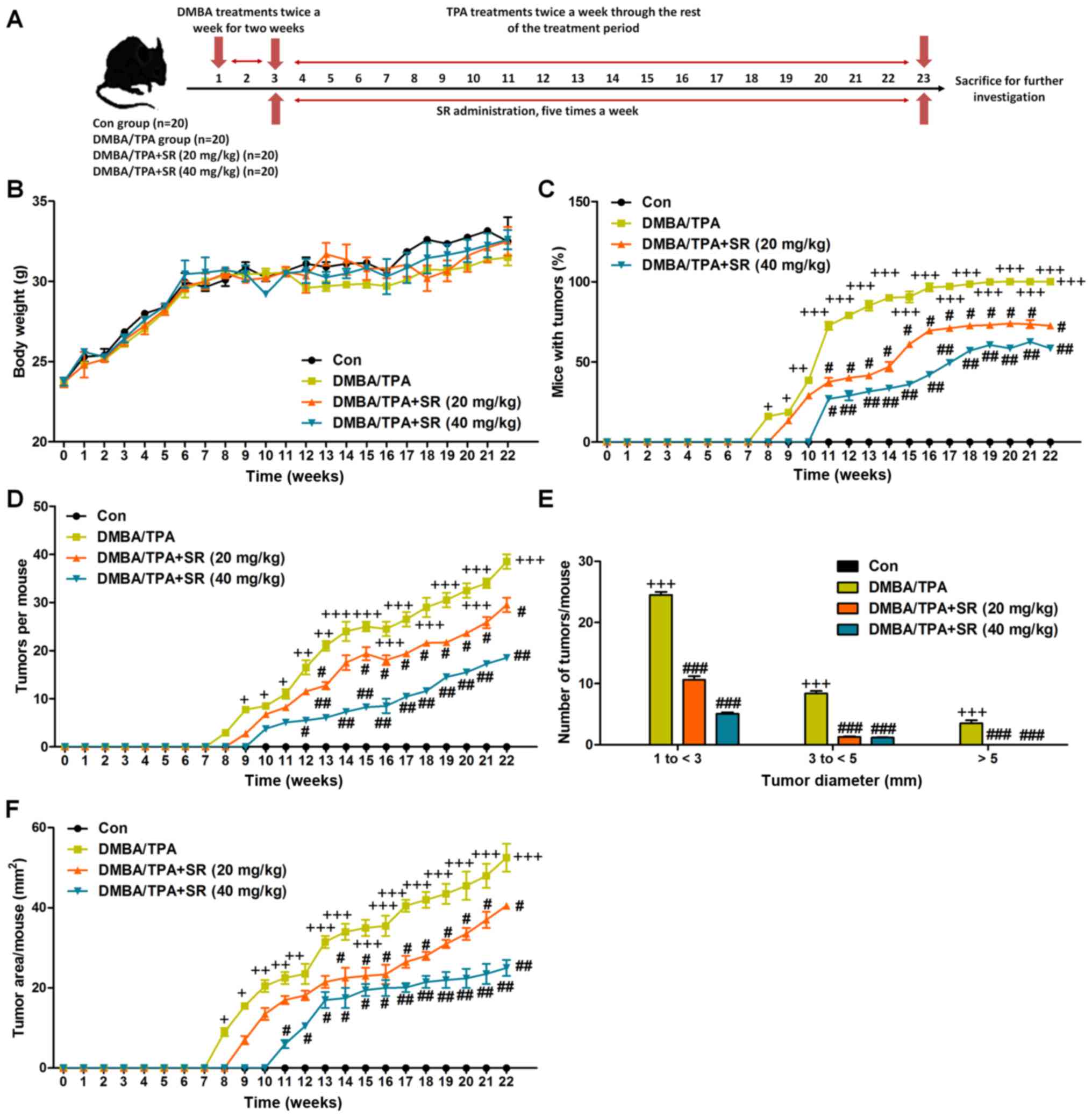
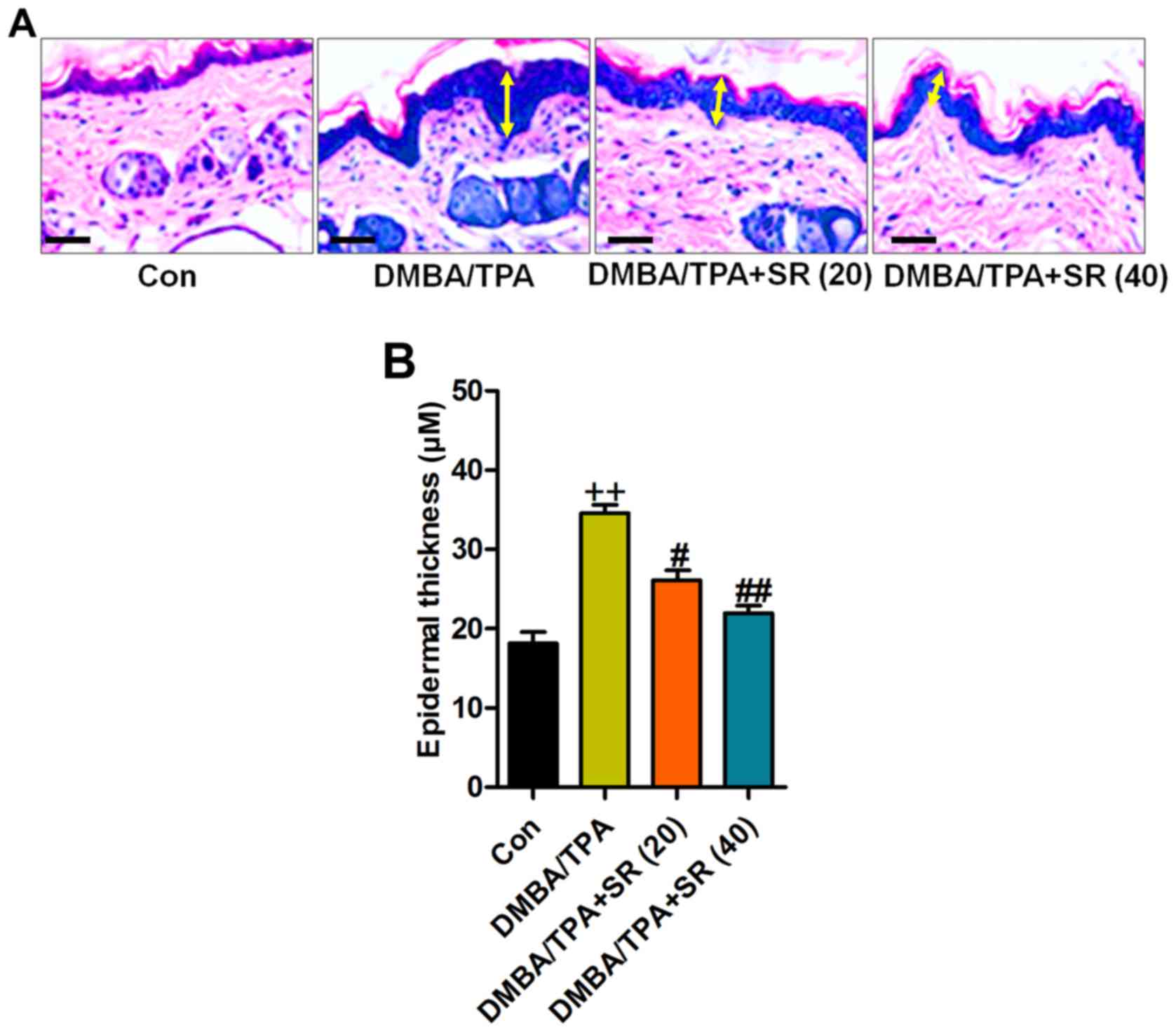
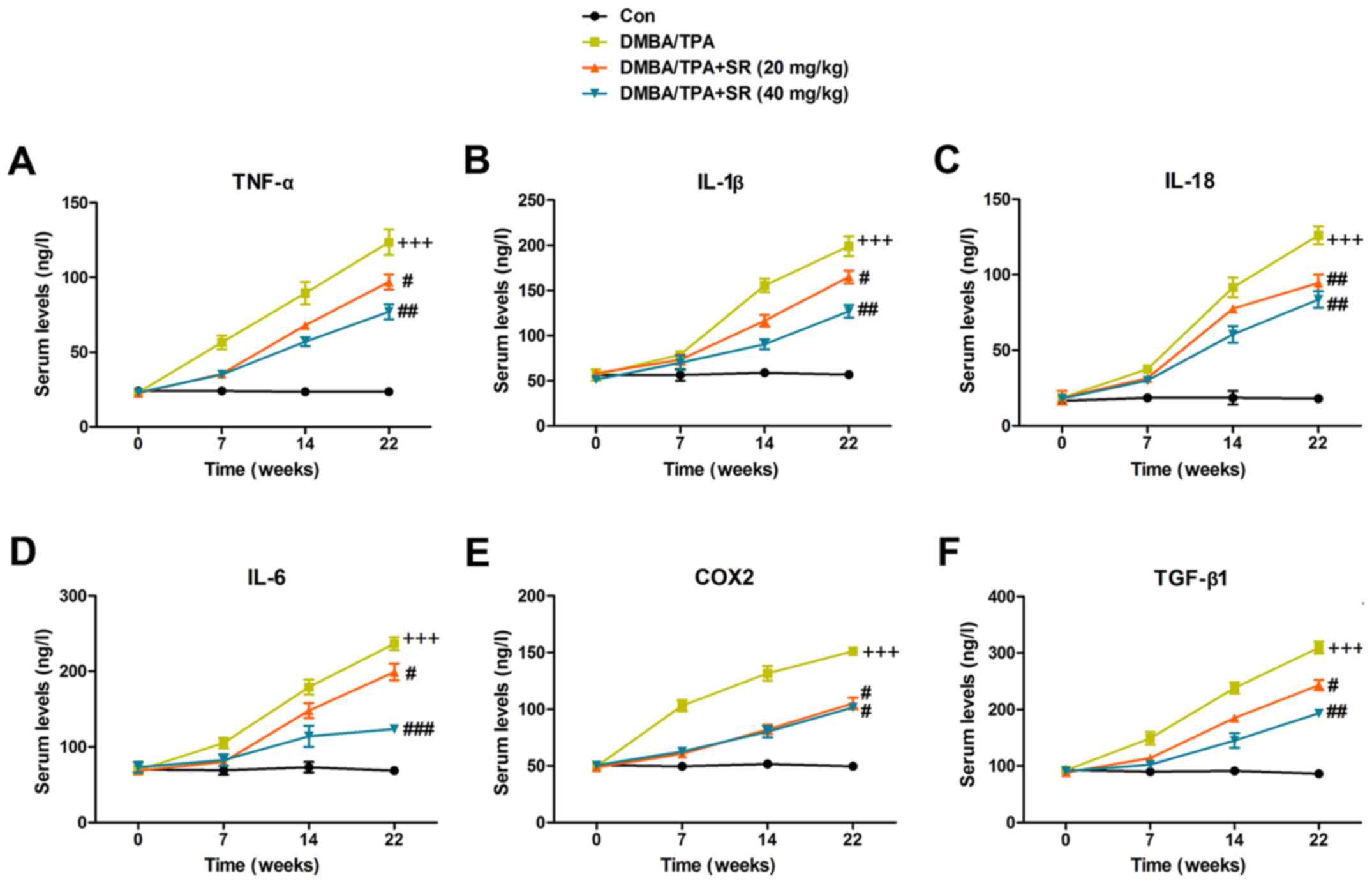
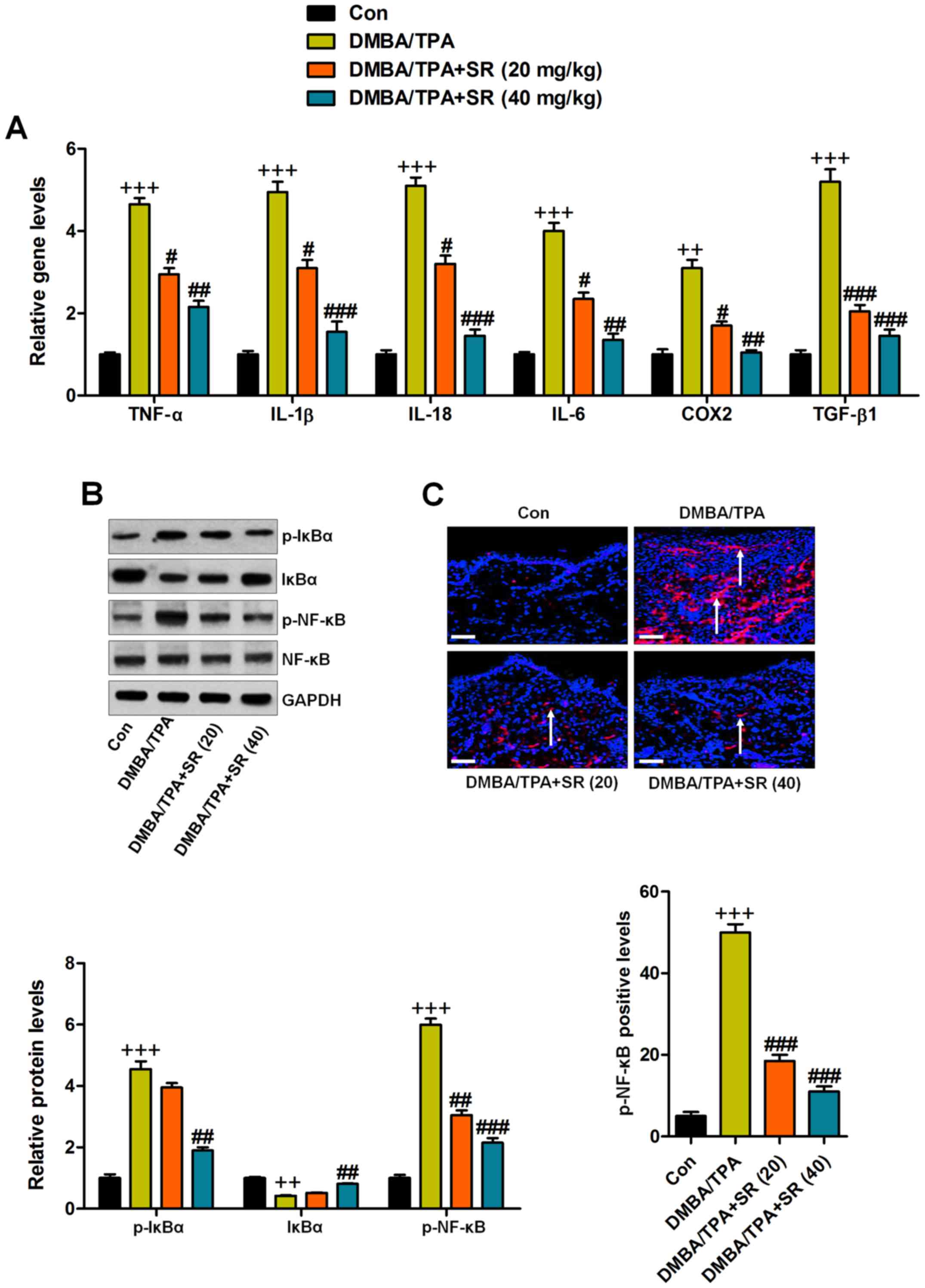
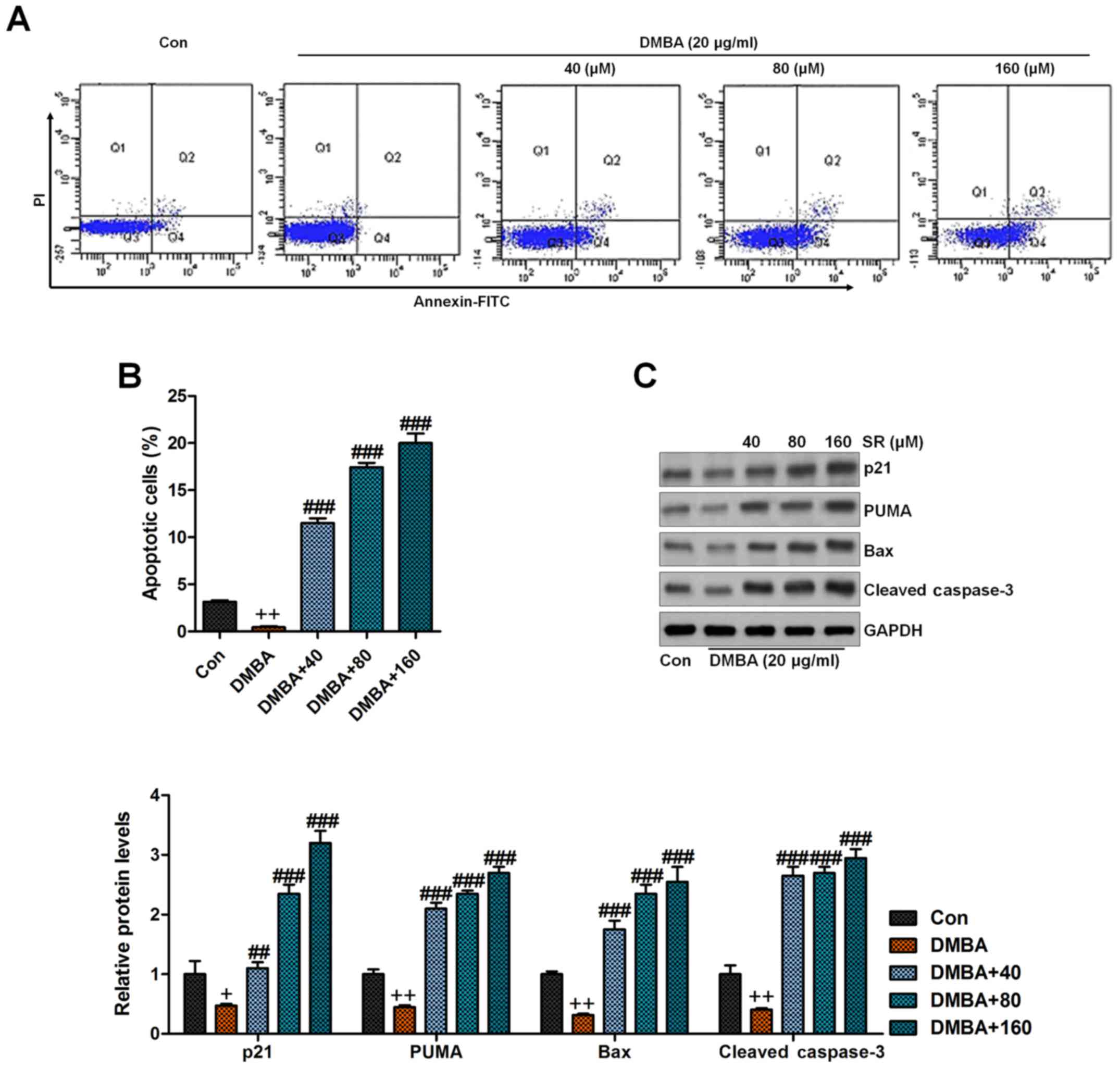
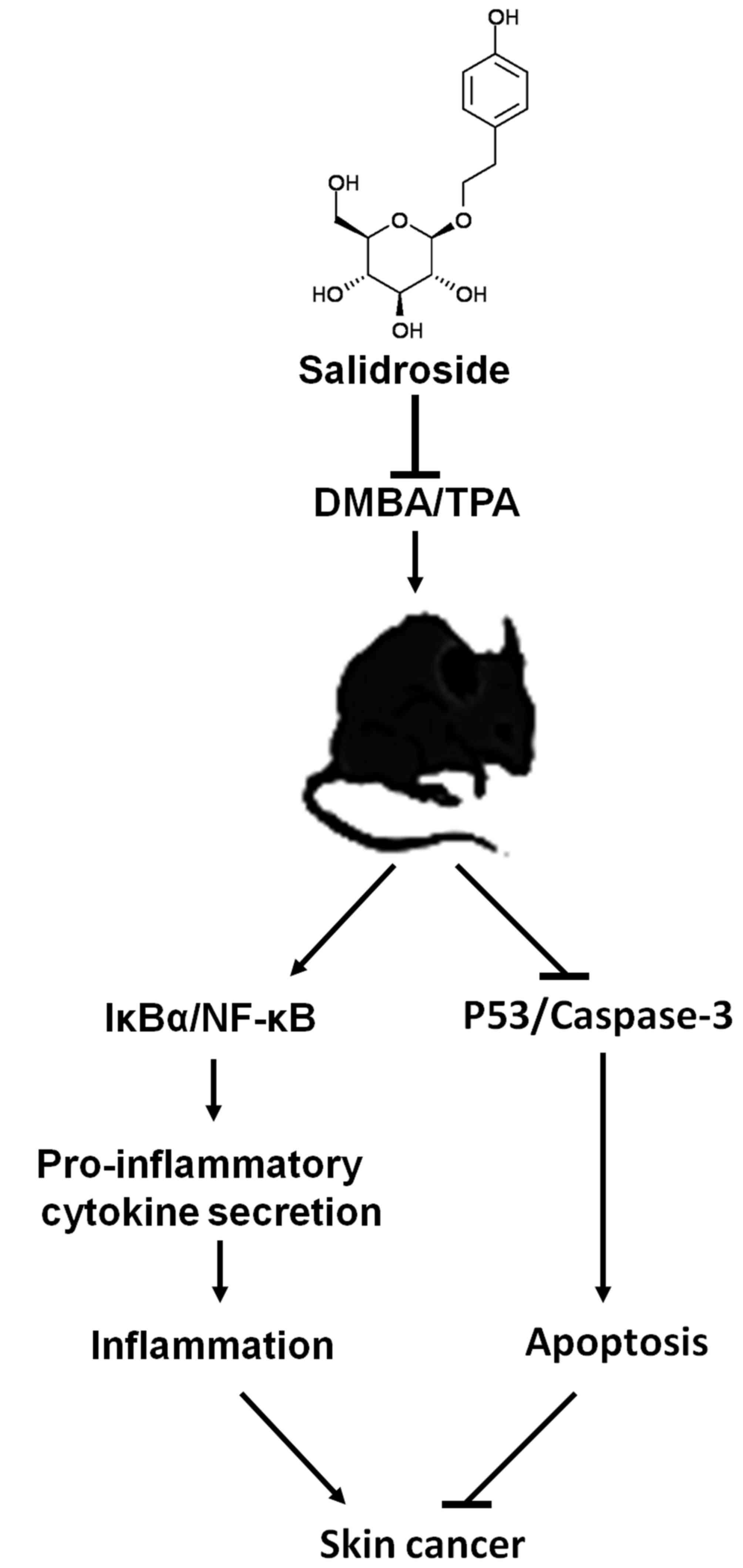
|
1
|
Eisemann N, Waldmann A, Geller AC,
Weinstock MA, Volkmer B, Greinert R, Breitbart EW and Katalinic A:
Non-melanoma skin cancer incidence and impact of skin cancer
screening on incidence. J Invest Dermatol. 134:43–50. 2014.
View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
2
|
Katalinic A, Eisemann N and Waldmann A:
Skin cancer screening in Germany. Dtsch Arztebl Int. 112:629–634.
2015.
|
|
3
|
Fusi C, Materazzi S, Minocci D, Maio V,
Oranges T, Massi D and Nassini R: Transient receptor potential
vanilloid 4 (TRPV4) is downregulated in keratinocytes in human
non-melanoma skin cancer. J Invest Dermatol. 134:2408–2417. 2014.
View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
4
|
Brantsch KD, Meisner C, Schönfisch B,
Trilling B, Wehner-Caroli J, Röcken M and Breuninger H: Analysis of
risk factors determining prognosis of cutaneous squamous-cell
carcinoma: a prospective study. Lancet Oncol. 9:713–720. 2008.
View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
5
|
Surdu S, Fitzgerald EF, Bloom MS, Boscoe
FP, Carpenter DO, Haase RF, Gurzau E, Rudnai P, Koppova K, Vahter
M, et al: Polymorphisms in DNA repair genes XRCC1 and XRCC3,
occupational exposure to arsenic and sunlight, and the risk of
non-melanoma skin cancer in a European case-control study. Environ
Res. 134:382–389. 2014. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
6
|
Ju Q and Zouboulis CC:
Endocrine-disrupting chemicals and skin manifestations. Rev Endocr
Metab Disord. 17:449–457. 2016. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
7
|
Goldenberg A, Ortiz A, Kim SS and Jiang
SB: Squamous cell carcinoma with aggressive subclinical extension:
5-year retrospective review of diagnostic predictors. J Am Acad
Dermatol. 73:120–126. 2015. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
8
|
Goldstein J, Roth E, Roberts N, Zwick R,
Lin S, Fletcher S, Tadeu A, Wu C, Beck A, Zeiss C, et al: Loss of
endogenous Nfatc1 reduces the rate of DMBA/TPA-induced skin
tumorigenesis. Mol Biol Cell. 26:3606–3614. 2015. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
9
|
Bai Y, Edamatsu H, Maeda S, Saito H,
Suzuki N, Satoh T and Kataoka T: Crucial role of phospholipase
Cepsilon in chemical carcinogen-induced skin tumor development.
Cancer Res. 64:8808–8810. 2004. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
10
|
Wang Z, Pedersen E, Basse A, Lefever T,
Peyrollier K, Kapoor S, Mei Q, Karlsson R, Chrostek-Grashoff A and
Brakebusch C: Rac1 is crucial for Ras-dependent skin tumor
formation by controlling Pak1-Mek-Erk hyperactivation and
hyperproliferation in vivo. Oncogene. 29:3362–3373. 2010.
View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
11
|
Drexler SK, Bonsignore L, Masin M,
Tardivel A, Jackstadt R, Hermeking H, Schneider P, Gross O, Tschopp
J and Yazdi AS: Tissue-specific opposing functions of the
inflammasome adaptor ASC in the regulation of epithelial skin
carcinogenesis. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA. 109:18384–18389. 2012.
View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
12
|
Kang NJ, Jung SK, Lee KW and Lee HJ:
Myricetin is a potent chemopreventive phytochemical in skin
carcinogenesis. Ann NY Acad Sci. 1229:124–132. 2011. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
13
|
Manoharan S and Selvan MV: Chemopreventive
potential of geraniol in 7,12-dimethylbenz(a) anthracene (DMBA)
induced skin carcinogenesis in Swiss albino mice. J Environ Biol.
33:255–260. 2012.
|
|
14
|
Qian EW, Ge DT and Kong SK: Salidroside
protects human erythrocytes against hydrogen peroxide-induced
apoptosis. J Nat Prod. 75:531–537. 2012. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
15
|
Wang S, He H, Chen L, Zhang W, Zhang X and
Chen J: Protective effects of salidroside in the
MPTP/MPP(+)-induced model of Parkinson's disease through
ROS-NO-related mitochondrion pathway. Mol Neurobiol. 51:718–728.
2015. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
16
|
Zhu L, Chen T, Chang X, Zhou R, Luo F, Liu
J, Zhang K, Wang Y, Yang Y, Long H, et al: Salidroside ameliorates
arthritis-induced brain cognition deficits by regulating
Rho/ROCK/NF-κB pathway. Neuropharmacology. 103:134–142. 2016.
View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
17
|
Zhang S, Chen X, Yang Y, Zhou X, Liu J and
Ding F: Neuroprotection against cobalt chloride-induced cell
apoptosis of primary cultured cortical neurons by salidroside. Mol
Cell Biochem. 354:161–170. 2011. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
18
|
Li X, Ye X, Li X, Sun X, Liang Q, Tao L,
Kang X and Chen J: Salidroside protects against MPP(+)-induced
apoptosis in PC12 cells by inhibiting the NO pathway. Brain Res.
1382:9–18. 2011. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
19
|
Yang DW, Kang OH, Lee YS, Han SH, Lee SW,
Cha SW, Seo YS, Mun SH, Gong R, Shin DW, et al: Anti-inflammatory
effect of salidroside on phorbol-12-myristate-13-acetate plus
A23187-mediated inflammation in HMC-1 cells. Int J Mol Med.
38:1864–1870. 2016. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
20
|
Shan Y, Wei Z, Tao L, Wang S, Zhang F,
Shen C, Wu H, Liu Z, Zhu P, Wang A, et al: Prophylaxis of diallyl
disulfide on skin carcinogenic model via p21-dependent Nrf2
stabilization. Sci Rep. 6:356762016. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
21
|
Saw CL, Huang MT, Liu Y, Khor TO, Conney
AH and Kong AN: Impact of Nrf2 on UVB-induced skin
inflammation/photoprotection and photoprotective effect of
sulforaphane. Mol Carcinog. 50:479–486. 2011. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
22
|
Kim EJ, Park H, Kim J and Park JH:
3,3′-diindolylmethane suppresses
12-O-tetradecanoylphorbol-13-acetate-induced inflammation and tumor
promotion in mouse skin via the downregulation of inflammatory
mediators. Mol Carcinog. 49:672–683. 2010. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
23
|
Delavary Mahdavian B, van der Veer WM, van
Egmond M, Niessen FB and Beelen RH: Macrophages in skin injury and
repair. Immunobiology. 216:753–762. 2011. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
24
|
Sellami H, Said-Sadier N, Znazen A, Gdoura
R, Ojcius DM and Hammami A: Chlamydia trachomatis infection
increases the expression of inflammatory tumorigenic cytokines and
chemokines as well as components of the Toll-like receptor and
NF-κB pathways in human prostate epithelial cells. Mol Cell Probes.
28:147–154. 2014. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
25
|
Xu X, Yang H, Wang X and Tu Y: The
significance of nuclear factor-kappa B signaling pathway in glioma:
A review. Cancer Transl Med. 3:181–184. 2017. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
26
|
Liu Y, Liu Y, Xu D and Li J:
Latanoprost-induced cytokine and chemokine release rrom human
Tenon's capsule fibroblasts: Role of MAPK and NF-κB signaling
pathways. J Glaucoma. 24:635–641. 2015. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
27
|
Wang HC, Yang JH, Hsieh SC and Sheen LY:
Allyl sulfides inhibit cell growth of skin cancer cells through
induction of DNA damage mediated G2/M arrest and apoptosis. J Agric
Food Chem. 58:7096–7103. 2010. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
28
|
Wang T, Yang S, Mei LA, Parmar CK,
Gillespie JW, Praveen KP, Petrenko VA and Torchilin VP:
Paclitaxel-loaded PEG-PE-based micellar nanopreparations targeted
with tumor-specific landscape phage fusion protein enhance
apoptosis and efficiently reduce tumors. Mol Cancer Ther.
13:2864–2875. 2014. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
29
|
Zhao Y, Guo Q, Chen J, Hu J, Wang S and
Sun Y: Role of long non-coding RNA HULC in cell proliferation,
apoptosis and tumor metastasis of gastric cancer: A clinical and in
vitro investigation. Oncol Rep. 31:358–364. 2014. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
30
|
Claerhout S, Verschooten L, Van Kelst S,
De Vos R, Proby C, Agostinis P and Garmyn M: Concomitant inhibition
of AKT and autophagy is required for efficient cisplatin-induced
apoptosis of metastatic skin carcinoma. Int J Cancer.
127:2790–2803. 2010. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
31
|
Strozyk E and Kulms D: The role of
AKT/mTOR pathway in stress response to UV-irradiation: Implication
in skin carcinogenesis by regulation of apoptosis, autophagy and
senescence. Int J Mol Sci. 14:15260–15285. 2013. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
32
|
Li D, Fu Y, Zhang W, Su G, Liu B, Guo M,
Li F, Liang D, Liu Z, Zhang X, et al: Salidroside attenuates
inflammatory responses by suppressing nuclear factor-κB and mitogen
activated protein kinases activation in lipopolysaccharide-induced
mastitis in mice. Inflamm Res. 62:9–15. 2013. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
33
|
Zhu L, Wei T, Gao J, Chang X, He H, Luo F,
Zhou R, Ma C, Liu Y and Yan T: The cardioprotective effect of
salidroside against myocardial ischemia reperfusion injury in rats
by inhibiting apoptosis and inflammation. Apoptosis. 20:1433–1443.
2015. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
34
|
Fu W, McCormick T, Qi X, Luo L, Zhou L, Li
X, Wang BC, Gibbons HE, Abdul-Karim FW and Gorodeski GI: Activation
of P2X(7)-mediated apoptosis inhibits DMBA/TPA-induced formation of
skin papillomas and cancer in mice. BMC Cancer. 9:1142009.
View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
35
|
Zhang XR, Fu XJ, Zhu DS, Zhang CZ, Hou S,
Li M and Yang XH: Salidroside-regulated lipid metabolism with
down-regulation of miR-370 in type 2 diabetic mice. Eur J
Pharmacol. 779:46–52. 2016. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
36
|
Xu MX, Zhao L, Deng C, Yang L, Wang Y, Guo
T, Li L, Lin J and Zhang L: Curcumin suppresses proliferation and
induces apoptosis of human hepatocellular carcinoma cells via the
wnt signaling pathway. Int J Oncol. 43:1951–1959. 2013. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
37
|
Wang X, Simpson ER and Brown KA: p53:
protection against tumor growth beyond effects on cell cycle and
apoptosis. Cancer Res. 75:5001–5007. 2015. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
38
|
Madan V, Lear JT and Szeimies RM:
Non-melanoma skin cancer. Lancet. 375:673–685. 2010. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
39
|
Saw CLL, Yang AY, Huang MT, Liu Y, Lee JH,
Khor TO, Su ZY, Shu L, Lu Y, Conney AH, et al: Nrf2 null enhances
UVB-induced skin inflammation and extracellular matrix damages.
Cell Biosci. 4:392014. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
40
|
Chinembiri TN, du Plessis LH, Gerber M,
Hamman JH and du Plessis J: Review of natural compounds for
potential skin cancer treatment. Molecules. 19:11679–11721. 2014.
View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
41
|
Simões MCF, Sousa JJS and Pais AA: Skin
cancer and new treatment perspectives: A review. Cancer Lett.
357:8–42. 2015. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
42
|
Ma C, Hu L, Tao G, Lv W and Wang H: An
UPLC-MS-based metabolomics investigation on the anti-fatigue effect
of salidroside in mice. J Pharm Biomed Anal. 105:84–90. 2015.
View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
43
|
Zhong X, Lin R, Li Z, Mao J and Chen L:
Effects of Salidroside on cobalt chloride-induced hypoxia damage
and mTOR signaling repression in PC12 cells. Biol Pharm Bull.
37:1199–1206. 2014. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
44
|
Tsimikas S, Duff GW, Berger PB, Rogus J,
Huttner K, Clopton P, Brilakis E, Kornman KS and Witztum JL:
Pro-inflammatory interleukin-1 genotypes potentiate the risk of
coronary artery disease and cardiovascular events mediated by
oxidized phospholipids and lipoprotein(a). J Am Coll Cardiol.
63:1724–1734. 2014. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
45
|
Lofrumento DD, Nicolardi G, Cianciulli A,
De Nuccio F, La Pesa V, Carofiglio V, Dragone T, Calvello R and
Panaro MA: Neuroprotective effects of resveratrol in an MPTP mouse
model of Parkinson's-like disease: Possible role of SOCS-1 in
reducing pro-inflammatory responses. Innate Immun. 20:249–260.
2014. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
46
|
Kim BH, Choi MS, Lee HG, Lee SH, Noh KH,
Kwon S, Jeong AJ, Lee H, Yi EH, Park JY, et al: Photoprotective
potential of penta-O-galloyl-β-Dglucose by targeting NF-κB and MAPK
signaling in UVB radiation-induced human dermal fibroblasts and
mouse skin. Mol Cells. 38:982–990. 2015. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
47
|
Yuan L, Wu Y, Ren X, Liu Q, Wang J and Liu
X: Isoorientin attenuates lipopolysaccharide-induced
pro-inflammatory responses through down-regulation of ROS-related
MAPK/NF-κB signaling pathway in BV-2 microglia. Mol Cell Biochem.
386:153–165. 2014. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
48
|
Lin TH, Yao Z, Sato T, Keeney M, Li C,
Pajarinen J, Yang F, Egashira K and Goodman SB: Suppression of
wear-particle-induced pro-inflammatory cytokine and chemokine
production in macrophages via NF-κB decoy oligodeoxynucleotide: A
preliminary report. Acta Biomater. 10:3747–3755. 2014. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
49
|
Choi H, Nguyen HN and Lamb FS: Inhibition
of endocytosis exacerbates TNF-α-induced endothelial dysfunction
via enhanced JNK and p38 activation. Am J Physiol Heart Circ
Physiol. 306:H1154–H1163. 2014. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
50
|
Schett G, Dayer JM and Manger B:
Interleukin-1 function and role in rheumatic disease. Nat Rev
Rheumatol. 12:14–24. 2016. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
51
|
Wu L, Zhou Y, Zhou Z, Liu Y, Bai Y, Xing X
and Wang X: Nicotine induces the production of IL-1β and IL-8 via
the α7 nAChR/NF-κB pathway in human periodontal ligament cells: An
in vitro study. Cell Physiol Biochem. 34:423–431. 2014. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
52
|
Wang Q, He Y, Shen Y, Zhang Q, Chen D, Zuo
C, Qin J, Wang H, Wang J and Yu Y: Vitamin D inhibits COX-2
expression and inflammatory response by targeting thioesterase
superfamily member 4. J Biol Chem. 289:11681–11694. 2014.
View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
53
|
Kumar D, Tewari-Singh N, Agarwal C, Jain
AK, Inturi S, Kant R, White CW and Agarwal R: Nitrogen mustard
exposure of murine skin induces DNA damage, oxidative stress and
activation of MAPK/Akt-AP1 pathway leading to induction of
inflammatory and proteolytic mediators. Toxicol Lett. 235:161–171.
2015. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
54
|
Marvel D and Gabrilovich DI:
Myeloid-derived suppressor cells in the tumor microenvironment:
Expect the unexpected. J Clin Invest. 125:3356–3364. 2015.
View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
55
|
Song J, Feng L, Zhong R, Xia Z, Zhang L,
Cui L, Yan H, Jia X and Zhang Z: Icariside II inhibits the EMT of
NSCLC cells in inflammatory microenvironment via down-regulation of
Akt/NF-κB signaling pathway. Mol Carcinog. 56:36–48. 2017.
View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
56
|
Nie FQ, Sun M, Yang JS, Xie M, Xu TP, Xia
R, Liu YW, Liu XH, Zhang EB, Lu KH, et al: Long noncoding RNA ANRIL
promotes non-small cell lung cancer cell proliferation and inhibits
apoptosis by silencing KLF2 and P21 expression. Mol Cancer Ther.
14:268–277. 2015. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
57
|
Dai H, Meng XW and Kaufmann SH: BCL2
family, mitochondrial apoptosis, and beyond. Cancer Transl Med.
2:7–20. 2016. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
58
|
White MJ, McArthur K, Metcalf D, Lane RM,
Cambier JC, Herold MJ, van Delft MF, Bedoui S, Lessene G, Ritchie
ME, et al: Apoptotic caspases suppress mtDNA-induced STING-mediated
type I IFN production. Cell. 159:1549–1562. 2014. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
59
|
Samarghandian S, Nezhad Azimi M and
Mohammadi G: Role of caspases, Bax and Bcl-2 in chrysin-induced
apoptosis in the A549 human lung adenocarcinoma epithelial cells.
Anticancer Agents Med Chem. 14:901–909. 2014. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
60
|
Jiang X, Jiang H, Shen Z and Wang X:
Activation of mitochondrial protease OMA1 by Bax and Bak promotes
cytochrome c release during apoptosis. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA.
111:14782–14787. 2014. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
61
|
Seth R, Corniola RS, Gower-Winter SD,
Morgan TJ Jr, Bishop B and Levenson CW: Zinc deficiency induces
apoptosis via mitochondrial p53- and caspase-dependent pathways in
human neuronal precursor cells. J Trace Elem Med Biol. 30:59–65.
2015. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
62
|
Al-Fatlawi AA, Al-Fatlawi AA, Irshad M,
Zafaryab M, Rizvi MM and Ahmad A: Rice bran phytic acid induced
apoptosis through regulation of Bcl-2/Bax and p53 genes in HepG2
human hepatocellular carcinoma cells. Asian Pac J Cancer Prev.
15:3731–3736. 2014. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
63
|
Gu JJ, Zhang Q, Mavis C, Czuczman MS and
Hernandez-Ilizaliturri FJ: Metformin induces p53-dependent
mitochondrial stress in therapy-sensitive and-resistant lymphoma
pre-clinical model and primary patients sample with B-cell
non-Hodgkin lymphoma (NHL). Blood. 126:4008. 2015.
|
|
64
|
Song H, Wei M, Liu W, Shen S, Li J and
Wang L: Cisplatin induced apoptosis of ovarian cancer A2780s cells
by activation of ERK/p53/PUMA signals. Histol Histopathol. Mar
13–2017.(Epub ahead of print). doi: 10.14670/HH-11-889.
|
|
65
|
Renault TT, Floros KV, Elkholi R, Corrigan
KA, Kushnareva Y, Wieder SY, Lindtner C, Serasinghe MN, Asciolla
JJ, Buettner C, et al: Mitochondrial shape governs BAX-induced
membrane permeabilization and apoptosis. Mol Cell. 57:69–82. 2015.
View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
66
|
Singh N, Sarkar J, Sashidhara KV, Ali S
and Sinha S: Anti-tumour activity of a novel coumarin-chalcone
hybrid is mediated through intrinsic apoptotic pathway by inducing
PUMA and altering Bax/Bcl-2 ratio. Apoptosis. 19:1017–1028. 2014.
View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
67
|
Shamanna RA, Hoque M, Pe'ery T and Mathews
MB: Induction of p53, p21 and apoptosis by silencing the NF90/NF45
complex in human papilloma virus-transformed cervical carcinoma
cells. Oncogene. 32:5176–5185. 2013. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
68
|
Dong X, Zhang X, Li D, Li B, Wang J, Meng
S, Luo W and Zhang W: Protective effect of salidroside against high
altitude hypoxia-induced brain injury in rats. Xi Bao Yu Fen Zi
Mian Yi Xue Za Zhi. 31:1327–1331. 2015.(In Chinese).
|
|
69
|
Teng L, Gao JF, Zhou L, Xian QY, Li JK and
Yang SJ: Influence of salidroside on expression level of
endothelin-1 and its receptors under hypoxic conditions in chicken
embryonic pulmonary artery smooth muscle cells. Pak Vet J.
36:214–218. 2016.
|
|
70
|
Fan XJ, Wang Y, Wang L and Zhu M:
Salidroside induces apoptosis and autophagy in human colorectal
cancer cells through inhibition of PI3K/Akt/mTOR pathway. Oncol
Rep. 36:3559–3567. 2016. View Article : Google Scholar
|