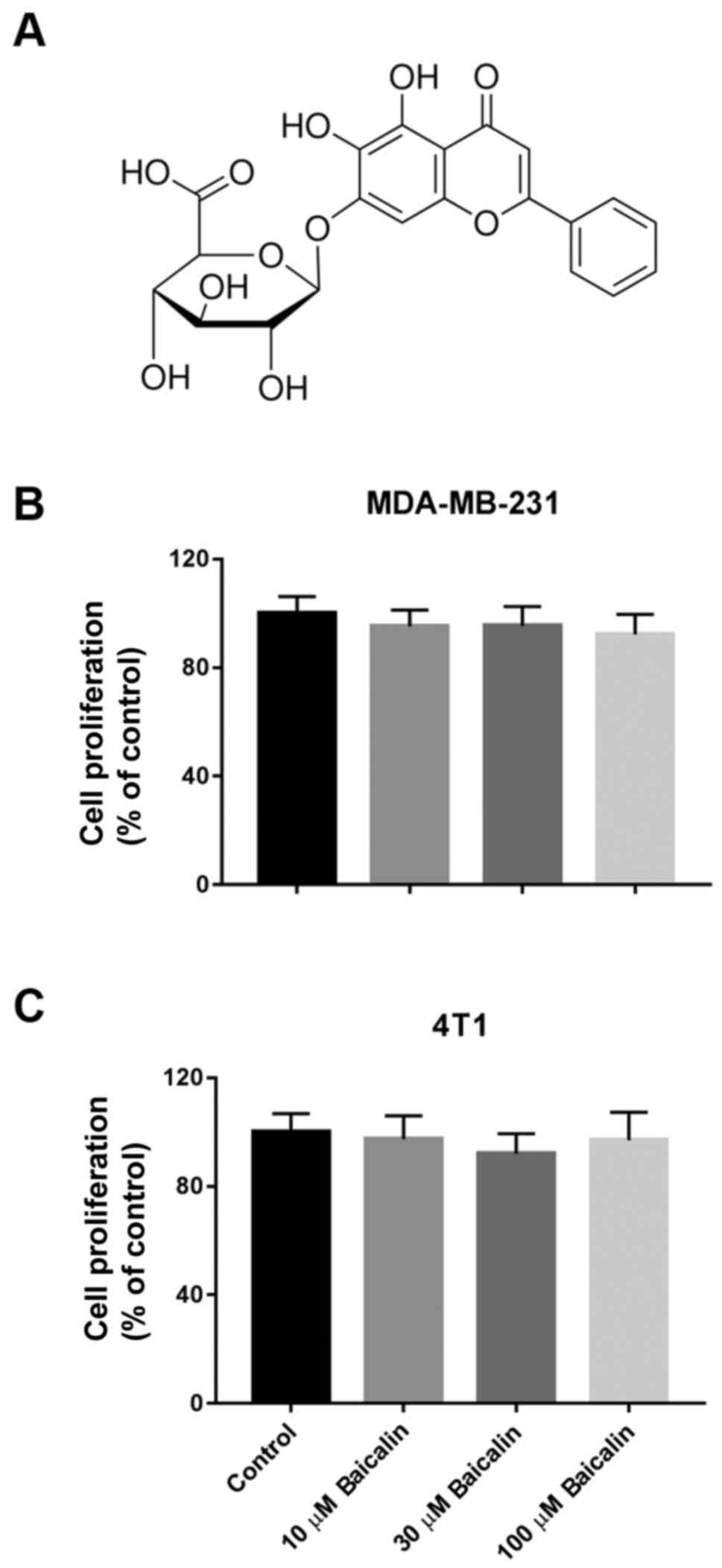
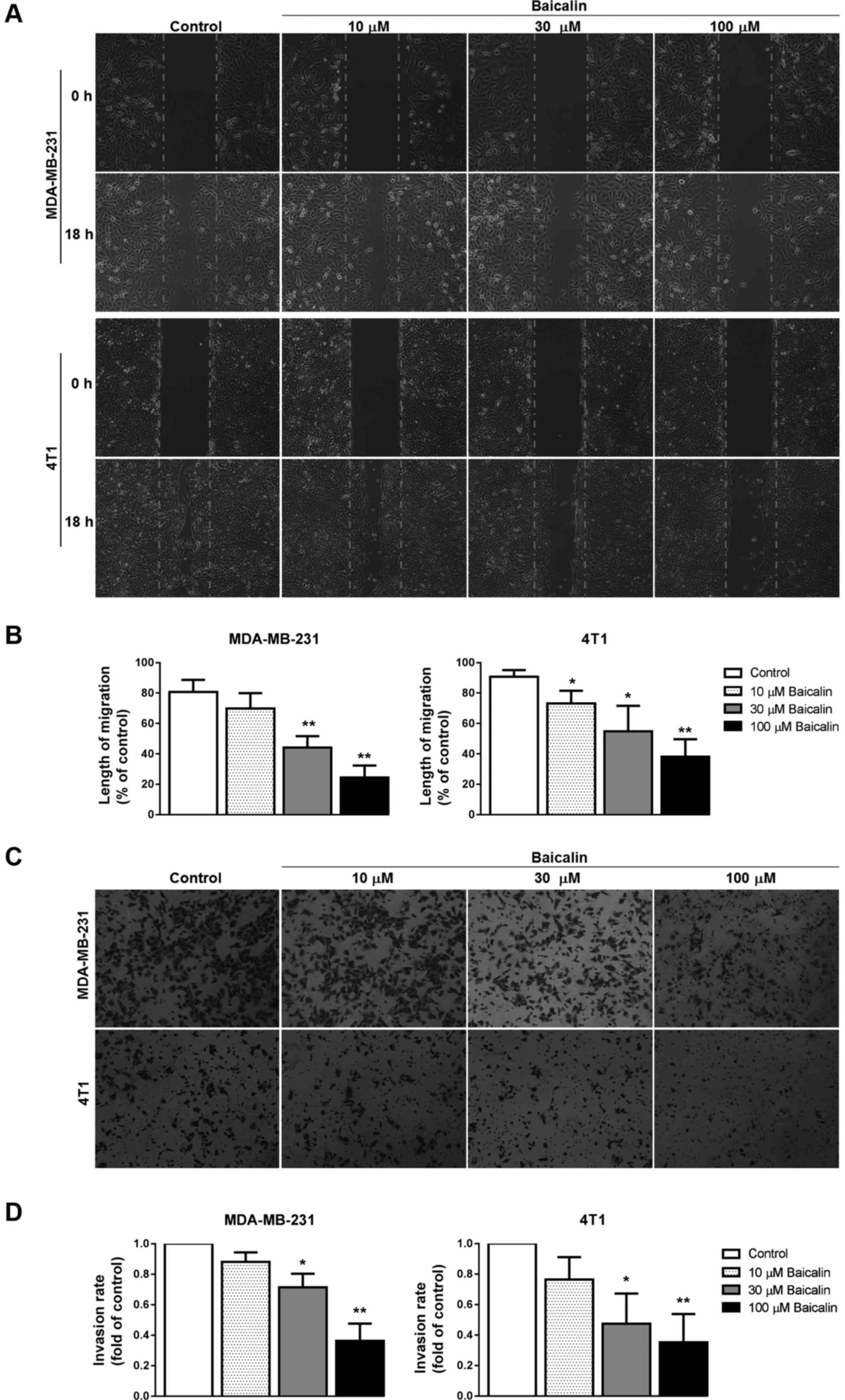
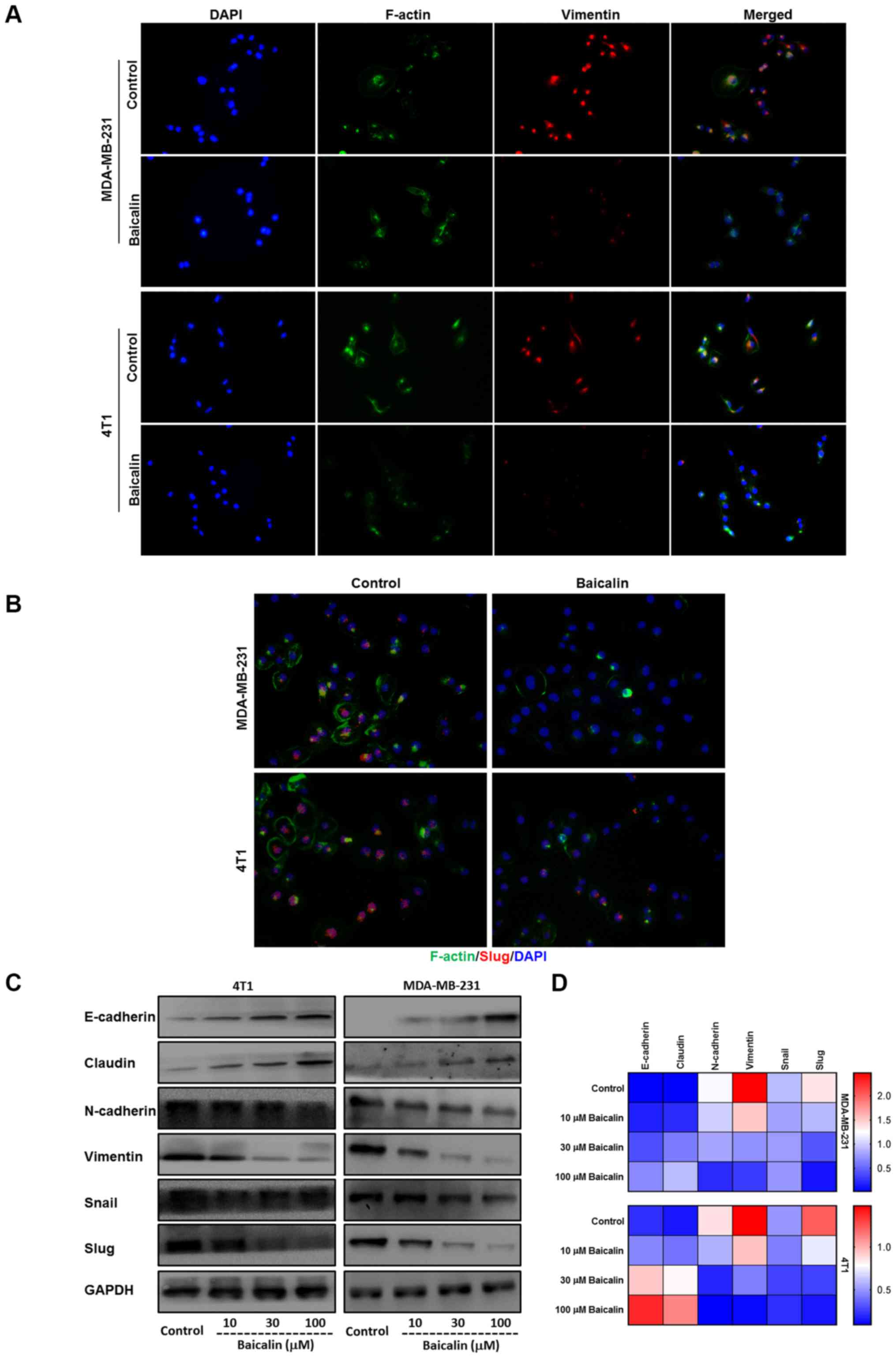
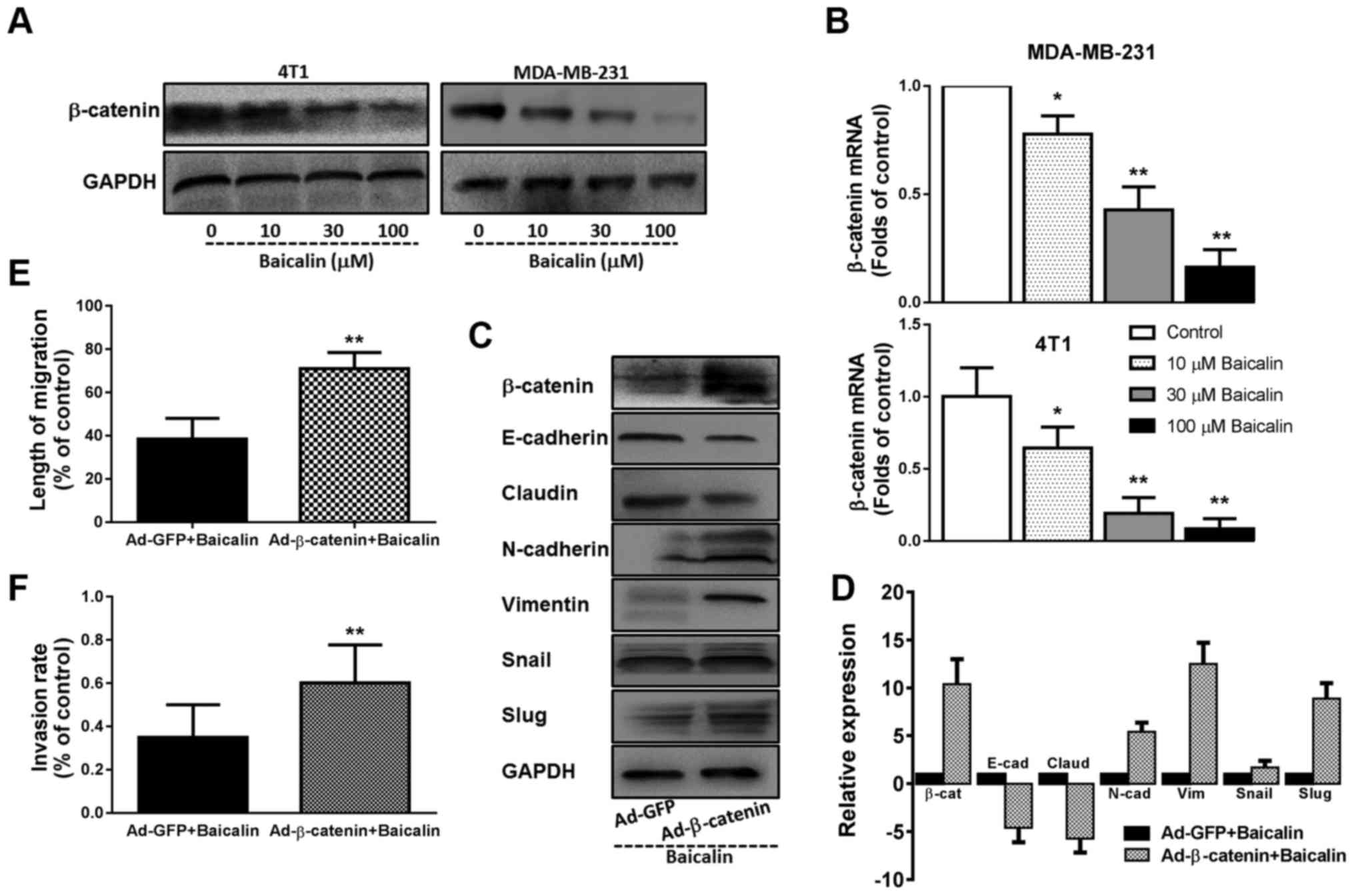
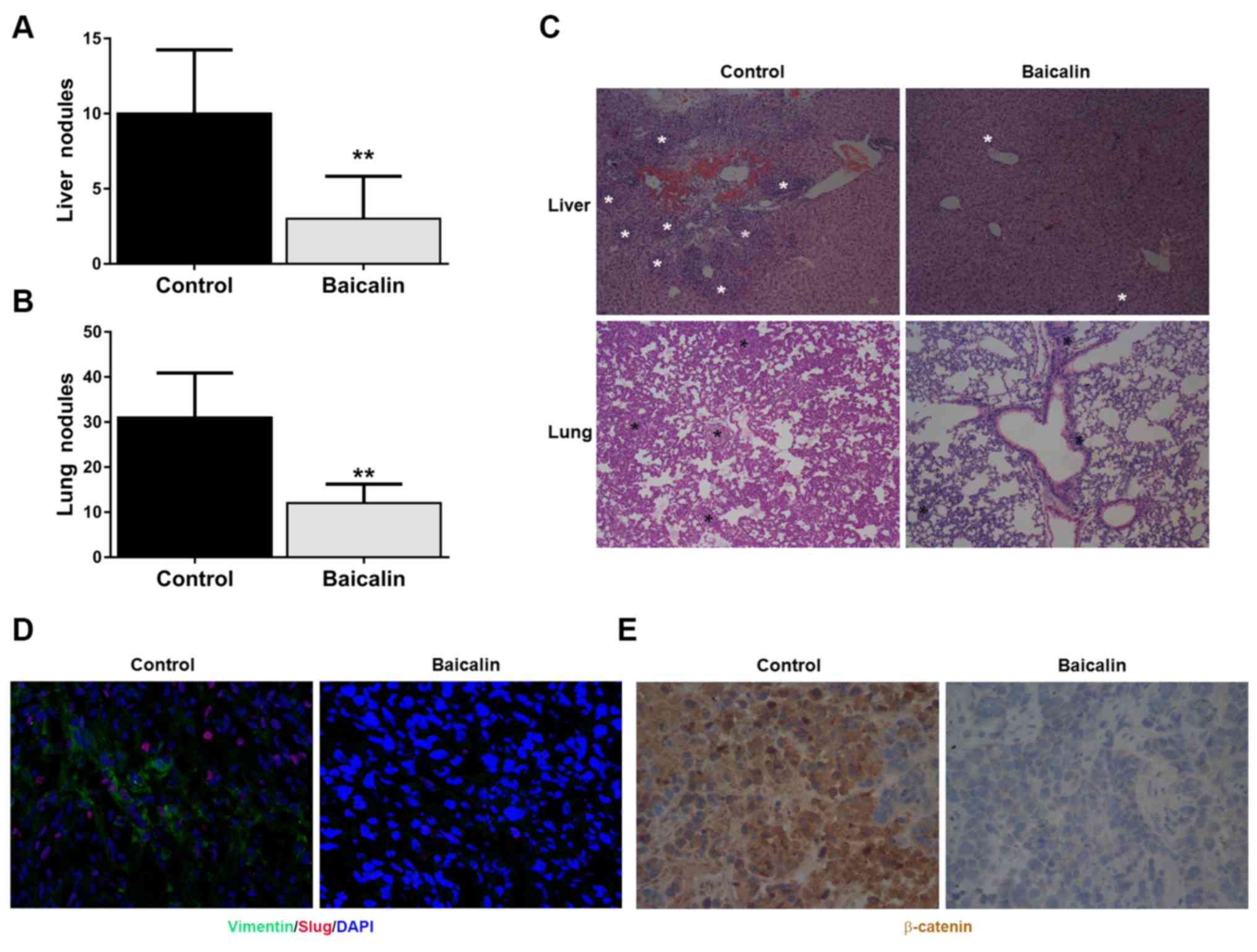
|
1
|
Torre LA, Bray F, Siegel RL, Ferlay J,
Lortet-Tieulent J and Jemal A: Global cancer statistics, 2012. CA
Cancer J Clin. 65:87–108. 2015. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
2
|
Chen W, Zheng R, Baade PD, Zhang S, Zeng
H, Bray F, Jemal A, Yu XQ and He J: Cancer statistics in China,
2015. CA Cancer J Clin. 66:115–132. 2016. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
3
|
Arnedos M, Vicier C, Loi S, Lefebvre C,
Michiels S, Bonnefoi H and Andre F: Precision medicine for
metastatic breast cancer - limitations and solutions. Nat Rev Clin
Oncol. 12:693–704. 2015. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
4
|
Samatov TR, Tonevitsky AG and Schumacher
U: Epithelial-mesenchymal transition: Focus on metastatic cascade,
alternative splicing, non-coding RNAs and modulating compounds. Mol
Cancer. 12:1072013. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
5
|
Drasin DJ, Robin TP and Ford HL: Breast
cancer epithelial-to-mesenchymal transition: Examining the
functional consequences of plasticity. Breast Cancer Res.
13:2262011. View
Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
6
|
Takebe N, Warren RQ and Ivy SP: Breast
cancer growth and metastasis: Interplay between cancer stem cells,
embryonic signaling pathways and epithelial-to-mesenchymal
transition. Breast Cancer Res. 13:2112011. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
7
|
Pan MH and Ho CT: Chemopreventive effects
of natural dietary compounds on cancer development. Chem Soc Rev.
37:2558–2574. 2008. View
Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
8
|
Peng-Fei L, Fu-Gen H, Bin-Bin D,
Tian-Sheng D, Xiang-Lin H and Ming-Qin Z: Purification and
antioxidant activities of baicalin isolated from the root of
huangqin (Scutellaria baicalensis gcorsi). J Food Sci
Technol. 50:615–619. 2013. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
9
|
Burnett BP, Jia Q, Zhao Y and Levy RM: A
medicinal extract of Scutellaria baicalensis and Acacia
catechu acts as a dual inhibitor of cyclooxygenase and
5-lipoxygenase to reduce inflammation. J Med Food. 10:442–451.
2007. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
10
|
Li BQ, Fu T, Gong WH, Dunlop N, Kung H,
Yan Y, Kang J and Wang JM: The flavonoid baicalin exhibits
anti-inflammatory activity by binding to chemokines.
Immunopharmacology. 49:295–306. 2000. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
11
|
Li BQ, Fu T, Dongyan Y, Mikovits JA,
Ruscetti FW and Wang JM: Flavonoid baicalin inhibits HIV-1
infection at the level of viral entry. Biochem Biophys Res Commun.
276:534–538. 2000. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
12
|
Shieh DE, Cheng HY, Yen MH, Chiang LC and
Lin CC: Baicalin-induced apoptosis is mediated by Bcl-2-dependent,
but not p53-dependent, pathway in human leukemia cell lines. Am J
Chin Med. 34:245–261. 2006. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
13
|
Chen H, Gao Y, Wu J, Chen Y, Chen B, Hu J
and Zhou J: Exploring therapeutic potentials of baicalin and its
aglycone baicalein for hematological malignancies. Cancer Lett.
354:5–11. 2014. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
14
|
Yu Y, Pei M and Li L: Baicalin induces
apoptosis in hepatic cancer cells in vitro and suppresses tumor
growth in vivo. Int J Clin Exp Med. 8:8958–8967. 2015.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
15
|
Shu YJ, Bao RF, Wu XS, Weng H, Ding Q, Cao
Y, Li ML, Mu JS, Wu WG, Ding QC, et al: Baicalin induces apoptosis
of gallbladder carcinoma cells in vitro via a
mitochondrial-mediated pathway and suppresses tumor growth in vivo.
Anticancer Agents Med Chem. 14:1136–1145. 2014. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
16
|
Gong WY, Wu JF, Liu BJ, Zhang HY, Cao YX,
Sun J, Lv YB, Wu X and Dong JC: Flavonoid components in
Scutellaria baicalensis inhibit nicotine-induced
proliferation, metastasis and lung cancer-associated inflammation
in vitro. Int J Oncol. 44:1561–1570. 2014. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
17
|
Yang BL, Chen HJ, Chen YG, Gu YF, Zhang
SP, Lin Q and Sun Y: Inhibitory effects of baicalin on orthotopic
xenografts of colorectal cancer cells that are deficient in a
mismatch repair gene in nude mice. Int J Colorectal Dis.
28:547–553. 2013. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
18
|
Wang XF, Zhou QM, Du J, Zhang H, Lu YY and
Su SB: Baicalin suppresses migration, invasion and metastasis of
breast cancer via p38MAPK signaling pathway. Anticancer Agents Med
Chem. 13:923–931. 2013. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
19
|
Lin C, Tsai SC, Tseng MT, Peng SF, Kuo SC,
Lin MW, Hsu YM, Lee MR, Amagaya S, Huang WW, et al: AKT
serine/threonine protein kinase modulates baicalin-triggered
autophagy in human bladder cancer T24 cells. Int J Oncol.
42:993–1000. 2013. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
20
|
Gao J, Morgan WA, Sanchez-Medina A and
Corcoran O: The ethanol extract of Scutellaria baicalensis
and the active compounds induce cell cycle arrest and apoptosis
including upregulation of p53 and Bax in human lung cancer cells.
Toxicol Appl Pharmacol. 254:221–228. 2011. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
21
|
Wang B, Wan JY, Zhang L and Min S:
Synthetic RGDS peptide attenuates mechanical ventilation-induced
lung injury in rats. Exp Lung Res. 38:204–210. 2012. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
22
|
Tao Z, Shi A, Lu C, Song T, Zhang Z and
Zhao J: Breast cancer: Epidemiology and etiology. Cell Biochem
Biophys. 72:333–338. 2015. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
23
|
Pulaski BA and Ostrand-Rosenberg S: Mouse
4T1 breast tumor model. Curr Protoc Immunol: Chapter 20: Unit 20.2.
2001.doi: 10.1002/0471142735.im2002s39. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
24
|
Chen WC, Kuo TH, Tzeng YS and Tsai YC:
Baicalin induces apoptosis in SW620 human colorectal carcinoma
cells in vitro and suppresses tumor growth in vivo. Molecules.
17:3844–3857. 2012. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
25
|
Dong LH, Wen JK, Miao SB, Jia Z, Hu HJ,
Sun RH, Wu Y and Han M: Baicalin inhibits PDGF-BB-stimulated
vascular smooth muscle cell proliferation through suppressing
PDGFRβ-ERK signaling and increase in p27 accumulation and prevents
injury-induced neointimal hyperplasia. Cell Res. 20:1252–1262.
2010. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
26
|
Huang Y, Hu J, Zheng J, Li J, Wei T, Zheng
Z and Chen Y: Down-regulation of the PI3K/Akt signaling pathway and
induction of apoptosis in CA46 Burkitt lymphoma cells by baicalin.
J Exp Clin Cancer Res. 31:482012. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
27
|
Grzegrzolka J, Biala M, Wojtyra P,
Kobierzycki C, Olbromski M, Gomulkiewicz A, Piotrowska A, Rys J,
Podhorska-Okolow M and Dziegiel P: Expression of EMT markers SLUG
and TWIST in breast cancer. Anticancer Res. 35:3961–3968.
2015.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
28
|
Siegel RL, Miller KD and Jemal A: Cancer
statistics, 2016. CA Cancer J Clin. 66:7–30. 2016. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
29
|
Nickel A and Stadler SC: Role of
epigenetic mechanisms in epithelial-to-mesenchymal transition of
breast cancer cells. Transl Res. 165:126–142. 2015. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
30
|
Thiery JP: Epithelial-mesenchymal
transitions in tumour progression. Nat Rev Cancer. 2:442–454. 2002.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
31
|
Bulfoni M, Gerratana L, Del Ben F,
Marzinotto S, Sorrentino M, Turetta M, Scoles G, Toffoletto B,
Isola M, Beltrami CA, et al: In patients with metastatic breast
cancer the identification of circulating tumor cells in
epithelial-to-mesenchymal transition is associated with a poor
prognosis. Breast Cancer Res. 18:302016. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
32
|
Wang LK, Pan SH, Chang YL, Hung PF, Kao
SH, Wang WL, Lin CW, Yang SC, Liang CH, Wu CT, et al:
MDA-9/Syntenin-Slug transcriptional complex promote
epithelial-mesenchymal transition and invasion/metastasis in lung
adenocarcinoma. Oncotarget. 7:386–401. 2016.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
33
|
Ganesan R, Mallets E and Gomez-Cambronero
J: The transcription factors Slug (SNAI2) and Snail (SNAI1)
regulate phospholipase D (PLD) promoter in opposite ways towards
cancer cell invasion. Mol Oncol. 10:663–676. 2016. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
34
|
Hino M, Kamo M, Saito D, Kyakumoto S,
Shibata T, Mizuki H and Ishisaki A: Transforming growth factor-β1
induces invasion ability of HSC-4 human oral squamous cell
carcinoma cells through the Slug/Wnt-5b/MMP-10 signalling axis. J
Biochem. 159:631–640. 2016. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
35
|
Tsai JH, Hsu LS, Lin CL, Hong HM, Pan MH,
Way TD and Chen WJ: 3,5,4-Trimethoxystilbene, a natural
methoxylated analog of resveratrol, inhibits breast cancer cell
invasiveness by downregulation of PI3K/Akt and Wnt/β-catenin
signaling cascades and reversal of epithelial-mesenchymal
transition. Toxicol Appl Pharmacol. 272:746–756. 2013. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
36
|
Chung H, Choi HS, Seo EK, Kang DH and Oh
ES: Baicalin and baicalein inhibit transforming growth
factor-β1-mediated epithelial-mesenchymal transition in human
breast epithelial cells. Biochem Biophys Res Commun. 458:707–713.
2015. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
37
|
Ghahhari NM and Babashah S: Interplay
between microRNAs and WNT/β-catenin signalling pathway regulates
epithelial-mesenchymal transition in cancer. Eur J Cancer.
51:1638–1649. 2015. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
38
|
Nowicki A, Sporny S and Duda-Szymańska J:
β-catenin as a prognostic factor for prostate cancer (PCa). Cent
European J Urol. 65:119–123. 2012. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
39
|
Chien AJ, Moore EC, Lonsdorf AS,
Kulikauskas RM, Rothberg BG, Berger AJ, Major MB, Hwang ST, Rimm DL
and Moon RT: Activated Wnt/beta-catenin signaling in melanoma is
associated with decreased proliferation in patient tumors and a
murine melanoma model. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA. 106:1193–1198. 2009.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
40
|
Cuello-Carrión FD, Shortrede JE,
Alvarez-Olmedo D, Cayado-Gutiérrez N, Castro GN, Zoppino FC,
Guerrero M, Martinis E, Wuilloud R, Gómez NN, et al: HER2 and
β-catenin protein location: Importance in the prognosis of breast
cancer patients and their correlation when breast cancer cells
suffer stressful situations. Clin Exp Metastasis. 32:151–168. 2015.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|