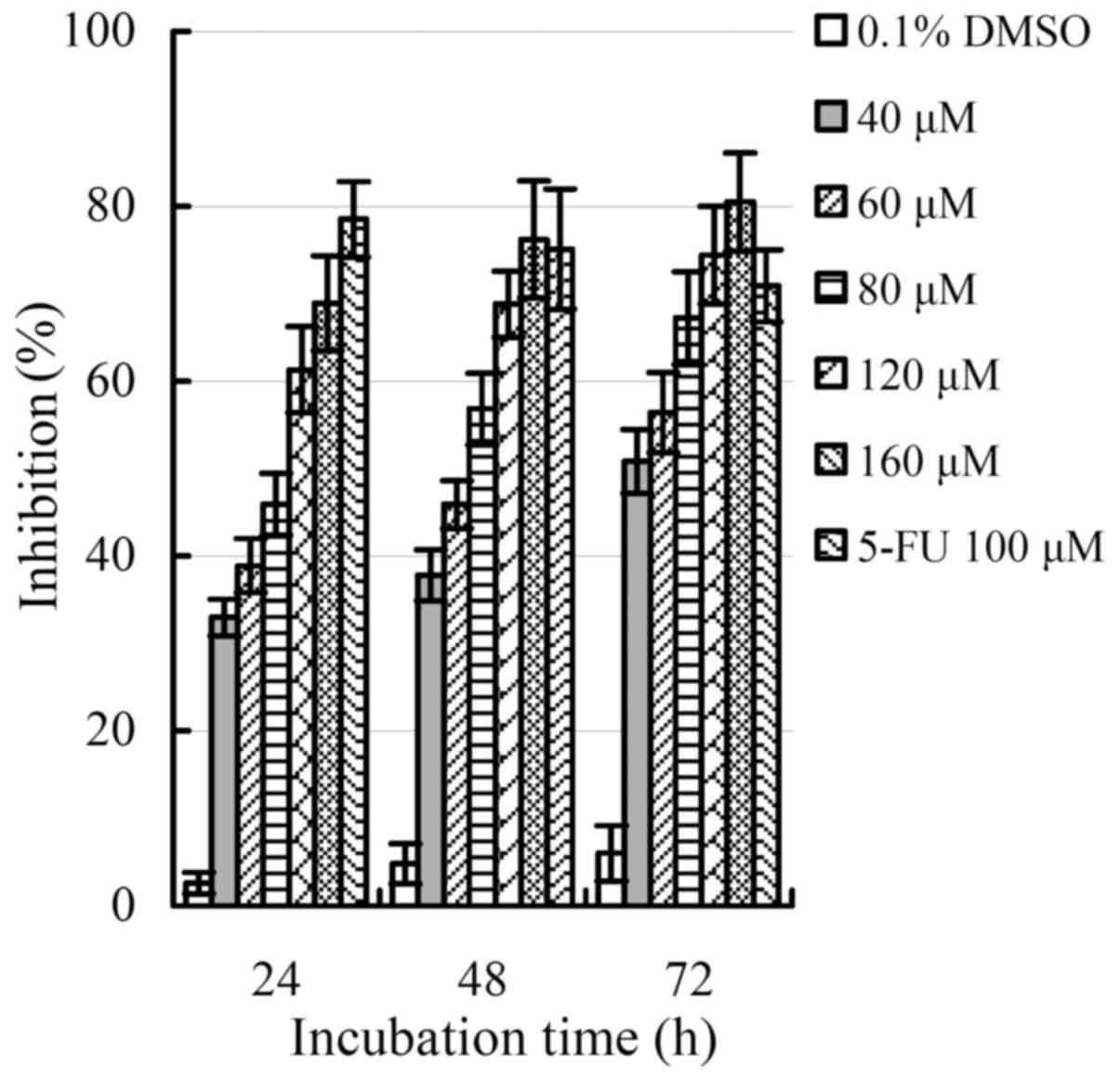
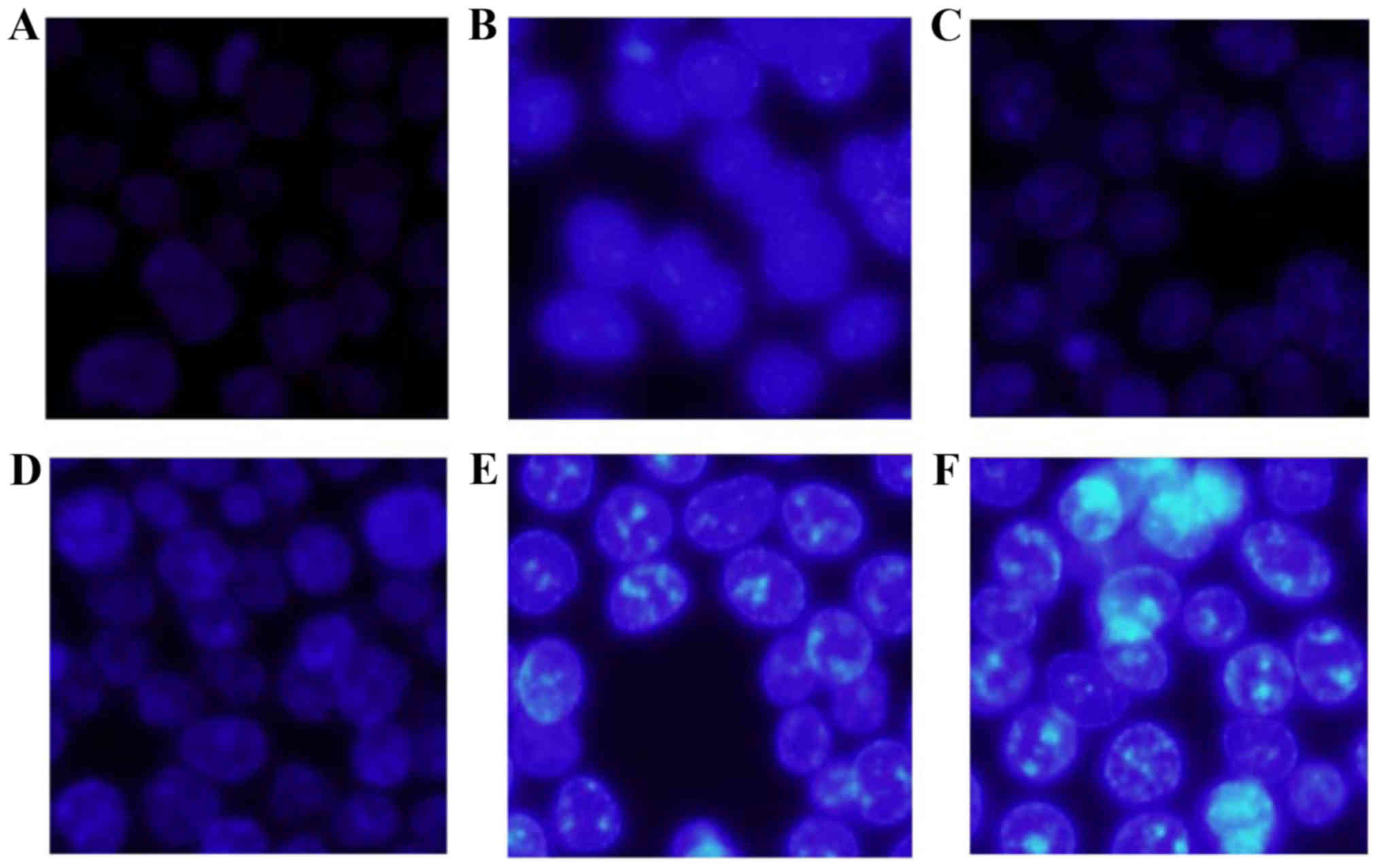
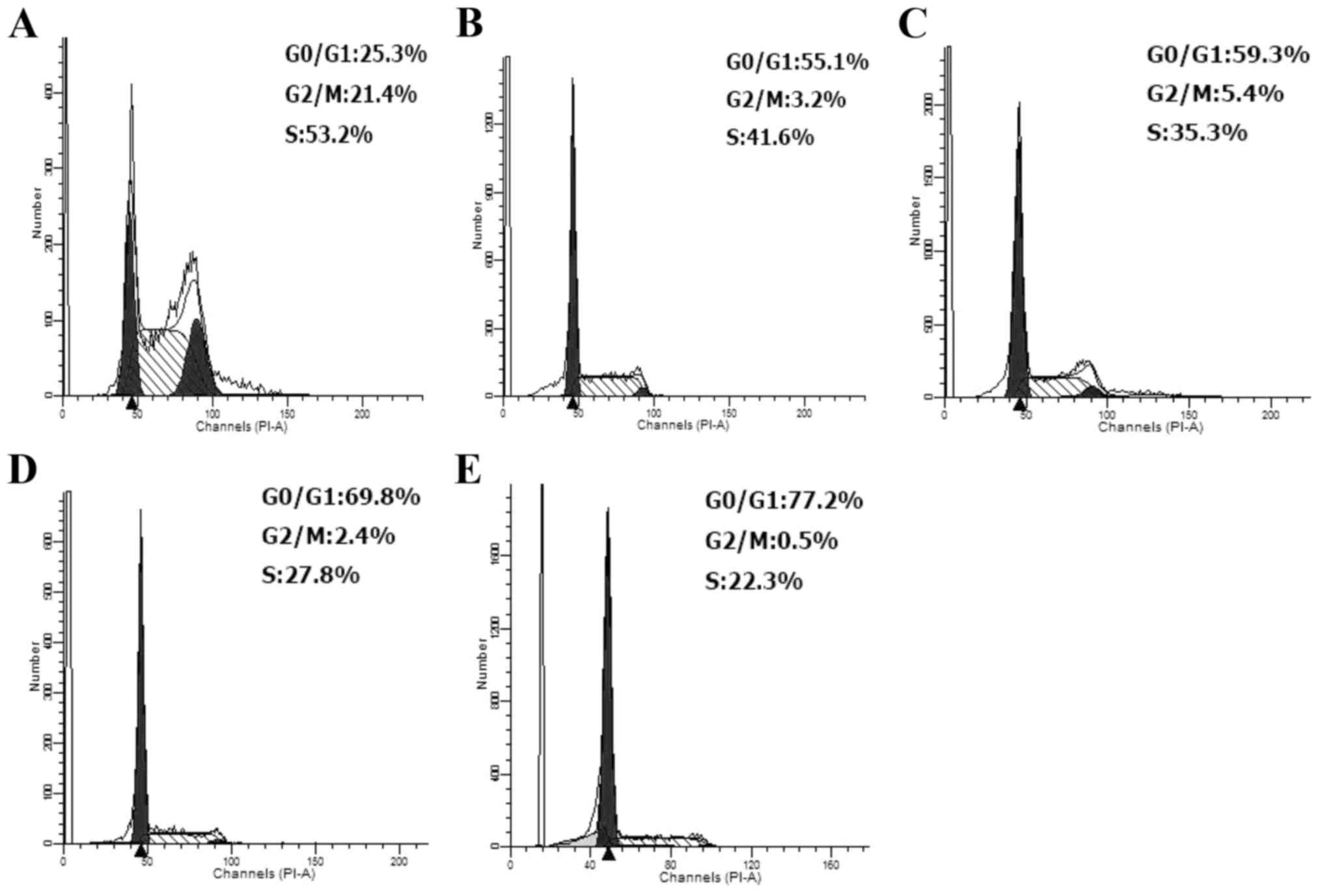
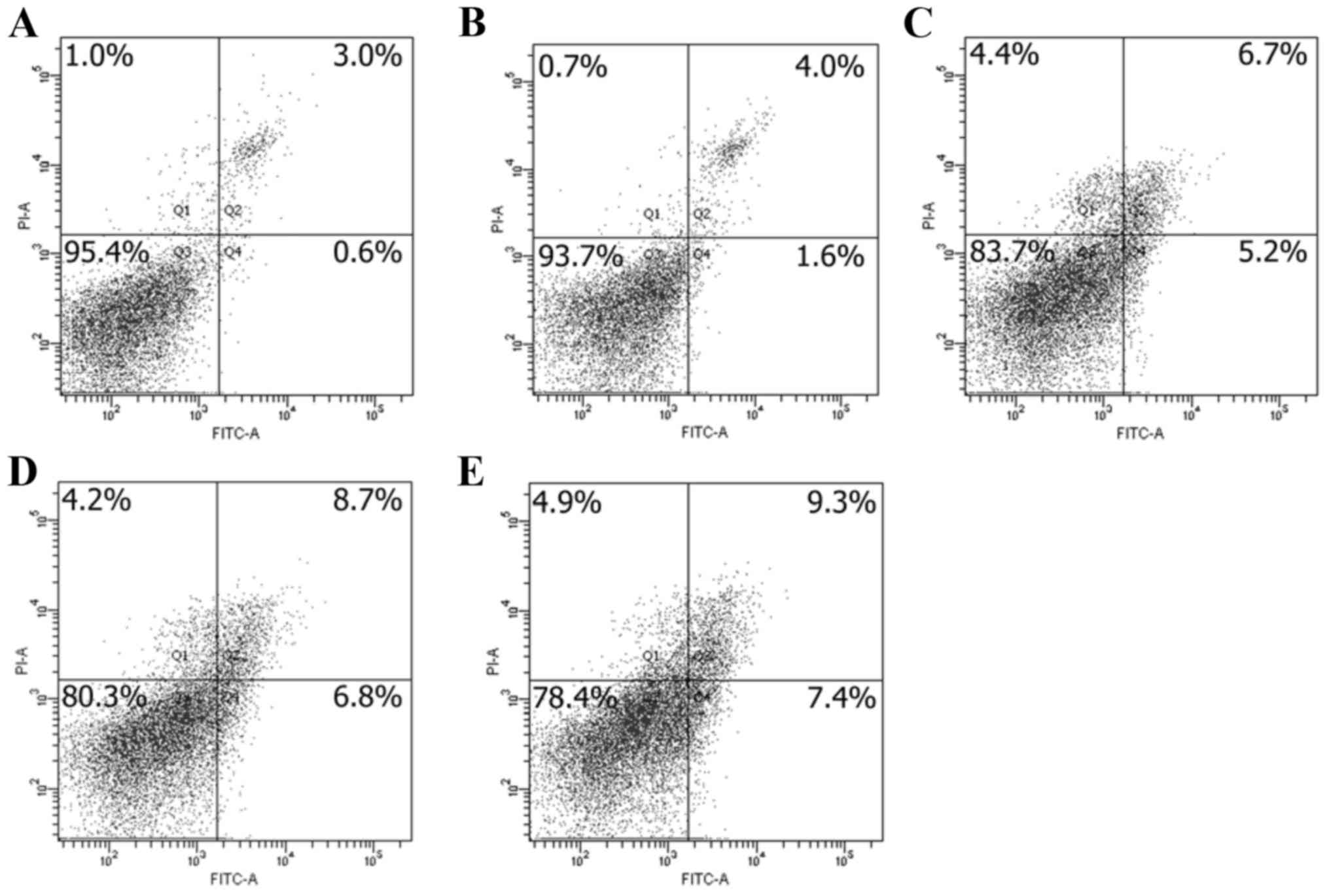
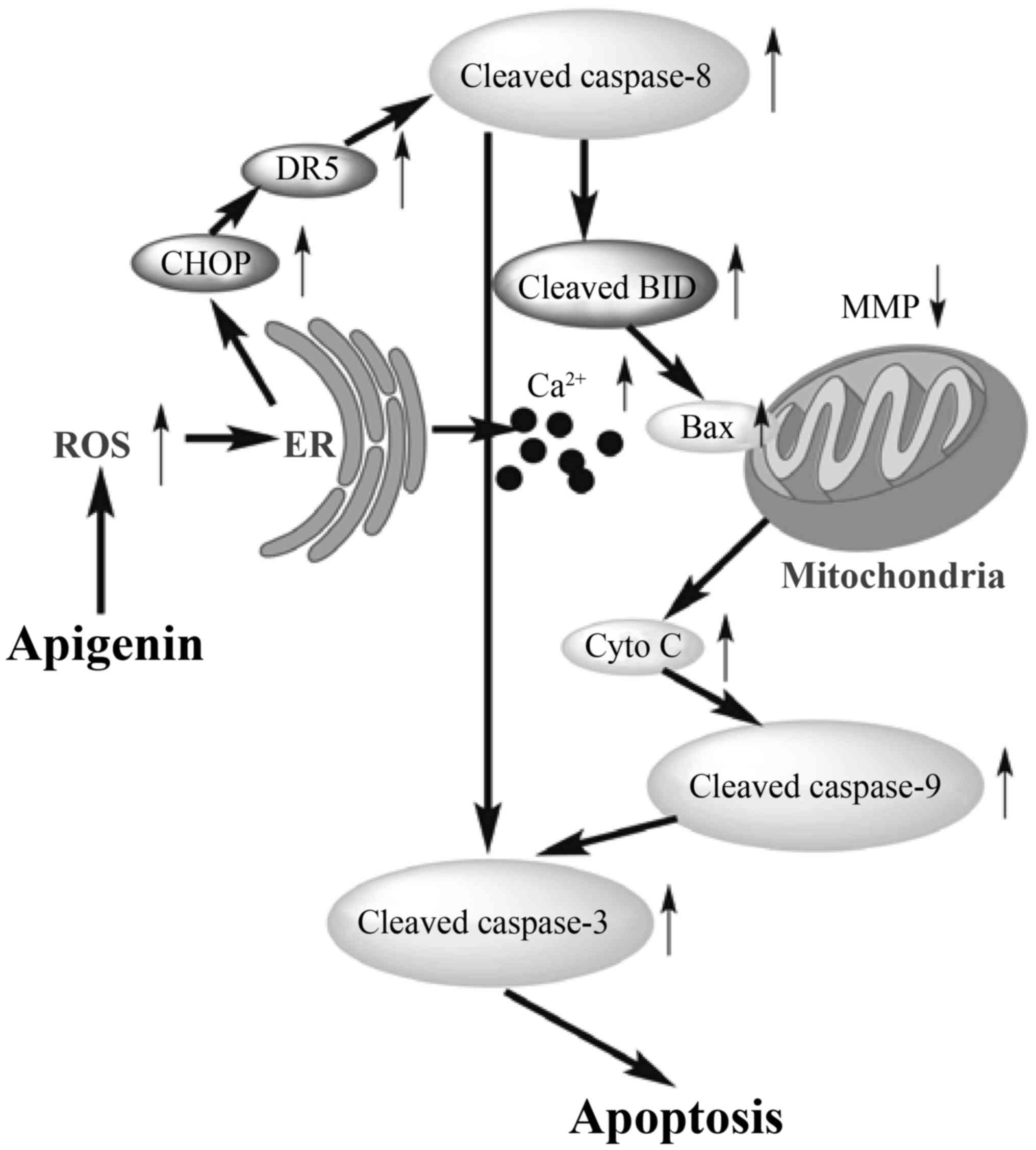
|
1
|
Yang CS, Landau JM, Huang MT and Newmark
HL: Inhibition of carcinogenesis by dietary polyphenolic compounds.
Annu Rev Nutr. 21:381–406. 2001. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
2
|
Patel D, Shukla S and Gupta S: Apigenin
and cancer chemoprevention: Progress, potential and promise
(Review). Int J Oncol. 30:233–245. 2007.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
3
|
Li ZD, Hu XW, Wang YT and Fang J: Apigenin
inhibits proliferation of ovarian cancer A2780 cells through Id1.
FEBS Lett. 583:1999–2003. 2009. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
4
|
Mak P, Leung YK, Tang WY, Harwood C and Ho
SM: Apigenin suppresses cancer cell growth through ERbeta.
Neoplasia. 8:896–904. 2006. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
5
|
Wang IK, Lin-Shiau SY and Lin JK:
Induction of apoptosis by apigenin and related flavonoids through
cytochrome c release and activation of caspase-9 and caspase-3 in
leukaemia HL-60 cells. Eur J Cancer. 35:1517–1525. 1999. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
6
|
Xu C, Bailly-Maitre B and Reed JC:
Endoplasmic reticulum stress: Cell life and death decisions. J Clin
Invest. 115:2656–2664. 2005. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
7
|
Kim R, Emi M, Tanabe K and Murakami S:
Role of the unfolded protein response in cell death. Apoptosis.
11:5–13. 2006. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
8
|
Malhotra JD and Kaufman RJ: The
endoplasmic reticulum and the unfolded protein response. Semin Cell
Dev Biol. 18:716–731. 2007. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
9
|
Oyadomari S and Mori M: Roles of
CHOP/GADD153 in endoplasmic reticulum stress. Cell Death Differ.
11:381–389. 2004. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
10
|
Meares GP, Mines MA, Beurel E, Eom TY,
Song L, Zmijewska AA and Jope RS: Glycogen synthase kinase-3
regulates endoplasmic reticulum (ER) stress-induced CHOP expression
in neuronal cells. Exp Cell Res. 317:1621–1628. 2011. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
11
|
Yamaguchi H and Wang HG: CHOP is involved
in endoplasmic reticulum stress-induced apoptosis by enhancing DR5
expression in human carcinoma cells. J Biol Chem. 279:45495–45502.
2004. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
12
|
Gorman AM, Healy SJ, Jäger R and Samali A:
Stress management at the ER: Regulators of ER stress-induced
apoptosis. Pharmacol Ther. 134:306–316. 2012. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
13
|
Trachootham D, Alexandre J and Huang P:
Targeting cancer cells by ROS-mediated mechanisms: A radical
therapeutic approach? Nat Rev Drug Discov. 8:579–591. 2009.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
14
|
Fruehauf JP and Meyskens FL Jr: Reactive
oxygen species: A breath of life or death? Clin Cancer Res.
13:789–794. 2007. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
15
|
Rigas B and Sun Y: Induction of oxidative
stress as a mechanism of action of chemopreventive agents against
cancer. Br J Cancer. 98:1157–1160. 2008. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
16
|
Schumacker PT: Reactive oxygen species in
cancer cells: Live by the sword, die by the sword. Cancer Cell.
10:175–176. 2006. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
17
|
Trachootham D, Zhou Y, Zhang H, Demizu Y,
Chen Z, Pelicano H, Chiao PJ, Achanta G, Arlinghaus RB, Liu J, et
al: Selective killing of oncogenically transformed cells through a
ROS-mediated mechanism by beta-phenylethyl isothiocyanate. Cancer
Cell. 10:241–252. 2006. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
18
|
Zou P, Chen M, Ji J, Chen W, Chen X, Ying
S, Zhang J, Zhang Z, Liu Z, Yang S, et al: Auranofin induces
apoptosis by ROS-mediated ER stress and mitochondrial dysfunction
and displayed synergistic lethality with piperlongumine in gastric
cancer. Oncotarget. 6:36505–36521. 2015.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
19
|
Shen S, Zhang Y, Zhang R and Gong X:
Sarsasapogenin induces apoptosis via the reactive oxygen
species-mediated mitochondrial pathway and ER stress pathway in
HeLa cells. Biochem Biophys Res Commun. 441:519–524. 2013.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
20
|
Shin SY, Lee JM, Lee MS, Koh D, Jung H,
Lim Y and Lee YH: Targeting cancer cells via the reactive oxygen
species-mediated unfolded protein response with a novel synthetic
polyphenol conjugate. Clin Cancer Res. 20:4302–4313. 2014.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
21
|
Chen CY, Yiin SJ, Hsu JL, Wang WC, Lin SC
and Chern CL: Isoobtusilactone A sensitizes human hepatoma Hep G2
cells to TRAIL-induced apoptosis via ROS and CHOP-mediated
up-regulation of DR5. J Agric Food Chem. 60:3533–3539. 2012.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
22
|
Johnson JL and de Mejia E Gonzalez:
Interactions between dietary flavonoids apigenin or luteolin and
chemotherapeutic drugs to potentiate anti-proliferative effect on
human pancreatic cancer cells, in vitro. Food Chem Toxicol.
60:83–91. 2013. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
23
|
Salvioli S, Ardizzoni A, Franceschi C and
Cossarizza A: JC-1, but not DiOC6(3) or rhodamine 123, is a
reliable fluorescent probe to assess delta psi changes in intact
cells: Implications for studies on mitochondrial functionality
during apoptosis. FEBS Lett. 411:77–82. 1997. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
24
|
Boissy RE, Trinkle LS and Nordlund JJ:
Separation of pigmented and albino melanocytes and the concomitant
evaluation of endogenous peroxide content using flow cytometry.
Cytometry. 10:779–787. 1989. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
25
|
Vega A, Chacón P, Monteseirín J, El Bekay
R, Alba G, Martín-Nieto J and Sobrino F: Expression of the
transcription factor NFAT2 in human neutrophils: IgE-dependent,
Ca2+- and calcineurin-mediated NFAT2 activation. J Cell
Sci. 120:2328–2337. 2007. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
26
|
Livak KJ and Schmittgen TD: Analysis of
relative gene expression data using real-time quantitative PCR and
the 2−∆∆CT method. Methods. 25:402–408. 2001. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
27
|
Van Dross R, Xue Y, Knudson A and Pelling
JC: The chemopreventive bioflavonoid apigenin modulates signal
transduction pathways in keratinocyte and colon carcinoma cell
lines. J Nutr. 133:(Suppl 1). S3800–S3804. 2003.
|
|
28
|
Shukla S and Gupta S: Dietary agents in
the chemoprevention of prostate cancer. Nutr Cancer. 53:18–32.
2005. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
29
|
Turktekin M, Konac E, Onen HI, Alp E,
Yilmaz A and Menevse S: Evaluation of the effects of the flavonoid
apigenin on apoptotic pathway gene expression on the colon cancer
cell line (HT29). J Med Food. 14:1107–1117. 2011. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
30
|
Shi MD, Shiao CK, Lee YC and Shih YW:
Apigenin, a dietary flavonoid, inhibits proliferation of human
bladder cancer T-24 cells via blocking cell cycle progression and
inducing apoptosis. Cancer Cell Int. 15:33–45. 2015. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
31
|
Vargo MA, Voss OH, Poustka F, Cardounel
AJ, Grotewold E and Doseff AI: Apigenin-induced-apoptosis is
mediated by the activation of PKCdelta and caspases in leukemia
cells. Biochem Pharmacol. 72:681–692. 2006. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
32
|
Seo HS, Ku JM, Choi HS, Woo JK, Jang BH,
Shin YC and Ko SG: Induction of caspase-dependent apoptosis by
apigenin by inhibiting STAT3 signaling in HER2-overexpressing
MDA-MB-453 breast cancer cells. Anticancer Res. 34:2869–2882.
2014.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
33
|
Horinaka M, Yoshida T, Shiraishi T, Nakata
S, Wakada M and Sakai T: The dietary flavonoid apigenin sensitizes
malignant tumor cells to tumor necrosis factor-related
apoptosis-inducing ligand. Mol Cancer Ther. 5:945–951. 2006.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
34
|
Miyoshi N, Naniwa K, Yamada T, Osawa T and
Nakamura Y: Dietary flavonoid apigenin is a potential inducer of
intracellular oxidative stress: The role in the interruptive
apoptotic signal. Arch Biochem Biophys. 466:274–282. 2007.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
35
|
Andueza A, García-Garzón A, de Galarreta M
Ruiz, Ansorena E, Iraburu MJ, López-Zabalza MJ and Martínez-Irujo
JJ: Oxidation pathways underlying the pro-oxidant effects of
apigenin. Free Radic Biol Med. 87:169–180. 2015. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
36
|
Lu HF, Chie YJ, Yang MS, Lee CS, Fu JJ,
Yang JS, Tan TW, Wu SH, Ma YS, Ip SW, et al: Apigenin induces
caspase-dependent apoptosis in human lung cancer A549 cells through
Bax- and Bcl-2-triggered mitochondrial pathway. Int J Oncol.
36:1477–1484. 2010.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
37
|
Harrison ME, Coombs MR Power, Delaney LM
and Hoskin DW: Exposure of breast cancer cells to a subcytotoxic
dose of apigenin causes growth inhibition, oxidative stress, and
hypophosphorylation of Akt. Exp Mol Pathol. 97:211–217. 2014.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
38
|
Shin GC, Kim C, Lee JM, Cho WS, Lee SG,
Jeong M, Cho J and Lee K: Apigenin-induced apoptosis is mediated by
reactive oxygen species and activation of ERK1/2 in rheumatoid
fibroblast-like synoviocytes. Chem Biol Interact. 182:29–36. 2009.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
39
|
Hale AJ, Smith CA, Sutherland LC, Stoneman
VE, Longthorne VL, Culhane AC and Williams GT: Apoptosis: Molecular
regulation of cell death. Eur J Biochem. 236:1–26. 1996. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
40
|
Wang C and Youle RJ: The role of
mitochondria in apoptosis. Annu Rev Genet. 43:95–118. 2009.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
41
|
Inoue S, Browne G, Melino G and Cohen GM:
Ordering of caspases in cells undergoing apoptosis by the intrinsic
pathway. Cell Death Differ. 16:1053–1061. 2009. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
42
|
Cory S, Huang DCS and Adams JM: The Bcl-2
family: Roles in cell survival and oncogenesis. Oncogene.
22:8590–8607. 2003. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
43
|
Ashkenazi A: Targeting the extrinsic
apoptosis pathway in cancer. Cytokine Growth Factor Rev.
19:325–331. 2008. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
44
|
Nagata S: Apoptosis by death factor. Cell.
88:355–365. 1997. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
45
|
Wang X: The expanding role of mitochondria
in apoptosis. Genes Dev. 15:2922–2933. 2001.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
46
|
Berridge MJ: The endoplasmic reticulum: A
multifunctional signaling organelle. Cell Calcium. 32:235–249.
2002. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
47
|
Banjerdpongchai R, Wudtiwai B, Khaw-On P,
Rachakhom W, Duangnil N and Kongtawelert P: Hesperidin from Citrus
seed induces human hepatocellular carcinoma HepG2 cell apoptosis
via both mitochondrial and death receptor pathways. Tumour Biol.
37:227–237. 2016. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
48
|
Oh H, Yoon G, Shin JC, Park SM, Cho SS,
Cho JH, Lee MH, Liu K, Cho YS, Chae JI, et al: Licochalcone B
induces apoptosis of human oral squamous cell carcinoma through the
extrinsic- and intrinsic-signaling pathways. Int J Oncol.
48:1749–1757. 2016.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
49
|
Yaoxian W, Hui Y, Yunyan Z, Yanqin L, Xin
G and Xiaoke W: Emodin induces apoptosis of human cervical cancer
heLa cells via intrinsic mitochondrial and extrinsic death receptor
pathway. Cancer Cell Int. 13:71–78. 2013. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|