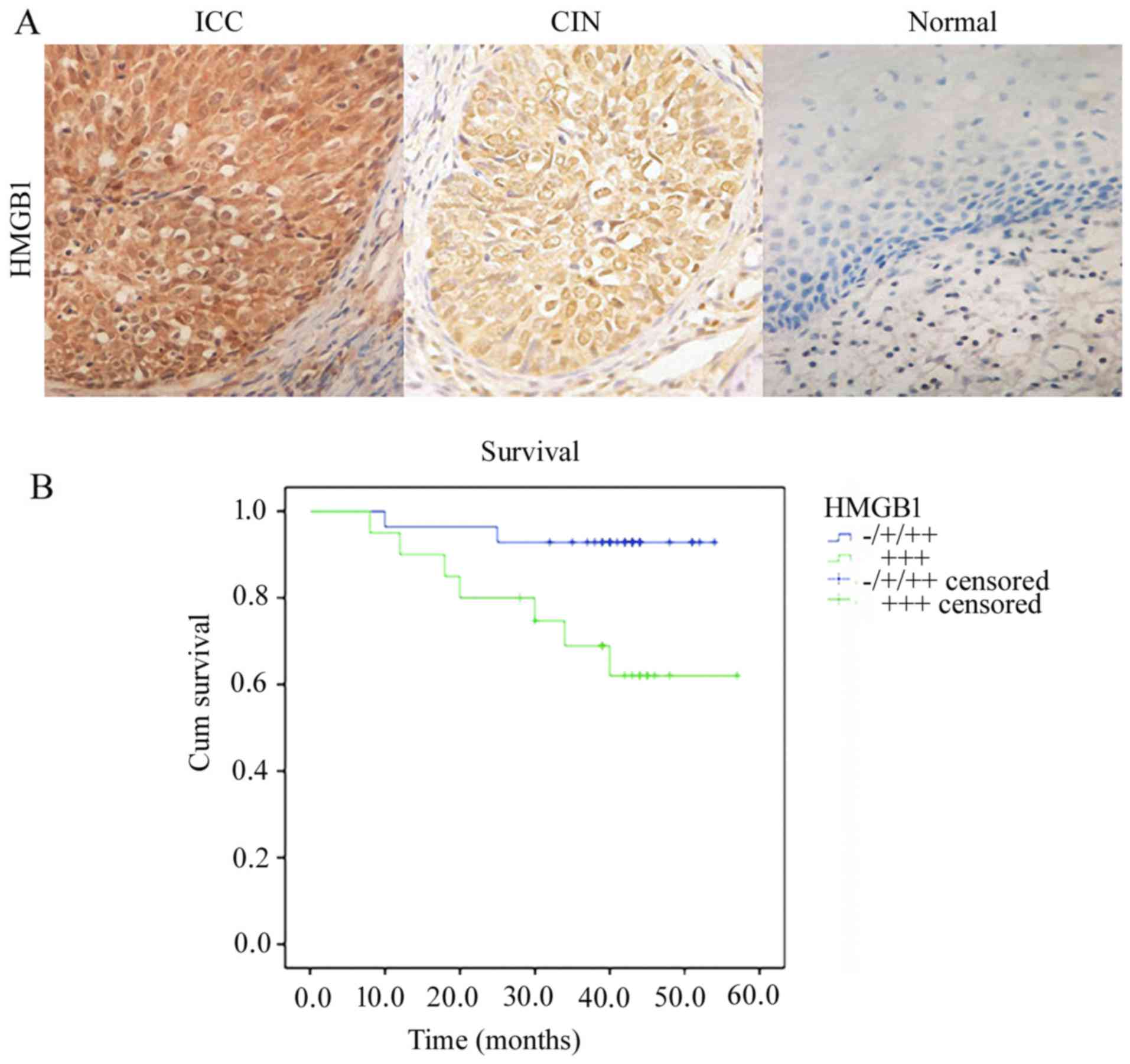
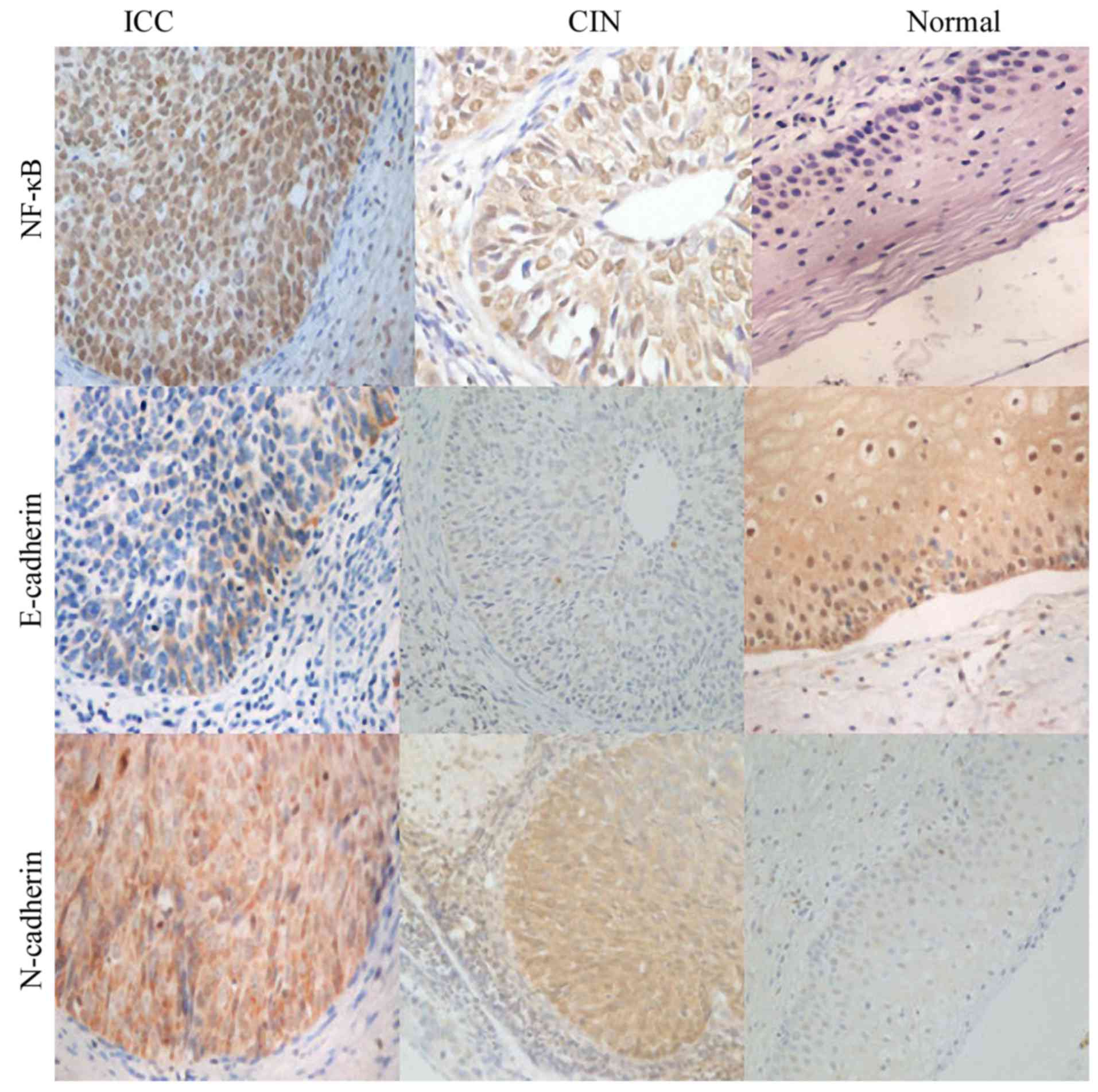
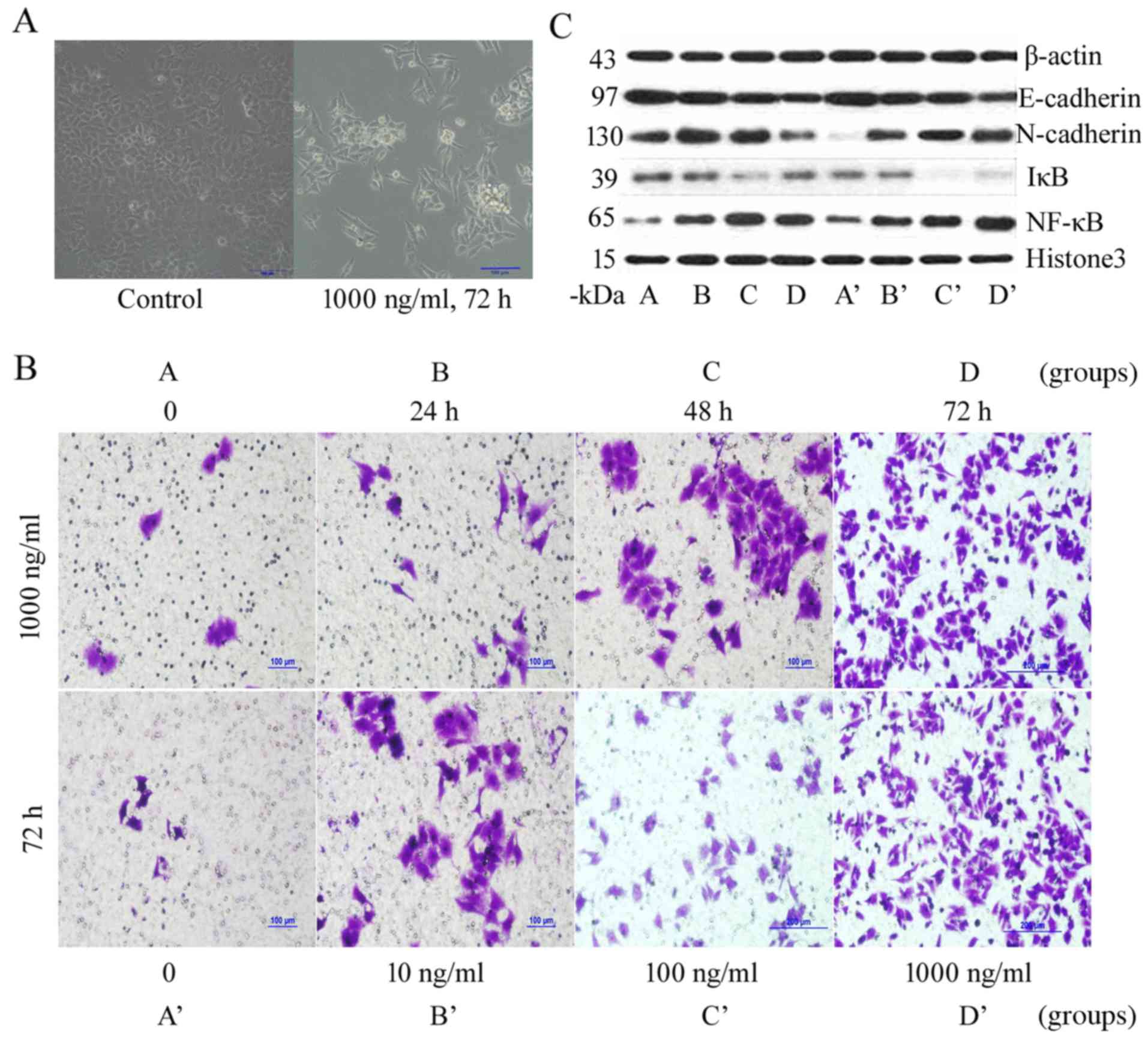
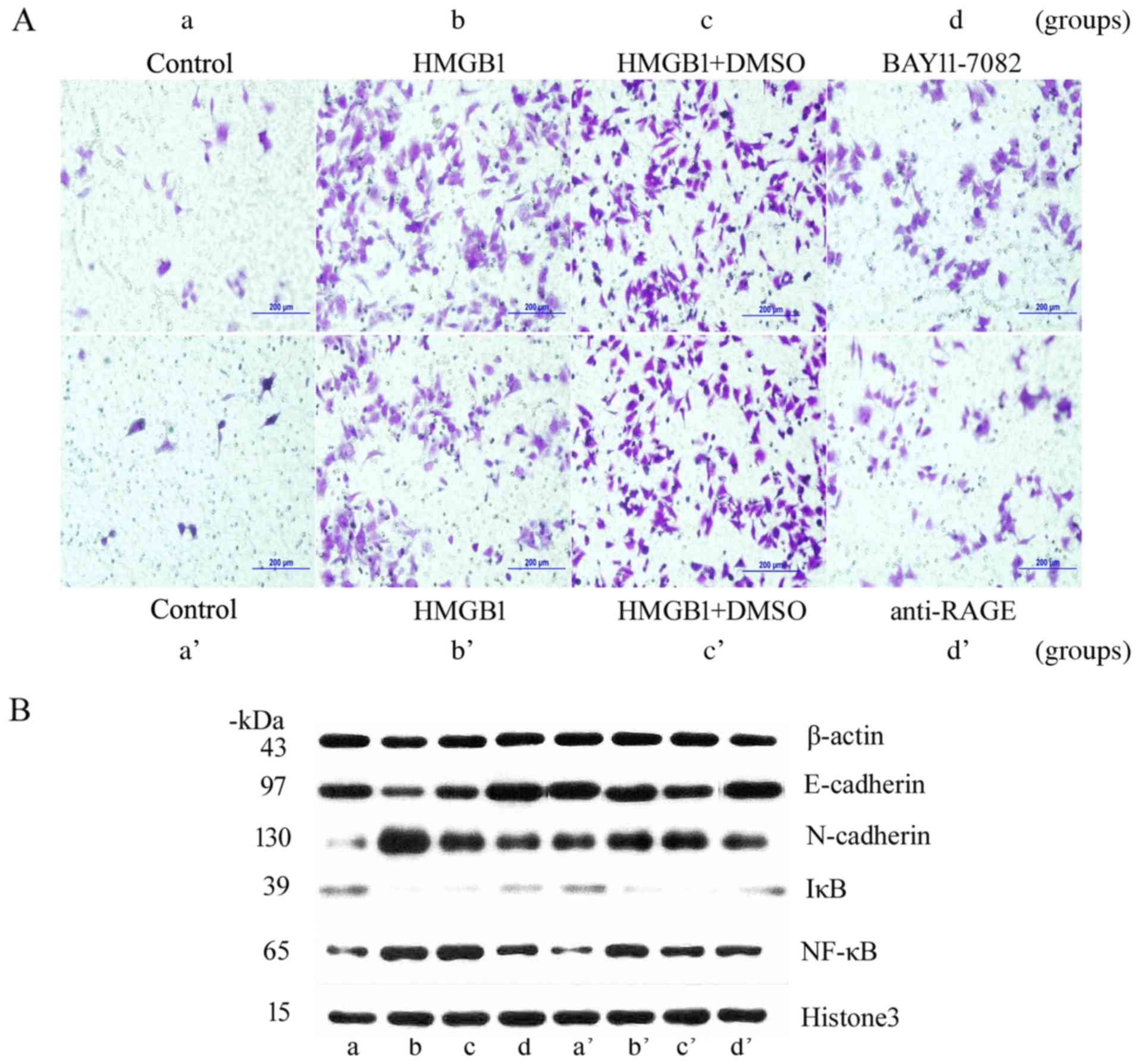
|
1
|
Lee MY and Shen MR: Epithelial-mesenchymal
transition in cervical carcinoma. Am J Transl Res. 4:1–13.
2012.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
2
|
Iwatsuki M, Mimori K, Yokobori T, Ishi H,
Beppu T, Nakamori S, Baba H and Mori M: Epithelial-mesenchymal
transition in cancer development and its clinical significance.
Cancer Sci. 101:293–299. 2010. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
3
|
Chen RC, Yi PP, Zhou RR, Xiao MF, Huang
ZB, Tang DL, Huang Y and Fan XG: The role of HMGB1-RAGE axis in
migration and invasion of hepatocellular carcinoma cell lines. Mol
Cell Biochem. 390:271–280. 2014. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
4
|
Evans A, Lennard TW and Davies BR:
High-mobility group protein 1(Y): Metastasis-associated or
metastasis-inducing? J Surg Oncol. 88:86–99. 2004. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
5
|
Chen XY and Yuan R: Expression and
significance of HMGB1 and E-cadherin in ovarian carcinoma. J
Chongqing Med Univ. 37:614–616. 2012.(In Chinese).
|
|
6
|
Zhao FH, Tiggelaar SM, Hu SY, Xu LN, Hong
Y, Niyazi M, Gao XH, Ju LR, Zhang LQ, Feng XX, et al: A
multi-center survey of age of sexual debut and sexual behavior in
Chinese women: Suggestions for optimal age of human papillomavirus
vaccination in China. Cancer Epidemiol. 36:384–390. 2012.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
7
|
Jemal A, Bray F, Center MM, Ferlay J, Ward
E and Forman D: Global cancer statistics. CA Cancer J Clin.
61:69–90. 2011. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
8
|
López-Novoa JM and Nieto MA: Inflammation
and EMT: An alliance towards organ fibrosis and cancer progression.
EMBO Mol Med. 1:303–314. 2009. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
9
|
Savagner P: The epithelial-mesenchymal
transition (EMT) phenomenon. Ann Oncol. 21:(Suppl 7). vii89–vii92.
2010. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
10
|
Wu ST, Sun GH, Hsu CY, Huang CS, Wu YH,
Wang HH and Sun KH: Tumor necrosis factor-α induces
epithelial-mesenchymal transition of renal cell carcinoma cells via
a nuclear factor kappa B-independent mechanism. Exp Biol Med
(Maywood). 236:1022–1029. 2011. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
11
|
Li CW, Xia W, Huo L, Lim SO, Wu Y, Hsu JL,
Chao CH, Yamaguchi H, Yang NK, Ding Q, et al:
Epithelial-mesenchymal transition induced by TNF-α requires
NF-κB-mediated transcriptional upregulation of Twist1. Cancer Res.
72:1290–1300. 2012. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
12
|
Chua HL, Bhat-Nakshatri P, Clare SE,
Morimiya A, Badve S and Nakshatri H: NF-kappaB represses E-cadherin
expression and enhances epithelial to mesenchymal transition of
mammary epithelial cells: Potential involvement of ZEB-1 and ZEB-2.
Oncogene. 26:711–724. 2007. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
13
|
Wang SC, Lin XL, Wang HY, Qin YJ, Chen L,
Li J, Jia JS, Shen HF, Yang S, Xie RY, et al: Hes1 triggers
epithelial-mesenchymal transition (EMT)-like cellular marker
alterations and promotes invasion and metastasis of nasopharyngeal
carcinoma by activating the PTEN/AKT pathway. Oncotarget.
6:36713–36730. 2015.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
14
|
Lin Z, Li W, Zhang H, Wu W, Peng Y, Zeng
Y, Wan Y, Wang J and Ouyang N: CCL18/PITPNM3 enhances migration,
invasion, and EMT through the NF-κB signaling pathway in
hepatocellular carcinoma. Tumour Biol. 37:3461–3468. 2016.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
15
|
Lee MY, Chou CY, Tang MJ and Shen MR:
Epithelial-mesenchymal transition in cervical cancer: Correlation
with tumor progression, epidermal growth factor receptor
overexpression, and snail up-regulation. Clin Cancer Res.
14:4743–4750. 2008. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
16
|
Strippoli R, Benedicto I, Pérez Lozano ML,
Cerezo A, López-Cabrera M and del Pozo MA:
Epithelial-to-mesenchymal transition of peritoneal mesothelial
cells is regulated by an ERK/NF-kappaB/Snail1 pathway. Dis Model
Mech. 1:264–274. 2008. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
17
|
Huber MA, Azoitei N, Baumann B, Grünert S,
Sommer A, Pehamberger H, Kraut N, Beug H and Wirth T: NF-kappaB is
essential for epithelial-mesenchymal transition and metastasis in a
model of breast cancer progression. J Clin Invest. 114:569–581.
2004. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
18
|
Huber MA, Beug H and Wirth T:
Epithelial-mesenchymal transition: NF-kappaB takes center stage.
Cell Cycle. 3:1477–1480. 2004. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
19
|
Dong XE, Ito N, Lotze MT, Demarco RA,
Popovic P, Shand SH, Watkins S, Winikoff S, Brown CK, Bartlett DL,
et al: High mobility group box I (HMGB1) release from tumor cells
after treatment: Implications for development of targeted
chemoimmunotherapy. J Immunother. 30:596–606. 2007. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
20
|
Wang H, Bloom O, Zhang M, Vishnubhakat JM,
Ombrellino M, Che J, Frazier A, Yang H, Ivanova S, Borovikova L, et
al: HMG-1 as a late mediator of endotoxin lethality in mice.
Science. 285:248–251. 1999. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
21
|
Klune JR, Dhupar R, Cardinal J, Billiar TR
and Tsung A: HMGB1: Endogenous danger signaling. Mol Med.
14:476–484. 2008. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
22
|
Olkhanud PB, Damdinsuren B, Bodogai M,
Gress RE, Sen R, Wejksza K, Malchinkhuu E, Wersto RP and Biragyn A:
Tumor-evoked regulatory B cells promote breast cancer metastasis by
converting resting CD4+ T cells to T-regulatory cells.
Cancer Res. 71:3505–3515. 2011. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
23
|
Tian J, Avalos AM, Mao SY, Chen B, Senthil
K, Wu H, Parroche P, Drabic S, Golenbock D, Sirois C, et al:
Toll-like receptor 9-dependent activation by DNA-containing immune
complexes is mediated by HMGB1 and RAGE. Nat Immunol. 8:487–496.
2007. View
Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
24
|
Sha Y, Zmijewski J, Xu Z and Abraham E:
HMGB1 develops enhanced proinflammatory activity by binding to
cytokines. J Immunol. 180:2531–2537. 2008. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
25
|
Yang D, Chen Q, Yang H, Tracey KJ, Bustin
M and Oppenheim JJ: High mobility group box-1 protein induces the
migration and activation of human dendritic cells and acts as an
alarmin. J Leukoc Biol. 81:59–66. 2007. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
26
|
Lynch J, Nolan S, Slattery C, Feighery R,
Ryan MP and McMorrow T: High-mobility group box protein 1: A novel
mediator of inflammatory-induced renal epithelial-mesenchymal
transition. Am J Nephrol. 32:590–602. 2010. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
27
|
He M, Kubo H, Ishizawa K, Hegab AE,
Yamamoto Y, Yamamoto H and Yamaya M: The role of the receptor for
advanced glycation end-products in lung fibrosis. Am J Physiol Lung
Cell Mol Physiol. 293:L1427–L1436. 2007. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
28
|
van Beijnum JR, Buurman WA and Griffioen
AW: Convergence and amplification of toll-like receptor (TLR) and
receptor for advanced glycation end products (RAGE) signaling
pathways via high mobility group B1 (HMGB1). Angiogenesis.
11:91–99. 2008. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
29
|
Sims GP, Rowe DC, Rietdijk ST, Herbst R
and Coyle AJ: HMGB1 and RAGE in inflammation and cancer. Annu Rev
Immunol. 28:367–388. 2010. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
30
|
Palumbo R, Galvez BG, Pusterla T, De
Marchis F, Cossu G, Marcu KB and Bianchi ME: Cells migrating to
sites of tissue damage in response to the danger signal HMGB1
require NF-kappaB activation. J Cell Biol. 179:33–40. 2007.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|