Introduction
Pancreatic neoplasms are highly malignant tumors and
a major cause of cancer-related mortality worldwide (1). The majority of pancreatic carcinomas
are pancreatic ductal adenocarcinomas (PDACs). In recent years, the
5-year survival rate of PDAC patients has not significantly
improved, and remains at ~6% (2).
The prognosis of PDAC is extremely poor, which is mostly ascribed
to the fast growth, high migration, invasiveness and recurrence
rates (3). To improve the
efficiency of pancreatic cancer treatment, researchers must aim to
understand the mechanisms underlying the migration, invasion and
apoptosis of PDAC.
Ubiquitin specific peptidase 9, X-linked (USP9X), a
deubiquitination enzyme, is a multifunctional post-translational
modifier that regulates many aspects of cell physiology (4,5), such
as DNA repair, and regulation of cell cycle and several signaling
pathways. USP9X expression constantly changes in tumor progression
(6,7). Abnormal USP9X expression has been
confirmed in several neoplasms, including lymphoma (8), colorectal cancer (9) and hepatocellular carcinoma (10). However, whether USP9X acts as a
proto-oncogene or tumor-suppressor gene in pancreatic cancer cells
is still controversial. Cox et al reported that USP9X
possesses growth promotor functions in several established
pancreatic cell lines (11), while
Pérez-Mancera et al states that USP9X acts as a
tumor-suppressor gene at the early stage of PDAC formation in mice
(12). Thus, the concrete mechanism
remains unclear as to how USP9X regulates PDAC development. In the
present study, we discussed the effect of USP9X on
epithelial-mesenchymal transition (EMT) in PANC-1 cells, aiming to
understand its effect on cell migration and invasion. In terms of
apoptosis, we observed the effect of USP9X downregulation on
survivin expression.
EMT is a bio-process in which epithelial cells are
transformed via specific procedures into a mesenchymal phenotype,
and it is the molecular basis underlying the occurrence, invasion
and metastasis of tumors (13). EMT
plays an important role in the metastasis and invasion of neoplasms
(14). It has been confirmed that
EMT can be promoted by Snail and Twist genes, which induce the
migration and invasion of tumor cells (15,16).
However, the specific connection between USP9X and EMT in PDAC and
the effect of USP9X on PDAC remain poorly understood.
Survivin, which is highly inhibitory against cell
apoptosis, was first identified at Altieri Laboratory of Yale
University in 1997 by screening a human genomic library using
effector cell protease receptor-1 (17). The bio-functions of survivin mainly
involve the regulation of the cell cycle and stress response,
mitosis promotion, cell and vascular proliferation, apoptosis
inhibition and cancer cell autophagy regulation (18). However, high survivin expression has
been detected in several tumors (19). Liu et al found that survivin
is degraded by the ubiquitin proteasome pathway (20). Yet, the relationship between
survivin and USP9X in pancreatic cancer is also unknown.
In the present study, we demonstrated that USP9X
acts as a tumor metastasis supporter in PANC-1 cells, and
downregulation of USP9X expression inhibited the migration and
invasion of PANC-1 cells, while high expression of USP9X inhibited
the apoptosis of PANC-1 cells. Therefore, USP9X functioned as an
oncogene in PANC-1 cells and is closely related with the expression
of Snail, Twist and survivin.
Materials and methods
Patients and samples
Tumor and paired adjacent non-tumor tissues for
immunohistochemical (IHC) analysis were obtained from 55 patients
with malignant pancreatic tumors, who underwent surgical resection
at The Affiliated Hospital of Xuzhou Medical University between
2009 and 2012 (Table I). None of
the patients received chemotherapy or radiotherapy before surgery.
Written informed consent was received from all patients or relevant
family members. The present study was approved by the Ethics
Committee of The Affiliated Hospital of Xuzhou Medical
University.
 | Table I.Clinicopathological association of
USP9X expression in pancreatic cancer tissues. |
Table I.
Clinicopathological association of
USP9X expression in pancreatic cancer tissues.
|
|
| USP9X
expression |
|
|---|
|
|
|
|
|
|---|
| Variables | No. of cases | High n (%) | Low n (%) | P-value |
|---|
| Age
(years) |
|
|
| 0.803 |
|
<60 | 25 | 15 (27.27) | 10 (18.18) |
|
|
≥60 | 30 | 17 (30.09) | 13 (23.63) |
|
| Sex |
|
|
| 0.444 |
|
Male | 32 | 20 (36.36) | 12 (26.63) |
|
|
Female | 23 | 12 (26.63) | 11 (20.00) |
|
| Tumor size
(cm) |
|
|
| 0.262 |
|
<4.0 | 24 | 16 (29.09) | 8
(14.55) |
|
|
≥4.0 | 31 | 16 (29.09) | 15 (27.27) |
|
| Grade |
|
|
| 0.019 |
|
High | 7 | 2 (3.64) | 5 (9.09) |
|
|
Middle | 34 | 18 (32.73) | 16 (29.09) |
|
|
Low | 14 | 12 (26.63) | 2 (3.64) |
|
| Lymph node status
(metastasis) |
|
|
| 0.002 |
|
Yes | 20 | 17 (30.90) | 3 (5.45) |
|
| No | 35 | 15 (27.27) | 20 (36.36) |
|
| TNM
stagea |
|
|
| 0.006 |
| I | 25 | 9
(16.36) | 16 (29.09) |
|
| II | 28 | 22 (40.00) | 6
(10.91) |
|
| IV | 2 | 1 (1.82) | 1 (1.82) |
|
Cell culture and treatment
PANC-1, a human pancreatic cancer cell line, was
provided by Professor Changqing Su (Shanghai Oriental Hepatic
Hospital of China). The cells were first cultured in Dulbecco's
modified Eagles medium (DMEM) containing 10% fetal bovine serum
(FBS) (both from HyClone, Shanghai, China), 100 µg/ml streptomycin
and 100 U/ml penicillin. Then, the cells were routinely incubated
in a humidified atmosphere at 37°C in 5% CO2. The medium
was refreshed every two days. Cell digestion and passage were
conducted using 0.25% trypsin.
IHC analysis
Paraffin-embedded specimens were stained according
to the kit manual. The primary antibody was anti-USP9X [1:1,000;
Cell Signaling Technology (CST), Beverly, MA, USA]. In the IHC
analysis, the staining intensity was rated as follows: 0, 1, 2 and
3 points: negative, weak, moderate and strong intensity,
respectively (21). The percentage
of positively-stained cells was rated as follows: 0, 1, 2, 3 and 4
points: 0, 1–10, 11–50, 51–80 and >80%, respectively. Then, the
total score of immunoreactivity for each case was determined by
multiplying the two sub-scores above. The average score from all
five random fields at a magnification of ×400 was used as the
histological score. Tumors were categorized by the histological
score into a negative group (≤4) and a positive group (>4). The
results were analyzed using Chi-square test.
shRNA transfection
USP9X-treated cells were plated into 6-well plates
(3.0×105 cells/well), for 24 h of adherence, and then
transfected with shRNA (GenePharma, Shanghai, China; shRNA group)
using SiLenFect (Bio-Rad Laboratories, Inc., Hercules, CA, USA).
The sequence of shRNA was: GCTGCT
AGGTTCCTCTTTCAAGAGAAGTAAAGAGGAACCTAG CAGCTT. In the vector group,
the cells were transfected with NC-shRNA in the same way following
the manufacturer's instructions. After 24 h, the media were
refreshed. After 48 h, the cells were harvested for subsequent
experiments.
Wound-healing assay
For the wound-healing assays, PANC-1 cells
transfected according to the above-mentioned method were seeded in
6-well plates at a density of 2×106/well. After 24 h,
the monolayers were scratched with a sterile pipette tip, followed
by addition of serum-free medium. The sizes of the wounds were
photographed at 0, 12, and 24 h separately. Each experiment was
performed in triplicate.
Protein isolation and western
blotting
The cultured PANC-1 cells were lysed by a modified
radio-immunoprecipitation assay (RIPA) buffer (Shanghai, China)
containing 0.5 M pheylmethylsulfonyl fluoride (PMSF) and protease
inhibitor cocktail (Complete Mini; Mannheim, Germany). Then, the
homogenates were lysed on ice for 30 min. The lysates were
centrifuged at 4°C for 15 min and the supernatants were extracted.
Total proteins were quantified with a bicinchoninic acid (BCA)
protein assay kit (Pierce, Thermo Fisher Scientific, Inc., Waltham,
MA, USA). For western blotting, protein samples (50 µg) were loaded
onto 8 or 12% sodium dodecyl sulfate-polyacrylamide gel
electrophoresis (SDS-PAGE) and were then transferred onto
polyvinylidene difluoride (PVDF) membranes (Millipore, Bedford, MA,
USA). Then, the membranes were blocked with 5% non-fat milk at room
temperature for 1 h, and incubated with primary antibodies
overnight at 4°C, including anti-USP9X (1:1,000; CST),
anti-survivin (1:200; Bioworld Technology, Nanjing, China),
anti-Twist (1:1,000), anti-Snail (1:1,000), anti-N-cadherin
(1:1,000), anti-vimentin (1:1,500), anti-E-cadherin (1:1,500) (all
from ABclonal Inc., Cambridge, MA, USA) and anti-β-actin (1:1,000;
Bioworld Technology). One day later, the membranes were washed with
Tris-buffered saline and 0.05% Tween-20 (TBST), and then incubated
with anti-rabbit or anti-mouse secondary antibody at room
temperature for 1 h. The intensities of the protein bands were
assessed using ImageJ [National Institutes of Health (NIH),
Bethesda, MD, USA].
Cell migration and invasion
assays
The migration and invasion abilities of PANC-1 cells
were assessed by cell migration and Matrigel invasion assays,
respectively. After 24 h of transfection, the cells were suspended
with serum-free medium and counted. In the assays, we furnished the
invasion/migration chambers with 6.5-mm diameter tissue culture
inserts and 8.0-µm pore size polycarbonate membranes (Transwell;
Corning, Corning, NY, USA USA). For invasion assays, Matrigel (1:6;
BD Biosciences, Bedford, MA, USA) was blended with serum-free DMEM,
and 50 µl of the mixture was added into the chamber. The chambers
were set into 24-well tissue culture plates, and then put in a
sterile ultra-clean bench overnight. On the next day, after the
Matrigel was solidified, 5.0×104 PANC-1 cells were added
to the upper chamber. The total volume was 200 µl, with adequate
addition of the serum-free medium. For the migration assays, the
operation method was the same as the invasion assays, except for
the addition of Matrigel. In both trials, the lower chamber was
filled with 600 µl of 20% FBS. After 24 h of incubation at 37°C
with 5% CO2, 90% paraformaldehyde was used to fix the
cells invading the lower surfaces of the polycarbonate membranes.
Then, the cells were stained with crystal violet and counted under
a microscope. The cells were washed with phosphate-buffered saline
(PBS) two times. Then, the water on the surfaces was gently wiped
off and five views were taken for each insert.
Cell apoptosis assay
Cell apoptosis was detected by flow cytometry via a
double staining method using an Annexin V-fluorescein
isothiocyanate (FITC)-conjugated propidium iodide (PI) apoptosis
kit (KeyGen Biotech. Co, Ltd., Nanjing, China). We performed the
apoptosis assay after 48 h of transfection. PANC-1 cells were
inoculated in 6-well plates at a density of 3×105
cells/well. When the cells covered ~50% of the 6-well plates, the
6-well plates were divided into a normal control (NC group), a
negative control (vector group) and a shRNA-transfected group
(shRNA group; transfected similarly as the above method). After 48
h, the cells in the three groups were digested with 0.25% trypsin
without ethylenediamine tetraacetic acid (EDTA; Invitrogen,
Carlsbad, CA, USA). Then, the cells were washed with PBS for two
times, (each 5 min) and centrifuged at a speed of 5,000 rpm for 5
min. Next, the cells were resuspended in 500 µl of binding buffer
and stained with 5 µl Annexin V-FITC and 5 µl of PI, for 15 to 20
min of reaction in a darkroom. Finally, the three groups of cells
were stained, counted and analyzed using a flow cytometer
(FACSCalibur; BD Biosciences).
CCK-8 assay for cell viability
Cells which were transfected for 48 h were plated in
96-well plates with 5×103 cells/well. Six repetitive
wells were prepared for each group. Control wells were created
adding the same volume of culture medium. After 6, 24, 48, 72 and
96 h of incubation, the cells were then treated with 10 µl Cell
Counting Kit-8 (CCK-8) (Dojindo, Kumamoto, Japan) for another 2 h
in an incubator at 37°C. An automated microplate reader (Sunrise,
Tecan, Switzerland) was applied to assess the OD values for each
well at 450 nm.
Statistical analysis
Data are expressed as mean ± standard deviation
(SD). Differences between groups were examined by Student's t-test
or one-way analysis of variance (ANOVA). P<0.05 and P<0.01
were considered to indicate statistically significant results. All
statistical analyses were performed using SPSS (version 13.0; SPSS,
Inc., Chicago, IL, USA) and GraphPad Prism (version 5.0; GraphPad
Software, Inc., La Jolla, CA, USA).
Results
USP9X is highly expressed in human
pancreatic cancer tissues
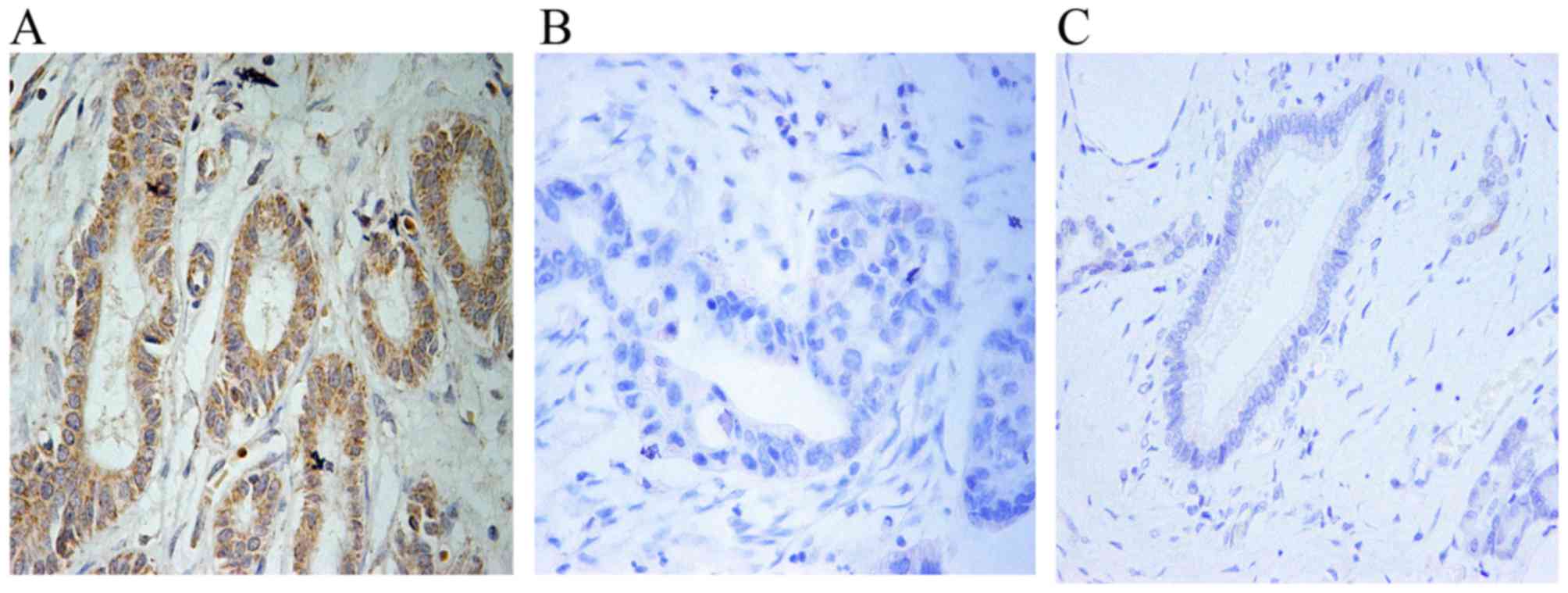
IHC analysis revealed that USP9X expression was
upregulated in 32 of 55 tumor tissues compared to the adjacent
non-tumor tissues (Fig. 1A-C and
Table I). Moreover, high expression
of USP9X was markedly associated with stage, grade and lymph node
metastasis (all P<0.05) (Table
I). The results imply that USP9X is positively correlated with
the degree of tumor malignancy and may be closely related with
pathophysiological progression of PDAC.
USP9X expression after
transfection
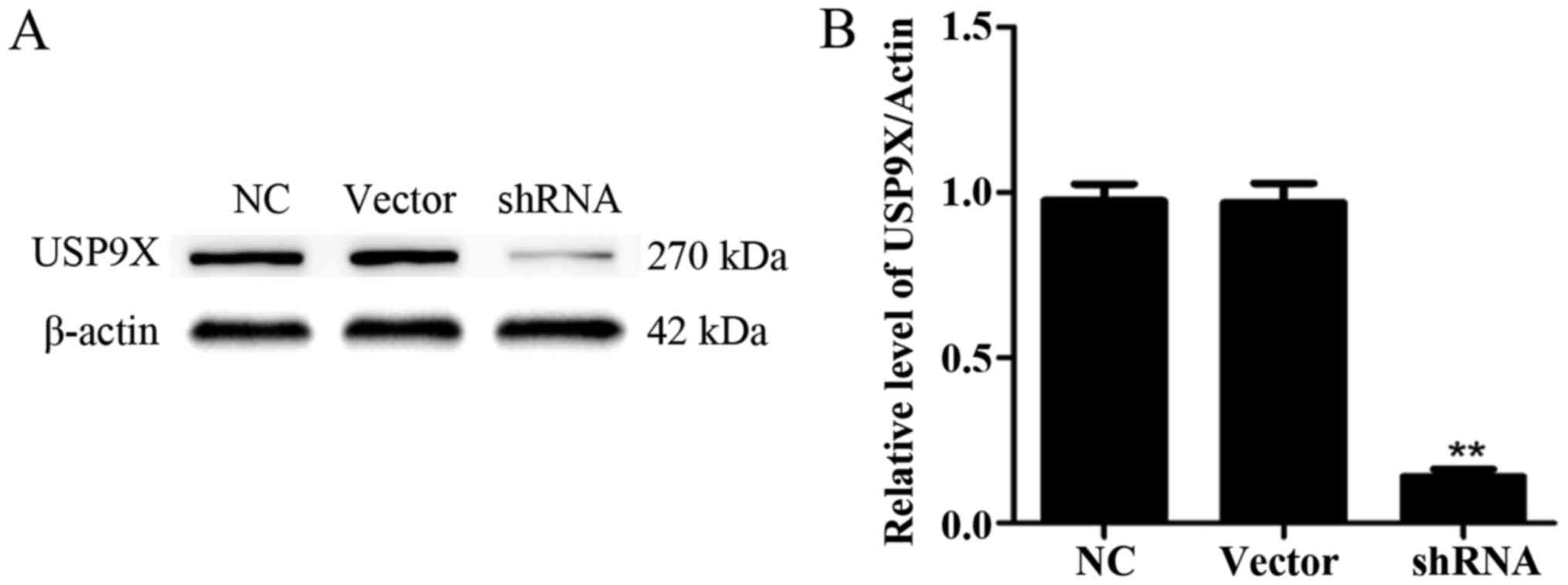
First, we confirmed the alteration of the expression
of USP9X. Thus, four shRNA sequences (purchased from GenePharma
Co.) directed against USP9X were evaluated. As a control, an empty
plasmid vector was transduced into PANC-1 cells. After 48 h, the
USP9X expression in PANC-1 cells was detected via western blotting.
After filtration, we chose one group of plasmids with the best
effect. The USP9X expression was significantly downregulated
(P<0.01) (Fig. 2A and B).
Depletion of USP9X inhibits cell
migration and invasion
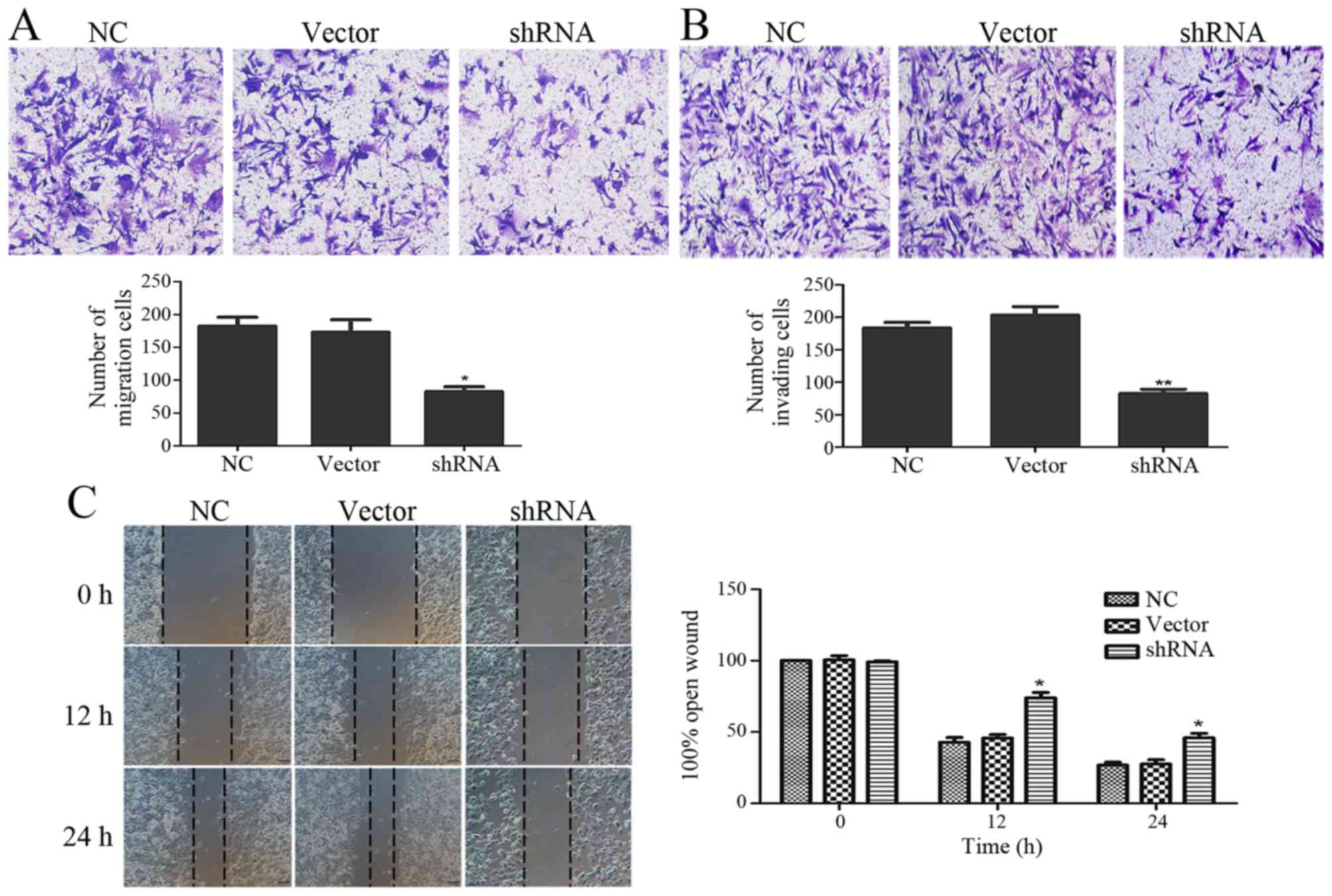
The functional effects of USP9X on pancreatic cancer
cell migration and invasion abilities were examined via Transwell
and wound healing assays. The suppression of USP9X expression
significantly inhibited cell migration (Fig. 3A) and invasion ability (Fig. 3B). Next, we monitored the wound
healing assays and similar results were found. The migration
ability of the PANC-1 cells was significantly decreased when USP9X
was suppressed (Fig. 3C).
Depletion of USP9X reverses EMT of
PANC-1 cells
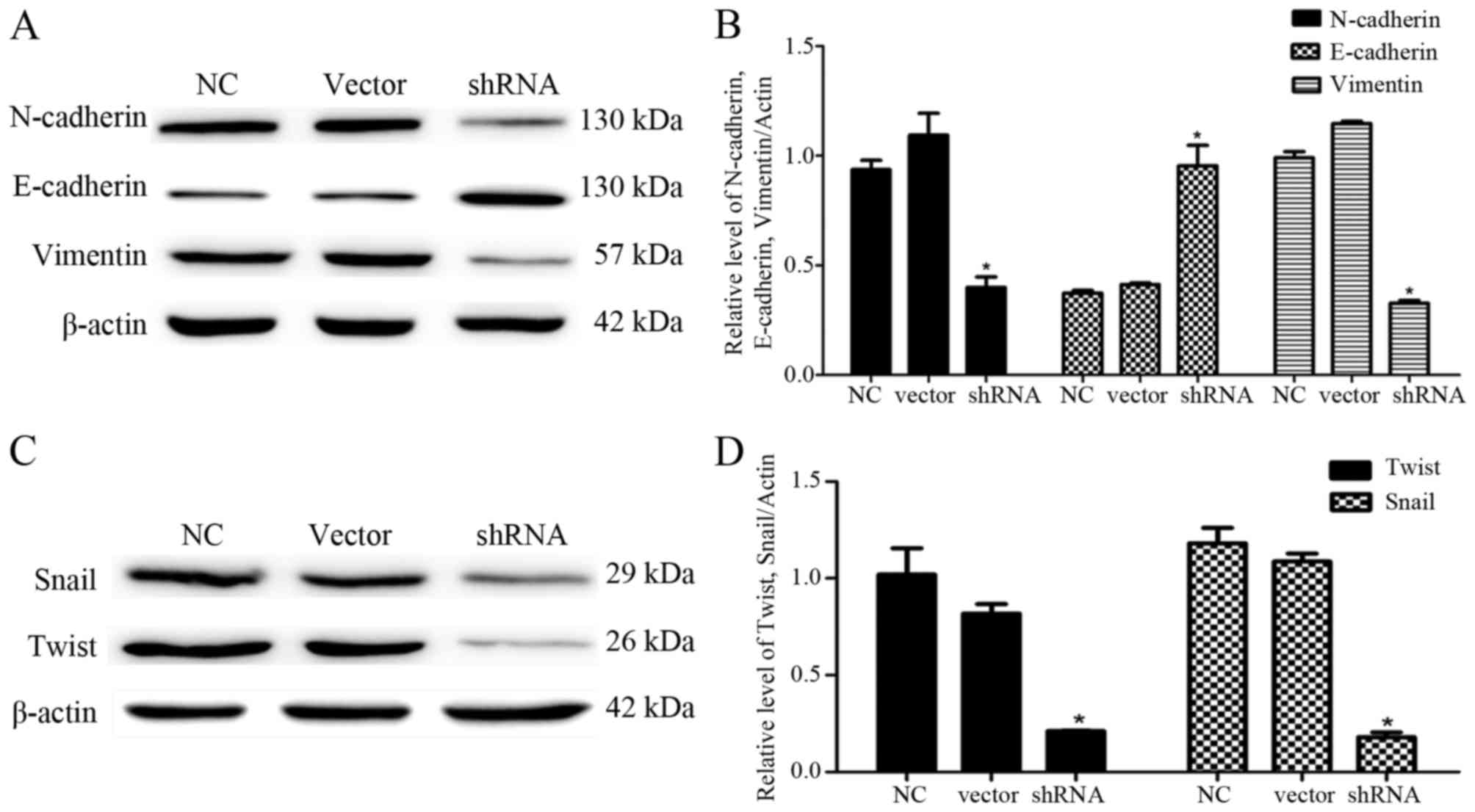
To explore the effects of USP9X on the EMT of PANC-1
cells, we examined the expression levels of mesenchymal cell
markers (N-cadherin and vimentin) and epithelial cell marker
(E-cadherin) by western blotting. The results showed that the
downregulation of USP9X expression significantly reduced the
expression of N-cadherin and vimentin compared with these levels in
the control groups (P<0.05; Fig. 4A
and B). In contrast, the E-cadherin expression was increased
(P<0.05; Fig. 4A and B).
To further confirm the effect of USP9X on the EMT of
PANC-1 cells, we determined the expression levels of Snail and
Twist, two upstream target proteins of N-cadherin, vimentin and
E-cadherin by western blotting. The results revealed that
expression of both proteins was significantly decreased (P<0.05;
Fig. 4C and D), suggesting that
USP9X may be involved in regulating the migration and invasion of
PANC-1 cells. As Snail and Twist were activated in pancreatic
cancer cells, USP9X may be highly associated with disease
progression by regulating the expression of downstream target
proteins, including N-cadherin, vimentin and E-cadherin.
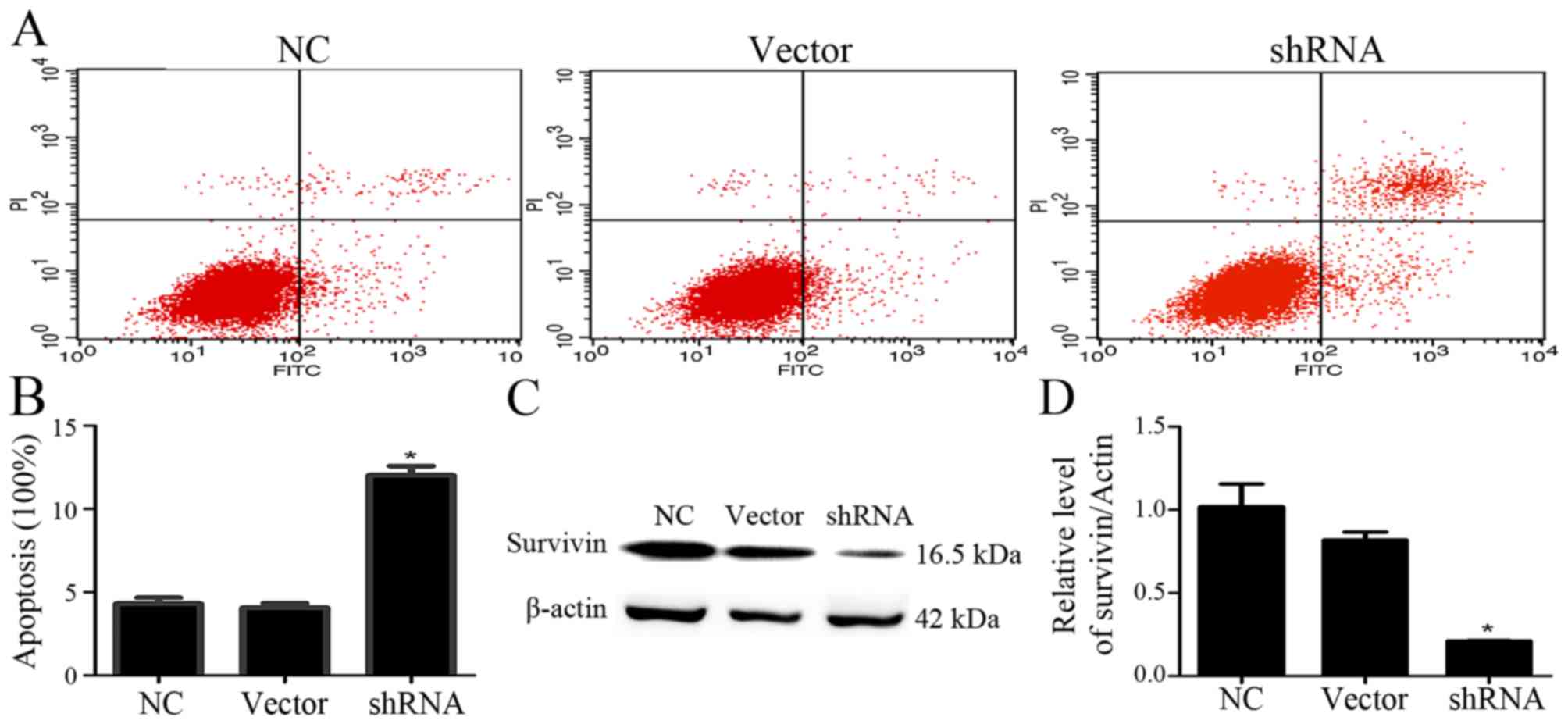
Inhibition of USP9X induces
apoptosis
The effect of USP9X on cell apoptosis was detected
using flow cytometry. After the given plasmid was transfected into
PANC-1 cells for 48 h, shRNA-USP9X effectively inhibited USP9X
expression compared with that noted in the control groups (Fig. 1). Then, the cells were stained with
Annexin V-FITC/PI for assaying cell apoptosis. The apoptotic rate
of PANC-1 cells increased after inhibition of USP9X expression in
comparison with the uninduced counterparts (Fig. 5A and B), indicating that depletion
of USP9X induced the apoptosis of PANC-1 cells. To confirm the
effects of USP9X on the protein expression of survivin in PANC-1
cells, we measured survivin by western blotting. The results
indicated that survivin expression in PANC-1 cells was markedly
reduced compared with that noted in the control groups (P<0.05,
Fig. 5C and D).
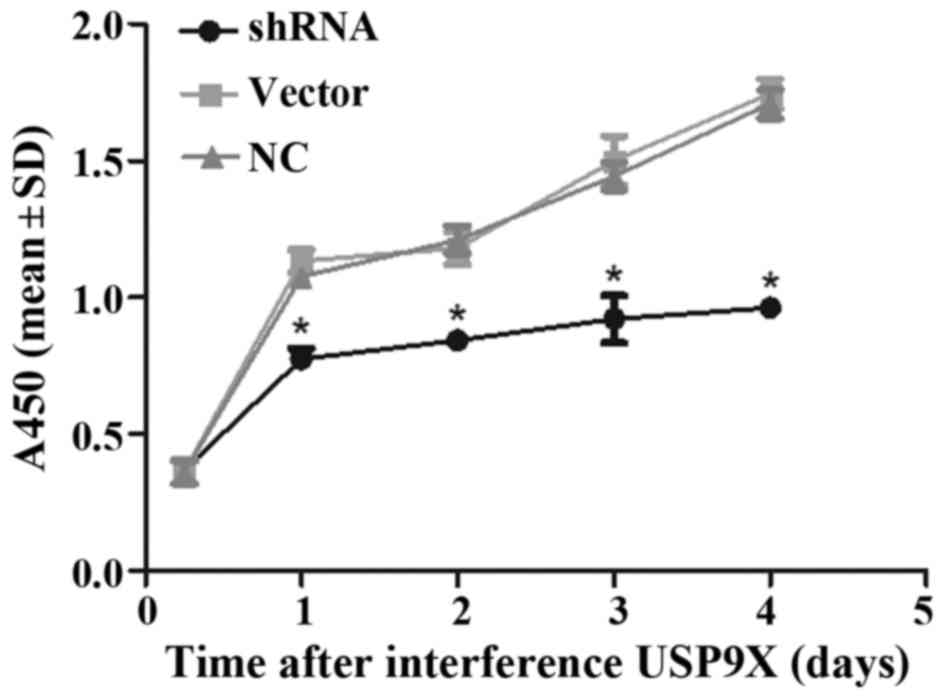
Depletion of USP9X impacts cell
viability
As revealed by the CCK-8 assay, depletion of USP9X
in PANC-1 cells resulted in decreased cell viability compared to
the cell viability of another two groups of cells (P<0.05;
Fig. 6).
Discussion
Pancreatic neoplasms are highly malignant tumors,
and the prognosis of patients with PDAC is extremely poor, which is
mostly ascribed to the high migration, invasiveness and high
recurrence rate (22). Due to the
broad range of its targets, the roles of USP9X are various and rely
on different environments (8,9,12,23,24).
Abnormal expression of USP9X in several types of cancers has been
reported (8,11,23,24).
Particularly, whether PDAC USP9X acts as a proto-oncogene or
tumor-suppressor gene remains controversial (11), and the concrete effects of USP9X on
migration, invasion and apoptosis of PDAC are still poorly
understood.
Our experimental data support the role of USP9X as a
growth promoter in tumor genesis and progression. As shown in
Fig. 1A and B, the USP9X expression
in human pancreatic cancer tissues was markedly increased compared
with that noted in the adjacent non-tumor tissues. We believe that
USP9X is positively correlated with the degree of tumor malignancy
and may be closely related with pathophysiological progression of
PDAC (Table I). Notably,
downregulation of USP9X expression reduced the invasion and
migration abilities of the PANC-1 cells (Fig. 3A-C). Depletion of USP9X reversed the
EMT of PANC-1 cells, which is reflected in the changes of
N-cadherin, vimentin and E-cadherin expression. Moreover, cell
apoptosis was increased after the downregulation of USP9X (Fig. 5A and B). The survivin expression was
positively correlated with the USP9X level. Furthermore, inhibition
of USP9X expression effectively decreased the viability of the
PANC-1 cells (Fig. 6).
Notably, Cox et al demonstrated that USP9X
acted principally as an oncogene in five tested PDAC cell lines
(11). However, Pérez-Mancera et
al found that USP9X acted as a tumor-suppressor in a mouse
model of pancreatic malignant tumors in which the USP9X expression
was interfered at the early stage of tumor development by Sleeping
Beauty transposon (12). In the
present study, we believe that USP9X may be an oncogene in PANC-1
cells. Our results are similar to those of Cox et al. We
suggest that downregulation of USP9X can inhibit the migration and
invasion of pancreatic cancer PANC-1 cells and lead to a decrease
in cell viability. The apoptosis rate of the PANC-1 cells was
increased with the decrease in USP9X expression. The migratory
ability of PANC-1 cells was weakened after downregulation of the
expression of USP9X (Fig. 3A). We
also found that our results differed from those of Perez-Mancera
et al. The difference may be due to the pathological type of
pancreatic cancer, the location of the pancreatic tumor or the
difference in race. However, the specific reasons remain unclear
and further research is needed.
Furthermore, we studied the specific proteins
related to the migration and invasion functions of USP9X. We found
that cell migration and invasion abilities were suppressed
(Fig. 3A-C). Moreover, it is very
possible that USP9X may affect the migration and invasion of PANC-1
cells by EMT. EMT is the process in which epithelial cells are
transformed by specific procedures into a mesenchymal phenotype.
Epithelial cells undergoing EMT lose polarity and some properties
such as their connection to the basement membrane, which is an
important process of tumor invasion and metastasis (3). It has also been confirmed that EMT is
the molecular basis underlying the occurrence, invasion and
metastasis of many tumors (25,26).
Furthermore, we examined the expression levels of N-cadherin,
vimentin and E-cadherin in PANC-1 cells by western blotting.
However, the E-cadherin expression was significantly upregulated,
while the expression of N-cadherin and vimentin was downregulated
in PANC-1 cells. This finding is consistent with other studies
(27–29). We also tested Snail and Twist, which
are the upstream target proteins of N-cadherin, vimentin and
E-cadherin. Twist belongs to the bHLH transcription factor family
and plays an important role in tumor metastasis (15). Snail, a zinc finger transcription
factor is combined with the promoter of the gene expression related
to cell adhesion, and opens to regulate the transcription process
(16). We found that the expression
levels of both proteins were significantly downregulated (Fig. 4C and D). These results are
consistent with previous research (13,14,30).
We conclude that USP9X is highly linked with disease formation and
progression by activating EMT.
Moreover, we studied PANC-1 cell apoptosis after the
expression of USP9X was silenced. The apoptotic rate of PANC-1
cells increased after the inhibition of USP9X expression compared
with the uninduced groups (Fig. 5A and
B). As reported, survivin is degraded by the ubiquitin
proteasome pathway (20).
Theoretically, downregulated expression of survivin can cause cell
apoptosis. Thus, we detected the expression of survivin, which is
the strongest apoptosis inhibitor (15). Survivin may inhibit apoptosis mainly
by the following two ways: one way by directly inhibiting the
activities of caspase-3 and −7, the end effectors of apoptosis
protein, and another way by interacting with CDK-2 and CDK-4 and
blocking the apoptotic signal transduction pathway (31). In PDAC, survivin is involved in many
biological processes, such as gene transcription regulation, cell
differentiation, tumor formation and metastasis (32,33).
We also found that the survivin expression in PANC-1 cells was
markedly reduced after the inhibition of USP9X. The change in
survivin expression was positively proportional to USP9X, but the
concrete mechanism between them is still unclear and needs further
study.
Taken together, USP9X participates in a variety of
biological processes in pancreatic cancer cells. In the present
study, we first demonstrated that USP9X activated the EMT pathway
and altered cell migration and invasion abilities. We then explored
the close relationship between USP9X and survivin in pancreatic
cancer. Future studies are needed to reveal the specific mechanisms
between Snail/Twist and USP9X, and between survivin and USP9X. Our
findings may provide a novel strategy for the treatment of
pancreatic cancer. Early inhibition of USP9X may delay the invasion
and metastasis of PDAC, which makes it possible to improve the
clinical outcomes of PDAC patients. However, our findings are not
fully consistent with previous experts, thus deeper investigation
is required to elucidate the significant role of USP9X in PDAC.
References
|
1
|
Siegel R, Ma J, Zou Z and Jemal A: Cancer
statistics, 2014. CA Cancer J Clin. 64:9–29. 2014. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
2
|
Hidalgo M: Pancreatic cancer. N Engl J
Med. 362:1605–1617. 2010. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
3
|
Bonnomet A, Brysse A, Tachsidis A, Waltham
M, Thompson EW, Polette M and Gilles C: Epithelial-to-mesenchymal
transitions and circulating tumor cells. J Mammary Gland Biol
Neoplasia. 15:261–273. 2010. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
4
|
Kapuria V, Peterson LF, Fang D, Bornmann
WG, Talpaz M and Donato NJ: Deubiquitinase inhibition by
small-molecule WP1130 triggers aggresome formation and tumor cell
apoptosis. Cancer Res. 70:9265–9276. 2010. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
5
|
Kerscher O, Felberbaum R and Hochstrasser
M: Modification of proteins by ubiquitin and ubiquitin-like
proteins. Annu Rev Cell Dev Biol. 22:159–180. 2006. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
6
|
Hussain S, Zhang Y and Galardy PJ: DUBs
and cancer: The role of deubiquitinating enzymes as oncogenes,
non-oncogenes and tumor suppressors. Cell Cycle. 8:1688–1697. 2009.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
7
|
Reyes-Turcu FE, Ventii KH and Wilkinson
KD: Regulation and cellular roles of ubiquitin-specific
deubiquitinating enzymes. Annu Rev Biochem. 78:363–397. 2009.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
8
|
Schwickart M, Huang X, Lill JR, Liu J,
Ferrando R, French DM, Maecker H, O'Rourke K, Bazan F,
Eastham-Anderson J, et al: Deubiquitinase USP9X stabilizes MCL1 and
promotes tumour cell survival. Nature. 463:103–107. 2010.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
9
|
Harris DR, Mims A and Bunz F: Genetic
disruption of USP9X sensitizes colorectal cancer cells to
5-fluorouracil. Cancer Biol Ther. 13:1319–1324. 2012. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
10
|
Liu H, Chen W, Liang C, Chen BW, Zhi X,
Zhang S, Zheng X, Bai X and Liang T: WP1130 increases doxorubicin
sensitivity in hepatocellular carcinoma cells through
usp9×-dependent p53 degradation. Cancer Lett. 361:218–225. 2015.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
11
|
Cox JL, Wilder PJ, Wuebben EL, Ouellette
MM, Hollingsworth MA and Rizzino A: Context-dependent function of
the deubiquitinating enzyme USP9X in pancreatic ductal
adenocarcinoma. Cancer Biol Ther. 15:1042–1052. 2014. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
12
|
Pérez-Mancera PA, Rust AG, van der Weyden
L, Kristiansen G, Li A, Sarver AL, Silverstein KA, Grützmann R,
Aust D, Rümmele P, et al: Australian Pancreatic Cancer Genome
Initiative: The deubiquitinase USP9X suppresses pancreatic ductal
adenocarcinoma. Nature. 486:266–270. 2012.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
13
|
De Craene B and Berx G: Regulatory
networks defining EMT during cancer initiation and progression. Nat
Rev Cancer. 13:97–110. 2013. View
Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
14
|
Yang J and Weinberg RA:
Epithelial-mesenchymal transition: At the crossroads of development
and tumor metastasis. Dev Cell. 14:818–829. 2008. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
15
|
Khan MA, Chen HC, Zhang D and Fu J: Twist:
A molecular target in cancer therapeutics. Tumour Biol.
34:2497–2506. 2013. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
16
|
Smith BN and Odero-Marah VA: The role of
Snail in prostate cancer. Cell Adhes Migr. 6:433–441. 2012.
View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
17
|
Ambrosini G, Adida C and Altieri DC: A
novel anti-apoptosis gene, survivin, expressed in cancer and
lymphoma. Nat Med. 3:917–921. 1997. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
18
|
Roca H, Varsos ZS, Mizutani K and Pienta
KJ: CCL2, survivin and autophagy: New links with implications in
human cancer. Autophagy. 4:969–971. 2008. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
19
|
Farnebo L, Tiefenböck K, Ansell A, Thunell
LK, Garvin S and Roberg K: Strong expression of survivin is
associated with positive response to radiotherapy and improved
overall survival in head and neck squamous cell carcinoma patients.
Int J Cancer. 133:1994–2003. 2013. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
20
|
Liu YB, Gao X, Deeb D, Brigolin C, Zhang
Y, Shaw J, Pindolia K and Gautam SC: Ubiquitin-proteasomal
degradation of antiapoptotic survivin facilitates induction of
apoptosis in prostate cancer cells by pristimerin. Int J Oncol.
45:1735–1741. 2014. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
21
|
Peng J, Hu Q, Liu W, He X, Cui L, Chen X,
Yang M, Liu H, Wei W, Liu S, et al: USP9X expression correlates
with tumor progression and poor prognosis in esophageal squamous
cell carcinoma. Diagn Pathol. 8:177–185. 2013. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
22
|
Ahmad R: Cheema, Eileen M. O'Reilly.
Management of metastatic pancreatic adenocarcinoma. Surg Clin North
Am. 7:1391–1414. 2016.
|
|
23
|
Murtaza M, Jolly LA, Gecz J and Wood SA:
La FAM fatale: USP9X in development and disease. Cell Mol Life Sci.
72:2075–2089. 2015. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
24
|
Wang Y, Liu Y, Yang B, Cao H, Yang CX,
Ouyang W, Zhang SM, Yang GF, Zhou FX, Zhou YF, et al: Elevated
expression of USP9X correlates with poor prognosis in human
non-small cell lung cancer. J Thorac Dis. 7:672–679.
2015.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
25
|
Vermeulen L, Todaro M, de Sousa Mello F,
Sprick MR, Kemper K, Alea Perez M, Richel DJ, Stassi G and Medema
JP: Single-cell cloning of colon cancer stem cells reveals a
multi-lineage differentiation capacity. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA.
105:13427–13432. 2008. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
26
|
Findlay VJ, Wang C, Watson DK and Camp ER:
Epithelial-to-mesenchymal transition and the cancer stem cell
phenotype: Insights from cancer biology with therapeutic
implications for colorectal cancer. Cancer Gene Ther. 21:181–187.
2014. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
27
|
von Burstin J, Eser S, Paul MC, Seidler B,
Brandl M, Messer M, von Werder A, Schmidt A, Mages J, Pagel P, et
al: E-cadherin regulates metastasis of pancreatic cancer in vivo
and is suppressed by a SNAIL/HDAC1/HDAC2 repressor complex.
Gastroentemlogy. 137:361–371. 2009. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
28
|
Lang SH, Hyde C, Reid IN, Hitchcock IS,
Hart CA, Bryden AA, Villette JM, Stower MJ and Maitland NJ:
Enhanced expression of vimentin in motile prostate cell lines and
in poorly differentiated and metastatic prostate carcinoma.
Prostate. 52:253–263. 2002. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
29
|
Lee MY, Chou CY, Tang MJ and Shen MR:
Epithelial-mesenchymal transition in cervical cancer: Correlation
with tumor progression, epidermal growth factor receptor
overexpression, and snail up-regulation. Clin Cancer Res.
14:4743–4750. 2008. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
30
|
Francí C, Takkunen M, Dave N, Alameda F,
Gómez S, Rodríguez R, Escrivà M, Montserrat-Sentís B, Baró T,
Garrido M, et al: Expression of Snail protein in tumor-stroma
interface. Oncogene. 25:5134–5144. 2006. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
31
|
Xu JH, Wang AX, Huang HZ, Wang JG, Pan CB
and Zhang B: Survivin shRNA induces caspase-3-dependent apoptosis
and enhances cisplatin sensitivity in squamous cell carcinoma of
the tongue. Oncol Res. 18:377–385. 2010. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
32
|
Lopes RB, Gangeswaran R, McNeish IA, Wang
Y and Lemoine NR: Expression of the IAP protein family is
dysregulated in pancreatic cancer cells and is important for
resistance to chemotherapy. Int J Cancer. 120:2344–2352. 2007.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
33
|
Jhala N, Jhala D, Vickers SM, Eltoum I,
Batra SK, Manne U, Eloubeidi M, Jones JJ and Grizzle WE: Biomarkers
in diagnosis of pancreatic carcinoma in fine-needle aspirates. Am J
Clin Pathol. 126:572–579. 2006. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|