|
1
|
Balkau B, Deanfield JE, Després JP,
Bassand JP, Fox KA, Smith SC Jr, Barter P, Tan CE, Van Gaal L,
Wittchen HU, et al: International Day for the Evaluation of
Abdominal Obesity (IDEA): a study of waist circumference,
cardiovascular disease, and diabetes mellitus in 168,000 primary
care patients in 63 countries. Circulation. 116:1942–1951. 2007.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
2
|
Grundy SM: Metabolic syndrome pandemic.
Arterioscler Thromb Vasc Biol. 28:629–636. 2008. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
3
|
Prasad DS, Kabir Z, Dash AK and Das BC:
Prevalence and risk factors for metabolic syndrome in Asian
Indians: a community study from urban Eastern India. J Cardiovasc
Dis Res. 3:204–211. 2012. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
4
|
Gu D, Reynolds K, Wu X, Chen J, Duan X,
Reynolds RF, Whelton PK and He J: InterASIA Collaborative Group:
Prevalence of the metabolic syndrome and overweight among adults in
China. Lancet. 365:1398–1405. 2005. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
5
|
Reynolds K and He J: Epidemiology of the
metabolic syndrome. Am J Med Sci. 330:273–279. 2005. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
6
|
Wilson PW: Metabolic risk factors for
coronary heart disease: current and future prospects. Curr Opin
Cardiol. 14:176–185. 1999. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
7
|
Miranda PJ, DeFronzo RA, Califf RM and
Guyton JR: Metabolic syndrome: definition, pathophysiology, and
mechanisms. Am Heart J. 149:33–45. 2005. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
8
|
Dentali F, di Minno MN, Gianni M, di Minno
G, Squizzato A and Ageno W: The role of the metabolic syndrome in
patients with provoked venous thromboembolic events. Thromb
Haemost. 109:759–761. 2013. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
9
|
van Rooy MJ, Duim W, Ehlers R, Buys AV and
Pretorius E: Platelet hyperactivity and fibrin clot structure in
transient ischemic attack individuals in the presence of metabolic
syndrome: a microscopy and thromboelastography study. Cardiovasc
Diabetol. 14:862015. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
10
|
Ebrahimi F and Christ-Crain M: Metabolic
syndrome and hypogonadism - two peas in a pod. Swiss Med Wkly.
146:w142832016.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
11
|
Uzunlulu M, Telci Caklili O and Oguz A:
Association between metabolic syndrome and cancer. Ann Nutr Metab.
68:173–179. 2016. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
12
|
Chen J, He X and Huang J: Diet effects in
gut microbiome and obesity. J Food Sci. 79:R442–R451. 2014.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
13
|
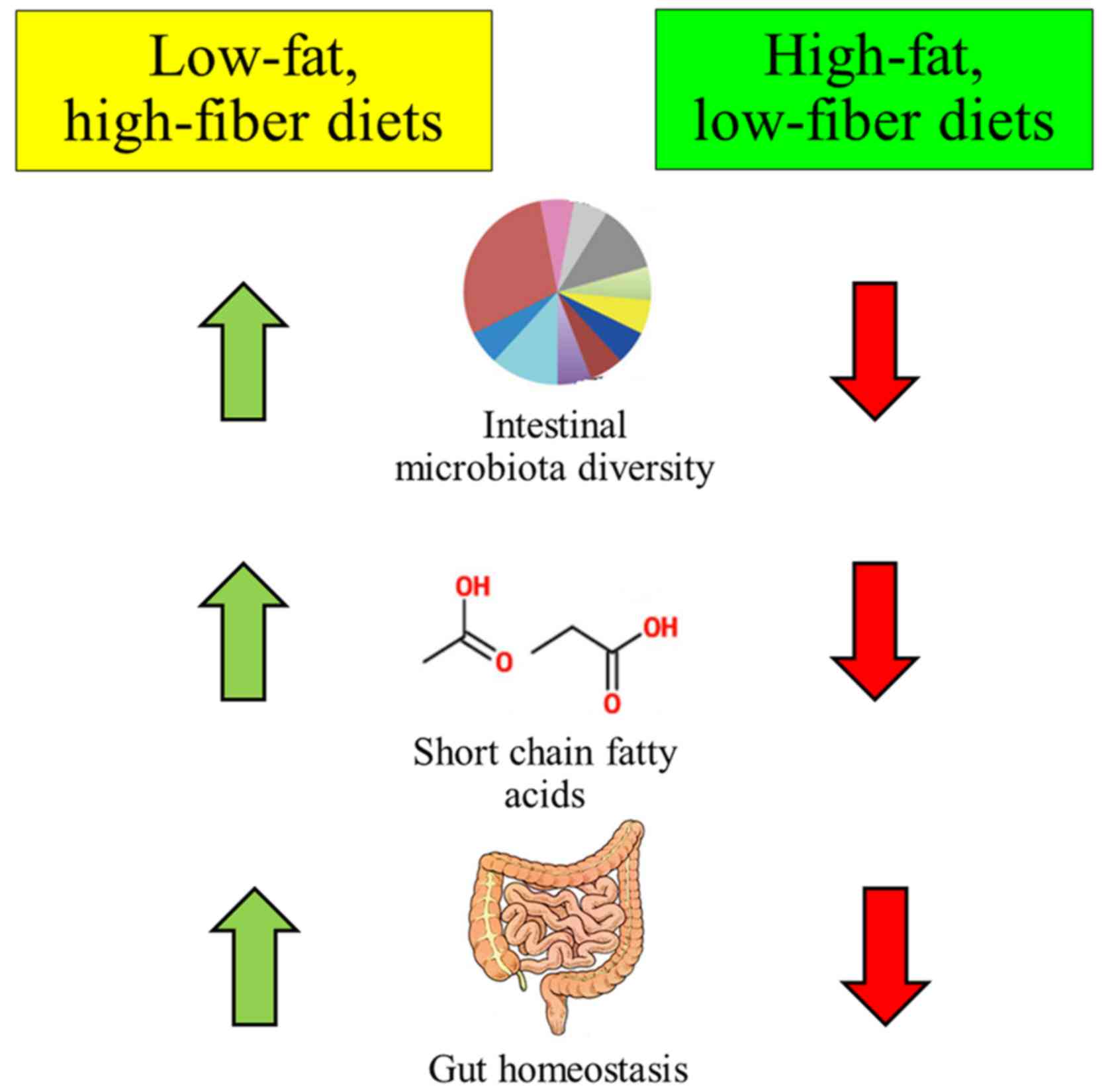
Festi D, Schiumerini R, Eusebi LH, Marasco
G, Taddia M and Colecchia A: Gut microbiota and metabolic syndrome.
World J Gastroenterol. 20:16079–16094. 2014. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
14
|
Parekh PJ, Balart LA and Johnson DA: The
Influence of the gut microbiome on obesity, metabolic syndrome and
gastrointestinal disease. Clin Transl Gastroenterol. 6:e912015.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
15
|
Marchesi JR, Adams DH, Fava F, Hermes GD,
Hirschfield GM, Hold G, Quraishi MN, Kinross J, Smidt H, Tuohy KM,
et al: The gut microbiota and host health: a new clinical frontier.
Gut. 65:330–339. 2016. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
16
|
Pigrau M, Rodiño-Janeiro BK, Casado-Bedmar
M, Lobo B, Vicario M, Santos J and Alonso-Cotoner C: The joint
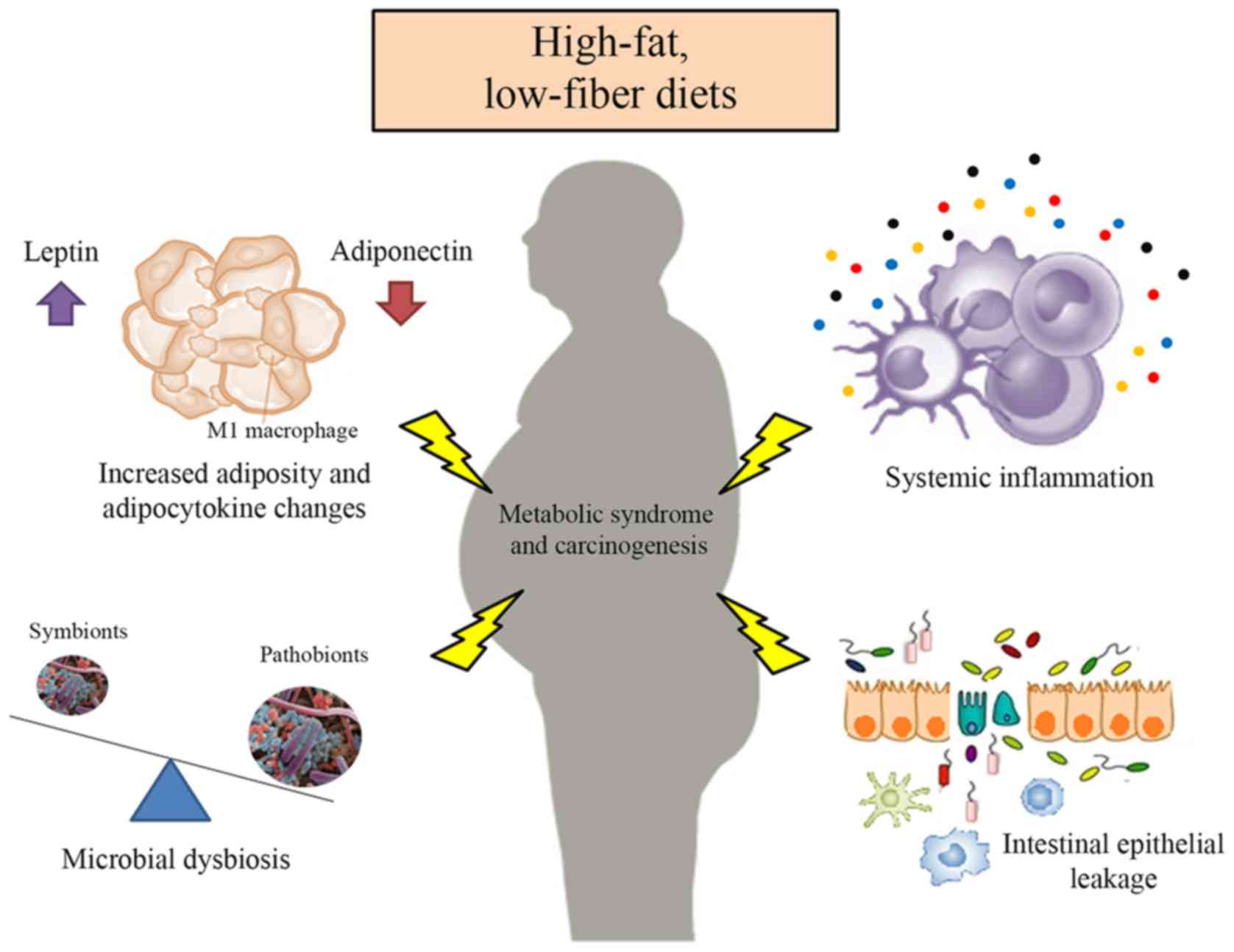
power of sex and stress to modulate brain-gut-microbiota axis and
intestinal barrier homeostasis: implications for irritable bowel
syndrome. Neurogastroenterol Motil. 28:463–486. 2016. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
17
|
Aballay LR, Eynard AR, Díaz M, del P,
Navarro A and Muñoz SE: Overweight and obesity: a review of their
relationship to metabolic syndrome, cardiovascular disease, and
cancer in South America. Nutr Rev. 71:168–179. 2013. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
18
|
Welty FK, Alfaddagh A and Elajami TK:
Targeting inflammation in metabolic syndrome. Transl Res.
167:257–280. 2016. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
19
|
Ley RE, Bäckhed F, Turnbaugh P, Lozupone
CA, Knight RD and Gordon JI: Obesity alters gut microbial ecology.
Proc Natl Acad Sci USA. 102:11070–11075. 2005. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
20
|
Pischon T, Lahmann PH, Boeing H,
Friedenreich C, Norat T, Tjønneland A, Halkjaer J, Overvad K,
Clavel-Chapelon F, Boutron-Ruault MC, et al: Body size and risk of
colon and rectal cancer in the European Prospective Investigation
Into Cancer and Nutrition (EPIC). J Natl Cancer Inst. 98:920–931.
2006. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
21
|
Pelucchi C, Negri E, Talamini R, Levi F,
Giacosa A, Crispo A, Bidoli E, Montella M, Franceschi S and La
Vecchia C: Metabolic syndrome is associated with colorectal cancer
in men. Eur J Cancer. 46:1866–1872. 2010. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
22
|
Esposito K, Chiodini P, Colao A, Lenzi A
and Giugliano D: Metabolic syndrome and risk of cancer: a
systematic review and meta-analysis. Diabetes Care. 35:2402–2411.
2012. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
23
|
Kyrou I, Randeva HS and Weickert MO:
Clinical problems caused by obesity: Endotext (Internet). De Groot
LJ, Chrousos G, Dungan K, Feingold KR, Grossman A, Hershman JM,
Koch C, Korbonits M, McLachlan R, New M, et al: MDText.com, Inc.;
South Dartmouth, MA, USA: 2000 https://www.endotext.orgApril 24–2014
|
|
24
|
Knecht S, Ellger T and Levine JA: Obesity
in neurobiology. Prog Neurobiol. 84:85–103. 2008. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
25
|
Sheth RD: Metabolic concerns associated
with antiepileptic medications. Neurology. 63 Suppl 4:S24–S29.
2004. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
26
|
Broberger C: Brain regulation of food
intake and appetite: molecules and networks. J Intern Med.
258:301–327. 2005. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
27
|
Peters A, Schweiger U, Pellerin L, Hubold
C, Oltmanns KM, Conrad M, Schultes B, Born J and Fehm HL: The
selfish brain: competition for energy resources. Neurosci Biobehav
Rev. 28:143–180. 2004. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
28
|
Peters A, Pellerin L, Dallman MF, Oltmanns
KM, Schweiger U, Born J and Fehm HL: Causes of obesity: looking
beyond the hypothalamus. Prog Neurobiol. 81:61–88. 2007. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
29
|
Woods SC, Stein LJ, McKay LD and D Jr
Porte: Suppression of food intake by intravenous nutrients and
insulin in the baboon. Am J Physiol. 247:R393–R401. 1984.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
30
|
Ahima RS, Prabakaran D, Mantzoros C, Qu D,
Lowell B, Maratos-Flier E and Flier JS: Role of leptin in the
neuroendocrine response to fasting. Nature. 382:250–252. 1996.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
31
|
Kreier F, Kap YS, Mettenleiter TC, van
Heijningen C, van der Vliet J, Kalsbeek A, Sauerwein HP, Fliers E,
Romijn JA and Buijs RM: Tracing from fat tissue, liver, and
pancreas: a neuroanatomical framework for the role of the brain in
type 2 diabetes. Endocrinology. 147:1140–1147. 2006. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
32
|
Uno K, Katagiri H, Yamada T, Ishigaki Y,
Ogihara T, Imai J, Hasegawa Y, Gao J, Kaneko K, Iwasaki H, et al:
Neuronal pathway from the liver modulates energy expenditure and
systemic insulin sensitivity. Science. 312:1656–1659. 2006.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
33
|
Dhillon H, Zigman JM, Ye C, Lee CE,
McGovern RA, Tang V, Kenny CD, Christiansen LM, White RD, Edelstein
EA, et al: Leptin directly activates SF1 neurons in the VMH, and
this action by leptin is required for normal body-weight
homeostasis. Neuron. 49:191–203. 2006. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
34
|
Brown FD, Fessler RG, Rachlin JR and
Mullan S: Changes in food intake with electrical stimulation of the
ventromedial hypothalamus in dogs. J Neurosurg. 60:1253–1257. 1984.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
35
|
Choi S, Sparks R, Clay M and Dallman MF:
Rats with hypothalamic obesity are insensitive to central leptin
injections. Endocrinology. 140:4426–4433. 1999. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
36
|
Grundmann SJ, Pankey EA, Cook MM, Wood AL,
Rollins BL and King BM: Combination unilateral amygdaloid and
ventromedial hypothalamic lesions: evidence for a feeding pathway.
Am J Physiol Regul Integr Comp Physiol. 288:R702–R707. 2005.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
37
|
Majdic G, Young M, Gomez-Sanchez E,
Anderson P, Szczepaniak LS, Dobbins RL, McGarry JD and Parker KL:
Knockout mice lacking steroidogenic factor 1 are a novel genetic
model of hypothalamic obesity. Endocrinology. 143:607–614. 2002.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
38
|
Bingham NC, Anderson KK, Reuter AL,
Stallings NR and Parker KL: Selective loss of leptin receptors in
the ventromedial hypothalamic nucleus results in increased
adiposity and a metabolic syndrome. Endocrinology. 149:2138–2148.
2008. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
39
|
Coleman DL: Obese and diabetes: two mutant
genes causing diabetes-obesity syndromes in mice. Diabetologia.
14:141–148. 1978. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
40
|
Clément K, Vaisse C, Lahlou N, Cabrol S,
Pelloux V, Cassuto D, Gourmelen M, Dina C, Chambaz J, Lacorte JM,
et al: A mutation in the human leptin receptor gene causes obesity
and pituitary dysfunction. Nature. 392:398–401. 1998. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
41
|
Montague CT, Farooqi IS, Whitehead JP,
Soos MA, Rau H, Wareham NJ, Sewter CP, Digby JE, Mohammed SN, Hurst
JA, et al: Congenital leptin deficiency is associated with severe
early-onset obesity in humans. Nature. 387:903–908. 1997.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
42
|
Kaszubska W, Falls HD, Schaefer VG, Haasch
D, Frost L, Hessler P, Kroeger PE, White DW, Jirousek MR and
Trevillyan JM: Protein tyrosine phosphatase 1B negatively regulates
leptin signaling in a hypothalamic cell line. Mol Cell Endocrinol.
195:109–118. 2002. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
43
|
Egawa K, Maegawa H, Shimizu S, Morino K,
Nishio Y, Bryer-Ash M, Cheung AT, Kolls JK, Kikkawa R and Kashiwagi
A: Protein-tyrosine phosphatase-1B negatively regulates insulin
signaling in l6 myocytes and Fao hepatoma cells. J Biol Chem.
276:10207–10211. 2001. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
44
|
Bence KK, Delibegovic M, Xue B, Gorgun CZ,
Hotamisligil GS, Neel BG and Kahn BB: Neuronal PTP1B regulates body
weight, adiposity and leptin action. Nat Med. 12:917–924. 2006.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
45
|
Cox JE and Powley TL: Prior vagotomy
blocks VMH obesity in pair-fed rats. Am J Physiol. 240:E573–E583.
1981.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
46
|
Brüning JC, Gautam D, Burks DJ, Gillette
J, Schubert M, Orban PC, Klein R, Krone W, Müller-Wieland D and
Kahn CR: Role of brain insulin receptor in control of body weight
and reproduction. Science. 289:2122–2125. 2000. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
47
|
Volkow ND and Wise RA: How can drug
addiction help us understand obesity? Nat Neurosci. 8:555–560.
2005. View
Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
48
|
Wallenius V, Wallenius K, Ahrén B, Rudling
M, Carlsten H, Dickson SL, Ohlsson C and Jansson JO:
Interleukin-6-deficient mice develop mature-onset obesity. Nat Med.
8:75–79. 2002. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
49
|
King BM: Amygdaloid lesion-induced
obesity: relation to sexual behavior, olfaction, and the
ventromedial hypothalamus. Am J Physiol Regul Integr Comp Physiol.
291:R1201–R1214. 2006. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
50
|
Peters A: The selfish brain: competition
for energy resources. Am J Hum Biol. 23:29–34. 2011. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
51
|
Peters A and McEwen BS: Stress
habituation, body shape and cardiovascular mortality. Neurosci
Biobehav Rev. 56:139–150. 2015. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
52
|
Hitze B, Hubold C, van Dyken R,
Schlichting K, Lehnert H, Entringer S and Peters A: How the selfish
brain organizes its supply and demand. Front Neuroenergetics.
2:72010.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
53
|
Kubera B, Hubold C, Zug S, Wischnath H,
Wilhelm I, Hallschmid M, Entringer S, Langemann D and Peters A: The
brain's supply and demand in obesity. Front Neuroenergetics.
4:42012. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
54
|
Khodabandehloo H, Gorgani-Firuzjaee S,
Panahi G and Meshkani R: Molecular and cellular mechanisms linking
inflammation to insulin resistance and β-cell dysfunction. Transl
Res. 167:228–256. 2016. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
55
|
Cai D and Liu T: Hypothalamic
inflammation: a double-edged sword to nutritional diseases. Ann N Y
Acad Sci. 1243:E1–E39. 2011. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
56
|
Cai D and Liu T: Inflammatory cause of
metabolic syndrome via brain stress and NF-κB. Aging (Albany, NY).
4:98–115. 2012. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
57
|
Gregor MF and Hotamisligil GS:
Inflammatory mechanisms in obesity. Annu Rev Immunol. 29:415–445.
2011. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
58
|
Weisberg SP, McCann D, Desai M, Rosenbaum
M, Leibel RL and Ferrante AW Jr: Obesity is associated with
macrophage accumulation in adipose tissue. J Clin Invest.
112:1796–1808. 2003. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
59
|
Lee BC and Lee J: Cellular and molecular
players in adipose tissue inflammation in the development of
obesity-induced insulin resistance. Biochim Biophys Acta.
1842:446–462. 2014. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
60
|
Lynch L, Nowak M, Varghese B, Clark J,
Hogan AE, Toxavidis V, Balk SP, O'Shea D, O'Farrelly C and Exley
MA: Adipose tissue invariant NKT cells protect against diet-induced
obesity and metabolic disorder through regulatory cytokine
production. Immunity. 37:574–587. 2012. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
61
|
Yoshimura A, Ohnishi S, Orito C, Kawahara
Y, Takasaki H, Takeda H, Sakamoto N and Hashino S: Association of
peripheral total and differential leukocyte counts with
obesity-related complications in young adults. Obes Facts. 8:1–16.
2015. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
62
|
Krinninger P, Ensenauer R, Ehlers K, Rauh
K, Stoll J, Krauss-Etschmann S, Hauner H and Laumen H: Peripheral
monocytes of obese women display increased chemokine receptor
expression and migration capacity. J Clin Endocrinol Metab.
99:2500–2509. 2014. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
63
|
Poitou C, Dalmas E, Renovato M, Benhamo V,
Hajduch F, Abdennour M, Kahn JF, Veyrie N, Rizkalla S, Fridman WH,
et al: CD14dimCD16+ and CD14+CD16+ monocytes in obesity and during
weight loss: relationships with fat mass and subclinical
atherosclerosis. Arterioscler Thromb Vasc Biol. 31:2322–2330. 2011.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
64
|
Christiansen T, Richelsen B and Bruun JM:
Monocyte chemoattractant protein-1 is produced in isolated
adipocytes, associated with adiposity and reduced after weight loss
in morbid obese subjects. Int J Obes. 29:146–150. 2005. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
65
|
Kanda H, Tateya S, Tamori Y, Kotani K,
Hiasa K, Kitazawa R, Kitazawa S, Miyachi H, Maeda S, Egashira K, et
al: MCP-1 contributes to macrophage infiltration into adipose
tissue, insulin resistance, and hepatic steatosis in obesity. J
Clin Invest. 116:1494–1505. 2006. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
66
|
Weisberg SP, Hunter D, Huber R, Lemieux J,
Slaymaker S, Vaddi K, Charo I, Leibel RL and Ferrante AW Jr: CCR2
modulates inflammatory and metabolic effects of high-fat feeding. J
Clin Invest. 116:115–124. 2006. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
67
|
Bolus WR, Gutierrez DA, Kennedy AJ,
Anderson-Baucum EK and Hasty AH: CCR2 deficiency leads to increased
eosinophils, alternative macrophage activation, and type 2 cytokine
expression in adipose tissue. J Leukoc Biol. 98:467–477. 2015.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
68
|
Kim D, Kim J, Yoon JH, Ghim J, Yea K, Song
P, Park S, Lee A, Hong CP, Jang MS, et al: CXCL12 secreted from
adipose tissue recruits macrophages and induces insulin resistance
in mice. Diabetologia. 57:1456–1465. 2014. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
69
|
Nara N, Nakayama Y, Okamoto S, Tamura H,
Kiyono M, Muraoka M, Tanaka K, Taya C, Shitara H, Ishii R, et al:
Disruption of CXC motif chemokine ligand-14 in mice ameliorates
obesity-induced insulin resistance. J Biol Chem. 282:30794–30803.
2007. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
70
|
Kitade H, Sawamoto K, Nagashimada M, Inoue
H, Yamamoto Y, Sai Y, Takamura T, Yamamoto H, Miyamoto K, Ginsberg
HN, et al: CCR5 plays a critical role in obesity-induced adipose
tissue inflammation and insulin resistance by regulating both
macrophage recruitment and M1/M2 status. Diabetes. 61:1680–1690.
2012. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
71
|
Dalmas E, Clément K and Guerre-Millo M:
Defining macrophage phenotype and function in adipose tissue.
Trends Immunol. 32:307–314. 2011. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
72
|
Lumeng CN, Bodzin JL and Saltiel AR:
Obesity induces a phenotypic switch in adipose tissue macrophage
polarization. J Clin Invest. 117:175–184. 2007. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
73
|
Kratz M, Coats BR, Hisert KB, Hagman D,
Mutskov V, Peris E, Schoenfelt KQ, Kuzma JN, Larson I, Billing PS,
et al: Metabolic dysfunction drives a mechanistically distinct
proinflammatory phenotype in adipose tissue macrophages. Cell
Metab. 20:614–625. 2014. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
74
|
Elgazar-Carmon V, Rudich A, Hadad N and
Levy R: Neutrophils transiently infiltrate intra-abdominal fat
early in the course of high-fat feeding. J Lipid Res. 49:1894–1903.
2008. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
75
|
Talukdar S, Oh DY, Bandyopadhyay G, Li D,
Xu J, McNelis J, Lu M, Li P, Yan Q, Zhu Y, et al: Neutrophils
mediate insulin resistance in mice fed a high-fat diet through
secreted elastase. Nat Med. 18:1407–1412. 2012. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
76
|
Xu X, Su S and Wang X, Barnes V, De Miguel
C, Ownby D, Pollock J, Snieder H, Chen W and Wang X: Obesity is
associated with more activated neutrophils in African American male
youth. Int J Obes (Lond). 39:26–32. 2015.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
77
|
Sell H, Habich C and Eckel J: Adaptive
immunity in obesity and insulin resistance. Nat Rev Endocrinol.
8:709–716. 2012. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
78
|
Feuerer M, Herrero L, Cipolletta D, Naaz
A, Wong J, Nayer A, Lee J, Goldfine AB, Benoist C, Shoelson S, et
al: Lean, but not obese, fat is enriched for a unique population of
regulatory T cells that affect metabolic parameters. Nat Med.
15:930–939. 2009. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
79
|
Strissel KJ, DeFuria J, Shaul ME, Bennett
G, Greenberg AS and Obin MS: T-cell recruitment and Th1
polarization in adipose tissue during diet-induced obesity in
C57BL/6 mice. Obesity (Silver Spring). 18:1918–1925. 2010.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
80
|
Winer S, Paltser G, Chan Y, Tsui H,
Engleman E, Winer D and Dosch HM: Obesity predisposes to Th17 bias.
Eur J Immunol. 39:2629–2635. 2009. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
81
|
Nishimura S, Manabe I, Nagasaki M, Eto K,
Yamashita H, Ohsugi M, Otsu M, Hara K, Ueki K, Sugiura S, et al:
CD8+ effector T cells contribute to macrophage recruitment and
adipose tissue inflammation in obesity. Nat Med. 15:914–920. 2009.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
82
|
Wu H, Ghosh S, Perrard XD, Feng L, Garcia
GE, Perrard JL, Sweeney JF, Peterson LE, Chan L, Smith CW, et al:
T-cell accumulation and regulated on activation, normal T cell
expressed and secreted upregulation in adipose tissue in obesity.
Circulation. 115:1029–1038. 2007. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
83
|
Winer DA, Winer S, Shen L, Wadia PP,
Yantha J, Paltser G, Tsui H, Wu P, Davidson MG, Alonso MN, et al: B
cells promote insulin resistance through modulation of T cells and
production of pathogenic IgG antibodies. Nat Med. 17:610–617. 2011.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
84
|
Sun S, Ji Y, Kersten S and Qi L:
Mechanisms of inflammatory responses in obese adipose tissue. Annu
Rev Nutr. 32:261–286. 2012. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
85
|
Duffaut C, Galitzky J, Lafontan M and
Bouloumié A: Unexpected trafficking of immune cells within the
adipose tissue during the onset of obesity. Biochem Biophys Res
Commun. 384:482–485. 2009. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
86
|
DeFuria J, Belkina AC, Jagannathan-Bogdan
M, Snyder-Cappione J, Carr JD, Nersesova YR, Markham D, Strissel
KJ, Watkins AA, Zhu M, et al: B cells promote inflammation in
obesity and type 2 diabetes through regulation of T-cell function
and an inflammatory cytokine profile. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA.
110:5133–5138. 2013. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
87
|
Jagannathan M, McDonnell M, Liang Y,
Hasturk H, Hetzel J, Rubin D, Kantarci A, Van Dyke TE, Ganley-Leal
LM and Nikolajczyk BS: Toll-like receptors regulate B cell cytokine
production in patients with diabetes. Diabetologia. 53:1461–1471.
2010. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
88
|
van Exel E, Gussekloo J, De Craen AJM,
Frölich M, Bootsma-Van Der Wiel A and Westendorp RGJ: Leiden 85
Plus Study: Low production capacity of interleukin-10 associates
with the metabolic syndrome and type 2 diabetes: The Leiden 85-Plus
Study. Diabetes. 51:1088–1092. 2002. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
89
|
Gomes AC, Bueno AA, de Souza RGM and Mota
JF: Gut microbiota, probiotics and diabetes. Nutr J. 13:602014.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
90
|
Bajzer M and Seeley RJ: Physiology:
obesity and gut flora. Nature. 444:1009–1010. 2006. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
91
|
Sekirov I, Russell SL, Antunes LCM and
Finlay BB: Gut microbiota in health and disease. Physiol Rev.
90:859–904. 2010. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
92
|
David LA, Maurice CF, Carmody RN,
Gootenberg DB, Button JE, Wolfe BE, Ling AV, Devlin AS, Varma Y,
Fischbach MA, et al: Diet rapidly and reproducibly alters the human
gut microbiome. Nature. 505:559–563. 2014. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
93
|
Turnbaugh PJ, Hamady M, Yatsunenko T,
Cantarel BL, Duncan A, Ley RE, Sogin ML, Jones WJ, Roe BA,
Affourtit JP, et al: A core gut microbiome in obese and lean twins.
Nature. 457:480–484. 2009. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
94
|
Trompette A, Gollwitzer ES, Yadava K,
Sichelstiel AK, Sprenger N, Ngom-Bru C, Blanchard C, Junt T, Nicod
LP, Harris NL, et al: Gut microbiota metabolism of dietary fiber
influences allergic airway disease and hematopoiesis. Nat Med.
20:159–166. 2014. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
95
|
Ley RE, Turnbaugh PJ, Klein S and Gordon
JI: Microbial ecology: human gut microbes associated with obesity.
Nature. 444:1022–1023. 2006. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
96
|
Schwiertz A, Taras D, Schäfer K, Beijer S,
Bos NA, Donus C and Hardt PD: Microbiota and SCFA in lean and
overweight healthy subjects. Obesity (Silver Spring). 18:190–195.
2010. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
97
|
Duncan SH, Lobley GE, Holtrop G, Ince J,
Johnstone AM, Louis P and Flint HJ: Human colonic microbiota
associated with diet, obesity and weight loss. Int J Obes.
32:1720–1724. 2008. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
98
|
Bäckhed F, Ding H, Wang T, Hooper LV, Koh
GY, Nagy A, Semenkovich CF and Gordon JI: The gut microbiota as an
environmental factor that regulates fat storage. Proc Natl Acad Sci
USA. 101:15718–15723. 2004. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
99
|
Le Chatelier E, Nielsen T, Qin J, Prifti
E, Hildebrand F, Falony G, Almeida M, Arumugam M, Batto JM, Kennedy
S, et al: MetaHIT consortium: Richness of human gut microbiome
correlates with metabolic markers. Nature. 500:541–546. 2013.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
100
|
Ridaura VK, Faith JJ, Rey FE, Cheng J,
Duncan AE, Kau AL, Griffin NW, Lombard V, Henrissat B, Bain JR, et
al: Gut microbiota from twins discordant for obesity modulate
metabolism in mice. Science. 341:12412142013. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
101
|
Ferlay J, Soerjomataram I, Dikshit R, Eser
S, Mathers C, Rebelo M, Parkin DM, Forman D and Bray F: Cancer
incidence and mortality worldwide: sources, methods and major
patterns in GLOBOCAN 2012. Int J Cancer. 136:E359–E386. 2015.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
102
|
Sears CL and Garrett WS: Microbes,
microbiota, and colon cancer. Cell Host Microbe. 15:317–328. 2014.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
103
|
Center MM, Jemal A and Ward E:
International trends in colorectal cancer incidence rates. Cancer
Epidemiol Biomarkers Prev. 18:1688–1694. 2009. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
104
|
Center MM, Jemal A, Smith RA and Ward E:
Worldwide variations in colorectal cancer. CA Cancer J Clin.
59:366–378. 2009. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
105
|
Duncan SH, Belenguer A, Holtrop G,
Johnstone AM, Flint HJ and Lobley GE: Reduced dietary intake of
carbohydrates by obese subjects results in decreased concentrations
of butyrate and butyrate-producing bacteria in feces. Appl Environ
Microbiol. 73:1073–1078. 2007. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
106
|
Keku TO, Dulal S, Deveaux A, Jovov B and
Han X: The gastrointestinal microbiota and colorectal cancer. Am J
Physiol Gastrointest Liver Physiol. 308:G351–G363. 2015. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
107
|
Medzhitov R: Origin and physiological
roles of inflammation. Nature. 454:428–435. 2008. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
108
|
Nyangale EP, Mottram DS and Gibson GR: Gut
microbial activity, implications for health and disease: the
potential role of metabolite analysis. J Proteome Res.
11:5573–5585. 2012. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
109
|
Greer JB and O'Keefe SJ: Microbial
induction of immunity, inflammation, and cancer. Front Physiol.
1:1682011. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
110
|
Módis K, Coletta C, Erdélyi K,
Papapetropoulos A and Szabo C: Intramitochondrial hydrogen sulfide
production by 3-mercaptopyruvate sulfurtransferase maintains
mitochondrial electron flow and supports cellular bioenergetics.
FASEB J. 27:601–611. 2013. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
111
|
Nistal E, Fernández-Fernández N, Vivas S
and Olcoz JL: Factors determining colorectal cancer: the role of
the intestinal microbiota. Front Oncol. 5:2202015. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
112
|
Dvorak K, Payne CM, Chavarria M, Ramsey L,
Dvorakova B, Bernstein H, Holubec H, Sampliner RE, Guy N, Condon A,
et al: Bile acids in combination with low pH induce oxidative
stress and oxidative DNA damage: relevance to the pathogenesis of
Barrett's oesophagus. Gut. 56:763–771. 2007. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
113
|
Gill CI and Rowland IR: Diet and cancer:
assessing the risk. Br J Nutr. 88 Suppl 1:S73–S87. 2002. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
114
|
Sobko T, Huang L, Midtvedt T, Norin E,
Gustafsson LE, Norman M, Jansson EA and Lundberg JO: Generation of
NO by probiotic bacteria in the gastrointestinal tract. Free Radic
Biol Med. 41:985–991. 2006. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
115
|
Sobko T, Reinders CI, Jansson E, Norin E,
Midtvedt T and Lundberg JO: Gastrointestinal bacteria generate
nitric oxide from nitrate and nitrite. Nitric Oxide. 13:272–278.
2005. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
116
|
Grivennikov SI, Wang K, Mucida D, Stewart
CA, Schnabl B, Jauch D, Taniguchi K, Yu GY, Osterreicher CH, Hung
KE, et al: Adenoma-linked barrier defects and microbial products
drive IL-23/IL-17-mediated tumour growth. Nature. 491:254–258.
2012.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
117
|
Sprong RC, Schonewille AJ and van der Meer
R: Dietary cheese whey protein protects rats against mild dextran
sulfate sodium-induced colitis: role of mucin and microbiota. J
Dairy Sci. 93:1364–1371. 2010. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
118
|
Hursting SD, Digiovanni J, Dannenberg AJ,
Azrad M, Leroith D, Demark-Wahnefried W, Kakarala M, Brodie A and
Berger NA: Obesity, energy balance, and cancer: new opportunities
for prevention. Cancer Prev Res (Phila). 5:1260–1272. 2012.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
119
|
Tilg H and Moschen AR: Adipocytokines:
mediators linking adipose tissue, inflammation and immunity. Nat
Rev Immunol. 6:772–783. 2006. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
120
|
Bardou M, Barkun AN and Martel M: Obesity
and colorectal cancer. Gut. 62:933–947. 2013. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
121
|
Barb D, Williams CJ, Neuwirth AK and
Mantzoros CS: Adiponectin in relation to malignancies: a review of
existing basic research and clinical evidence. Am J Clin Nutr.
86:s858–s866. 2007.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
122
|
Scherer PE, Williams S, Fogliano M,
Baldini G and Lodish HF: A novel serum protein similar to C1q,
produced exclusively in adipocytes. J Biol Chem. 270:26746–26749.
1995. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
123
|
Kadowaki T, Yamauchi T, Kubota N, Hara K,
Ueki K and Tobe K: Adiponectin and adiponectin receptors in insulin
resistance, diabetes, and the metabolic syndrome. J Clin Invest.
116:1784–1792. 2006. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
124
|
Nakashima R, Kamei N, Yamane K, Nakanishi
S, Nakashima A and Kohno N: Decreased total and high molecular
weight adiponectin are independent risk factors for the development
of type 2 diabetes in Japanese-Americans. J Clin Endocrinol Metab.
91:3873–3877. 2006. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
125
|
Renehan AG, Zwahlen M and Egger M:
Adiposity and cancer risk: new mechanistic insights from
epidemiology. Nat Rev Cancer. 15:484–498. 2015. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
126
|
Guffey CR, Fan D, Singh UP and Murphy EA:
Linking obesity to colorectal cancer: recent insights into
plausible biological mechanisms. Curr Opin Clin Nutr Metab Care.
16:595–600. 2013. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
127
|
Hillenbrand A, Fassler J, Huber N, Xu P,
Henne-Bruns D, Templin M, Schrezenmeier H, Wolf AM and Knippschild
U: Changed adipocytokine concentrations in colorectal tumor
patients and morbidly obese patients compared to healthy controls.
BMC Cancer. 12:5452012. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
128
|
Xu XT, Xu Q, Tong JL, Zhu MM, Huang ML,
Ran ZH and Xiao SD: Meta-analysis: circulating adiponectin levels
and risk of colorectal cancer and adenoma. J Dig Dis. 12:234–244.
2011. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
129
|
An W, Bai Y, Deng SX, Gao J, Ben QW, Cai
QC, Zhang HG and Li ZS: Adiponectin levels in patients with
colorectal cancer and adenoma: a meta-analysis. Eur J Cancer Prev.
21:126–133. 2012. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
130
|
Gulcelik MA, Colakoglu K, Dincer H, Dogan
L, Yenidogan E and Gulcelik NE: Associations between adiponectin
and two different cancers: breast and colon. Asian Pac J Cancer
Prev. 13:395–398. 2012. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
131
|
Fujisawa T, Endo H, Tomimoto A, Sugiyama
M, Takahashi H, Saito S, Inamori M, Nakajima N, Watanabe M, Kubota
N, et al: Adiponectin suppresses colorectal carcinogenesis under
the high-fat diet condition. Gut. 57:1531–1538. 2008. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
132
|
Sugiyama M, Takahashi H, Hosono K, Endo H,
Kato S, Yoneda K, Nozaki Y, Fujita K, Yoneda M, Wada K, et al:
Adiponectin inhibits colorectal cancer cell growth through the
AMPK/mTOR pathway. Int J Oncol. 34:339–344. 2009.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
133
|
Moon HS, Liu X, Nagel JM, Chamberland JP,
Diakopoulos KN, Brinkoetter MT, Hatziapostolou M, Wu Y, Robson SC,
Iliopoulos D, et al: Salutary effects of adiponectin on colon
cancer: in vivo and in vitro studies in mice. Gut. 62:561–570.
2013. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
134
|
Sun Y and Lodish HF: Adiponectin
deficiency promotes tumor growth in mice by reducing macrophage
infiltration. PLoS One. 5:e119872010. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
135
|
Vansaun MN: Molecular pathways:
adiponectin and leptin signaling in cancer. Clin Cancer Res.
19:1926–1932. 2013. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
136
|
Friedman JM and Halaas JL: Leptin and the
regulation of body weight in mammals. Nature. 395:763–770. 1998.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
137
|
Ryan AS, Berman DM, Nicklas BJ, Sinha M,
Gingerich RL, Meneilly GS, Egan JM and Elahi D: Plasma adiponectin
and leptin levels, body composition, and glucose utilization in
adult women with wide ranges of age and obesity. Diabetes Care.
26:2383–2388. 2003. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
138
|
Tamakoshi K, Toyoshima H, Wakai K, Kojima
M, Suzuki K, Watanabe Y, Hayakawa N, Yatsuya H, Kondo T, Tokudome
S, et al: Leptin is associated with an increased female colorectal
cancer risk: a nested case-control study in Japan. Oncology.
68:454–461. 2005. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
139
|
Delort L, Rossary A, Farges MC, Vasson MP
and Caldefie-Chézet F: Leptin, adipocytes and breast cancer: focus
on inflammation and anti-tumor immunity. Life Sci. 140:37–48. 2015.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
140
|
Wang D, Chen J, Chen H, Duan Z, Xu Q, Wei
M, Wang L and Zhong M: Leptin regulates proliferation and apoptosis
of colorectal carcinoma through PI3K/Akt/mTOR signalling pathway. J
Biosci. 37:91–101. 2012. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
141
|
Padidar S, Farquharson AJ, Williams LM,
Kearney R, Arthur JR and Drew JE: High-fat diet alters gene
expression in the liver and colon: links to increased development
of aberrant crypt foci. Dig Dis Sci. 57:1866–1874. 2012. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
142
|
Endo H, Hosono K, Uchiyama T, Sakai E,
Sugiyama M, Takahashi H, Nakajima N, Wada K, Takeda K, Nakagama H,
et al: Leptin acts as a growth factor for colorectal tumours at
stages subsequent to tumour initiation in murine colon
carcinogenesis. Gut. 60:1363–1371. 2011. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
143
|
Braun S, Bitton-Worms K and LeRoith D: The
link between the metabolic syndrome and cancer. Int J Biol Sci.
7:1003–1015. 2011. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
144
|
Grossmann ME, Mizuno NK, Bonorden MJL, Ray
A, Sokolchik I, Narasimhan ML and Cleary MP: Role of the
adiponectin leptin ratio in prostate cancer. Oncol Res. 18:269–277.
2009. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
145
|
Sharma D, Wang J, Fu PP, Sharma S,
Nagalingam A, Mells J, Handy J, Page AJ, Cohen C, Anania FA, et al:
Adiponectin antagonizes the oncogenic actions of leptin in
hepatocellular carcinogenesis. Hepatology. 52:1713–1722. 2010.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
146
|
Liu Z, Brooks RS, Ciappio ED, Kim SJ,
Crott JW, Bennett G, Greenberg AS and Mason JB: Diet-induced
obesity elevates colonic TNF-α in mice and is accompanied by an
activation of Wnt signaling: a mechanism for obesity-associated
colorectal cancer. J Nutr Biochem. 23:1207–1213. 2012. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
147
|
Dolcet X, Llobet D, Pallares J and
Matias-Guiu X: NF-κB in development and progression of human
cancer. Virchows Arch. 446:475–482. 2005. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
148
|
Pais R, Silaghi H, Silaghi AC, Rusu ML and
Dumitrascu DL: Metabolic syndrome and risk of subsequent colorectal
cancer. World J Gastroenterol. 15:5141–5148. 2009. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
149
|
Clayton PE, Banerjee I, Murray PG and
Renehan AG: Growth hormone, the insulin-like growth factor axis,
insulin and cancer risk. Nat Rev Endocrinol. 7:11–24. 2011.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
150
|
Singh P and Rubin N: Insulinlike growth
factors and binding proteins in colon cancer. Gastroenterology.
105:1218–1237. 1993. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
151
|
Giovannucci E: Nutrition, insulin,
insulin-like growth factors and cancer. Horm Metab Res. 35:694–704.
2003. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
152
|
Komninou D, Ayonote A, Richie JP Jr and
Rigas B: Insulin resistance and its contribution to colon
carcinogenesis. Exp Biol Med (Maywood). 228:396–405.
2003.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
153
|
Hart LS, Dolloff NG, Dicker DT, Koumenis
C, Christensen JG, Grimberg A and El-Deiry WS: Human colon cancer
stem cells are enriched by insulin-like growth factor-1 and are
sensitive to figitumumab. Cell Cycle. 10:2331–2338. 2011.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|