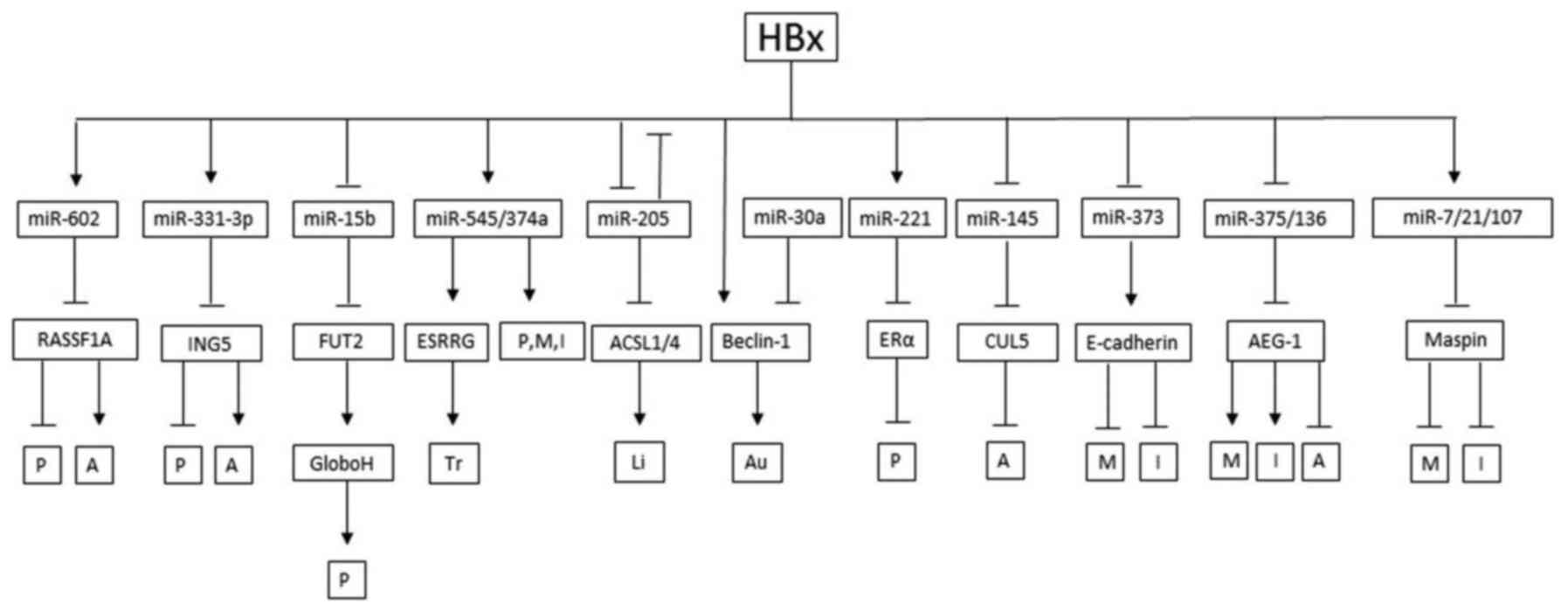
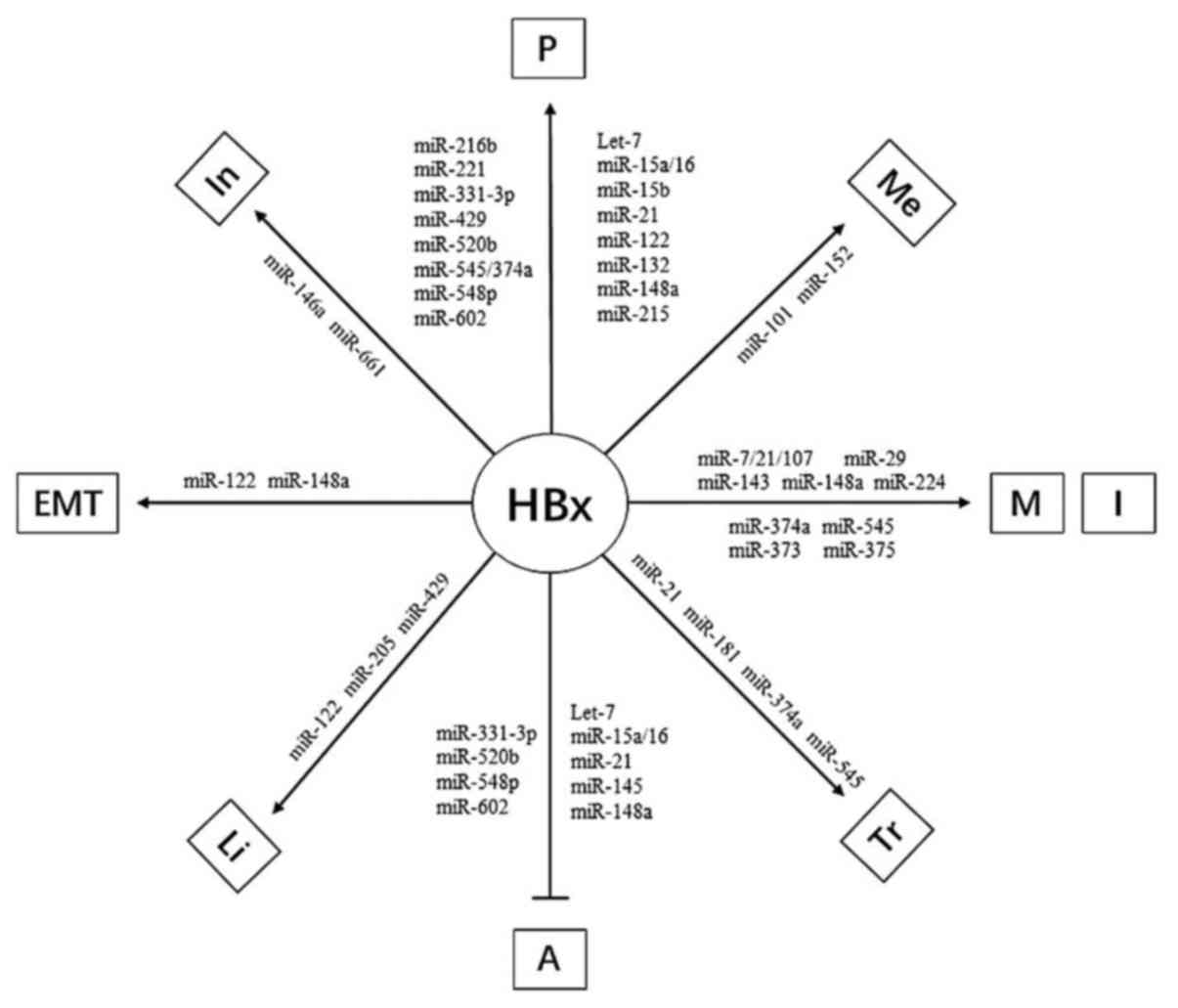
|
1
|
Torre LA, Bray F, Siegel RL, Ferlay J,
Lortet-Tieulent J and Jemal A: Global cancer statistics, 2012. CA
Cancer J Clin. 65:87–108. 2015. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
2
|
McGlynn KA, Petrick JL and London WT:
Global epidemiology of hepatocellular carcinoma: An emphasis on
demographic and regional variability. Clin Liver Dis. 19:223–238.
2015. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
3
|
Center MM and Jemal A: International
trends in liver cancer incidence rates. Cancer Epidemiol Biomarkers
Prev. 20:2362–2368. 2011. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
4
|
Parkin DM: The global health burden of
infection-associated cancers in the year 2002. Int J Cancer.
118:3030–3044. 2006. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
5
|
Seeger C and Mason WS: Hepatitis B virus
biology. Microbiol Mol Biol Rev. 64:51–68. 2000. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
6
|
Tang H, Oishi N, Kaneko S and Murakami S:
Molecular functions and biological roles of hepatitis B virus ×
protein. Cancer Sci. 97:977–983. 2006. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
7
|
Xu C, Zhou W, Wang Y and Qiao L: Hepatitis
B virus-induced hepatocellular carcinoma. Cancer Lett. 345:216–222.
2014. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
8
|
Kremsdorf D, Soussan P, Paterlini-Brechot
P and Brechot C: Hepatitis B virus-related hepatocellular
carcinoma: Paradigms for viral-related human carcinogenesis.
Oncogene. 25:3823–3833. 2006. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
9
|
Bartel DP: MicroRNAs: Genomics,
biogenesis, mechanism, and function. Cell. 116:281–297. 2004.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
10
|
Wu SY, Lan SH and Liu HS: Autophagy and
microRNA in hepatitis B virus-related hepatocellular carcinoma.
World J Gastroenterol. 22:176–187. 2016. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
11
|
Zhang J and Ma L: MicroRNA control of
epithelial-mesenchymal transition and metastasis. Cancer Metastasis
Rev. 31:653–662. 2012. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
12
|
de Gómez Cedrón M and de Ramírez Molina A:
Microtargeting cancer metabolism: Opening new therapeutic windows
based on lipid metabolism. J Lipid Res. 57:193–206. 2016.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
13
|
Peschansky VJ and Wahlestedt C: Non-coding
RNAs as direct and indirect modulators of epigenetic regulation.
Epigenetics. 9:3–12. 2014. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
14
|
Callegari E, Elamin BK, Sabbioni S,
Gramantieri L and Negrini M: Role of microRNAs in hepatocellular
carcinoma: A clinical perspective. Onco Targets Ther. 6:1167–1178.
2013.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
15
|
Shan X, Ren M, Chen K, Huang A and Tang H:
Regulation of the microRNA processor DGCR8 by hepatitis B virus
proteins via the transcription factor YY1. Arch Virol. 160:795–803.
2015. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
16
|
Rodriguez A, Griffiths-Jones S, Ashurst JL
and Bradley A: Identification of mammalian microRNA host genes and
transcription units. Genome Res. 14:(10A). 1902–1910. 2004.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
17
|
Ruby JG, Jan CH and Bartel DP: Intronic
microRNA precursors that bypass Drosha processing. Nature.
448:83–86. 2007. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
18
|
Okamura K, Hagen JW, Duan H, Tyler DM and
Lai EC: The mirtron pathway generates microRNA-class regulatory
RNAs in Drosophila. Cell. 130:89–100. 2007. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
19
|
Wang Y, Jiang L, Ji X, Yang B, Zhang Y and
Fu XD: Hepatitis B viral RNA directly mediates down-regulation of
the tumor suppressor microRNA miR-15a/miR-16-1 in hepatocytes. J
Biol Chem. 288:18484–18493. 2013. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
20
|
Li C, Wang Y, Wang S, Wu B, Hao J, Fan H,
Ju Y, Ding Y, Chen L, Chu X, et al: Hepatitis B virus mRNA-mediated
miR-122 inhibition upregulates PTTG1-binding protein, which
promotes hepatocellular carcinoma tumor growth and cell invasion. J
Virol. 87:2193–2205. 2013. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
21
|
Cazalla D, Yario T, Steitz JA and Steitz
J: Down-regulation of a host microRNA by a Herpesvirus saimiri
noncoding RNA. Science. 328:1563–1566. 2010. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
22
|
Feitelson MA and Lee J: Hepatitis B virus
integration, fragile sites, and hepatocarcinogenesis. Cancer Lett.
252:157–170. 2007. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
23
|
Zhang X, Liu S, Hu T, Liu S, He Y and Sun
S: Up-regulated microRNA-143 transcribed by nuclear factor kappa B
enhances hepatocarcinoma metastasis by repressing fibronectin
expression. Hepatology. 50:490–499. 2009. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
24
|
Li JF, Dai XP, Zhang W, Sun SH, Zeng Y,
Zhao GY, Kou ZH, Guo Y, Yu H, Du LY, et al: Upregulation of
microRNA-146a by hepatitis B virus X protein contributes to
hepatitis development by downregulating complement factor H. MBio.
6:e02459–14. 2015. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
25
|
Xu X, Fan Z, Kang L, Han J, Jiang C, Zheng
X, Zhu Z, Jiao H, Lin J, Jiang K, et al: Hepatitis B virus X
protein represses miRNA-148a to enhance tumorigenesis. J Clin
Invest. 123:630–645. 2013.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
26
|
Peng F, Xiao X, Jiang Y, Luo K, Tian Y,
Peng M, Zhang M, Xu Y and Gong G: HBx down-regulated Gld2 plays a
critical role in HBV-related dysregulation of miR-122. PLoS One.
9:e929982014. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
27
|
Hu XM, Yan XH, Hu YW, Huang JL, Cao SW,
Ren TY, Tang YT, Lin L, Zheng L and Wang Q: MicroRNA-548p
suppresses hepatitis B virus X protein associated hepatocellular
carcinoma by downregulating oncoprotein HBXIP. Hepatol Res.
46:804–815. 2016. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
28
|
Liu FY, Zhou SJ, Deng YL, Zhang ZY, Zhang
EL, Wu ZB, Huang ZY and Chen XP: MiR-216b is involved in
pathogenesis and progression of hepatocellular carcinoma through
HBx-miR-216b-IGF2BP2 signaling pathway. Cell Death Dis.
6:e16702015. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
29
|
Wu G, Yu F, Xiao Z, Xu K, Xu J, Tang W,
Wang J and Song E: Hepatitis B virus X protein downregulates
expression of the miR-16 family in malignant hepatocytes in vitro.
Br J Cancer. 105:146–153. 2011. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
30
|
Wu G, Huang P, Ju X, Li Z and Wang Y:
Lin28B over-expression mediates the repression of let-7 by
hepatitis B virus X protein in hepatoma cells. Int J Clin Exp Med.
8:15108–15116. 2015.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
31
|
Qiu X, Dong S, Qiao F, Lu S, Song Y, Lao
Y, Li Y, Zeng T, Hu J, Zhang L, et al: HBx-mediated miR-21
upregulation represses tumor-suppressor function of PDCD4 in
hepatocellular carcinoma. Oncogene. 32:3296–3305. 2013. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
32
|
Zhang W, Lu Z, Kong G, Gao Y, Wang T, Wang
Q, Cai N, Wang H, Liu F, Ye L, et al: Hepatitis B virus X protein
accelerates hepatocarcinogenesis with partner survivin through
modulating miR-520b and HBXIP. Mol Cancer. 13:1282014. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
33
|
Wei X, Tan C, Tang C, Ren G, Xiang T, Qiu
Z, Liu R and Wu Z: Epigenetic repression of miR-132 expression by
the hepatitis B virus × protein in hepatitis B virus-related
hepatocellular carcinoma. Cell Signal. 25:1037–1043. 2013.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
34
|
Yuan K, Lian Z, Sun B, Clayton MM, Ng IO
and Feitelson MA: Role of miR-148a in hepatitis B associated
hepatocellular carcinoma. PLoS One. 7:e353312012. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
35
|
Chen YJ, Chien PH, Chen WS, Chien YF, Hsu
YY, Wang LY, Chen JY, Lin CW, Huang TC, Yu YL, et al: Hepatitis B
Virus-encoded X Protein downregulates EGFR expression via inducing
MicroRNA-7 in hepatocellular carcinoma cells. Evid Based Complement
Alternat Med. 2013:6823802013.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
36
|
Chen WS, Yen CJ, Chen YJ, Chen JY, Wang
LY, Chiu SJ, Shih WL, Ho CY, Wei TT, Pan HL, et al: miRNA-7/21/107
contribute to HBx-induced hepatocellular carcinoma progression
through suppression of maspin. Oncotarget. 6:25962–25974. 2015.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
37
|
Li CH, Xu F, Chow S, Feng L, Yin D, Ng TB
and Chen Y: Hepatitis B virus X protein promotes hepatocellular
carcinoma transformation through interleukin-6 activation of
microRNA-21 expression. Eur J Cancer. 50:2560–2569. 2014.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
38
|
Damania P, Sen B, Dar SB, Kumar S, Kumari
A, Gupta E, Sarin SK and Venugopal SK: Hepatitis B virus induces
cell proliferation via HBx-induced microRNA-21 in hepatocellular
carcinoma by targeting programmed cell death protein4 (PDCD4) and
phosphatase and tensin homologue (PTEN). PLoS One. 9:e917452014.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
39
|
Dai X, Zhang W, Zhang H, Sun S, Yu H, Guo
Y, Kou Z, Zhao G, Du L, Jiang S, et al: Modulation of HBV
replication by microRNA-15b through targeting hepatocyte nuclear
factor 1α. Nucleic Acids Res. 42:6578–6590. 2014. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
40
|
Wu CS, Yen CJ, Chou RH, Chen JN, Huang WC,
Wu CY and Yu YL: Downregulation of microRNA-15b by hepatitis B
virus X enhances hepatocellular carcinoma proliferation via
fucosyltransferase 2-induced Globo H expression. Int J Cancer.
134:1638–1647. 2014. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
41
|
Kong G, Zhang J, Zhang S, Shan C, Ye L and
Zhang X: Upregulated microRNA-29a by hepatitis B virus X protein
enhances hepatoma cell migration by targeting PTEN in cell culture
model. PLoS One. 6:e195182011. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
42
|
Mosca N, Castiello F, Coppola N, Trotta
MC, Sagnelli C, Pisaturo M, Sagnelli E, Russo A and Potenza N:
Functional interplay between hepatitis B virus X protein and human
miR-125a in HBV infection. Biochem Biophys Res Commun. 449:141–145.
2014. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
43
|
Wei X, Xiang T, Ren G, Tan C, Liu R, Xu X
and Wu Z: miR-101 is down-regulated by the hepatitis B virus ×
protein and induces aberrant DNA methylation by targeting DNA
methyltransferase 3A. Cell Signal. 25:439–446. 2013. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
44
|
Liang HW, Wang N, Wang Y, Wang F, Fu Z,
Yan X, Zhu H, Diao W, Ding Y, Chen X, et al: Hepatitis B
virus-human chimeric transcript HBx-LINE1 promotes hepatic injury
via sequestering cellular microRNA-122. J Hepatol. 64:278–291.
2016. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
45
|
Zhao J, Wang W, Huang Y, Wu J, Chen M, Cui
P, Zhang W and Zhang Y: HBx elevates oncoprotein AEG-1 expression
to promote cell migration by downregulating miR-375 and miR-136 in
malignant hepatocytes. DNA Cell Biol. 33:715–722. 2014. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
46
|
Gao F, Sun X, Wang L, Tang S and Yan C:
Downregulation of MicroRNA-145 caused by hepatitis B virus X
protein promotes expression of CUL5 and contributes to pathogenesis
of hepatitis B Virus-associated hepatocellular carcinoma. Cell
Physiol Biochem. 37:1547–1559. 2015. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
47
|
Arzumanyan A, Friedman T, Ng IO, Clayton
MM, Lian Z and Feitelson MA: Does the hepatitis B antigen HBx
promote the appearance of liver cancer stem cells? Cancer Res.
71:3701–3708. 2011. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
48
|
Huang J, Wang Y, Guo Y and Sun S:
Down-regulated microRNA-152 induces aberrant DNA methylation in
hepatitis B virus-related hepatocellular carcinoma by targeting DNA
methyltransferase 1. Hepatology. 52:60–70. 2010. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
49
|
Liu F, You X, Chi X, Wang T, Ye L, Niu J
and Zhang X: Hepatitis B virus X protein mutant HBxΔ127 promotes
proliferation of hepatoma cells through up-regulating miR-215
targeting PTPRT. Biochem Biophys Res Commun. 444:128–134. 2014.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
50
|
Yip WK, Cheng AS, Zhu R, Lung RW, Tsang
DP, Lau SS, Chen Y, Sung JG, Lai PB, Ng EK, et al:
Carboxyl-terminal truncated HBx regulates a distinct microRNA
transcription program in hepatocellular carcinoma development. PLoS
One. 6:e228882011. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
51
|
Chen JJ, Tang YS, Huang SF, Ai JG, Wang HX
and Zhang LP: HBx protein-induced upregulation of microRNA-221
promotes aberrant proliferation in HBV-related hepatocellular
carcinoma by targeting estrogen receptor-α. Oncol Rep. 33:792–798.
2015.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
52
|
Zhang T, Zhang J, Cui M, Liu F, You X, Du
Y, Gao Y, Zhang S, Lu Z, Ye L, et al: Hepatitis B virus X protein
inhibits tumor suppressor miR-205 through inducing hypermethylation
of miR-205 promoter to enhance carcinogenesis. Neoplasia.
15:1282–1291. 2013. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
53
|
Cui M, Xiao Z, Sun B, Wang Y, Zheng M, Ye
L and Zhang X: Involvement of cholesterol in hepatitis B virus X
protein-induced abnormal lipid metabolism of hepatoma cells via
up-regulating miR-205-targeted ACSL4. Biochem Biophys Res Commun.
445:651–655. 2014. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
54
|
Cui M, Wang Y, Sun B, Xiao Z, Ye L and
Zhang X: MiR-205 modulates abnormal lipid metabolism of hepatoma
cells via targeting acyl-CoA synthetase long-chain family member 1
(ACSL1) mRNA. Biochem Biophys Res Commun. 444:270–275. 2014.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
55
|
Lan SH, Wu SY, Zuchini R, Lin XZ, Su IJ,
Tsai TF, Lin YJ, Wu CT and Liu HS: Autophagy suppresses
tumorigenesis of hepatitis B virus-associated hepatocellular
carcinoma through degradation of microRNA-224. Hepatology.
59:505–517. 2014. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
56
|
Cao Y, Chen J, Wang D, Peng H, Tan X,
Xiong D, Huang A and Tang H: Upregulated in hepatitis B
virus-associated hepatocellular carcinoma cells, miR-331-3p
promotes proliferation of hepatocellular carcinoma cells by
targeting ING5. Oncotarget. 6:38093–38106. 2015.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
57
|
Arzumanyan A, Friedman T, Kotei E, Ng IO,
Lian Z and Feitelson MA: Epigenetic repression of E-cadherin
expression by hepatitis B virus × antigen in liver cancer.
Oncogene. 31:563–572. 2012.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
58
|
Zhao Q, Li T, Qi J, Liu J and Qin C: The
miR-545/374a cluster encoded in the Ftx lncRNA is overexpressed in
HBV-related hepatocellular carcinoma and promotes tumorigenesis and
tumor progression. PLoS One. 9:e1097822014. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
59
|
You X, Liu F, Zhang T, Li Y, Ye L and
Zhang X: Hepatitis B virus X protein upregulates oncogene Rab18 to
result in the dysregulation of lipogenesis and proliferation of
hepatoma cells. Carcinogenesis. 34:1644–1652. 2013. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
60
|
Bui-Nguyen TM, Pakala SB, Sirigiri DR,
Martin E, Murad F and Kumar R and Kumar R and Kumar R: Stimulation
of inducible nitric oxide by hepatitis B virus transactivator
protein HBx requires MTA1 coregulator. J Biol Chem. 291:11982016.
View Article : Google Scholar :
|
|
61
|
Yang L, Ma Z, Wang D, Zhao W, Chen L and
Wang G: MicroRNA-602 regulating tumor suppressive gene RASSF1A is
overexpressed in hepatitis B virus-infected liver and
hepatocellular carcinoma. Cancer Biol Ther. 9:803–808. 2010.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
62
|
Kew MC: Hepatitis B virus × protein in the
pathogenesis of hepatitis B virus-induced hepatocellular carcinoma.
J Gastroenterol Hepatol. 26:(Suppl 1). 144–152. 2011. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
63
|
Lizzano RA, Yang B, Clippinger AJ and
Bouchard MJ: The C-terminal region of the hepatitis B virus X
protein is essential for its stability and function. Virus Res.
155:231–239. 2011. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
64
|
Schuster R, Gerlich WH and Schaefer S:
Induction of apoptosis by the transactivating domains of the
hepatitis B virus X gene leads to suppression of oncogenic
transformation of primary rat embryo fibroblasts. Oncogene.
19:1173–1180. 2000. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
65
|
Tu H, Bonura C, Giannini C, Mouly H,
Soussan P, Kew M, Paterlini-Bréchot P, Bréchot C and Kremsdorf D:
Biological impact of natural COOH-terminal deletions of hepatitis B
virus X protein in hepatocellular carcinoma tissues. Cancer Res.
61:7803–7810. 2001.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
66
|
Sirma H, Giannini C, Poussin K, Paterlini
P, Kremsdorf D and Bréchot C: Hepatitis B virus X mutants, present
in hepatocellular carcinoma tissue abrogate both the
antiproliferative and transactivation effects of HBx. Oncogene.
18:4848–4859. 1999. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
67
|
Ma NF, Lau SH, Hu L, Xie D, Wu J, Yang J,
Wang Y, Wu MC, Fung J, Bai X, et al: COOH-terminal truncated HBV X
protein plays key role in hepatocarcinogenesis. Clin Cancer Res.
14:5061–5068. 2008. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
68
|
Sze KM, Chu GK, Lee JM and Ng IO:
C-terminal truncated hepatitis B virus × protein is associated with
metastasis and enhances invasiveness by C-Jun/matrix
metalloproteinase protein 10 activation in hepatocellular
carcinoma. Hepatology. 57:131–139. 2013. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
69
|
Zhang H, Shan CL, Li N, Zhang X, Zhang XZ,
Xu FQ, Zhang S, Qiu LY, Ye LH and Zhang XD: Identification of a
natural mutant of HBV X protein truncated 27 amino acids at the
COOH terminal and its effect on liver cell proliferation. Acta
Pharmacol Sin. 29:473–480. 2008. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
70
|
McDaniel K, Herrera L, Zhou T, Francis H,
Han Y, Levine P, Lin E, Glaser S, Alpini G and Meng F: The
functional role of microRNAs in alcoholic liver injury. J Cell Mol
Med. 18:197–207. 2014. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
71
|
Ding D, Lou X, Hua D, Yu W, Li L, Wang J,
Gao F, Zhao N, Ren G, Li L, et al: Recurrent targeted genes of
hepatitis B virus in the liver cancer genomes identified by a
next-generation sequencing-based approach. PLoS Genet.
8:e10030652012. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
72
|
Lau CC, Sun T, Ching AK, He M, Li JW, Wong
AM, Co NN, Chan AW, Li PS, Lung RW, et al: Viral-human chimeric
transcript predisposes risk to liver cancer development and
progression. Cancer Cell. 25:335–349. 2014. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
73
|
Lanford RE, Hildebrandt-Eriksen ES, Petri
A, Persson R, Lindow M, Munk ME, Kauppinen S and Ørum H:
Therapeutic silencing of microRNA-122 in primates with chronic
hepatitis C virus infection. Science. 327:198–201. 2010. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
74
|
Shimakami T, Yamane D, Jangra RK, Kempf
BJ, Spaniel C, Barton DJ and Lemon SM: Stabilization of hepatitis C
virus RNA by an Ago2-miR-122 complex. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA.
109:941–946. 2012. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
75
|
Bandiera S, Pfeffer S, Baumert TF and
Zeisel MB: miR-122 - a key factor and therapeutic target in liver
disease. J Hepatol. 62:448–457. 2015. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
76
|
Luna JM, Scheel TK, Danino T, Shaw KS,
Mele A, Fak JJ, Nishiuchi E, Takacs CN, Catanese MT, de Jong YP, et
al: Hepatitis C virus RNA functionally sequesters miR-122. Cell.
160:1099–1110. 2015. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
77
|
Romito A and Rougeulle C: Origin and
evolution of the long non-coding genes in the X-inactivation
center. Biochimie. 93:1935–1942. 2011. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
78
|
Astronomo RD and Burton DR: Carbohydrate
vaccines: Developing sweet solutions to sticky situations? Nat Rev
Drug Discov. 9:308–324. 2010. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
79
|
Kim YC, Song KS, Yoon G, Nam MJ and Ryu
WS: Activated ras oncogene collaborates with HBx gene of hepatitis
B virus to transform cells by suppressing HBx-mediated apoptosis.
Oncogene. 20:16–23. 2001. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
80
|
Zhang W, Kong G, Zhang J, Wang T, Ye L and
Zhang X: MicroRNA-520b inhibits growth of hepatoma cells by
targeting MEKK2 and cyclin D1. PLoS One. 7:e314502012. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
81
|
Melegari M, Scaglioni PP and Wands JR:
Cloning and characterization of a novel hepatitis B virus × binding
protein that inhibits viral replication. J Virol. 72:1737–1743.
1998.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
82
|
Naugler WE, Sakurai T, Kim S, Maeda S, Kim
K, Elsharkawy AM and Karin M: Gender disparity in liver cancer due
to sex differences in MyD88-dependent IL-6 production. Science.
317:121–124. 2007. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
83
|
Zhao JJ, Lin J, Yang H, Kong W, He L, Ma
X, Coppola D and Cheng JQ: MicroRNA-221/222 negatively regulates
estrogen receptor alpha and is associated with tamoxifen resistance
in breast cancer. J Biol Chem. 283:31079–31086. 2008. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
84
|
Pike MC and Spicer DV: Hormonal
contraception and chemoprevention of female cancers. Endocr Relat
Cancer. 7:73–83. 2000. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
85
|
Dutertre M and Smith CL: Molecular
mechanisms of selective estrogen receptor modulator (SERM) action.
J Pharmacol Exp Ther. 295:431–437. 2000.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
86
|
Chou YT, Lin HH, Lien YC, Wang YH, Hong
CF, Kao YR, Lin SC, Chang YC, Lin SY, Chen SJ, et al: EGFR promotes
lung tumorigenesis by activating miR-7 through a Ras/ERK/Myc
pathway that targets the Ets2 transcriptional repressor ERF. Cancer
Res. 70:8822–8831. 2010. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
87
|
Lubbers J, Lewis S, Harper E, Hledin MP,
Marquez GA, Johnson AE, Graves DR and Burnatowska-Hledin MA:
Resveratrol enhances anti-proliferative effect of VACM-1/cul5 in
T47D cancer cells. Cell Biol Toxicol. 27:95–105. 2011. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
88
|
Frisch SM and Francis H: Disruption of
epithelial cell-matrix interactions induces apoptosis. J Cell Biol.
124:619–626. 1994. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
89
|
Taddei ML, Giannoni E, Fiaschi T and
Chiarugi P: Anoikis: An emerging hallmark in health and diseases. J
Pathol. 226:380–393. 2012. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
90
|
Zou Z, Anisowicz A, Hendrix MJ, Thor A,
Neveu M, Sheng S, Rafidi K, Seftor E and Sager R: Maspin, a serpin
with tumor-suppressing activity in human mammary epithelial cells.
Science. 263:526–529. 1994. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
91
|
Bailey CM, Khalkhali-Ellis Z, Seftor EA
and Hendrix MJ: Biological functions of maspin. J Cell Physiol.
209:617–624. 2006. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
92
|
Zhang H, Ozaki I, Mizuta T, Hamajima H,
Yasutake T, Eguchi Y, Ideguchi H, Yamamoto K and Matsuhashi S:
Involvement of programmed cell death 4 in transforming growth
factor-beta1-induced apoptosis in human hepatocellular carcinoma.
Oncogene. 25:6101–6112. 2006. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
93
|
Tanaka Y, Kanai F, Ichimura T, Tateishi K,
Asaoka Y, Guleng B, Jazag A, Ohta M, Imamura J, Ikenoue T, et al:
The hepatitis B virus X protein enhances AP-1 activation through
interaction with Jab1. Oncogene. 25:633–642. 2006.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
94
|
Talotta F, Cimmino A, Matarazzo MR,
Casalino L, De Vita G, DEsposito M, Di Lauro R and Verde P: An
autoregulatory loop mediated by miR-21 and PDCD4 controls the AP-1
activity in RAS transformation. Oncogene. 28:73–84. 2009.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
95
|
Yang HS, Jansen AP, Nair R, Shibahara K,
Verma AK, Cmarik JL and Colburn NH: A novel transformation
suppressor, Pdcd4, inhibits AP-1 transactivation but not NF-kappaB
or ODC transactivation. Oncogene. 20:669–676. 2001. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
96
|
Guo Y, Chen Y, Ito H, Watanabe A, Ge X,
Kodama T and Aburatani H: Identification and characterization of
lin-28 homolog B (LIN28B) in human hepatocellular carcinoma. Gene.
384:51–61. 2006. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
97
|
Terradillos O, Pollicino T, Lecoeur H,
Tripodi M, Gougeon ML, Tiollais P and Buendia MA: p53-independent
apoptotic effects of the hepatitis B virus HBx protein in vivo and
in vitro. Oncogene. 17:2115–2123. 1998. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
98
|
Ng SA and Lee C: Hepatitis B virus X gene
and hepatocarcinogenesis. J Gastroenterol. 46:974–990. 2011.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
99
|
Kim SY, Kim JC, Kim JK, Kim HJ, Lee HM,
Choi MS, Maeng PJ and Ahn JK: Hepatitis B virus X protein enhances
NFkappaB activity through cooperating with VBP1. BMB Rep.
41:158–163. 2008. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
100
|
Dasari VR, Kaur K, Velpula KK, Gujrati M,
Fassett D, Klopfenstein JD, Dinh DH and Rao JS: Upregulation of
PTEN in glioma cells by cord blood mesenchymal stem cells inhibits
migration via downregulation of the PI3K/Akt pathway. PLoS One.
5:e103502010. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
101
|
van Roy F and Berx G: The cell-cell
adhesion molecule E-cadherin. Cell Mol Life Sci. 65:3756–3788.
2008. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
102
|
Seftor RE, Seftor EA, Sheng S, Pemberton
PA, Sager R and Hendrix MJ: maspin suppresses the invasive
phenotype of human breast carcinoma. Cancer Res. 58:5681–5685.
1998.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
103
|
Fabbri M, Garzon R, Cimmino A, Liu Z,
Zanesi N, Callegari E, Liu S, Alder H, Costinean S,
Fernandez-Cymering C, et al: MicroRNA-29 family reverts aberrant
methylation in lung cancer by targeting DNA methyltransferases 3A
and 3B. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA. 104:15805–15810. 2007. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
104
|
Wang SC, Lin XL, Li J, Zhang TT, Wang HY,
Shi JW, Yang S, Zhao WT, Xie RY, Wei F, et al: MicroRNA-122
triggers mesenchymal-epithelial transition and suppresses
hepatocellular carcinoma cell motility and invasion by targeting
RhoA. PLoS One. 9:e1013302014. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
105
|
He C and Klionsky DJ: Regulation
mechanisms and signaling pathways of autophagy. Annu Rev Genet.
43:67–93. 2009. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
106
|
Tian Y, Sir D, Kuo CF, Ann DK and Ou JH:
Autophagy required for hepatitis B virus replication in transgenic
mice. J Virol. 85:13453–13456. 2011. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
107
|
Tang H, Da L, Mao Y, Li Y, Li D, Xu Z, Li
F, Wang Y, Tiollais P, Li T, et al: Hepatitis B virus X protein
sensitizes cells to starvation-induced autophagy via up-regulation
of beclin 1 expression. Hepatology. 49:60–71. 2009. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
108
|
Bhogal RH, Weston CJ, Curbishley SM, Adams
DH and Afford SC: Autophagy: A cyto-protective mechanism which
prevents primary human hepatocyte apoptosis during oxidative
stress. Autophagy. 8:545–558. 2012. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
109
|
Kumar S, Gupta P, Khanal S, Shahi A, Kumar
P, Sarin SK and Venugopal SK: Overexpression of microRNA-30a
inhibits hepatitis B virus X protein-induced autophagosome
formation in hepatic cells. FEBS J. 282:1152–1163. 2015. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
110
|
Huo TI, Lee SD and Wu JC: Is diabetes a
risk factor for hepatocellular carcinoma? Gastroenterology.
127:360–361; author reply 361–362. 2004. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
111
|
Hsieh JL, Wu CL, Lee CH and Shiau AL:
Hepatitis B virus X protein sensitizes hepatocellular carcinoma
cells to cytolysis induced by E1B-deleted adenovirus through the
disruption of p53 function. Clin Cancer Res. 9:338–345.
2003.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
112
|
Su F, Theodosis CN and Schneider RJ: Role
of NF-kappaB and myc proteins in apoptosis induced by hepatitis B
virus HBx protein. J Virol. 75:215–225. 2001. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
113
|
Majano P, Lara-Pezzi E, López-Cabrera M,
Apolinario A, Moreno-Otero R and García-Monzón C: Hepatitis B virus
X protein transactivates inducible nitric oxide synthase gene
promoter through the proximal nuclear factor kappaB-binding site:
Evidence that cytoplasmic location of X protein is essential for
gene transactivation. Hepatology. 34:1218–1224. 2001. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
114
|
Jahani-Asl A and Bonni A: iNOS: A
potential therapeutic target for malignant glioma. Curr Mol Med.
13:1241–1249. 2013. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
115
|
Chisari FV, Isogawa M and Wieland SF:
Pathogenesis of hepatitis B virus infection. Pathol Biol (Paris).
58:258–266. 2010. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
116
|
Fattovich G, Stroffolini T, Zagni I and
Donato F: Hepatocellular carcinoma in cirrhosis: Incidence and risk
factors. Gastroenterology. 127:(Suppl 1). S35–S50. 2004. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
117
|
Huang R and Rofstad EK: Cancer stem cells
(CSCs), cervical CSCs and targeted therapies. Oncotarget.
8:35351–35367. 2017.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
118
|
Schmelzer E, Wauthier E and Reid LM: The
phenotypes of pluripotent human hepatic progenitors. Stem Cells.
24:1852–1858. 2006. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
119
|
Munz M, Baeuerle PA and Gires O: The
emerging role of EpCAM in cancer and stem cell signaling. Cancer
Res. 69:5627–5629. 2009. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
120
|
Ji J, Zheng X, Forgues M, Yamashita T,
Wauthier EL, Reid LM, Wen X, Song Y, Wei JS, Khan J, et al:
Identification of microRNAs specific for epithelial cell adhesion
molecule-positive tumor cells in hepatocellular carcinoma.
Hepatology. 62:829–840. 2015. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
121
|
Zhang F and Du G: Dysregulated lipid
metabolism in cancer. World J Biol Chem. 3:167–174. 2012.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
122
|
Rysman E, Brusselmans K, Scheys K,
Timmermans L, Derua R, Munck S, Van Veldhoven PP, Waltregny D,
Daniëls VW, Machiels J, et al: De novo lipogenesis protects cancer
cells from free radicals and chemotherapeutics by promoting
membrane lipid saturation. Cancer Res. 70:8117–8126. 2010.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
123
|
Chia WJ and Tang BL: Emerging roles for
Rab family GTPases in human cancer. Biochim Biophys Acta.
1795:110–116. 2009.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
124
|
Pulido MR, Diaz-Ruiz A, Jiménez-Gómez Y,
Garcia-Navarro S, Gracia-Navarro F, Tinahones F, López-Miranda J,
Frühbeck G, Vázquez-Martínez R and Malagón MM: Rab18 dynamics in
adipocytes in relation to lipogenesis, lipolysis and obesity. PLoS
One. 6:e229312011. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
125
|
Morales A, Mari M, Garcia-Ruiz C, Colell A
and Fernandez-Checa JC: Hepatocarcinogenesis and
ceramide/cholesterol metabolism. Anticancer Agents Med Chem.
12:364–375. 2012. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
126
|
Parkes HA, Preston E, Wilks D, Ballesteros
M, Carpenter L, Wood L, Kraegen EW, Furler SM and Cooney GJ:
Overexpression of acyl-CoA synthetase-1 increases lipid deposition
in hepatic (HepG2) cells and rodent liver in vivo. Am J Physiol
Endocrinol Metab. 291:E737–E744. 2006. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
127
|
Li LO, Ellis JM, Paich HA, Wang S, Gong N,
Altshuller G, Thresher RJ, Koves TR, Watkins SM, Muoio DM, et al:
Liver-specific loss of long chain acyl-CoA synthetase-1 decreases
triacylglycerol synthesis and beta-oxidation and alters
phospholipid fatty acid composition. J Biol Chem. 284:27816–27826.
2009. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
128
|
Duarte A, Poderoso C, Cooke M, Soria G,
Maciel Cornejo F, Gottifredi V and Podestá EJ: Mitochondrial fusion
is essential for steroid biosynthesis. PLoS One. 7:e458292012.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
129
|
Wen J and Friedman JR: miR-122 regulates
hepatic lipid metabolism and tumor suppression. J Clin Invest.
122:2773–2776. 2012. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
130
|
DAmbrogio A, Gu W, Udagawa T, Mello CC and
Richter JD: Specific miRNA stabilization by Gld2-catalyzed
monoadenylation. Cell Rep. 2:1537–1545. 2012. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
131
|
Liu WH, Yeh SH and Chen PJ: Role of
microRNAs in hepatitis B virus replication and pathogenesis.
Biochim Biophys Acta. 1809:678–685. 2011. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
132
|
Li J, Xu Z, Zheng Y, Johnson DL and Ou JH:
Regulation of hepatocyte nuclear factor 1 activity by wild-type and
mutant hepatitis B virus X proteins. J Virol. 76:5875–5881. 2002.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
133
|
Piriyapongsa J and Jordan IK: A family of
human microRNA genes from miniature inverted-repeat transposable
elements. PLoS One. 2:e2032007. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
134
|
Yuan Z, Sun X, Liu H and Xie J: MicroRNA
genes derived from repetitive elements and expanded by segmental
duplication events in mammalian genomes. PLoS One. 6:e176662011.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|