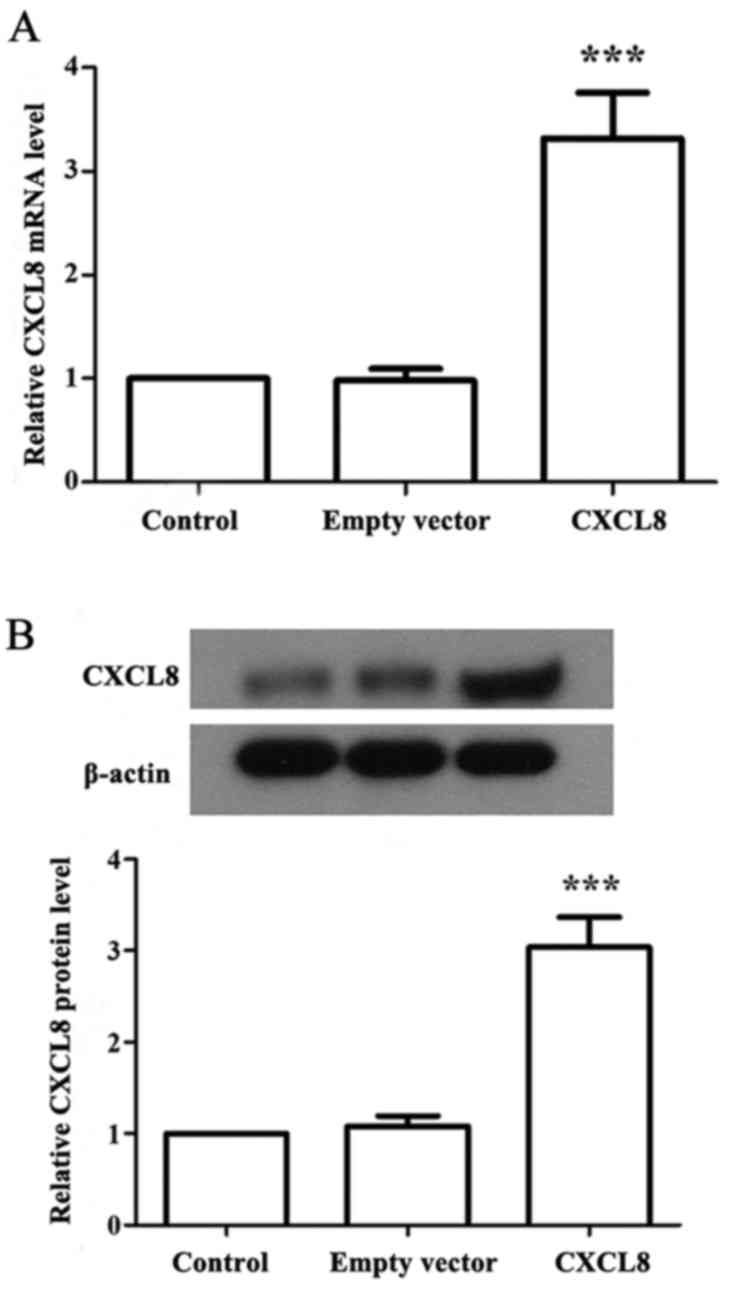
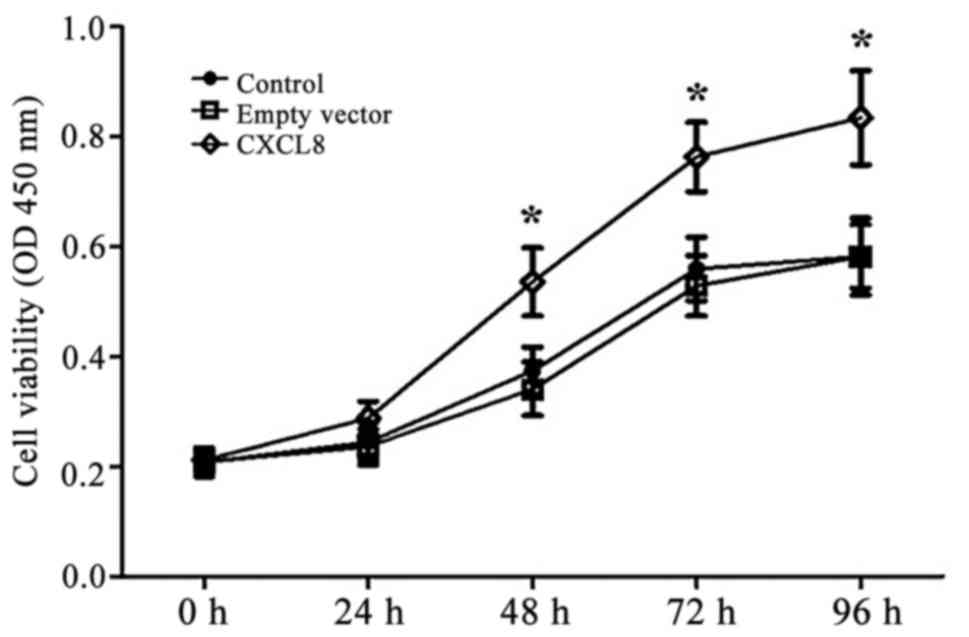
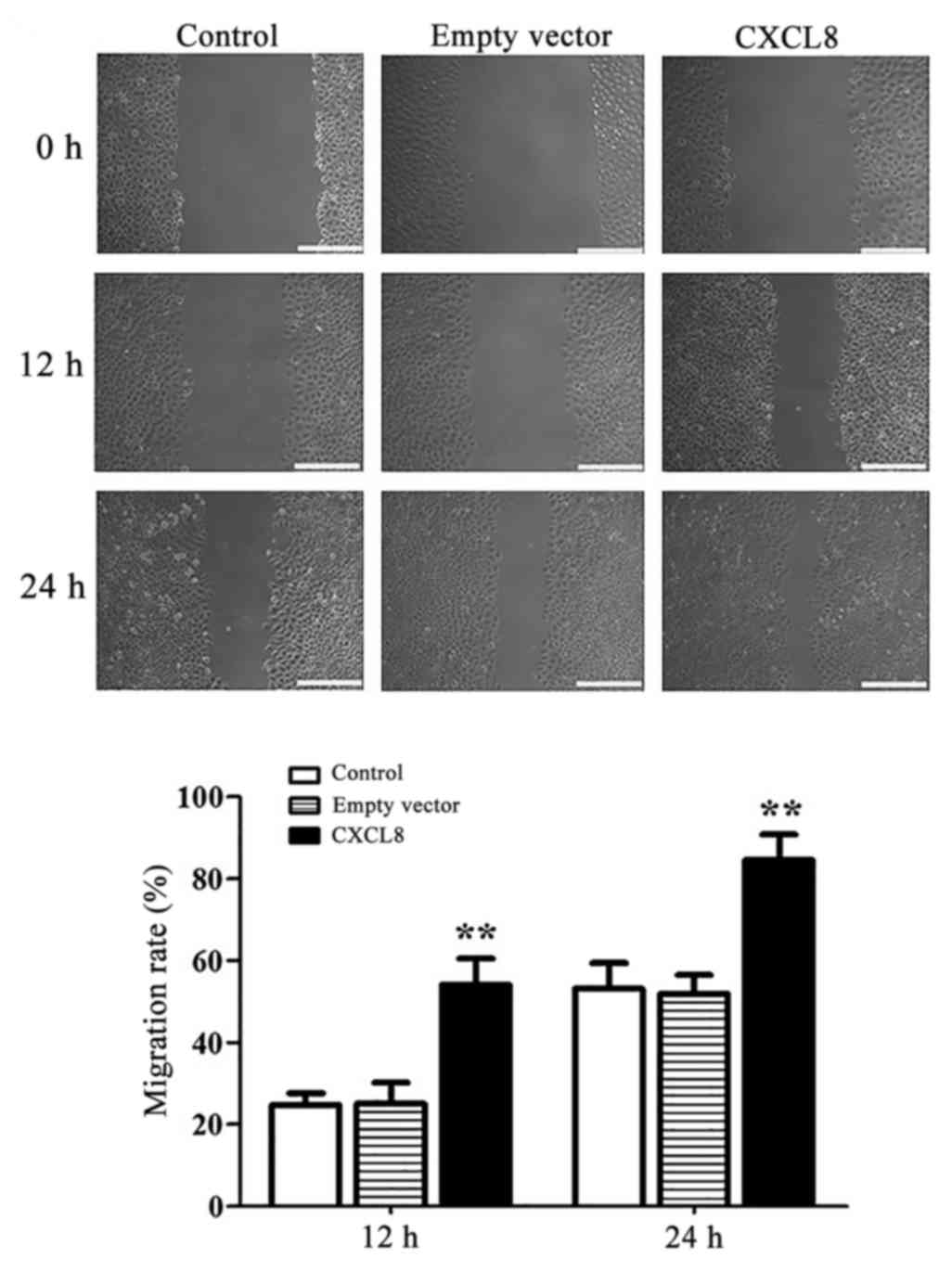
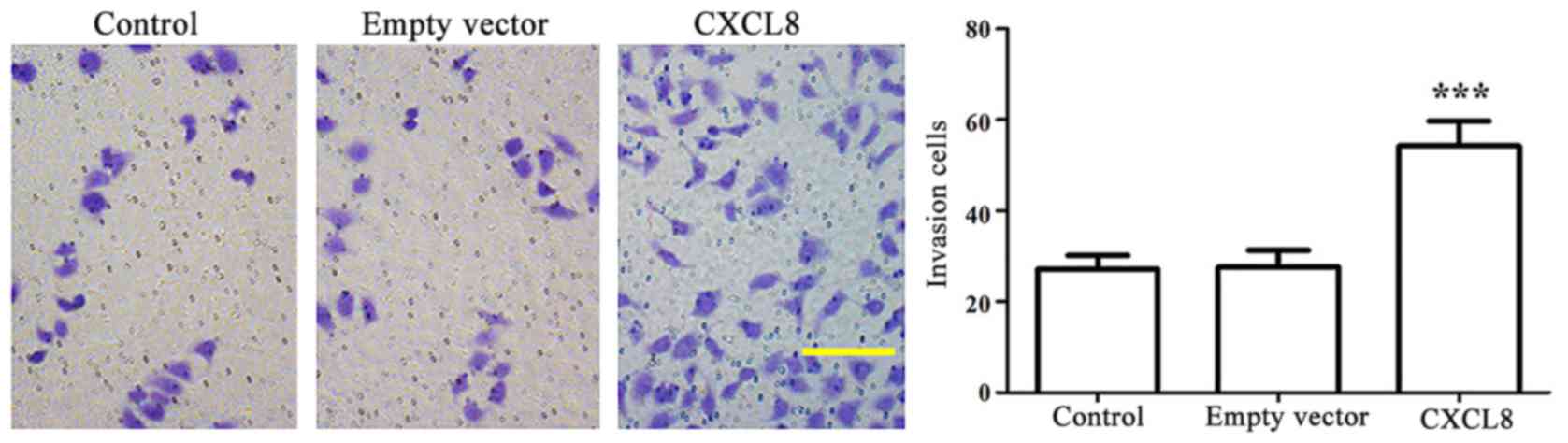
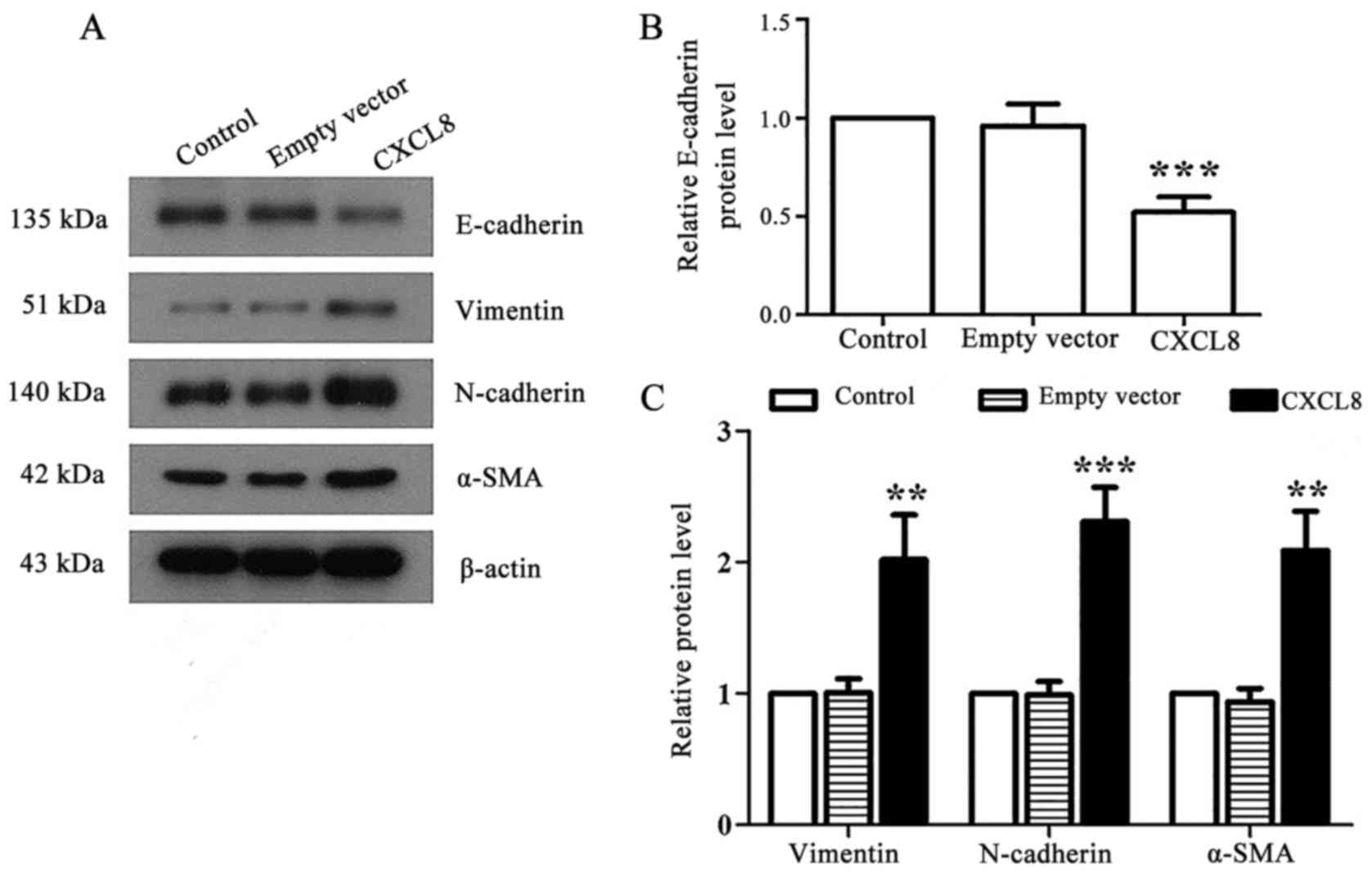
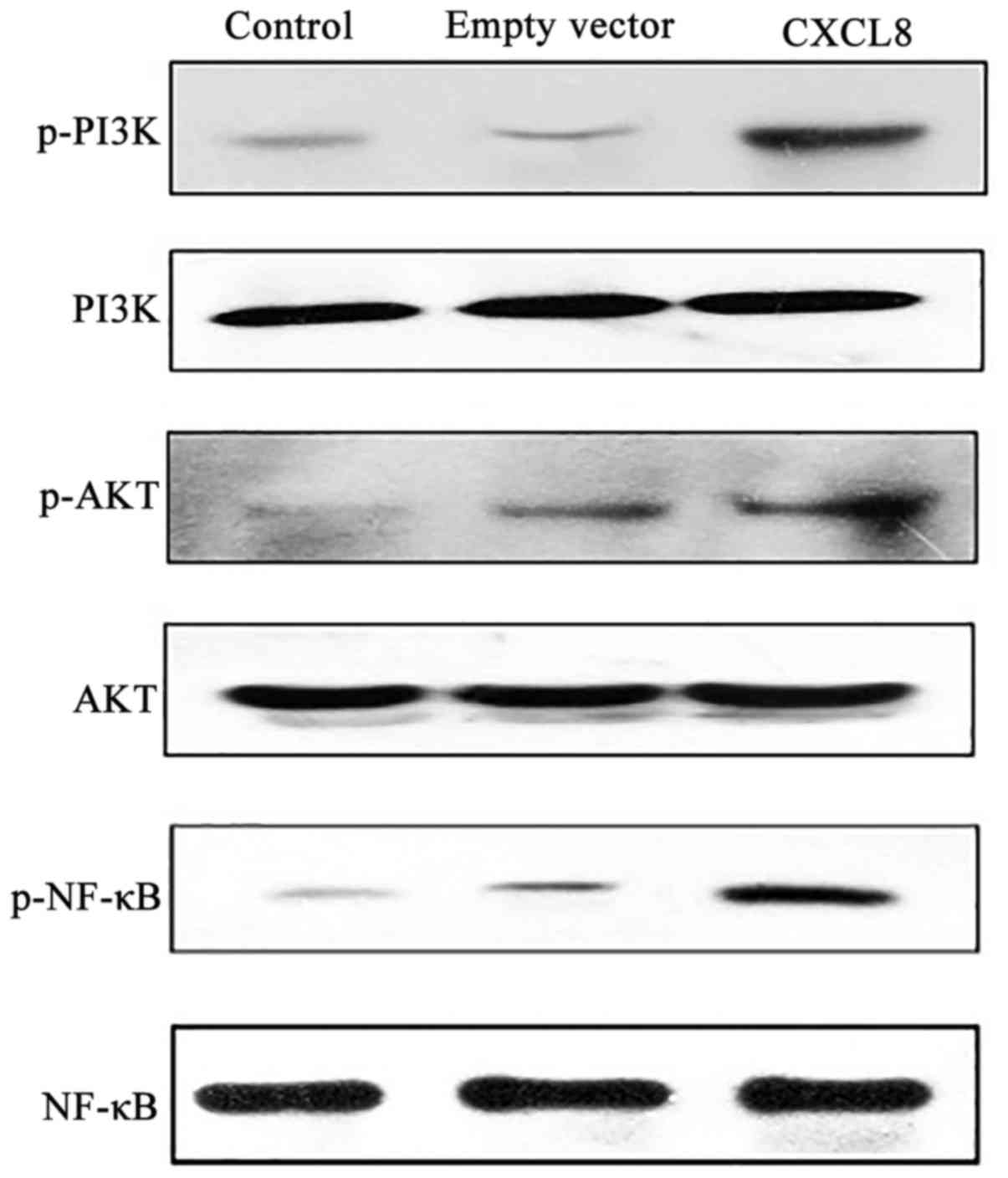
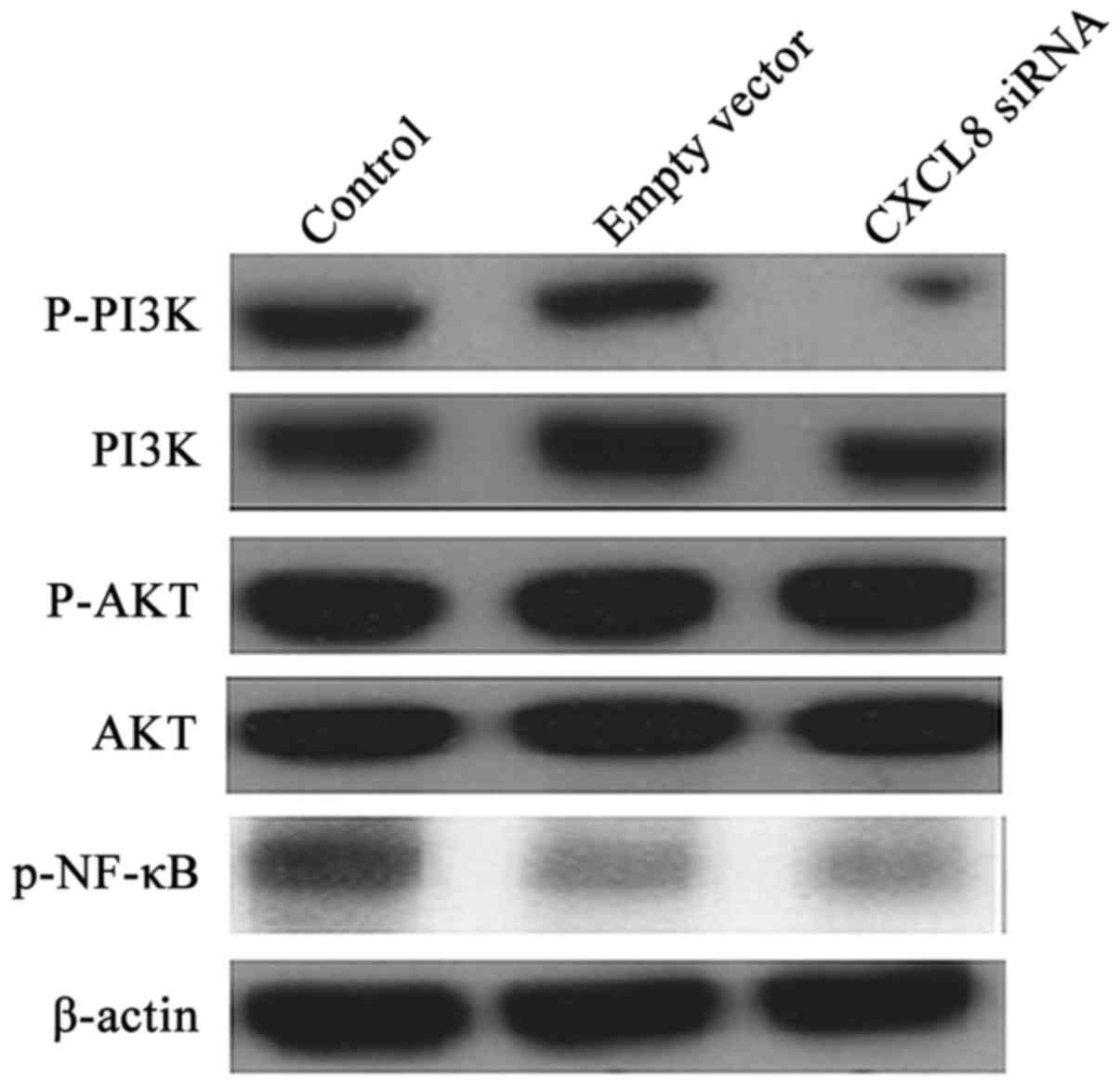
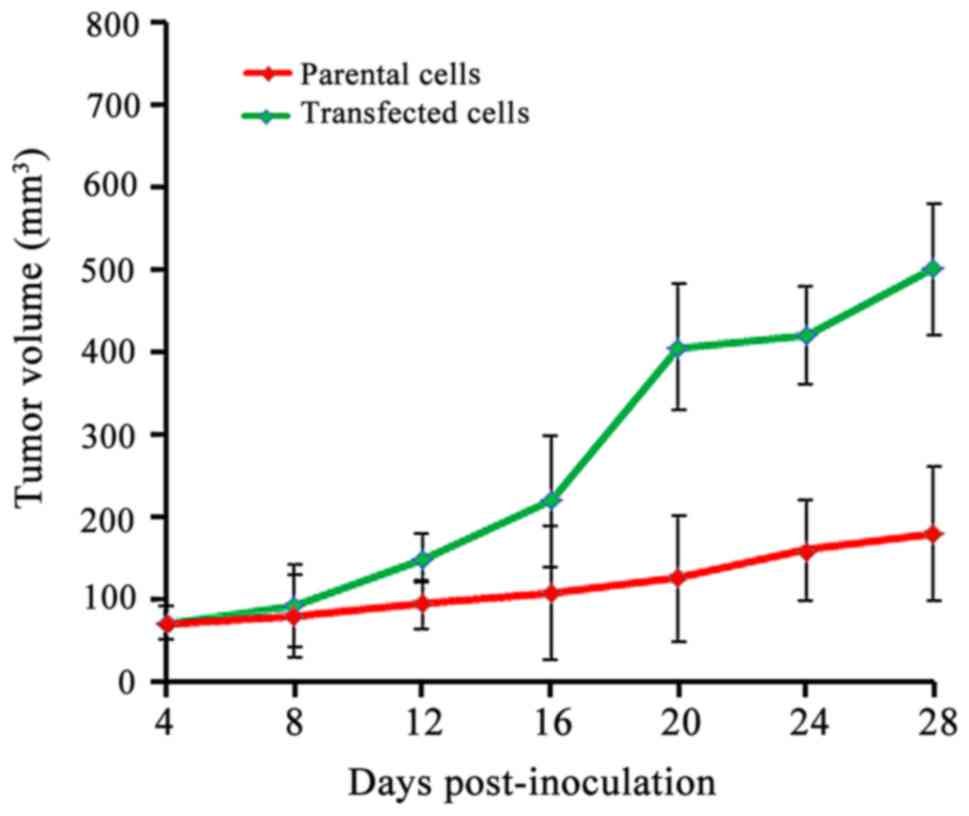
|
1
|
Jemal A, Bray F, Center MM, Ferlay J, Ward
E and Forman D: Global cancer statistics. CA Cancer J Clin.
61:69–90. 2011. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
2
|
Leporrier J, Maurel J, Chiche L, Bara S,
Segol P and Launoy G: A population-based study of the incidence,
management and prognosis of hepatic metastases from colorectal
cancer. Br J Surg. 93:465–474. 2006. View
Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
3
|
Thiery JP: Epithelial-mesenchymal
transitions in tumour progression. Nat Rev Cancer. 2:442–454. 2002.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
4
|
Brat DJ, Bellail AC and Van Meir EG: The
role of interleukin-8 and its receptors in gliomagenesis and
tumoral angiogenesis. Neuro Oncol. 7:122–133. 2005. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
5
|
Yoshimura T, Matsushima K, Oppenheim JJ
and Leonard EJ: Neutrophil chemotactic factor produced by
lipopolysaccharide (LPS)-stimulated human blood mononuclear
leukocytes: Partial characterization and separation from
interleukin 1 (IL 1). J Immunol. 175:5569–5574. 2005.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
6
|
Li A, Varney ML and Singh RK: Expression
of interleukin 8 and its receptors in human colon carcinoma cells
with different metastatic potentials. Clin Cancer Res. 7:3298–3304.
2001.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
7
|
Cheng XS, Li YF, Tan J, Sun B, Xiao YC,
Fang XB, Zhang XF, Li Q, Dong JH, Li M, et al: CCL20 and CXCL8
synergize to promote progression and poor survival outcome in
patients with colorectal cancer by collaborative induction of the
epithelial-mesenchymal transition. Cancer Lett. 348:77–87. 2014.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
8
|
Leroy P and Mostov KE: Slug is required
for cell survival during partial epithelial-mesenchymal transition
of HGF-induced tubulogenesis. Mol Biol Cell. 18:1943–1952. 2007.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
9
|
Tanaka T, Bai Z, Srinoulprasert Y, Yang
BG, Hayasaka H and Miyasaka M: Chemokines in tumor progression and
metastasis. Cancer Sci. 96:317–322. 2005. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
10
|
Lee YS, Choi I, Ning Y, Kim NY,
Khatchadourian V, Yang D, Chung HK, Choi D, LaBonte MJ, Ladner RD,
et al: Interleukin-8 and its receptor CXCR2 in the tumour
microenvironment promote colon cancer growth, progression and
metastasis. Br J Cancer. 106:1833–1841. 2012. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
11
|
McClelland MR, Carskadon SL, Zhao L, White
ES, Beer DG, Orringer MB, Pickens A, Chang AC and Arenberg DA:
Diversity of the angiogenic phenotype in non-small cell lung
cancer. Am J Respir Cell Mol Biol. 36:343–350. 2007. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
12
|
Doll D, Keller L, Maak M, Boulesteix AL,
Siewert JR, Holzmann B and Janssen KP: Differential expression of
the chemokines GRO-2, GRO-3, and interleukin-8 in colon cancer and
their impact on metastatic disease and survival. Int J Colorectal
Dis. 25:573–581. 2010. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
13
|
Ning Y, Manegold PC, Hong YK, Zhang W,
Pohl A, Lurje G, Winder T, Yang D, LaBonte MJ, Wilson PM, et al:
Interleukin-8 is associated with proliferation, migration,
angiogenesis and chemosensitivity in vitro and in vivo in colon
cancer cell line models. Int J Cancer. 128:2038–2049. 2011.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
14
|
Rubie C, Frick VO, Pfeil S, Wagner M,
Kollmar O, Kopp B, Graber S, Rau BM and Schilling MK: Correlation
of IL-8 with induction, progression and metastatic potential of
colorectal cancer. World J Gastroenterol. 13:4996–5002. 2007.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
15
|
Dozmorov MG, Azzarello JT, Wren JD, Fung
KM, Yang Q, Davis JS, Hurst RE, Culkin DJ, Penning TM and Lin HK:
Elevated AKR1C3 expression promotes prostate cancer cell survival
and prostate cell-mediated endothelial cell tube formation:
Implications for prostate cancer progression. BMC Cancer.
10:6722010. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
16
|
Jiao M and Nan KJ: Activation of PI3
kinase/Akt/HIF-1α pathway contributes to hypoxia-induced
epithelial-mesenchymal transition and chemoresistance in
hepatocellular carcinoma. Int J Oncol. 40:461–468. 2012.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
17
|
Song L, Xiong H, Li J, Liao W, Wang L, Wu
J and Li M: Sphingosine kinase-1 enhances resistance to apoptosis
through activation of PI3K/Akt/NF-κB pathway in human non-small
cell lung cancer. Clin Cancer Res. 17:1839–1849. 2011. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
18
|
Vredeveld LC, Possik PA, Smit MA, Meissl
K, Michaloglou C, Horlings HM, Ajouaou A, Kortman PC, Dankort D,
McMahon M, et al: Abrogation of BRAFV600E-induced
senescence by PI3K pathway activation contributes to
melanomagenesis. Genes Dev. 26:1055–1069. 2012. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
19
|
Wang D, Chen J, Chen H, Duan Z, Xu Q, Wei
M, Wang L and Zhong M: Leptin regulates proliferation and apoptosis
of colorectal carcinoma through PI3K/Akt/mTOR signalling pathway. J
Biosci. 37:91–101. 2012. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
20
|
Zhu G, Li X, Guo B, Ke Q, Dong M and Li F:
PAK5-mediated E47 phosphorylation promotes epithelial-mesenchymal
transition and metastasis of colon cancer. Oncogene. 35:1943–1954.
2016. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
21
|
Wang L, Li CL, Wang L, Yu WB, Yin HP,
Zhang GY, Zhang LF, Li S and Hu SY: Influence of CXCR4/SDF-1 axis
on E-cadherin/β-catenin complex expression in HT29 colon cancer
cells. World J Gastroenterol. 17:625–632. 2011. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
22
|
Malinowsky K, Nitsche U, Janssen KP, Bader
FG, Späth C, Drecoll E, Keller G, Höfler H, Slotta-Huspenina J and
Becker KF: Activation of the PI3K/AKT pathway correlates with
prognosis in stage II colon cancer. Br J Cancer. 110:2081–2089.
2014. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
23
|
Chen G, Chen SM, Wang X, Ding XF, Ding J
and Meng LH: Inhibition of chemokine (CXC motif) ligand
12/chemokine (CXC motif) receptor 4 axis (CXCL12/CXCR4)-mediated
cell migration by targeting mammalian target of rapamycin (mTOR)
pathway in human gastric carcinoma cells. J Biol Chem.
287:12132–12141. 2012. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
24
|
Huang CY, Fong YC, Lee CY, Chen MY, Tsai
HC, Hsu HC and Tang CH: CCL5 increases lung cancer migration via
PI3K, Akt and NF-kappaB pathways. Biochem Pharmacol. 77:794–803.
2009. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
25
|
Dolcet X, Llobet D, Pallares J and
Matias-Guiu X: NF-κB in development and progression of human
cancer. Virchows Arch. 446:475–482. 2005. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
26
|
Jacobs MD and Harrison SC: Structure of an
IkappaBalpha/NF-kappaB complex. Cell. 95:749–758. 1998. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
27
|
Kreuz S, Siegmund D, Scheurich P and
Wajant H: NF-kappaB inducers upregulate cFLIP, a
cycloheximide-sensitive inhibitor of death receptor signaling. Mol
Cell Biol. 21:3964–3973. 2001. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
28
|
Micheau O, Lens S, Gaide O, Alevizopoulos
K and Tschopp J: NF-kappaB signals induce the expression of c-FLIP.
Mol Cell Biol. 21:5299–5305. 2001. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
29
|
Guttridge DC, Albanese C, Reuther JY,
Pestell RG and Baldwin AS Jr: NF-kappaB controls cell growth and
differentiation through transcriptional regulation of cyclin D1.
Mol Cell Biol. 19:5785–5799. 1999. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
30
|
Hinz M, Krappmann D, Eichten A, Heder A,
Scheidereit C and Strauss M: NF-κB function in growth control:
Regulation of cyclin D1 expression and
G0/G1-to-S-phase transition. Mol Cell Biol.
19:2690–2698. 1999. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
31
|
Hinz M, Löser P, Mathas S, Krappmann D,
Dörken B and Scheidereit C: Constitutive NF-κB maintains high
expression of a characteristic gene network, including CD40, CD86,
and a set of antiapoptotic genes in Hodgkin/Reed-Sternberg cells.
Blood. 97:2798–2807. 2001. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|