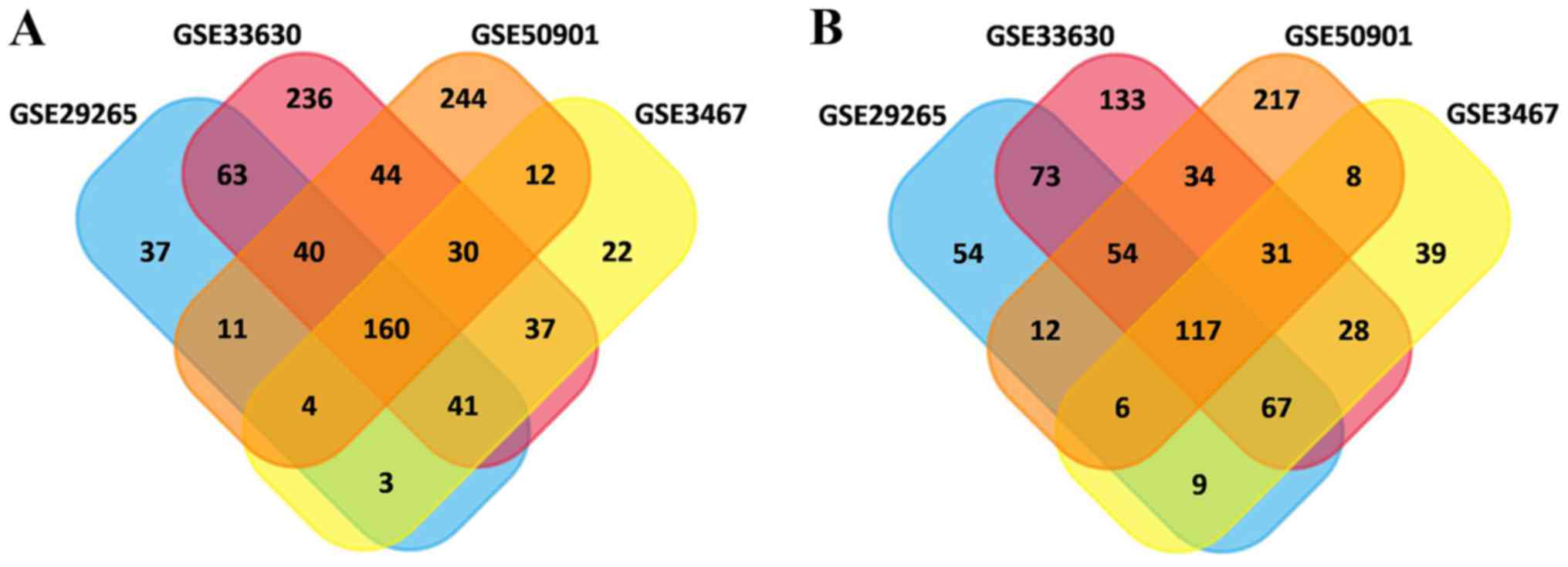
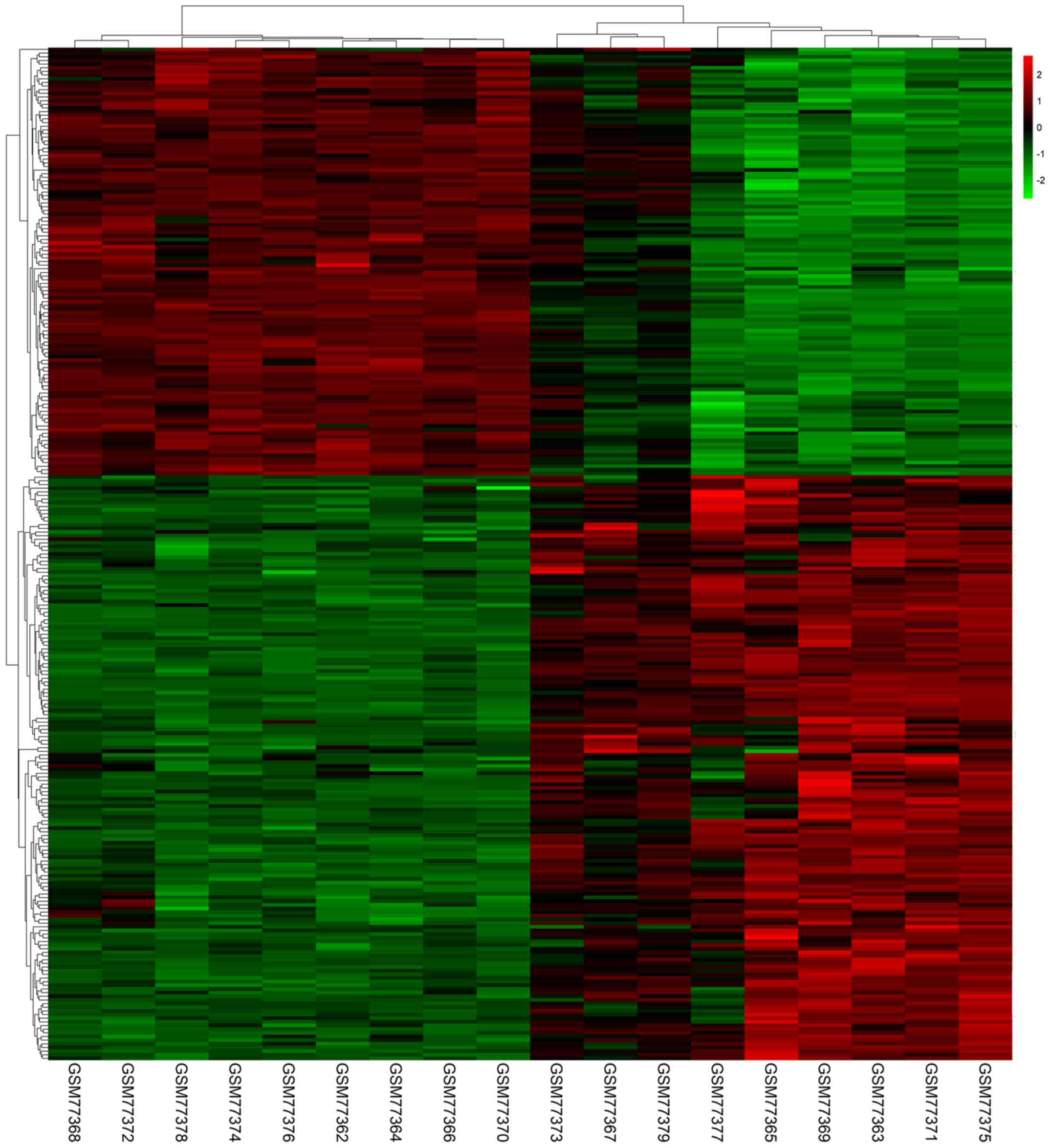
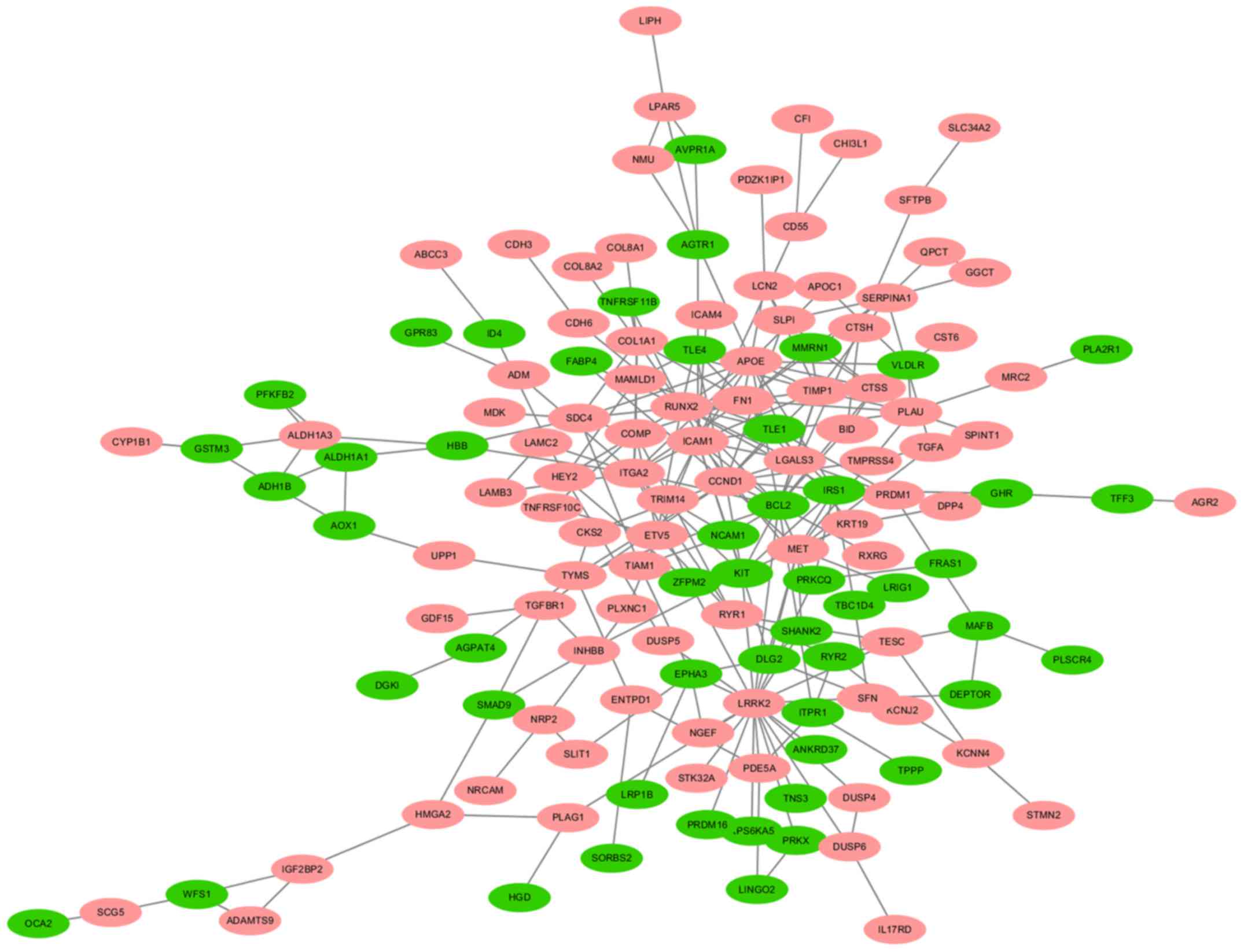
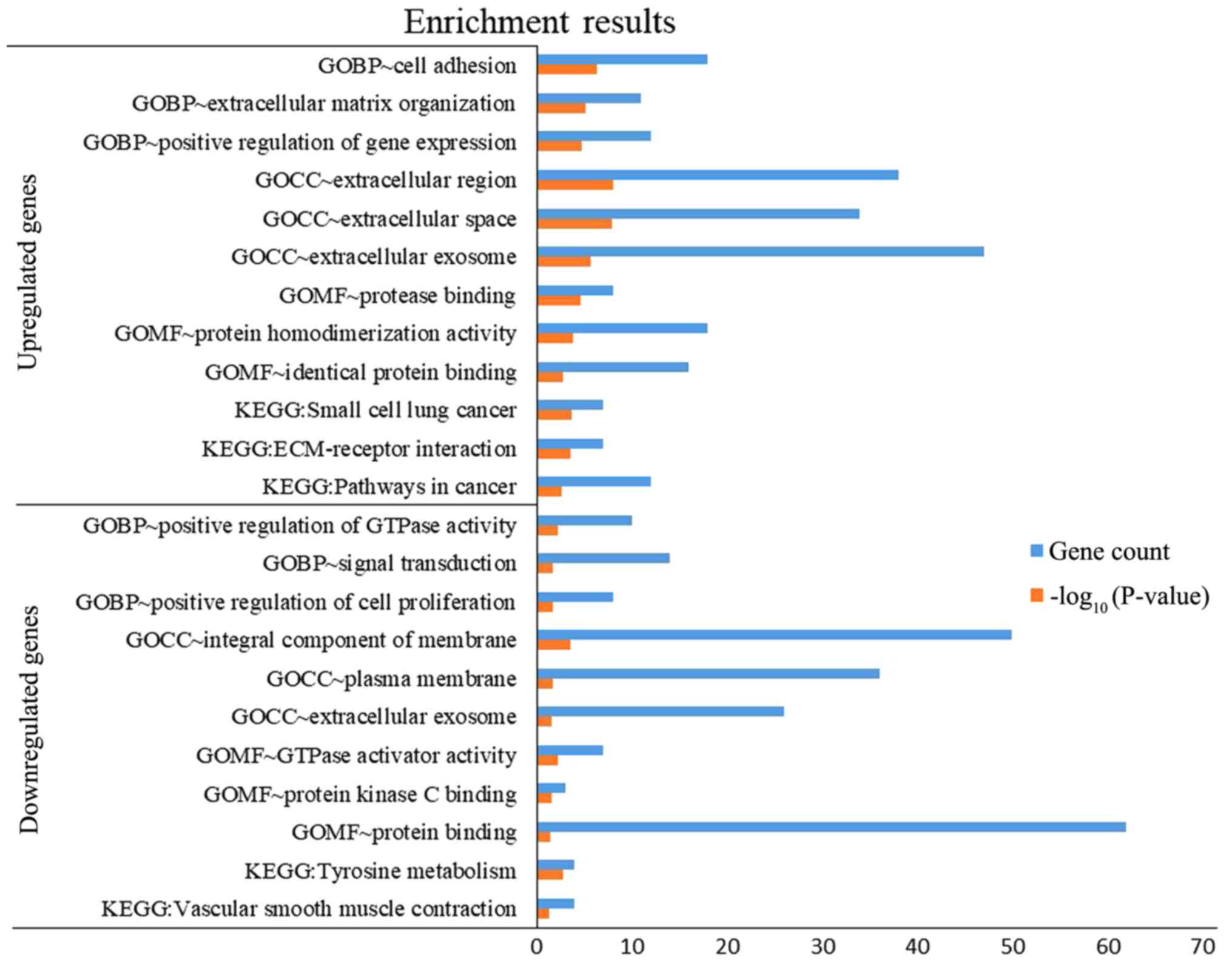
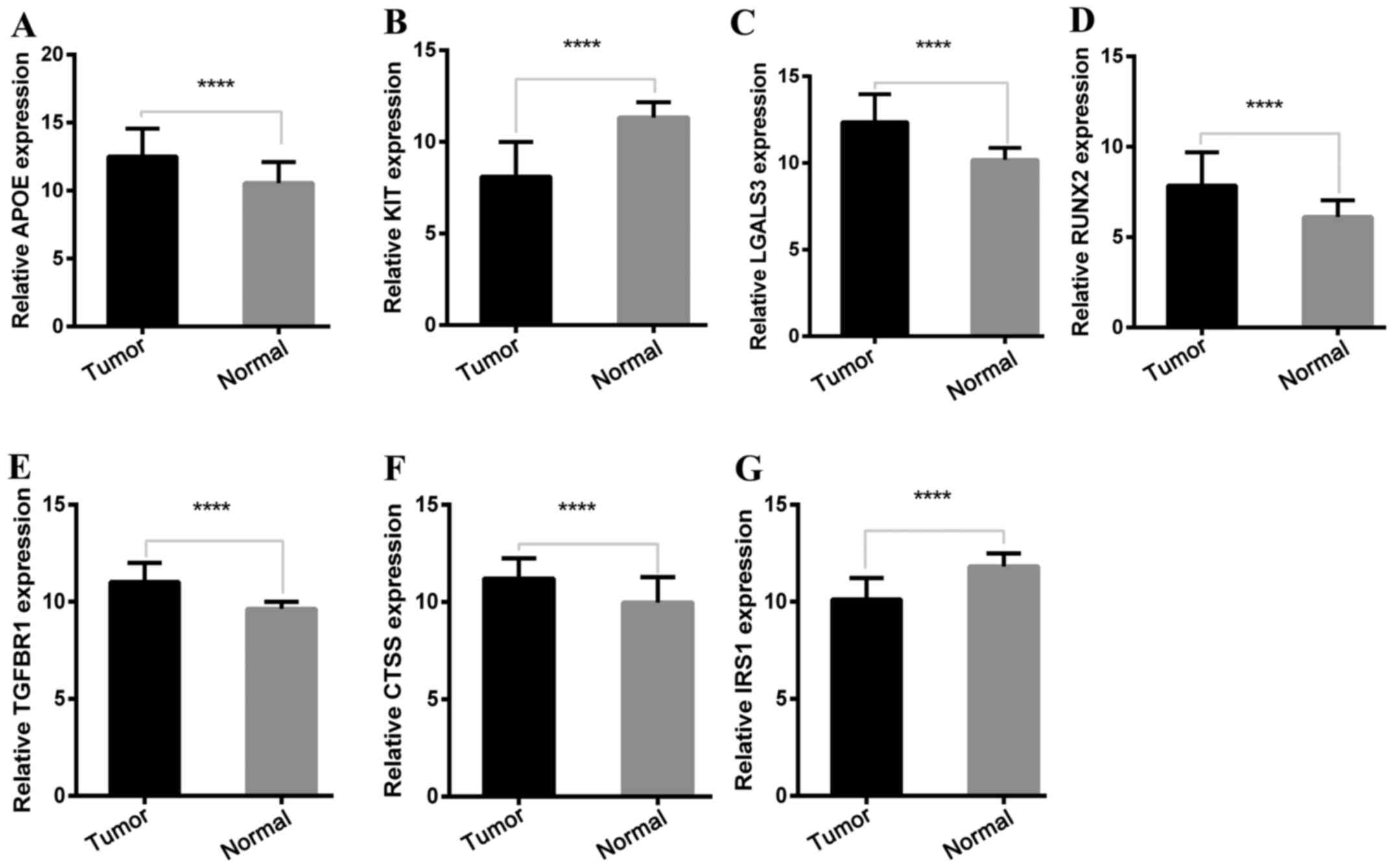
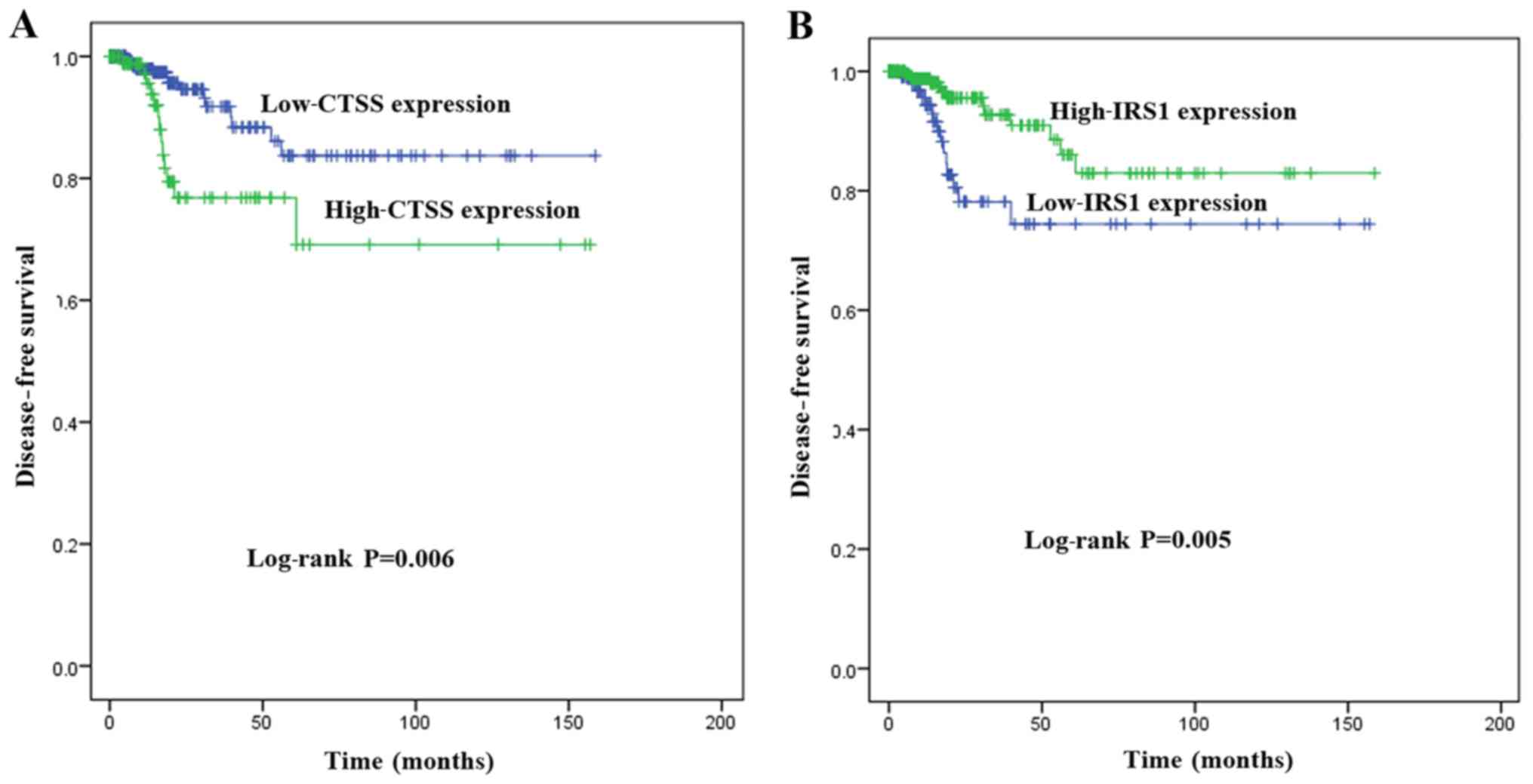
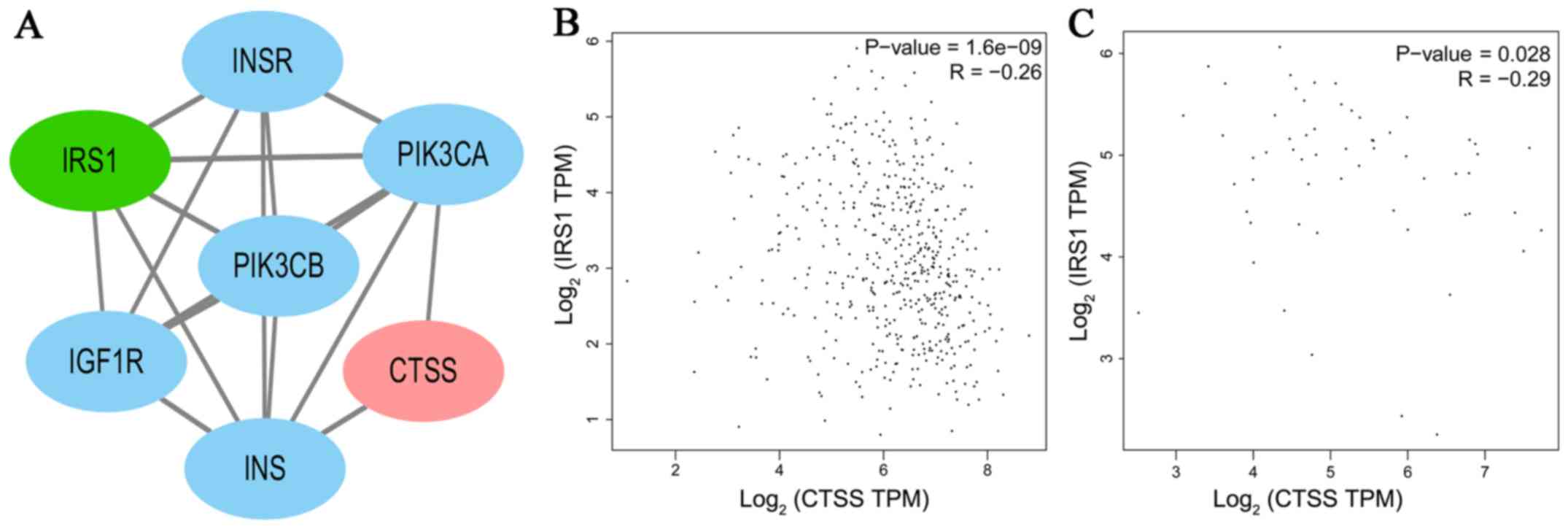
|
1
|
Siegel RL, Miller KD and Jemal A: Cancer
statistics, 2016. CA Cancer J Clin. 66:7–30. 2016. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
2
|
Siegel RL, Miller KD and Jemal A: Cancer
Statistics, 2017. CA Cancer J Clin. 67:7–30. 2017. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
3
|
Haugen BR: 2015 American Thyroid
Association Management Guidelines for Adult Patients with Thyroid
Nodules and Differentiated Thyroid Cancer: What is new and what has
changed? Cancer. 123:372–381. 2017. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
4
|
Grogan RH, Kaplan SP, Cao H, Weiss RE,
Degroot LJ, Simon CA, Embia OM, Angelos P, Kaplan EL and Schechter
RB: A study of recurrence and death from papillary thyroid cancer
with 27 years of median follow-up. Surgery. 154:1436–1446;
discussion 1446-7. 2013. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
5
|
Giordano TJ, Kuick R, Thomas DG, Misek DE,
Vinco M, Sanders D, Zhu Z, Ciampi R, Roh M, Shedden K, et al:
Molecular classification of papillary thyroid carcinoma: Distinct
BRAF, RAS, and RET/PTC mutation-specific gene expression profiles
discovered by DNA microarray analysis. Oncogene. 24:6646–6656.
2005. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
6
|
Adeniran AJ, Zhu Z, Gandhi M, Steward DL,
Fidler JP, Giordano TJ, Biddinger PW and Nikiforov YE: Correlation
between genetic alterations and microscopic features, clinical
manifestations, and prognostic characteristics of thyroid papillary
carcinomas. Am J Surg Pathol. 30:216–222. 2006. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
7
|
Greco A, Miranda C and Pierotti MA:
Rearrangements of NTRK1 gene in papillary thyroid carcinoma. Mol
Cell Endocrinol. 321:44–49. 2010. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
8
|
Ellis RJ, Wang Y, Stevenson HS, Boufraqech
M, Patel D, Nilubol N, Davis S, Edelman DC, Merino MJ, He M, et al:
Genome-wide methylation patterns in papillary thyroid cancer are
distinct based on histological subtype and tumor genotype. J Clin
Endocrinol Metab. 99:E329–E337. 2014. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
9
|
Saji M and Ringel MD: The PI3K-Akt-mTOR
pathway in initiation and progression of thyroid tumors. Mol Cell
Endocrinol. 321:20–28. 2010. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
10
|
Xing M: Molecular pathogenesis and
mechanisms of thyroid cancer. Nat Rev Cancer. 13:184–199. 2013.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
11
|
Li X, Abdel-Mageed AB, Mondal D and Kandil
E: The nuclear factor kappa-B signaling pathway as a therapeutic
target against thyroid cancers. Thyroid. 23:209–218. 2013.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
12
|
Bauerle KT, Schweppe RE, Lund G, Kotnis G,
Deep G, Agarwal R, Pozdeyev N, Wood WM and Haugen BR: Nuclear
factor κB-dependent regulation of angiogenesis, and metastasis in
an in vivo model of thyroid cancer is associated with secreted
interleukin-8. J Clin Endocrinol Metab. 99:E1436–E1444. 2014.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
13
|
Clevers H and Nusse R: Wnt/β-catenin
signaling and disease. Cell. 149:1192–1205. 2012. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
14
|
Agrawal N, Akbani R, Aksoy BA, Ally A,
Arachchi H, Asa SL, Auman JT, Balasundaram M, Balu S, Baylin SB, et
al: Cancer Genome Atlas Research Network: Integrated genomic
characterization of papillary thyroid carcinoma. Cell. 159:676–690.
2014. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
15
|
Chin CH, Chen SH, Wu HH, Ho CW, Ko MT and
Lin CY: cytoHubba: Identifying hub objects and sub-networks from
complex interactome. BMC Syst Biol. 8 Suppl 4:S112014. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
16
|
Barrett T, Wilhite SE, Ledoux P,
Evangelista C, Kim IF, Tomashevsky M, Marshall KA, Phillippy KH,
Sherman PM, Holko M, et al: NCBI GEO: Archive for functional
genomics data sets - update. Nucleic Acids Res. 41D:D991–D995.
2013.
|
|
17
|
Franceschini A, Szklarczyk D, Frankild S,
Kuhn M, Simonovic M, Roth A, Lin J, Minguez P, Bork P, von Mering
C, et al: STRING v9.1: Protein-protein interaction networks, with
increased coverage and integration. Nucleic Acids Res.
41D:D808–D815. 2013.
|
|
18
|
Shannon P, Markiel A, Ozier O, Baliga NS,
Wang JT, Ramage D, Amin N, Schwikowski B and Ideker T: Cytoscape: A
software environment for integrated models of biomolecular
interaction networks. Genome Res. 13:2498–2504. 2003. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
19
|
Liu Z, Gao Y, Hao F, Lou X, Zhang X, Li Y,
Wu D, Xiao T, Yang L, Li Q, et al: Secretomes are a potential
source of molecular targets for cancer therapies and indicate that
APOE is a candidate biomarker for lung adenocarcinoma metastasis.
Mol Biol Rep. 41:7507–7523. 2014. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
20
|
Su WP, Chen YT, Lai WW, Lin CC, Yan JJ and
Su WC: Apolipoprotein E expression promotes lung adenocarcinoma
proliferation and migration and as a potential survival marker in
lung cancer. Lung Cancer. 71:28–33. 2011. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
21
|
Boylan KL, Andersen JD, Anderson LB,
Higgins L and Skubitz AP: Quantitative proteomic analysis by
iTRAQ(R) for the identification of candidate biomarkers in ovarian
cancer serum. Proteome Sci. 8:312010. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
22
|
Chen EC, Karl TA, Kalisky T, Gupta SK,
O'Brien CA, Longacre TA, van de Rijn M, Quake SR, Clarke MF and
Rothenberg ME: KIT signaling promotes growth of colon xenograft
tumors in mice and is up-regulated in a subset of human colon
cancers. Gastroenterology. 149:705–17.e2. 2015. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
23
|
Joensuu H, Rutkowski P, Nishida T, Steigen
SE, Brabec P, Plank L, Nilsson B, Braconi C, Bordoni A, Magnusson
MK, et al: KIT and PDGFRA mutations and the risk of GI stromal
tumor recurrence. J Clin Oncol. 33:634–642. 2015. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
24
|
Gavert N, Shvab A, Sheffer M, Ben-Shmuel
A, Haase G, Bakos E, Domany E and Ben-Ze'ev A: c-Kit is suppressed
in human colon cancer tissue and contributes to L1-mediated
metastasis. Cancer Res. 73:5754–5763. 2013. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
25
|
Mainetti LE, Zhe X, Diedrich J, Saliganan
AD, Cho WJ, Cher ML, Heath E, Fridman R, Kim HR and Bonfil RD:
Bone-induced c-kit expression in prostate cancer: A driver of
intraosseous tumor growth. Int J Cancer. 136:11–20. 2015.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
26
|
Panebianco F, Mazzanti C, Tomei S, Aretini
P, Franceschi S, Lessi F, Di Coscio G, Bevilacqua G and Marchetti
I: The combination of four molecular markers improves thyroid
cancer cytologic diagnosis and patient management. BMC Cancer.
15:9182015. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
27
|
Pusztaszeri MP, Sadow PM and Faquin WC:
CD117: A novel ancillary marker for papillary thyroid carcinoma in
fine-needle aspiration biopsies. Cancer Cytopathol. 122:596–603.
2014. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
28
|
Trimboli P, Virili C, Romanelli F,
Crescenzi A and Giovanella L: Galectin-3 performance in histologic
a cytologic assessment of thyroid nodules: A systematic review and
meta-analysis. Int J Mol Sci. 18:182017. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
29
|
Xing M, Haugen BR and Schlumberger M:
Progress in molecular-based management of differentiated thyroid
cancer. Lancet. 381:1058–1069. 2013. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
30
|
Owens TW, Rogers RL, Best S, Ledger A,
Mooney AM, Ferguson A, Shore P, Swarbrick A, Ormandy CJ, Simpson
PT, et al: Runx2 is a novel regulator of mammary epithelial cell
fate in development and breast cancer. Cancer Res. 74:5277–5286.
2014. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
31
|
Sase T, Suzuki T, Miura K, Shiiba K, Sato
I, Nakamura Y, Takagi K, Onodera Y, Miki Y, Watanabe M, et al:
Runt-related transcription factor 2 in human colon carcinoma: A
potent prognostic factor associated with estrogen receptor. Int J
Cancer. 131:2284–2293. 2012. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
32
|
Boregowda RK, Olabisi OO, Abushahba W,
Jeong BS, Haenssen KK, Chen W, Chekmareva M, Lasfar A, Foran DJ,
Goydos JS, et al: RUNX2 is overexpressed in melanoma cells and
mediates their migration and invasion. Cancer Lett. 348:61–70.
2014. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
33
|
Ge C, Zhao G, Li Y, Li H, Zhao X, Pannone
G, Bufo P, Santoro A, Sanguedolce F, Tortorella S, et al: Role of
Runx2 phosphorylation in prostate cancer and association with
metastatic disease. Oncogene. 35:366–376. 2016. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
34
|
Pratap J, Lian JB and Stein GS: Metastatic
bone disease: Role of transcription factors and future targets.
Bone. 48:30–36. 2011. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
35
|
Sancisi V, Gandolfi G, Ambrosetti DC and
Ciarrocchi A: Histone deacetylase inhibitors repress tumoral
expression of the proinvasive factor RUNX2. Cancer Res.
75:1868–1882. 2015. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
36
|
Sancisi V, Borettini G, Maramotti S,
Ragazzi M, Tamagnini I, Nicoli D, Piana S and Ciarrocchi A: Runx2
isoform I controls a panel of proinvasive genes driving
aggressiveness of papillary thyroid carcinomas. J Clin Endocrinol
Metab. 97:E2006–E2015. 2012. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
37
|
Dalle Carbonare L, Frigo A, Francia G,
Davì MV, Donatelli L, Stranieri C, Brazzarola P, Zatelli MC,
Menestrina F and Valenti MT: Runx2 mRNA expression in the tissue,
serum, and circulating non-hematopoietic cells of patients with
thyroid cancer. J Clin Endocrinol Metab. 97:E1249–E1256. 2012.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
38
|
Kaptan E, Bas Sancar S, Sancakli A, Aktas
HG, Bayrak BB, Yanardag R and Bolkent S: Runt-related transcription
factor 2 (Runx2) Is responsible for galectin-3 overexpression in
human thyroid carcinoma. J Cell Biochem. 118:3911–3919. 2017.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
39
|
Carr FE, Tai PW, Barnum MS, Gillis NE,
Evans KG, Taber TH, White JH, Tomczak JA, Jaworski DM, Zaidi SK, et
al: Thyroid hormone receptor-β (TRβ) mediates runt-related
transcription factor 2 (Runx2) expression in thyroid cancer cells:
A novel signaling pathway in thyroid cancer. Endocrinology.
157:3278–3292. 2016. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
40
|
Bian Y, Terse A, Du J, Hall B, Molinolo A,
Zhang P, Chen W, Flanders KC, Gutkind JS, Wakefield LM, et al:
Progressive tumor formation in mice with conditional deletion of
TGF-beta signaling in head and neck epithelia is associated with
activation of the PI3K/Akt pathway. Cancer Res. 69:5918–5926. 2009.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
41
|
Wu T, Chen X, Peng R, Liu H, Yin P, Peng
H, Zhou Y, Sun Y, Wen L, Yi H, et al: Let-7a suppresses cell
proliferation via the TGF-β/SMAD signaling pathway in cervical
cancer. Oncol Rep. 36:3275–3282. 2016. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
42
|
He J, Jin Y, Zhou M, Li X, Chen W, Wang Y,
Gu S, Cao Y, Chu C, Liu X and Zou Q: Solute carrier family 35
member F2 is indispensable for papillary thyroid carcinoma
progression through activation of transforming growth factor-β type
I receptor/apoptosis signal-regulating kinase 1/mitogen-activated
protein kinase signaling axis. Cancer Sci. 109:642–655. 2018.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
43
|
Zha J and Lackner MR: Targeting the
insulin-like growth factor receptor-1R pathway for cancer therapy.
Clin Cancer Res. 16:2512–2517. 2010. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
44
|
Wang G, Pan J, Zhang L, Wei Y and Wang C:
Long non-coding RNA CRNDE sponges miR-384 to promote proliferation
and metastasis of pancreatic cancer cells through upregulating
IRS1. Cell Prolif. 50:502017. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
45
|
Bailey KL, Agarwal E, Chowdhury S, Luo J,
Brattain MG, Black JD and Wang J: TGFβ/Smad3 regulates
proliferation and apoptosis through IRS-1 inhibition in colon
cancer cells. PLoS One. 12:e01760962017. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
46
|
Luo X, Fan S, Huang W, Zhai S, Ma Z, Li P,
Sun SY and Wang X: Downregulation of IRS-1 promotes metastasis of
head and neck squamous cell carcinoma. Oncol Rep. 28:659–667. 2012.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
47
|
Houghton AM, Rzymkiewicz DM, Ji H, Gregory
AD, Egea EE, Metz HE, Stolz DB, Land SR, Marconcini LA, Kliment CR,
et al: Neutrophil elastase-mediated degradation of IRS-1
accelerates lung tumor growth. Nat Med. 16:219–223. 2010.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
48
|
Wang Y, Zhang X, Zou C, Kung HF, Lin MC,
Dress A, Wardle F, Jiang BH and Lai L: miR-195 inhibits tumor
growth and angiogenesis through modulating IRS1 in breast cancer.
Biomed Pharmacother. 80:95–101. 2016. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
49
|
Ma Z, Gibson SL, Byrne MA, Zhang J, White
MF and Shaw LM: Suppression of insulin receptor substrate 1 (IRS-1)
promotes mammary tumor metastasis. Mol Cell Biol. 26:9338–9351.
2006. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
50
|
Shi J, Wang DM, Wang CM, Hu Y, Liu AH,
Zhang YL, Sun B and Song JG: Insulin receptor substrate-1
suppresses transforming growth factor-beta1-mediated
epithelial-mesenchymal transition. Cancer Res. 69:7180–7187. 2009.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
51
|
Vasiljeva O, Reinheckel T, Peters C, Turk
D, Turk V and Turk B: Emerging roles of cysteine cathepsins in
disease and their potential as drug targets. Curr Pharm Des.
13:387–403. 2007. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
52
|
Clark AK, Yip PK, Grist J, Gentry C,
Staniland AA, Marchand F, Dehvari M, Wotherspoon G, Winter J, Ullah
J, et al: Inhibition of spinal microglial cathepsin S for the
reversal of neuropathic pain. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA.
104:10655–10660. 2007. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
53
|
Dennemärker J, Lohmüller T, Müller S,
Aguilar SV, Tobin DJ, Peters C and Reinheckel T: Impaired turnover
of autophagolysosomes in cathepsin L deficiency. Biol Chem.
391:913–922. 2010. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
54
|
Pan L, Li Y, Jia L, Qin Y, Qi G, Cheng J,
Qi Y, Li H and Du J: Cathepsin S deficiency results in abnormal
accumulation of autophagosomes in macrophages and enhances Ang
II-induced cardiac inflammation. PLoS One. 7:e353152012. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
55
|
Yin M, Soikkeli J, Jahkola T, Virolainen
S, Saksela O and Hölttä E: TGF-β signaling, activated stromal
fibroblasts, and cysteine cathepsins B and L drive the invasive
growth of human melanoma cells. Am J Pathol. 181:2202–2216. 2012.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
56
|
Olson OC and Joyce JA: Cysteine cathepsin
proteases: Regulators of cancer progression and therapeutic
response. Nat Rev Cancer. 15:712–729. 2015. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
57
|
Chen KL, Chang WS, Cheung CH, Lin CC,
Huang CC, Yang YN, Kuo CP, Kuo CC, Chang YH, Liu KJ, et al:
Targeting cathepsin S induces tumor cell autophagy via the EGFR-ERK
signaling pathway. Cancer Lett. 317:89–98. 2012. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
58
|
Gormley JA, Hegarty SM, O'Grady A,
Stevenson MR, Burden RE, Barrett HL, Scott CJ, Johnston JA, Wilson
RH, Kay EW, et al: The role of Cathepsin S as a marker of prognosis
and predictor of chemotherapy benefit in adjuvant CRC: A pilot
study. Br J Cancer. 105:1487–1494. 2011. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
59
|
Small DM, Burden RE, Jaworski J, Hegarty
SM, Spence S, Burrows JF, McFarlane C, Kissenpfennig A, McCarthy
HO, Johnston JA, et al: Cathepsin S from both tumor and
tumor-associated cells promote cancer growth and
neovascularization. Int J Cancer. 133:2102–2112. 2013. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
60
|
Yang M, Liu J, Shao J, Qin Y, Ji Q, Zhang
X and Du J: Cathepsin S-mediated autophagic flux in
tumor-associated macrophages accelerate tumor development by
promoting M2 polarization. Mol Cancer. 13:432014. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
61
|
Sage J, Mallèvre F, Barbarin-Costes F,
Samsonov SA, Gehrcke JP, Pisabarro MT, Perrier E, Schnebert S,
Roget A, Livache T, et al: Binding of chondroitin 4-sulfate to
cathepsin S regulates its enzymatic activity. Biochemistry.
52:6487–6498. 2013. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
62
|
Shi GP, Webb AC, Foster KE, Knoll JH,
Lemere CA, Munger JS and Chapman HA: Human cathepsin S: Chromosomal
localization, gene structure, and tissue distribution. J Biol Chem.
269:11530–11536. 1994.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
63
|
Jordans S, Jenko-Kokalj S, Kühl NM,
Tedelind S, Sendt W, Brömme D, Turk D and Brix K: Monitoring
compartment-specific substrate cleavage by cathepsins B, K, L, and
S at physiological pH and redox conditions. BMC Biochem. 10:232009.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
64
|
Burden RE, Gormley JA, Kuehn D, Ward C,
Kwok HF, Gazdoiu M, McClurg A, Jaquin TJ, Johnston JA, Scott CJ, et
al: Inhibition of Cathepsin S by Fsn0503 enhances the efficacy of
chemotherapy in colorectal carcinomas. Biochimie. 94:487–493. 2012.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
65
|
Liu WL, Liu D, Cheng K, Liu YJ, Xing S,
Chi PD, Liu XH, Xue N, Lai YZ, Guo L, et al: Evaluating the
diagnostic and prognostic value of circulating cathepsin S in
gastric cancer. Oncotarget. 7:28124–28138. 2016.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
66
|
Lindahl C, Simonsson M, Bergh A, Thysell
E, Antti H, Sund M and Wikström P: Increased levels of
macrophage-secreted cathepsin S during prostate cancer progression
in TRAMP mice and patients. Cancer Genomics Proteomics. 6:149–159.
2009.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
67
|
Wang X, Xiong L, Yu G, Li D, Peng T, Luo D
and Xu J: Cathepsin S silencing induces apoptosis of human
hepatocellular carcinoma cells. Am J Transl Res. 7:100–110.
2015.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
68
|
Gole B, Huszthy PC, Popović M, Jeruc J,
Ardebili YS, Bjerkvig R and Lah TT: The regulation of cysteine
cathepsins and cystatins in human gliomas. Int J Cancer.
131:1779–1789. 2012. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
69
|
Gautam J, Bae YK and Kim JA: Up-regulation
of cathepsin S expression by HSP90 and 5-HT7 receptor-dependent
serotonin signaling correlates with triple negativity of human
breast cancer. Breast Cancer Res Treat. 161:29–40. 2017. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
70
|
Kondo T, Ezzat S and Asa SL: Pathogenetic
mechanisms in thyroid follicular-cell neoplasia. Nat Rev Cancer.
6:292–306. 2006. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
71
|
Flannery T, McQuaid S, McGoohan C,
McConnell RS, McGregor G, Mirakhur M, Hamilton P, Diamond J, Cran
G, Walker B, et al: Cathepsin S expression: An independent
prognostic factor in glioblastoma tumours - A pilot study. Int J
Cancer. 119:854–860. 2006. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
72
|
Kos J, Sekirnik A, Kopitar G, Cimerman N,
Kayser K, Stremmer A, Fiehn W and Werle B: Cathepsin S in tumours,
regional lymph nodes and sera of patients with lung cancer:
Relation to prognosis. Br J Cancer. 85:1193–1200. 2001. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|