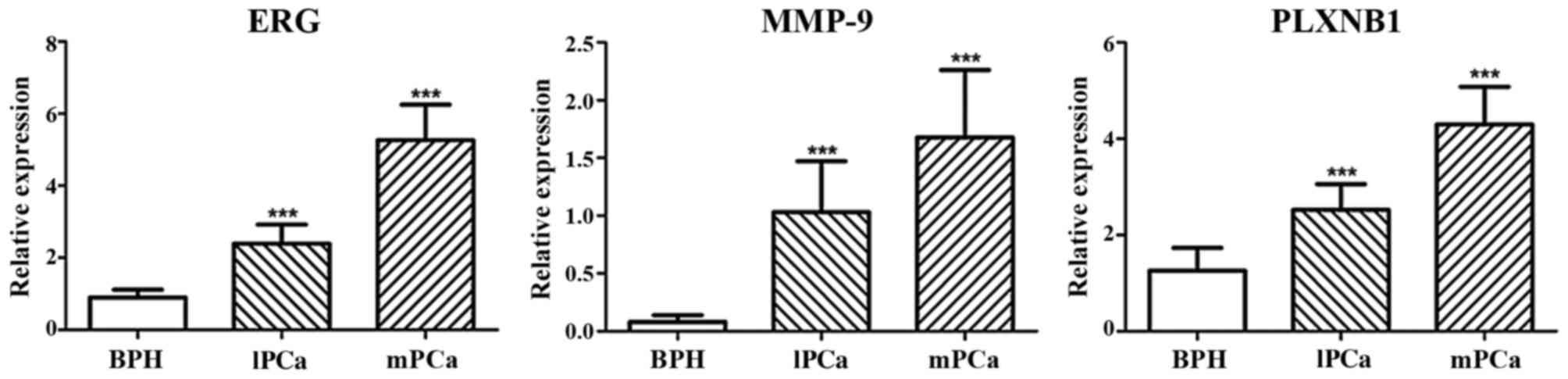
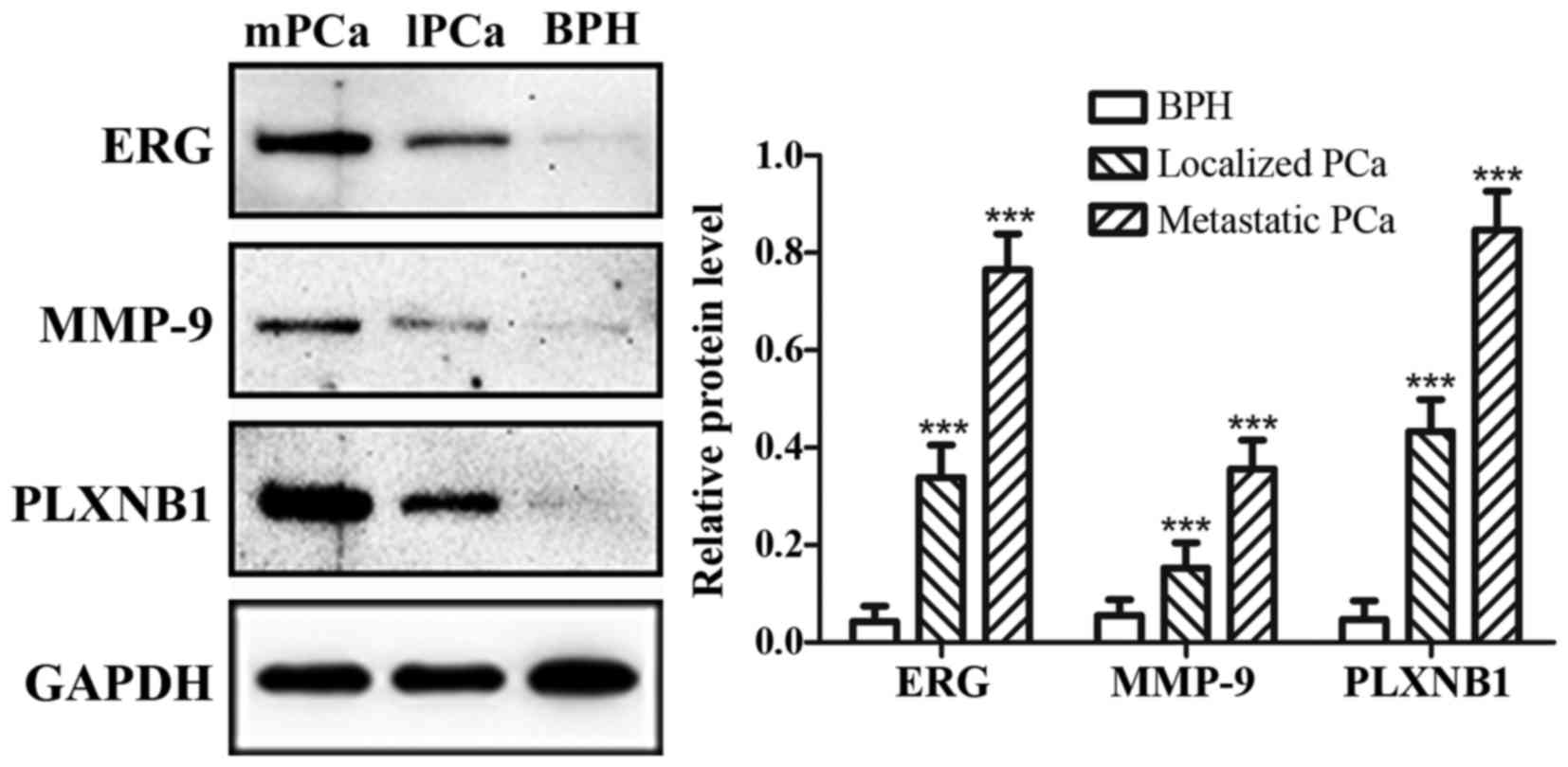
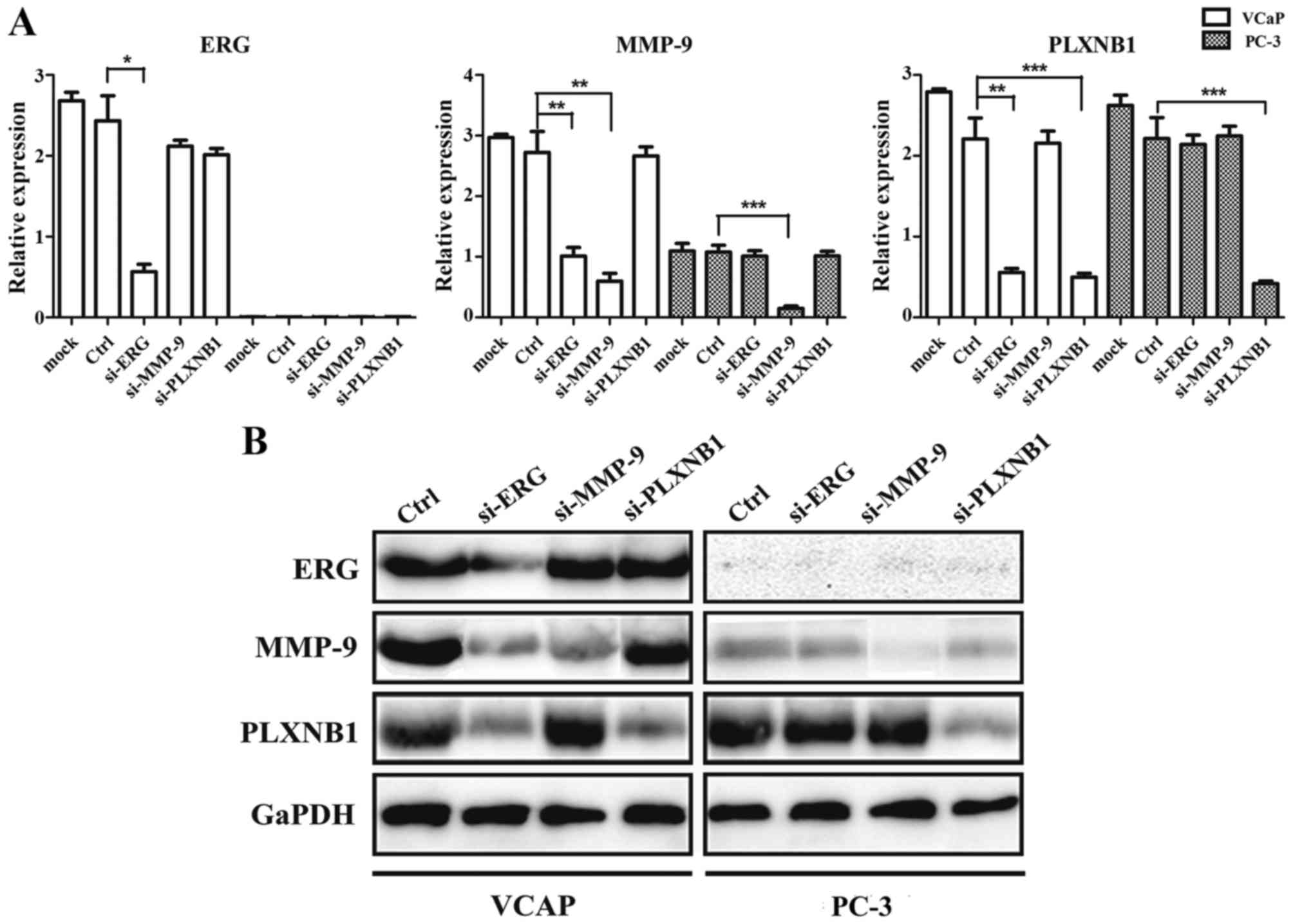
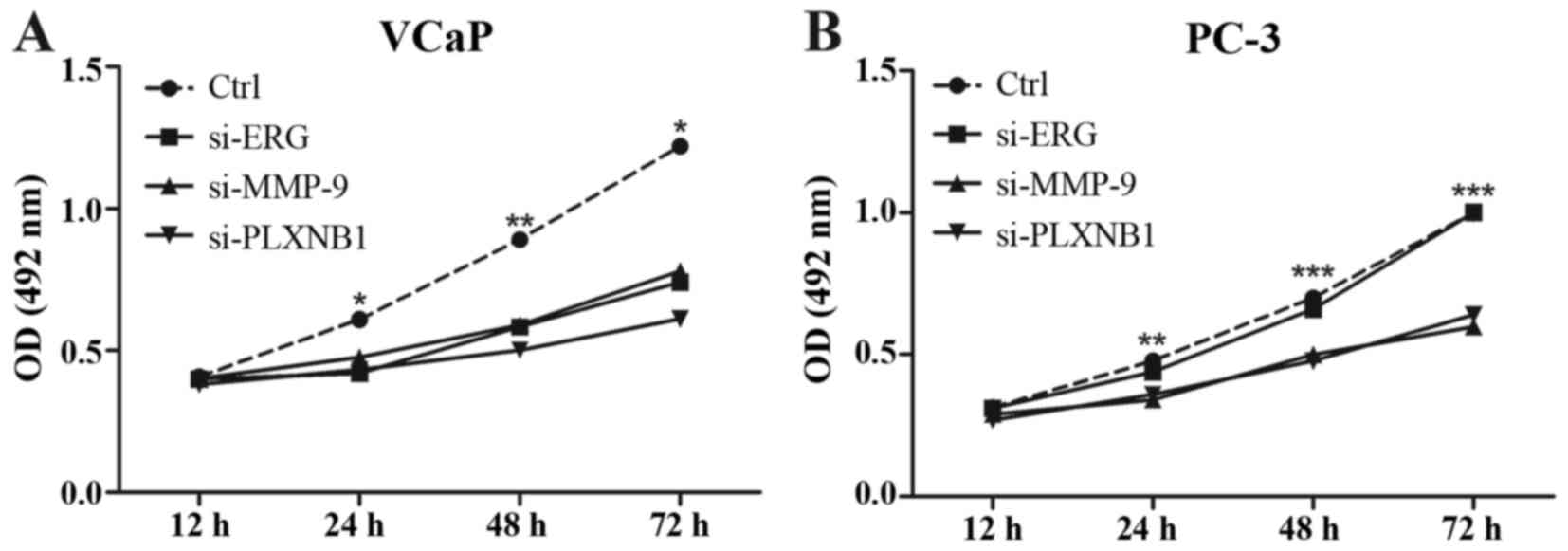
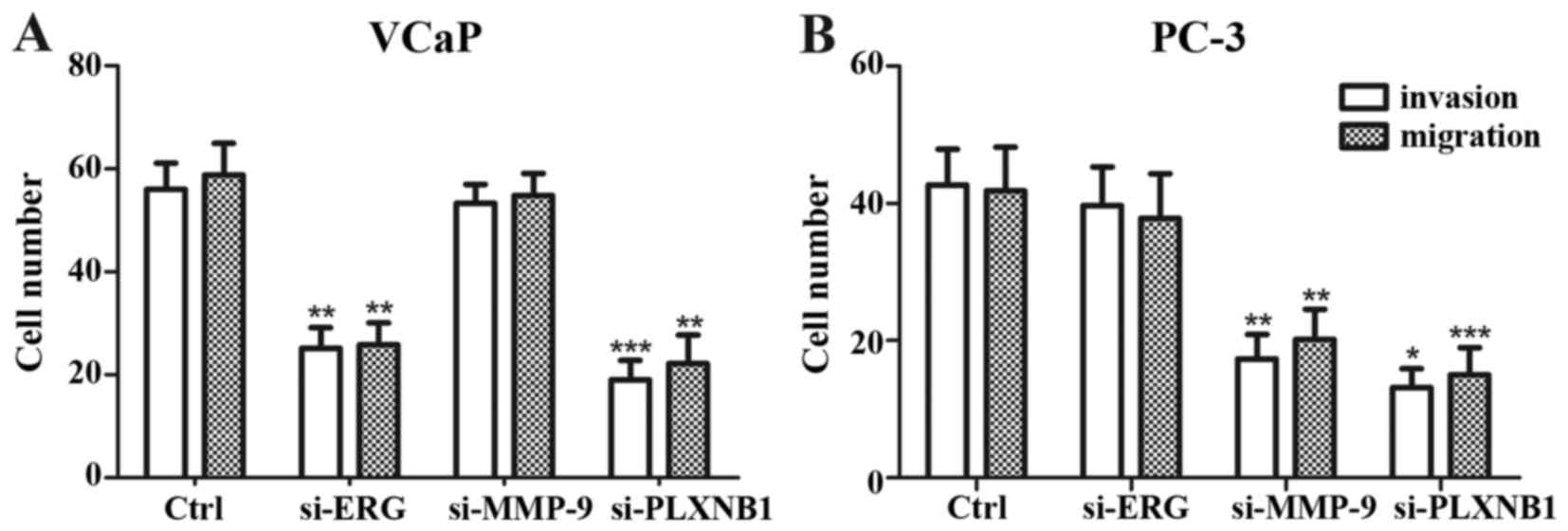
|
1
|
International Agency for Research on
Cancer, . Prostate cancer: estimated incidence, mortality, and
prevalence worldwide. http://globocan.iarc.fr/Pages/fact_sheets_cancer.aspxAccessed
March 20, 2014.
|
|
2
|
Tomlins SA, Rhodes DR, Perner S,
Dhanasekaran SM, Mehra R, Sun XW, Varambally S, Cao X, Tchinda J,
Kuefer R, et al: Recurrent fusion of TMPRSS2 and ETS transcription
factor genes in prostate cancer. Science. 310:644–648. 2005.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
3
|
Klezovitch O, Risk M, Coleman I, Lucas JM,
Null M, True LD, Nelson PS and Vasioukhin V: A causal role for ERG
in neoplastic transformation of prostate epithelium. Proc Natl Acad
Sci USA. 105:2105–2110. 2008. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
4
|
Park K, Dalton JT, Narayanan R, Barbieri
CE, Hancock ML, Bostwick DG, Steiner MS and Rubin MA: TMPRSS2:ERG
gene fusion predicts subsequent detection of prostate cancer in
patients with high-grade prostatic intraepithelial neoplasia. J
Clin Oncol. 32:206–211. 2014. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
5
|
Böttcher R, Henderson DJ, Dulla K, van
Strijp D, Waanders LF, Tevz G, Lehman ML, Merkle D, van Leenders
GJ, Baillie GS, et al: Human phosphodiesterase 4D7 (PDE4D7)
expression is increased in TMPRSS2-ERG-positive primary prostate
cancer and independently adds to a reduced risk of post-surgical
disease progression. Br J Cancer. 113:1502–1511. 2015. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
6
|
Fallahabadi ZR, Daloii MR Noori, Mahdian
R, Behjati F, Shokrgozar MA, Abolhasani M, Asgari M and Shahrokh H:
Frequency of PTEN alterations, TMPRSS2-ERG fusion and their
association in prostate cancer. Gene. 575:755–760. 2016. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
7
|
King JC, Xu J, Wongvipat J, Hieronymus H,
Carver BS, Leung DH, Taylor BS, Sander C, Cardiff RD, Couto SS, et
al: Cooperativity of TMPRSS2-ERG with PI3-kinase pathway activation
in prostate oncogenesis. Nat Genet. 41:524–526. 2009. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
8
|
Chen Y, Chi P, Rockowitz S, Iaquinta PJ,
Shamu T, Shukla S, Gao D, Sirota I, Carver BS, Wongvipat J, et al:
ETS factors reprogram the androgen receptor cistrome and prime
prostate tumorigenesis in response to PTEN loss. Nat Med.
19:1023–1029. 2013. View
Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
9
|
Damola A, Legendre A, Ball S, Masters JR
and Williamson M: Function of mutant and wild-type plexinb1 in
prostate cancer cells. Prostate. 73:1326–1335. 2013. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
10
|
Williamson M, de Winter P and Masters JR:
Plexin-B1 signalling promotes androgen receptor translocation to
the nucleus. Oncogene. 35:1066–1072. 2016. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
11
|
Santoni M, Scarpelli M, Mazzucchelli R,
Lopez-Beltran A, Cheng L, Epstein JI, Cascinu S, Briganti A, Catto
JW, Montorsi F, et al: Current histopathologic and molecular
characterisations of prostate cancer: towards individualised
prognosis and therapies. Eur Urol. 69:186–190. 2016. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
12
|
Urbinati G, Ali HM, Rousseau Q, Chapuis H,
Desmaële D, Couvreur P and Massaad-Massade L: Antineoplastic
effects of siRNA against TMPRSS2-ERG junction oncogene in prostate
cancer. PLoS One. 10:e01252772015. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
13
|
Tian TV, Tomavo N, Huot L, Flourens A,
Bonnelye E, Flajollet S, Hot D, Leroy X, de Launoit Y and
Duterque-Coquillaud M: Identification of novel TMPRSS2:ERG
mechanisms in prostate cancer metastasis: involvement of MMP9 and
PLXNA2. Oncogene. 33:2204–2214. 2014. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
14
|
Magi-Galluzzi C, Tsusuki T, Elson P,
Simmerman K, LaFargue C, Esgueva R, Klein E, Rubin MA and Zhou M:
TMPRSS2-ERG gene fusion prevalence and class are significantly
different in prostate cancer of Caucasian, African-American and
Japanese patients. Prostate. 71:489–497. 2011. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
15
|
Dong J, Xiao L, Sheng L, Xu J and Sun ZQ:
TMPRSS2:ETS fusions and clinicopathologic characteristics of
prostate cancer patients from Eastern China. Asian Pac J Cancer
Prev. 15:3099–3103. 2014. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
16
|
Kessenbrock K, Plaks V and Werb Z: Matrix
metalloproteinases: Regulators of the tumor microenvironment. Cell.
141:52–67. 2010. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
17
|
Wang D, Li Q, Li K, Xiao P and Yin R:
Twist-related protein 1-mediated regulation of mesenchymal change
contributes to the migration and invasion of cervical cancer cells.
Oncol Lett. 10:3107–3112. 2015.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
18
|
Shi Z, Li X, Wu D, Tang R, Chen R, Xue S
and Sun X: Silencing of HMGA2 suppresses cellular proliferation,
migration, invasion, and epithelial-mesenchymal transition in
bladder cancer. Tumour Biol. 37:7515–7523. 2016. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
19
|
Li XW, Tuergan M and Abulizi G: Expression
of MAPK1 in cervical cancer and effect of MAPK1 gene silencing on
epithelial-mesenchymal transition, invasion and metastasis. Asian
Pac J Trop Med. 8:937–943. 2015. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
20
|
Banerjee K and Resat H: Constitutive
activation of STAT3 in breast cancer cells: A review. Int J Cancer.
138:2570–2578. 2016. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
21
|
Kato T, Fujita Y, Nakane K, Kojima T,
Nozawa Y, Deguchi T and Ito M: ETS1 promotes chemoresistance and
invasion of paclitaxel-resistant, hormone-refractory PC3 prostate
cancer cells by up-regulating MDR1 and MMP9 expression. Biochem
Biophys Res Commun. 417:966–971. 2012. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
22
|
Qi M, Liu Z, Shen C, Wang L, Zeng J, Wang
C, Li C, Fu W, Sun Y and Han B: Overexpression of ETV4 is
associated with poor prognosis in prostate cancer: Involvement of
uPA/uPAR and MMPs. Tumour Biol. 36:3565–3572. 2015. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
23
|
Tomlins SA, Laxman B, Varambally S, Cao X,
Yu J, Helgeson BE, Cao Q, Prensner JR, Rubin MA, Shah RB, et al:
Role of the TMPRSS2-ERG gene fusion in prostate cancer. Neoplasia.
10:177–188. 2008. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
24
|
Trusolino L and Comoglio PM:
Scatter-factor and semaphorin receptors: Cell signalling for
invasive growth. Nat Rev Cancer. 2:289–300. 2002. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
25
|
Gabrovska PN, Smith RA, Tiang T, Weinstein
SR, Haupt LM and Griffiths LR: Semaphorin-plexin signalling genes
associated with human breast tumourigenesis. Gene. 489:63–69. 2011.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
26
|
Ye S, Hao X, Zhou T, Wu M, Wei J, Wang Y,
Zhou L, Jiang X, Ji L, Chen Y, et al: Plexin-B1 silencing inhibits
ovarian cancer cell migration and invasion. BMC Cancer. 10:6112010.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
27
|
Sun QP, Li LY, Chen Z, Pang J, Yang WJ,
Zhou XF, Qiu JG, Su ZL, He D and Gao X: Detection of TMPRSS2-ETS
fusions by a multiprobe fluorescence in situ hybridization assay
for the early diagnosis of prostate cancer: A pilot study. J Mol
Diagn. 12:718–724. 2010. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
28
|
Perner S, Mosquera JM, Demichelis F, Hofer
MD, Paris PL, Simko J, Collins C, Bismar TA, Chinnaiyan AM, De
Marzo AM, et al: TMPRSS2-ERG fusion prostate cancer: An early
molecular event associated with invasion. Am J Surg Pathol.
31:882–888. 2007. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
29
|
Mehra R, Tomlins SA, Shen R, Nadeem O,
Wang L, Wei JT, Pienta KJ, Ghosh D, Rubin MA, Chinnaiyan AM, et al:
Comprehensive assessment of TMPRSS2 and ETS family gene aberrations
in clinically localized prostate cancer. Mod Pathol. 20:538–544.
2007. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
30
|
Font-Tello A, Juanpere N, de Muga S,
Lorenzo M, Lorente JA, Fumado L, Serrano L, Serrano S, Lloreta J
and Hernández S: Association of ERG and TMPRSS2-ERG with grade,
stage, and prognosis of prostate cancer is dependent on their
expression levels. Prostate. 75:1216–1226. 2015. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|