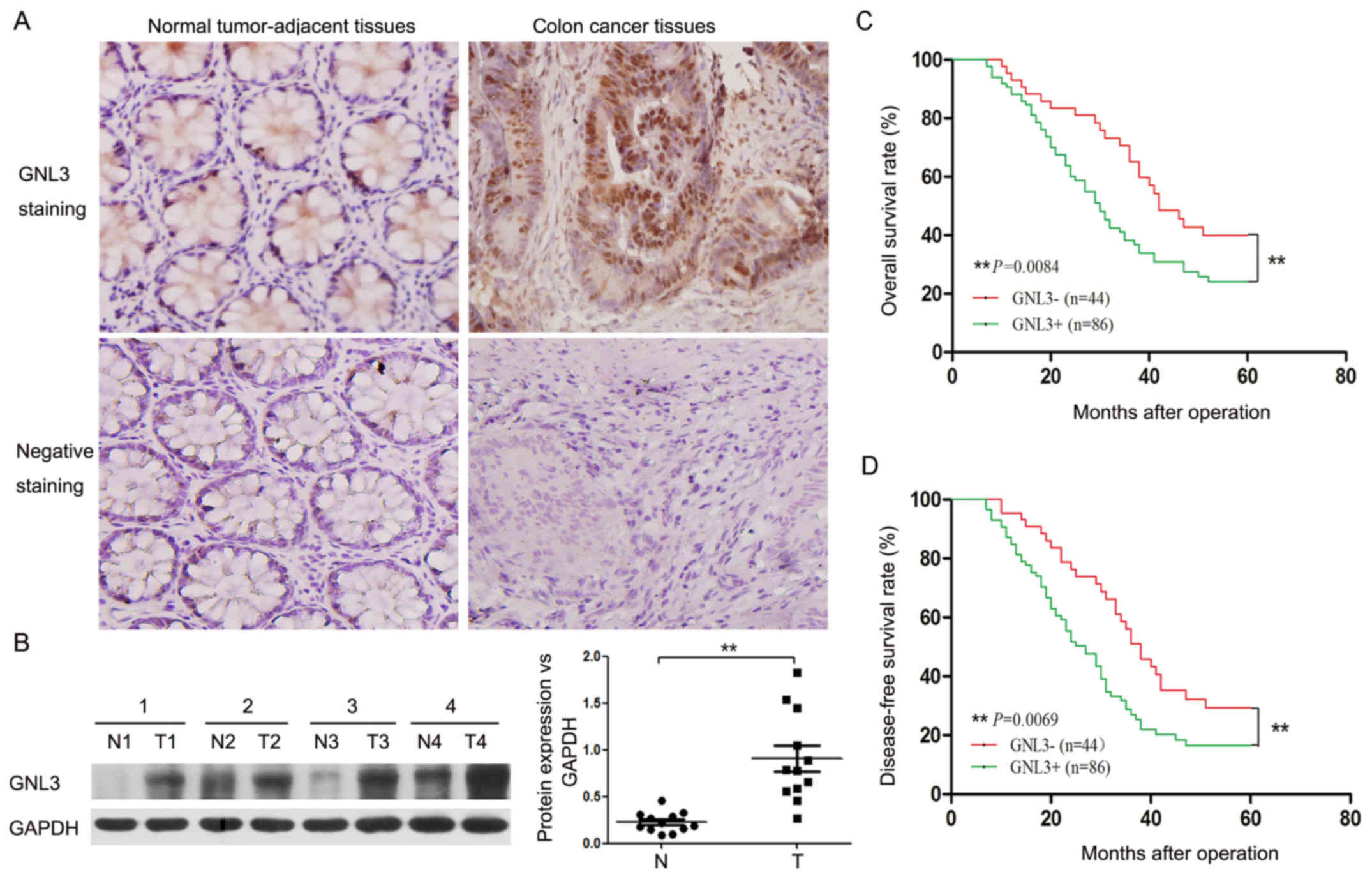
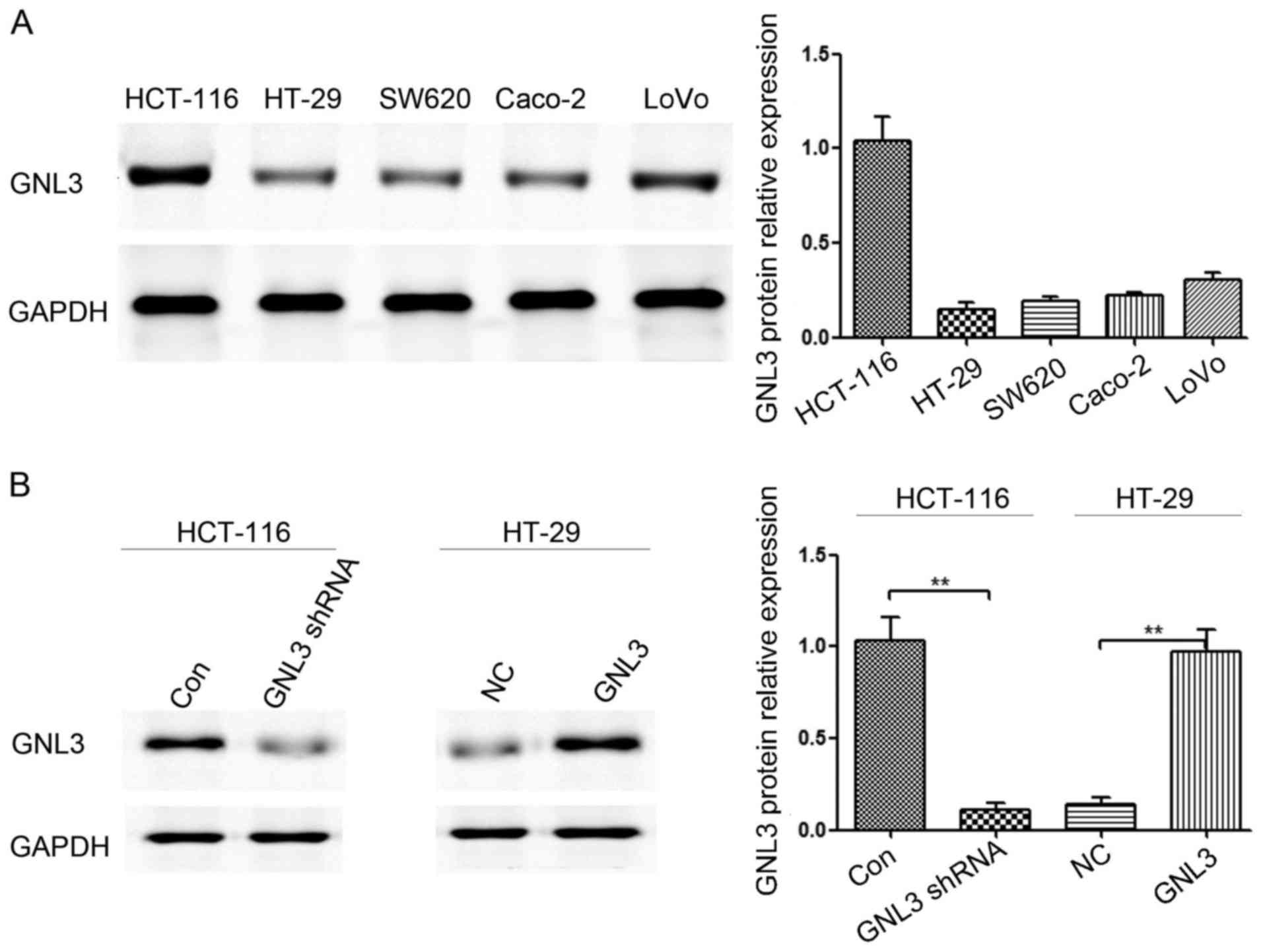
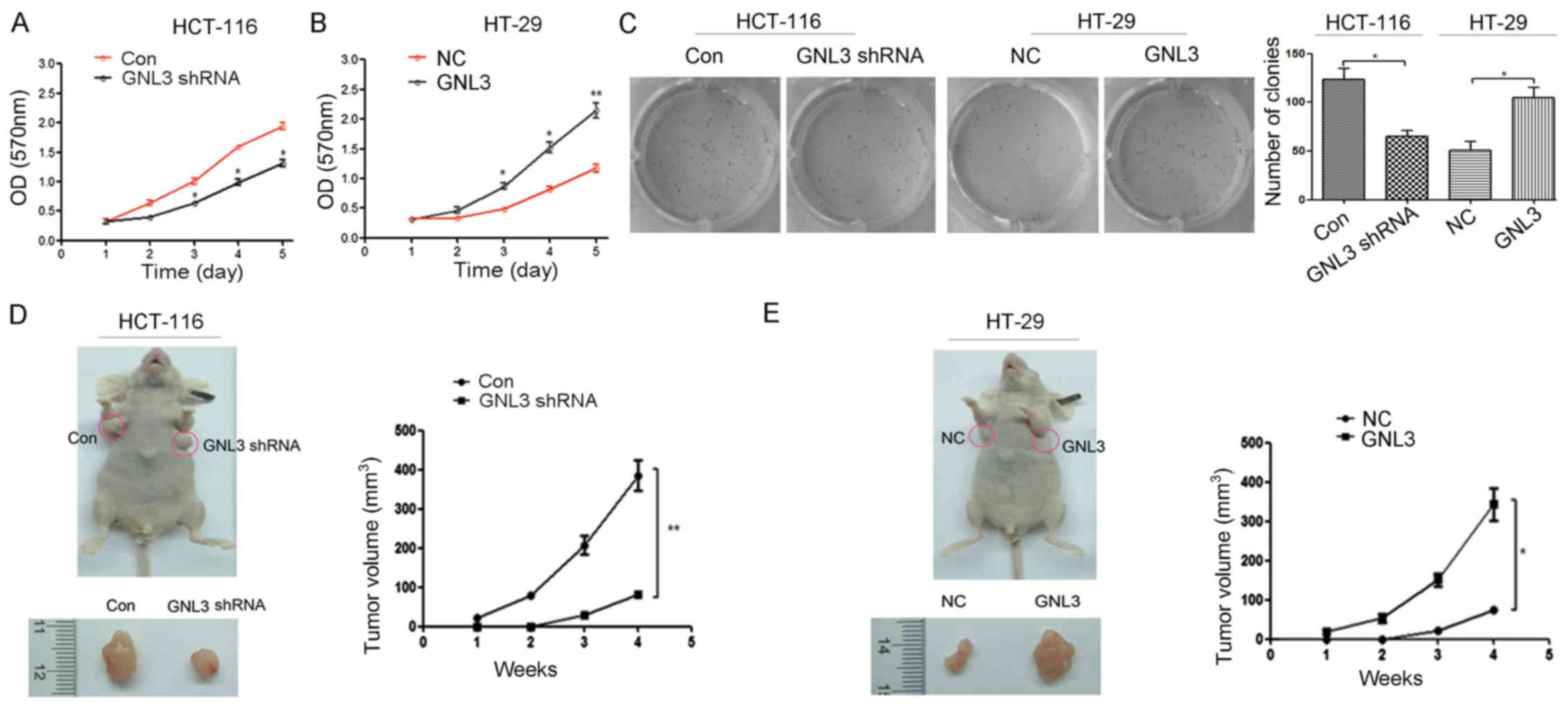
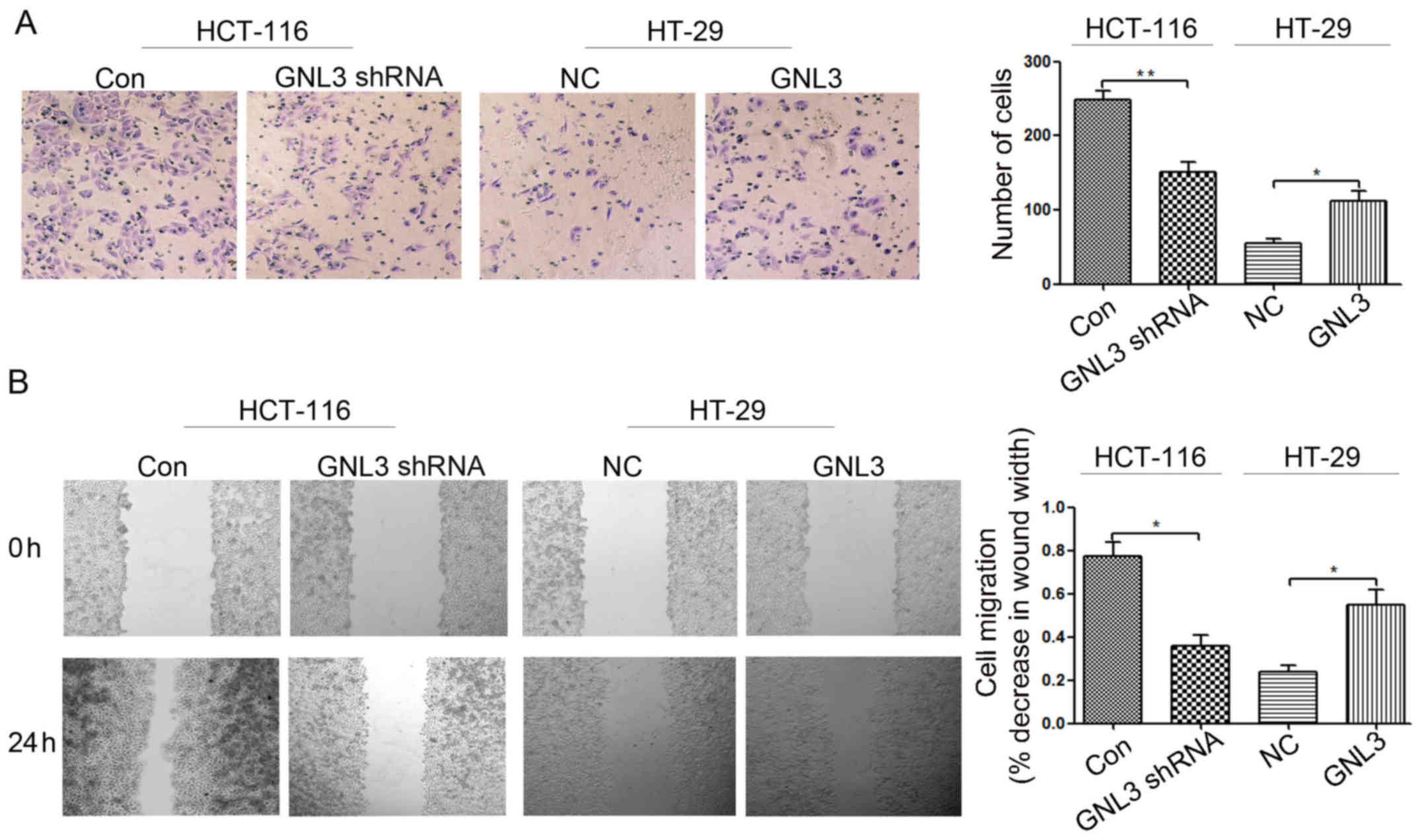
|
1
|
Torre LA, Bray F, Siegel RL, Ferlay J,
Lortet-Tieulent J and Jemal A: Global cancer statistics, 2012. CA
Cancer J Clin. 65:87–108. 2015. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
2
|
Nieto MA: Epithelial-mesenchymal
transitions in development and disease: Old views and new
perspectives. Int J Dev Biol. 53:1541–1547. 2009. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
3
|
Yang Y, Liu Q, Zhang H, Zhao H, Mao R, Li
Z, Ya S, Jia C and Bao Y: Silencing of GP73 inhibits invasion and
metastasis via suppression of epithelial-mesenchymal transition in
hepatocellular carcinoma. Oncol Rep. 37:1182–1188. 2017. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
4
|
Thiery JP: Epithelial-mesenchymal
transitions in tumour progression. Nat Rev Cancer. 2:442–454. 2002.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
5
|
Thiery JP and Sleeman JP: Complex networks
orchestrate epithelial-mesenchymal transitions. Nat Rev Mol Cell
Biol. 7:131–142. 2006. View
Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
6
|
Yang J and Weinberg RA:
Epithelial-mesenchymal transition: At the crossroads of development
and tumor metastasis. Dev Cell. 14:818–829. 2008. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
7
|
Mani SA, Guo W, Liao MJ, Eaton EN, Ayyanan
A, Zhou AY, Brooks M, Reinhard F, Zhang CC, Shipitsin M, et al: The
epithelial-mesenchymal transition generates cells with properties
of stem cells. Cell. 133:704–715. 2008. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
8
|
Lamouille S, Xu J and Derynck R: Molecular
mechanisms of epithelial-mesenchymal transition. Nat Rev Mol Cell
Biol. 15:178–196. 2014. View
Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
9
|
Chaudhury A, Hussey GS, Ray PS, Jin G, Fox
PL and Howe PH: TGF-beta-mediated phosphorylation of hnRNP E1
induces EMT via transcript-selective translational induction of
Dab2 and ILEI. Nat Cell Biol. 12:286–293. 2010.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
10
|
Timmerman LA, Grego-Bessa J, Raya A,
Bertrán E, Pérez-Pomares JM, Díez J, Aranda S, Palomo S, McCormick
F, Izpisúa-Belmonte JC, et al: Notch promotes
epithelial-mesenchymal transition during cardiac development and
oncogenic transformation. Genes Dev. 18:99–115. 2004. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
11
|
Huber MA, Azoitei N, Baumann B, Grünert S,
Sommer A, Pehamberger H, Kraut N, Beug H and Wirth T: NF-kappaB is
essential for epithelial-mesenchymal transition and metastasis in a
model of breast cancer progression. J Clin Invest. 114:569–581.
2004. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
12
|
Leung CO, Mak WN, Kai AK, Chan KS, Lee TK,
Ng IO and Lo RC: Sox9 confers stemness properties in hepatocellular
carcinoma through Frizzled-7 mediated Wnt/β-catenin signaling.
Oncotarget. 7:29371–29386. 2016. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
13
|
Yuan X, Sun X, Shi X, Wang H, Wu G, Jiang
C, Yu D, Zhang W, Xue B and Ding Y: USP39 promotes colorectal
cancer growth and metastasis through the Wnt/β-catenin pathway.
Oncol Rep. 37:2398–2404. 2017. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
14
|
Mao Y, Xu J, Li Z, Zhang N, Yin H and Liu
Z: The role of nuclear β-catenin accumulation in the Twist2-induced
ovarian cancer EMT. PLoS One. 8:e782002013. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
15
|
Azzolin L, Panciera T, Soligo S, Enzo E,
Bicciato S, Dupont S, Bresolin S, Frasson C, Basso G, Guzzardo V,
et al: YAP/TAZ incorporation in the β-catenin destruction complex
orchestrates the Wnt response. Cell. 158:157–170. 2014. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
16
|
Stambolic V, Ruel L and Woodgett JR:
Lithium inhibits glycogen synthase kinase-3 activity and mimics
wingless signalling in intact cells. Curr Biol. 6:1664–1668. 1996.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
17
|
Tsai RY and McKay RD: A nucleolar
mechanism controlling cell proliferation in stem cells and cancer
cells. Genes Dev. 16:2991–3003. 2002. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
18
|
Tsai RY: Turning a new page on
nucleostemin and self-renewal. J Cell Sci. 127:3885–3891. 2014.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
19
|
Liu SJ, Cai ZW, Liu YJ, Dong MY, Sun LQ,
Hu GF, Wei YY and Lao WD: Role of nucleostemin in growth regulation
of gastric cancer, liver cancer and other malignancies. World J
Gastroenterol. 10:1246–1249. 2004.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
20
|
Zia-Jahromi N, Hejazi SH, Panjepour M,
Parivar K and Gharagozloo M: Comparison of nucleostemin gene
expression in CD133+ and CD133− cell
population in colon cancer cell line HT29. J Cancer Res Ther.
10:68–72. 2014. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
21
|
Meng L, Lin T, Peng G, Hsu JK, Lee S, Lin
SY and Tsai RY: Nucleostemin deletion reveals an essential
mechanism that maintains the genomic stability of stem and
progenitor cells. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA. 110:11415–11420. 2013.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
22
|
Okamoto N, Yasukawa M, Nguyen C, Kasim V,
Maida Y, Possemato R, Shibata T, Ligon KL, Fukami K, Hahn WC, et
al: Maintenance of tumor initiating cells of defined genetic
composition by nucleostemin. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA.
108:20388–20393. 2011. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
23
|
Lin T, Ibrahim W, Peng CY, Finegold MJ and
Tsai RY: A novel role of nucleostemin in maintaining the genome
integrity of dividing hepatocytes during mouse liver development
and regeneration. Hepatology. 58:2176–2187. 2013. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
24
|
Meng L, Lin T and Tsai RY: Nucleoplasmic
mobilization of nucleostemin stabilizes MDM2 and promotes G2-M
progression and cell survival. J Cell Sci. 121:4037–4046. 2008.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
25
|
Tsai RY and McKay RD: A multistep,
GTP-driven mechanism controlling the dynamic cycling of
nucleostemin. J Cell Biol. 168:179–184. 2005. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
26
|
Yamashita M, Nitta E, Nagamatsu G,
Ikushima YM, Hosokawa K, Arai F and Suda T: Nucleostemin is
indispensable for the maintenance and genetic stability of
hematopoietic stem cells. Biochem Biophys Res Commun. 441:196–201.
2013. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
27
|
Zhu Q, Yasumoto H and Tsai RY:
Nucleostemin delays cellular senescence and negatively regulates
TRF1 protein stability. Mol Cell Biol. 26:9279–9290. 2006.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
28
|
Zhang G, Zhang Q, Zhang Q, Yin L, Li S,
Cheng K, Zhang Y, Xu H and Wu W: Expression of nucleostemin,
epidermal growth factor and epidermal growth factor receptor in
human esophageal squamous cell carcinoma tissues. J Cancer Res Clin
Oncol. 136:587–594. 2010. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
29
|
Hu B, Hua L, Ni W, Wu M, Yan D, Chen Y, Lu
C, Chen B and Wan C: Nucleostemin/GNL3 promotes nucleolar
polyubiquitylation of p27(kip1) to drive hepatocellular carcinoma
progression. Cancer Lett. 388:220–229. 2017. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
30
|
Li W, Wang Z, Zha L, Kong D, Liao G and Li
H: HMGA2 regulates epithelial-mesenchymal transition and the
acquisition of tumor stem cell properties through TWIST1 in gastric
cancer. Oncol Rep. 37:185–192. 2017. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
31
|
Xu MZ, Yao TJ, Lee NPY, Ng IO, Chan YT,
Zender L, Lowe SW, Poon RT and Luk JM: Yes-associated protein is an
independent prognostic marker in hepatocellular carcinoma. Cancer.
115:4576–4585. 2009. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
32
|
Zha L, Zhang J, Tang W, Zhang N, He M, Guo
Y and Wang Z: HMGA2 elicits EMT by activating the Wnt/β-catenin
pathway in gastric cancer. Dig Dis Sci. 58:724–733. 2013.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
33
|
Thiery JP, Acloque H, Huang RY and Nieto
MA: Epithelial-mesenchymal transitions in development and disease.
Cell. 139:871–890. 2009. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
34
|
Lee M, Williams KA, Hu Y, Andreas J, Patel
SJ, Zhang S and Crawford NP: GNL3 and SKA3 are novel prostate
cancer metastasis susceptibility genes. Clin Exp Metastasis.
32:769–782. 2015. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
35
|
Xie Y and Wang B: Downregulation of
TNFAIP2 suppresses proliferation and metastasis in esophageal
squamous cell carcinoma through activation of the Wnt/β-catenin
signaling pathway. Oncol Rep. 37:2920–2928. 2017. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
36
|
Bao Z, Wang Y, Yang L, Wang L, Zhu L, Ban
N, Fan S, Chen W, Sun J, Shen C, et al: Nucleostemin promotes the
proliferation of human glioma via Wnt/beta-Catenin pathway.
Neuropathology. 36:237–249. 2016. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|