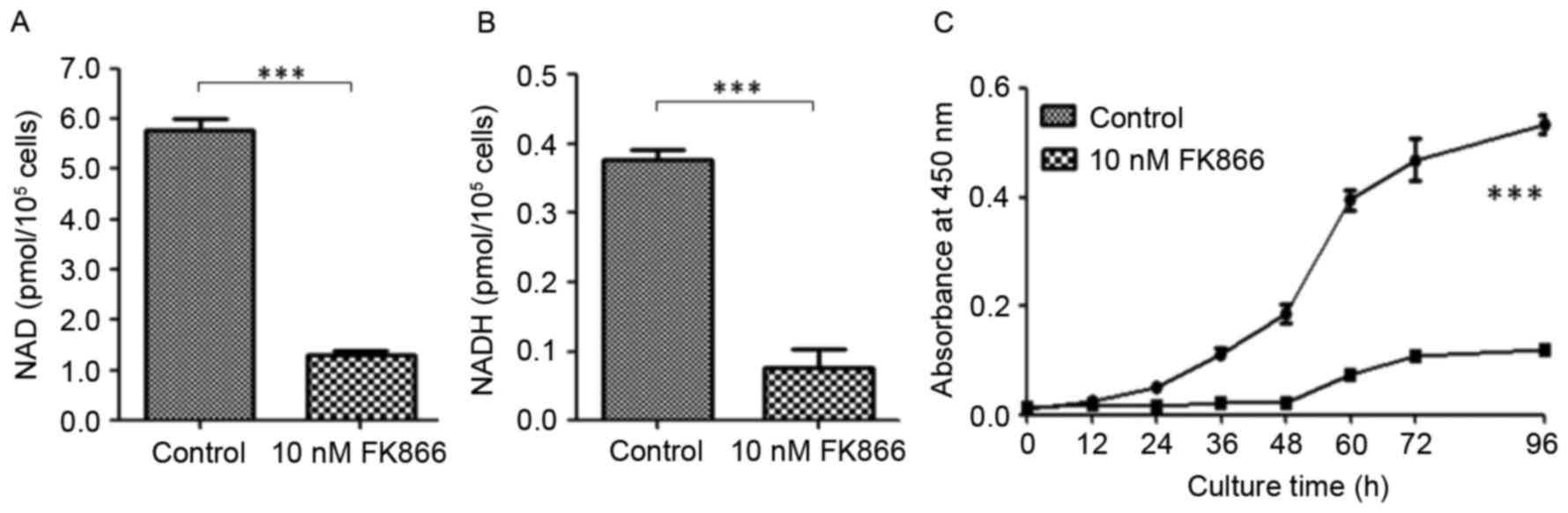
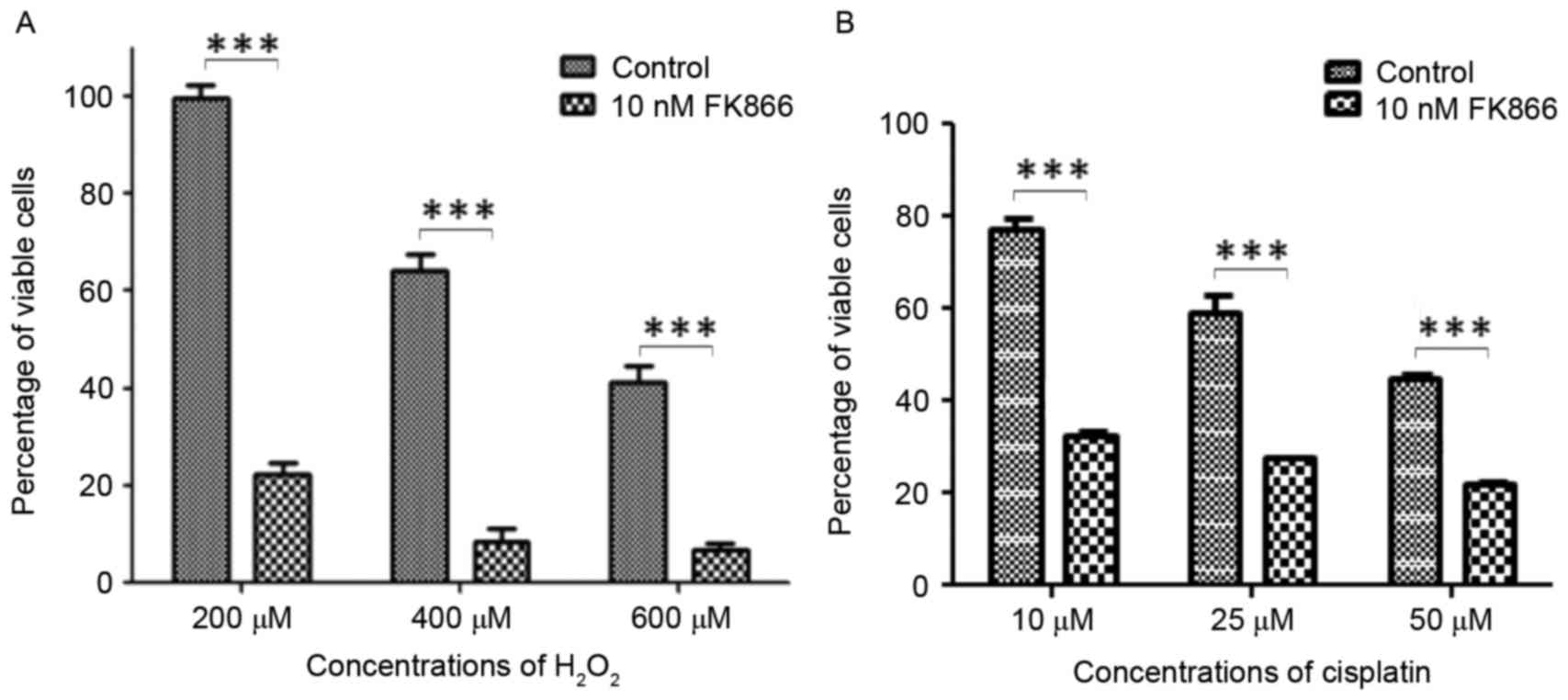
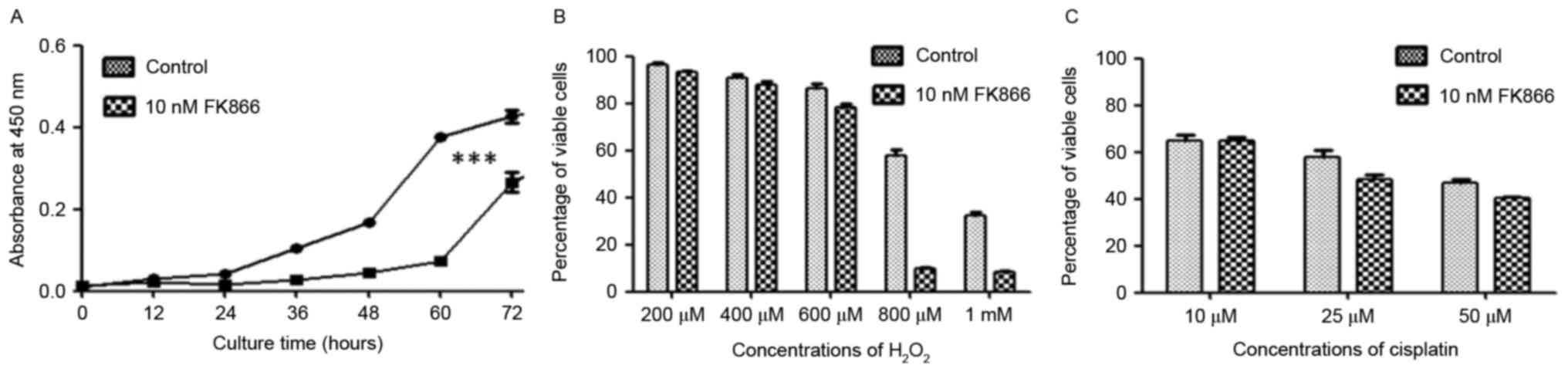
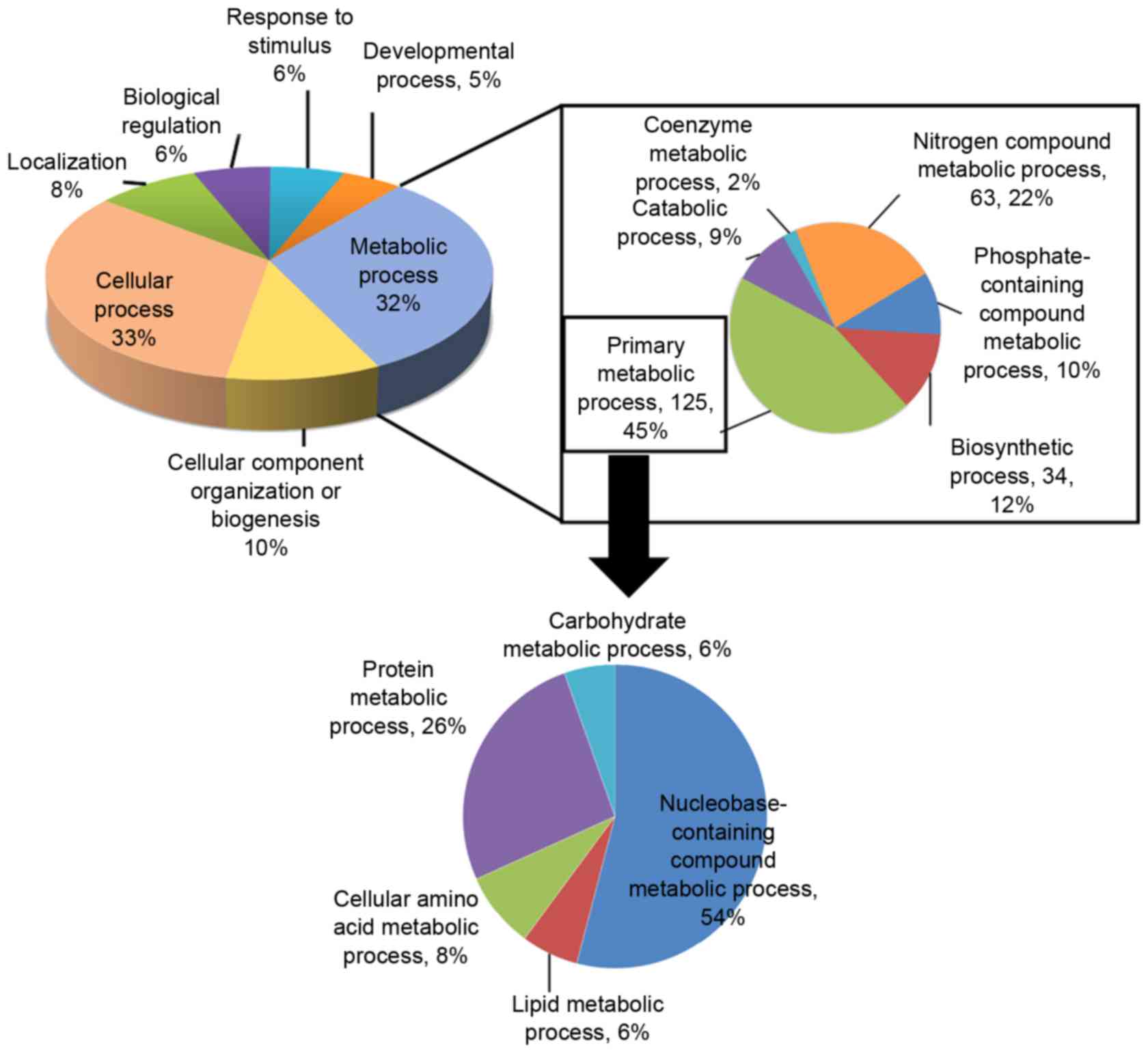
|
1
|
Yang Y and Sauve AA: NAD(+) metabolism:
Bioenergetics, signaling and manipulation for therapy. Biochim
Biophys Acta. 1864:1787–1800. 2016. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
2
|
Verdin E: NAD+ in aging,
metabolism, and neurodegeneration. Science. 350:1208–1213. 2015.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
3
|
Imai S and Guarente L: NAD+ and
sirtuins in aging and disease. Trends Cell Biol. 24:464–471. 2014.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
4
|
Viña J, Saez GT, Gambini J, Gomez-Cabrera
MC and Borrás C: Role of NAD(+)/NADH redox ratio in cell
metabolism: A tribute to Helmut Sies and Theodor Bücher and Hans A.
Krebs. Arch Biochem Biophys. 595:176–180. 2016. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
5
|
Ying W: NAD+/NADH and
NADP+/NADPH in cellular functions and cell death:
Regulation and biological consequences. Antioxid Redox Signal.
10:179–206. 2008. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
6
|
Xia W, Wang Z, Wang Q, Han J, Zhao C, Hong
Y, Zeng L, Tang L and Ying W: Roles of NAD(+)/NADH and
NADP(+)/NADPH in cell death. Curr Pharm Des. 15:12–19. 2009.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
7
|
Blander G and Guarente L: The Sir2 family
of protein deacetylases. Annu Rev Biochem. 73:417–435. 2004.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
8
|
Moazed D: Enzymatic activities of Sir2 and
chromatin silencing. Curr Opin Cell Biol. 13:232–238. 2001.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
9
|
Denu JM: The Sir 2 family of protein
deacetylases. Curr Opin Chem Biol. 9:431–440. 2005. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
10
|
Guarente L: Sirtuins and calorie
restriction. Nat Rev Mol Cell Biol. 13:2072012.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
11
|
Verdin E, Hirschey MD, Finley LW and
Haigis MC: Sirtuin regulation of mitochondria: Energy production,
apoptosis, and signaling. Trends Biochem Sci. 35:669–675. 2010.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
12
|
Brooks CL and Gu W: How does SIRT1 affect
metabolism, senescence and cancer? Nat Rev Cancer. 9:123–128. 2009.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
13
|
Yang H, Yang T, Baur JA, Perez E, Matsui
T, Carmona JJ, Lamming DW, Souza-Pinto NC, Bohr VA, Rosenzweig A,
et al: Nutrient-sensitive mitochondrial NAD+ levels
dictate cell survival. Cell. 130:1095–1107. 2007. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
14
|
Chang HC and Guarente L: SIRT1 mediates
central circadian control in the SCN by a mechanism that decays
with aging. Cell. 153:1448–1460. 2013. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
15
|
Luo X and Kraus WL: On PAR with PARP:
Cellular stress signaling through poly(ADP-ribose) and PARP-1.
Genes Dev. 26:417–432. 2012. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
16
|
Schreiber V, Dantzer F, Ame JC and de
Murcia G: Poly(ADP-ribose): Novel functions for an old molecule.
Nat Rev Mol Cell Biol. 7:517–528. 2006. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
17
|
Braidy N, Guillemin GJ, Mansour H,
Chan-Ling T, Poljak A and Grant R: Age related changes in
NAD+ metabolism oxidative stress and Sirt1 activity in
wistar rats. PLoS One. 6:e191942011. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
18
|
Prolla TA and Denu JM: NAD+
deficiency in age-related mitochondrial dysfunction. Cell Metab.
19:178–180. 2014. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
19
|
Mouchiroud L, Houtkooper RH, Moullan N,
Katsyuba E, Ryu D, Cantó C, Mottis A, Jo YS, Viswanathan M,
Schoonjans K, et al: The NAD(+)/sirtuin pathway modulates longevity
through activation of mitochondrial UPR and FOXO signaling. Cell.
154:430–441. 2013. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
20
|
Mills KF, Yoshida S, Stein LR, Grozio A,
Kubota S, Sasaki Y, Redpath P, Migaud ME, Apte RS, Uchida K, et al:
Long-term administration of nicotinamide mononucleotide mitigates
age-associated physiological decline in mice. Cell Metab.
24:795–806. 2016. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
21
|
Zhang H, Ryu D, Wu Y, Gariani K, Wang X,
Luan P, D'Amico D, Ropelle ER, Lutolf MP, Aebersold R, et al:
NAD+ repletion improves mitochondrial and stem cell
function and enhances life span in mice. Science. 352:1436–1443.
2016. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
22
|
Fang EF, Kassahun H, Croteau DL,
Scheibye-Knudsen M, Marosi K, Lu H, Shamanna RA, Kalyanasundaram S,
Bollineni RC, Wilson MA, et al: NAD(+) replenishment improves
lifespan and healthspan in ataxia telangiectasia models via
mitophagy and DNA repair. Cell Metab. 24:566–581. 2016. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
23
|
Camacho-Pereira J, Tarragó MG, Chini CC,
Nin V, Escande C, Warner GM, Puranik AS, Schoon RA, Reid JM, Galina
A, et al: CD38 dictates age-related NAD decline and mitochondrial
dysfunction through an SIRT3-dependent mechanism. Cell Metab.
23:1127–1139. 2016. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
24
|
Mei SC and Brenner C: NAD as a
genotype-specific drug target. Chem Biol. 20:1307–1308. 2013.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
25
|
Chiarugi A, Dölle C, Felici R and Ziegler
M: The NAD metabolome - a key determinant of cancer cell biology.
Nat Rev Cancer. 12:741–752. 2012. View
Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
26
|
Gallí M, Van Gool F, Rongvaux A, Andris F
and Leo O: The nicotinamide phosphoribosyltransferase: A molecular
link between metabolism, inflammation, and cancer. Cancer Res.
70:8–11. 2010. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
27
|
Garten A, Petzold S, Körner A, Imai S and
Kiess W: Nampt: Linking NAD biology, metabolism and cancer. Trends
Endocrinol Metab. 20:130–138. 2009. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
28
|
Hasmann M and Schemainda I: FK866, a
highly specific noncompetitive inhibitor of nicotinamide
phosphoribosyltransferase, represents a novel mechanism for
induction of tumor cell apoptosis. Cancer Res. 63:7436–7442.
2003.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
29
|
Khan JA, Tao X and Tong L: Molecular basis
for the inhibition of human NMPRTase, a novel target for anticancer
agents. Nat Struct Mol Biol. 13:582–588. 2006. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
30
|
Thakur BK, Dittrich T, Chandra P, Becker
A, Kuehnau W, Klusmann JH, Reinhardt D and Welte K: Involvement of
p53 in the cytotoxic activity of the NAMPT inhibitor FK866 in
myeloid leukemic cells. Int J Cancer. 132:766–774. 2013. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
31
|
Thakur BK, Dittrich T, Chandra P, Becker
A, Lippka Y, Selvakumar D, Klusmann JH, Reinhardt D and Welte K:
Inhibition of NAMPT pathway by FK866 activates the function of p53
in HEK293T cells. Biochem Biophys Res Commun. 424:371–377. 2012.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
32
|
Schuster S, Penke M, Gorski T, Gebhardt R,
Weiss TS, Kiess W and Garten A: FK866-induced NAMPT inhibition
activates AMPK and downregulates mTOR signaling in hepatocarcinoma
cells. Biochem Biophys Res Commun. 458:334–340. 2015. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
33
|
Cea M, Cagnetta A, Fulciniti M, Tai YT,
Hideshima T, Chauhan D, Roccaro A, Sacco A, Calimeri T, Cottini F,
et al: Targeting NAD+ salvage pathway induces autophagy
in multiple myeloma cells via mTORC1 and extracellular
signal-regulated kinase (ERK1/2) inhibition. Blood. 120:3519–3529.
2012. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
34
|
Billington RA, Genazzani AA, Travelli C
and Condorelli F: NAD depletion by FK866 induces autophagy.
Autophagy. 4:385–387. 2008. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
35
|
Xu R, Tian E, Tang H, Liu C and Wang Q:
Proteomic analysis of gossypol induces necrosis in multiple myeloma
cells. Biomed Res Int. 2014:8392322014. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
36
|
Brigelius-Flohé R and Maiorino M:
Glutathione peroxidases. Biochim Biophys Acta. 1830:3289–3303.
2013. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
37
|
Brigelius-Flohé R and Kipp A: Glutathione
peroxidases in different stages of carcinogenesis. Biochim Biophys
Acta. 1790:1555–1568. 2009. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
38
|
Novoselov SV, Kryukov GV, Xu XM, Carlson
BA, Hatfield DL and Gladyshev VN: Selenoprotein H is a nucleolar
thioredoxin-like protein with a unique expression pattern. J Biol
Chem. 282:11960–11968. 2007. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
39
|
Zhang T, Berrocal JG, Yao J, DuMond ME,
Krishnakumar R, Ruhl DD, Ryu KW, Gamble MJ and Kraus WL: Regulation
of poly(ADP-ribose) polymerase-1-dependent gene expression through
promoter-directed recruitment of a nuclear NAD+
synthase. J Biol Chem. 287:12405–12416. 2012. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
40
|
Bai P, Cantó C, Oudart H, Brunyánszki A,
Cen Y, Thomas C, Yamamoto H, Huber A, Kiss B, Houtkooper RH, et al:
PARP-1 inhibition increases mitochondrial metabolism through SIRT1
activation. Cell Metab. 13:461–468. 2011. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|