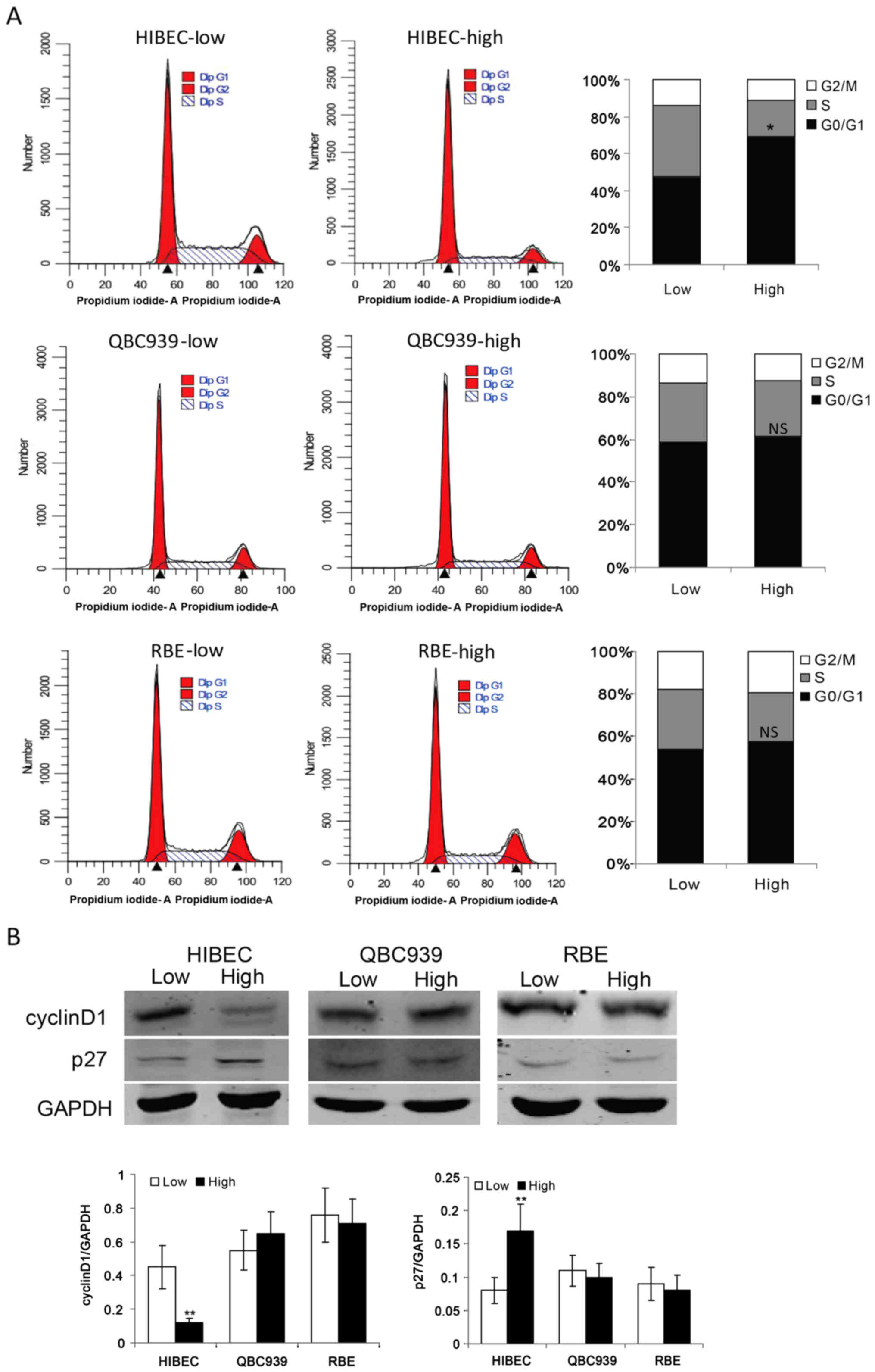
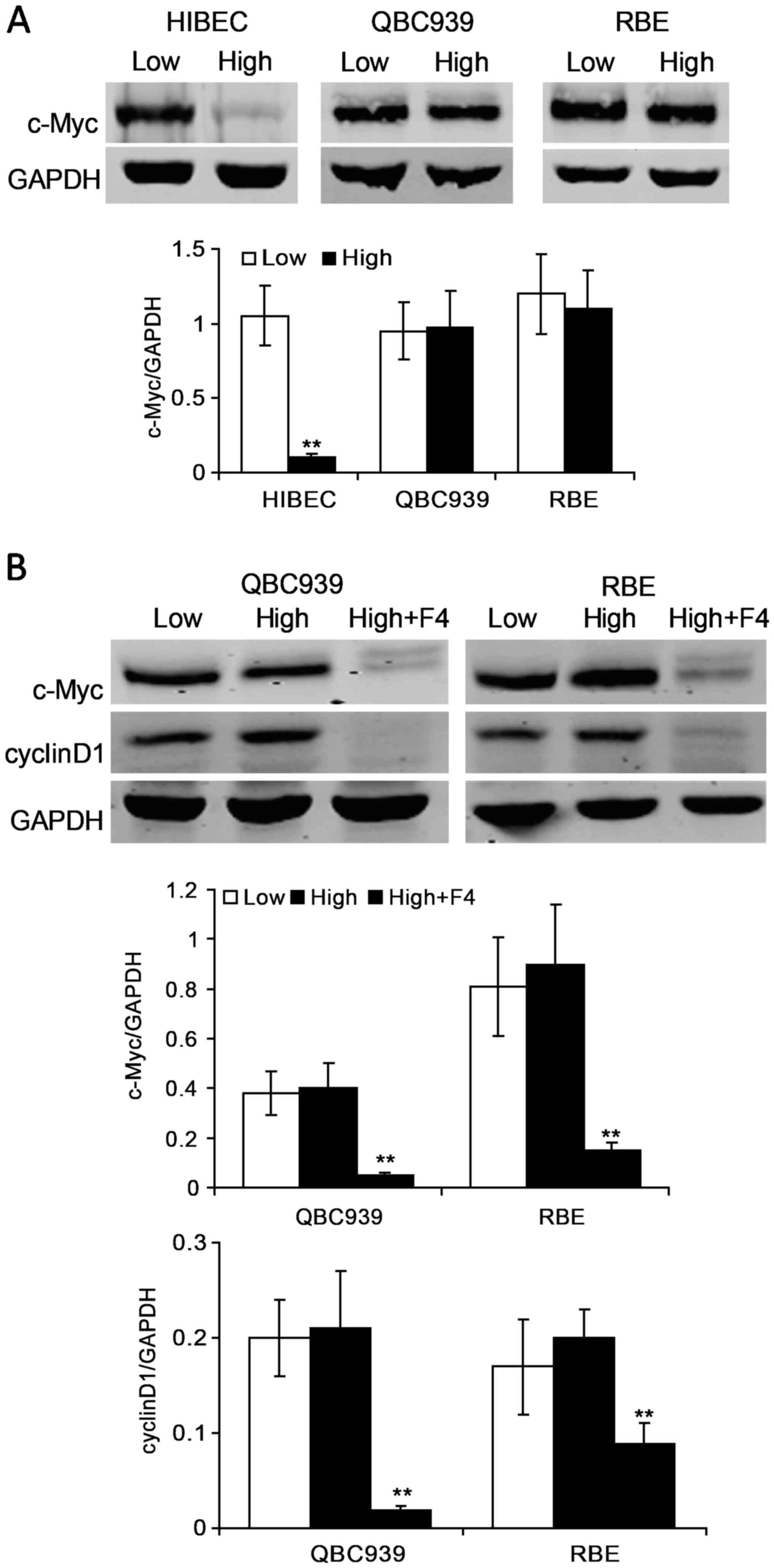
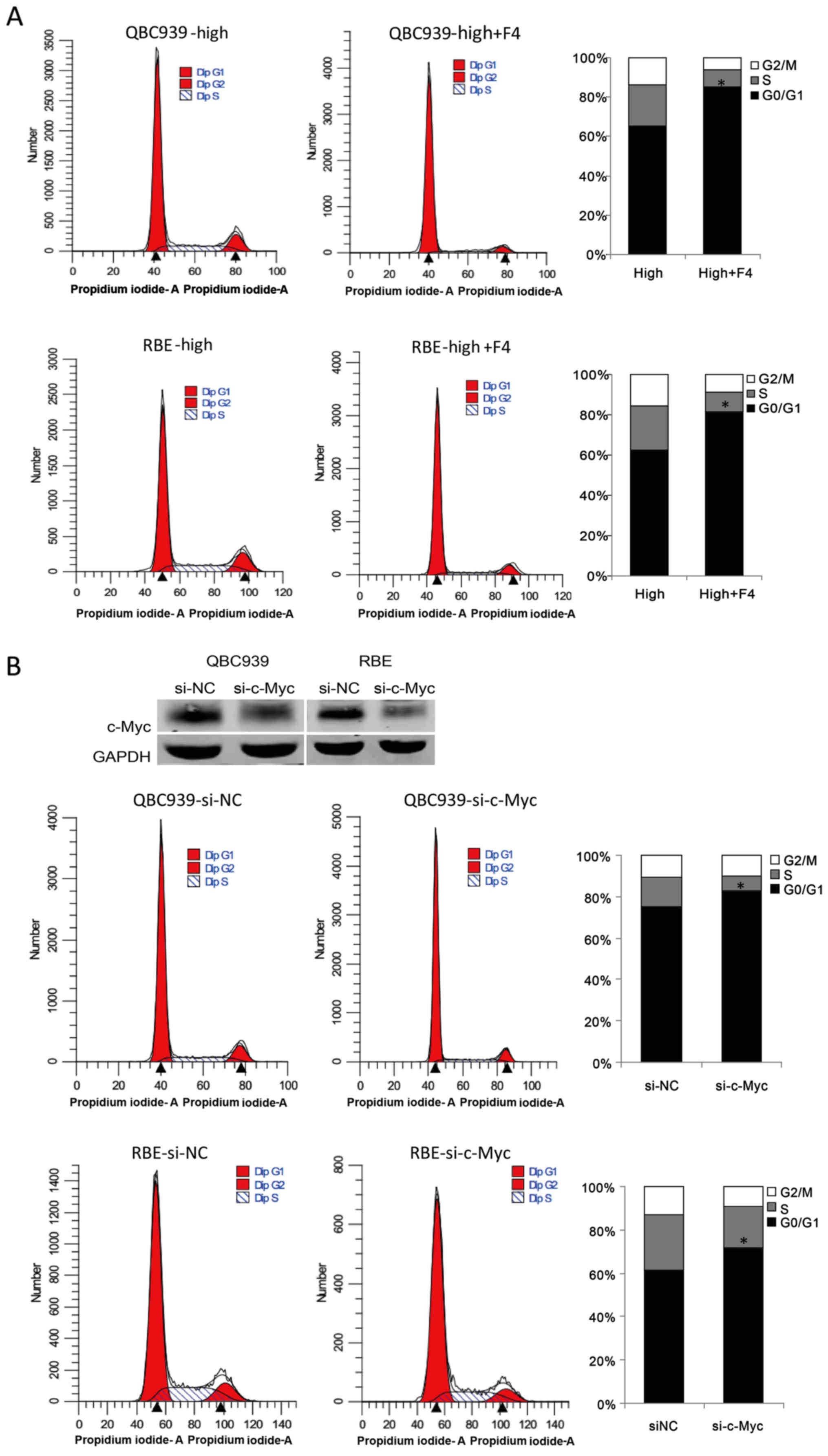
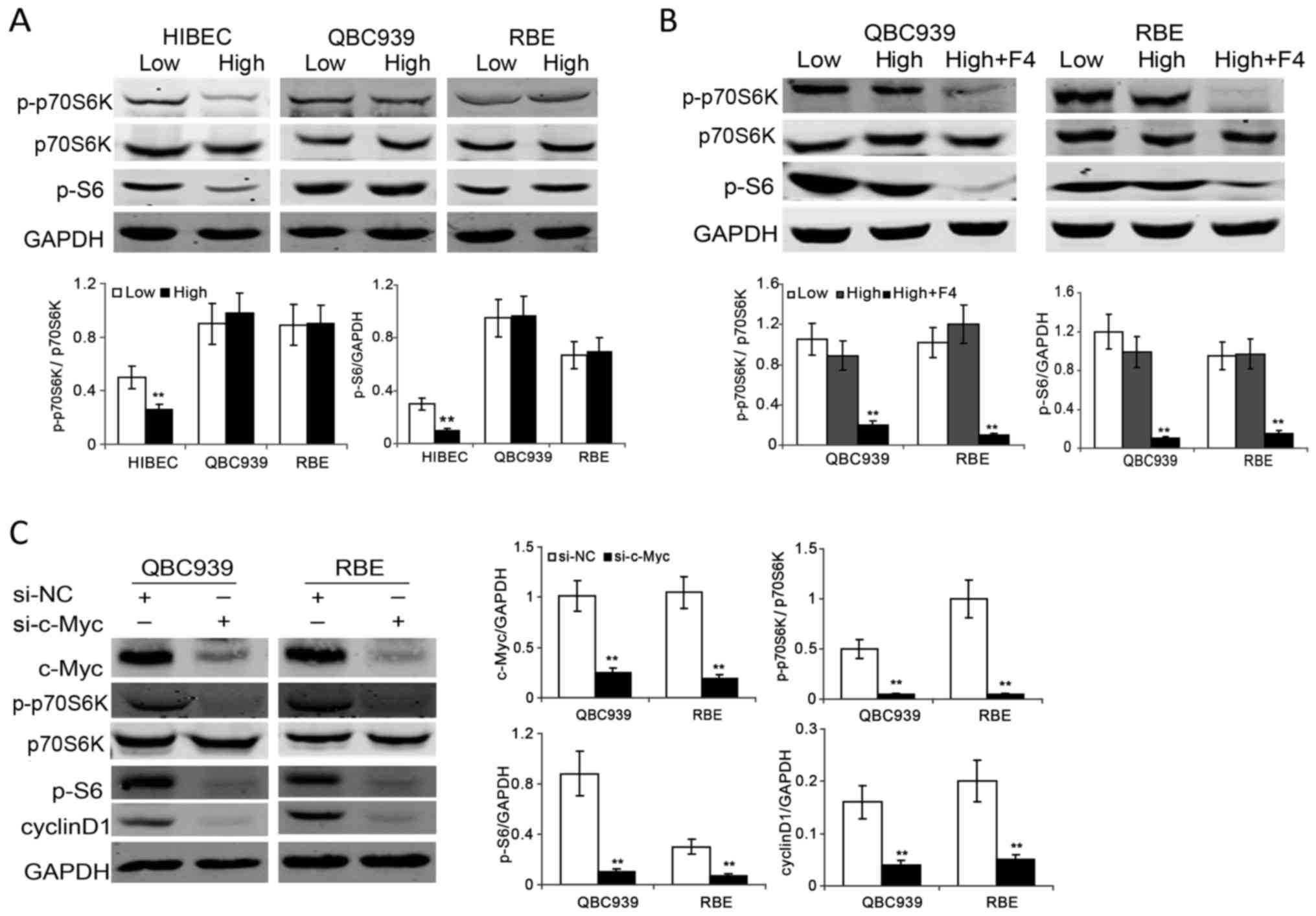
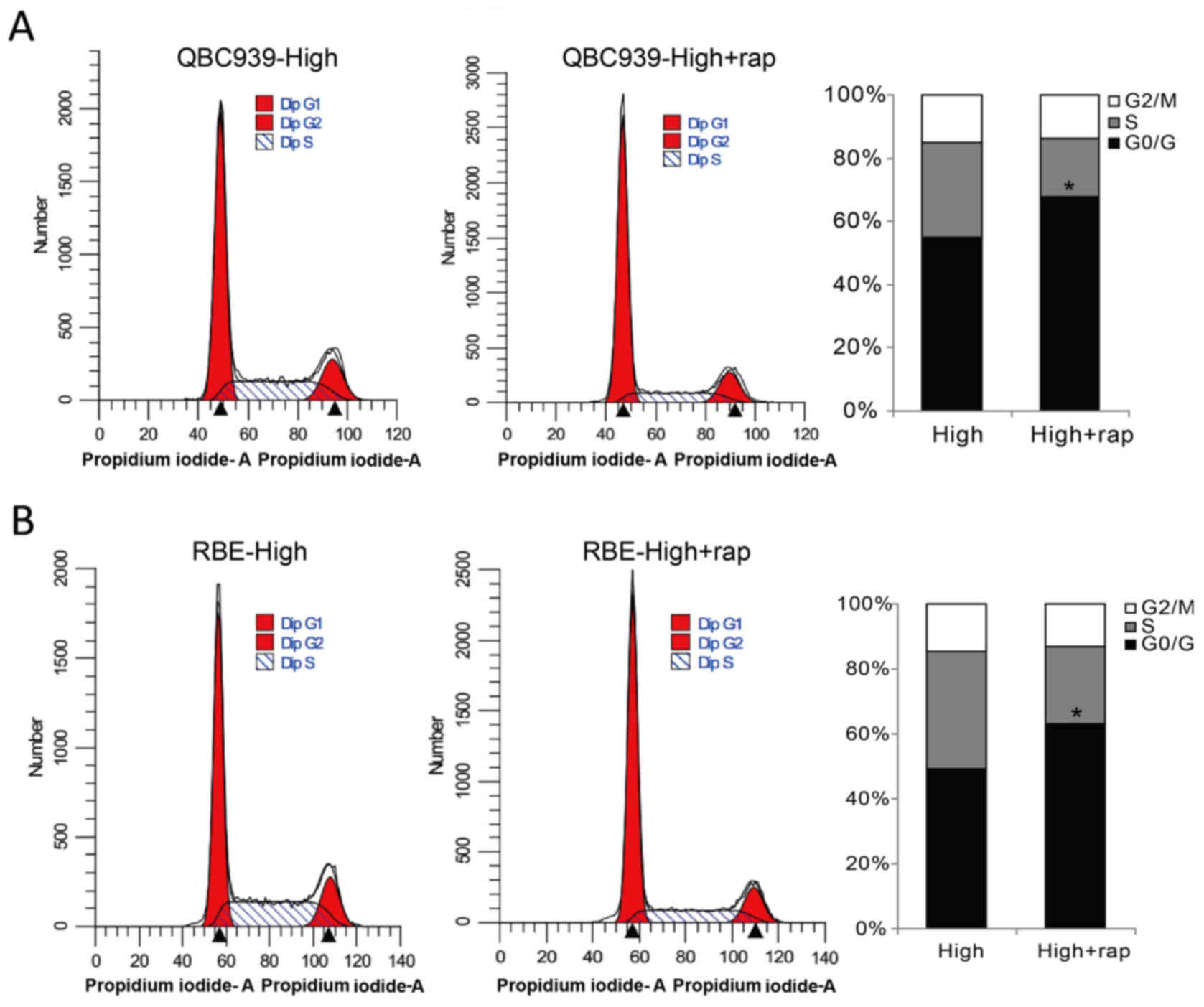
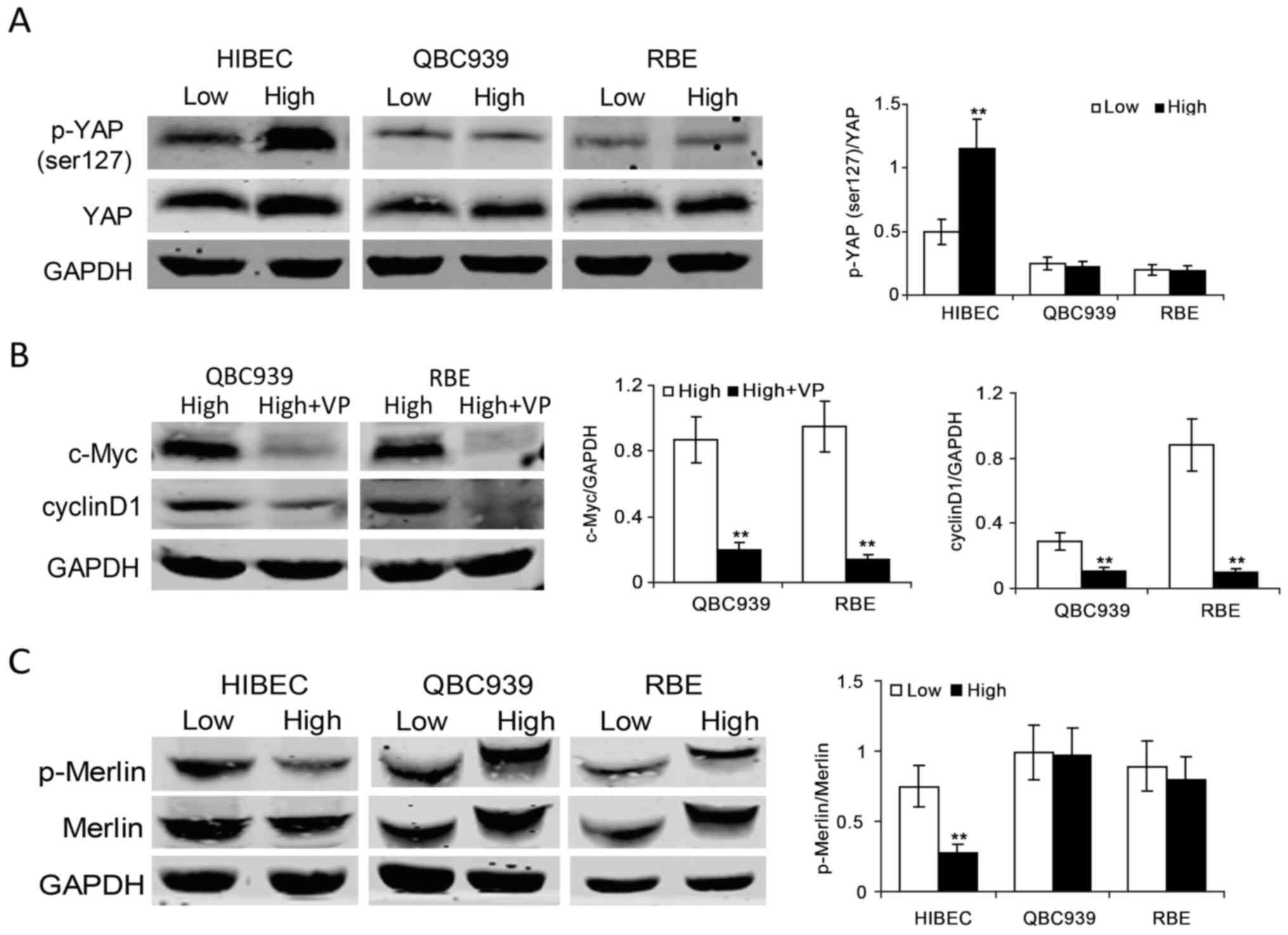
|
1
|
Eagle H and Levine EM: Growth regulatory
effects of cellular interaction. Nature. 213:1102–1106. 1967.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
2
|
Carter SB: Tissue homeostasis and the
biological basis of cancer. Nature. 220:970–974. 1968. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
3
|
Abercrombie M: Contact inhibition and
malignancy. Nature. 281:259–262. 1979. View
Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
4
|
Hanahan D and Weinberg RA: Hallmarks of
cancer: The next generation. Cell. 144:646–674. 2011. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
5
|
Brodeur GM, Seeger RC, Schwab M, Varmus HE
and Bishop JM: Amplification of N-myc in untreated human
neuroblastomas correlates with advanced disease stage. Science.
224:1121–1124. 1984. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
6
|
Vogelstein B, Papadopoulos N, Velculescu
VE, Zhou S, Diaz LA Jr and Kinzler KW: Cancer genome landscapes.
Science. 339:1546–1558. 2013. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
7
|
Kaposi-Novak P, Libbrecht L, Woo HG, Lee
YH, Sears NC, Coulouarn C, Conner EA, Factor VM, Roskams T and
Thorgeirsson SS: Central role of c-Myc during malignant conversion
in human hepatocarcinogenesis. Cancer Res. 69:2775–2782. 2009.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
8
|
Yang H, Liu T, Wang J, Li TW, Fan W, Peng
H, Krishnan A, Gores GJ, Mato JM and Lu SC: Deregulated methionine
adenosyltransferase α1, c-Myc, and Maf proteins together promote
cholangiocarcinoma growth in mice and humans. Hepatology.
64:439–455. 2016. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
9
|
Follis AV, Hammoudeh DI, Daab AT and
Metallo SJ: Small-molecule perturbation of competing interactions
between c-Myc and Max. Bioorg Med Chem Lett. 19:807–810. 2009.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
10
|
Hu J, Banerjee A and Goss DJ: Assembly of
b/HLH/z proteins c-Myc, Max, and Mad1 with cognate DNA: Importance
of protein-protein and protein-DNA interactions. Biochemistry.
44:11855–11863. 2005. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
11
|
Park S, Chung S, Kim KM, Jung KC, Park C,
Hahm ER and Yang CH: Determination of binding constant of
transcription factor myc-max/max-max and E-box DNA: The effect of
inhibitors on the binding. Biochim Biophys Acta. 1670:217–228.
2004. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
12
|
Dean M, Levine RA, Ran W, Kindy MS,
Sonenshein GE and Campisi J: Regulation of c-myc transcription and
mRNA abundance by serum growth factors and cell contact. J Biol
Chem. 261:9161–9166. 1986.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
13
|
Reed JC, Alpers JD, Nowell PC and Hoover
RG: Sequential expression of protooncogenes during
lectin-stimulated mitogenesis of normal human lymphocytes. Proc
Natl Acad Sci USA. 83:3982–3986. 1986. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
14
|
Schuhmacher M and Eick D: Dose-dependent
regulation of target gene expression and cell proliferation by
c-Myc levels. Transcription. 4:192–197. 2013. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
15
|
Wang H, Mannava S, Grachtchouk V, Zhuang
D, Soengas MS, Gudkov AV, Prochownik EV and Nikiforov MA: c-Myc
depletion inhibits proliferation of human tumor cells at various
stages of the cell cycle. Oncogene. 27:1905–1915. 2008. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
16
|
Blechacz BR and Gores GJ:
Cholangiocarcinoma. Clin Liver Dis. 12:131–150, ix. 2008.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
17
|
Yang H, Li TW, Ko KS, Xia M and Lu SC:
Switch from Mnt-Max to Myc-Max induces p53 and cyclin D1 expression
and apoptosis during cholestasis in mouse and human hepatocytes.
Hepatology. 49:860–870. 2009. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
18
|
Yang H, Li TW, Peng J, Tang X, Ko KS, Xia
M and Aller MA: A mouse model of cholestasis-associated
cholangiocarcinoma and transcription factors involved in
progression. Gastroenterology. 141(378–388): 388e371-374. 2011.
|
|
19
|
Zhao X, Fu J, Xu A, Yu L, Zhu J, Dai R, Su
B, Luo T, Li N, Qin W, et al: Gankyrin drives malignant
transformation of chronic liver damage-mediated fibrosis via the
Rac1/JNK pathway. Cell Death Dis. 6:e17512015. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
20
|
Quelle DE, Ashmun RA, Shurtleff SA, Kato
JY, Bar-Sagi D, Roussel MF and Sherr CJ: Overexpression of mouse
D-type cyclins accelerates G1 phase in rodent fibroblasts. Genes
Dev. 7:1559–1571. 1993. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
21
|
Sherr CJ and Roberts JM: CDK inhibitors:
Positive and negative regulators of G1-phase progression. Genes
Dev. 13:1501–1512. 1999. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
22
|
Motti ML, Califano D, Baldassarre G,
Celetti A, Merolla F, Forzati F, Napolitano M, Tavernise B, Fusco A
and Viglietto G: Reduced E-cadherin expression contributes to the
loss of p27kip1-mediated mechanism of contact inhibition in thyroid
anaplastic carcinomas. Carcinogenesis. 26:1021–1034. 2005.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
23
|
Bretones G, Delgado MD and León J: Myc and
cell cycle control. Biochim Biophys Acta. 1849:506–516. 2015.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
24
|
Leontieva OV, Demidenko ZN and
Blagosklonny MV: Contact inhibition and high cell density
deactivate the mammalian target of rapamycin pathway, thus
suppressing the senescence program. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA.
111:8832–8837. 2014. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
25
|
Zhao X, Zhang C, Zhou H, Xiao B, Cheng Y,
Wang J, Yao F, Duan C, Chen R, Liu Y, et al: Synergistic antitumor
activity of the combination of salubrinal and rapamycin against
human cholangiocarcinoma cells. Oncotarget. 7:85492–85501.
2016.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
26
|
Zhao B, Wei X, Li W, Udan RS, Yang Q, Kim
J, Xie J, Ikenoue T, Yu J, Li L, et al: Inactivation of YAP
oncoprotein by the Hippo pathway is involved in cell contact
inhibition and tissue growth control. Genes Dev. 21:2747–2761.
2007. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
27
|
Zeng Q and Hong W: The emerging role of
the hippo pathway in cell contact inhibition, organ size control,
and cancer development in mammals. Cancer Cell. 13:188–192. 2008.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
28
|
Zhang N, Bai H, David KK, Dong J, Zheng Y,
Cai J, Giovannini M, Liu P, Anders RA and Pan D: The Merlin/NF2
tumor suppressor functions through the YAP oncoprotein to regulate
tissue homeostasis in mammals. Dev Cell. 19:27–38. 2010. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
29
|
Berasain C, Fernández-Barrena MG and Avila
MA: New molecular interactions of c-Myc in cholangiocarcinoma may
open new therapeutic opportunities. Hepatology. 64:336–339. 2016.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
30
|
Li X, Wu C, Chen N, Gu H, Yen A, Cao L,
Wang E and Wang L: PI3K/Akt/mTOR signaling pathway and targeted
therapy for glioblastoma. Oncotarget. 7:33440–33450. 2016.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
31
|
Kim LC, Cook RS and Chen J: mTORC1 and
mTORC2 in cancer and the tumor microenvironment. Oncogene.
36:2191–2201. 2017. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
32
|
Yothaisong S, Dokduang H, Techasen A,
Namwat N, Yongvanit P, Bhudhisawasdi V, Puapairoj A, Riggins GJ and
Loilome W: Increased activation of PI3K/AKT signaling pathway is
associated with cholangiocarcinoma metastasis and PI3K/mTOR
inhibition presents a possible therapeutic strategy. Tumour Biol.
34:3637–3648. 2013. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
33
|
Turato C, Cannito S, Simonato D, Villano
G, Morello E, Terrin L, Quarta S, Biasiolo A, Ruvoletto M, Martini
A, et al: SerpinB3 and Yap interplay increases Myc oncogenic
activity. Sci Rep. 5:177012015. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
34
|
Zhou L, Ercolano E, Ammoun S, Schmid MC,
Barczyk MA and Hanemann CO: Merlin-deficient human tumors show loss
of contact inhibition and activation of Wnt/β-catenin signaling
linked to the PDGFR/Src and Rac/PAK pathways. Neoplasia.
13:1101–1112. 2011. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|