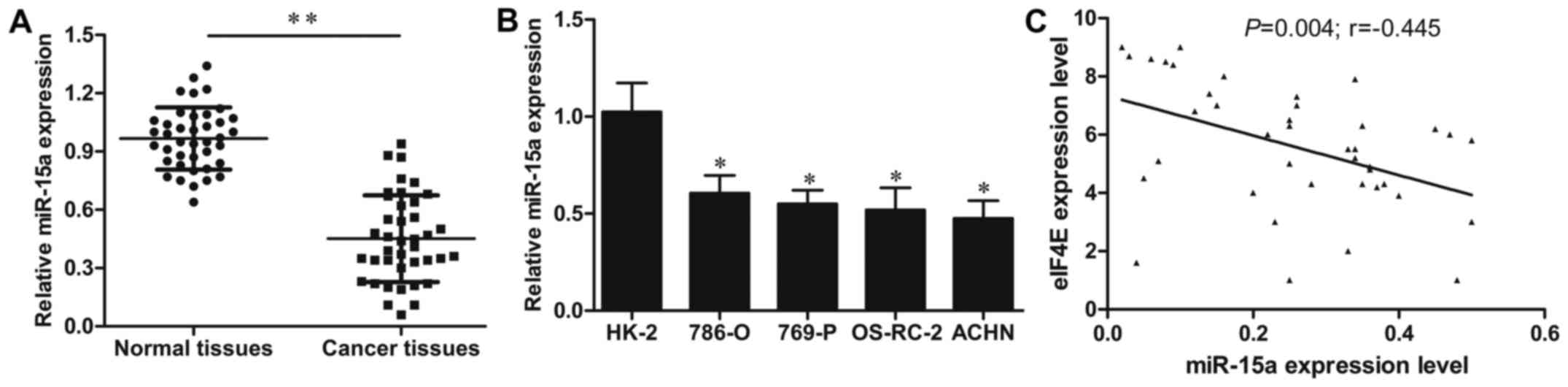
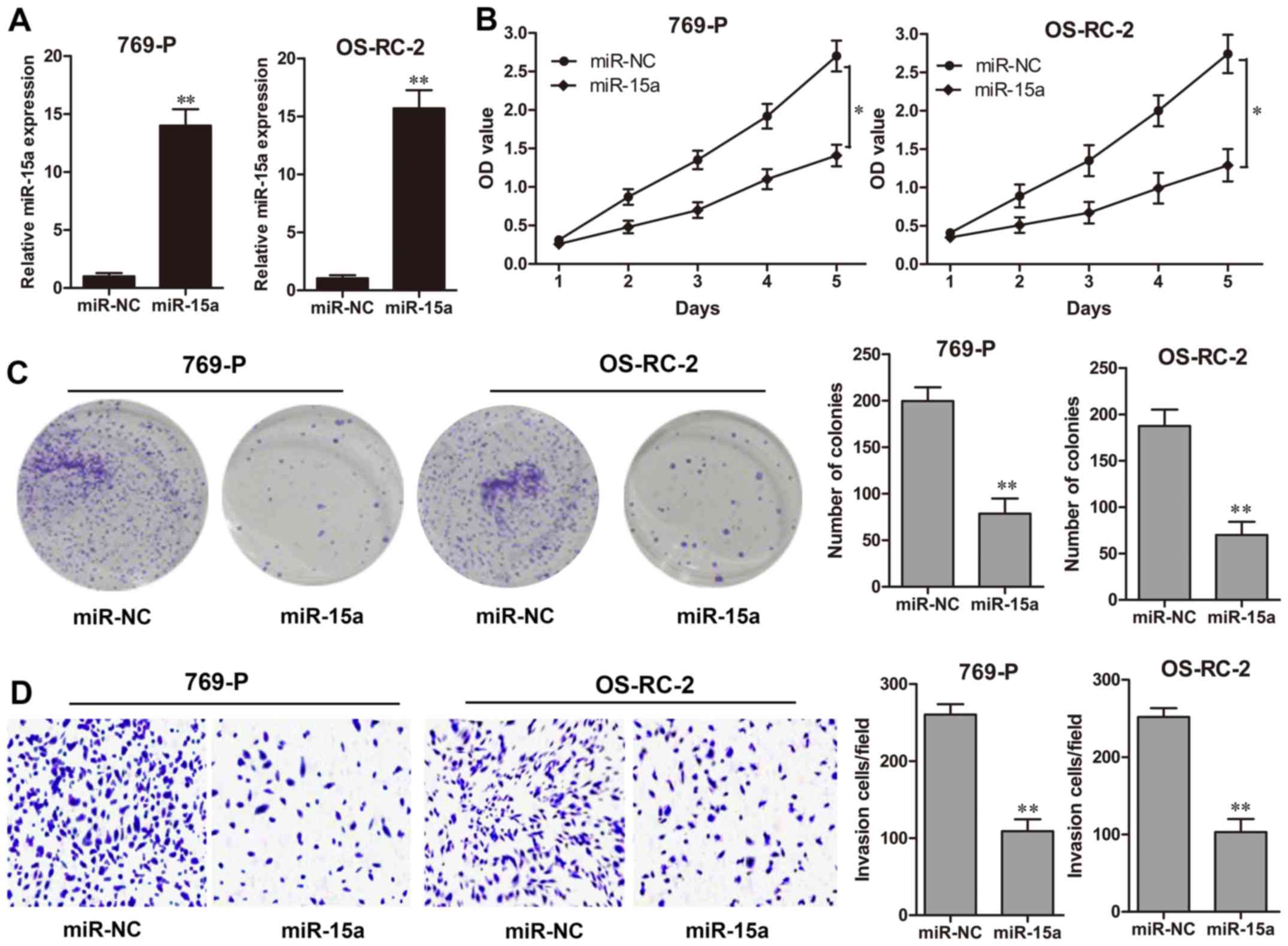
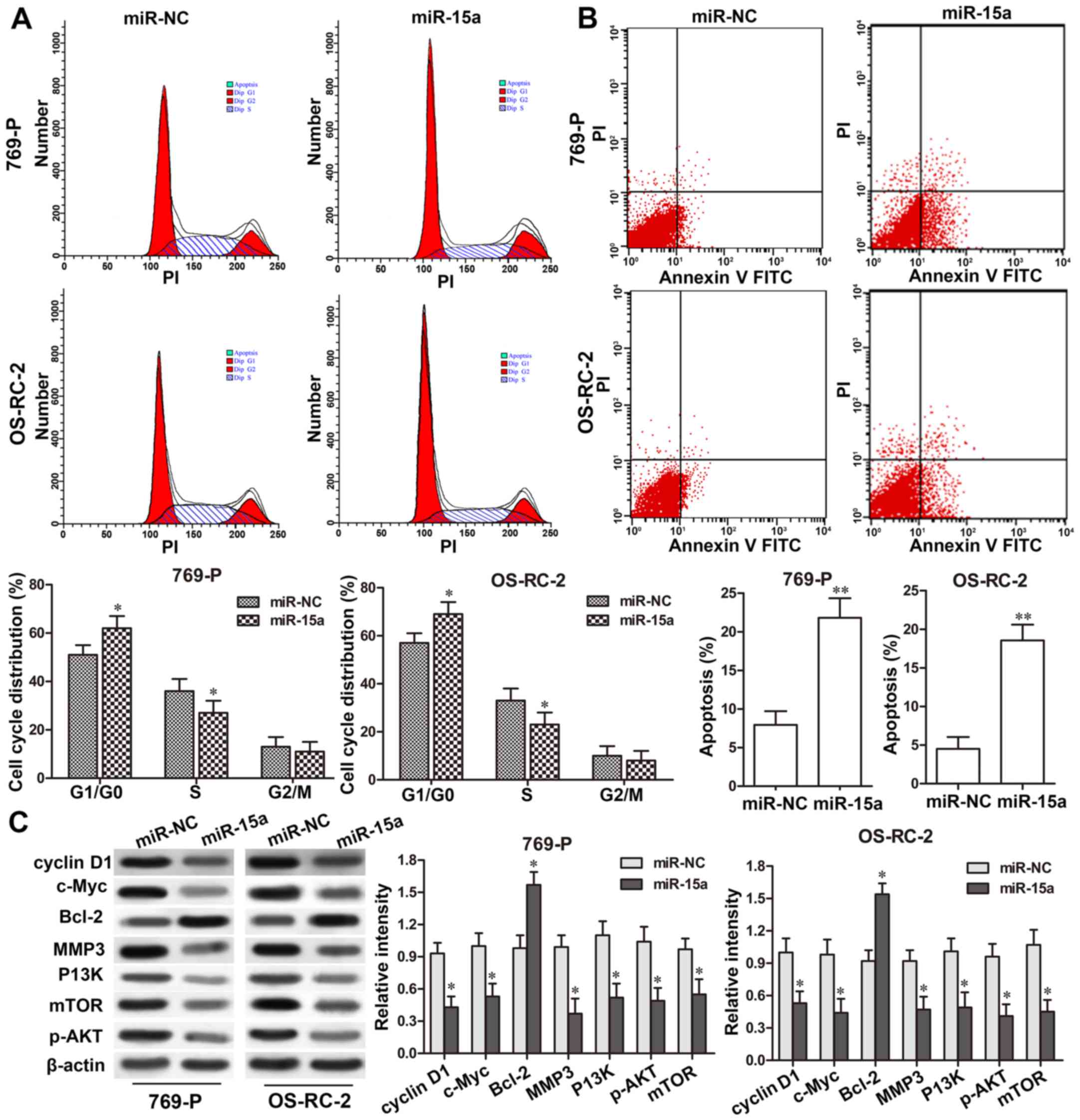
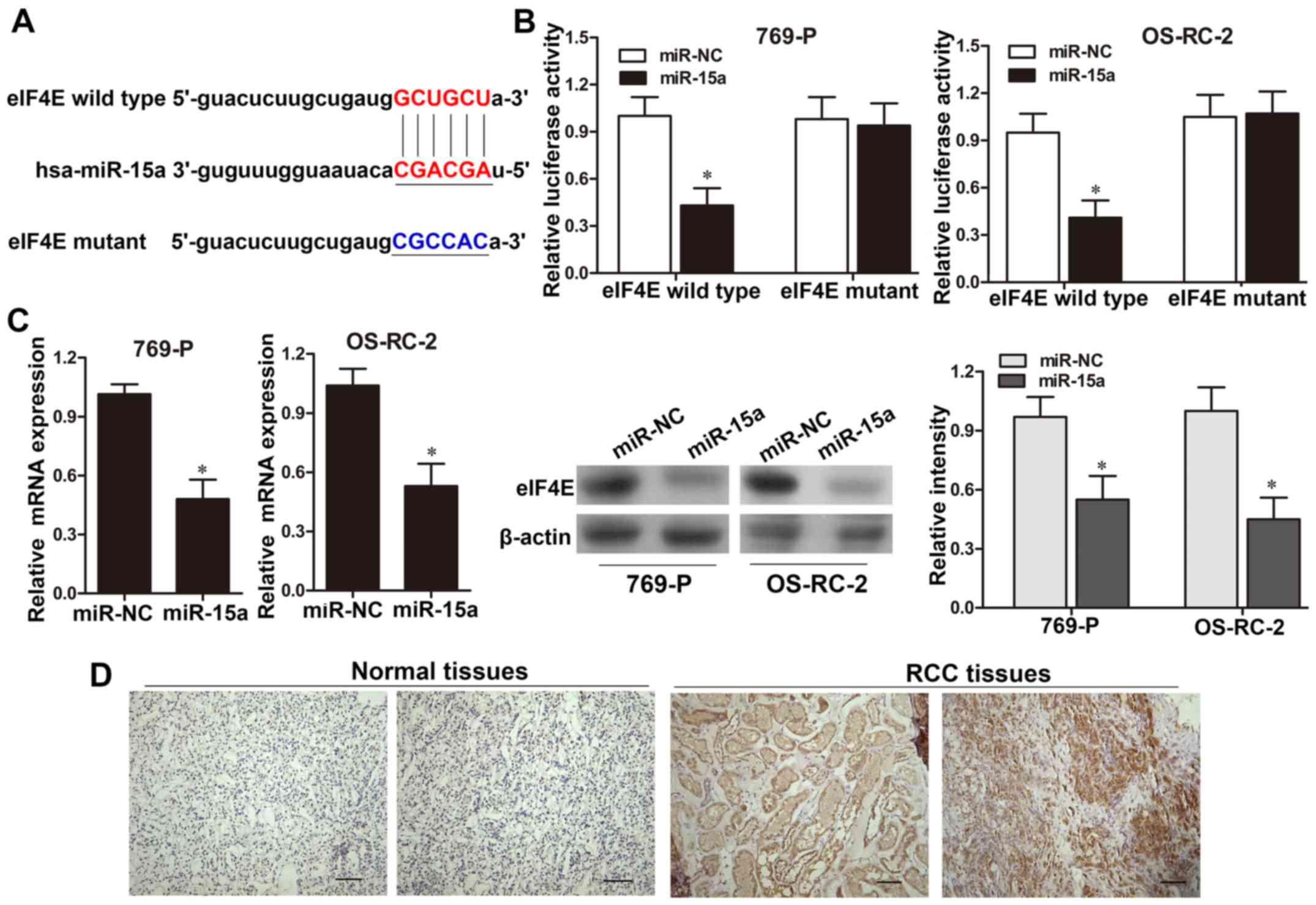
|
1
|
Chen W, Zheng R, Baade PD, Zhang S, Zeng
H, Bray F, Jemal A, Yu XQ and He J: Cancer statistics in China,
2015. CA Cancer J Clin. 66:115–132. 2016. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
2
|
Siegel RL, Miller KD and Jemal A: Cancer
Statistics, 2017. CA Cancer J Clin. 67:7–30. 2017. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
3
|
Buonerba C, Di Lorenzo G and Sonpavde G:
Combination therapy for metastatic renal cell carcinoma. Ann Transl
Med. 4:1002016. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
4
|
Escudier B: Advanced renal cell carcinoma:
Current and emerging management strategies. Drugs. 67:1257–1264.
2007. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
5
|
Afriansyah A, Hamid AR, Mochtar CA and
Umbas R: Targeted Therapy for Metastatic Renal Cell Carcinoma. Acta
Med Indones. 48:335–347. 2016.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
6
|
Hammond SM: An overview of microRNAs. Adv
Drug Deliv Rev. 87:3–14. 2015. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
7
|
Simonson B and Das S: MicroRNA
therapeutics: The next magic bullet? Mini Rev Med Chem. 15:467–474.
2015. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
8
|
Shah MY, Ferrajoli A, Sood AK,
Lopez-Berestein G and Calin GA: MicroRNA therapeutics in cancer -
an emerging concept. EBioMedicine. 12:34–42. 2016. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
9
|
Acunzo M, Romano G, Wernicke D and Croce
CM: MicroRNA and cancer - a brief overview. Adv Biol Regul. 57:1–9.
2015. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
10
|
Li X, Xin S, He Z, Che X, Wang J, Xiao X,
Chen J and Song X: MicroRNA-21 (miR-21) post-transcriptionally
downregulates tumor suppressor PDCD4 and promotes cell
transformation, proliferation, and metastasis in renal cell
carcinoma. Cell Physiol Biochem. 33:1631–1642. 2014. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
11
|
Xu M, Gu M, Zhang K, Zhou J, Wang Z and Da
J: miR-203 inhibition of renal cancer cell proliferation, migration
and invasion by targeting of FGF2. Diagn Pathol. 10:242015.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
12
|
Yang T, Thakur A, Chen T, Yang L, Lei G,
Liang Y, Zhang S, Ren H and Chen M: MicroRNA-15a induces cell
apoptosis and inhibits metastasis by targeting BCL2L2 in non-small
cell lung cancer. Tumour Biol. 36:4357–4365. 2015. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
13
|
Alderman C, Sehlaoui A, Xiao Z and Yang Y:
MicroRNA-15a inhibits the growth and invasiveness of malignant
melanoma and directly targets on CDCA4 gene. Tumour Biol.
37:13941–13950. 2016. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
14
|
Luo Q, Li X, Li J, Kong X, Zhang J, Chen
L, Huang Y and Fang L: MiR-15a is underexpressed and inhibits the
cell cycle by targeting CCNE1 in breast cancer. Int J Oncol.
43:1212–1218. 2013. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
15
|
Siddiqui N and Sonenberg N: Signalling to
eIF4E in cancer. Biochem Soc Trans. 43:763–772. 2015. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
16
|
Sonenberg N: eIF4E, the mRNA cap-binding
protein: From basic discovery to translational research. Biochem
Cell Biol. 86:178–183. 2008. View
Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
17
|
Jia Y, Polunovsky V, Bitterman PB and
Wagner CR: Cap-dependent translation initiation factor eIF4E: An
emerging anticancer drug target. Med Res Rev. 32:786–814. 2012.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
18
|
Truitt ML, Conn CS, Shi Z, Pang X,
Tokuyasu T, Coady AM, Seo Y, Barna M and Ruggero D: Differential
requirements for eIF4E dose in normal development and cancer. Cell.
162:59–71. 2015. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
19
|
Campbell L, Jasani B, Griffiths DF and
Gumbleton M: Phospho-4e-BP1 and eIF4E overexpression
synergistically drives disease progression in clinically confined
clear cell renal cell carcinoma. Am J Cancer Res. 5:2838–2848.
2015.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
20
|
Stewart GD, O'Mahony FC, Powles T, Riddick
ACP, Harrison DJ and Faratian D: What can molecular pathology
contribute to the management of renal cell carcinoma? Nat Rev Urol.
8:255–265. 2011. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
21
|
Di Leva G, Garofalo M and Croce CM:
MicroRNAs in cancer. Annu Rev Pathol. 9:287–314. 2014. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
22
|
Li P, Xie XB, Chen Q, Pang GL, Luo W, Tu
JC, Zheng F, Liu SM, Han L, Zhang J-K, et al: MiRNA-15a mediates
cell cycle arrest and potentiates apoptosis in breast cancer cells
by targeting synuclein-γ. Asian Pac J Cancer Prev. 15:6949–6954.
2014. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
23
|
Graff JR, Konicek BW, Carter JH and
Marcusson EG: Targeting the eukaryotic translation initiation
factor 4E for cancer therapy. Cancer Res. 68:631–634. 2008.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
24
|
De Benedetti A and Graff JR: eIF-4E
expression and its role in malignancies and metastases. Oncogene.
23:3189–3199. 2004. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
25
|
Wan J, Shi F, Xu Z and Zhao M: Knockdown
of eIF4E suppresses cell proliferation, invasion and enhances
cisplatin cytotoxicity in human ovarian cancer cells. Int J Oncol.
47:2217–2225. 2015. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
26
|
Li Y, Fan S, Koo J, Yue P, Chen ZG,
Owonikoko TK, Ramalingam SS, Khuri FR and Sun SY: Elevated
expression of eukaryotic translation initiation factor 4E is
associated with proliferation, invasion and acquired resistance to
erlotinib in lung cancer. Cancer Biol Ther. 13:272–280. 2012.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
27
|
Martineau Y, Azar R, Bousquet C and
Pyronnet S: Anti-oncogenic potential of the eIF4E-binding proteins.
Oncogene. 32:671–677. 2013. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
28
|
Hsieh AC and Ruggero D: Targeting
eukaryotic translation initiation factor 4E (eIF4E) in cancer. Clin
Cancer Res. 16:4914–4920. 2010. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
29
|
Li W, Jin X, Deng X, Zhang G, Zhang B and
Ma L: The putative tumor suppressor microRNA-497 modulates gastric
cancer cell proliferation and invasion by repressing eIF4E. Biochem
Biophys Res Commun. 449:235–240. 2014. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
30
|
Liu F, Wang X, Li J, Gu K, Lv L, Zhang S,
Che D, Cao J, Jin S and Yu Y: miR-34c-3p functions as a tumour
suppressor by inhibiting eIF4E expression in non-small cell lung
cancer. Cell Prolif. 48:582–592. 2015. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
31
|
Raught B and Gingras AC: eIF4E activity is
regulated at multiple levels. Int J Biochem Cell Biol. 31:43–57.
1999. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
32
|
Polivka J Jr and Janku F: Molecular
targets for cancer therapy in the PI3K/AKT/mTOR pathway. Pharmacol
Ther. 142:164–175. 2014. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
33
|
Zhang X, Shi H, Tang H, Fang Z, Wang J and
Cui S: miR-218 inhibits the invasion and migration of colon cancer
cells by targeting the PI3K/Akt/mTOR signaling pathway. Int J Mol
Med. 35:1301–1308. 2015. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
34
|
Dancey JE: Therapeutic targets: MTOR and
related pathways. Cancer Biol Ther. 5:1065–1073. 2006. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
35
|
Sun SY, Rosenberg LM, Wang X, Zhou Z, Yue
P, Fu H and Khuri FR: Activation of Akt and eIF4E survival pathways
by rapamycin-mediated mammalian target of rapamycin inhibition.
Cancer Res. 65:7052–7058. 2005. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
36
|
Ilic N, Utermark T, Widlund HR and Roberts
TM: PI3K-targeted therapy can be evaded by gene amplification along
the MYC-eukaryotic translation initiation factor 4E (eIF4E) axis.
Proc Natl Acad Sci USA. 108:E699–E708. 2011. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|