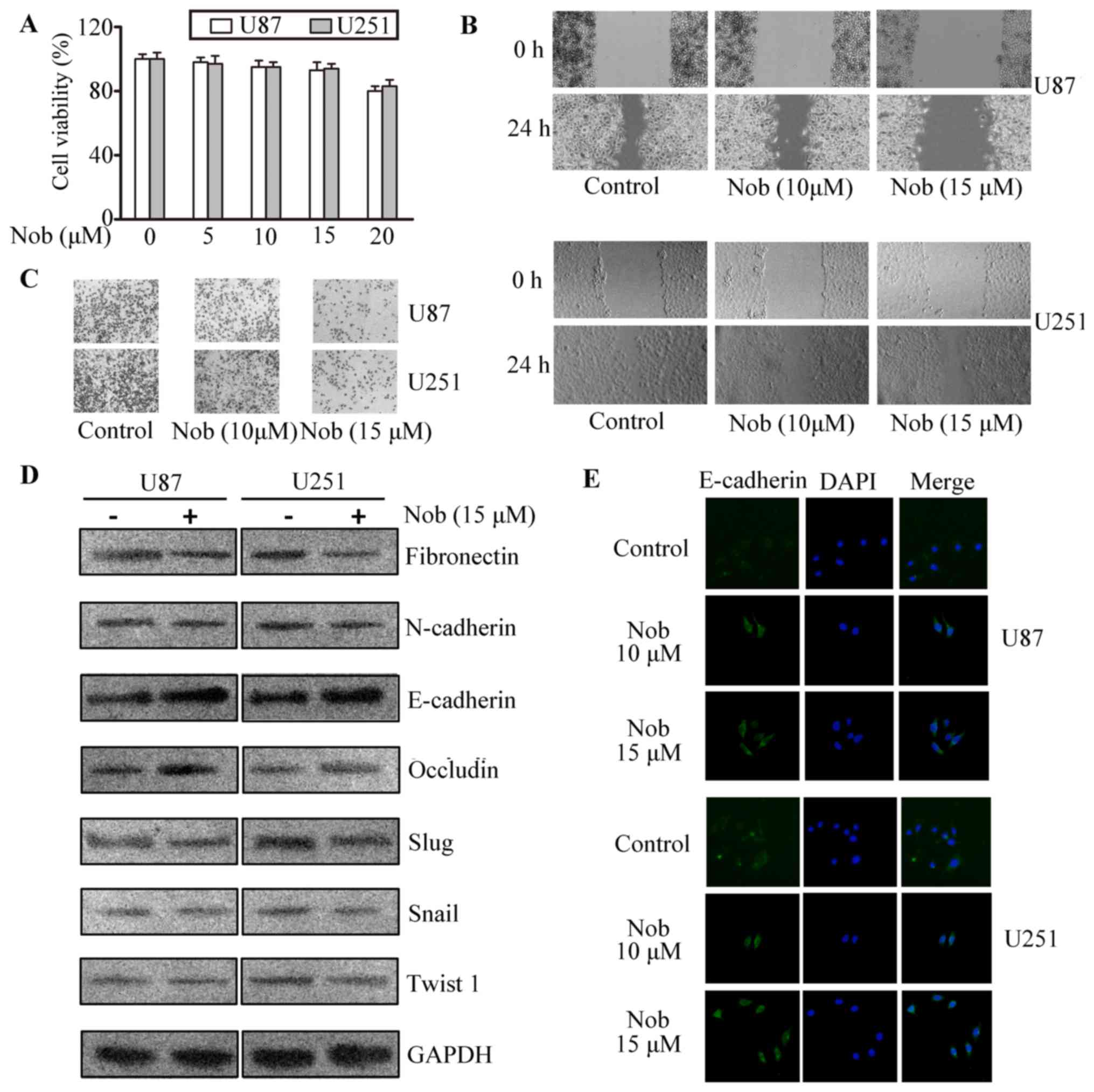
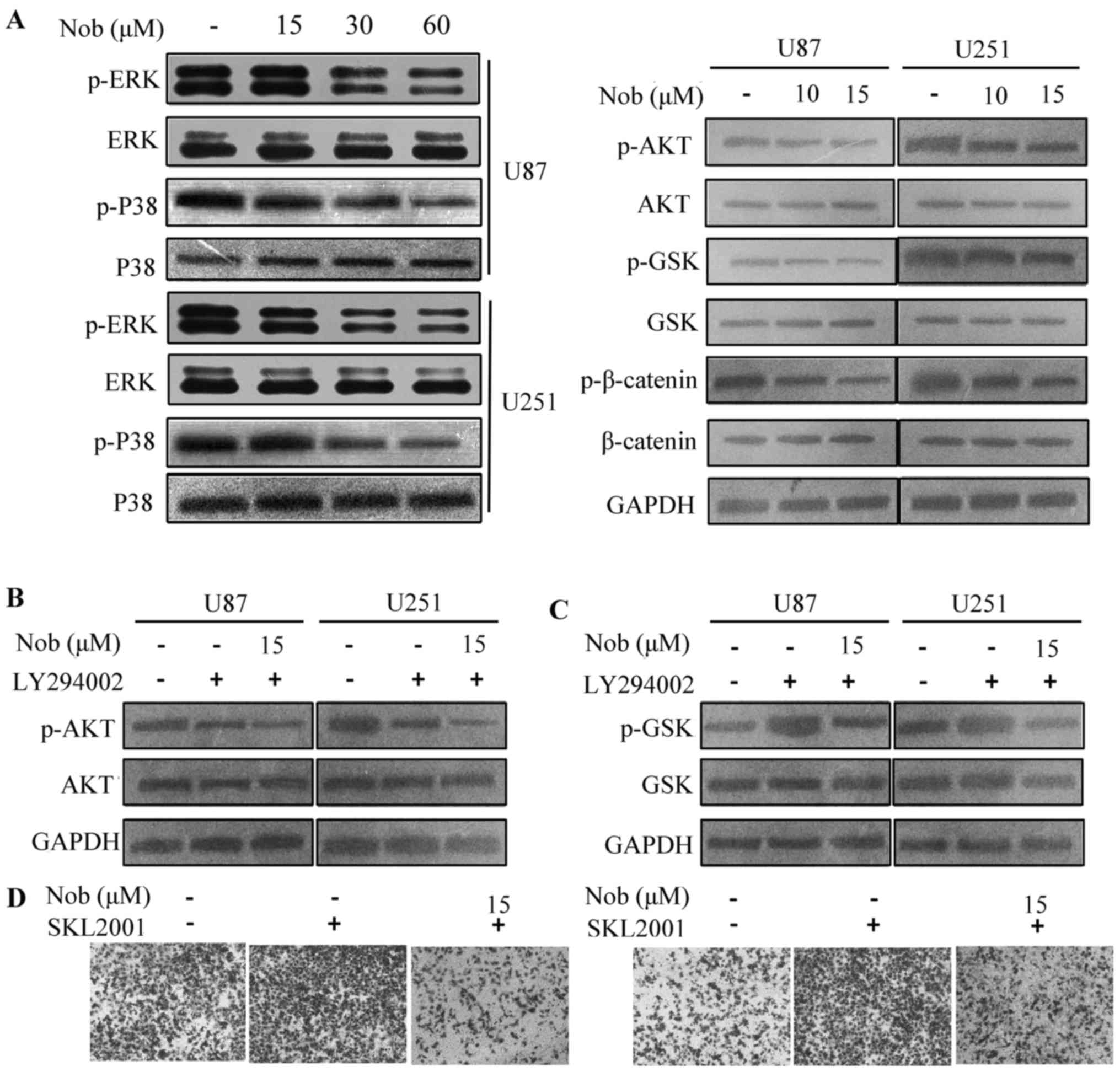
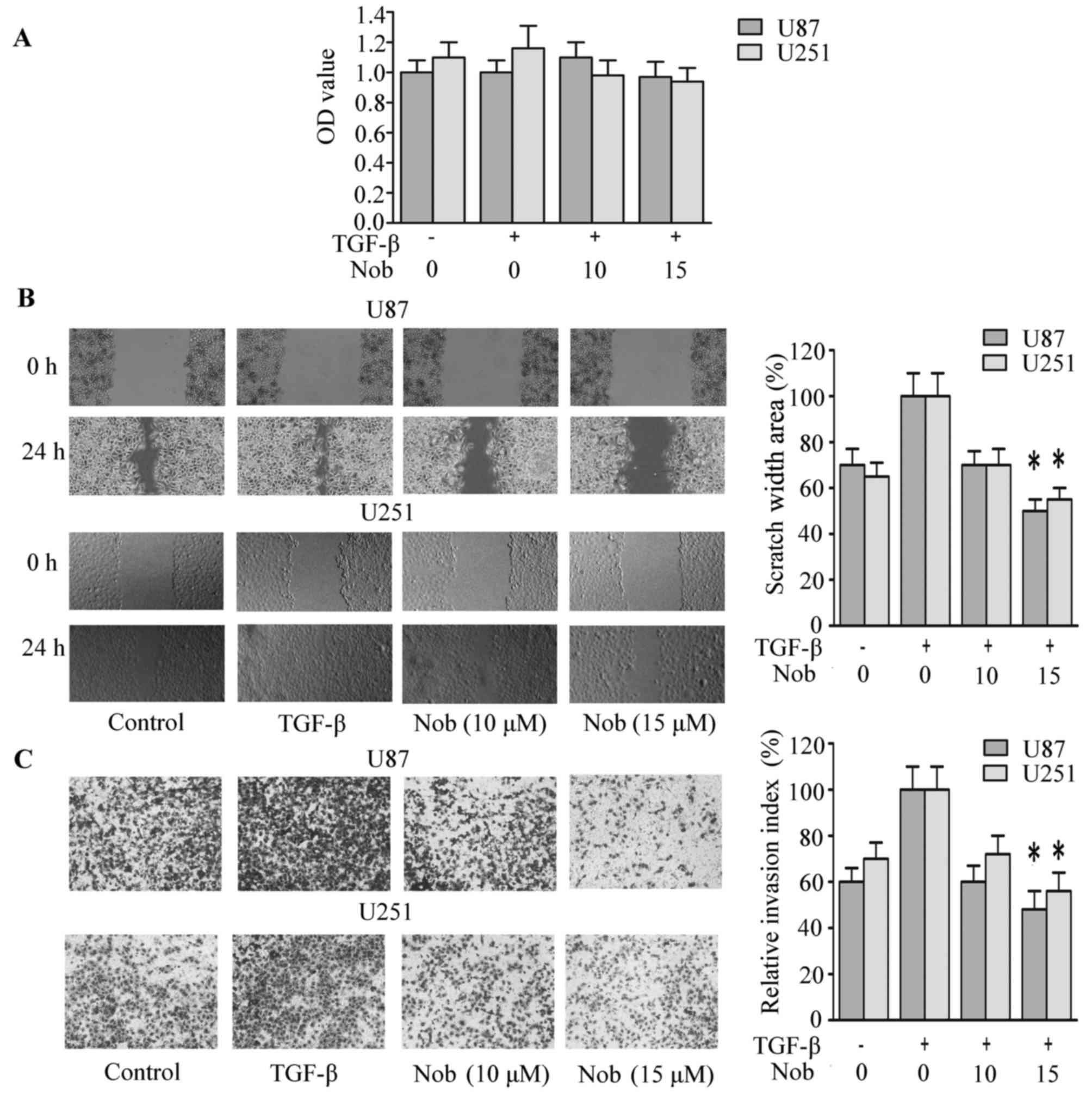
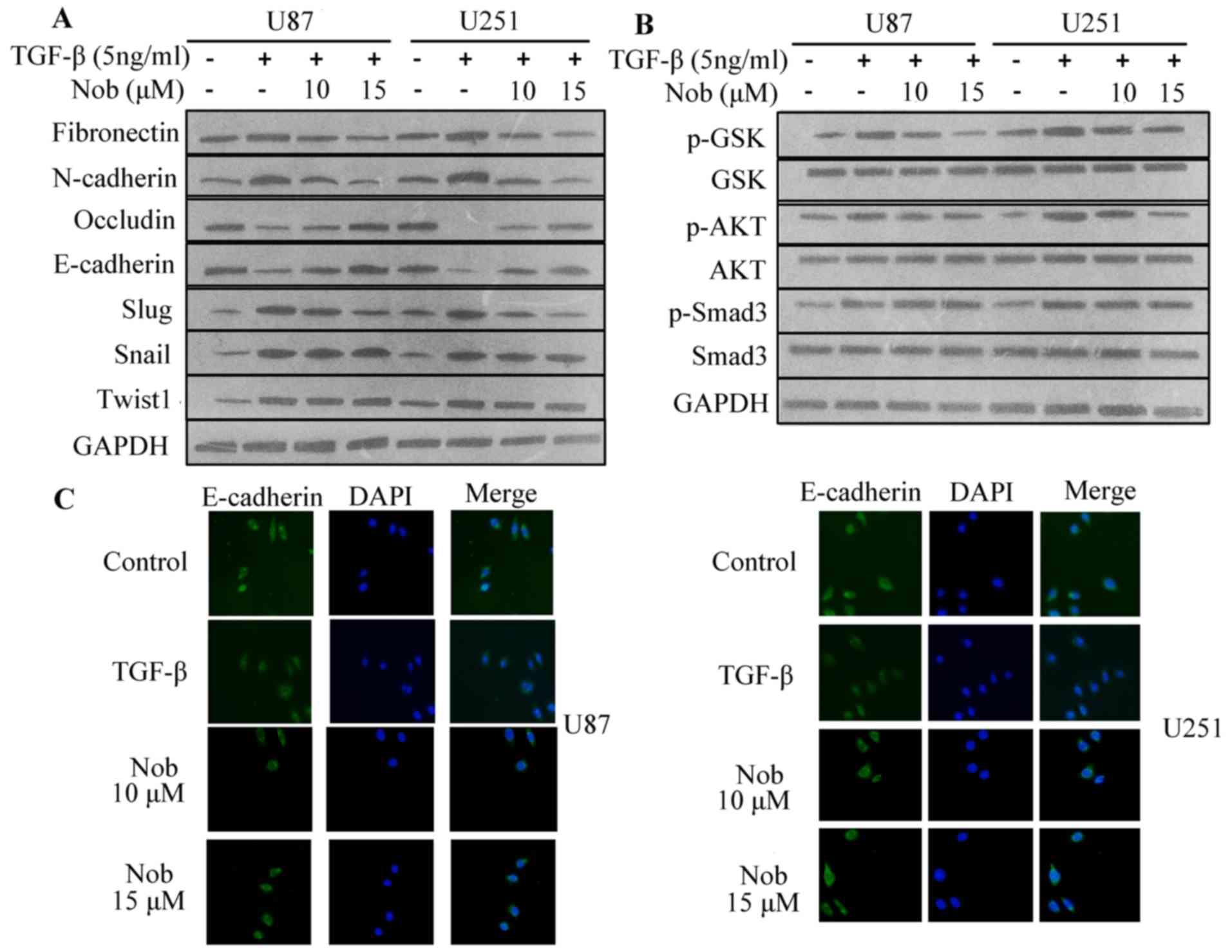
|
1
|
Wirsching HG and Weller M: The role of
molecular diagnostics in the management of patients with gliomas.
Curr Treat Options Oncol. 17:512016. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
2
|
Huse JT: Establishing a robust molecular
taxonomy for diffuse gliomas of adulthood. Surg Pathol Clin.
9:379–390. 2016. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
3
|
Zou M, Zhu W, Wang L, Shi L, Gao R, Ou Y,
Chen X, Wang Z, Jiang A, Liu K, et al: AEG-1/MTDH-activated
autophagy enhances human malignant glioma susceptibility to
TGF-β1-triggered epithelial-mesenchymal transition. Oncotarget.
7:13122–13138. 2016.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
4
|
Khan Z and Marshall JF: The role of
integrins in TGFβ activation in the tumour stroma. Cell Tissue Res.
365:657–673. 2016. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
5
|
Bussard KM, Mutkus L, Stumpf K,
Gomez-Manzano C and Marini FC: Tumor-associated stromal cells as
key contributors to the tumor microenvironment. Breast Cancer Res.
18:842016. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
6
|
Smith BN and Bhowmick NA: Role of EMT in
metastasis and therapy resistance. J Clin Med. 5:52016. View Article : Google Scholar :
|
|
7
|
Guo L, Zhang Y, Zhang L, Huang F, Li J and
Wang S: MicroRNAs, TGF-β signaling, and the inflammatory
microenvironment in cancer. Tumour Biol. 37:115–125. 2016.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
8
|
Cervantes-Arias A, Pang LY and Argyle DJ:
Epithelial-mesenchymal transition as a fundamental mechanism
underlying the cancer phenotype. Vet Comp Oncol. 11:169–184. 2013.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
9
|
Xu W, Yang Z and Lu N: A new role for the
PI3K/Akt signaling pathway in the epithelial-mesenchymal
transition. Cell Adhes Migr. 9:317–324. 2015. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
10
|
Papkoff J and Aikawa M: WNT-1 and HGF
regulate GSK3 beta activity and beta-catenin signaling in mammary
epithelial cells. Biochem Biophys Res Commun. 247:851–858. 1998.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
11
|
Clevers H and Nusse R: Wnt/β-catenin
signaling and disease. Cell. 149:1192–1205. 2012. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
12
|
Angers S and Moon RT: Proximal events in
Wnt signal transduction. Nat Rev Mol Cell Biol. 10:468–477.
2009.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
13
|
Lien LM, Wang MJ, Chen RJ, Chiu HC, Wu JL,
Shen MY, Chou DS, Sheu JR, Lin KH and Lu WJ: Nobiletin, a
polymethoxylated flavone, inhibits glioma cell growth and migration
via arresting cell cycle and suppressing MAPK and Akt pathways.
Phytother Res. 30:214–221. 2016. View
Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
14
|
Chen J, Chen AY, Huang H, Ye X, Rollyson
WD, Perry HE, Brown KC, Rojanasakul Y, Rankin GO, Dasgupta P, et
al: The flavonoid nobiletin inhibits tumor growth and angiogenesis
of ovarian cancers via the Akt pathway. Int J Oncol. 46:2629–2638.
2015.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
15
|
Shi MD, Liao YC, Shih YW and Tsai LY:
Nobiletin attenuates metastasis via both ERK and PI3K/Akt pathways
in HGF-treated liver cancer HepG2 cells. Phytomedicine.
20:743–752. 2013. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
16
|
Ma HW, Xie M, Sun M, Chen TY, Jin RR, Ma
TS, Chen QN, Zhang EB, He XZ, De W, et al: The pseudogene derived
long noncoding RNA DUXAP8 promotes gastric cancer cell
proliferation and migration via epigenetically silencing PLEKHO1
expression. Oncotarget. Aug 5–2016.(Epub ahead of print).
|
|
17
|
McCormick SM, Gowda N, Fang JX and Heller
NM: Suppressor of cytokine signaling (SOCS)1 regulates
interleukin-4 (IL-4)-activated insulin receptor substrate (IRS)-2
tyrosine phosphorylation in monocytes and macrophages via the
proteasome. J Biol Chem. 291:20574–20587. 2016. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
18
|
Navarro-Villarán E, Tinoco J, Jiménez G,
Pereira S, Wang J, Aliseda S, Rodríguez-Hernández MA, González R,
Marín-Gómez LM, Gómez-Bravo MA, et al: Differential antitumoral
properties and renal-associated tissue damage induced by tacrolimus
and mammalian target of rapamycin inhibitors in hepatocarcinoma: In
vitro and in vivo studies. PLoS One. 11:e01609792016. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
19
|
Gwak J, Hwang SG, Park HS, Choi SR, Park
SH, Kim H, Ha NC, Bae SJ, Han JK, Kim DE, et al: Small
molecule-based disruption of the Axin/β-catenin protein complex
regulates mesenchymal stem cell differentiation. Cell Res.
22:237–247. 2012. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
20
|
Kucuksayan H, Ozes ON and Akca H:
Downregulation of SATB2 is critical for induction of
epithelial-to-mesenchymal transition and invasion of NSCLC cells.
Lung Cancer. 98:122–129. 2016. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
21
|
Larsen JE, Nathan V, Osborne JK, Farrow
RK, Deb D, Sullivan JP, Dospoy PD, Augustyn A, Hight SK, Sato M, et
al: ZEB1 drives epithelial-to-mesenchymal transition in lung
cancer. J Clin Invest. 126:3219–3235. 2016. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
22
|
Gao F, Cui Y, Jiang H, Sui D, Wang Y,
Jiang Z, Zhao J and Lin S: Circulating tumor cell is a common
property of brain glioma and promotes the monitoring system.
Oncotarget. 7:71330–71340. 2016.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
23
|
Lau MT, So WK and Leung PC: Fibroblast
growth factor 2 induces E-cadherin down-regulation via
PI3K/Akt/mTOR and MAPK/ERK signaling in ovarian cancer cells. PLoS
One. 8:e590832013. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
24
|
Shirai K, Hagiwara N, Horigome T, Hirose
Y, Kadono N and Hirai Y: Extracellularly extruded syntaxin-4 binds
to laminin and syndecan-1 to regulate mammary epithelial
morphogenesis. J Cell Biochem. Jul 27–2016.(Epub ahead of
print).
|
|
25
|
Nagaishi M, Paulus W, Brokinkel B, Vital
A, Tanaka Y, Nakazato Y, Giangaspero F and Ohgaki H:
Transcriptional factors for epithelial-mesenchymal transition are
associated with mesenchymal differentiation in gliosarcoma. Brain
Pathol. 22:670–676. 2012. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
26
|
Yang G, Liang Y, Zheng T, Song R, Wang J,
Shi H, Sun B, Xie C, Li Y, Han J, et al: FCN2 inhibits
epithelial-mesenchymal transition-induced metastasis of
hepatocellular carcinoma via TGF-β/Smad signaling. Cancer Lett.
378:80–86. 2016. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
27
|
McCrea PD, Turck CW and Gumbiner B: A
homolog of the armadillo protein in Drosophila (plakoglobin)
associated with E-cadherin. Science. 254:1359–1361. 1991.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
28
|
Fang D, Hawke D, Zheng Y, Xia Y,
Meisenhelder J, Nika H, Mills GB, Kobayashi R, Hunter T and Lu Z:
Phosphorylation of beta-catenin by AKT promotes beta-catenin
transcriptional activity. J Biol Chem. 282:11221–11229. 2007.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
29
|
Spano D and Zollo M: Tumor
microenvironment: A main actor in the metastasis process. Clin Exp
Metastasis. 29:381–395. 2012. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
30
|
Inoue H, Takahashi H, Hashimura M, Eshima
K, Akiya M, Matsumoto T and Saegusa M: Cooperation of Sox4 with
β-catenin/p300 complex in transcriptional regulation of the Slug
gene during divergent sarcomatous differentiation in uterine
carcinosarcoma. BMC Cancer. 16:532016. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
31
|
Visciano C, Liotti F, Prevete N, Cali' G,
Franco R, Collina F, de Paulis A, Marone G, Santoro M and Melillo
RM: Mast cells induce epithelial-to-mesenchymal transition and stem
cell features in human thyroid cancer cells through an
IL-8-Akt-Slug pathway. Oncogene. 34:5175–5186. 2015. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
32
|
Kim JY, Kim YM, Yang CH, Cho SK, Lee JW
and Cho M: Functional regulation of Slug/Snail2 is dependent on
GSK-3β-mediated phosphorylation. FEBS J. 279:2929–2939. 2012.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|