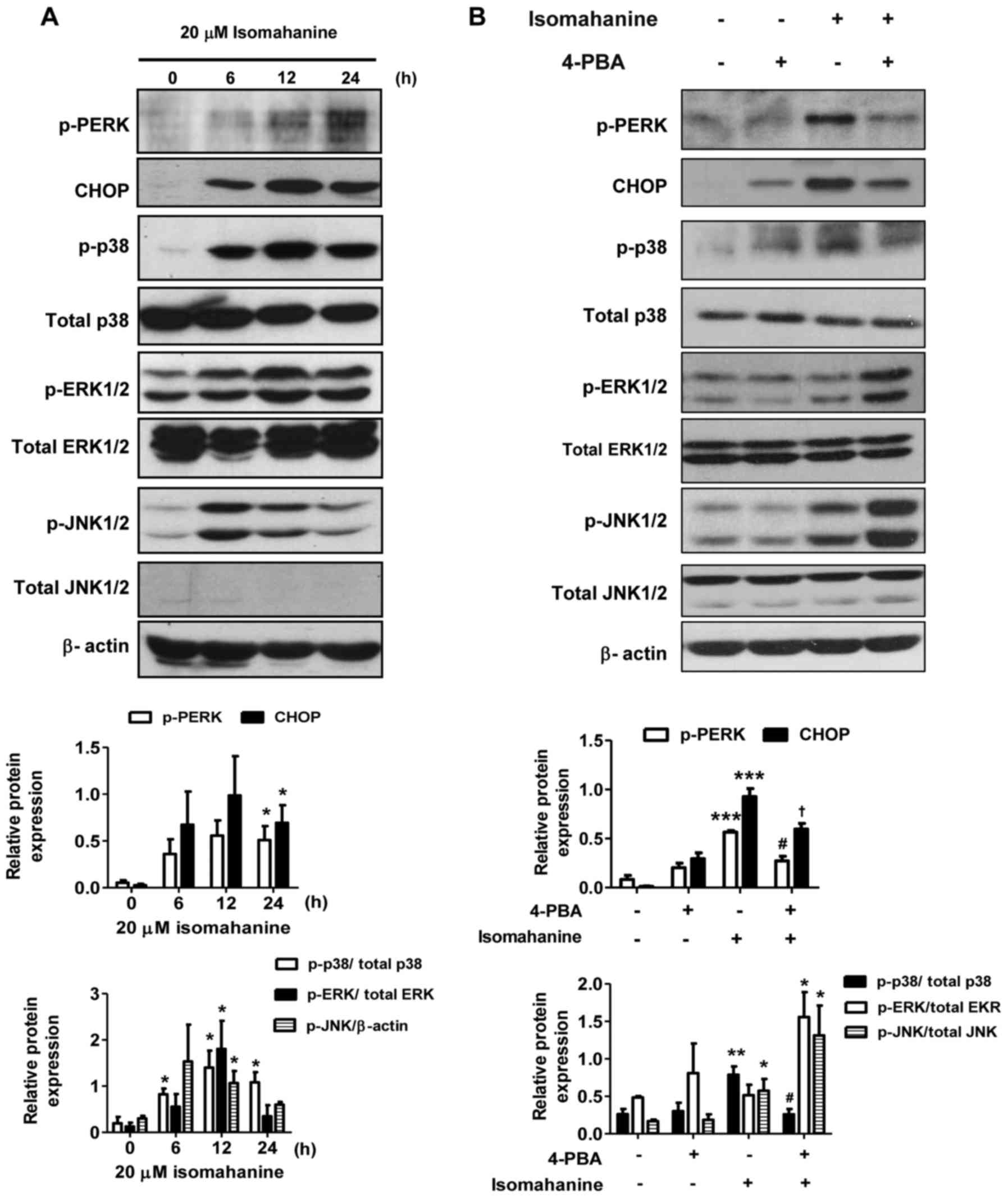
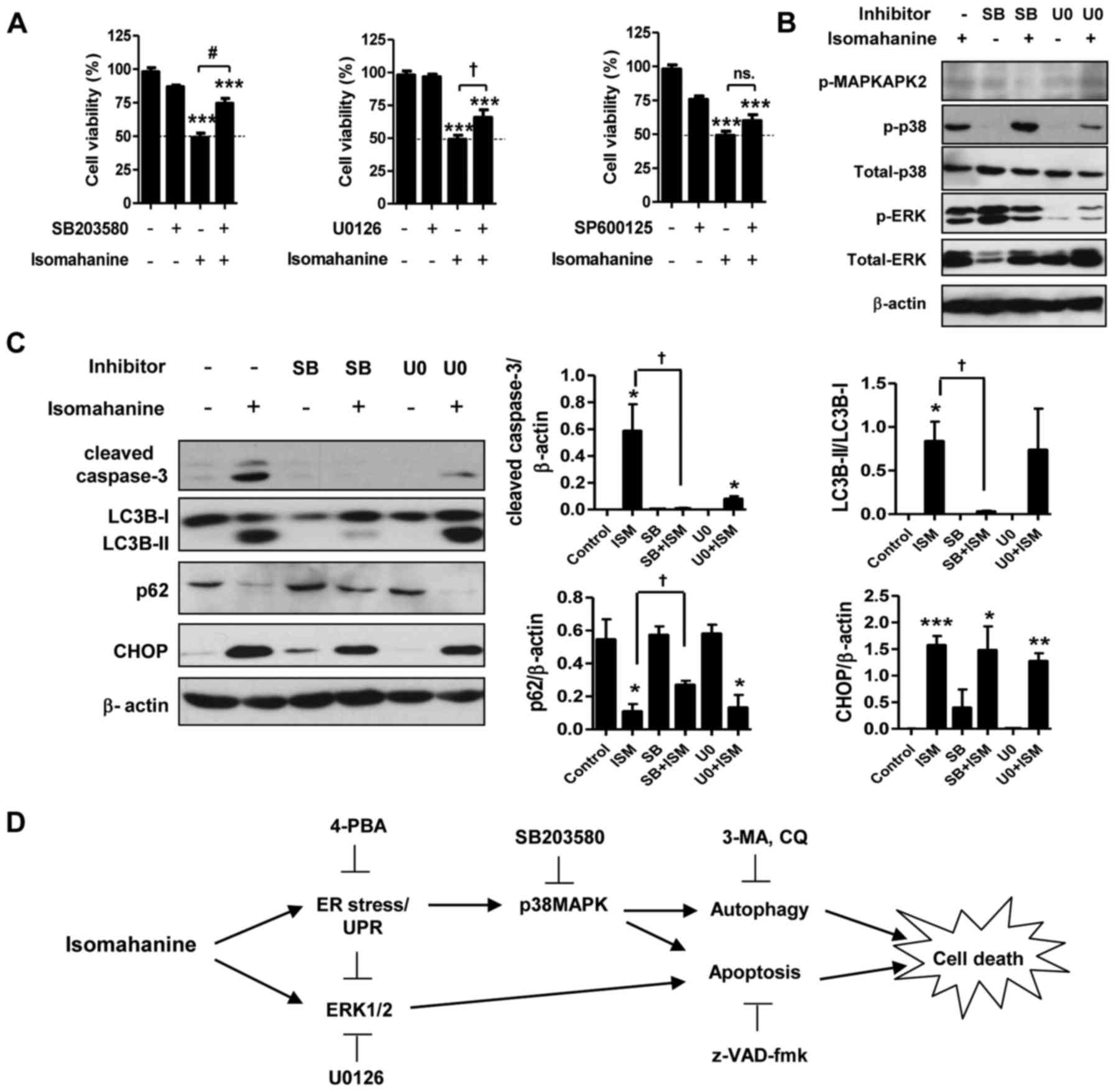
|
1
|
Rao SV Krishna, Mejia G, Roberts-Thomson K
and Logan R: Epidemiology of oral cancer in Asia in the past decade
- an update (2000–2012). Asian Pac J Cancer Prev. 14:5567–5577.
2013. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
2
|
Ferlay J, Soerjomataram I, Ervik M,
Dikshit R, Eser S, Mathers C, Rebelo M, Parkin DM, Forman D and
Bray F: GLOBOCAN 2012 v1.0, Cancer Incidence and Mortality
Worldwide: IARC CancerBase No. 11 (Internet). International Agency
for Research on Cancer; Lyon, France: 2014, doi:10.1002/ijc.29210
PMID:25220842. Accessed October, 9, 2014.
|
|
3
|
Wang C, Liu XQ, Hou JS, Wang JN and Huang
HZ: Molecular mechanisms of chemoresistance in oral cancer. Chin J
Dent Res. 19:25–33. 2016.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
4
|
Wu Q, Yang Z, Nie Y, Shi Y and Fan D:
Multi-drug resistance in cancer chemotherapeutics: Mechanisms and
lab approaches. Cancer Lett. 347:159–166. 2014. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
5
|
Meschini S, Condello M, Marra M, Formisano
G, Federici E and Arancia G: Autophagy-mediated chemosensitizing
effect of the plant alkaloid voacamine on multidrug resistant
cells. Toxicol In Vitro. 21:197–203. 2007. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
6
|
Chow MJ, Licona C, Pastorin G, Mellitzer
G, Ang WH and Gaiddon C: Structural tuning of organoruthenium
compounds allows oxidative switch to control ER stress pathways and
bypass multidrug resistance. Chem Sci. 7:4117–4124. 2016.
View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
7
|
Kumar P, Zhang DM, Degenhardt K and Chen
ZS: Autophagy and transporter-based multi-drug resistance. Cells.
1:558–575. 2012. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
8
|
Xuan Y and Hu X: Naturally-occurring
shikonin analogues - a class of necroptotic inducers that
circumvent cancer drug resistance. Cancer Lett. 274:233–242. 2009.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
9
|
Gewies A: Introduction to apoptosis.
ApoReview. 1–26. 2003.
|
|
10
|
Millimouno FM, Dong J, Yang L, Li J and Li
X: Targeting apoptosis pathways in cancer and perspectives with
natural compounds from mother nature. Cancer Prev Res. 7:1081–1107.
2014. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
11
|
Klionsky DJ and Emr SD: Autophagy as a
regulated pathway of cellular degradation. Science. 290:1717–1721.
2000. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
12
|
Zhang XJ, Chen S, Huang KX and Le WD: Why
should autophagic flux be assessed? Acta Pharmacol Sin. 34:595–599.
2013. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
13
|
Chen N and Karantza V: Autophagy as a
therapeutic target in cancer. Cancer Biol Ther. 11:157–168. 2011.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
14
|
Jiao JW and Wen F: Tanshinone IIA acts via
p38 MAPK to induce apoptosis and the down-regulation of ERCC1 and
lung-resistance protein in cisplatin-resistant ovarian cancer
cells. Oncol Rep. 25:781–788. 2011.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
15
|
Xu C, Bailly-Maitre B and Reed JC:
Endoplasmic reticulum stress: Cell life and death decisions. J Clin
Invest. 115:2656–2664. 2005. View
Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
16
|
Darling NJ and Cook SJ: The role of MAPK
signalling pathways in the response to endoplasmic reticulum
stress. Biochim Biophys Acta. 1843:2150–2163. 2014. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
17
|
Szegezdi E, Logue SE, Gorman AM and Samali
A: Mediators of endoplasmic reticulum stress-induced apoptosis.
EMBO Rep. 7:880–885. 2006. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
18
|
Wang Y, Wang JW, Xiao X, Shan Y, Xue B,
Jiang G, He Q, Chen J, Xu HG, Zhao RX, et al: Piperlongumine
induces autophagy by targeting p38 signaling. Cell Death Dis.
4:e8242013. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
19
|
Ma K, Zhang C, Huang MY, Li WY and Hu GQ:
Cinobufagin induces autophagy-mediated cell death in human
osteosarcoma U2OS cells through the ROS/JNK/p38 signaling pathway.
Oncol Rep. 36:90–98. 2016.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
20
|
Li JP, Yang YX, Liu QL, Pan ST, He ZX,
Zhang X, Yang T, Chen XW, Wang D, Qiu JX, et al: The
investigational Aurora kinase A inhibitor alisertib (MLN8237)
induces cell cycle G2/M arrest, apoptosis, and autophagy
via p38 MAPK and Akt/mTOR signaling pathways in human breast cancer
cells. Drug Des Devel Ther. 9:1627–1652. 2015.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
21
|
Roy MK, Thalang VN, Trakoontivakorn G and
Nakahara K: Mechanism of mahanine-induced apoptosis in human
leukemia cells (HL-60). Biochem Pharmacol. 67:41–51. 2004.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
22
|
Ito C, Itoigawa M, Nakao K, Murata T,
Tsuboi M, Kaneda N and Furukawa H: Induction of apoptosis by
carbazole alkaloids isolated from Murraya koenigii. Phytomedicine.
13:359–365. 2006. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
23
|
Sarkar S, Dutta D, Samanta SK,
Bhattacharya K, Pal BC, Li J, Datta K and Mandal C and Mandal C:
Oxidative inhibition of Hsp90 disrupts the super-chaperone complex
and attenuates pancreatic adenocarcinoma in vitro and in vivo. Int
J Cancer. 132:695–706. 2013. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
24
|
Shaikh MS, Karpoormath R, Thapliyal N,
Rane RA, Palkar MB, Faya AM, Patel HM, Alwan WS, Jain K and
Hampannavar GA: Current perspective of natural alkaloid carbazole
and its derivatives as antitumor agents. Anticancer Agents Med
Chem. 15:1049–1065. 2015. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
25
|
Das R, Bhattacharya K, Sarkar S, Samanta
SK, Pal BC and Mandal C: Mahanine synergistically enhances
cytotoxicity of 5-fluorouracil through ROS-mediated activation of
PTEN and p53/p73 in colon carcinoma. Apoptosis. 19:149–164. 2014.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
26
|
Das R, Bhattacharya K, Samanta SK, Pal BC
and Mandal C: Improved chemosensitivity in cervical cancer to
cisplatin: Synergistic activity of mahanine through STAT3
inhibition. Cancer Lett. 351:81–90. 2014. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
27
|
Chen CM, Syu JP, Way TD, Huang LJ, Kuo SC,
Lin CT and Lin CL: BC3EE2,9B, a synthetic carbazole derivative,
upregulates autophagy and synergistically sensitizes human GBM8901
glioblastoma cells to temozolomide. Int J Mol Med. 36:1244–1252.
2015.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
28
|
Reisch J, Goj O, Wickramasinghe A, Herath
B and Henkel G: Carbazole alkaloids from seeds of Murraya koenigii.
Phytochemistry. 31:2877–2879. 1992. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
29
|
Chamulitrat W, Schmidt R, Chunglok W, Kohl
A and Tomakidi P: Epithelium and fibroblast-like phenotypes derived
from HPV16 E6/E7-immortalized human gingival keratinocytes
following chronic ethanol treatment. Eur J Cell Biol. 82:313–322.
2003. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
30
|
Kim JW, Park Y, Roh JL, Cho KJ, Choi SH,
Nam SY and Kim SY: Prognostic value of glucosylceramide synthase
and P-glycoprotein expression in oral cavity cancer. Int J Clin
Oncol. 21:883–889. 2016. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
31
|
Friedrich RE, Punke C and Reymann A:
Expression of multi-drug resistance genes (mdr1, mrp1, bcrp) in
primary oral squamous cell carcinoma. In Vivo. 18:133–147.
2004.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
32
|
Saraswathy M and Gong S: Different
strategies to overcome multidrug resistance in cancer. Biotechnol
Adv. 31:1397–1407. 2013. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
33
|
Harada K, Ferdous T and Ueyama Y:
Establishment of 5-fluorouracil-resistant oral squamous cell
carcinoma cell lines with epithelial to mesenchymal transition
changes. Int J Oncol. 44:1302–1308. 2014.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
34
|
Yajima T, Ochiai H, Uchiyama T, Takano N,
Shibahara T and Azuma T: Resistance to cytotoxic
chemotherapy-induced apoptosis in side population cells of human
oral squamous cell carcinoma cell line Ho-1-N-1. Int J Oncol.
35:273–280. 2009.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
35
|
Negoro K, Yamano Y, Fushimi K, Saito K,
Nakatani K, Shiiba M, Yokoe H, Bukawa H, Uzawa K, Wada T, et al:
Establishment and characterization of a cisplatin-resistant cell
line, KB-R, derived from oral carcinoma cell line, KB. Int J Oncol.
30:1325–1332. 2007.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
36
|
Zhang B, Liu M, Tang HK, Ma HB, Wang C,
Chen X and Huang HZ: The expression and significance of MRP1, LRP,
TOPOIIβ, and BCL2 in tongue squamous cell carcinoma. J Oral Pathol
Med. 41:141–148. 2012. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
37
|
Kathawala RJ, Gupta P, Ashby CR Jr and
Chen ZS: The modulation of ABC transporter-mediated multidrug
resistance in cancer: A review of the past decade. Drug Resist
Updat. 18:1–17. 2015. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
38
|
Roy MK, Thalang VN, Trakoontivakorn G and
Nakahara K: Mahanine, a carbazole alkaloid from Micromelum minutum,
inhibits cell growth and induces apoptosis in U937 cells through a
mitochondrial dependent pathway. Br J Pharmacol. 145:145–155. 2005.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
39
|
Sinha S, Pal BC, Jagadeesh S, Banerjee PP,
Bandyopadhaya A and Bhattacharya S: Mahanine inhibits growth and
induces apoptosis in prostate cancer cells through the deactivation
of Akt and activation of caspases. Prostate. 66:1257–1265. 2006.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
40
|
Law BY, Mok SW, Chan WK, Xu SW, Wu AG, Yao
XJ, Wang JR, Liu L and Wong VK: Hernandezine, a novel AMPK
activator induces autophagic cell death in drug-resistant cancers.
Oncotarget. 7:8090–8104. 2016.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
41
|
Hasanain M, Bhattacharjee A, Pandey P,
Ashraf R, Singh N, Sharma S, Vishwakarma AL, Datta D, Mitra K and
Sarkar J: α-Solanine induces ROS-mediated autophagy through
activation of endoplasmic reticulum stress and inhibition of
Akt/mTOR pathway. Cell Death Dis. 6:e18602015. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
42
|
Meschini S, Condello M, Calcabrini A,
Marra M, Formisano G, Lista P, De Milito A, Federici E and Arancia
G: The plant alkaloid voacamine induces apoptosis-independent
autophagic cell death on both sensitive and multidrug resistant
human osteosarcoma cells. Autophagy. 4:1020–1033. 2008. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
43
|
Hägg M, Berndtsson M, Mandic A, Zhou R,
Shoshan MC and Linder S: Induction of endoplasmic reticulum stress
by ellipticine plant alkaloids. Mol Cancer Ther. 3:489–497.
2004.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
44
|
Tobiume K, Matsuzawa A, Takahashi T,
Nishitoh H, Morita K, Takeda K, Minowa O, Miyazono K, Noda T and
Ichijo H: ASK1 is required for sustained activations of JNK/p38 MAP
kinases and apoptosis. EMBO Rep. 2:222–228. 2001. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
45
|
Kim DS, Kim JH, Lee GH, Kim HT, Lim JM,
Chae SW, Chae HJ and Kim HR: p38 Mitogen-activated protein kinase
is involved in endoplasmic reticulum stress-induced cell death and
autophagy in human gingival fibroblasts. Biol Pharm Bull.
33:545–549. 2010. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
46
|
Pan ST, Qin Y, Zhou ZW, He ZX, Zhang X,
Yang T, Yang YX, Wang D, Qiu JX and Zhou SF: Plumbagin induces
G2/M arrest, apoptosis, and autophagy via p38 MAPK- and
PI3K/Akt/mTOR-mediated pathways in human tongue squamous cell
carcinoma cells. Drug Des Devel Ther. 9:1601–1626. 2015.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
47
|
Dai R, Chen R and Li H: Cross-talk between
PI3K/Akt and MEK/ERK pathways mediates endoplasmic reticulum
stress-induced cell cycle progression and cell death in human
hepatocellular carcinoma cells. Int J Oncol. 34:1749–1757.
2009.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
48
|
Cagnol S and Chambard JC: ERK and cell
death: Mechanisms of ERK-induced cell death - apoptosis, autophagy
and senescence. FEBS J. 277:2–21. 2010. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|