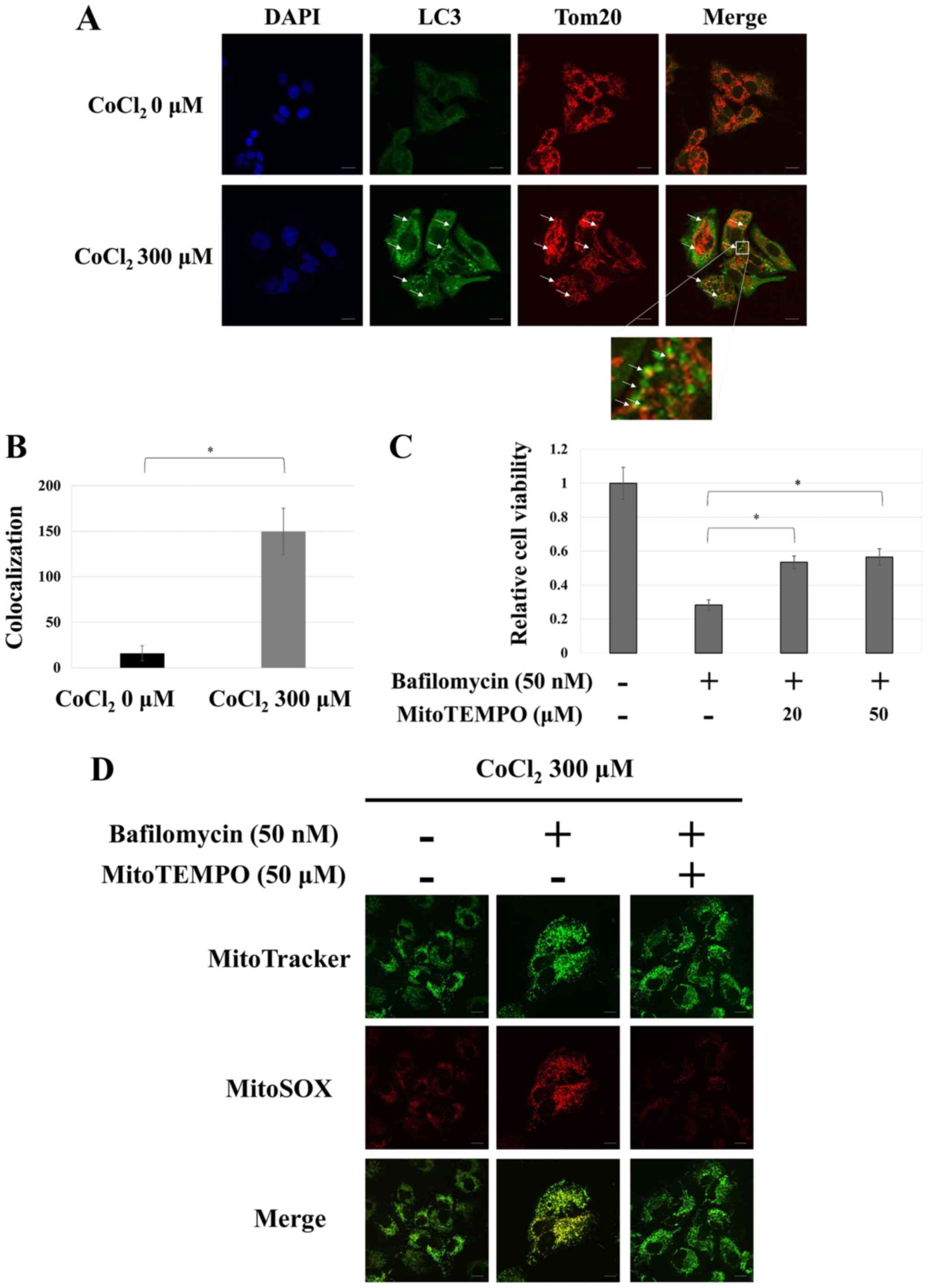
|
1
|
Ferlay J, Soerjomataram I, Dikshit R, Eser
S, Mathers C, Rebelo M, Parkin DM, Forman D and Bray F: Cancer
incidence and mortality worldwide: Sources, methods and major
patterns in GLOBOCAN 2012. Int J Cancer. 136:E359–E386. 2015.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
2
|
Llovet JM, Ricci S, Mazzaferro V, Hilgard
P, Gane E, Blanc JF, de Oliveira AC, Santoro A, Raoul JL, Forner A,
et al: Sorafenib in advanced hepatocellular carcinoma. N Engl J
Med. 359:378–390. 2008. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
3
|
Wörns M and Galle PR: HCC
therapies-lessons learned. Nat Rev Gastroenterol Hepatol.
11:447–452. 2014. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
4
|
Brown JM and Giaccia AJ: The unique
physiology of solid tumors: Opportunities (and problems) for cancer
therapy. Cancer Res. 58:1408–1416. 1998.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
5
|
Jain RK: Molecular regulation of vessel
maturation. Nat Med. 9:685–693. 2003. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
6
|
Less JR, Skalak TC, Sevick EM and Jain RK:
Microvascular architecture in a mammary carcinoma: Branching
patterns and vessel dimensions. Cancer Res. 51:265–273.
1991.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
7
|
Thomlinson RH and Gray LH: The
histological structure of some human lung cancers and the possible
implications for radiotherapy. Br J Cancer. 9:539–549. 1955.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
8
|
Helmlinger G, Yuan F, Dellian M and Jain
RK: Interstitial pH and pO2 gradients in solid tumors in
vivo: High-resolution measurements reveal a lack of correlation.
Nat Med. 3:177–182. 1997. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
9
|
Vaupel P, Höckel M and Mayer A: Detection
and characterization of tumor hypoxia using pO2
histography. Antioxid Redox Signal. 9:1221–1235. 2007. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
10
|
Heindryckx F, Mertens K, Charette N,
Vandeghinste B, Casteleyn C, Van Steenkiste C, Slaets D, Libbrecht
L, Staelens S, Starkel P, et al: Kinetics of angiogenic changes in
a new mouse model for hepatocellular carcinoma. Mol Cancer.
9:2192010. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
11
|
Liu L, Ning X, Sun L, Zhang H, Shi Y, Guo
C, Han S, Liu J, Sun S, Han Z, et al: Hypoxia-inducible factor-1
alpha contributes to hypoxia-induced chemoresistance in gastric
cancer. Cancer Sci. 99:121–128. 2008.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
12
|
Song J, Qu Z, Guo X, Zhao Q, Zhao X, Gao
L, Sun K, Shen F, Wu M and Wei L: Hypoxia-induced autophagy
contributes to the chemoresistance of hepatocellular carcinoma
cells. Autophagy. 5:1131–1144. 2009. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
13
|
Sullivan R, Paré GC, Frederiksen LJ,
Semenza GL and Graham CH: Hypoxia-induced resistance to anticancer
drugs is associated with decreased senescence and requires
hypoxia-inducible factor-1 activity. Mol Cancer Ther. 7:1961–1973.
2008. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
14
|
Yokoi K and Fidler IJ: Hypoxia increases
resistance of human pancreatic cancer cells to apoptosis induced by
gemcitabine. Clin Cancer Res. 10:2299–2306. 2004. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
15
|
Semenza GL: Hypoxia-inducible factor 1:
Master regulator of O2 homeostasis. Curr Opin Genet Dev.
8:588–594. 1998. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
16
|
Semenza GL: HIF-1 and tumor progression:
Pathophysiology and therapeutics. Trends Mol Med. 8:S62–S67. 2002.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
17
|
Zhang H, Bosch-Marce M, Shimoda LA, Tan
YS, Baek JH, Wesley JB, Gonzalez FJ and Semenza GL: Mitochondrial
autophagy is an HIF-1-dependent adaptive metabolic response to
hypoxia. J Biol Chem. 283:10892–10903. 2008. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
18
|
Mizushima N, Yamamoto A, Matsui M,
Yoshimori T and Ohsumi Y: In vivo analysis of autophagy in response
to nutrient starvation using transgenic mice expressing a
fluorescent autophagosome marker. Mol Biol Cell. 15:1101–1111.
2004. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
19
|
Lum JJ, Bauer DE, Kong M, Harris MH, Li C,
Lindsten T and Thompson CB: Growth factor regulation of autophagy
and cell survival in the absence of apoptosis. Cell. 120:237–248.
2005. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
20
|
Bursch W, Ellinger A, Kienzl H, Török L,
Pandey S, Sikorska M, Walker R and Hermann RS: Active cell death
induced by the anti-estrogens tamoxifen and ICI 164 384 in human
mammary carcinoma cells (MCF-7) in culture: The role of autophagy.
Carcinogenesis. 17:1595–1607. 1996. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
21
|
Azad MB, Chen Y, Henson ES, Cizeau J,
McMillan-Ward E, Israels SJ and Gibson SB: Hypoxia induces
autophagic cell death in apoptosis-competent cells through a
mechanism involving BNIP3. Autophagy. 4:195–204. 2008. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
22
|
Tasdemir E, Maiuri MC, Galluzzi L, Vitale
I, Djavaheri-Mergny M, D'Amelio M, Criollo A, Morselli E, Zhu C,
Harper F, et al: Regulation of autophagy by cytoplasmic p53. Nat
Cell Biol. 10:676–687. 2008. View
Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
23
|
Zhang R, Zhu F, Ren J, Huang L, Liu P and
Wu G: Beclin1/PI3K-mediated autophagy prevents hypoxia-induced
apoptosis in EAhy926 cell line. Cancer Biother Radiopharm.
26:335–343. 2011. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
24
|
Endo H, Niioka M, Kobayashi N, Tanaka M
and Watanabe T: Butyrate-producing probiotics reduce nonalcoholic
fatty liver disease progression in rats: New insight into the
probiotics for the gut-liver axis. PLoS One. 8:e633882013.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
25
|
Fan RH, Chen PS, Zhao D and Zhang WD:
Hypoxia induced by CoCl2 influencing the expression and the
activity of matrix metalloproteinase-2 in rat hepatic stellate
cells. Zhonghua Gan Zang Bing Za Zhi. 15:654–657. 2007.(In
Chinese). PubMed/NCBI
|
|
26
|
Karovic O, Tonazzini I, Rebola N, Edström
E, Lövdahl C, Fredholm BB and Daré E: Toxic effects of cobalt in
primary cultures of mouse astrocytes. Similarities with hypoxia and
role of HIF-1alpha. Biochem Pharmacol. 73:694–708. 2007. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
27
|
Blommaart EF, Luiken JJ, Blommaart PJ, van
Woerkom GM and Meijer AJ: Phosphorylation of ribosomal protein S6
is inhibitory for autophagy in isolated rat hepatocytes. J Biol
Chem. 270:2320–2326. 1995. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
28
|
Hahn-Windgassen A, Nogueira V, Chen CC,
Skeen JE, Sonenberg N and Hay N: Akt activates the mammalian target
of rapamycin by regulating cellular ATP level and AMPK activity. J
Biol Chem. 280:32081–32089. 2005. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
29
|
Inoki K, Zhu T and Guan K: TSC2 mediates
cellular energy response to control cell growth and survival. Cell.
115:577–590. 2003. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
30
|
Zhou Q, Liu H, Sun Q, Zhang L, Lin H, Yuan
G, Zhang L and Chen Z: Adenosine monophosphate-activated protein
kinase/mammalian target of rapamycin-dependent autophagy protects
human dental pulp cells against hypoxia. J Endod. 39:768–773. 2013.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
31
|
Bowman EJ, Siebers A and Altendorf K:
Bafilomycins: A class of inhibitors of membrane ATPases from
microorganisms, animal cells, and plant cells. Proc Natl Acad Sci
USA. 85:pp. 7972–7976. 1988; View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
32
|
Yoshimori T, Yamamoto A, Moriyama Y, Futai
M and Tashiro Y: Bafilomycin A1, a specific inhibitor of
vacuolar-type H(+)-ATPase, inhibits acidification and protein
degradation in lysosomes of cultured cells. J Biol Chem.
266:17707–17712. 1991.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
33
|
Blommaart EF, Krause U, Schellens JP,
Vreeling-Sindelárová H and Meijer AJ: The phosphatidylinositol
3-kinase inhibitors wortmannin and LY294002 inhibit autophagy in
isolated rat hepatocytes. Eur J Biochem. 243:240–246. 1997.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
34
|
Kim SE, Park HJ, Jeong HK, Kim MJ, Kim M,
Bae ON and Baek SH: Autophagy sustains the survival of human
pancreatic cancer PANC-1 cells under extreme nutrient deprivation
conditions. Biochem Biophys Res Commun. 463:205–210. 2015.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
35
|
Murphy MP and Smith RA: Targeting
antioxidants to mitochondria by conjugation to lipophilic cations.
Annu Rev Pharmacol Toxicol. 47:629–656. 2007. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
36
|
Hardie DG, Ross FA and Hawley SA: AMPK: A
nutrient and energy sensor that maintains energy homeostasis. Nat
Rev Mol Cell Biology. 13:251–262. 2012. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
37
|
Heerlein K, Schulze A, Hotz L, Bärtsch P
and Mairbäurl H: Hypoxia decreases cellular ATP demand and inhibits
mitochondrial respiration of a549 cells. Am J Respir Cell Mol Biol.
32:44–51. 2005. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
38
|
Owada S, Shimoda Y, Tsuchihara K and Esumi
H: Critical role of H2O2 generated by NOX4
during cellular response under glucose deprivation. PLoS One.
8:e566282013. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
39
|
Nogueira V and Hay N: Molecular pathways:
Reactive oxygen species homeostasis in cancer cells and
implications for cancer therapy. Clin Cancer Res. 19:4309–4314.
2013. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
40
|
Chandel NS, McClintock DS, Feliciano CE,
Wood TM, Melendez JA, Rodriguez AM and Schumacker PT: Reactive
oxygen species generated at mitochondrial complex III stabilize
hypoxia-inducible factor-1alpha during hypoxia: A mechanism of
O2 sensing. J Biol Chem. 275:25130–25138. 2000.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
41
|
Diebold I, Petry A, Hess J and Görlach A:
The NADPH oxidase subunit NOX4 is a new target gene of the
hypoxia-inducible factor-1. Mol Biol Cell. 21:2087–2096. 2010.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
42
|
Mansfield KD, Simon MC and Keith B:
Hypoxic reduction in cellular glutathione levels requires
mitochondrial reactive oxygen species. J Appl Physiol (1985).
97:1358–1366. 2004. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
43
|
Hirayama A, Kami K, Sugimoto M, Sugawara
M, Toki N, Onozuka H, Kinoshita T, Saito N, Ochiai A, Tomita M, et
al: Quantitative metabolome profiling of colon and stomach cancer
microenvironment by capillary electrophoresis time-of-flight mass
spectrometry. Cancer Res. 69:4918–4925. 2009. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|