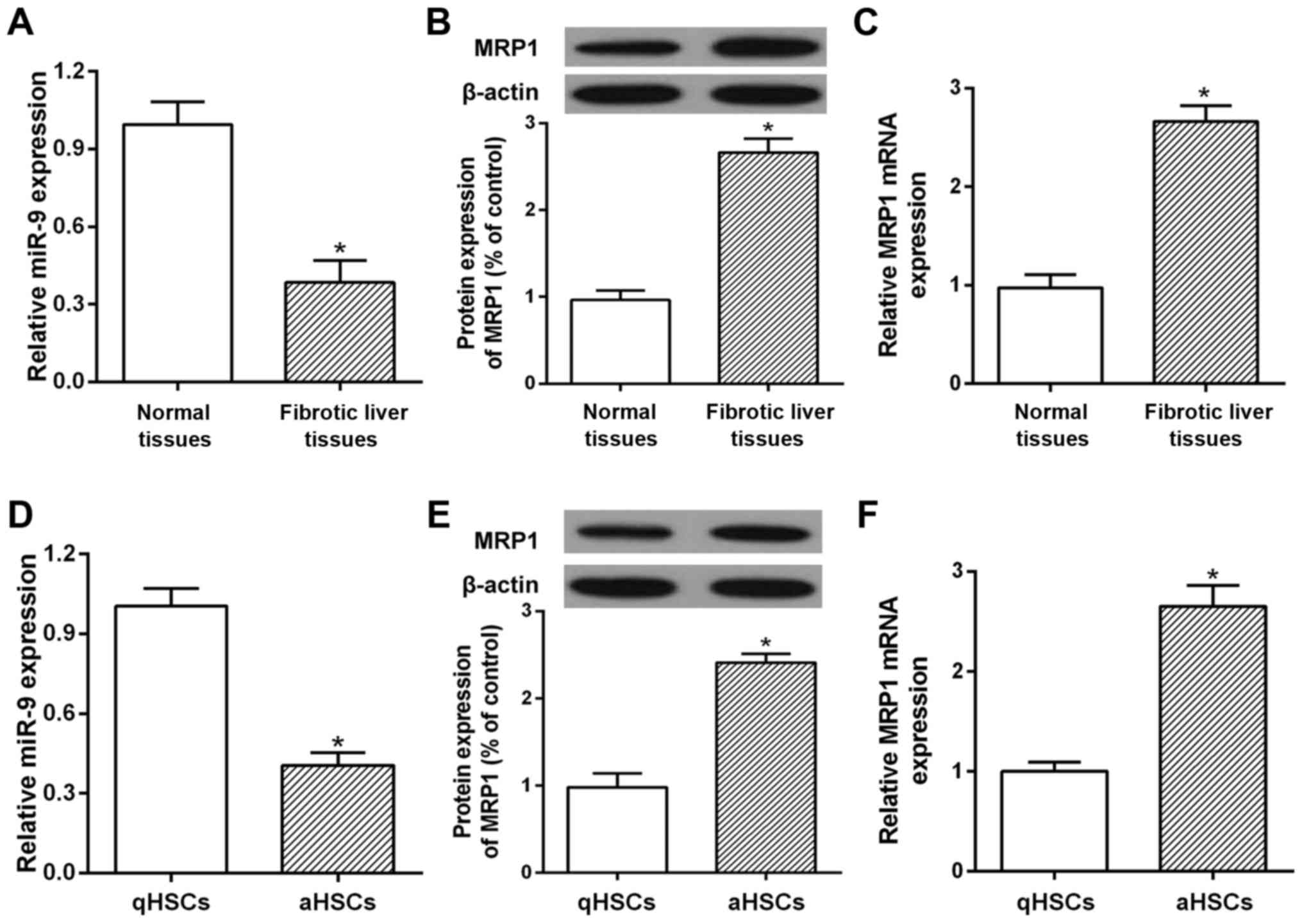
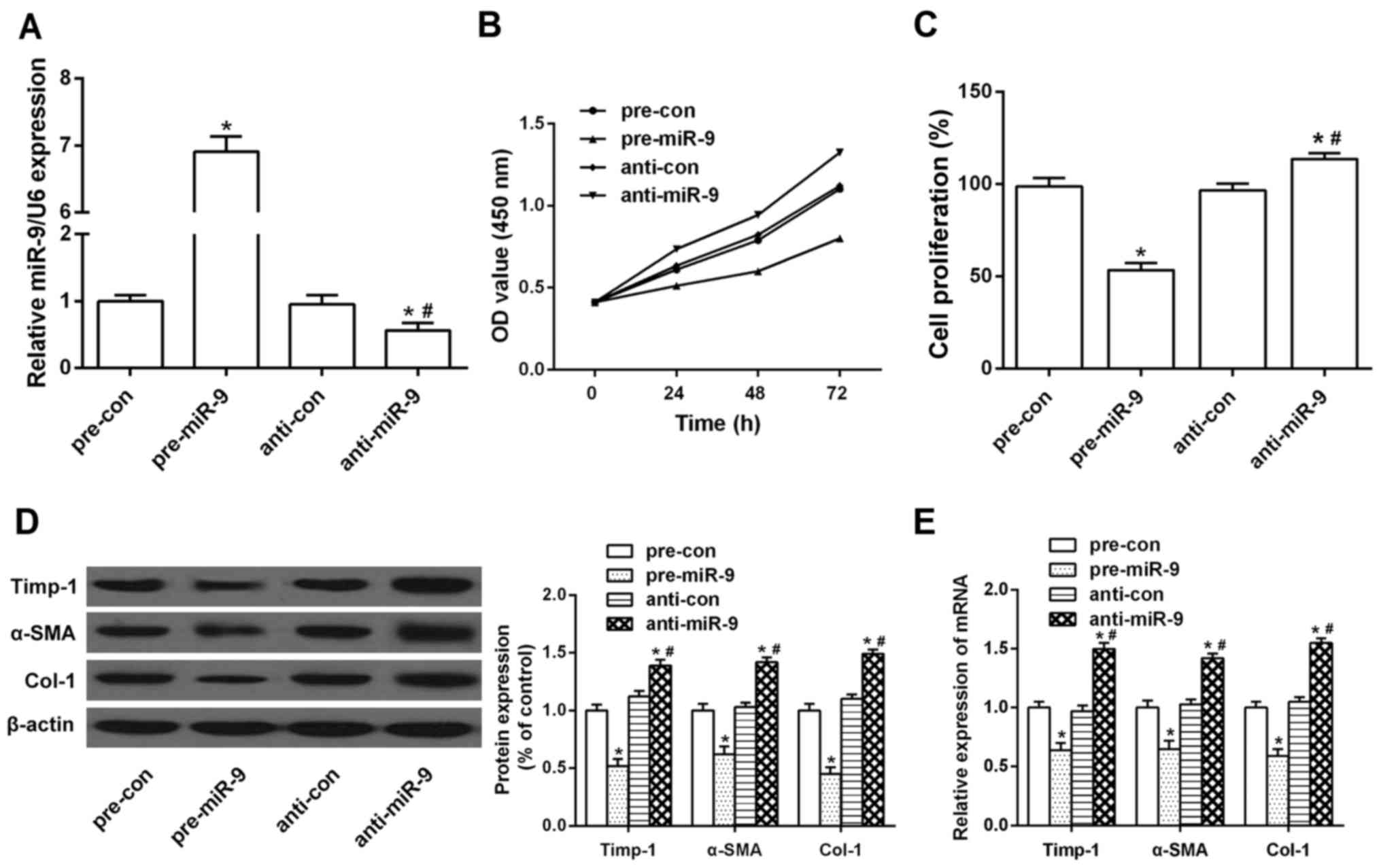
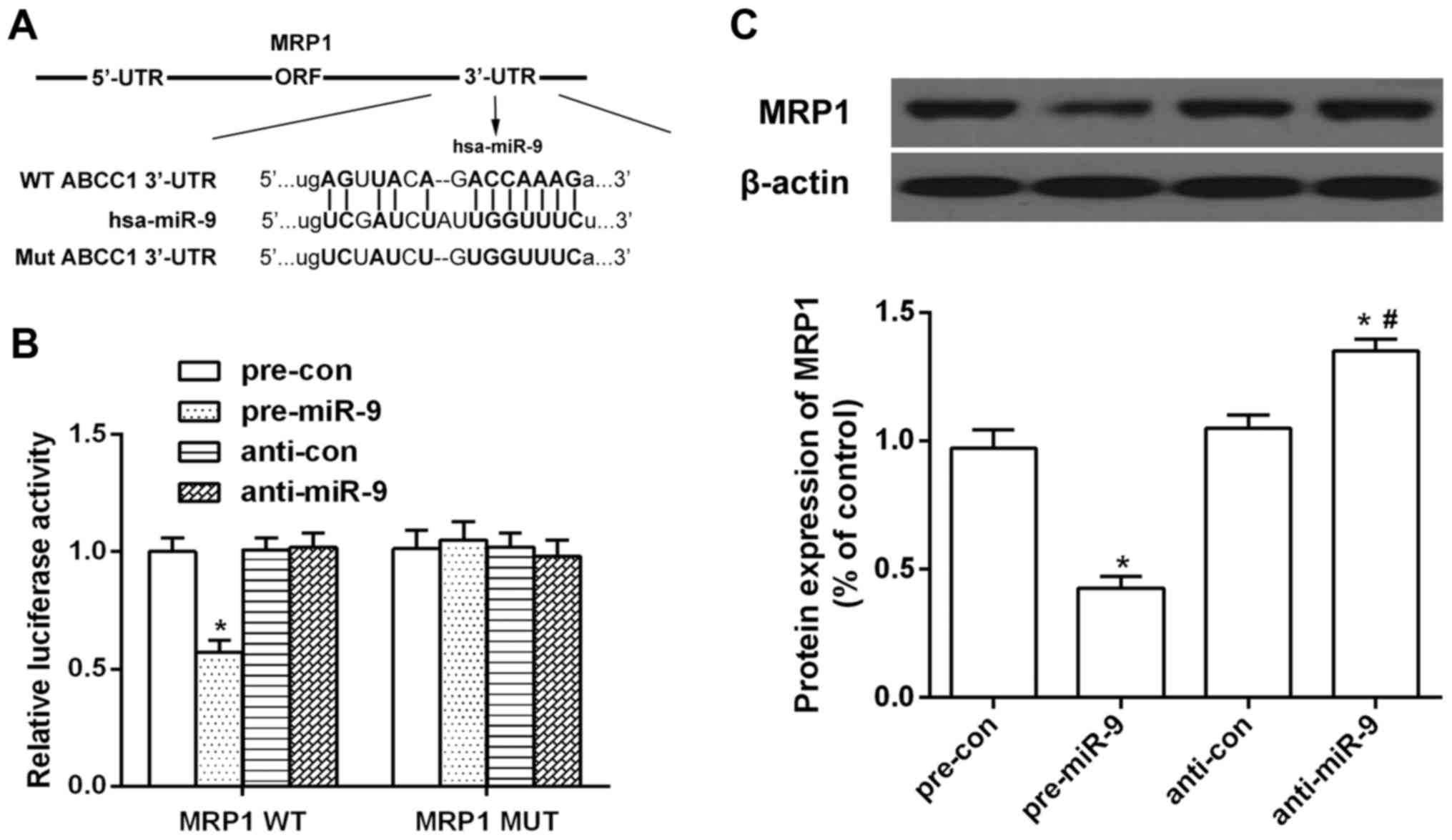
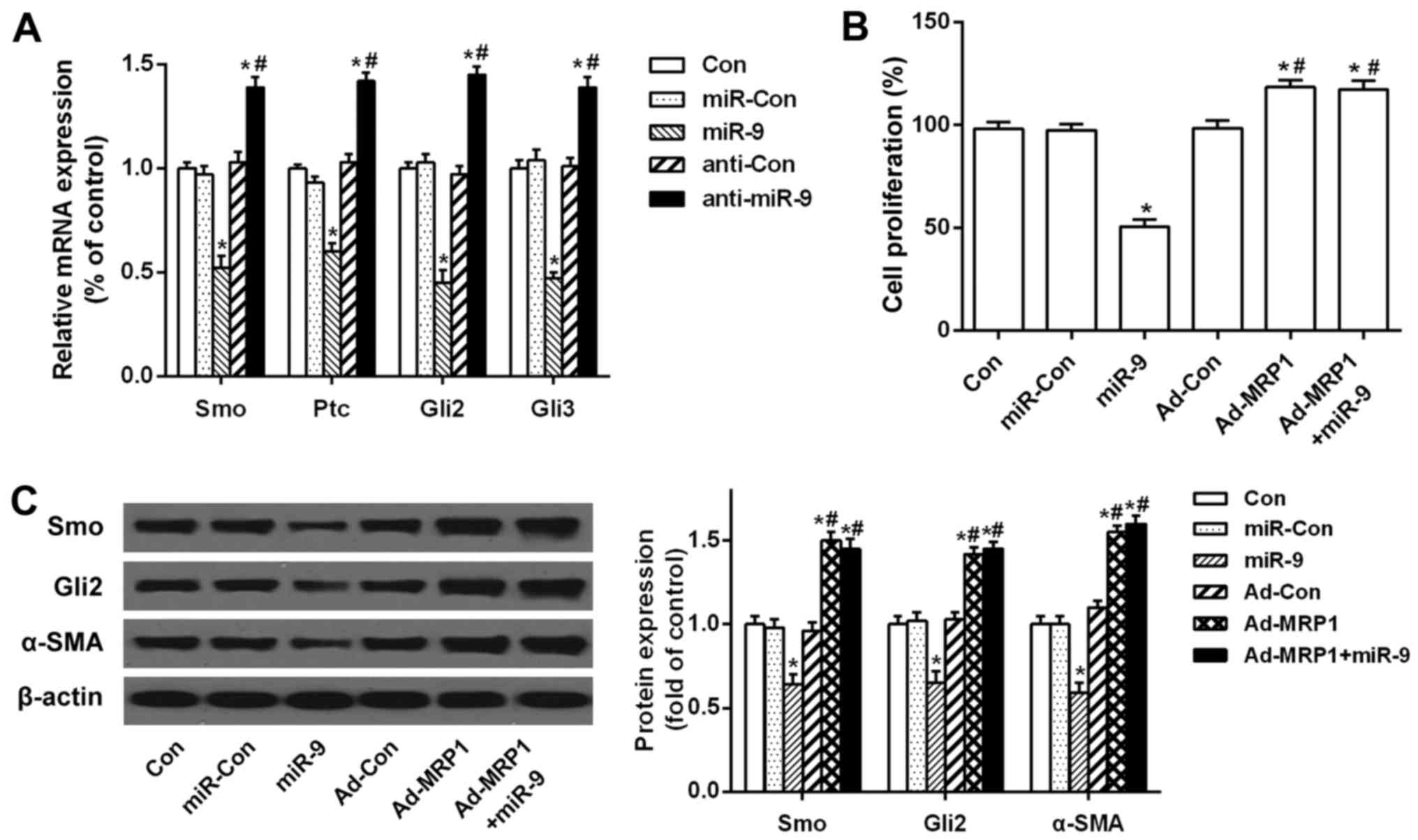
|
1
|
Kim Y, Ejaz A, Tayal A, Spolverato G,
Bridges JF, Anders RA and Pawlik TM: Temporal trends in
population-based death rates associated with chronic liver disease
and liver cancer in the United States over the last 30 years.
Cancer. 120:3058–3065. 2014. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
2
|
Popov Y and Schuppan D: Targeting liver
fibrosis: Strategies for development and validation of antifibrotic
therapies. Hepatology. 50:1294–1306. 2009. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
3
|
Fagone P, Mangano K, Pesce A, Portale TR,
Puleo S and Nicoletti F: Emerging therapeutic targets for the
treatment of hepatic fibrosis. Drug Discov Today. 21:369–375. 2016.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
4
|
Fagone P, Mangano K, Mammana S, Pesce A,
Pesce A, Caltabiano R, Giorlandino A, Portale TR, Cavalli E,
Lombardo GA, et al: Identification of novel targets for the
diagnosis and treatment of liver fibrosis. Int J Mol Med.
36:747–752. 2015.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
5
|
Puche JE, Saiman Y and Friedman SL:
Hepatic stellate cells and liver fibrosis. Compr Physiol.
3:1473–1492. 2013. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
6
|
Lade A, Noon LA and Friedman SL:
Contributions of metabolic dysregulation and inflammation to
nonalcoholic steatohepatitis, hepatic fibrosis, and cancer. Curr
Opin Oncol. 26:100–107. 2014. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
7
|
Peverill W, Powell LW and Skoien R:
Evolving concepts in the pathogenesis of NASH: Beyond steatosis and
inflammation. Int J Mol Sci. 15:8591–8638. 2014. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
8
|
König J, Hartel M, Nies AT, Martignoni ME,
Guo J, Büchler MW, Friess H and Keppler D: Expression and
localization of human multidrug resistance protein (ABCC) family
members in pancreatic carcinoma. Int J Cancer. 115:359–367. 2005.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
9
|
Borst P and Elferink RO: Mammalian ABC
transporters in health and disease. Annu Rev Biochem. 71:537–592.
2002. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
10
|
Ros JE, Roskams TA, Geuken M, Havinga R,
Splinter PL, Petersen BE, LaRusso NF, van der Kolk DM, Kuipers F,
Faber KN, et al: ATP binding cassette transporter gene expression
in rat liver progenitor cells. Gut. 52:1060–1067. 2003. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
11
|
Jeon BH, Lee YH, Yun MR, Kim SH, Lee BW,
Kang ES, Lee HC and Cha BS: Increased expression of ATP-binding
cassette transporter A1 (ABCA1) as a possible mechanism for the
protective effect of cilostazol against hepatic steatosis.
Metabolism. 64:1444–1453. 2015. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
12
|
Hannivoort RA, Dunning S, Borght S Vander,
Schroyen B, Woudenberg J, Oakley F, Buist-Homan M, van den Heuvel
FA, Geuken M, Geerts A, et al: Multidrug resistance-associated
proteins are crucial for the viability of activated rat hepatic
stellate cells. Hepatology. 48:624–634. 2008. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
13
|
Hayes CN and Chayama K: MicroRNAs as
biomarkers for liver disease and hepatocellular carcinoma. Int J
Mol Sci. 17:2802016. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
14
|
Kitano M and Bloomston PM: Hepatic
stellate cells and microRNAs in pathogenesis of liver fibrosis. J
Clin Med. 5:52016. View Article : Google Scholar :
|
|
15
|
Szabo G and Bala S: MicroRNAs in liver
disease. Nat Rev Gastroenterol Hepatol. 10:542–552. 2013.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
16
|
Bartel DP: MicroRNAs: Target recognition
and regulatory functions. Cell. 136:215–233. 2009. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
17
|
Li G, Li J, Li C, Qi H, Dong P, Zheng J
and Yu F: MicroRNA-125a-5p contributes to hepatic stellate cell
activation through targeting FIH1. Cell Physiol Biochem.
38:1544–1552. 2016. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
18
|
Omenetti A, Choi S, Michelotti G and Diehl
AM: Hedgehog signaling in the liver. J Hepatol. 54:366–373. 2011.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
19
|
Choi SS, Omenetti A, Syn WK and Diehl AM:
The role of Hedgehog signaling in fibrogenic liver repair. Int J
Biochem Cell Biol. 43:238–244. 2011. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
20
|
Chen Y, Choi SS, Michelotti GA, Chan IS,
Swiderska-Syn M, Karaca GF, Xie G, Moylan CA, Garibaldi F, Premont
R, et al: Hedgehog controls hepatic stellate cell fate by
regulating metabolism. Gastroenterology. 143:1319–1329.e1-11. 2012.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
21
|
Rombouts K and Carloni V: Determination
and characterization of tetraspanin-associated phosphoinositide-4
kinases in primary and neoplastic liver cells. Methods Mol Biol.
1376:203–212. 2016. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
22
|
Görbig MN, Ginès P, Bataller R, Nicolás
JM, Garcia-Ramallo E, Cejudo P, Sancho-Bru P, Jiménez W, Arroyo V
and Rodés J: Human hepatic stellate cells secrete adrenomedullin:
Potential autocrine factor in the regulation of cell contractility.
J Hepatol. 34:222–229. 2001. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
23
|
Jalan R, De Chiara F, Balasubramaniyan V,
Andreola F, Khetan V, Malago M, Pinzani M, Mookerjee RP and
Rombouts K: Ammonia produces pathological changes in human hepatic
stellate cells and is a target for therapy of portal hypertension.
J Hepatol. 64:823–833. 2016. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
24
|
Hyun J, Wang S, Kim J, Rao KM, Park SY,
Chung I, Ha CS, Kim SW, Yun YH and Jung Y: MicroRNA-378 limits
activation of hepatic stellate cells and liver fibrosis by
suppressing Gli3 expression. Nat Commun. 7:109932016. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
25
|
Roderburg C, Urban GW, Bettermann K, Vucur
M, Zimmermann H, Schmidt S, Janssen J, Koppe C, Knolle P, Castoldi
M, et al: Micro-RNA profiling reveals a role for miR-29 in human
and murine liver fibrosis. Hepatology. 53:209–218. 2011. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
26
|
Zhang DW, Zhao YX, Wei D, Li YL, Zhang Y,
Wu J, Xu J, Chen C, Tang H, Zhang W, et al: HAb18G/CD147 promotes
activation of hepatic stellate cells and is a target for antibody
therapy of liver fibrosis. J Hepatol. 57:1283–1291. 2012.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
27
|
Friedman SL: Seminars in medicine of the
Beth Israel Hospital, Boston. The cellular basis of hepatic
fibrosis. Mechanisms and treatment strategies. N Engl J Med.
328:1828–1835. 1993. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
28
|
Abu-Elsaad NM and Elkashef WF: Modified
citrus pectin stops progression of liver fibrosis by inhibiting
galectin-3 and inducing apoptosis of stellate cells. Can J Physiol
Pharmacol. 94:554–562. 2016. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
29
|
Gao B, Chang C, Zhou J, Zhao T, Wang C, Li
C and Gao G: Pycnogenol protects against rotenone-induced
neurotoxicity in PC12 cells through regulating NF-κB-iNOS signaling
pathway. DNA Cell Biol. 34:643–649. 2015. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
30
|
Yan G, Li B, Xin X, Xu M, Ji G and Yu H:
MicroRNA-34a promotes hepatic stellate cell activation via
targeting ACSL1. Med Sci Monit. 21:3008–3015. 2015. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
31
|
Ji J, Zhang J, Huang G, Qian J, Wang X and
Mei S: Over-expressed microRNA-27a and 27b influence fat
accumulation and cell proliferation during rat hepatic stellate
cell activation. FEBS Lett. 583:759–766. 2009. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
32
|
Wang L, Ma L, Fan H, Yang Z, Li L and Wang
H: MicroRNA-9 regulates cardiac fibrosis by targeting PDGFR-β in
rats. J Physiol Biochem. 72:213–223. 2016. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
33
|
Liu C, Yuan X, Tao L, Cheng Z, Dai X,
Sheng X and Xue D: Xia-yu-xue decoction (XYXD) reduces carbon
tetrachloride (CCl4)-induced liver fibrosis through inhibition
hepatic stellate cell activation by targeting NF-κB and TGF-β1
signaling pathways. BMC Complement Altern Med. 15:2012015.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
34
|
Xu L, Hui AY, Albanis E, Arthur MJ,
O'Byrne SM, Blaner WS, Mukherjee P, Friedman SL and Eng FJ: Human
hepatic stellate cell lines, LX-1 and LX-2: New tools for analysis
of hepatic fibrosis. Gut. 54:142–151. 2005. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
35
|
Omenetti A, Popov Y, Jung Y, Choi SS,
Witek RP, Yang L, Brown KD, Schuppan D and Diehl AM: The hedgehog
pathway regulates remodelling responses to biliary obstruction in
rats. Gut. 57:1275–1282. 2008. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
36
|
Fleig SV, Choi SS, Yang L, Jung Y,
Omenetti A, VanDongen HM, Huang J, Sicklick JK and Diehl AM:
Hepatic accumulation of Hedgehog-reactive progenitors increases
with severity of fatty liver damage in mice. Lab Invest.
87:1227–1239. 2007. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
37
|
Choi SS, Omenetti A, Witek RP, Moylan CA,
Syn WK, Jung Y, Yang L, Sudan DL, Sicklick JK, Michelotti GA, et
al: Hedgehog pathway activation and epithelial-to-mesenchymal
transitions during myofibroblastic transformation of rat hepatic
cells in culture and cirrhosis. Am J Physiol Gastrointest Liver
Physiol. 297:G1093–G1106. 2009. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
38
|
Lian N, Jiang Y, Zhang F, Jin H, Lu C, Wu
X, Lu Y and Zheng S: Curcumin regulates cell fate and metabolism by
inhibiting hedgehog signaling in hepatic stellate cells. Lab
Invest. 95:790–803. 2015. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
39
|
Zhang Y, Laterra J and Pomper MG: Hedgehog
pathway inhibitor HhAntag691 is a potent inhibitor of ABCG2/BCRP
and ABCB1/Pgp. Neoplasia. 11:96–101. 2009. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|