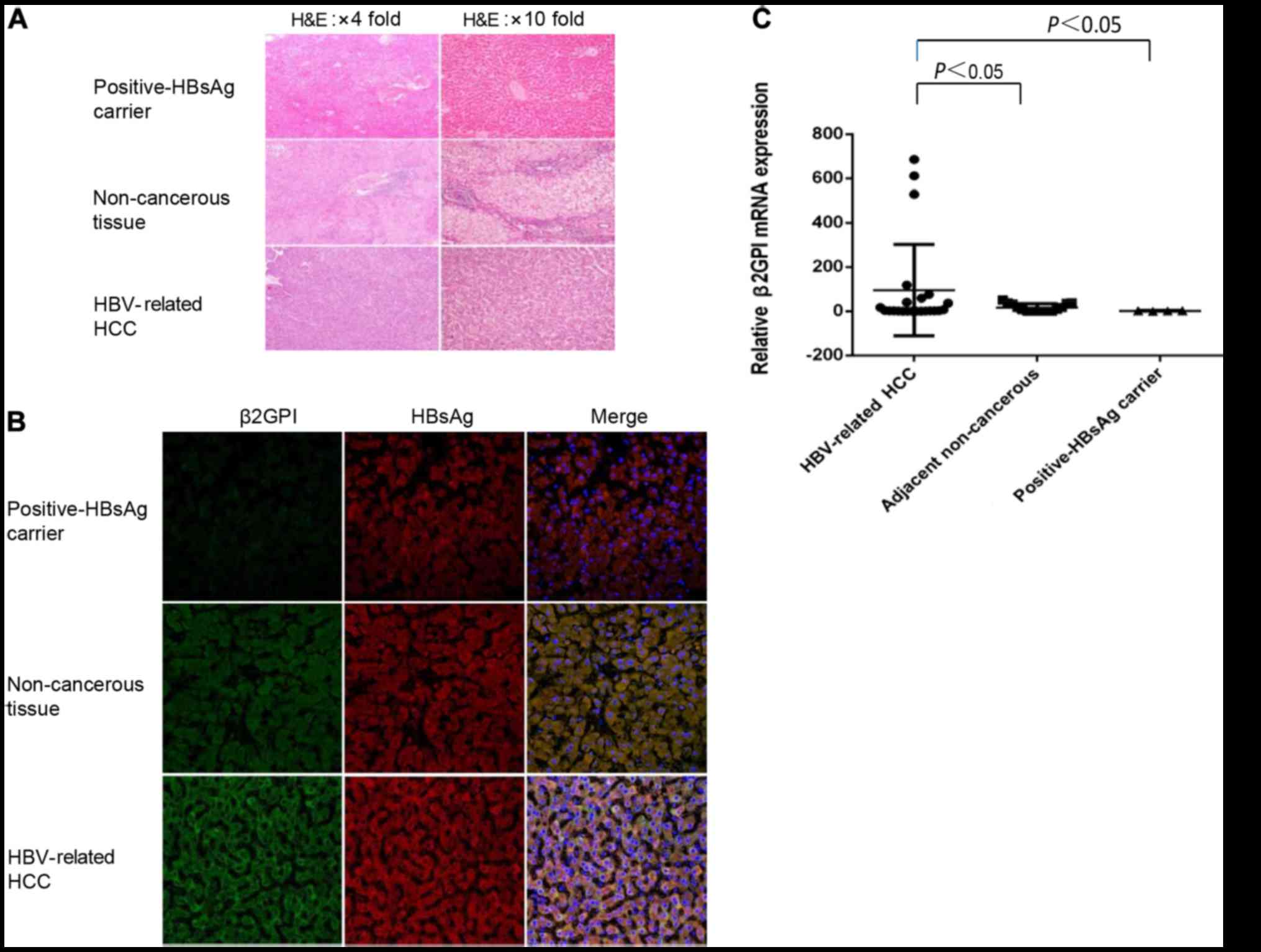
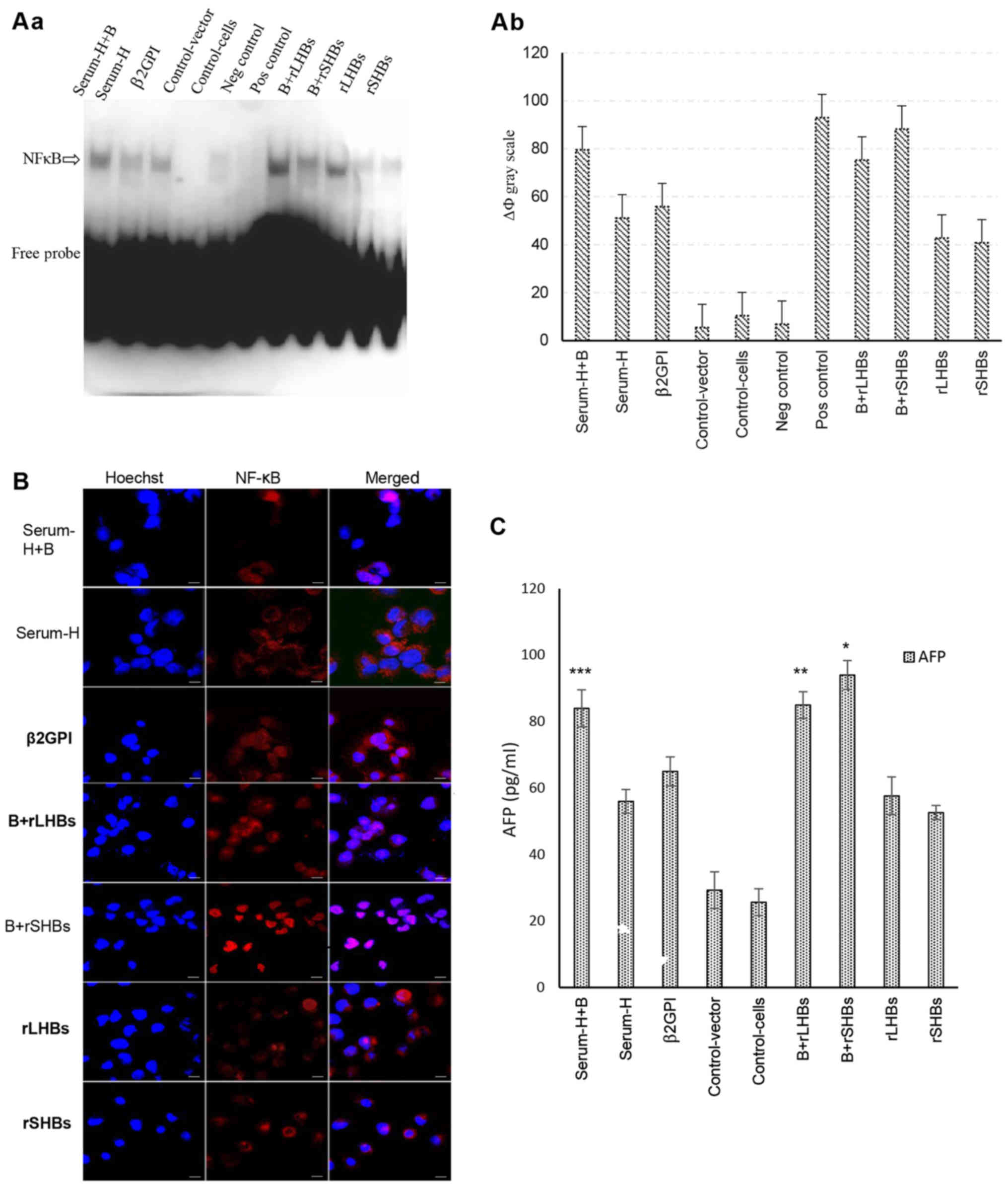
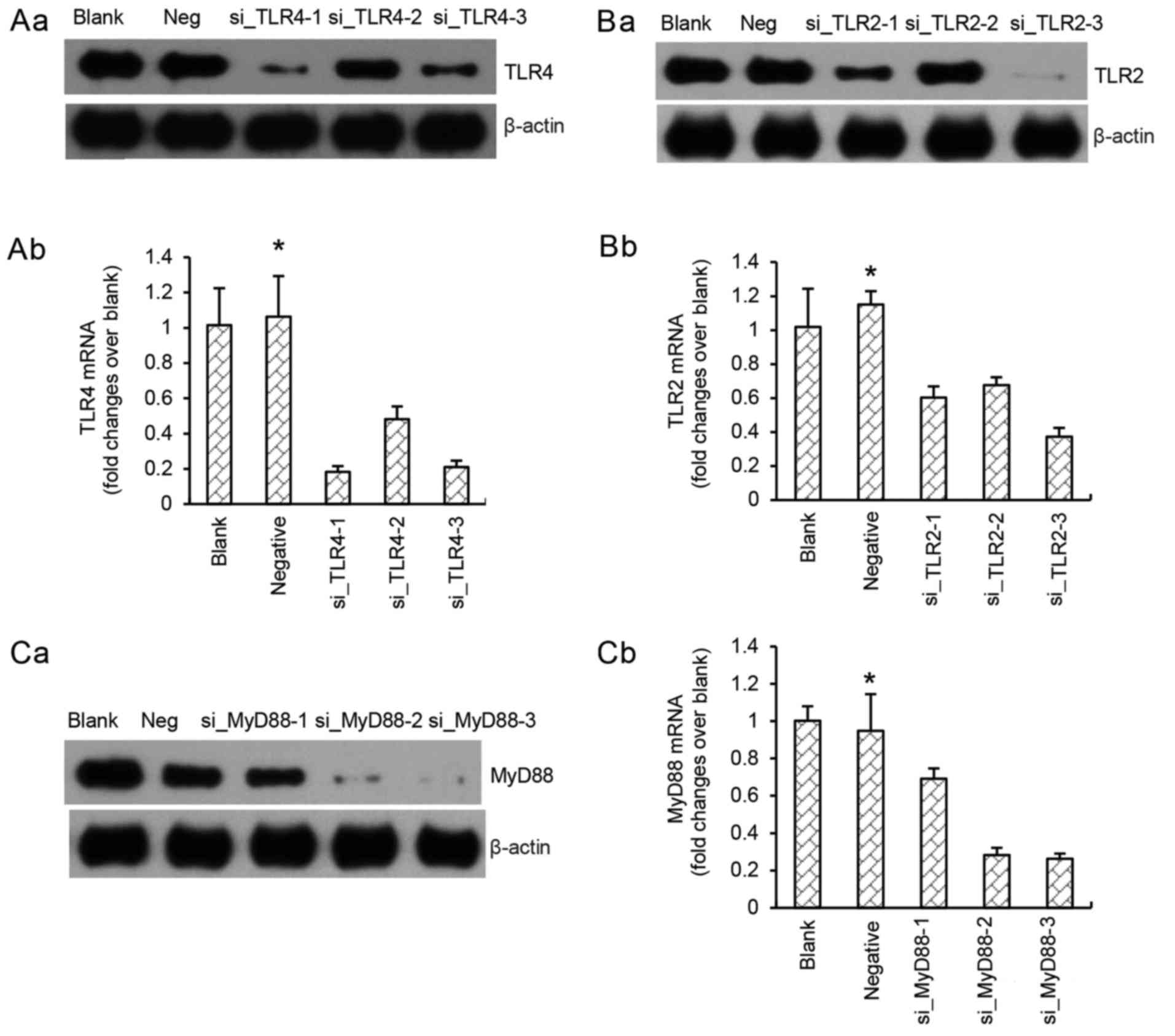
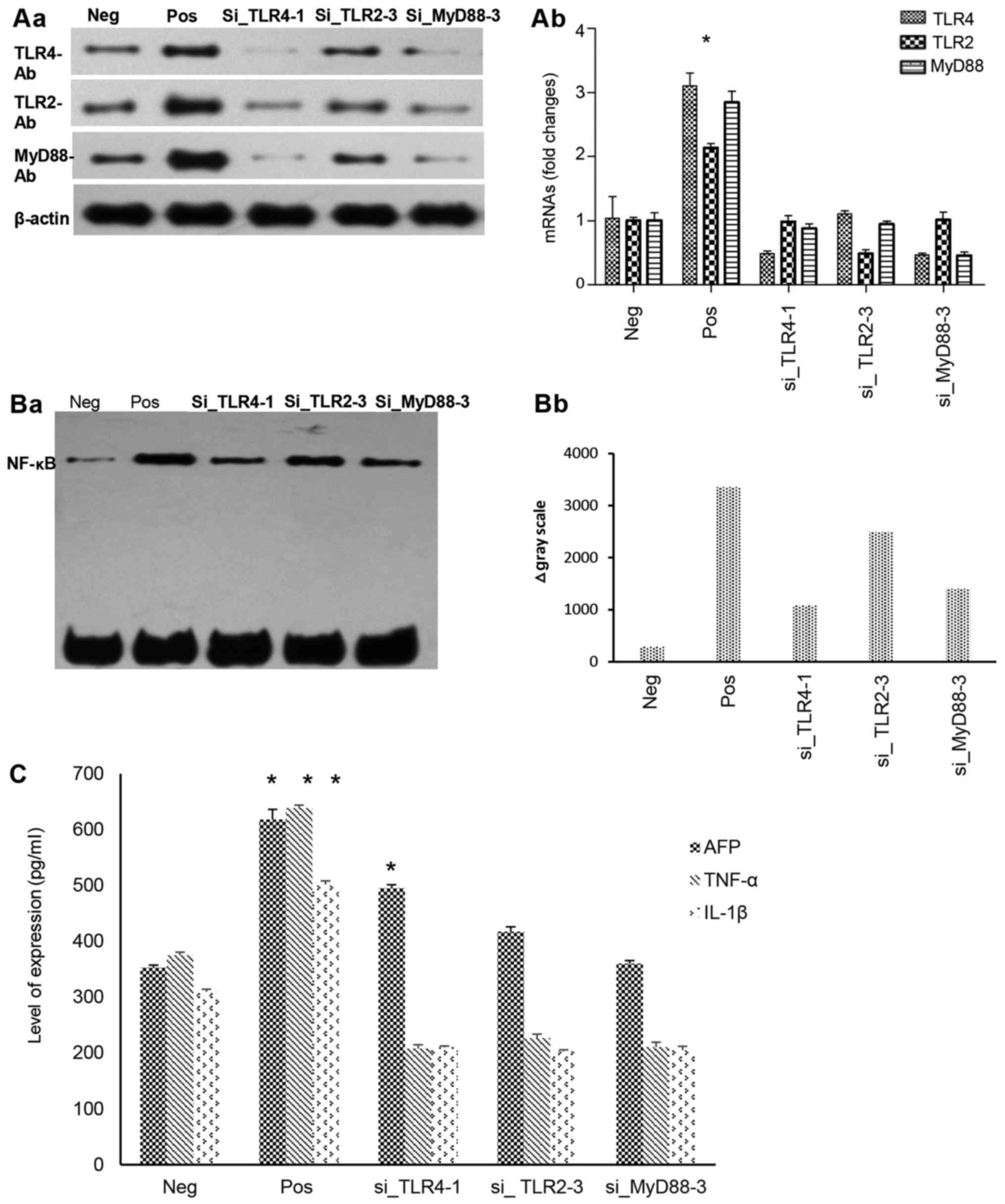
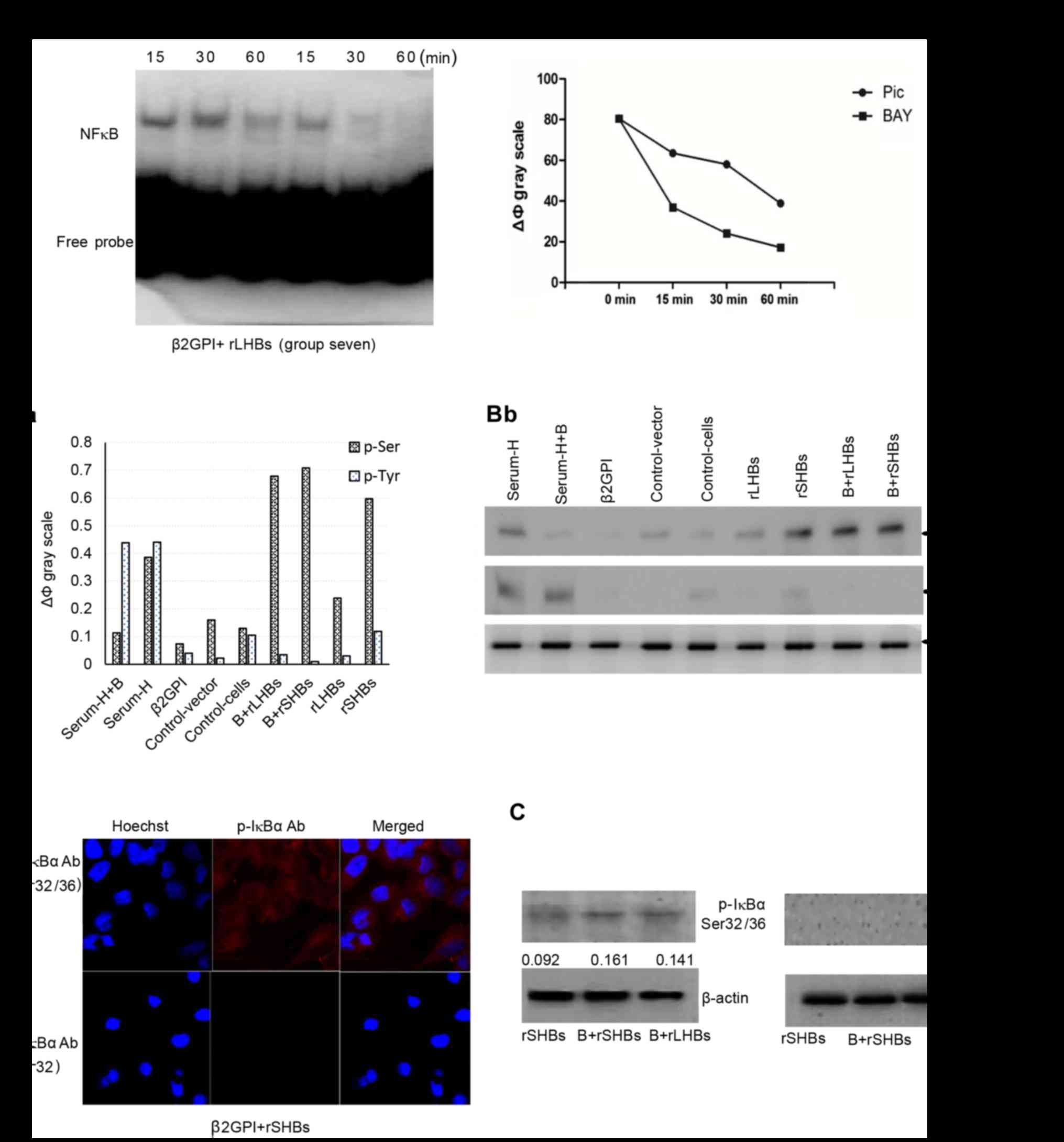
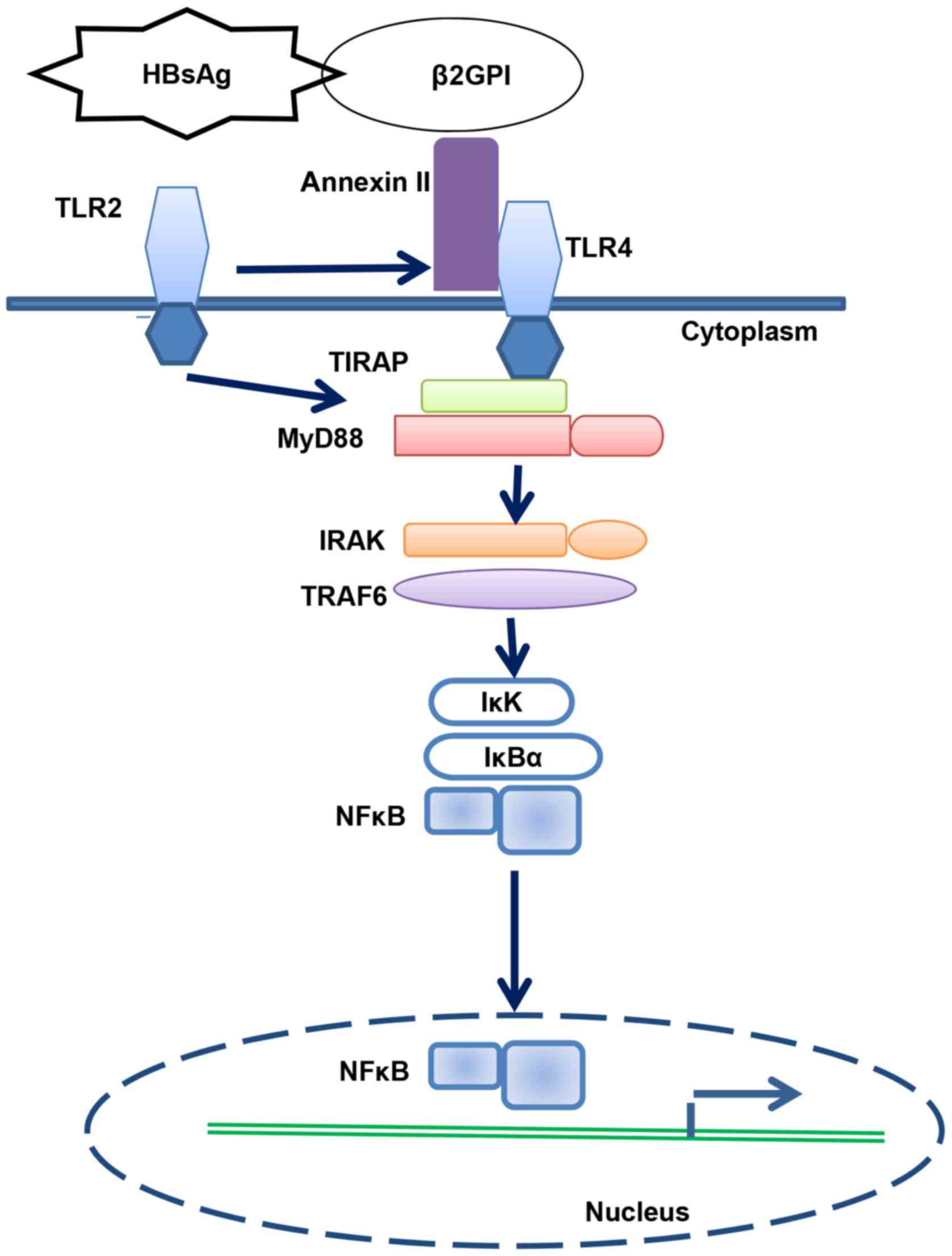
|
1
|
Sakamaki A, Kamimura K, Abe S, Tsuchiya A,
Takamura M, Kawai H, Yamagiwa S and Terai S: Spontaneous regression
of hepatocellular carcinoma: A mini-review. World J Gastroenterol.
23:3797–3804. 2017. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
2
|
McMahon BJ: The natural history of chronic
hepatitis B virus infection. Hepatology. 49 (5 Suppl):S45–S55.
2009. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
3
|
Tseng TC and Kao JH: Elimination of
hepatitis B: Is it a mission possible? BMC Med. 15:532017.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
4
|
Liu J, Yang HI, Lee MH, Lu SN, Jen CL,
Batrla-Utermann R, Wang LY, You SL, Hsiao CK, Chen PJ, et al:
Spontaneous seroclearance of hepatitis B seromarkers and subsequent
risk of hepatocellular carcinoma. Gut. 63:1648–1657. 2014.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
5
|
Karin M: NF-kappaB as a critical link
between inflammation and cancer. Cold Spring Harbor Perspect Biol.
1:a0001412009. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
6
|
Mehdi H, Kaplan MJ, Anlar FY, Yang X,
Bayer R, Sutherland K and Peeples ME: Hepatitis B virus surface
antigen binds to apolipoprotein H. J Virol. 68:2415–2424.
1994.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
7
|
Liu YM, Zhang WY, Wang ZF, Yan CY and Gao
PJ: High expression of beta2-glycoprotein I is associated
significantly with the earliest stages of hepatitis B virus
infection. J Med Virol. 86:1296–1306. 2014. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
8
|
Jing X, Piao YF, Liu Y and Gao PJ:
Beta2-GPI: A novel factor in the development of hepatocellular
carcinoma. J Cancer Res Clin Oncol. 136:1671–1680. 2010. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
9
|
Jing X: Positive effect of Beta2-GPI and
HBsAg in the pathogenesis of hepatocellular carcinoma. JiLin: JiLin
University; pp. 47–82. 2010
|
|
10
|
Hu J and Liu K: Complete and incomplete
hepatitis B virus particles: Formation, function, and application.
Viruses. 9:pii: E56. 2017. View
Article : Google Scholar
|
|
11
|
Li YW, Yang FC, Lu HQ and Zhang JS:
Hepatocellular carcinoma and hepatitis B surface protein. World J
Gastroenterol. 22:1943–1952. 2016. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
12
|
Meier A, Mehrle S, Weiss TS, Mier W and
Urban S: Myristoylated PreS1-domain of the hepatitis B virus
L-protein mediates specific binding to differentiated hepatocytes.
Hepatology. 58:31–42. 2013. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
13
|
Roh YS and Seki E: Toll-like receptors in
alcoholic liver disease, non-alcoholic steatohepatitis and
carcinogenesis. J Gastroenterol Hepatol. 28 (Suppl 1):S38–S42.
2013. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
14
|
Li K, Qu S, Chen X, Wu Q and Shi M:
Promising targets for cancer immunotherapy: TLRs, RLRs, and
STING-mediated innate immune pathways. Int J Mol Sci. 18:pii: E404.
2017.
|
|
15
|
Zhe Y, Li Y, Liu D, Su DM, Liu JG and Li
HY: Extracellular HSP70-peptide complexes promote the proliferation
of hepatocellular carcinoma cells via TLR2/4/JNK1/2MAPK pathway.
Tumour Biol. 37:13951–13959. 2016. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
16
|
Shi W, Su L, Li Q, Sun L, Lv J, Li J and
Cheng B: Suppression of toll-like receptor 2 expression inhibits
the bioactivity of human hepatocellular carcinoma. Tumour Biol.
35:9627–9637. 2014. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
17
|
Wang Y, Cai J, Zeng X, Chen Y, Yan W,
Ouyang Y, Xiao D, Zeng Z, Huang L and Liu A: Downregulation of
toll-like receptor 4 induces suppressive effects on hepatitis B
virus-related hepatocellular carcinoma via ERK1/2 signaling. BMC
Cancer. 15:8212015. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
18
|
Liang B, Chen R, Wang T, Cao L, Liu Y, Yin
F, Zhu M, Fan X, Liang Y, Zhang L, et al: Myeloid differentiation
factor 88 promotes growth and metastasis of human hepatocellular
carcinoma. Clin Cancer Res. 19:2905–2916. 2013. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
19
|
Jia RJ, Cao L, Zhang L, Jing W, Chen R,
Zhu MH, Guo SW, Wu GB, Fan XY, Wang H, et al: Enhanced myeloid
differentiation factor 88 promotes tumor metastasis via induction
of epithelial-mesenchymal transition in human hepatocellular
carcinoma. Cell Death Dis. 5:e11032014. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
20
|
Sweeney TE, Suliman HB, Hollingsworth JW,
Welty-Wolf KE and Piantadosi CA: A toll-like receptor 2 pathway
regulates the Ppargc1a/b metabolic co-activators in mice with
Staphylococcal aureus sepsis. PLoS One. 6:e252492011. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
21
|
Yamamoto M, Sato S, Hemmi H, Sanjo H,
Uematsu S, Kaisho T, Hoshino K, Takeuchi O, Kobayashi M, Fujita T,
et al: Essential role for TIRAP in activation of the signalling
cascade shared by TLR2 and TLR4. Nature. 420:324–329. 2002.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
22
|
Capece D, Fischietti M, Verzella D,
Gaggiano A, Cicciarelli G, Tessitore A, Zazzeroni F and Alesse E:
The inflammatory microenvironment in hepatocellular carcinoma: A
pivotal role for tumor-associated macrophages. Biomed Res Int.
2013:1872042013. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
23
|
Joe Y and Valerie C: The role of nuclear
factor-kappa B and endoplasmic reticulum stress in hepatitis B
viral-induced hepatocellular carcinoma. Translational Cancer Res. 5
(Suppl 1):S13–S17. 2016. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
24
|
Sun B and Karin M: NF-kappaB signaling,
liver disease and hepatoprotective agents. Oncogene. 27:6228–6244.
2008. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|