Introduction
Apoptosis is defined as a programmed cell death
which is responsible for the maintenance of tissue homeostasis
during normal physiological as well as pathological conditions.
There are a variety of cell surface receptors that contribute to
the regulation of the apoptosis mechanism, for example, surface
immunoglobulin, T-cell antigen receptor, and tumor necrosis
receptor (1–3). Among these surface receptors, Fas
belongs to the tumor necrosis factor (TNF) receptor family of death
receptors and is able to initiate the apoptosis pathway through
binding to specific death ligands of the cells which include, Fas
ligand (FasL), tumor necrosis factor-α (TNF-α) and Fas-specific
monoclonal antibody CH11 (mAb CH11) (4,5).
Fas-mediated apoptosis is believed to play a crucial role in
cytotoxic T-cell and natural killer cell-mediated apoptosis in
cancer, as their activation leads to the expression of Fas ligand
on the cell surface which eventually induces apoptosis in targeted
cancer cells (6–8).
The induction of apoptosis by Fas is sophisticated
and it starts with the formation of the death-inducing signaling
complex (DISC) which acts as the cellular switch for the apoptosis
pathway. However, the DISC formation initiates right after the
interaction of FasL to Fas, followed by the aggregation of receptor
molecules and the recruitment of the Fas-associated death domain
(FADD), through the death domain interaction. Furthermore FADD
contains a death effector domain that leads to the recruitment of
pro-caspase-8 resulting in the formation of a multimeric protein
complex and the activation of caspase-8 (9,10).
Conversely, there are several proteins that have a
regulatory effect on Fas-mediated apoptosis, which when activated,
suppress the apoptosis pathway induced by Fas. Among these, a key
protein that regulates Fas-mediated apoptosis at DISC level, is
cellular FLICE-like inhibitory protein (cFLIP). cFLIP interferes
with caspase to prevent the cleavage and activation of caspase
(11). cFLIP has been extensively
studied for its anti-apoptotic potential and is found to be
expressed in various cancer cells, for example, ovarian, colon,
glioblastoma, breast, colorectal, renal and prostate cancer in a
considerable amount where it is found to cause TRAIL resistance
(12–14). Furthermore, cFLIP has been reported
having 11 distinct splicing variants, three among which are
expressed predominantly i.e. cFLIP(L), cFLIP(S) and cFLIP(R)
(12,15). Apart from the other two variants,
cFLIP(L) has gained attention in the scientific community as a
major variant involved in the blockage of caspase-8/10 activation.
However, comprehensive studies on cFLIP(L) revealed that it had
binary function, for example, ectopic overexpression of cFLIP(L)
inhibited the activation of caspase-8 and ectopic expression
equivalent to endogenous cFLIP(L) was found to promote caspase-8
processing in HeLa and MCF cells (16,17).
Therefore, the role of cFLIP(L) soon became controversial.
Furthermore, despite the fact that cFLIP(S) also plays an important
role in Fas-mediated apoptosis, cFLIP(S) remains neglected, with
few exceptions (18,19). These observations were the
motivation behind the present study.
In the present study we examined the regulation of
both isoforms of cFLIP (long and short) during Fas-mediated
apoptosis in renal carcinoma cell lines and revealed that both
isoforms are differentially regulated during Fas-mediated apoptosis
at the translational level, however this expression was unaffected
at the transcriptional level.
Materials and methods
Cells and materials
Caki-1 cells were obtained from the American Type
Culture Collection (ATCC, Manassas, VA, USA). The culture medium
used throughout these experiments was Dulbecco's modified Eagle's
medium (DMEM; WelGene, Inc., Daegu, Korea), containing 10% fetal
bovine serum (FBS; WelGene), 20 mM HEPES buffer and 100 mg/ml
gentamycin. Anti-Fas antibody (human, activating) clone CH11
(1:5,000; 1:2,500; 1:1,000; cat. no. 05-201) was purchased from EDM
Millipore (Darmstadt, Germany). Anti-caspase-3 (1:700; cat. no.
ADI-AAP-113) and anti-c-FLIP (1:700; cat. no. ALX-804-961-0100)
antibodies were purchased from Enzo Life Sciences (Farmington, NY,
USA). Anti-PARP antibody (1:700; cat. no. 9542S) was purchased from
Cell Signaling Technology (Beverly, MA, USA). Other chemicals were
obtained from Sigma-Aldrich (St. Louis, MO, USA).
Western blotting
The cells were washed with cold PBS and lysed on ice
in 50 µl of lysis buffer (50 mM Tris-HCl, 1 mM EGTA, 1% Triton
X-100, 1 mM phenylmethylsulfonyl fluoride, pH 7.5) (20,21).
Lysates were centrifuged at 10,000 × g for 15 min at 4°C and the
supernatant fractions were collected. Proteins were separated by
SDS-PAGE and transferred to an Immobilon-P membrane (GE Healthcare
Life Science, Marlborough, MA USA). Specific proteins were detected
using an enhanced chemiluminescence (ECL) western blot kit (EMD
Millipore) according to the manufacturer's instructions.
Cell count and flow cytometric
analysis
Cell counts were performed using a hemocytometer
(Marienfeld-Superior, Lauda-Königshofen, Germany). Approximately
0.4×06 Caki cells were suspended in 100 ml of PBS and
200 ml of 95% ethanol were added while vortexing. The cells were
incubated at 4°C for 1 h, washed with PBS and resuspended in 250 ml
of 1.12% sodium citrate buffer (pH 8.4) together with 12.5 mg of
RNase. Incubation continued at 37°C for 30 min. The cellular DNA
was then stained by applying 250 ml of propidium iodide (PI; 50
mg/ml) for 30 min at room temperature. The stained cells were
analyzed by fluorescent activated cell sorting (FACS) on a FACScan
flow cytometer (BD Biosciences, San Jose, CA, USA) for relative DNA
content based on red fluorescence.
RNA isolation and RT-PCR
To determine whether the potential sensitizing
effects of FasL-mediated apoptosis were a result of increased
levels of mRNA encoding cFLIP(L) and cFLIP(S), we compared the
levels of cFLIP in Caki cells, which were treated with or without
various concentrations of FasL. cFLIP mRNA expression was
determined by RT-PCR. Total cellular RNA was extracted from cells
using the TRIzol reagent (Life Technologies; Thermo Fisher
Scientific, Inc., Waltham, MA, USA). A cDNA was synthesized from 2
µg of total RNA using M-MLV reverse transcriptase (Gibco-BRL;
Thermo Fisher Scientific). The cDNA for cFLIP(L) and cFLIP(S) was
amplified by PCR with specific primers. The primer sequences for
cFLIP(L) and cFLIP(S) were as follows: Sense for cFLIP(L) and
cFLIP(S), 5′-CGGACTATAGAGTGCTGATGG-3′ and antisense for cFLIP(L),
5′-GATTATCAGGCAGATTCCTAG-3′ and for cFLIP(S),
5′-AGATCAGGACAATGGGCATAG-3′.
Small-interfering RNAs (siRNAs)
The GFP (control) siRNA duplexes used in the present
study were purchased from Santa Cruz Biotechnology (Santa Cruz, CA,
USA). cFLIP(S) and cFLIP(L) siRNA duplexes were obtained from
Invitrogen (Thermo Fisher Scientific). The sequences of cFLIP(S)
and cFLIP(L) were AACAUGGAACUGCCUCUACUU and AAGGAACAGCUUGGCGCUCAA,
respectively. The cells were transfected with siRNA
oligonucleotides using Oligofectamine reagent (Invitrogen; Thermo
Fisher Scientific) according to the manufacturer's
instructions.
Statistical analysis
The data were analyzed using a one-way ANOVA and
post hoc comparisons (Student-Newman-Keuls) using the Statistical
Package for Social Sciences 22.0 software (SPSS, Inc., Chicago, IL,
USA). P<0.05 were considered to indicate a statistically
significant result.
Results
Effect of FasL treatment on the
expression levels of cFLIP(L) and cFLIP(S) in human renal cancer
cells
To determine the expression pattern of cFLIP(L) and
cFLIP(S) during FasL-mediated apoptosis, the renal carcinoma Caki
cells were treated with various concentrations of FasL (100–500
ng/ml) and then, flow cytometric and western blot analyses were
performed to evaluate the apoptosis induction and the expression
pattern of cFLIP(L) and cFLIP(S). FasL treatment caused an increase
in sub-G1 population in a concentration- and time-dependent manner
(Fig. 1A and D) which was further
verified by the PARP cleavage in western blot analysis (Fig. 1B and E). The expression of cFLIP(L)
was found to be highly downregulated after treatment of FasL.
However, the expression of cFLIP(S) was significantly upregulated
in a concentration- and time-dependent manner (Fig. 1B and E). In addition, there were no
changes in either of the cFLIP variants at the mRNA levels
(Fig. 1C and F), indicating that
FasL treatment induced differential expression patterns of cFLIP(L)
and cFLIP(S) and this expression was regulated at the
post-transcriptional level in Caki cells.
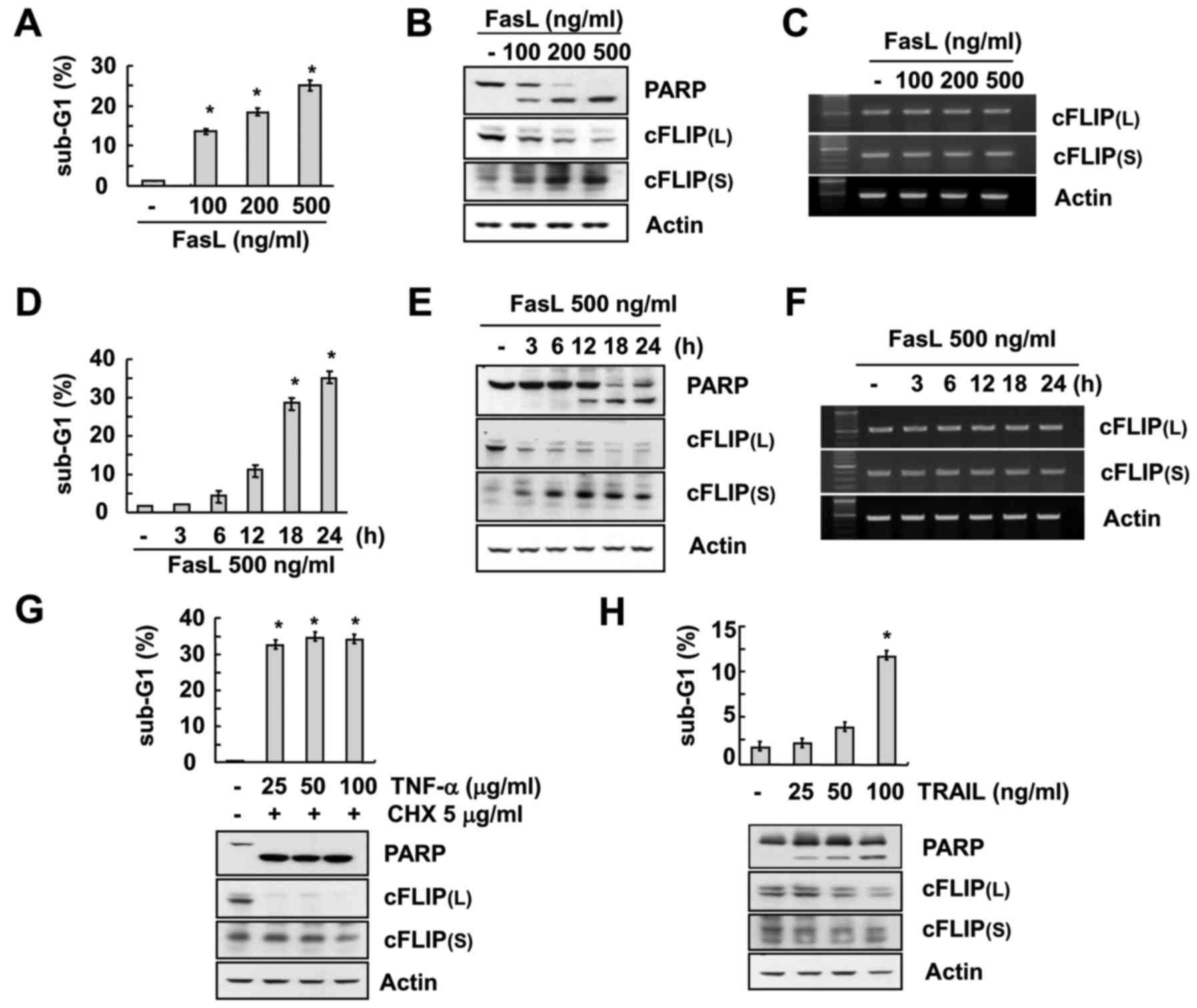 | Figure 1.FasL induces downregulation of
cFLIP(L) and upregulation of cFLIP(S) in human renal cancer cells.
(A-C) Caki cells were treated with the indicated concentrations of
FasL for 24 h. The level of apoptosis was assessed by the sub-G1
fraction using flow cytometry (A). The protein expression levels of
PARP, cFLIP(L), cFLIP(S) and actin were determined by western
blotting (B). The mRNA expression levels of cFLIP(L), cFLIP(S) and
actin were determined by RT-PCR (C). (D-F) Caki cells were treated
with 500 ng/ml FasL for the indicated time-points. The level of
apoptosis was determined by the sub-G1 fraction using flow
cytometry (D). The protein expression levels of PARP, cFLIP(L),
cFLIP(S) and actin were determined by western blotting (E). The
mRNA expression levels of cFLIP(L), cFLIP(S) and actin were
determined by RT-PCR (F). (G-H) Caki cells were treated with the
indicated concentrations of TNF-α plus 5 µg/ml cycloheximide (CHX)
(G) or TRAIL (H) for 24 h. The level of apoptosis was determined by
the sub-G1 fraction using flow cytometry. The protein expression
levels of PARP, cFLIP(L), cFLIP(S) and actin were determined by
western blotting. The values in A, D, G and H represent the means ±
SD from three independent samples. *P<0.01 compared to the
control. |
Furthermore, we investigated the effect of other
cell death-receptor mediated apoptosis inducers (TNF-α and TRAIL)
on the expression pattern of cFLIP variants with the treatment of
various concentrations of TNF-α or TRAIL to Caki cells. The results
of the experiment indicated that both TNF-α and TRAIL induced
apoptosis in Caki cells along with downregulation of cFLIP(L)
(Fig. 1G and H). However, they had
no effect on the expression of cFLIP(S) (Fig. 1G and H).
Role of caspase in FasL-mediated
differential expression of cFLIP(L) and cFLIP(S) in human renal
cancer cells
Based on the above mentioned data we observed that
FasL-mediated apoptosis differentially regulated the expression of
cFLIP(L) and cFLIP(S). Therefore, we determined whether this
regulation was dependent on caspase regulation. In order to examine
the role of caspase in FasL-mediated differential expression of
cFLIP variants, treatment with pan-caspase inhibitor (z-VAD-fmk)
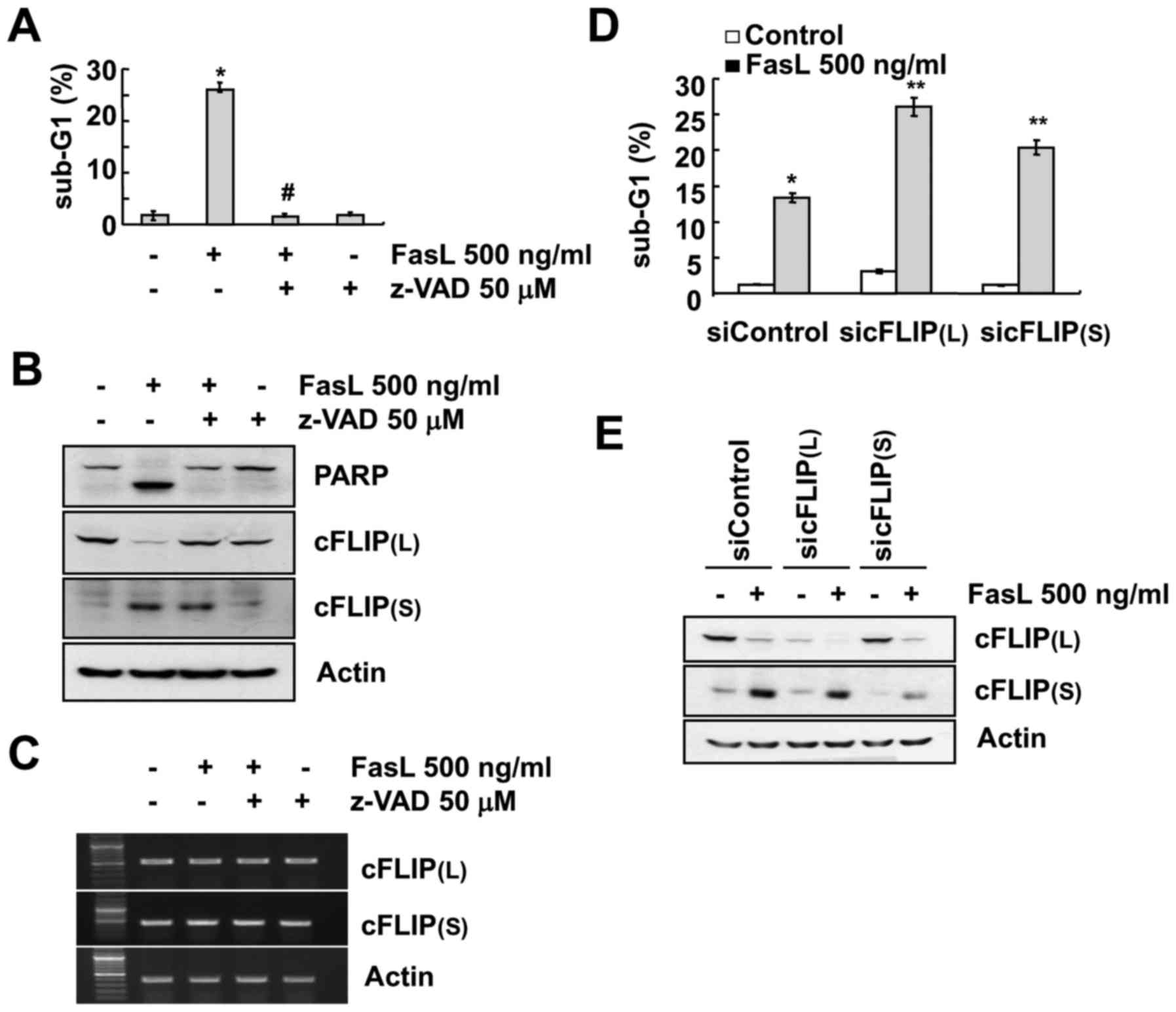
was applied which inhibited FasL-mediated apoptosis (Fig. 2A). Inhibition of caspase prevented
the downregulation of cFLIP(L). However, z-VAD did not have an
effect on FasL-induced cFLIP(S) upregulation and mRNA levels of
cFLIP(L) and cFLIP(S) (Fig. 2B and
C). We examined whether both cFLIP variants play a role in
FasL-induced apoptosis. Downregulation of each cFLIP variant by
specific siRNA induced increased cell apoptotic populations in Fas
L-treated Caki cells, compared with the control siRNA (Fig. 2D and E).
Effect of proteasome inhibitors and
MAPK inhibitors on the expression of cFLIP(L)/(S) in FasL-treated
cells
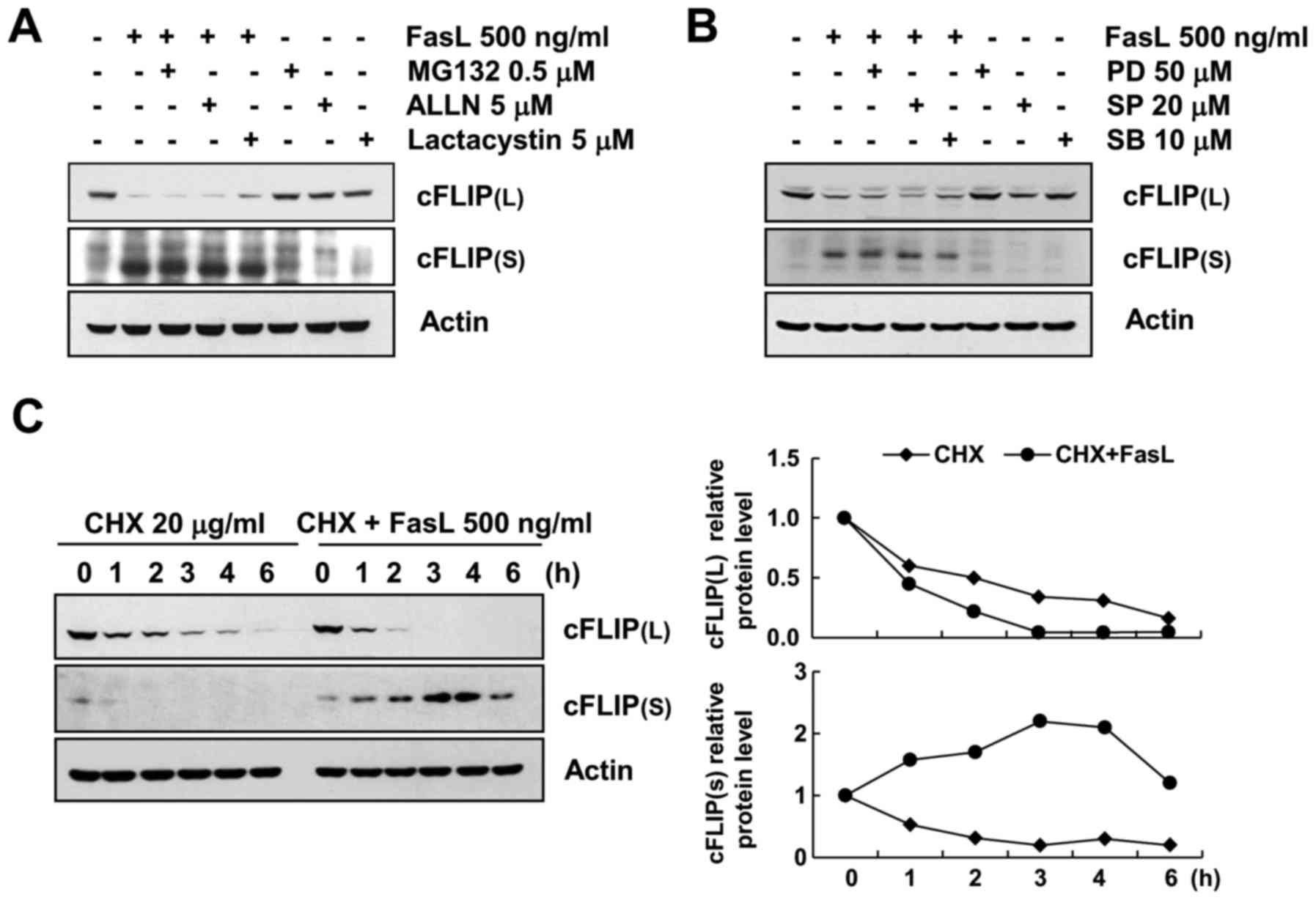
RT-PCR analysis revealed that the mRNA levels of
cFLIP(L)/(S) were unchanged following FasL treatment. To
investigate the possible involvement of the proteasome pathway in
the FasL-mediated regulation of cFLIP(L)/(S), we assessed the
expression levels of cFLIP(L)/(S) in cells treated with various
proteasome inhibitors (0.5 mM MG132, 5 mM ALLN and 5 mM
lactacystin) in the presence or absence of FasL. As displayed in
Fig. 3A, FasL-induced cFLIP(S)
upregulation and cFLIP(L) downregulation was not inhibited by any
of the proteasome-inhibitors treatment. These results indicated
that proteasomal degradation was not associated with FasL-induced
cFLIP expression regulation. In addition, in order to investigate
whether the MAPKs pathways were involved in FasL-treated Caki
cells, Caki cells were treated with each MAPK specific inhibitor.
As displayed in Fig. 3B,
FasL-induced cFLIP(S) upregulation and cFLIP(L) downregulation was
not inhibited by MAPKs inhibitors treatment. These results
indicated that MAPK signaling pathway was not associated with
FasL-induced cFLIP expression regulation.
Not with standing, we examined whether protein
stability was directly associated with FasL-induced expression
regulation of cFLIP(L)/(S). In order to investigate this, we
treated Caki cells with cycloheximide (CHX), an inhibitor of
protein translation. Untreated and FasL-treated Caki cells were
exposed to CHX for various time-points and cFLIP(L) and cFLIP(S)
protein levels were determined by western blot analysis. As
displayed in Fig. 3C, FasL
treatment caused much more rapid cFLIP(L) degradation than that of
untreated cells. Notably, cFLIP(S) protein levels were maintained
until 6 h, and then declined in the presence of FasL and CHX.
However, cFLIP(S) protein levels rapidly degraded by CHX treatment
alone. Therefore, these results demonstrated that FasL-induced
cFLIP(S) upregulation was associated with enhanced stability of
cFLIP(S) protein.
FasL-mediated apoptosis and expression
regulation of cFLIP are caused by ROS generation
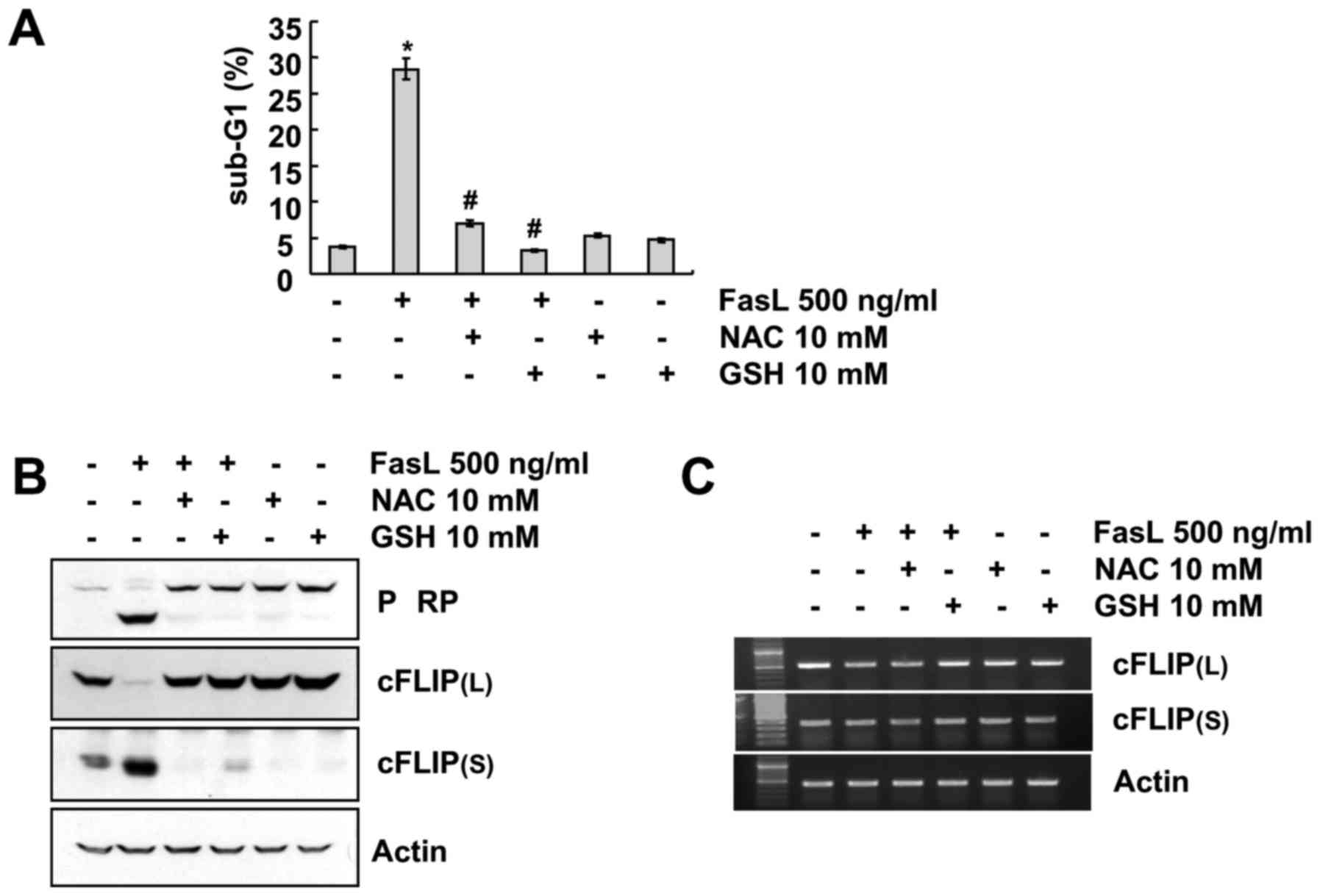
Recently, Fas death signaling pathway has been
reported to have an association with reactive oxygen species (ROS)
generation and cFLIP(L) downregulation (22). Therefore, we examined whether ROS
generation could be involved in FasL-mediated differential
expression pattern of cFLIP(L)/(S) in Caki cells along with its
direct association with FasL-induced apoptosis. As displayed in
Fig. 4, pretreatment with ROS
scavengers, N-acetylcysteine (NAC) and glutathione (GSH), markedly
blocked FasL-induced apoptosis and attenuated the cleavage of PARP
(Fig. 4A and B). In addition,
FasL-mediated cFLIP(L) downregulation and cFLIP(S) upregulation was
prevented by NAC and GSH treatment (Fig. 4B). The RT-PCR data revealed that
cFLIP(L)/(S) protein expression levels were not controlled by the
transcriptional regulation, as there was no change in cFLIP(L)/(S)
mRNA level regardless of whether the cells were treated with FasL
in the presence or absence of ROS scavengers (Fig. 4C). Collectivelly, these data clearly
indicated that FasL-induced apoptosis and expression regulation of
cFLIP were mediated by ROS generation.
Discussion
In the present study, we explored the differential
regulation patterns of two major variants of cFLIP i.e. cFLIP(L)
and cFLIP(S) during Fas-mediated apoptosis and found that the short
form of cFLIP was upregulated. In addition, this differential
regulation pattern of cFLIP(S) was observed at a post-translational
level but not at a transcriptional level. In addition, our data
demonstrated that the upregulation of cFLIP(S) was associated with
ROS generation.
cFLIP is a well-recognized anti-apoptotic protein
and it has been reported that both the principle variants of this
protein, cFLIP(L) and cFLIP(S), are able to bind to the death
effector domain (DED) region of the adaptor protein FADD along with
caspase-8 and 10 (16). However,
structurally, cFLIP(S) contains two tandem DEDs and cFLIP(L)
contains only one tandem, thus, cFLIP(S) is believed to have a more
potent role in the prevention of caspase activation than cFLIP(L)
(23,24). Although some studies have been
carried out to elucidate the role of these variants during death
receptor-mediated apoptosis, the expression pattern of both
variants and the principle behind their expression remains largely
unclear.
In order to explore this, we have treated Caki cells
with FasL and evaluated the expression pattern of cFLIP(S) and
cFLIP(L). We found that FasL treatment caused the downregulation of
cFLIP(L) and the upregulation of cFLIP(S) which was concentration-
and time-dependent. Furthermore, the differential expression of
both variants was observed at a post-translational but not at a
transcriptional level. However, as above stated, these variants
were able to prevent caspase activation. Therefore we examined
their expression level by using pan-caspase inhibitor (z-VAD).
Notably, inhibition of caspase prevented the downregulation of
cFLIP(L), however, it did not have an effect on FasL-induced
cFLIP(S) upregulation. We observed that knockdown of any cFLIP
variant induced apoptosis, indicating that both variants were
involved in the protection of FasL-mediated apoptosis in Caki
cells. However, a study carried out by Chang et al (17), also revealed a similar expression
pattern of cFLIP(S) in MCF cells.
Although, numerous studies have been carried out on
Fas-mediated apoptosis which revealed its molecular mechanism from
activation to apoptosis, more recent studies have reported the role
of ROS in the activation of FasL-mediated apoptosis (25,26).
Excessive generation of free radicals could cause the damage of
plasma membrane integrity resulting in leakage of cellular material
which eventually leads to cell death (25). Notwithstanding, excessive ROS
production has been reported to play a role in the activation of
caspase (27) and the
downregulation the cFLIP proteins (22). Therefore, in the present study, we
examined the role of ROS in Fas-mediated apoptosis and expression
of cFLIP(L) and cFLIP(S). As expected, FasL treatment exhibited
ROS-mediated apoptosis which was markedly blocked by the treatment
of ROS scavengers NAC and GSH. The differential expression of cFLIP
isoforms was also the result of post-transcriptional regulation,
suggesting that cFLIP(S) expression is associated with the
generation of ROS.
In conclusion, we revealed that FasL treatment
caused downregulation of cFLIP(L) and upregulation of cFLIP(S).
However, the upregulation of cFLIP(S) was not associated with
apoptosis, instead the knockdown of cFLIP(S) eventually triggered
FasL-mediated apoptosis. Furthermore, this differential expression
of both variants was the result of post-transcriptional regulation
and was highly associated with the generation of ROS in Caki cells.
In the present study although we revealed the divergent expression
of cFLIP(L)/(S), there is still a strong need to explore the
precise mechanism of the expression of cFLIP(S) during
FasL-mediated cell death which may provide some insight to this
complex apoptotic mechanism.
Acknowledgements
Not applicable.
Glossary
Abbreviations
Abbreviations:
|
TRAIL
|
tumor necrosis factor-related
apoptosis-inducing ligand
|
|
ROS
|
reactive oxygen species
|
|
cFLIP
|
cellular FLICE-like inhibitory
protein
|
|
TNF
|
tumor necrosis factor
|
References
|
1
|
Kikuchi H, Kuribayashi F and Imajoh-Ohmi
S: Down-regulation of Fas-mediated apoptosis by plasma
transglutaminase factor XIII that catalyzes fetal-specific
cross-link of the Fas molecule. Biochem Biophys Res Commun.
443:13–17. 2014. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
2
|
Wiegers GJ, Kaufmann M, Tischner D and
Villunger A: Shaping the T-cell repertoire: A matter of life and
death. Immunol Cell Biol. 89:33–39. 2011. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
3
|
Kikuchi H and Nakayama T: GCN5 and BCR
signalling collaborate to induce pre-mature B cell apoptosis
through depletion of ICAD and IAP2 and activation of caspase
activities. Gene. 419:48–55. 2008. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
4
|
Geng L, Zhu B, Dai BH, Sui CJ, Xu F, Kan
T, Shen WF and Yang JM: A let-7/Fas double-negative feedback loop
regulates human colon carcinoma cells sensitivity to Fas-related
apoptosis. Biochem Biophys Res Commun. 408:494–499. 2011.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
5
|
Barnhart BC, Legembre P, Pietras E, Bubici
C, Franzoso G and Peter ME: CD95 ligand induces motility and
invasiveness of apoptosis-resistant tumor cells. EMBO J.
23:3175–3185. 2004. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
6
|
Wu XX, Mizutani Y, Kakehi Y, Yoshida O and
Ogawa O: Enhancement of Fas-mediated apoptosis in renal cell
carcinoma cells by adriamycin. Cancer Res. 60:2912–2918.
2000.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
7
|
Arase H, Arase N and Saito T: Fas-mediated
cytotoxicity by freshly isolated natural killer cells. J Exp Med.
181:1235–1238. 1995. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
8
|
Itoh N, Yonehara S, Ishii A, Yonehara M,
Mizushima S, Sameshima M, Hase A, Seto Y and Nagata S: The
polypeptide encoded by the cDNA for human cell surface antigen Fas
can mediate apoptosis. Cell. 66:233–243. 1991. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
9
|
Kischkel FC, Hellbardt S, Behrmann I,
Germer M, Pawlita M, Krammer PH and Peter ME:
Cytotoxicity-dependent APO-1 (Fas/CD95)-associated proteins form a
death-inducing signaling complex (DISC) with the receptor. EMBO J.
14:5579–5588. 1995.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
10
|
Wang X, Wang Y, Lee SJ, Kim HP, Choi AM
and Ryter SW: Carbon monoxide inhibits Fas activating
antibody-induced apoptosis in endothelial cells. Med Gas Res.
1:82011. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
11
|
Gloire G, Charlier E and Piette J:
Regulation of CD95/APO-1/Fas-induced apoptosis by protein
phosphatases. Biochem Pharmacol. 76:1451–1458. 2008. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
12
|
Safa AR, Day TW and Wu CH: Cellular
FLICE-like inhibitory protein (C-FLIP): A novel target for cancer
therapy. Curr Cancer Drug Targets. 8:37–46. 2008. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
13
|
Malhi H and Gores GJ: TRAIL resistance
results in cancer progression: A TRAIL to perdition? Oncogene.
25:7333–7335. 2006. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
14
|
Shin EC, Seong YR, Kim CH, Kim H, Ahn YS,
Kim K, Kim SJ, Hong SS and Park JH: Human hepatocellular carcinoma
cells resist to TRAIL-induced apoptosis, and the resistance is
abolished by cisplatin. Exp Mol Med. 34:114–122. 2002. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
15
|
Golks A, Brenner D, Fritsch C, Krammer PH
and Lavrik IN: c-FLIPR, a new regulator of death receptor-induced
apoptosis. J Biol Chem. 280:14507–14513. 2005. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
16
|
Sharp DA, Lawrence DA and Ashkenazi A:
Selective knockdown of the long variant of cellular FLICE
inhibitory protein augments death receptor-mediated caspase-8
activation and apoptosis. J Biol Chem. 280:19401–19409. 2005.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
17
|
Chang DW, Xing Z, Pan Y,
Algeciras-Schimnich A, Barnhart BC, Yaish-Ohad S, Peter ME and Yang
X: c-FLIP(L) is a dual function regulator for caspase-8 activation
and CD95-mediated apoptosis. EMBO J. 21:3704–3714. 2002. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
18
|
Krueger A, Schmitz I, Baumann S, Krammer
PH and Kirchhoff S: Cellular FLICE-inhibitory protein splice
variants inhibit different steps of caspase-8 activation at the
CD95 death-inducing signaling complex. J Biol Chem.
276:20633–20640. 2001. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
19
|
Ram DR, Ilyukha V, Volkova T, Buzdin A,
Tai A, Smirnova I and Poltorak A: Balance between short and long
isoforms of cFLIP regulates Fas-mediated apoptosis in vivo. Proc
Natl Acad Sci USA. 113:1606–1611. 2016. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
20
|
Park YS, Kwon YJ and Chun YJ: CYP1B1
activates Wnt/β-catenin signaling through suppression of
Herc5-mediated ISGylation for protein degradation on β-catenin in
HeLa cells. Toxicol Res. 33:211–218. 2017. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
21
|
Jo Y and Shin DY: Repression of the F-box
protein Skp2 is essential for actin damage-induced tetraploid G1
arrest. BMB Rep. 50:379–383. 2017. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
22
|
Wang L, Azad N, Kongkaneramit L, Chen F,
Lu Y, Jiang BH and Rojanasakul Y: The Fas death signaling pathway
connecting reactive oxygen species generation and FLICE inhibitory
protein down-regulation. J Immunol. 180:3072–3080. 2008. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
23
|
Krueger A, Baumann S, Krammer PH and
Kirchhoff S: FLICE-inhibitory proteins: Regulators of death
receptor-mediated apoptosis. Mol Cell Biol. 21:8247–8254. 2001.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
24
|
Thome M and Tschopp J: Regulation of
lymphocyte proliferation and death by FLIP. Nat Rev Immunol.
1:50–58. 2001. View
Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
25
|
Medan D, Wang L, Toledo D, Lu B, Stehlik
C, Jiang BH, Shi X and Rojanasakul Y: Regulation of Fas
(CD95)-induced apoptotic and necrotic cell death by reactive oxygen
species in macrophages. J Cell Physiol. 203:78–84. 2005. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
26
|
Sato T, Machida T, Takahashi S, Iyama S,
Sato Y, Kuribayashi K, Takada K, Oku T, Kawano Y, Okamoto T, et al:
Fas-mediated apoptosome formation is dependent on reactive oxygen
species derived from mitochondrial permeability transition in
Jurkat cells. J Immunol. 173:285–296. 2004. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
27
|
Vercammen D, Brouckaert G, Denecker G, Van
de Craen M, Declercq W, Fiers W and Vandenabeele P: Dual signaling
of the Fas receptor: Initiation of both apoptotic and necrotic cell
death pathways. J Exp Med. 188:919–930. 1998. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|