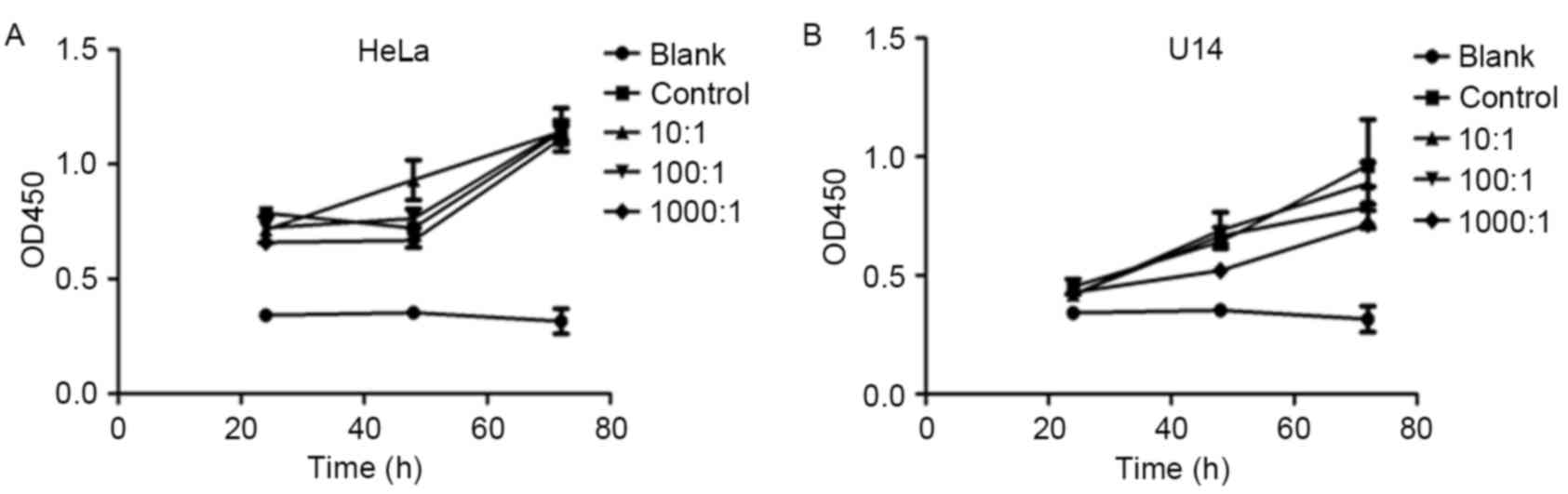
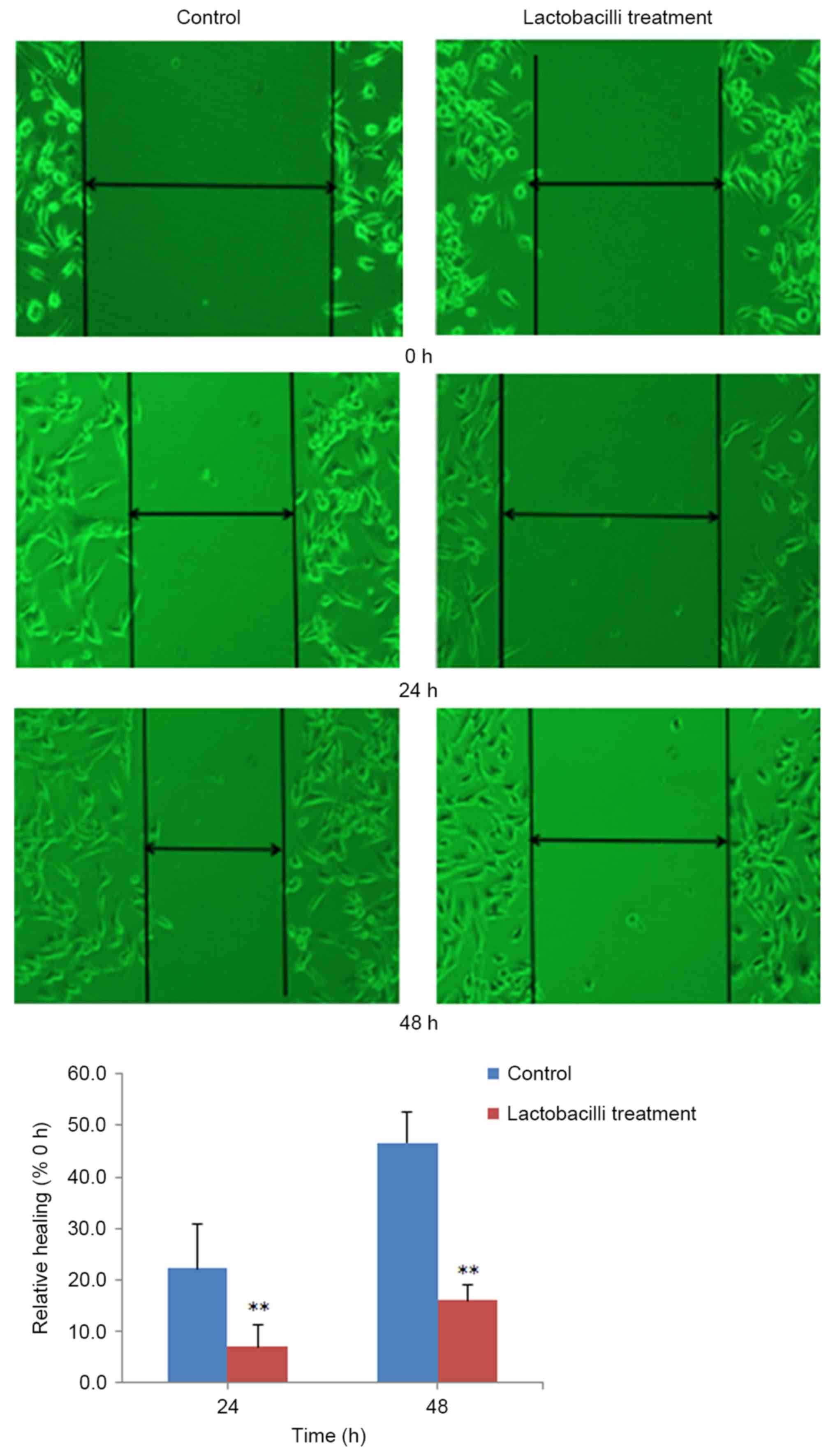
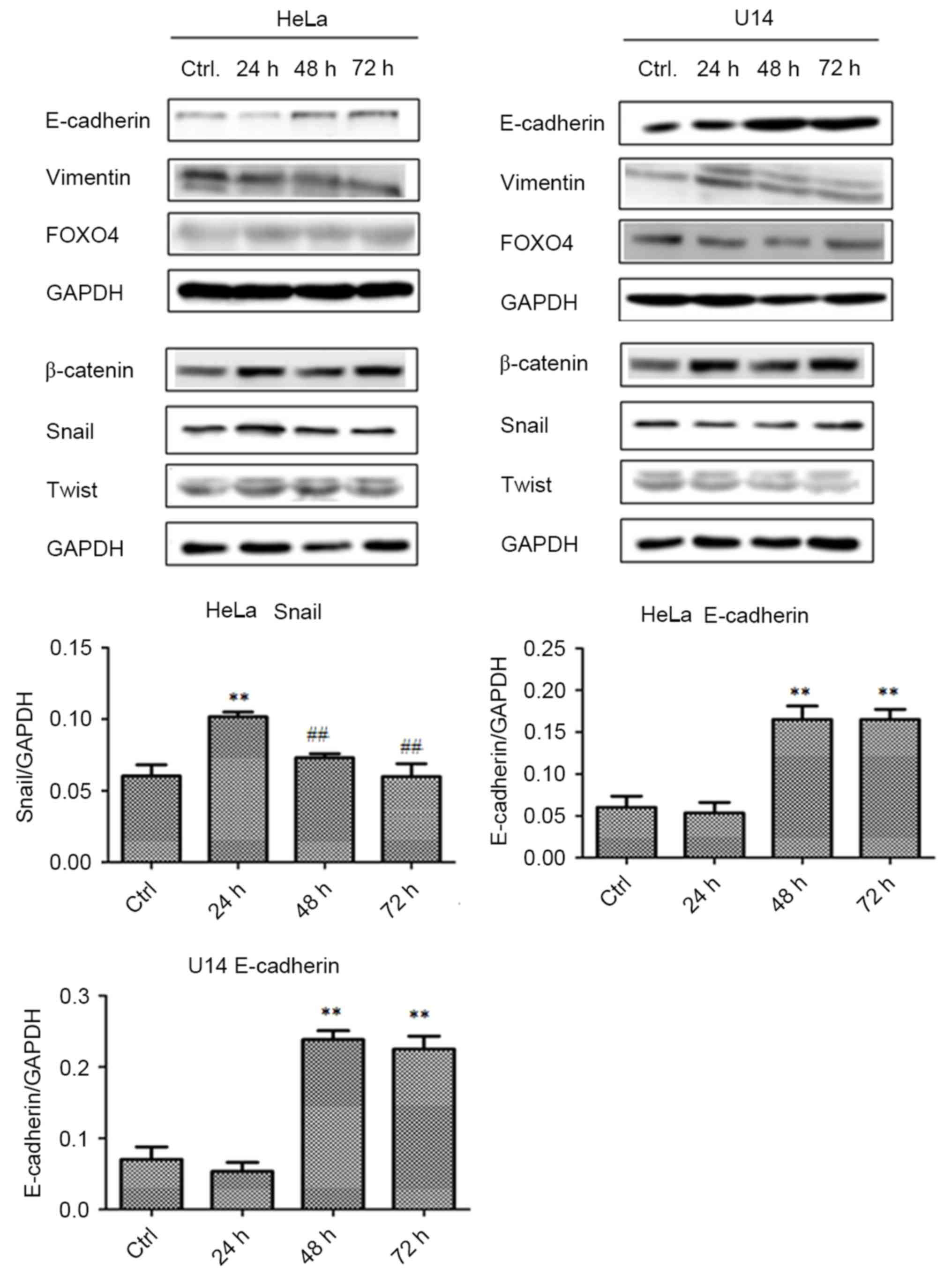
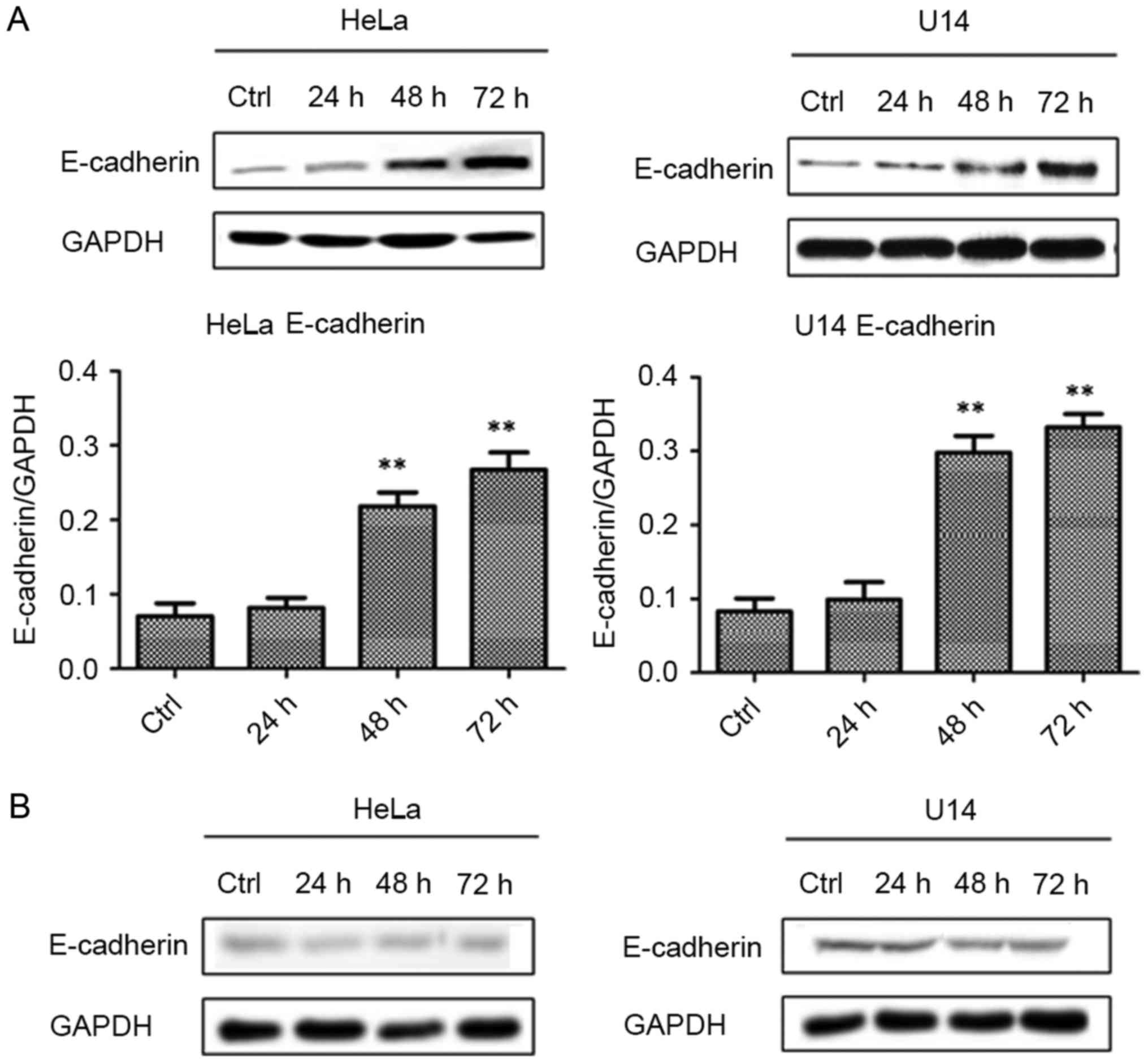
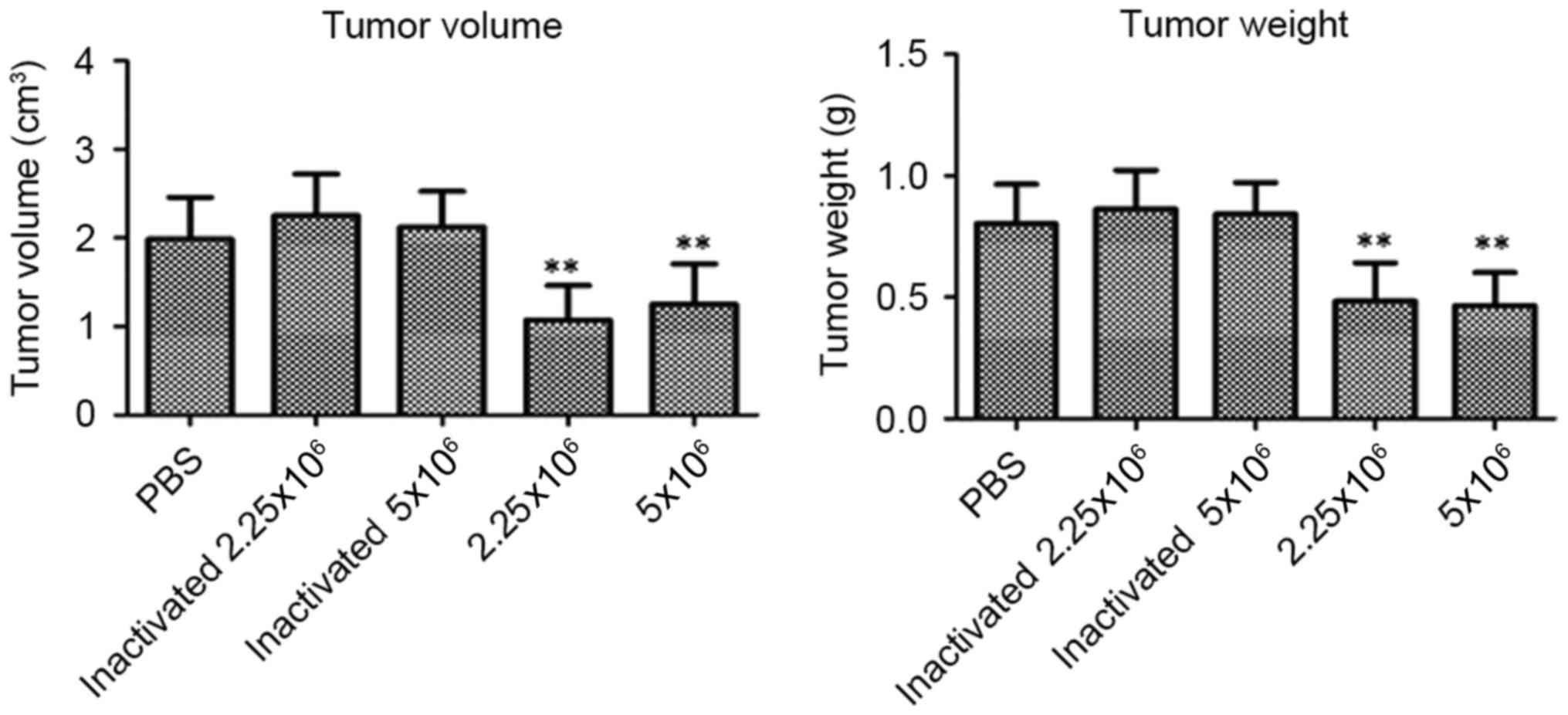
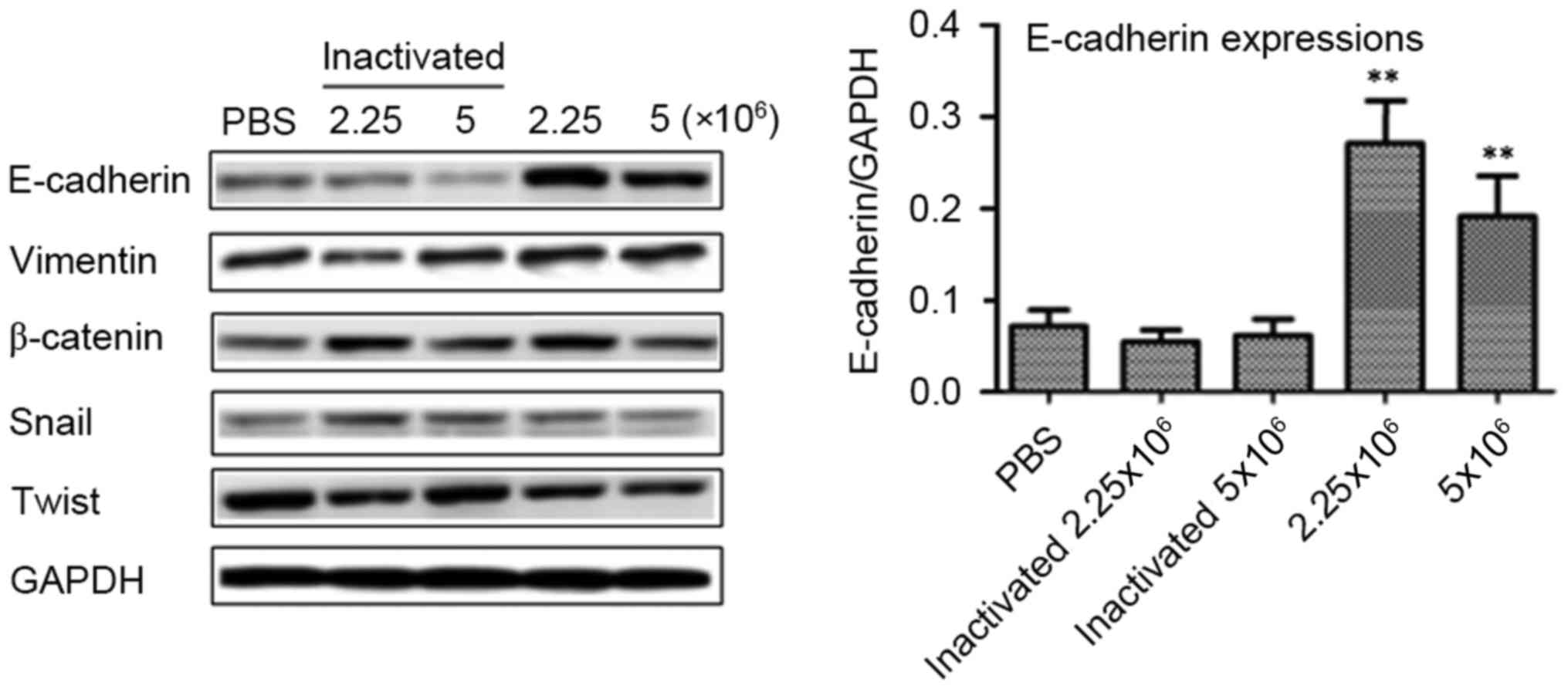
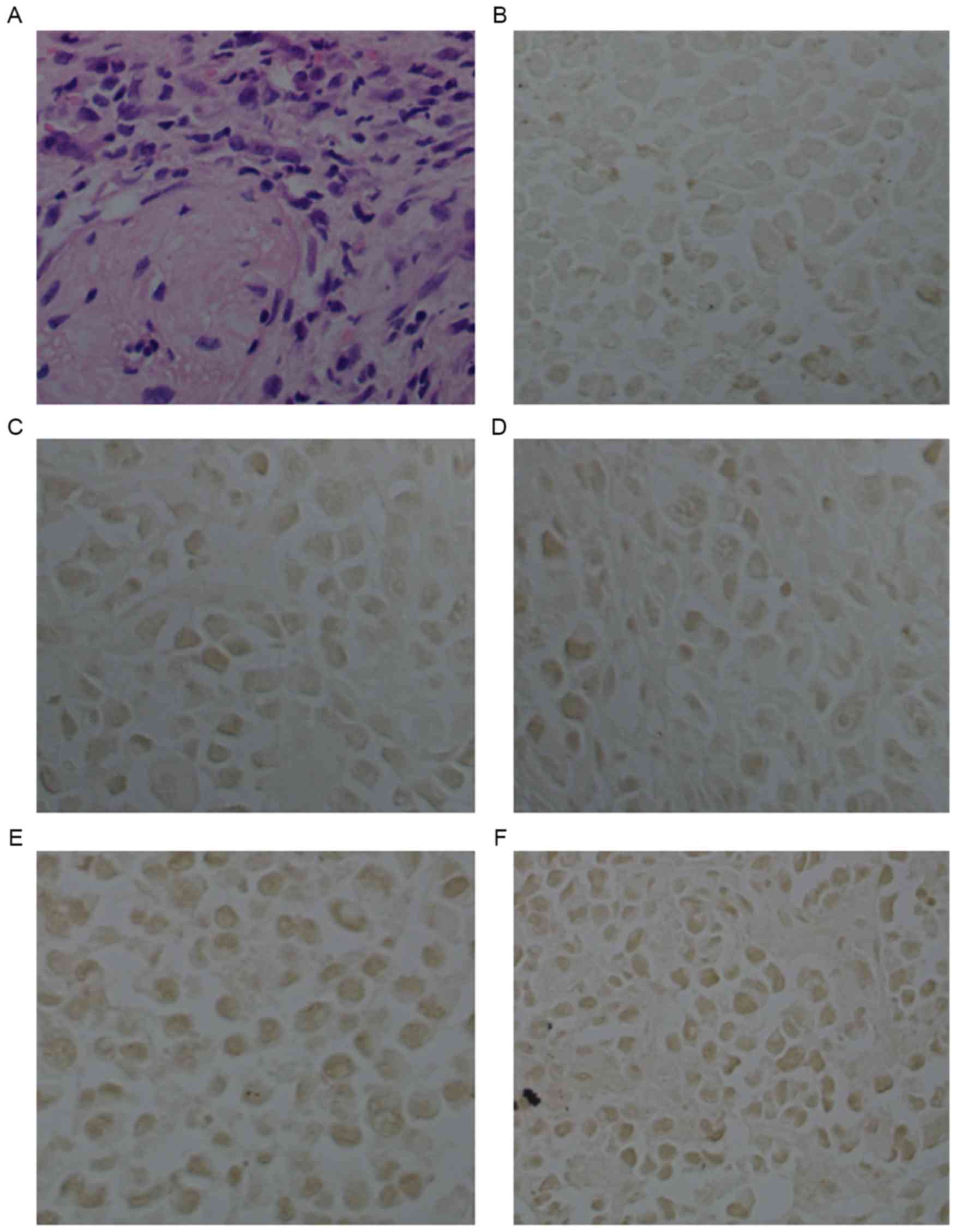
|
1
|
Vaccarella S, Franceschi S, Zaridze D,
Poljak M, Veerus P, Plummer M and Bray F: Preventable fractions of
cervical cancer via effective screening in six Baltic, central, and
eastern European countries 2017–40: A population-based study.
Lancet Oncol. 17:1445–1452. 2016. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
2
|
Lee SJ, Yang A, Wu TC and Hung CF:
Immunotherapy for human papillomavirus-associated disease and
cervical cancer: Review of clinical and translational research. J
Gynecol Oncol. 27:e512016. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
3
|
Muñoz N, Bosch FX, de Sanjosé S, Herrero
R, Castellsagué X, Shah KV, Snijders PJ and Meijer CJ:
International Agency for Research on Cancer Multicenter Cervical
Cancer Study Group: Epidemiologic classification of human
papillomavirus types associated with cervical cancer. N Engl J Med.
348:518–527. 2003. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
4
|
Dochez C, Bogers JJ, Verhelst R and Rees
H: HPV vaccines to prevent cervical cancer and genital warts: An
update. Vaccine. 32:1595–1601. 2014. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
5
|
Xiao BB and Liao QP: Research progress of
vaginal micro-ecology. J Int Obstet Gynecol. 38:479–482. 2011.
|
|
6
|
Lu FG, Hu JZ, Wu CR, Hu ZG and Zhao WN:
Study of biological antagonism on lactobacilli in human vaginae.
Pract Prev Med. 8:19–20. 2001.
|
|
7
|
Voravuthikunchai SP, Bilasoi S and
Supamala O: Antagonistic activity against pathogenic bacteria by
human vaginal lactobacilli. Anaerobe. 12:221–226. 2006. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
8
|
Mlcochova H, Machackova T, Rabien A,
Radova L, Fabian P, Iliev R, Slaba K, Poprach A, Kilic E, Stanik M,
et al: Epithelial- mesenchymal transition-associated microRNA/mRNA
signature is linked to metastasis and prognosis in clear-cell renal
cell carcinoma. Sci Rep. 6:318522016. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
9
|
Zhang Z, Chen H, Xu C, Song L, Huang L,
Lai Y, Wang Y, Chen H, Gu D, Ren L, et al: Curcumin inhibits tumor
epithelial- mesenchymal transition by downregulating the Wnt
signaling pathway and upregulating NKD2 expression in colon cancer
cells. Oncol Rep. 35:2615–2623. 2016.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
10
|
Braga V: Spatial integration of E-cadherin
adhesion, signalling and the epithelial cytoskeleton. Curr Opin
Cell Biol. 42:138–145. 2016. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
11
|
Carvalho S, Oliveira T, Bartels MF,
Miyoshi E, Pierce M, Taniguchi N, Carneiro F, Seruca R, Reis CA,
Strahl S, et al: O-mannosylation and N-glycosylation:
Two coordinated mechanisms regulating the tumour suppressor
functions of E-cadherin in cancer. Oncotarget. 7:65231–65246.
2016.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
12
|
Yang XK, Yang YD and Tang SQ: Inhibitory
effect of polysaccharides from Scutellaria barbata D. Don on
invasion and metastasis of 95-D cells lines via regulation of C-MET
and E-CAD expressions. Trop J Pharm Res. 12:517–522. 2013.
|
|
13
|
Peng W, Wu JG, Jiang YB, Liu YJ, Sun T, Wu
N and Wu CJ: Antitumor activity of
4-O-(2″-O-acetyl-6″-O-p-coumaroyl-β-D-glucopyranosyl)-p-coumaric
acid against lung cancers via mitochondrial-mediated apoptosis.
Chem Biol Interact. 233:8–13. 2015. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
14
|
Zhou T, Li G, Cao B, Liu L, Cheng Q, Kong
H, Shan C, Huang X, Chen J and Gao N: Downregulation of Mcl-1
through inhibition of translation contributes to benzyl
isothiocyanate-induced cell cycle arrest and apoptosis in human
leukemia cells. Cell Death Dis. 4:e5152013. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
15
|
Kalluri R and Weinberg RA: The basics of
epithelial-mesenchymal transition. J Clin Invest. 119:1420–1428.
2009. View
Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
16
|
Martínez A, Spencer ML, Borlando J, Flores
M and Rojas IG: E-cadherin and c-Met expression in actinic cheilits
and lip squamous cell carcinoma. Rehabil Oral. 4:122–125. 2011.
|
|
17
|
Yao Z and Shulan Z: Inhibition effect of
Guizhi-Fuling-decoction on the invasion of human cervical cancer. J
Ethnopharmacol. 120:25–35. 2008. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
18
|
Dohadwala M, Yang SC, Luo J, Sharma S,
Batra RK, Huang M, Lin Y, Goodglick L, Krysan K, Fishbein MC, et
al: Cyclooxygenase-2-dependent regulation of E-cadherin:
Prostaglandin E2 induces transcriptional repressors ZEB1
and snail in non-small cell lung cancer. Cancer Res. 66:5338–5345.
2006. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
19
|
Valizadeh A, Karayiannakis AJ, el-Hariry
I, Kmiot W and Pignatelli M: Expression of E-cadherin-associated
molecules (alpha-, beta-, and gamma-catenins and p120) in
colorectal polyps. Am J Pathol. 150:1977–1984. 1997.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
20
|
Hlubek F, Spaderna S, Schmalhofer O, Jung
A, Kirchner T and Brabletz T: Wnt/FZD signaling and colorectal
cancer morphogenesis. Front Biosci. 12:458–470. 2007. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
21
|
Rattner A, Hsieh JC, Smallwood PM, Gilbert
DJ, Copeland NG, Jenkins NA and Nathans J: A family of secreted
proteins contains homology to the cysteine-rich ligand-binding
domain of frizzled receptors. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA. 94:2859–2863.
1997. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
22
|
Wissmann C, Wild PJ, Kaiser S, Roepcke S,
Stoehr R, Woenckhaus M, Kristiansen G, Hsieh JC, Hofstaedter F,
Hartmann A, et al: WIF1, a component of the Wnt pathway, is
down-regulated in prostate, breast, lung, and bladder cancer. J
Pathol. 201:204–212. 2003. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
23
|
Yee DS, Tang Y, Li X, Liu Z, Guo Y,
Ghaffar S, McQueen P, Atreya D, Xie J, Simoneau AR, et al: The Wnt
inhibitory factor 1 restoration in prostate cancer cells was
associated with reduced tumor growth, decreased capacity of cell
migration and invasion and a reversal of epithelial to mesenchymal
transition. Mol Cancer. 9:1622010. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
24
|
Galván JA, González MV, Crespo G,
Folgueras MV and Astudillo A: Snail nuclear expression parallels
higher malignancy potential in neuroendocrine lung tumors. Lung
Cancer. 69:289–295. 2010. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
25
|
Lee SH, Kim JH and Lee YS: M1958
regulation of GLI1 and snail in Helicobacter pylori infected
gastric epithelial cells. Gastroenterology. 138:447–448.
2010.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
26
|
Casas E, Kim J, Bendesky A, Ohno-Machado
L, Wolfe CJ and Yang J: Snail2 is an essential mediator of
Twist1-induced epithelial mesenchymal transition and metastasis.
Cancer Res. 71:245–254. 2011. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
27
|
Yang J, Mani SA, Donaher JL, Ramaswamy S,
Itzykson RA, Come C, Savagner P, Gitelman I, Richardson A and
Weinberg RA: Twist, a master regulator of morphogenesis, plays an
essential role in tumor metastasis. Cell. 117:927–939. 2004.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
28
|
Tang TT and Lasky LA: The forkhead
transcription factor FOXO4 induces the down-regulation of
hypoxia-inducible factor 1 alpha by a von Hippel-Lindau
protein-independent mechanism. J Biol Chem. 278:30125–30135. 2003.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
29
|
Yang H, Zhao R, Yang HY and Lee MH:
Constitutively active FOXO4 inhibits Akt activity, regulates p27
Kip1 stability, and suppresses HER2-mediated tumorigenicity.
Oncogene. 24:1924–1935. 2005. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|