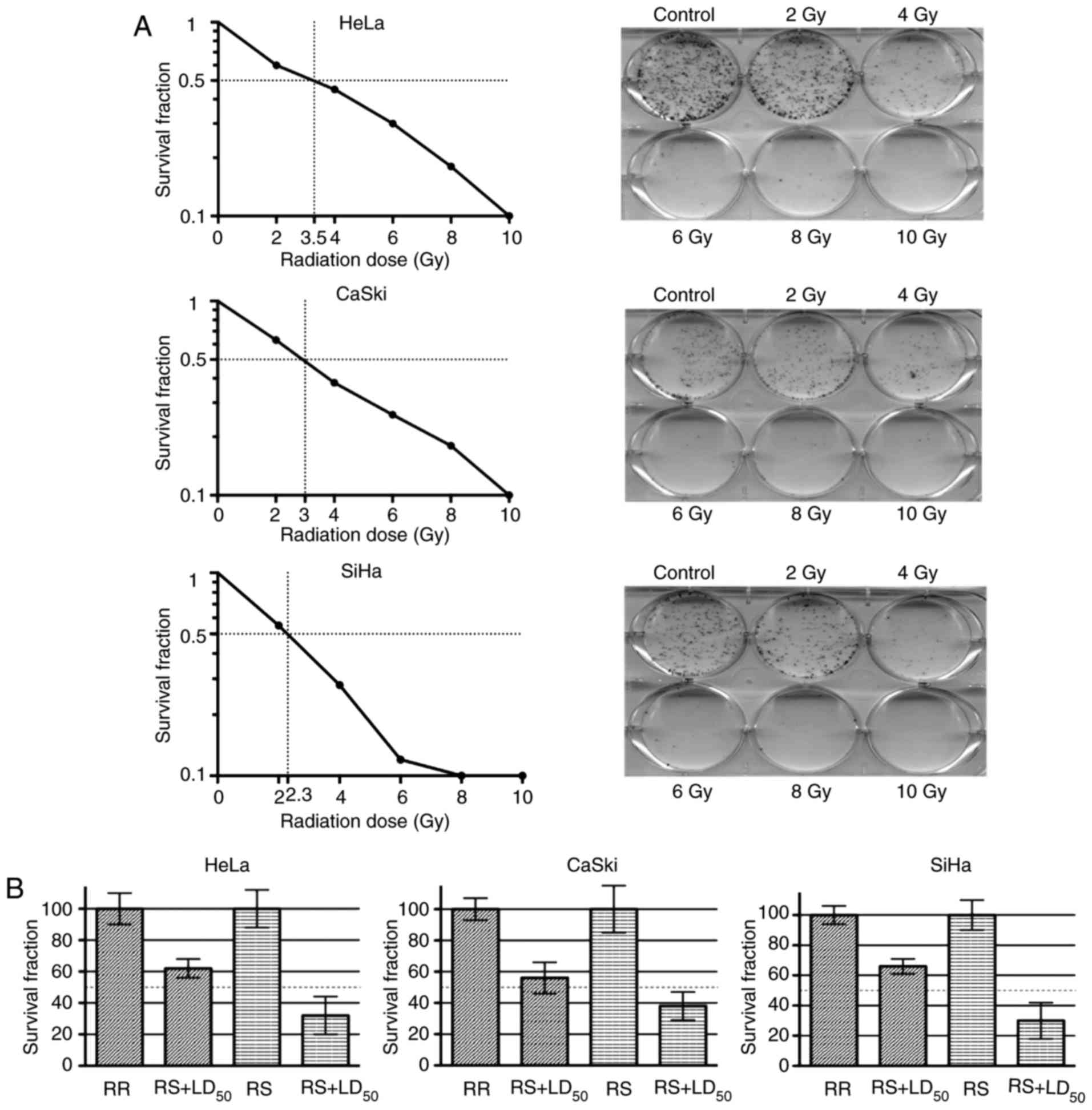
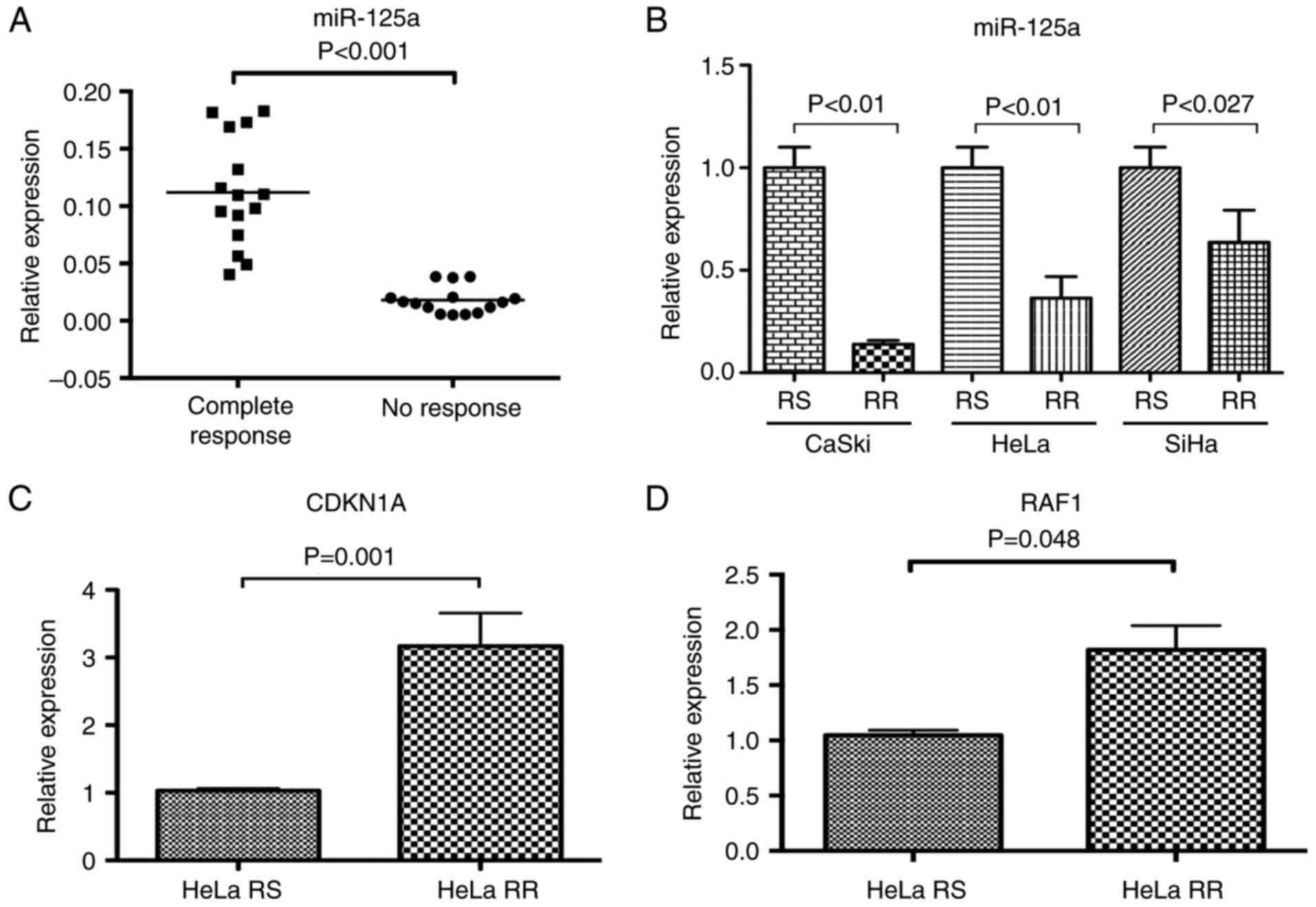
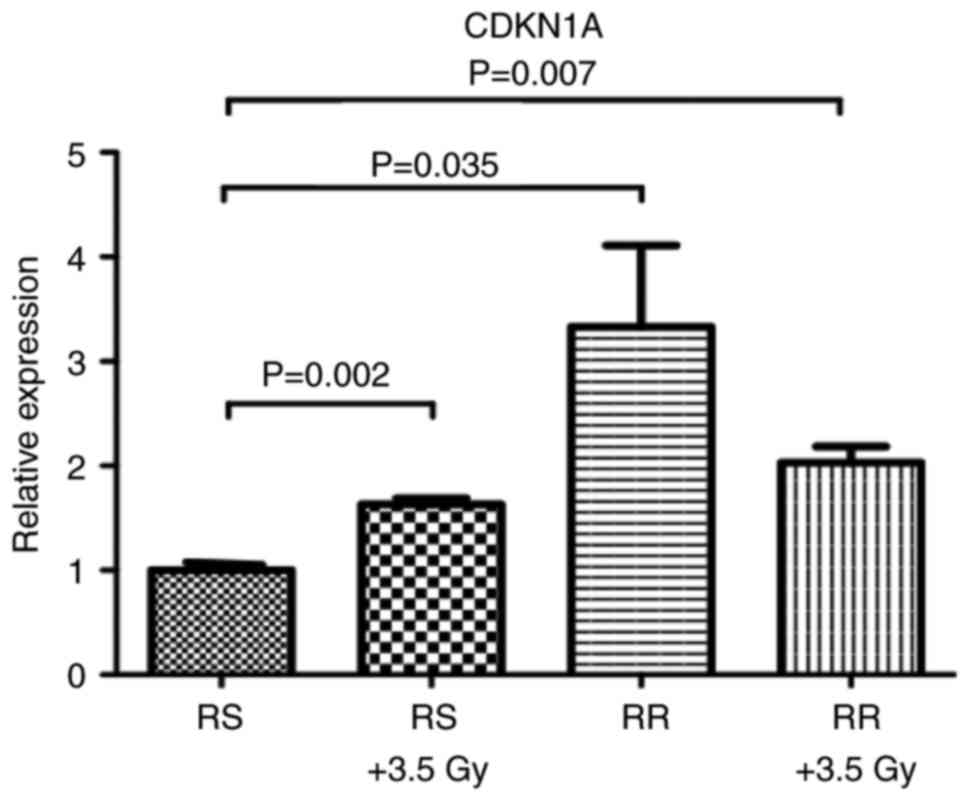
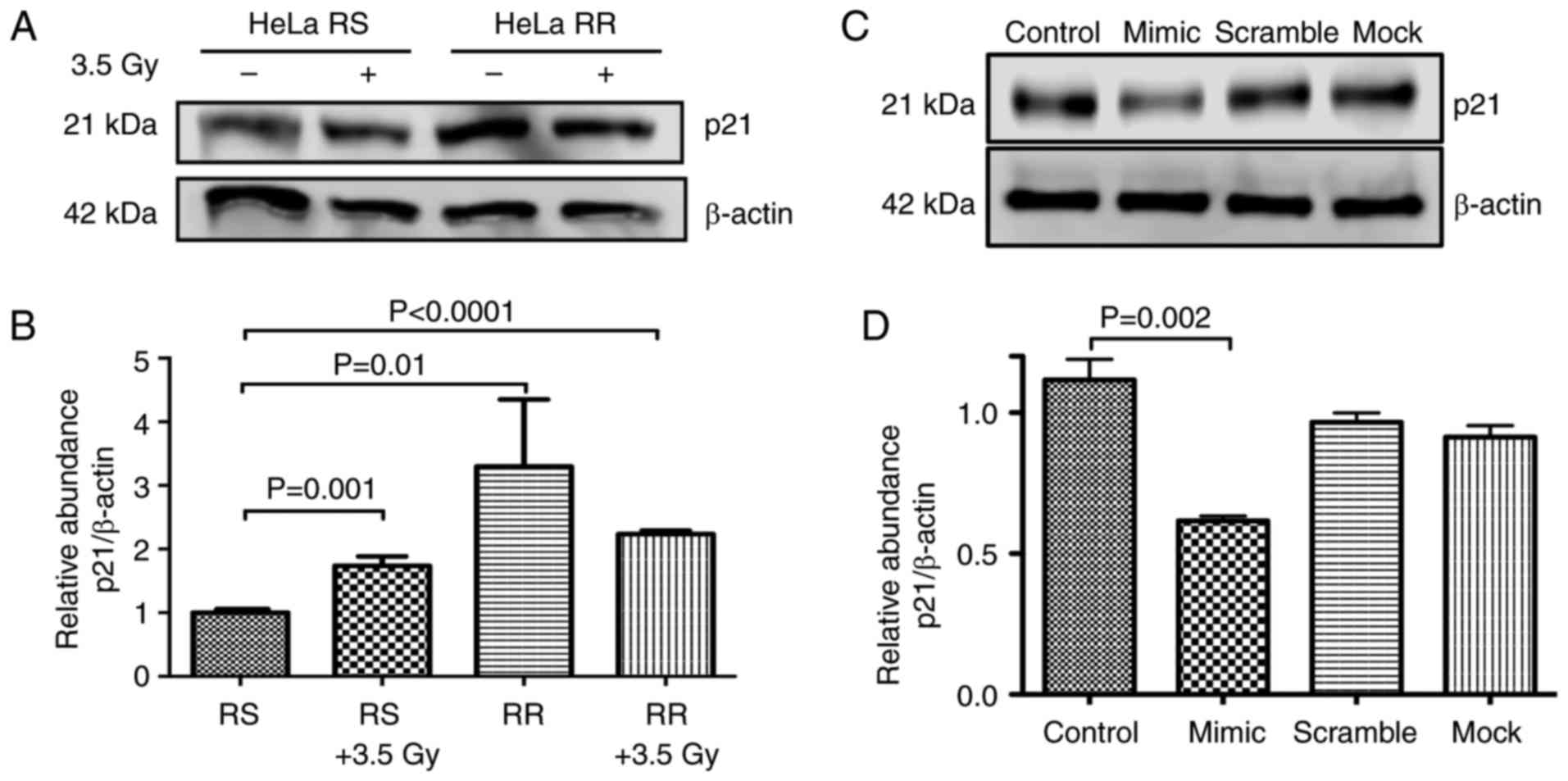
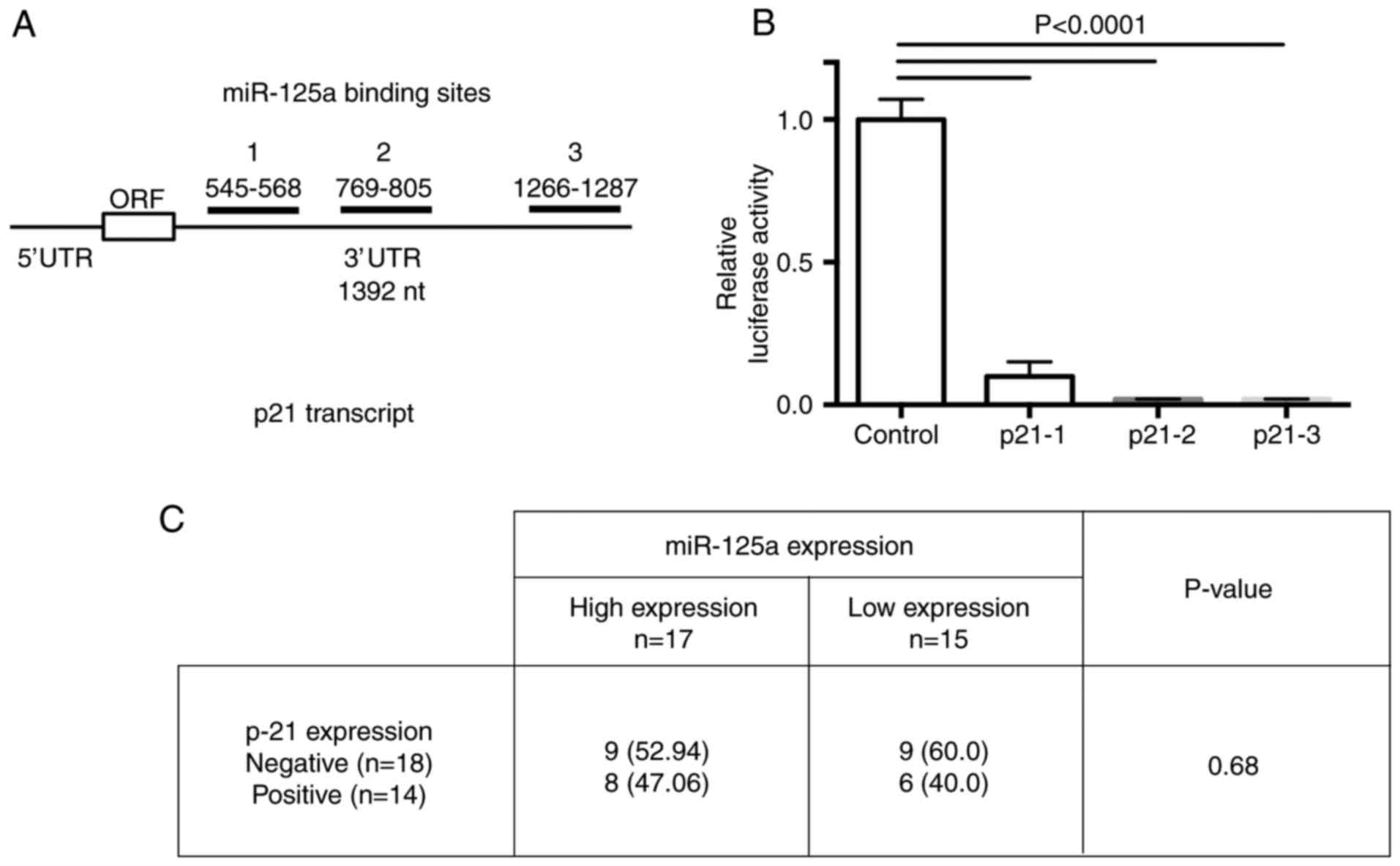
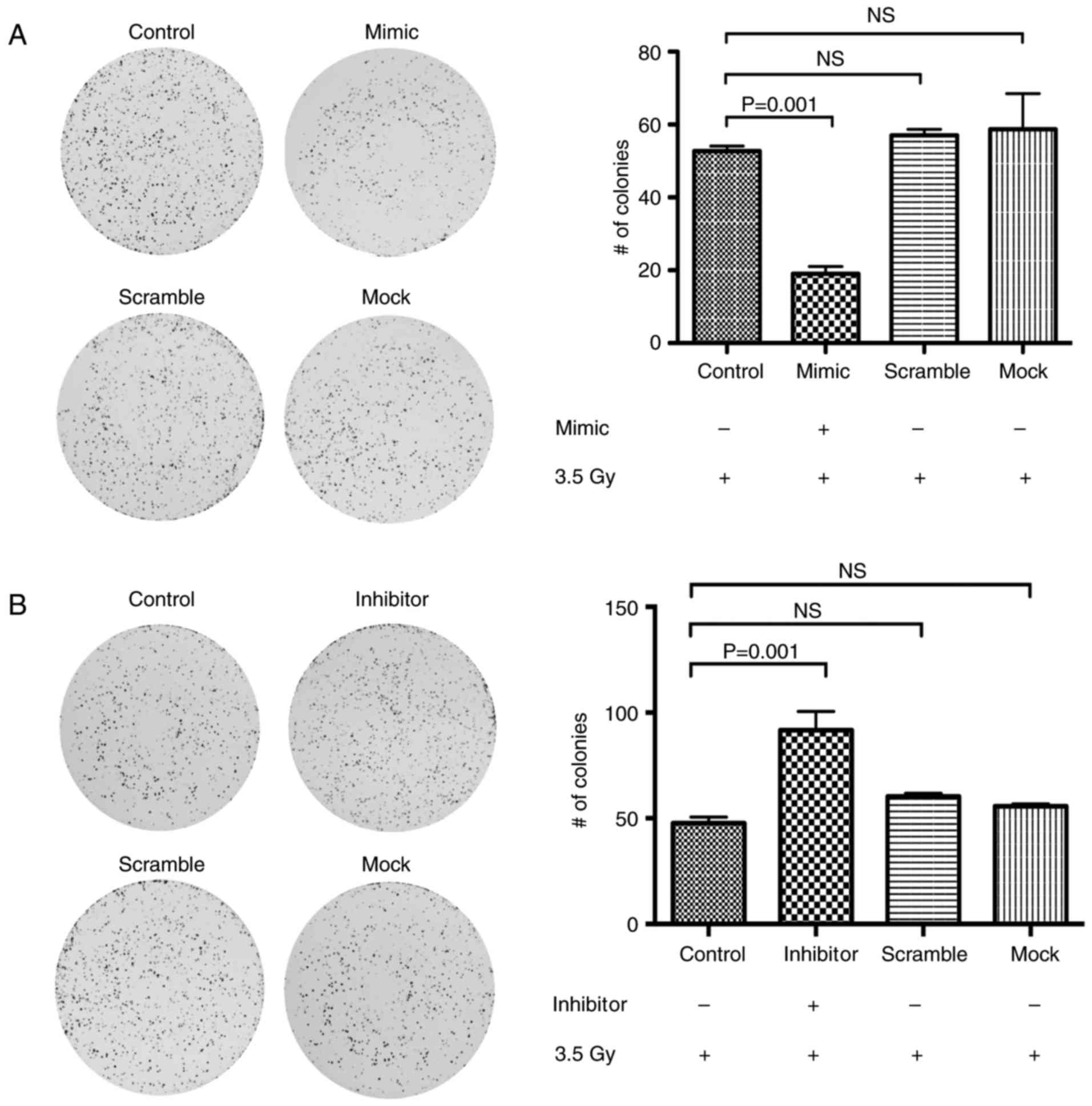
|
1
|
Torre LA, Bray F, Siegel RL, Ferlay J,
Lortet-Tieulent J and Jemal A: Global cancerstatistics, 2012. CA
Cancer J Clin. Mar;65:87–108. 2015. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
2
|
Delaney G, Jacob S, Featherstone C and
Barton M: The role of radiotherapy in cancer treatment: Estimating
optimal utilization from a review of evidence-based clinical
guidelines. Cancer. 104:1129–1137. 2005. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
3
|
Benedet JL, Odicino F, Maisonneuve P,
Beller U, Creasman WT, Heintz AP, Ngan HY and Pecorelli S:
Carcinoma of the cérvix uteri. Int J Gynaecol Obstet. 83 Suppl
1:S41–S78. 2003. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
4
|
Zhang B, Chen J, Ren Z, Chen Y, Li J, Miao
X, Song Y, Zhao T, Li Y, Shi Y, et al: A specific miRNA signature
promotes radioresistance of human cervical cancer cells. Cancer
Cell Int. 13:1182013. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
5
|
Yang CX, Zhang SM, Li J, Yang B, Ouyang W,
Mei ZJ, Chen J, Dai J, Ke S, Zhou FX, et al: MicroRNA-320 regulates
the radiosensitivity of cervical cancer cells C33AR by targeting
β-catenin. Oncol Lett. 12:4983–4990. 2016. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
6
|
Pedroza-Torres A, Fernández-Retana J,
Peralta-Zaragoza O, Jacobo-Herrera N, Cantú de Leon D, Cerna-Cortés
JF, Lopez-Camarillo C and Pérez-Plasencia C: A microRNA expression
signature for clinical response in locally advanced cervical
cancer. Gynecol Oncol. 142:557–565. 2016. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
7
|
Bousquet M, Harris MH, Zhou B and Lodish
HF: MicroRNA miR-125b causes leukemia. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA.
107:pp. 21558–21563. 2010; View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
8
|
Hulanicka M, Garncarz M,
Parzeniecka-Jaworska M and Jank M: Plasma miRNAs as potential
biomarkers of chronic degenerative valvular disease in Dachshunds.
BMC Vet Res. 10:2052014. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
9
|
Cowden Dahl KD, Dahl R, Kruichak JN and
Hudson LG: The epidermal growth factor receptor responsive miR-125a
represses mesenchymal morphology in ovarian cancer cells.
Neoplasia. 11:1208–1215. 2009. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
10
|
Betel D, Wilson M, Gabow A, Marks DS and
Sander C: The microRNA.org resource: Targets and expression.
Nucleic Acids Res. 36:D149–D153. 2008. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
11
|
Asgharian A, Banan M and Najmabadi H:
Optimizing a lipocomplex-based gene transfer method into HeLa cell
line. Cell J. 15:372–377. 2014.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
12
|
Li G, Qiu Y, Su Z, Ren S, Liu C, Tian Y
and Liu Y: Genome-wide analyses of radioresistance-associated miRNA
expression profile in nasopharyngeal carcinoma using next
generation deep sequencing. PLoS One. 8:e844862013. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
13
|
Guo W, Xie L, Zhao L and Zhao Y: mRNA and
microRNA expression profiles of radioresistant NCI-H520 non-small
cell lung cancer cells. Mol Med Rep. 12:1857–1867. 2015. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
14
|
McDermott N, Meunier A, Wong S, Buchete V
and Marignol L: Profiling of a panel of radioresistant prostate
cancer cells identifiesde regulation of key miRNAs. Clin Transl
Radiat Oncol. 2:63–68. 2017. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
15
|
Maier P, Hartmann L, Wenz F and Herskind
C: Cellular pathways in response to ionizin gradiation and their
target ability for tumor radio sensitization. Int J Mol Sci.
17:1022016. View Article : Google Scholar :
|
|
16
|
Ishigami T, Uzawa K, Higo M, Nomura H,
Saito K, Kato Y, Nakashima D, Shiiba M, Bukawa H, Yokoe H, et al:
Genes and molecular pathways related to radioresistance of oral
squamous cell carcinoma cells. Int J Cancer. 120:2262–2270. 2007.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
17
|
Skvortsova I, Skvortsov S, Stasyk T, Raju
U, Popper BA, Schiestl B, Guggenberg Ev, Neher A, Bonn GK, Huber LA
and Lukas P: Intracellular signaling pathways regulating
radioresistance of human prostate carcinoma cells. Proteomics.
8:4521–4533. 2008. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
18
|
Moskwa P, Zinn PO, Choi YE, Shukla SA,
Fendler W, Chen CC, Lu J, Golub TR, Hjelmeland A and Chowdhury D: A
functional screen identifies miRs that induce radioresistance in
glioblastomas. Mol Cancer Res. 12:1767–1778. 2014. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
19
|
Shiiba M, Shinozuka K, Saito K, Fushimi K,
Kasamatsu A, Ogawara K, Uzawa K, Ito H, Takiguchi Y and Tanzawa H:
MicroRNA-125b regulates proliferation and radioresistance of oral
squamous cell carcinoma. Br J Cancer. 108:1817–1821. 2013.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
20
|
Fan Z, Cui H, Xu X, Lin Z, Zhang X, Kang
L, Han B, Meng J, Yan Z, Yan X and Jiao S: MiR-125a suppresses
tumor growth, invasion and metastasis in cervical cancerbytargeting
STAT3. Oncotarget. 6:25266–25280. 2015. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
21
|
Fan Z, Cui H, Yu H, Ji Q, Kang L, Han B,
Wang J, Dong Q, Li Y, Yan Z, et al: MiR-125a promotes paclitaxel
sensitivity in cervical cancer through altering STAT3 expression.
Oncogenesis. 5:e1972016. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
22
|
Kraus A, Gross MW, Knuechel R, Münkel K,
Neff F and Schlegel J: Aberrant p21 regulation in radioresistant
primary glioblastoma multiforme cells bearing wild-type p53. J
Neurosurg. 93:863–872. 2000. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
23
|
Kokunai T, Urui S, Tomita H and Tamaki N:
Overcoming of radioresistance in human gliomas by p21WAF1/CIP1
antisense oligonucleotide. J Neurooncol. 51:111–119. 2001.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|