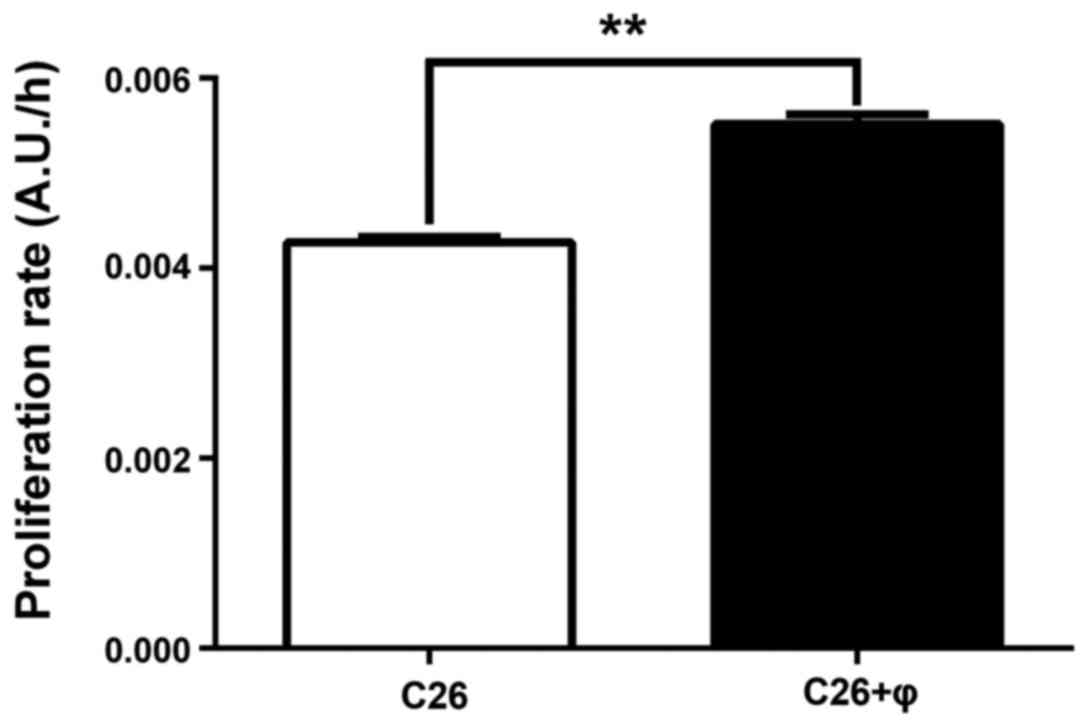
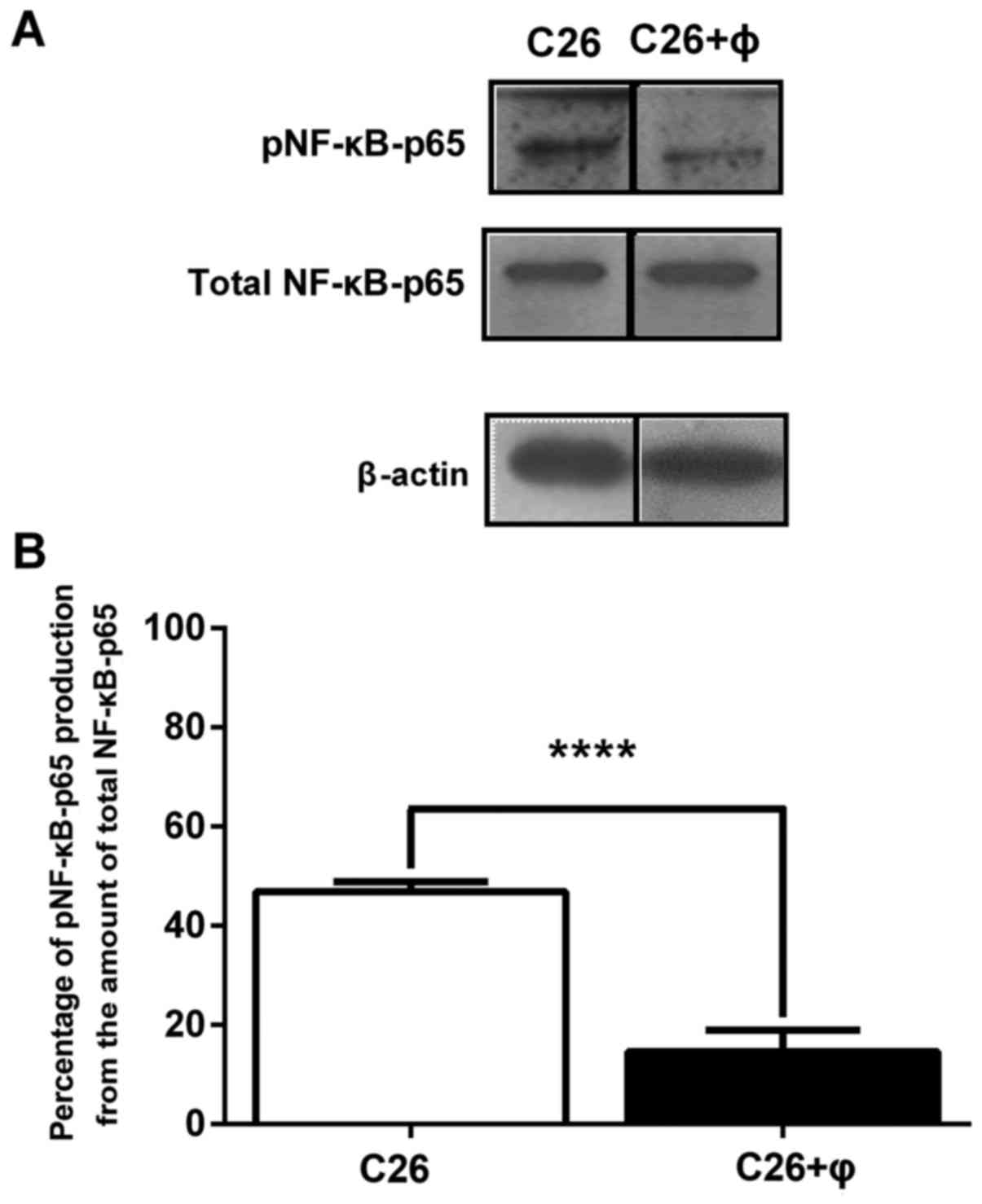
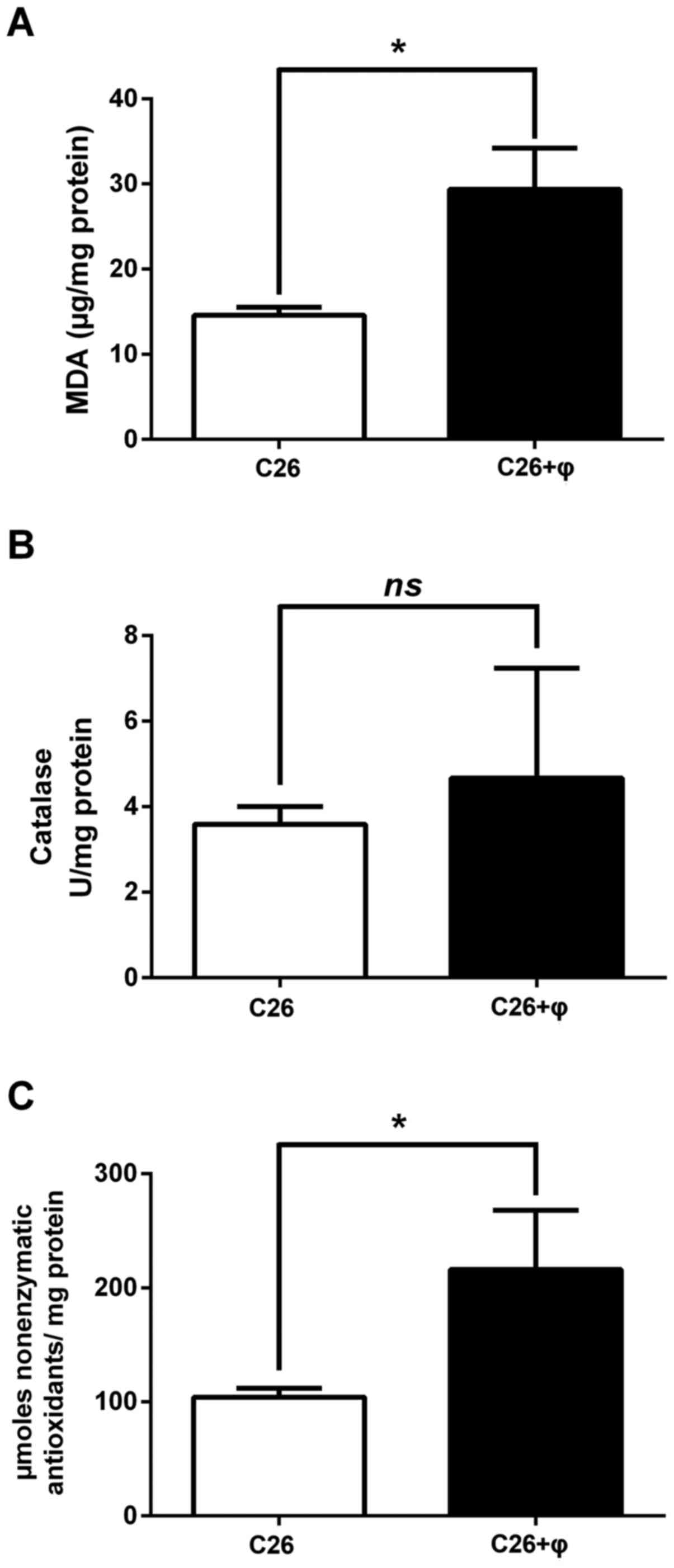
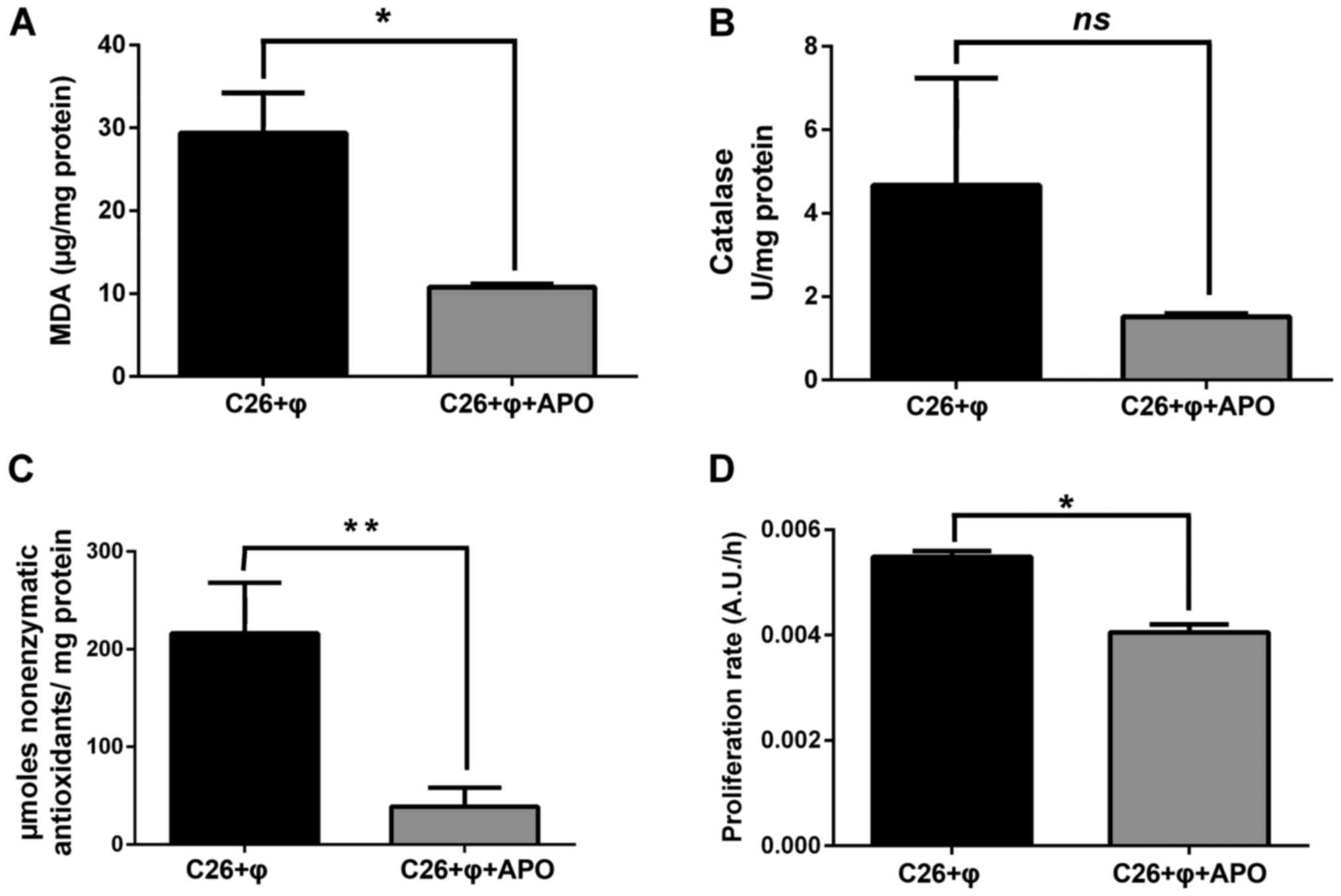
|
1
|
Albini A, Tosetti F, Benelli R and Noonan
DM: Tumor inflammatory angiogenesis and its chemoprevention. Cancer
Res. 65:10637–10641. 2005. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
2
|
Allavena P, Sica A, Garlanda C and
Mantovani A: The Yin-Yang of tumor-associated macrophages in
neoplastic progression and immune surveillance. Immunol Rev.
222:155–161. 2008. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
3
|
Quail DF and Joyce JA: Microenvironmental
regulation of tumor progression and metastasis. Nat Med.
19:1423–1437. 2013. View
Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
4
|
Alupei MC, Licarete E, Patras L and Banciu
M: Liposomal simvastatin inhibits tumor growth via targeting
tumor-associated macrophages-mediated oxidative stress. Cancer
Lett. 356:946–952. 2015. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
5
|
Banciu M, Metselaar JM, Schiffelers RM and
Storm G: Antitumor activity of liposomal prednisolone phosphate
depends on the presence of functional tumor-associated macrophages
in tumor tissue. Neoplasia. 10:108–117. 2008. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
6
|
Mantovani A, Sica A, Sozzani S, Allavena
P, Vecchi A and Locati M: The chemokine system in diverse forms of
macrophage activation and polarization. Trends Immunol. 25:677–686.
2004. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
7
|
Solinas G, Germano G, Mantovani A and
Allavena P: Tumor-associated macrophages (TAM) as major players of
the cancer-related inflammation. J Leukoc Biol. 86:1065–1073. 2009.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
8
|
Mantovani A, Sozzani S, Locati M, Allavena
P and Sica A: Macrophage polarization: Tumor-associated macrophages
as a paradigm for polarized M2 mononuclear phagocytes. Trends
Immunol. 23:549–555. 2002. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
9
|
Brown NS and Bicknell R: Hypoxia and
oxidative stress in breast cancer. Oxidative stress: Its effects on
the growth, metastatic potential and response to therapy of breast
cancer. Breast Cancer Res. 3:323–327. 2001. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
10
|
Brown NS, Jones A, Fujiyama C, Harris AL
and Bicknell R: Thymidine phosphorylase induces carcinoma cell
oxidative stress and promotes secretion of angiogenic factors.
Cancer Res. 60:6298–6302. 2000.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
11
|
Fruehauf JP, Meyskens FL Jr, et al:
Reactive oxygen species: A breath of life or death? Clin Cancer
Res. 13:789–794. 2007. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
12
|
Guo C, Buranych A, Sarkar D, Fisher PB and
Wang XY: The role of tumor-associated macrophages in tumor
vascularization. Vasc Cell. 5:202013. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
13
|
Sundaresan M, Yu ZX, Ferrans VJ, Sulciner
DJ, Gutkind JS, Irani K, Goldschmidt-Clermont PJ and Finkel T:
Regulation of reactive-oxygen-species generation in fibroblasts by
Rac1. Biochem J. 318:379–382. 1996. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
14
|
Tammali R, Reddy AB, Srivastava SK and
Ramana KV: Inhibition of aldose reductase prevents angiogenesis in
vitro and in vivo. Angiogenesis. 14:209–221. 2011. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
15
|
Zhang Y, Choksi S, Chen K, Pobezinskaya Y,
Linnoila I and Liu ZG: ROS play a critical role in the
differentiation of alternatively activated macrophages and the
occurrence of tumor-associated macrophages. Cell Res. 23:898–914.
2013. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
16
|
Forssell J, Oberg A, Henriksson ML,
Stenling R, Jung A and Palmqvist R: High macrophage infiltration
along the tumor front correlates with improved survival in colon
cancer. Clin Cancer Res. 13:1472–1479. 2007. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
17
|
Sickert D, Aust DE, Langer S, Haupt I,
Baretton GB and Dieter P: Characterization of macrophage
subpopulations in colon cancer using tissue microarrays.
Histopathology. 46:515–521. 2005. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
18
|
van der Bij GJ, Bögels M, Oosterling SJ,
Kroon J, Schuckmann DT, de Vries HE, Meijer S, Beelen RH and van
Egmond M: Tumor infiltrating macrophages reduce development of
peritoneal colorectal carcinoma metastases. Cancer Lett. 262:77–86.
2008. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
19
|
Zins K, Abraham D, Sioud M and Aharinejad
S: Colon cancer cell-derived tumor necrosis factor-alpha mediates
the tumor growth-promoting response in macrophages by up-regulating
the colony-stimulating factor-1 pathway. Cancer Res. 67:1038–1045.
2007. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
20
|
Calorini L, Bianchini F, Mannini A, Mugnai
G and Ruggieri S: Enhancement of nitric oxide release in mouse
inflammatory macrophages co-cultivated with tumor cells of a
different origin. Clin Exp Metastasis. 22:413–419. 2005. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
21
|
Herbeuval JP, Lelievre E, Lambert C, Dy M
and Genin C: Recruitment of STAT3 for production of IL-10 by colon
carcinoma cells induced by macrophage-derived IL-6. J Immunol.
172:4630–4636. 2004. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
22
|
James AD, Patel W, Butt Z, Adiamah M,
Dakhel R, Latif A, Uggenti C, Swanton E, Imamura H, Siriwardena AK,
et al: The plasma membrane calcium pump in pancreatic cancer cells
exhibiting the Warburg effect relies on glycolytic ATP. J Biol
Chem. 290:24760–24771. 2015. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
23
|
Banciu M, Schiffelers RM, Fens MH,
Metselaar JM and Storm G: Anti-angiogenic effects of liposomal
prednisolone phosphate on B16 melanoma in mice. J Control Release.
113:1–8. 2006. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
24
|
Siu FKY, Lee LTO and Chow BKC:
Southwestern blotting in investigating transcriptional regulation.
Nat Protoc. 3:51–58. 2008. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
25
|
Bradford MM: A rapid and sensitive method
for the quantitation of microgram quantities of protein utilizing
the principle of protein-dye binding. Anal Biochem. 72:248–254.
1976. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
26
|
Karin M and Greten FR: NF-kappaB: Linking
inflammation and immunity to cancer development and progression.
Nat Rev Immunol. 5:749–759. 2005. View
Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
27
|
Karatas F, Karatepe M and Baysar A:
Determination of free malondialdehyde in human serum by
high-performance liquid chromatography. Anal Biochem. 311:76–79.
2002. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
28
|
Erel O: A novel automated direct
measurement method for total antioxidant capacity using a new
generation, more stable ABTS radical cation. Clin Biochem.
37:277–285. 2004. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
29
|
Aebi H: Catalase in vitro. Methods
Enzymol. 105:121–126. 1984. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
30
|
Sica A and Bronte V: Altered macrophage
differentiation and immune dysfunction in tumor development. J Clin
Invest. 117:1155–1166. 2007. View
Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
31
|
Pick E: Role of the Rho GTPase Rac in the
activation of the phagocyte NADPH oxidase: Outsourcing a key task.
Small GTPases. 5:e279522014. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
32
|
Zhang QW, Liu L, Gong CY, Shi HS, Zeng YH,
Wang XZ, Zhao YW and Wei YQ: Prognostic significance of
tumor-associated macrophages in solid tumor: A meta-analysis of the
literature. PLoS One. 7:e509462012. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
33
|
Biswas SK, Allavena P and Mantovani A:
Tumor-associated macrophages: Functional diversity, clinical
significance, and open questions. Semin Immunopathol. 35:585–600.
2013. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
34
|
Siveen KS and Kuttan G: Role of
macrophages in tumour progression. Immunol Lett. 123:97–102. 2009.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
35
|
van der Bij GJ, Oosterling SJ, Meijer S,
Beelen RH and van Egmond M: The role of macrophages in tumor
development. Cell Oncol. 27:203–213. 2005.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
36
|
Coffelt SB, Hughes R and Lewis CE:
Tumor-associated macrophages: Effectors of angiogenesis and tumor
progression. Biochim Biophys Acta. 1796:11–18. 2009.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
37
|
Joyce JA and Pollard JW:
Microenvironmental regulation of metastasis. Nat Rev Cancer.
9:239–252. 2009. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
38
|
Barbera-Guillem E, Nyhus JK, Wolford CC,
Friece CR and Sampsel JW: Vascular endothelial growth factor
secretion by tumor-infiltrating macrophages essentially supports
tumor angiogenesis, and IgG immune complexes potentiate the
process. Cancer Res. 62:7042–7049. 2002.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
39
|
Patras L, Sesarman A, Licarete E, Luca L,
Alupei MC, Rakosy-Tican E and Banciu M: Dual role of macrophages in
the response of C26 colon carcinoma cells to 5-fluorouracil
administration. Oncol Lett. 12:1183–1191. 2016.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
40
|
Yang Z, Li C, Wang X, Zhai C, Yi Z, Wang
L, Liu B, Du B, Wu H, Guo X, et al: Dauricine induces apoptosis,
inhibits proliferation and invasion through inhibiting NF-kappaB
signaling pathway in colon cancer cells. J Cell Physiol.
225:266–275. 2010. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
41
|
Ryan AE, Colleran A, O'Gorman A, O'Flynn
L, Pindjacova J, Lohan P, O'Malley G, Nosov M, Mureau C and Egan
LJ: Targeting colon cancer cell NF-κB promotes an anti-tumour
M1-like macrophage phenotype and inhibits peritoneal metastasis.
Oncogene. 34:1563–1574. 2015. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
42
|
Grivennikov SI and Karin M: Dangerous
liaisons: STAT3 and NF-kappaB collaboration and crosstalk in
cancer. Cytokine Growth Factor Rev. 21:11–19. 2010. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
43
|
Lin WW and Karin M: A cytokine-mediated
link between innate immunity, inflammation, and cancer. J Clin
Invest. 117:1175–1183. 2007. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
44
|
Saccani A, Schioppa T, Porta C, Biswas SK,
Nebuloni M, Vago L, Bottazzi B, Colombo MP, Mantovani A and Sica A:
p50 nuclear factor-kappaB overexpression in tumor-associated
macrophages inhibits M1 inflammatory responses and antitumor
resistance. Cancer Res. 66:11432–11440. 2006. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
45
|
Kühnemuth B and Michl P: The role of CUX1
in antagonizing NF-κB signaling in TAMs. OncoImmunology.
3:e282702014. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
46
|
Connelly L, Barham W, Onishko HM, Chen L,
Sherrill TP, Zabuawala T, Ostrowski MC, Blackwell TS and Yull FE:
NF-kappaB activation within macrophages leads to an anti-tumor
phenotype in a mammary tumor lung metastasis model. Breast Cancer
Res. 13:R832011. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
47
|
Tabruyn SP and Griffioen AW: A new role
for NF-kappaB in angiogenesis inhibition. Cell Death Differ.
14:1393–1397. 2007. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
48
|
Ushio-Fukai M and Alexander RW: Reactive
oxygen species as mediators of angiogenesis signaling: Role of
NAD(P)H oxidase. Mol Cell Biochem. 264:85–97. 2004. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
49
|
Morgan MJ and Liu ZG: Crosstalk of
reactive oxygen species and NF-κB signaling. Cell Res. 21:103–115.
2011. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
50
|
Kabe Y, Ando K, Hirao S, Yoshida M and
Handa H: Redox regulation of NF-kappaB activation: Distinct redox
regulation between the cytoplasm and the nucleus. Antioxid Redox
Signal. 7:395–403. 2005. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
51
|
Wu M, Bian Q, Liu Y, Fernandes AF, Taylor
A, Pereira P and Shang F: Sustained oxidative stress inhibits
NF-kappaB activation partially via inactivating the proteasome.
Free Radic Biol Med. 46:62–69. 2009. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
52
|
Alupei MC, Licarete E, Cristian FB and
Banciu M: Cytotoxicity of lipophilic statins depends on their
combined actions on HIF-1α expression and redox status in B16.F10
melanoma cells. Anticancer Drugs. 25:393–405. 2014. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|