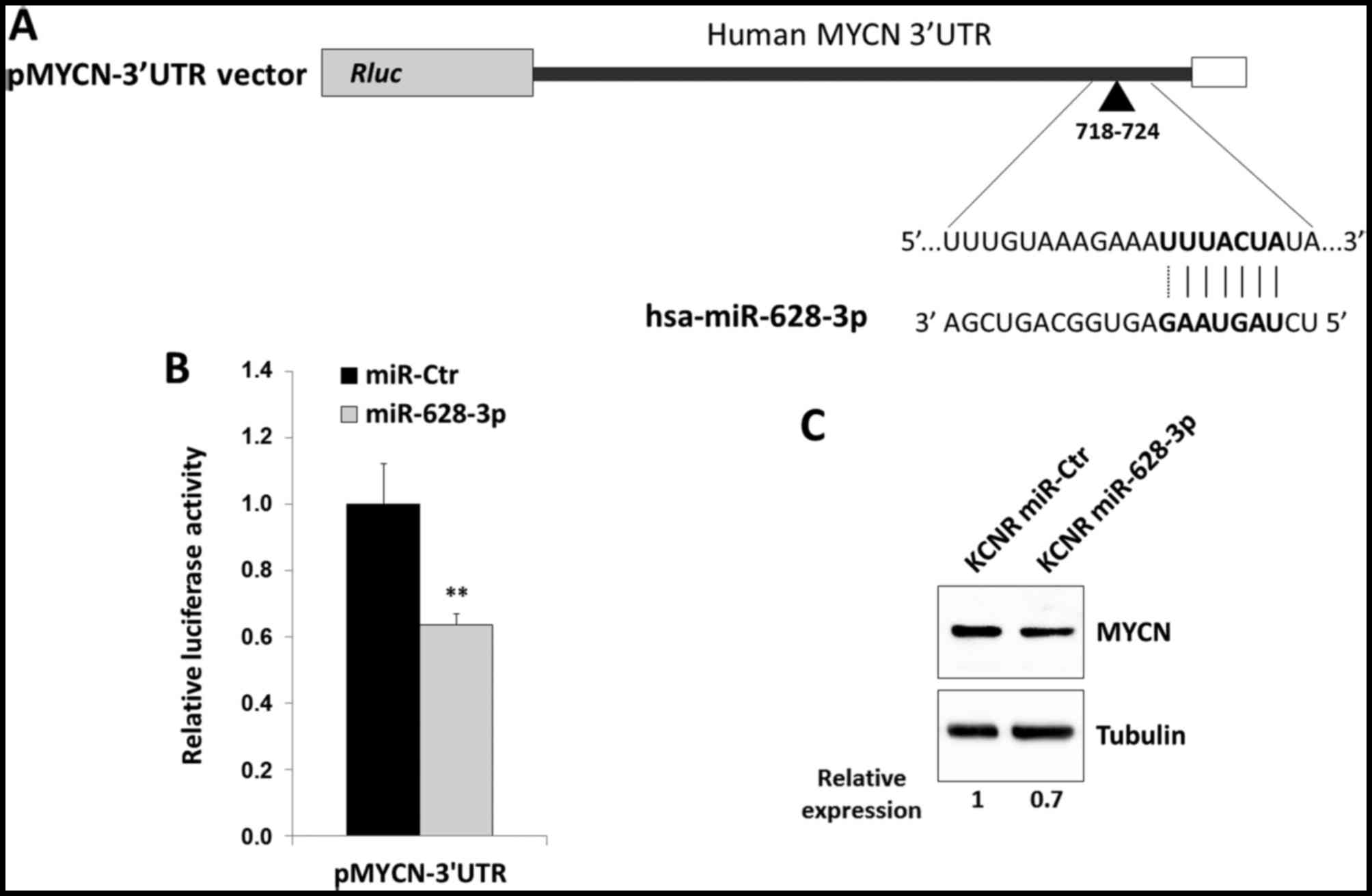
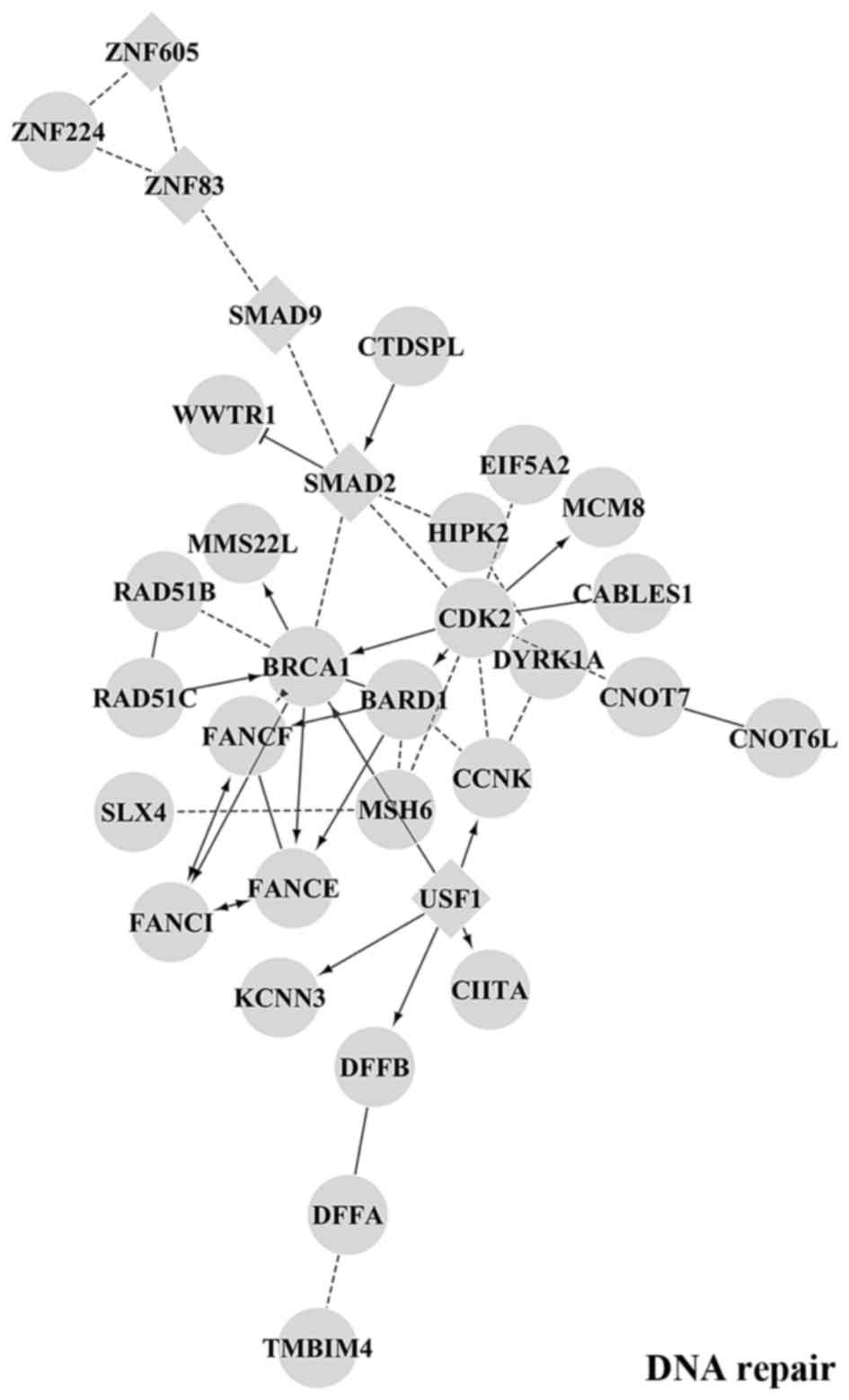
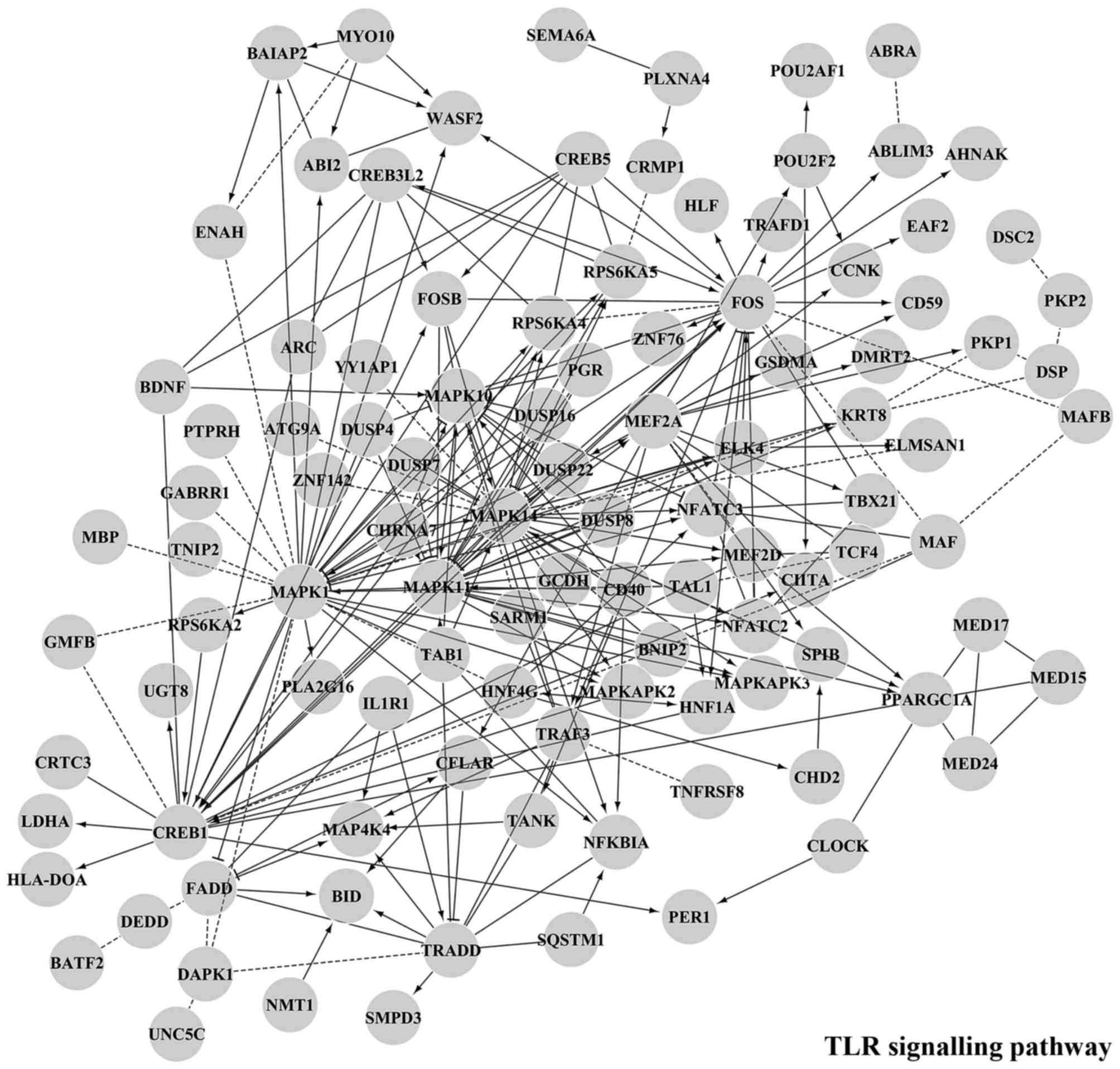
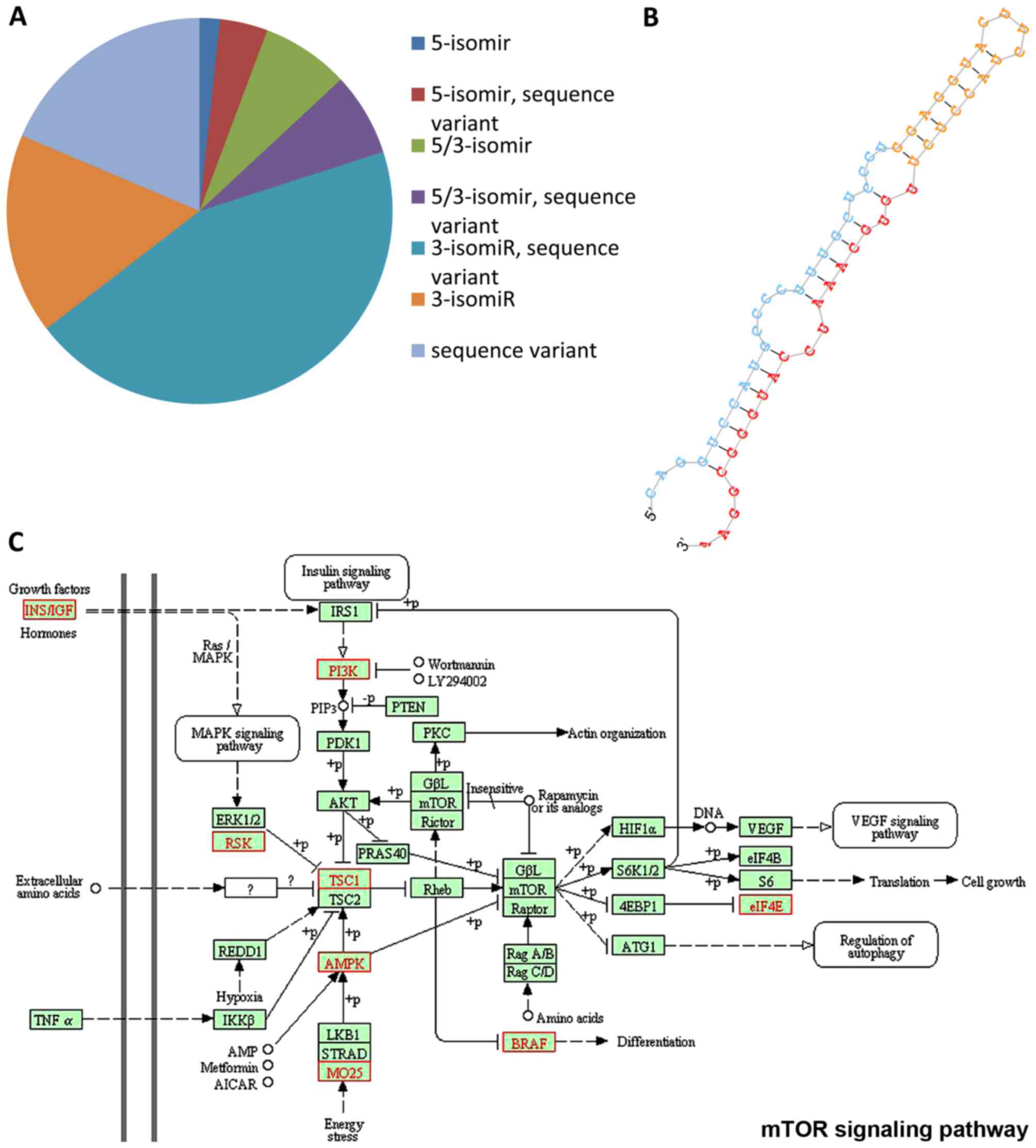
|
1
|
Irwin MS and Park JR: Neuroblastoma:
Paradigm for precision medicine. Pediatr Clin North Am. 62:225–256.
2015. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
2
|
Cohn SL, Pearson AD, London WB, Monclair
T, Ambros PF, Brodeur GM, Faldum A, Hero B, Iehara T, Machin D, et
al: INRG Task Force: The International Neuroblastoma Risk Group
(INRG) classification system: An INRG Task Force report. J Clin
Oncol. 27:289–297. 2009. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
3
|
Maris JM: Recent advances in
neuroblastoma. N Engl J Med. 362:2202–2211. 2010. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
4
|
Schwab M, Varmus HE, Bishop JM, Grzeschik
KH, Naylor SL, Sakaguchi AY, Brodeur G and Trent J: Chromosome
localization in normal human cells and neuroblastomas of a gene
related to c-myc. Nature. 308:288–291. 1984. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
5
|
Weiss WA, Aldape K, Mohapatra G,
Feuerstein BG and Bishop JM: Targeted expression of MYCN causes
neuroblastoma in transgenic mice. EMBO J. 16:2985–2995. 1997.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
6
|
Yoshimoto M, De Toledo SR Caminada, Caran
EM Monteiro, de Seixas MT, de Martino Lee ML, de Campos Vieira Abib
S, Vianna SM, Schettini ST and Andrade J Anderson Duffles: MYCN
gene amplification. Identification of cell populations containing
double minutes and homogeneously staining regions in neuroblastoma
tumors. Am J Pathol. 155:1439–1443. 1999. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
7
|
Guglielmi L, Cinnella C, Nardella M,
Maresca G, Valentini A, Mercanti D, Felsani A and DAgnano I: MYCN
gene expression is required for the onset of the differentiation
programme in neuroblastoma cells. Cell Death Dis. 5:e10812014.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
8
|
Kaneko Y, Suenaga Y, Islam SM, Matsumoto
D, Nakamura Y, Ohira M, Yokoi S and Nakagawara A: Functional
interplay between MYCN, NCYM, and OCT4 promotes aggressiveness of
human neuroblastomas. Cancer Sci. 106:840–847. 2015. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
9
|
Lau DT, Flemming CL, Gherardi S, Perini G,
Oberthuer A, Fischer M, Juraeva D, Brors B, Xue C, Norris MD, et
al: MYCN amplification confers enhanced folate dependence and
methotrexate sensitivity in neuroblastoma. Oncotarget.
6:15510–15523. 2015. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
10
|
Beltran H: The N-myc Oncogene: Maximizing
its targets, regulation, and therapeutic potential. Mol Cancer Res.
12:815–822. 2014. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
11
|
Zeng Y, Yi R and Cullen BR: MicroRNAs and
small interfering RNAs can inhibit mRNA expression by similar
mechanisms. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA. 100:9779–9784. 2003. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
12
|
Bartel DP: MicroRNAs: Genomics,
biogenesis, mechanism, and function. Cell. 116:281–297. 2004.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
13
|
He L and Hannon GJ: MicroRNAs: Small RNAs
with a big role in gene regulation. Nat Rev Genet. 5:522–531. 2004.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
14
|
Kozomara A and Griffiths-Jones S: miRBase:
Integrating microRNA annotation and deep-sequencing data. Nucleic
Acids Res. 39(Database): D152–D157. 2011. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
15
|
Friedman RC, Farh KK, Burge CB and Bartel
DP: Most mammalian mRNAs are conserved targets of microRNAs. Genome
Res. 19:92–105. 2009. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
16
|
Domingo-Fernandez R, Watters K, Piskareva
O, Stallings RL and Bray I: The role of genetic and epigenetic
alterations in neuroblastoma disease pathogenesis. Pediatr Surg
Int. 29:101–119. 2013. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
17
|
Leichter AL, Sullivan MJ, Eccles MR and
Chatterjee A: MicroRNA expression patterns and signalling pathways
in the development and progression of childhood solid tumours. Mol
Cancer. 16:152017. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
18
|
Mei H, Lin ZY and Tong QS: The roles of
microRNAs in neuroblastoma. World J Pediatr. 10:10–16. 2014.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
19
|
Bray I, Tivnan A, Bryan K, Foley NH,
Watters KM, Tracey L, Davidoff AM and Stallings RL: MicroRNA-542-5p
as a novel tumor suppressor in neuroblastoma. Cancer Lett.
303:56–64. 2011. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
20
|
Tivnan A, Tracey L, Buckley PG, Alcock LC,
Davidoff AM and Stallings RL: MicroRNA-34a is a potent tumor
suppressor molecule in vivo in neuroblastoma. BMC Cancer.
11:332011. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
21
|
Chen Y, Tsai YH, Fang Y and Tseng SH:
Micro-RNA-21 regulates the sensitivity to cisplatin in human
neuroblastoma cells. J Pediatr Surg. 47:1797–1805. 2012. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
22
|
Ryan J, Tivnan A, Fay J, Bryan K, Meehan
M, Creevey L, Lynch J, Bray IM, O'Meara A, Tracey L, et al:
MicroRNA-204 increases sensitivity of neuroblastoma cells to
cisplatin and is associated with a favourable clinical outcome. Br
J Cancer. 107:967–976. 2012. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
23
|
Teillet MA, Kalcheim C and Le Douarin NM:
Formation of the dorsal root ganglia in the avian embryo: Segmental
origin and migratory behavior of neural crest progenitor cells. Dev
Biol. 120:329–347. 1987. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
24
|
Beckwith JB and Martin RF: Observations on
the histopathology of neuroblastomas. J Pediatr Surg. 3:106–110.
1968. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
25
|
Griffiths-Jones S, Saini HK, van Dongen S
and Enright AJ: miRBase: Tools for microRNA genomics. Nucleic Acids
Res. 36(Database): D154–D158. 2008. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
26
|
Robinson MD and Oshlack A: A scaling
normalization method for differential expression analysis of
RNA-seq data. Genome Biol. 11:R252010. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
27
|
Bullard JH, Purdom E, Hansen KD and Dudoit
S: Evaluation of statistical methods for normalization and
differential expression in mRNA-Seq experiments. BMC
Bioinformatics. 11:942010. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
28
|
Hsu SD, Tseng YT, Shrestha S, Lin YL,
Khaleel A, Chou CH, Chu CF, Huang HY, Lin CM, Ho SY, et al:
miRTarBase update 2014: An information resource for experimentally
validated miRNA-target interactions. Nucleic Acids Res. 42(D1):
D78–D85. 2014. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
29
|
Enright AJ, John B, Gaul U, Tuschl T,
Sander C and Marks DS: MicroRNA targets in Drosophila. Genome Biol.
5:R12003. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
30
|
Huang W, Sherman BT and Lempicki RA:
Systematic and integrative analysis of large gene lists using DAVID
bioinformatics resources. Nat Protoc. 4:44–57. 2009. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
31
|
Wu G, Feng X and Stein L: A human
functional protein interaction network and its application to
cancer data analysis. Genome Biol. 11:R532010. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
32
|
Wang J, Huang Q, Liu ZP, Wang Y, Wu LY,
Chen L and Zhang XS: NOA: A novel network ontology analysis method.
Nucleic Acids Res. 39:e872011. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
33
|
Grant CE, Bailey TL and Noble WS: FIMO:
Scanning for occurrences of a given motif. Bioinformatics.
27:1017–1018. 2011. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
34
|
Li H, Handsaker B, Wysoker A, Fennell T,
Ruan J, Homer N, Marth G, Abecasis G and Durbin R: 1000 Genome
Project Data Processing Subgroup: The Sequence Alignment/Map format
and SAMtools. Bioinformatics. 25:2078–2079. 2009. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
35
|
Friedländer MR, Chen W, Adamidi C,
Maaskola J, Einspanier R, Knespel S and Rajewsky N: Discovering
microRNAs from deep sequencing data using miRDeep. Nat Biotechnol.
26:407–415. 2008. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
36
|
Megiorni F, Camero S, Ceccarelli S,
McDowell HP, Mannarino O, Marampon F, Pizer B, Shukla R, Pizzuti A,
Marchese C, et al: DNMT3B in vitro knocking-down is able to reverse
embryonal rhabdomyosarcoma cell phenotype through inhibition of
proliferation and induction of myogenic differentiation.
Oncotarget. 7:79342–79356. 2016.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
37
|
Afanasyeva EA, Hotz-Wagenblatt A, Glatting
KH and Westermann F: New miRNAs cloned from neuroblastoma. BMC
Genomics. 9:522008. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
38
|
Mestdagh P, Fredlund E, Pattyn F, Schulte
JH, Muth D, Vermeulen J, Kumps C, Schlierf S, De Preter K, Van Roy
N, et al: MYCN/c-MYC-induced microRNAs repress coding gene networks
associated with poor outcome in MYCN/c-MYC-activated tumors.
Oncogene. 29:1394–1404. 2010. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
39
|
Bienertova-Vasku J, Mazanek P, Hezova R,
Curdova A, Nekvindova J, Kren L, Sterba J and Slaby O: Extension of
microRNA expression pattern associated with high-risk
neuroblastoma. Tumour Biol. 34:2315–2319. 2013. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
40
|
Uppal A, Wightman SC, Mallon S, Oshima G,
Pitroda SP, Zhang Q, Huang X, Darga TE, Huang L, Andrade J, et al:
14q32-encoded microRNAs mediate an oligometastatic phenotype.
Oncotarget. 6:3540–3552. 2015. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
41
|
Liu L, Chen R, Zhang Y, Fan W, Xiao F and
Yan X: Low expression of circulating microRNA-328 is associated
with poor prognosis in patients with acute myeloid leukemia. Diagn
Pathol. 10:1092015. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
42
|
Yuan J, Zheng Z, Zheng Y, Lu X, Xu L and
Lin L: microRNA-328 is a favorable prognostic marker in human
glioma via suppressing invasive and proliferative phenotypes of
malignant cells. Int J Neurosci. 126:145–153. 2015. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
43
|
Anwar SL, Albat C, Krech T, Hasemeier B,
Schipper E, Schweitzer N, Vogel A, Kreipe H and Lehmann U:
Concordant hypermethylation of intergenic microRNA genes in human
hepatocellular carcinoma as new diagnostic and prognostic marker.
Int J Cancer. 133:660–670. 2013. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
44
|
Shi S, Lu Y, Qin Y, Li W, Cheng H, Xu Y,
Xu J, Long J, Liu L, Liu C, et al: miR-1247 is correlated with
prognosis of pancreatic cancer and inhibits cell proliferation by
targeting neuropilins. Curr Mol Med. 14:316–327. 2014. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
45
|
Karjalainen K, Jaalouk DE, Bueso-Ramos CE,
Zurita AJ, Kuniyasu A, Eckhardt BL, Marini FC, Lichtiger B, OBrien
S, Kantarjian HM, et al: Targeting neuropilin-1 in human leukemia
and lymphoma. Blood. 117:920–927. 2011. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
46
|
Yan H, Choi AJ, Lee BH and Ting AH:
Identification and functional analysis of epigenetically silenced
microRNAs in colorectal cancer cells. PLoS One. 6:e206282011.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
47
|
Charlet J, Schnekenburger M, Brown KW and
Diederich M: DNA demethylation increases sensitivity of
neuroblastoma cells to chemotherapeutic drugs. Biochem Pharmacol.
83:858–865. 2012. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
48
|
Mestdagh P, Boström AK, Impens F, Fredlund
E, Van Peer G, De Antonellis P, von Stedingk K, Ghesquière B,
Schulte S, Dews M, et al: The miR-17-92 microRNA cluster regulates
multiple components of the TGF-β pathway in neuroblastoma. Mol
Cell. 40:762–773. 2010. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
49
|
Miao T, Wu D, Zhang Y, Bo X, Xiao F, Zhang
X, Magoulas C, Subang MC, Wang P and Richardson PM: SOCS3
suppresses AP-1 transcriptional activity in neuroblastoma cells
through inhibition of c-Jun N-terminal kinase. Mol Cell Neurosci.
37:367–375. 2008. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
50
|
Morgan K, Stewart AJ, Miller N, Mullen P,
Muir M, Dodds M, Medda F, Harrison D, Langdon S and Millar RP:
Gonadotropin-releasing hormone receptor levels and cell context
affect tumor cell responses to agonist in vitro and in vivo. Cancer
Res. 68:6331–6340. 2008. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
51
|
Weng WC, Lin KH, Wu PY, Lu YC, Weng YC,
Wang BJ, Liao YF, Hsu WM, Lee WT and Lee H: Calreticulin regulates
VEGF-A in neuroblastoma cells. Mol Neurobiol. 52:758–770. 2015.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
52
|
Lodrini M, Oehme I, Schroeder C, Milde T,
Schier MC, Kopp-Schneider A, Schulte JH, Fischer M, De Preter K,
Pattyn F, et al: MYCN and HDAC2 cooperate to repress miR-183
signaling in neuroblastoma. Nucleic Acids Res. 41:6018–6033. 2013.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
53
|
Rihani A, Van Goethem A, Ongenaert M, De
Brouwer S, Volders PJ, Agarwal S, De Preter K, Mestdagh P, Shohet
J, Speleman F, et al: Genome wide expression profiling of p53
regulated miRNAs in neuroblastoma. Sci Rep. 5:90272015. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
54
|
Murphy DM, Buckley PG, Bryan K, Das S,
Alcock L, Foley NH, Prenter S, Bray I, Watters KM, Higgins D, et
al: Global MYCN transcription factor binding analysis in
neuroblastoma reveals association with distinct E-box motifs and
regions of DNA hypermethylation. PLoS One. 4:e81542009. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
55
|
Schulte JH, Horn S, Otto T, Samans B,
Heukamp LC, Eilers UC, Krause M, Astrahantseff K, Klein-Hitpass L,
Buettner R, et al: MYCN regulates oncogenic MicroRNAs in
neuroblastoma. Int J Cancer. 122:699–704. 2008. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
56
|
Lovén J, Zinin N, Wahlström T, Müller I,
Brodin P, Fredlund E, Ribacke U, Pivarcsi A, Påhlman S and
Henriksson M: MYCN-regulated microRNAs repress estrogen
receptor-alpha (ESR1) expression and neuronal differentiation in
human neuroblastoma. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA. 107:1553–1558. 2010.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
57
|
He L, Thomson JM, Hemann MT,
Hernando-Monge E, Mu D, Goodson S, Powers S, Cordon-Cardo C, Lowe
SW, Hannon GJ, et al: A microRNA polycistron as a potential human
oncogene. Nature. 435:828–833. 2005. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
58
|
Mogilyansky E and Rigoutsos I: The
miR-17/92 cluster: A comprehensive update on its genomics,
genetics, functions and increasingly important and numerous roles
in health and disease. Cell Death Differ. 20:1603–1614. 2013.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
59
|
Thorsen SB, Obad S, Jensen NF, Stenvang J
and Kauppinen S: The therapeutic potential of microRNAs in cancer.
Cancer J. 18:275–284. 2012. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
60
|
Fontana L, Fiori ME, Albini S, Cifaldi L,
Giovinazzi S, Forloni M, Boldrini R, Donfrancesco A, Federici V,
Giacomini P, et al: Antagomir-17-5p abolishes the growth of
therapy-resistant neuroblastoma through p21 and BIM. PLoS One.
3:e22362008. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
61
|
Guo J, Dong Q, Fang Z, Chen X, Lu H, Wang
K, Yin Y, Cai X, Zhao N, Chen J, et al: Identification of miRNAs
that are associated with tumor metastasis in neuroblastoma. Cancer
Biol Ther. 9:446–452. 2010. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
62
|
Schulte JH, Marschall T, Martin M,
Rosenstiel P, Mestdagh P, Schlierf S, Thor T, Vandesompele J,
Eggert A, Schreiber S, et al: Deep sequencing reveals differential
expression of microRNAs in favorable versus unfavorable
neuroblastoma. Nucleic Acids Res. 38:5919–5928. 2010. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
63
|
Rahmann S, Martin M, Schulte JH, Köster J,
Marschall T and Schramm A: Identifying transcriptional miRNA
biomarkers by integrating high-throughput sequencing and real-time
PCR data. Methods. 59:154–163. 2013. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
64
|
Chang YY, Kuo WH, Hung JH, Lee CY, Lee YH,
Chang YC, Lin WC, Shen CY, Huang CS, Hsieh FJ, et al: Deregulated
microRNAs in triple-negative breast cancer revealed by deep
sequencing. Mol Cancer. 14:362015. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
65
|
Zhang Y, Hu Y, Fang JY and Xu J:
Gain-of-function miRNA signature by mutant p53 associates with poor
cancer outcome. Oncotarget. 7:11056–11066. 2016.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
66
|
Pehserl AM, Ress AL, Stanzer S, Resel M,
Karbiener M, Stadelmeyer E, Stiegelbauer V, Gerger A, Mayr C,
Scheideler M, et al: Comprehensive analysis of miRNome alterations
in response to sorafenib treatment in colorectal cancer cells. Int
J Mol Sci. 17:E20112016. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
67
|
Wang H, Zhi H, Ma D and Li T: MiR-217
promoted the proliferation and invasion of glioblastoma by
repressing YWHAG. Cytokine. 92:93–102. 2017. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
68
|
Kos A, Loohuis NF Olde, Wieczorek ML,
Glennon JC, Martens GJ, Kolk SM and Aschrafi A: A potential
regulatory role for intronic microRNA-338-3p for its host gene
encoding apoptosis-associated tyrosine kinase. PLoS One.
7:e310222012. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
69
|
Chen X, Pan M, Han L, Lu H, Hao X and Dong
Q: miR-338-3p suppresses neuroblastoma proliferation, invasion and
migration through targeting PREX2a. FEBS Lett. 587:3729–3737. 2013.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
70
|
Chiang HR, Schoenfeld LW, Ruby JG, Auyeung
VC, Spies N, Baek D, Johnston WK, Russ C, Luo S, Babiarz JE, et al:
Mammalian microRNAs: Experimental evaluation of novel and
previously annotated genes. Genes Dev. 24:992–1009. 2010.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
71
|
Müller S and Nowak K: Exploring the
miRNA-mRNA regulatory network in clear cell renal cell carcinomas
by next-generation sequencing expression profiles. BioMed Res Int.
2014:9484082014. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
72
|
Murphy DM, Buckley PG, Das S, Watters KM,
Bryan K and Stallings RL: Co-localization of the oncogenic
transcription factor MYCN and the DNA methyl binding protein MeCP2
at genomic sites in neuroblastoma. PLoS One. 6:e214362011.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
73
|
Corvetta D, Chayka O, Gherardi S, DAcunto
CW, Cantilena S, Valli E, Piotrowska I, Perini G and Sala A:
Physical interaction between MYCN oncogene and polycomb repressive
complex 2 (PRC2) in neuroblastoma: Functional and therapeutic
implications. J Biol Chem. 288:8332–8341. 2013. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
74
|
Buechner J and Einvik C: N-myc and
noncoding RNAs in neuroblastoma. Mol Cancer Res. 10:1243–1253.
2012. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
75
|
Jackstadt R and Hermeking H: MicroRNAs as
regulators and mediators of c-MYC function. Biochim Biophys Acta.
1849:544–553. 2015. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
76
|
Guo L and Chen F: A challenge for miRNA:
Multiple isomiRs in miRNAomics. Gene. 544:1–7. 2014. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
77
|
Iżycka-Świeszewska E, Drożyńska E, Rzepko
R, Kobierska-Gulida G, Grajkowska W, Perek D and Balcerska A:
Analysis of PI3K/AKT/mTOR signalling pathway in high risk
neuroblastic tumours. Pol J Pathol. 61:192–198. 2010.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
78
|
King D, Yeomanson D and Bryant HE: PI3King
the lock: Targeting the PI3K/Akt/mTOR pathway as a novel
therapeutic strategy in neuroblastoma. J Pediatr Hematol Oncol.
37:245–251. 2015. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
79
|
Vaughan L, Clarke PA, Barker K, Chanthery
Y, Gustafson CW, Tucker E, Renshaw J, Raynaud F, Li X, Burke R, et
al: Inhibition of mTOR-kinase destabilizes MYCN and is a potential
therapy for MYCN-dependent tumors. Oncotarget. 7:57525–57544.
2016.PubMed/NCBI
|