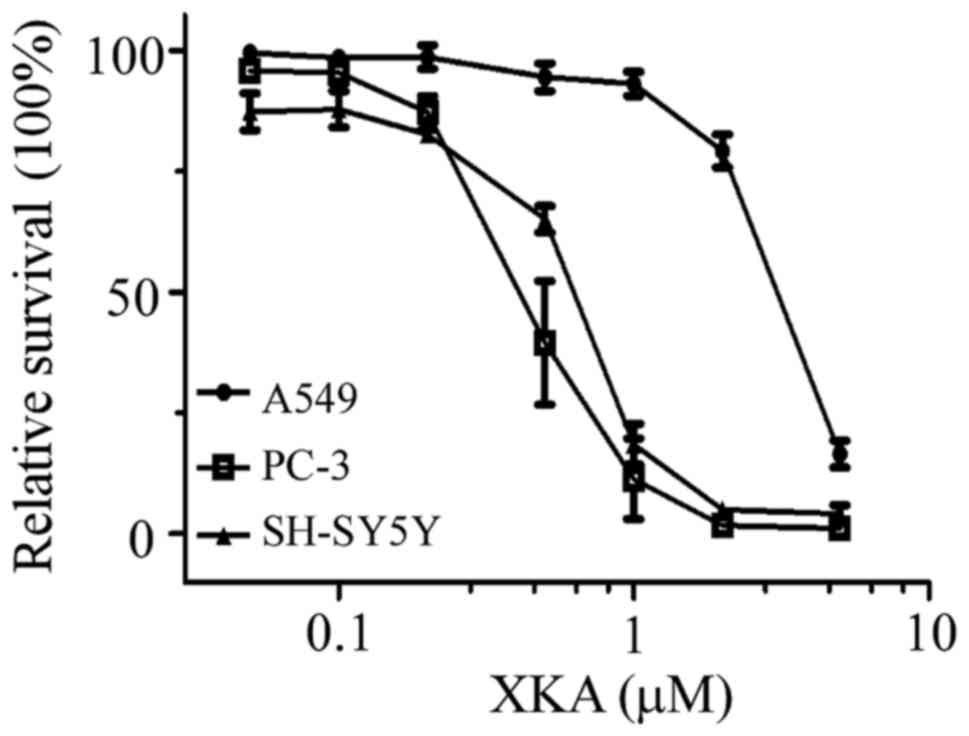
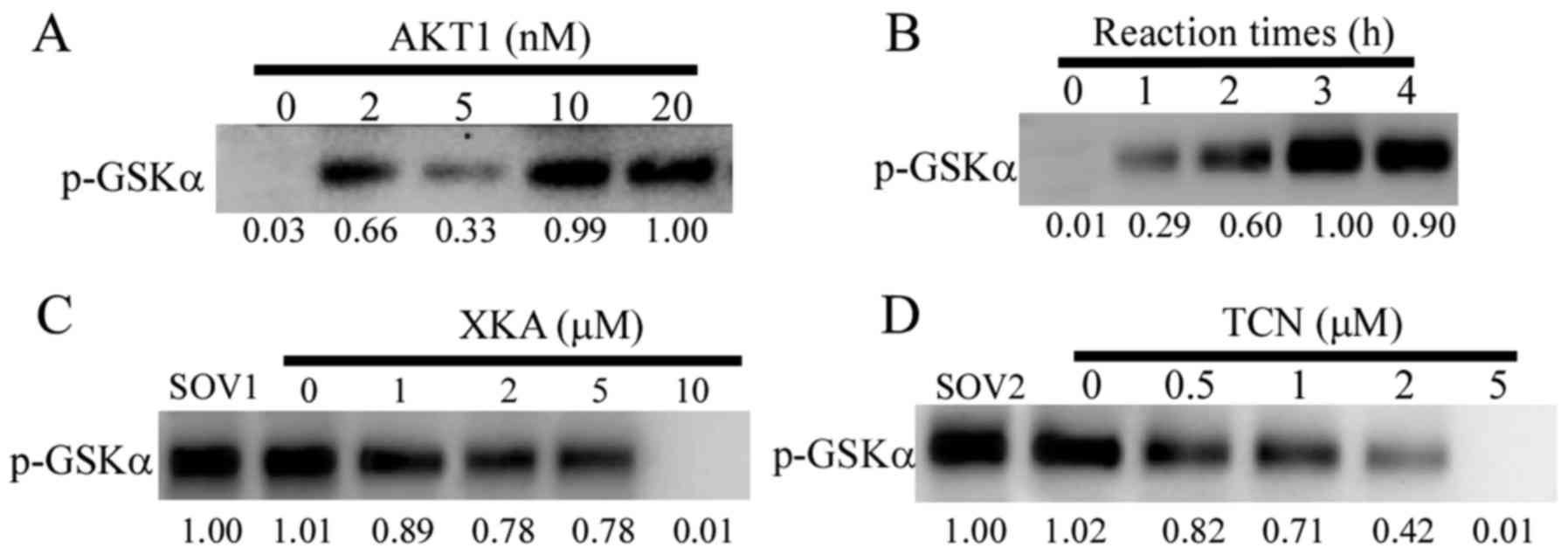
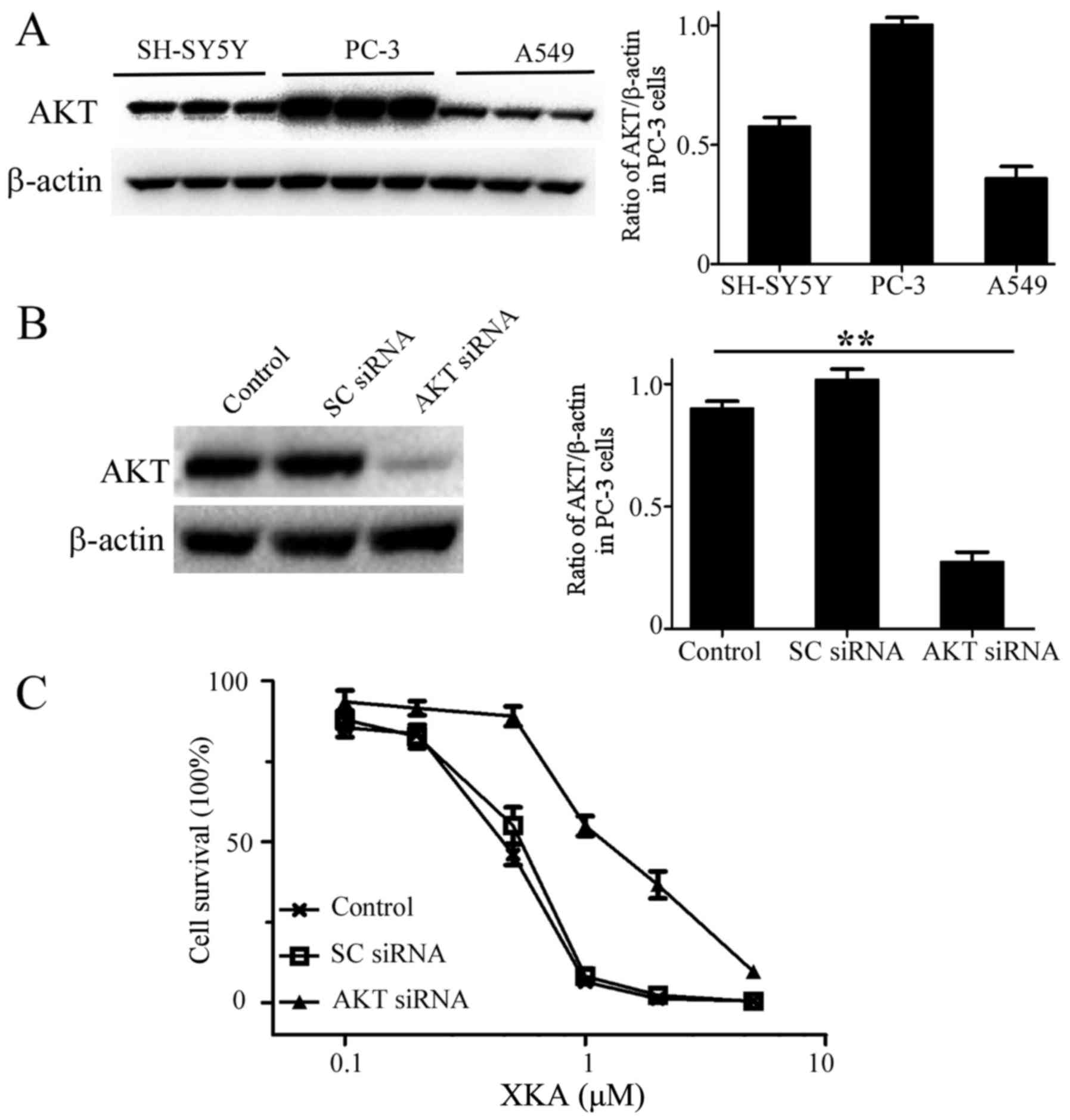
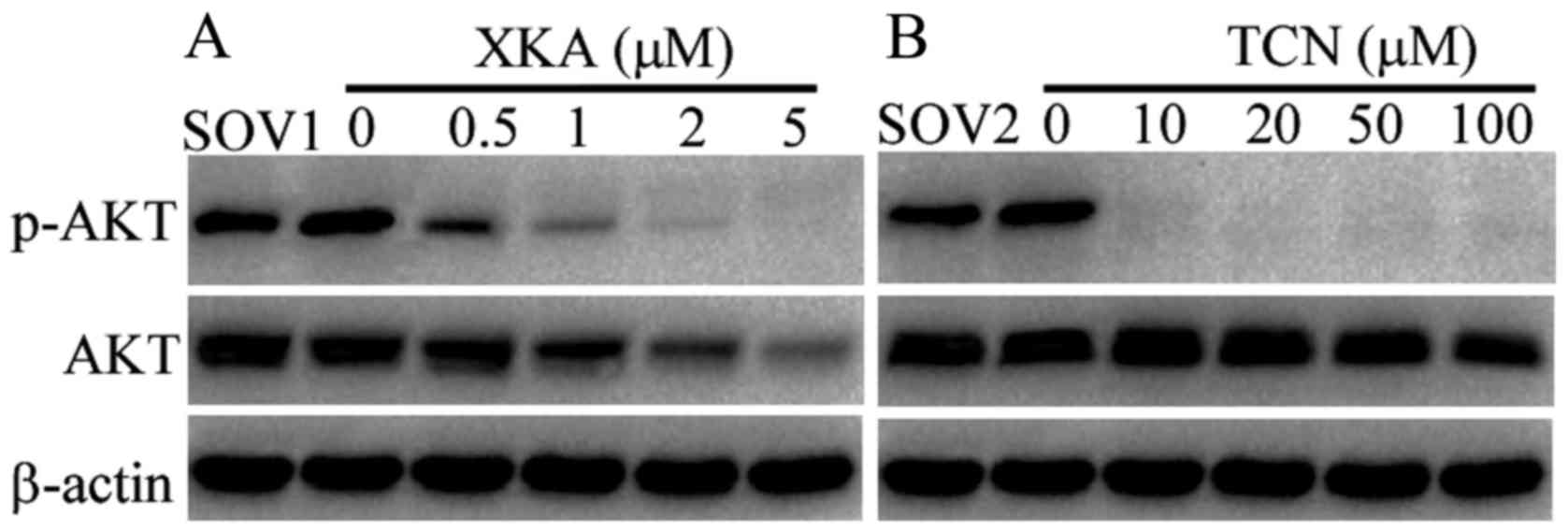
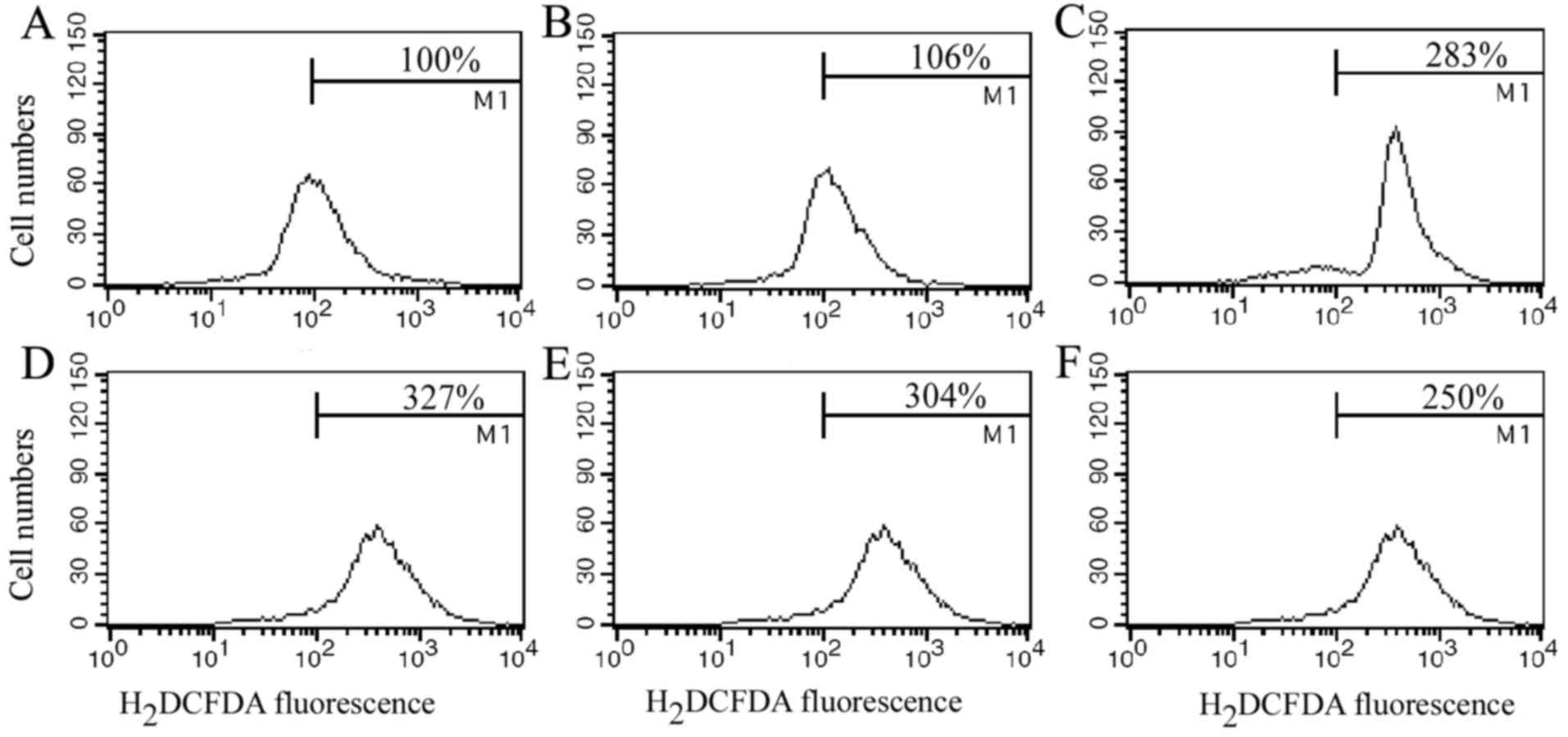
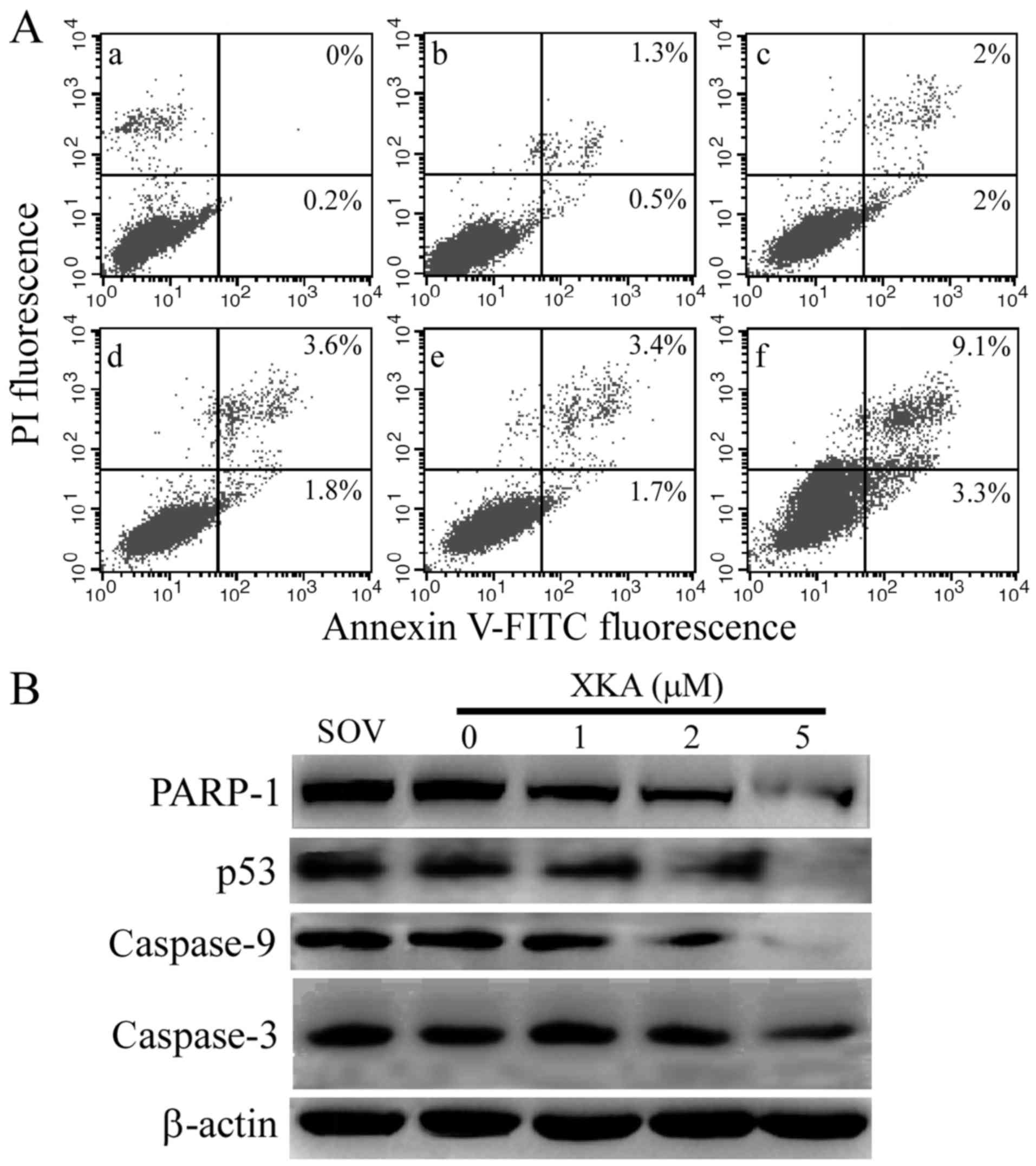
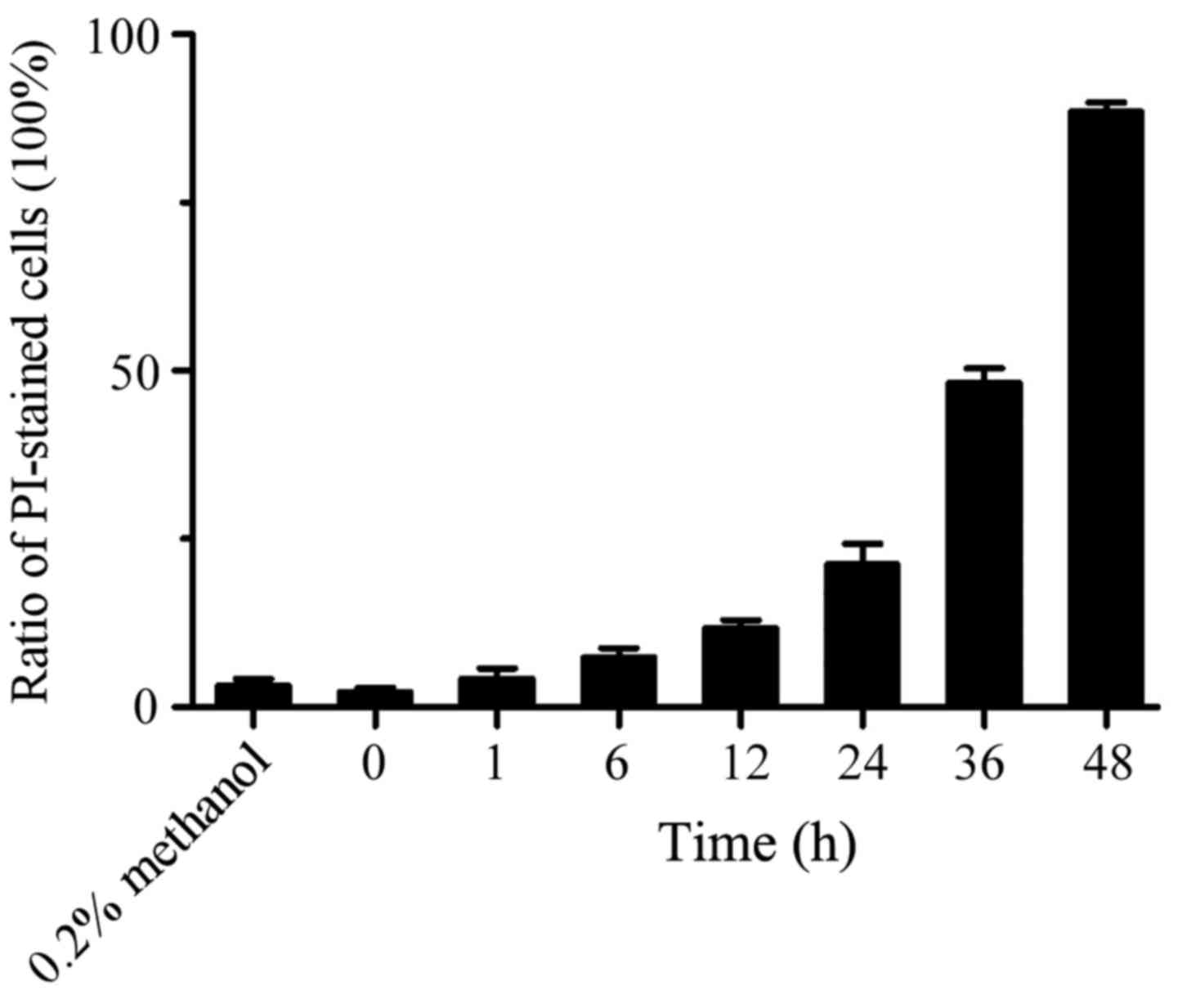
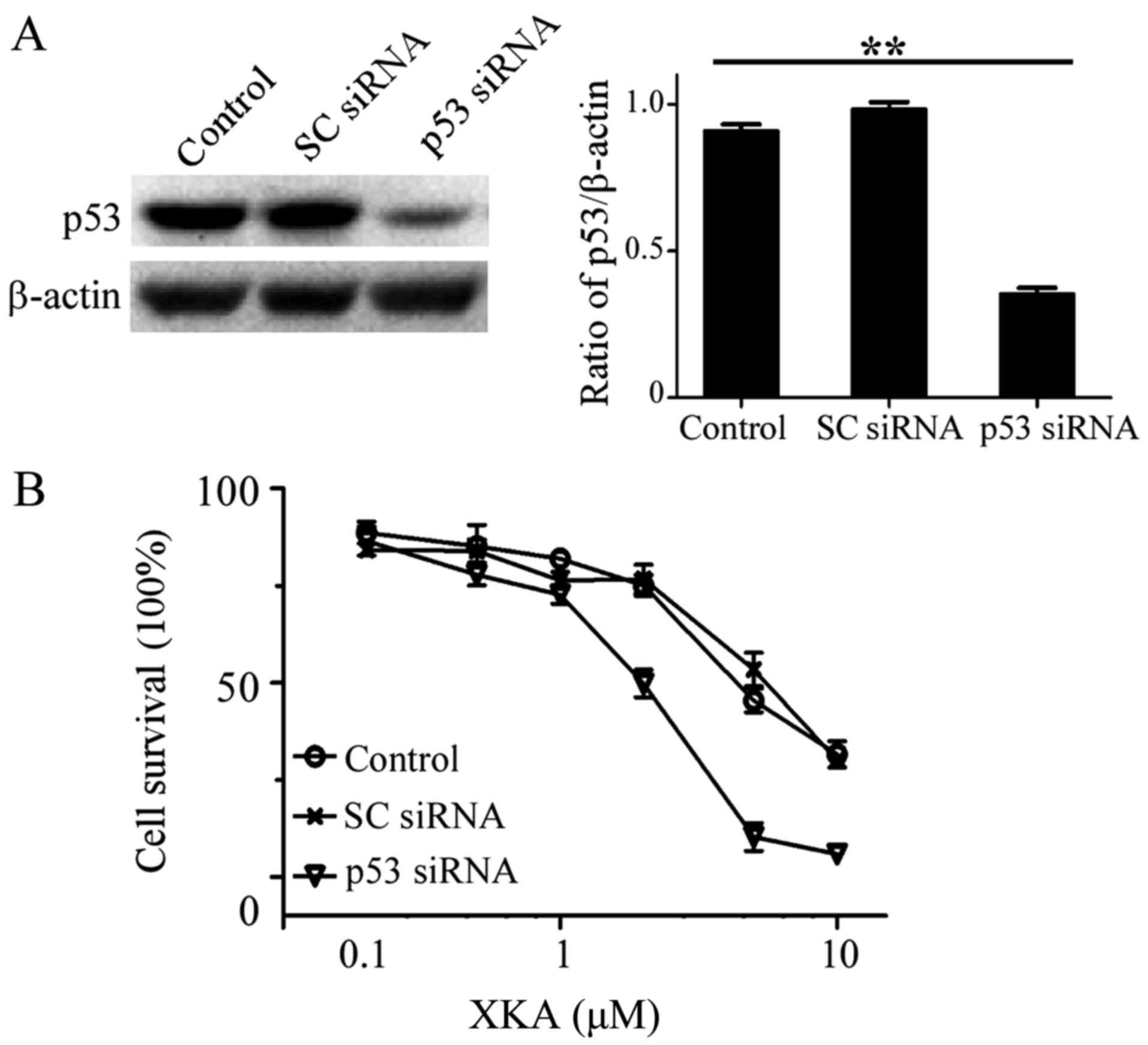
|
1
|
Manning BD and Toker A: AKT/PKB signaling:
Navigating the Network. Cell. 169:381–405. 2017. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
2
|
Mundi PS, Sachdev J, McCourt C and
Kalinsky K: AKT in cancer: New molecular insights and advances in
drug development. Br J Clin Pharmacol. 82:943–956. 2016. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
3
|
Chan CH, Jo U, Kohrman A, Rezaeian AH,
Chou PC, Logothetis C and Lin HK: Posttranslational regulation of
Akt in human cancer. Cell Biosci. 4:592014. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
4
|
Kim D, Dan HC, Park S, Yang L, Liu Q,
Kaneko S, Ning J, He L, Yang H, Sun M, et al: AKT/PKB signaling
mechanisms in cancer and chemoresistance. Front Biosci. 10:975–987.
2005. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
5
|
Nitulescu GM, Margina D, Juzenas P, Peng
Q, Olaru OT, Saloustros E, Fenga C, Spandidos DΑ, Libra M and
Tsatsakis AM: Akt inhibitors in cancer treatment: The long journey
from drug discovery to clinical use (Review). Int J Oncol.
48:869–885. 2016. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
6
|
Kumar CC and Madison V: AKT crystal
structure and AKT-specific inhibitors. Oncogene. 24:7493–7501.
2005. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
7
|
Jiang ZK, Guo L, Chen C, Liu SW, Zhang L,
Dai SJ, He QY, You XF, Hu XX, Tuo L, et al: Xiakemycin A, a novel
pyranonaphthoquinone antibiotic, produced by the
Streptomyces sp. CC8-201 from the soil of a karst cave. J
Antibiot (Tokyo). 68:771–774. 2015. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
8
|
Sperry J, Bachu P and Brimble MA:
Pyranonaphthoquinones - isolation, biological activity and
synthesis. Nat Prod Rep. 25:376–400. 2008. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
9
|
Brimble MA, Duncalf LJ and Nairn MR:
Pyranonaphthoquinone antibiotics - isolation, structure and
biological activity. Nat Prod Rep. 16:267–281. 1999. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
10
|
Jiménez-Alonso S, Orellana HC,
Estévez-Braun A, Ravelo AG, Pérez-Sacau E and Machín F: Design and
synthesis of a novel series of pyranonaphthoquinones as
topoisomerase II catalytic inhibitors. J Med Chem. 51:6761–6772.
2008. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
11
|
Toral-Barza L, Zhang WG, Huang X, McDonald
LA, Salaski EJ, Barbieri LR, Ding WD, Krishnamurthy G, Hu YB, Lucas
J, et al: Discovery of lactoquinomycin and related
pyranonaphthoquinones as potent and allosteric inhibitors of
AKT/PKB: Mechanistic involvement of AKT catalytic activation loop
cysteines. Mol Cancer Ther. 6:3028–3038. 2007. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
12
|
Korwar S, Nguyen T and Ellis KC:
Preparation and evaluation of deconstruction analogues of
7-deoxykalafungin as AKT kinase inhibitors. Bioorg Med Chem Lett.
24:271–274. 2014. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
13
|
Chen J, Chen Y and He Q: Action of
bleomycin is affected by bleomycin hydrolase but not by caveolin-1.
Int J Oncol. 41:2245–2252. 2012. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
14
|
Chen Y, Zhang H and He Q: Involvement of
bleomycin hydrolase and poly(ADP-ribose) polymerase-1 in
Ubc9-mediated resistance to chemotherapy agents. Int J Oncol.
50:223–231. 2017. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
15
|
Salaski EJ, Krishnamurthy G, Ding WD, Yu
K, Insaf SS, Eid C, Shim J, Levin JI, Tabei K, Toral-Barza L, et
al: Pyranonaphthoquinone lactones: A new class of AKT selective
kinase inhibitors alkylate a regulatory loop cysteine. J Med Chem.
52:2181–2184. 2009. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
16
|
Léo PM, Morin C and Philouze C: Structure
revision of medermycin/lactoquinomycin a and of related C-8
glycosylated naphthoquinones. Org Lett. 4:2711–2714. 2002.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
17
|
Gottlieb TM, Leal JF, Seger R, Taya Y and
Oren M: Cross-talk between Akt, p53 and Mdm2: Possible implications
for the regulation of apoptosis. Oncogene. 21:1299–1303. 2002.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
18
|
Mayo LD, Dixon JE, Durden DL, Tonks NK and
Donner DB: PTEN protects p53 from Mdm2 and sensitizes cancer cells
to chemotherapy. J Biol Chem. 277:5484–5489. 2002. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
19
|
Sangai T, Akcakanat A, Chen H, Tarco E, Wu
Y, Do KA, Miller TW, Arteaga CL, Mills GB, Gonzalez-Angulo AM, et
al: Biomarkers of response to Akt inhibitor MK-2206 in breast
cancer. Clin Cancer Res. 18:5816–5828. 2012. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
20
|
Weinlich R, Oberst A, Beere HM and Green
DR: Necroptosis in development, inflammation and disease. Nat Rev
Mol Cell Biol. 18:127–136. 2017. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
21
|
Csizmar CM, Kim DH and Sachs Z: The role
of the proteasome in AML. Blood Cancer J. 6:e5032016. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|