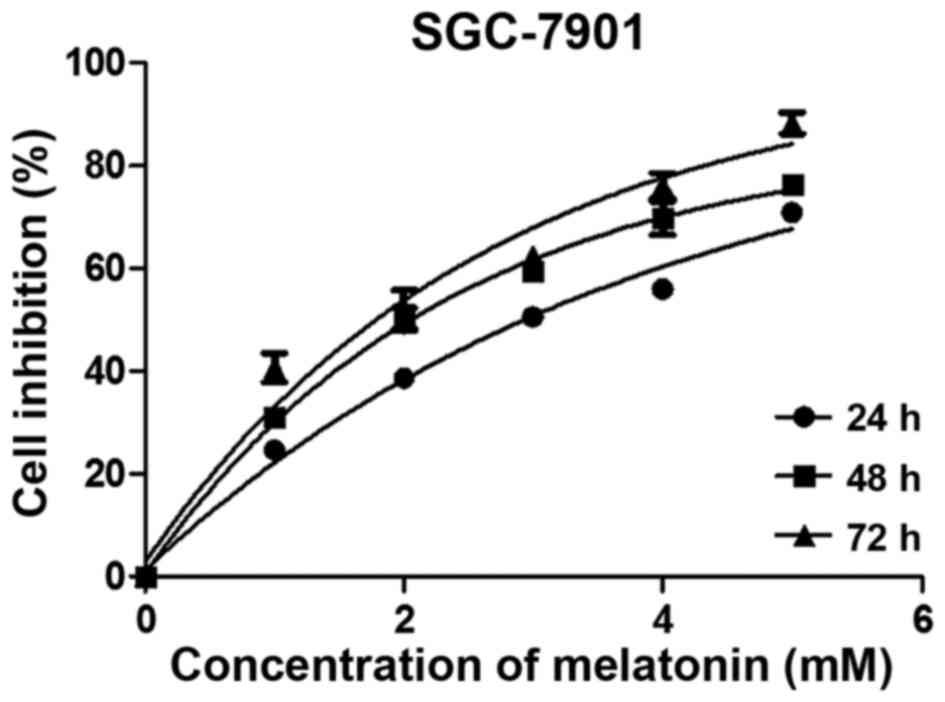
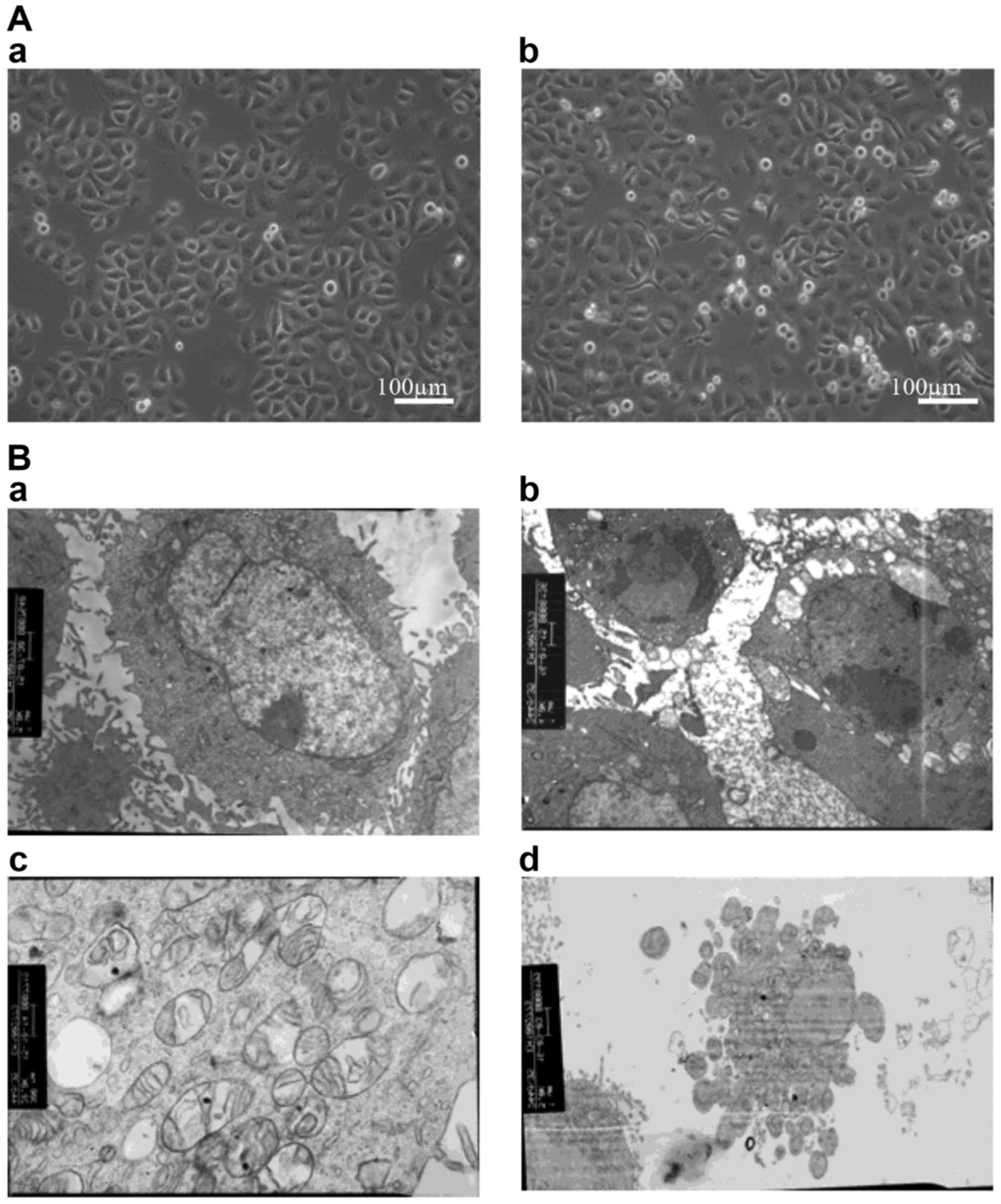
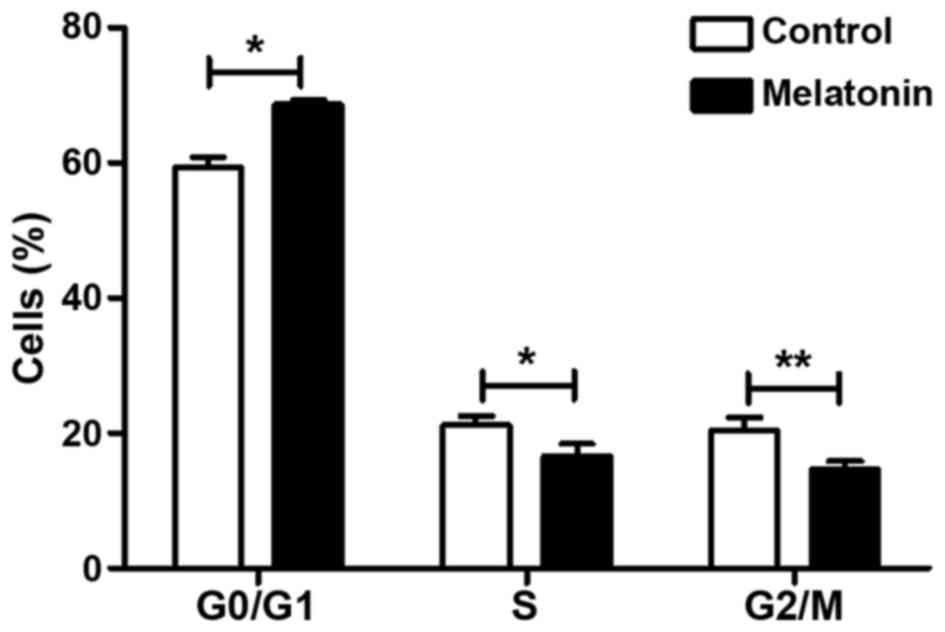
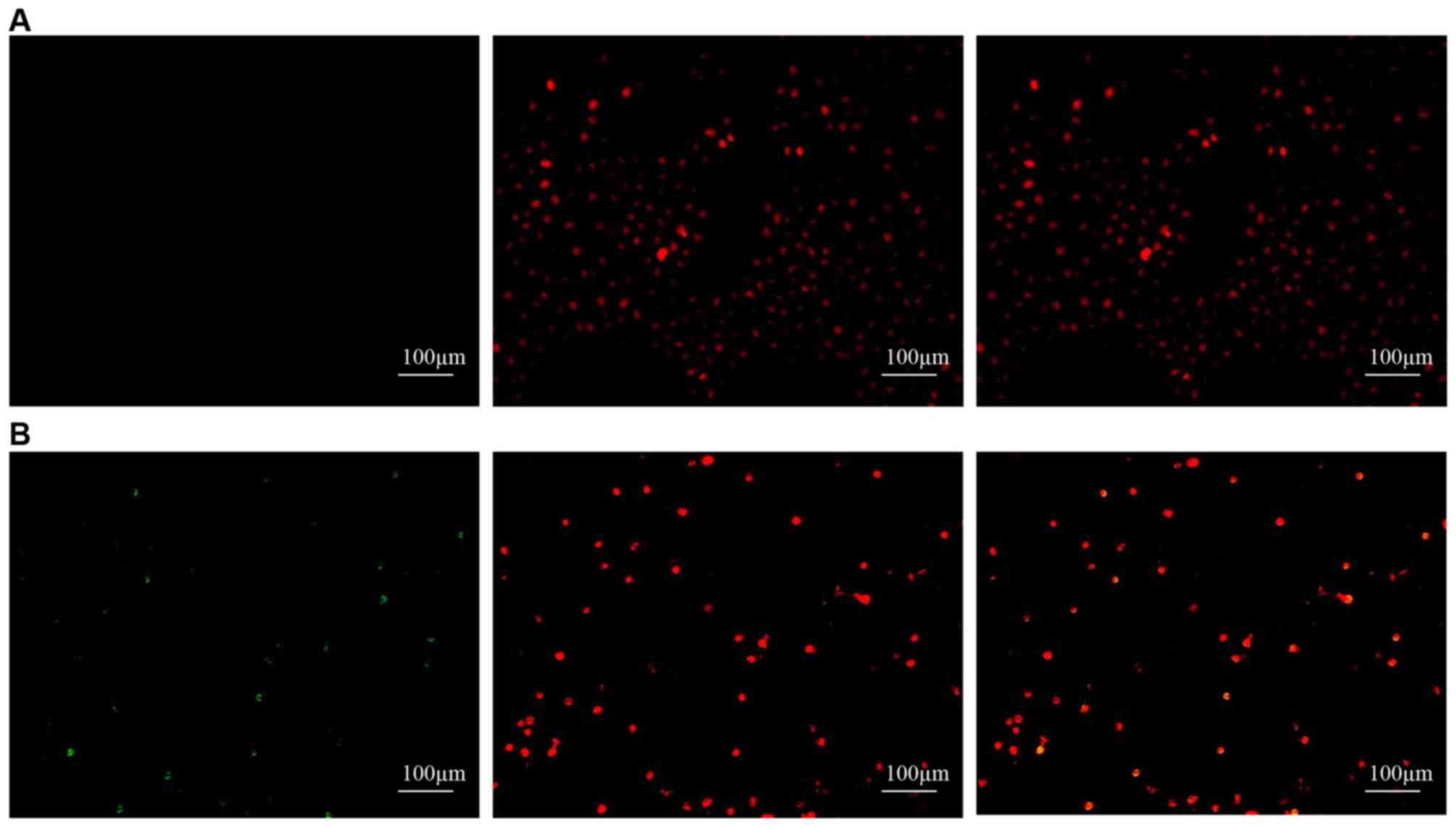
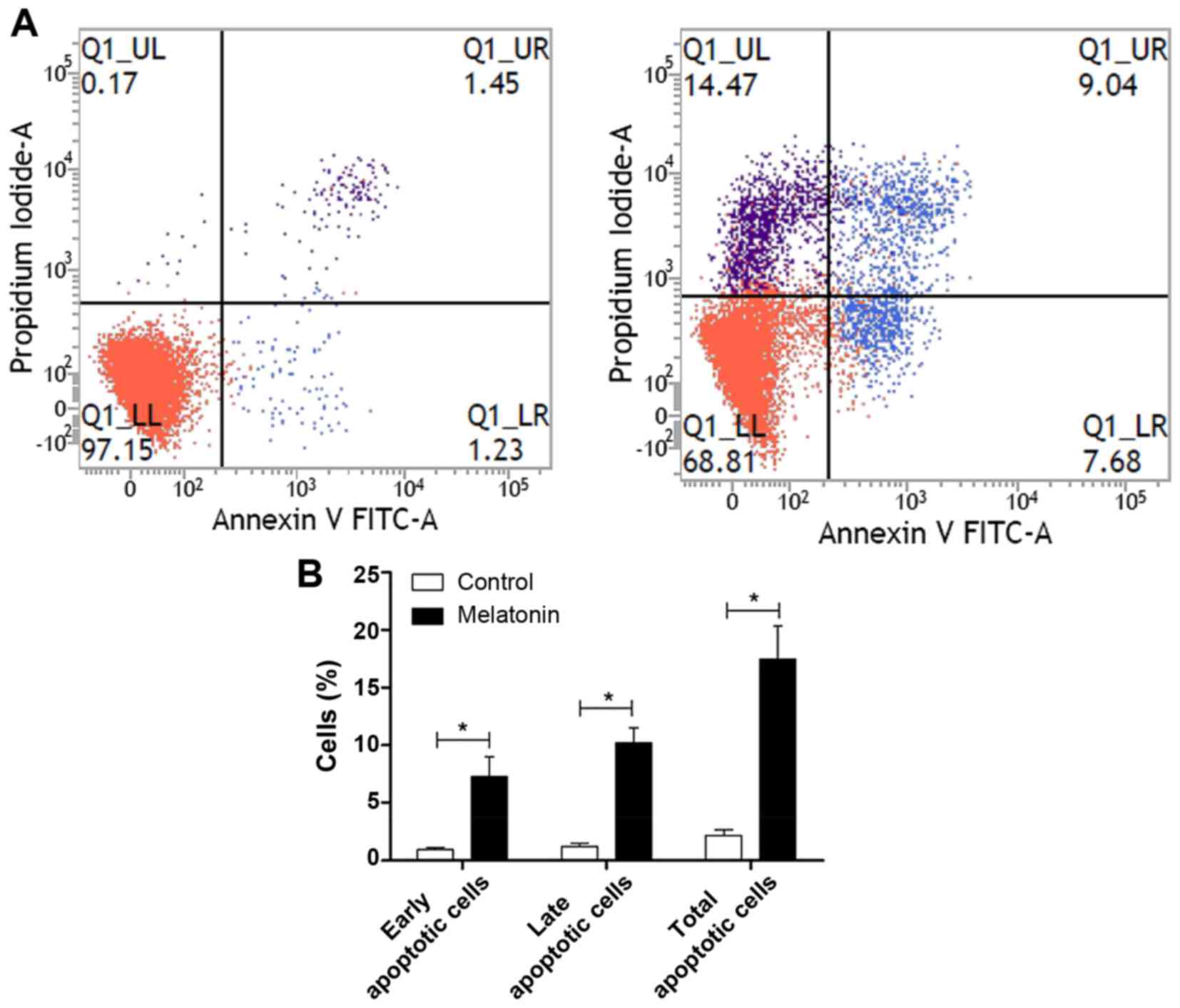
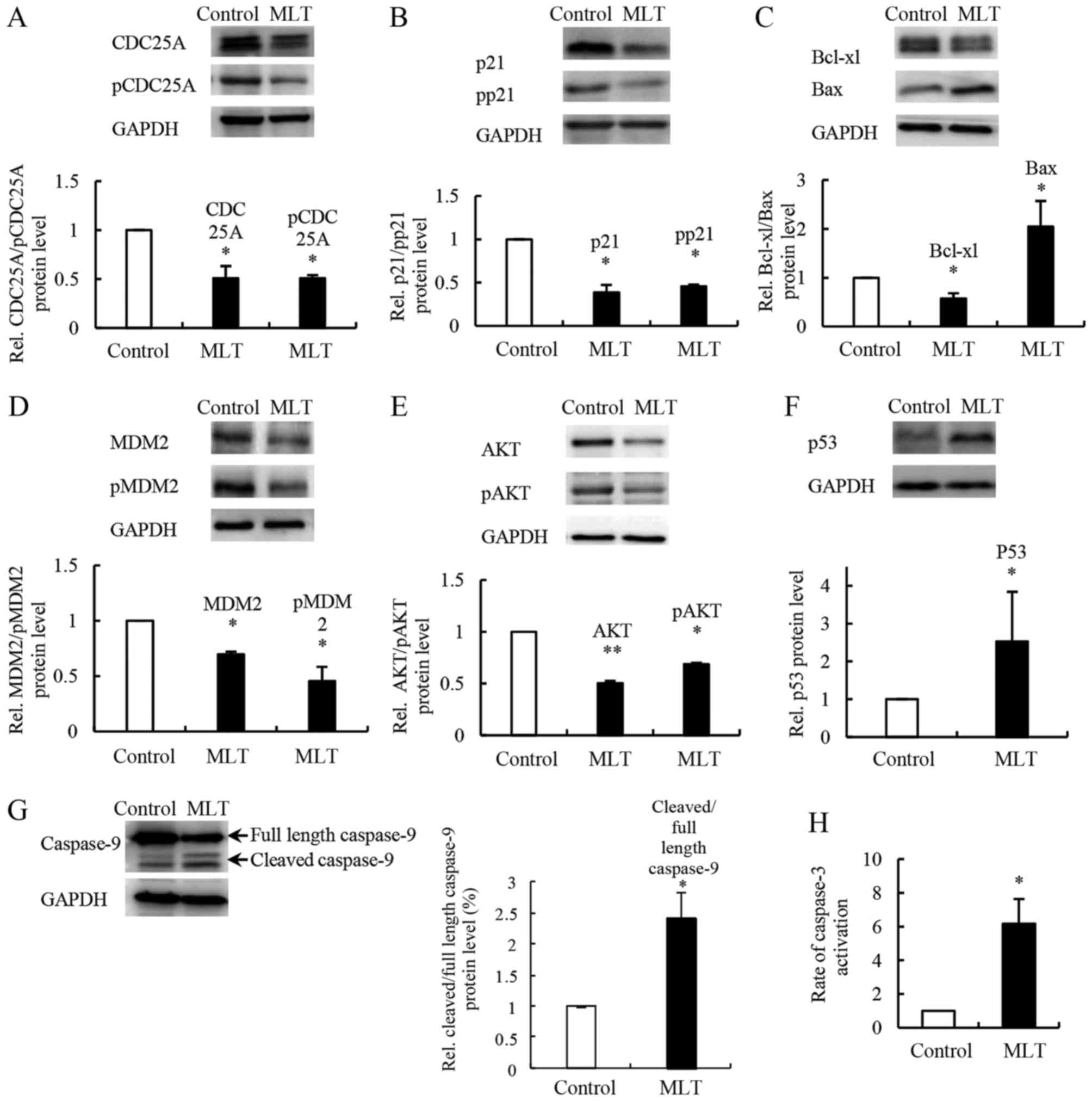
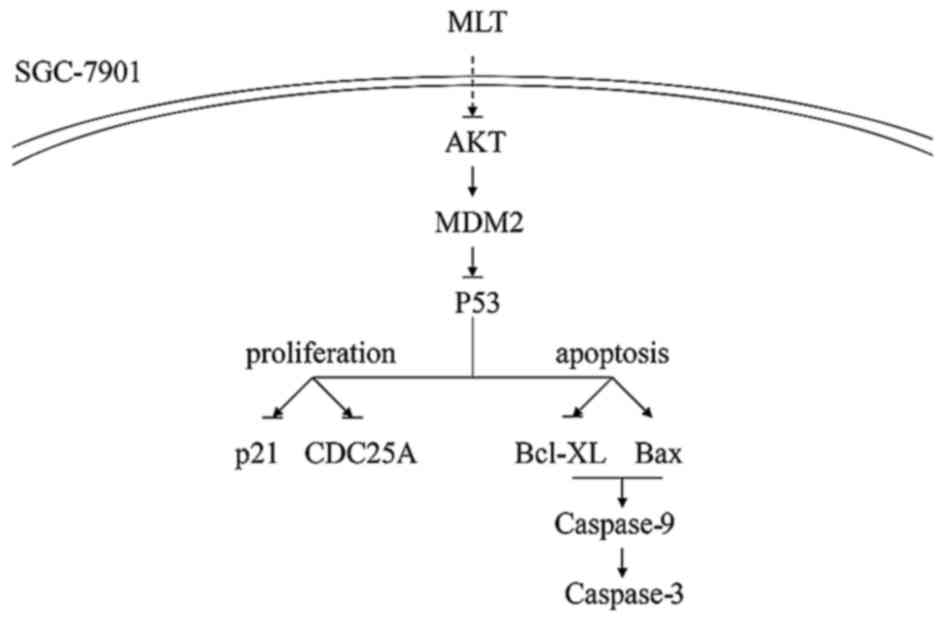
|
1
|
Jemal A, Bray F, Center MM, Ferlay J, Ward
E and Forman D: Global cancer statistics. CA Cancer J Clin.
61:69–90. 2011. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
2
|
World Health Organization, . World Cancer
Report 2014. World Health Organization; Geneva: 2014
|
|
3
|
Voiculescu SE, Zygouropoulos N, Zahiu CD
and Zagrean AM: Role of melatonin in embryo fetal development. J
Med Life. 7:488–492. 2014.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
4
|
Karaaslan C and Suzen S: Antioxidant
properties of melatonin and its potential action in diseases. Curr
Top Med Chem. 15:894–903. 2015. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
5
|
Acuña-Castroviejo D, Escames G, Venegas C,
Díaz-Casado ME, Lima-Cabello E, López LC, Rosales-Corral S, Tan DX
and Reiter RJ: Extrapineal melatonin: Sources, regulation, and
potential functions. Cell Mol Life Sci. 71:2997–3025. 2014.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
6
|
Bubenik GA: Thirty four years since the
discovery of gastrointestinal melatonin. J Physiol Pharmacol. 59
Suppl 2:33–51. 2008.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
7
|
Bubenik GA: Gastrointestinal melatonin:
Localization, function, and clinical relevance. Dig Dis Sci.
47:2336–2348. 2002. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
8
|
Kolli VK, Kanakasabapathy I, Faith M,
Ramamoorthy H, Isaac B, Natarajan K and Abraham P: A preclinical
study on the protective effect of melatonin against
methotrexate-induced small intestinal damage: Effect mediated by
attenuation of nitrosative stress, protein tyrosine nitration, and
PARP activation. Cancer Chemother Pharmacol. 71:1209–1218. 2013.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
9
|
Lissoni P, Barni S, Crispino S, Tancini G
and Fraschini F: Endocrine and immune effects of melatonin therapy
in metastatic cancer patients. Eur J Cancer Clin Oncol. 25:789–795.
1989. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
10
|
Zhang S, Qi Y, Zhang H, He W, Zhou Q, Gui
S and Wang Y: Melatonin inhibits cell growth and migration, but
promotes apoptosis in gastric cancer cell line, SGC7901. Biotech
Histochem. 88:281–289. 2013. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
11
|
Wang RX, Liu H, Xu L, Zhang H and Zhou RX:
Involvement of nuclear receptor RZR/RORγ in melatonin-induced
HIF-1α inactivation in SGC-7901 human gastric cancer cells. Oncol
Rep. 34:2541–2546. 2015. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
12
|
Wang RX, Liu H, Xu L, Zhang H and Zhou RX:
Melatonin downregulates nuclear receptor RZR/RORγ expression
causing growth-inhibitory and anti-angiogenesis activity in human
gastric cancer cells in vitro and in vivo. Oncol Lett. 12:897–903.
2016. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
13
|
Li W, Fan M, Chen Y, Zhao Q, Song C, Yan
Y, Jin Y, Huang Z, Lin C and Wu J: Melatonin induces cell apoptosis
in AGS cells through the activation of JNK and P38 MAPK and the
suppression of nuclear factor-kappa B: A novel therapeutic
implication for gastric cancer. Cell Physiol Biochem. 37:2323–2338.
2015. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
14
|
Carbajo-Pescador S, Ordoñez R, Benet M,
Jover R, García-Palomo A, Mauriz JL and González-Gallego J:
Inhibition of VEGF expression through blockade of Hif1α and STAT3
signalling mediates the anti-angiogenic effect of melatonin in
HepG2 liver cancer cells. Br J Cancer. 109:83–91. 2013. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
15
|
Fan L, Sun G, Ma T, Zhong F and Wei W:
Melatonin overcomes apoptosis resistance in human hepatocellular
carcinoma by targeting survivin and XIAP. J Pineal Res. 55:174–183.
2013. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
16
|
Fan L, Sun G, Ma T, Zhong F, Lei Y, Li X
and Wei W: Melatonin reverses tunicamycin-induced endoplasmic
reticulum stress in human hepatocellular carcinoma cells and
improves cytotoxic response to doxorubicin by increasing CHOP and
decreasing survivin. J Pineal Res. 55:184–194. 2013. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
17
|
Ordoñez R, Carbajo-Pescador S,
Prieto-Dominguez N, García-Palomo A, González-Gallego J and Mauriz
JL: Inhibition of matrix metalloproteinase-9 and nuclear factor
kappa B contribute to melatonin prevention of motility and
invasiveness in HepG2 liver cancer cells. J Pineal Res. 56:20–30.
2014. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
18
|
Alvarez-García V, González A,
Alonso-González C, Martínez-Campa C and Cos S: Regulation of
vascular endothelial growth factor by melatonin in human breast
cancer cells. J Pineal Res. 54:373–380. 2013. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
19
|
Blask DE, Dauchy RT, Dauchy EM, Mao L,
Hill SM, Greene MW, Belancio VP, Sauer LA and Davidson L: Light
exposure at night disrupts host/cancer circadian regulatory
dynamics: Impact on the Warburg effect, lipid signaling and tumor
growth prevention. PLoS One. 9:e1027762014.doi:
10.1371/journal.pone.0102776. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
20
|
Cos S, Alvarez-García V, González A,
Alonso-González C and Martínez-Campa C: Melatonin modulation of
crosstalk among malignant epithelial, endothelial and adipose cells
in breast cancer (Review). Oncol Lett. 8:487–492. 2014. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
21
|
Proietti S, Cucina A, Dobrowolny G,
D'Anselmi F, Dinicola S, Masiello MG, Pasqualato A, Palombo A,
Morini V, Reiter RJ, et al: Melatonin down-regulates MDM2 gene
expression and enhances p53 acetylation in MCF-7 cells. J Pineal
Res. 57:120–129. 2014. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
22
|
Cutando A, López-Valverde A, DE Vicente J,
Gimenez JL, Carcía IA and DE Diego RG: Action of melatonin on
squamous cell carcinoma and other tumors of the oral cavity
(Review). Oncol Lett. 7:923–926. 2014. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
23
|
Goncalves NN, Rodrigues RV, Jardim-Perassi
BV, Moschetta MG, Lopes JR, Colombo J and Zuccari DA: Molecular
markers of angiogenesis and metastasis in lines of oral carcinoma
after treatment with melatonin. Anticancer Agents Med Chem.
14:1302–1311. 2014. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
24
|
Rodriguez-Garcia A, Mayo JC, Hevia D,
Quiros-Gonzalez I, Navarro M and Sainz RM: Phenotypic changes
caused by melatonin increased sensitivity of prostate cancer cells
to cytokine-induced apoptosis. J Pineal Res. 54:33–45. 2013.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
25
|
Shiu SY, Leung WY, Tam CW, Liu VW and Yao
KM: Melatonin MT1 receptor-induced transcriptional up-regulation of
p27(Kip1) in prostate cancer antiproliferation is mediated via
inhibition of constitutively active nuclear factor kappa B (NF-κB):
Potential implications on prostate cancer chemoprevention and
therapy. J Pineal Res. 54:69–79. 2013. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
26
|
Paroni R, Terraneo L, Bonomini F, Finati
E, Virgili E, Bianciardi P, Favero G, Fraschini F, Reiter RJ,
Rezzani R, et al: Antitumour activity of melatonin in a mouse model
of human prostate cancer: Relationship with hypoxia signalling. J
Pineal Res. 57:43–52. 2014. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
27
|
Liu H, Xu L, Wei JE, Xie MR, Wang SE and
Zhou RX: Role of CD4+ CD25+ regulatory T
cells in melatonin-mediated inhibition of murine gastric cancer
cell growth in vivo and in vitro. Anat Rec (Hoboken). 294:781–788.
2011. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
28
|
Xu L, Jin QD, Gong X, Liu H and Zhou RX:
Anti-gastric cancer effect of melatonin and Bcl-2, Bax, p21 and p53
expression changes. Sheng Li Xue Bao. 66:723–729. 2014.(In
Chinese). PubMed/NCBI
|
|
29
|
Fakharzadeh SS, Trusko SP and George DL:
Tumorigenic potential associated with enhanced expression of a gene
that is amplified in a mouse tumor cell line. EMBO J. 10:1565–1569.
1991.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
30
|
Zak K, Pecak A, Rys B, Wladyka B, Dömling
A, Weber L, Holak TA and Dubin G: Mdm2 and MdmX inhibitors for the
treatment of cancer: A patent review (2011-present). Expert Opin
Ther Pat. 23:425–448. 2013. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
31
|
Shaikh MF, Morano WF, Lee J, Gleeson E,
Babcock BD, Michl J, Sarafraz-Yazdi E, Pincus MR and Bowne WB:
Emerging role of MDM2 as target for anti-cancer therapy: A review.
Ann Clin Lab Sci. 46:627–634. 2016.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
32
|
He J, Zhu G, Gao L, Chen P, Long Y, Liao
S, Yi H, Yi W, Pei Z, Wu M, et al: Fra-1 is upregulated in gastric
cancer tissues and affects the PI3K/Akt and p53 signaling pathway
in gastric cancer. Int J Oncol. 47:1725–1734. 2015. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
33
|
Eischen CM and Lozano G: p53 and MDM2:
Antagonists or partners in crime? Cancer Cell. 15:161–162. 2009.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
34
|
Nakajima N, Ito Y, Yokoyama K, Uno A,
Kinukawa N, Nemoto N and Moriyama M: The expression of murine
double minute 2 (MDM2) on Helicobacter pylori-infected intestinal
metaplasia and gastric cancer. J Clin Biochem Nutr. 44:196–202.
2009. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
35
|
Günther T, Schneider-Stock R, Häckel C,
Kasper HU, Pross M, Hackelsberger A, Lippert H and Roessner A: Mdm2
gene amplification in gastric cancer correlation with expression of
Mdm2 protein and p53 alterations. Mod Pathol. 13:621–626. 2000.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
36
|
Sun LP, Jiang NJ, Fu W, Xue YX and Zhao
YS: Relationship between gastric cancer and gene amplification of
p14 and mdm2. Ai Zheng. 23:36–39. 2004.(In Chinese). PubMed/NCBI
|
|
37
|
Manfredi JJ: The Mdm2-p53 relationship
evolves: Mdm2 swings both ways as an oncogene and a tumor
suppressor. Genes Dev. 24:1580–1589. 2010. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
38
|
Carter S, Bischof O, Dejean A and Vousden
KH: C-terminal modifications regulate MDM2 dissociation and nuclear
export of p53. Nat Cell Biol. 9:428–435. 2007. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
39
|
Lohrum MA, Woods DB, Ludwig RL, Bálint E
and Vousden KH: C-terminal ubiquitination of p53 contributes to
nuclear export. Mol Cell Biol. 21:8521–8532. 2001. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
40
|
Zauberman A, Barak Y, Ragimov N, Levy N
and Oren M: Sequence-specific DNA binding by p53: Identification of
target sites and lack of binding to p53 - MDM2 complexes. EMBO J.
12:2799–2808. 1993.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
41
|
Poyurovsky MV, Katz C, Laptenko O,
Beckerman R, Lokshin M, Ahn J, Byeon IJ, Gabizon R, Mattia M,
Zupnick A, et al: The C terminus of p53 binds the N-terminal domain
of MDM2. Nat Struct Mol Biol. 17:982–989. 2010. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
42
|
Cross B, Chen L, Cheng Q, Li B, Yuan ZM
and Chen J: Inhibition of p53 DNA binding function by the MDM2
protein acidic domain. J Biol Chem. 286:16018–16029. 2011.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
43
|
Biderman L, Poyurovsky MV, Assia Y, Manley
JL and Prives C: MdmX is required for p53 interaction with and full
induction of the Mdm2 promoter after cellular stress. Mol Cell
Biol. 32:1214–1225. 2012. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
44
|
Bond GL, Hu W, Bond EE, Robins H, Lutzker
SG, Arva NC, Bargonetti J, Bartel F, Taubert H, Wuerl P, et al: A
single nucleotide polymorphism in the MDM2 promoter attenuates the
p53 tumor suppressor pathway and accelerates tumor formation in
humans. Cell. 119:591–602. 2004. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
45
|
Bond GL, Hu W and Levine A: A single
nucleotide polymorphism in the MDM2 gene: From a molecular and
cellular explanation to clinical effect. Cancer Res. 65:5481–5484.
2005. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
46
|
Ofir-Rosenfeld Y, Boggs K, Michael D,
Kastan MB and Oren M: Mdm2 regulates p53 mRNA translation through
inhibitory interactions with ribosomal protein L26. Mol Cell.
32:180–189. 2008. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
47
|
Mayo LD and Donner DB: A
phosphatidylinositol 3-kinase/Akt pathway promotes translocation of
Mdm2 from the cytoplasm to the nucleus. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA.
98:pp. 11598–11603. 2001; View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
48
|
Zhou BP, Liao Y, Xia W, Zou Y, Spohn B and
Hung MC: HER-2/neu induces p53 ubiquitination via Akt-mediated MDM2
phosphorylation. Nat Cell Biol. 3:973–982, 2001. Nat Cell Biol 3:
973–982. 2001. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
49
|
Gottlieb TM, Leal JF, Seger R, Taya Y and
Oren M: Cross-talk between Akt, p53 and Mdm2: Possible implications
for the regulation of apoptosis. Oncogene. 21:1299–1303. 2002.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
50
|
Jones SN, Hancock AR, Vogel H, Donehower
LA and Bradley A: Overexpression of Mdm2 in mice reveals a
p53-independent role for Mdm2 in tumorigenesis. Proc Natl Acad Sci
USA. 95:pp. 15608–15612. 1998; View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
51
|
McDonnell TJ, Montes de Oca Luna R, Cho S,
Amelse LL, Chavez-Reyes A and Lozano G: Loss of one but not two
mdm2 null alleles alters the tumour spectrum in p53 null mice. J
Pathol. 188:322–328. 1999. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
52
|
Dobbelstein M, Wienzek S, König C and Roth
J: Inactivation of the p53-homologue p73 by the mdm2-oncoprotein.
Oncogene. 18:2101–2106. 1999. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
53
|
Zeng X, Chen L, Jost CA, Maya R, Keller D,
Wang X, Kaelin WG Jr, Oren M, Chen J and Lu H: MDM2 suppresses p73
function without promoting p73 degradation. Mol Cell Biol.
19:3257–3266. 1999. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
54
|
Gu J, Nie L, Kawai H and Yuan ZM:
Subcellular distribution of p53 and p73 are differentially
regulated by MDM2. Cancer Res. 61:6703–6707. 2001.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
55
|
Watson IR, Blanch A, Lin DC, Ohh M and
Irwin MS: Mdm2-mediated NEDD8 modification of TAp73 regulates its
transactivation function. J Biol Chem. 281:34096–34103. 2006.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
56
|
Cheney MD, McKenzie PP, Volk EL, Fan L and
Harris LC: MDM2 displays differential activities dependent upon the
activation status of NFkappaB. Cancer Biol Ther. 7:38–44. 2008.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
57
|
Sun P, Dong P, Dai K, Hannon GJ and Beach
D: p53-independent role of MDM2 in TGF-beta1 resistance. Science.
282:2270–2272. 1998. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
58
|
Yam CH, Siu WY, Arooz T, Chiu CH, Lau A,
Wang XQ and Poon RY: MDM2 and MDMX inhibit the transcriptional
activity of ectopically expressed SMAD proteins. Cancer Res.
59:5075–5078. 1999.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
59
|
Xiao ZX, Chen J, Levine AJ, Modjtahedi N,
Xing J, Sellers WR and Livingston DM: Interaction between the
retinoblastoma protein and the oncoprotein MDM2. Nature.
375:694–698. 1995. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
60
|
Sdek P, Ying H, Zheng H, Margulis A, Tang
X, Tian K and Xiao ZX: The central acidic domain of MDM2 is
critical in inhibition of retinoblastoma-mediated suppression of
E2F and cell growth. J Biol Chem. 279:53317–53322. 2004. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
61
|
Zhou S, Gu L, He J, Zhang H and Zhou M:
MDM2 regulates vascular endothelial growth factor mRNA
stabilization in hypoxia. Mol Cell Biol. 31:4928–4937. 2011.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
62
|
Thut CJ, Goodrich JA and Tjian R:
Repression of p53-mediated transcription by MDM2: A dual mechanism.
Genes Dev. 11:1974–1986. 1997. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
63
|
Minsky N and Oren M: The RING domain of
Mdm2 mediates histone ubiquitylation and transcriptional
repression. Mol Cell. 16:631–639. 2004. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
64
|
Ji W, Ma J, Zhang H, Zhong H, Li L, Ding
N, Jiao J and Gao Z: Role of p53β in the inhibition of
proliferation of gastric cancer cells expressing wild-type or
mutated p53. Mol Med Rep. 12:691–695. 2015. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
65
|
Hoffmann I, Draetta G and Karsenti E:
Activation of the phosphatase activity of human cdc25A by a
cdk2-cyclin E dependent phosphorylation at the G1/S transition.
EMBO J. 13:4302–4310. 1994.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
66
|
Zou X, Tsutsui T, Ray D, Blomquist JF,
Ichijo H, Ucker DS and Kiyokawa H: The cell cycle-regulatory CDC25A
phosphatase inhibits apoptosis signal-regulating kinase 1. Mol Cell
Biol. 21:4818–4828. 2001. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
67
|
Goloudina A, Yamaguchi H, Chervyakova DB,
Appella E, Fornace AJ Jr and Bulavin DV: Regulation of human Cdc25A
stability by Serine 75 phosphorylation is not sufficient to
activate a S phase checkpoint. Cell Cycle. 2:473–478. 2003.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
68
|
Boutros R, Lobjois V and Ducommun B: CDC25
phosphatases in cancer cells: Key players? Good targets? Nat Rev
Cancer. 7:495–507. 2007. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
69
|
Cheng M, Olivier P, Diehl JA, Fero M,
Roussel MF, Roberts JM and Sherr CJ: The p21(Cip1) and p27(Kip1)
CDK ‘inhibitors’ are essential activators of cyclin D-dependent
kinases in murine fibroblasts. EMBO J. 18:1571–1583. 1999.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
70
|
Martín V, Herrera F, García-Santos G,
Antolín I, Rodriguez-Blanco J, Medina M and Rodriguez C:
Involvement of protein kinase C in melatonin's oncostatic effect in
C6 glioma cells. J Pineal Res. 43:
|
|
71
|
Rother K, Kirschner R, Sänger K, Böhlig L,
Mössner J and Engeland K: p53 downregulates expression of the
G1/S cell cycle phosphatase Cdc25A. Oncogene.
26:1949–1953. 2007. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|