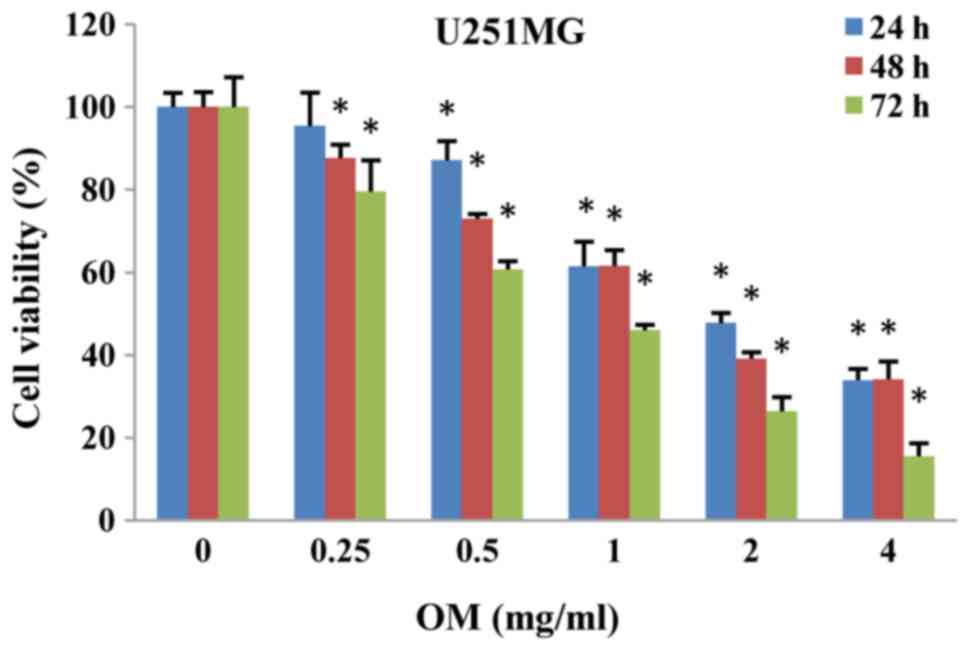
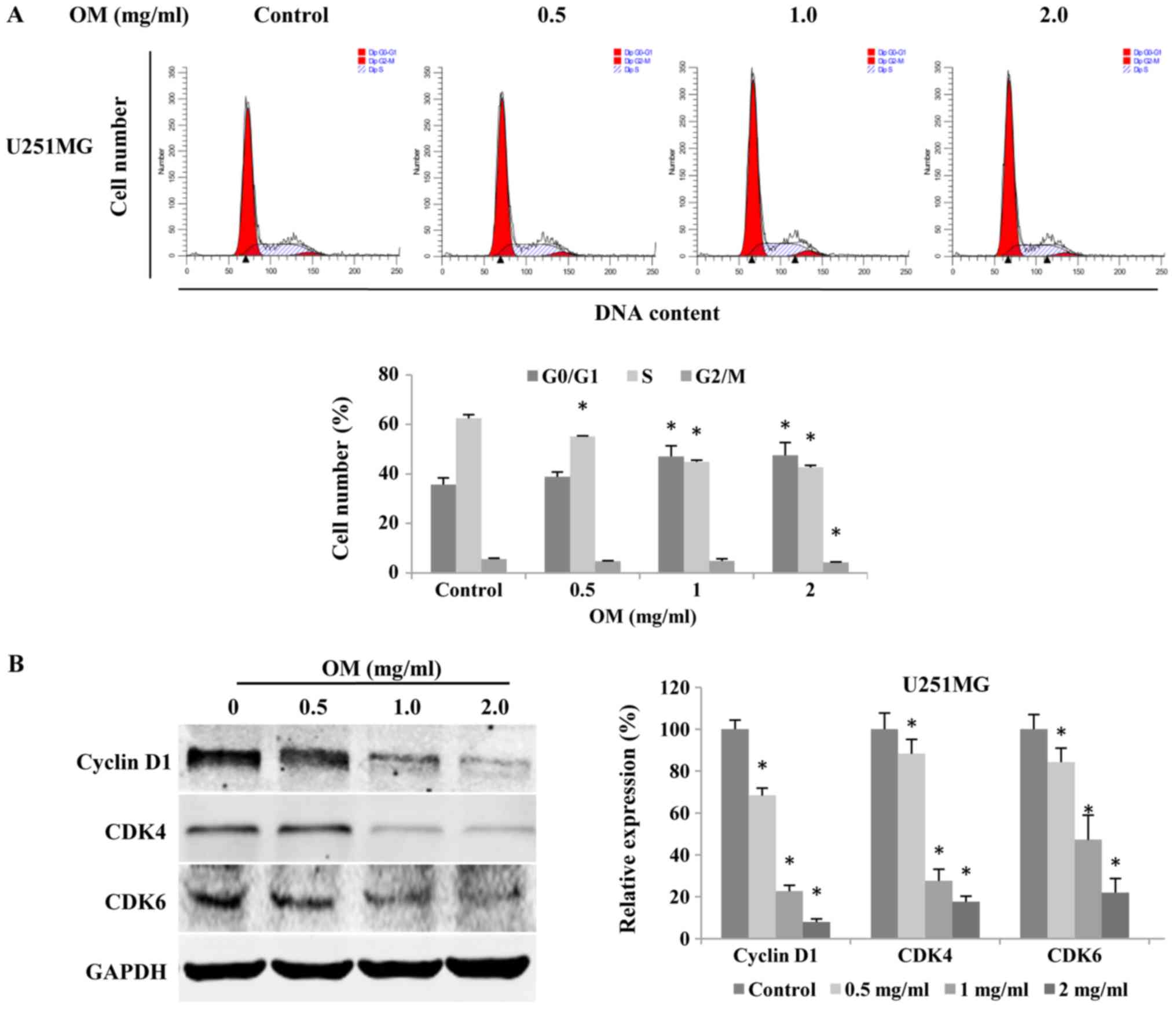
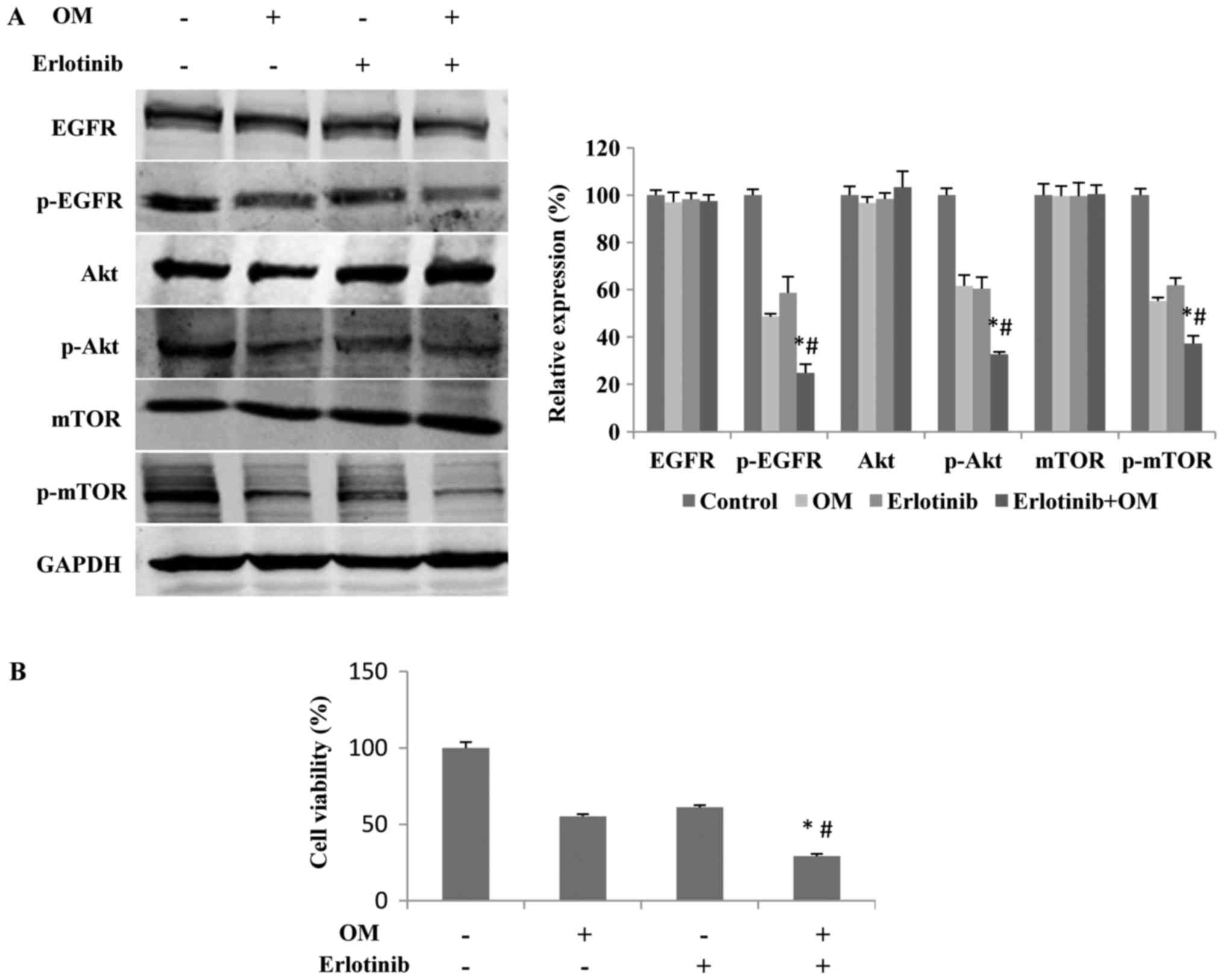
|
1
|
Gunther W, Pawlak E, Damasceno R, Arnold H
and Terzis AJ: Temozolomide induces apoptosis and senescence in
glioma cells cultured as multicellular spheroids. Br J Cancer.
88:463–469. 2003. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
2
|
Louis DN, Ohgaki H, Wiestler OD, Cavenee
WK, Burger PC, Jouvet A, Scheithauer BW and Kleihues P: The 2007
WHO classification of tumours of the central nervous system. Acta
Neuropathol. 114:97–109. 2007. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
3
|
Saito N, Fu J, Zheng S, Yao J, Wang S, Liu
DD, Yuan Y, Sulman EP, Lang FF, Colman H, et al: A high Notch
pathway activation predicts response to γ secretase inhibitors in
proneural subtype of glioma tumor-initiating cells. Stem Cells.
32:301–312. 2014. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
4
|
Hynes NE and Lane HA: ERBB receptors and
cancer: The complexity of targeted inhibitors. Nat Rev Cancer.
5:341–354. 2005. View
Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
5
|
Lieto E, Ferraraccio F, Orditura M,
Castellano P, Mura AL, Pinto M, Zamboli A, De Vita F and Galizia G:
Expression of vascular endothelial growth factor (VEGF) and
epidermal growth factor receptor (EGFR) is an independent
prognostic indicator of worse outcome in gastric cancer patients.
Ann Surg Oncol. 15:69–79. 2008. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
6
|
Gusterson BA: Identification and
interpretation of epidermal growth factor and c-erbB-2
overexpression. Eur J Cancer. 28:263–267. 1992. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
7
|
Xiao LJ, Lin P, Lin F, Liu X, Qin W, Zou
HF, Guo L, Liu W, Wang SJ and Yu XG: ADAM17 targets MMP-2 and MMP-9
via EGFR-MEK-ERK pathway activation to promote prostate cancer cell
invasion. Int J Oncol. 40:1714–1724. 2012.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
8
|
Taylor TE, Furnari FB and Cavenee WK:
Targeting EGFR for treatment of glioblastoma: Molecular basis to
overcome resistance. Curr Cancer Drug Targets. 12:197–209. 2012.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
9
|
Libermann TA, Nusbaum HR, Razon N, Kris R,
Lax I, Soreq H, Whittle N, Waterfield MD, Ullrich A and
Schlessinger J: Amplification, enhanced expression and possible
rearrangement of EGF receptor gene in primary human brain tumours
of glial origin. Nature. 313:144–147. 1985. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
10
|
Wang B, Wang G and Xu J: Inhibitory effect
of oxymatrine on vascular endothelial cell proliferation induced by
tumor. J Pract Oncol. 15:297–300. 2000.
|
|
11
|
Cao YG, Jing S, Li L, Gao JQ, Shen ZY, Liu
Y, Xing Y, Wu ML, Wang Y, Xu CQ, et al: Antiarrhythmic effects and
ionic mechanisms of oxymatrine from sophora flavescens. Phytother
Res. 24:1844–1849. 2010. View
Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
12
|
Cui X, Wang Y, Kokudo N, Fang D and Tang
W: Traditional Chinese medicine and related active compounds
against hepatitis B virus infection. Biosci Trends. 4:39–47.
2010.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
13
|
Deng ZY, Li J, Jin Y, Chen XL and Lu XW:
Effect of oxymatrine on the p38 mitogen-activated protein kinases
signalling pathway in rats with CCl4 induced hepatic fibrosis. Chin
Med J (Engl). 122:1449–1454. 2009.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
14
|
Fan H, Li L, Zhang X, Liu Y, Yang C, Yang
Y and Yin J: Oxymatrine downregulates TLR4, TLR2, MyD88, and
NF-kappaB and protects rat brains against focal ischemia. Mediators
Inflamm. 2009:7047062009. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
15
|
Ho JW, Ngan Hon PL and Chim WO: Effects of
oxymatrine from Ku Shen on cancer cells. Anticancer Agents Med
Chem. 9:823–826. 2009. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
16
|
Chen H, Zhang J, Luo J, Lai F, Wang Z,
Tong H, Lu D, Bu H, Zhang R and Lin S: Antiangiogenic effects of
oxymatrine on pancreatic cancer by inhibition of the NF-κB-mediated
VEGF signaling pathway. Oncol Rep. 30:589–595. 2013. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
17
|
Ling Q, Xu X, Wei X, Wang W, Zhou B, Wang
B and Zheng S: Oxymatrine induces human pancreatic cancer PANC-1
cells apoptosis via regulating expression of Bcl-2 and IAP
families, and releasing of cytochrome c. J Exp Clin Cancer Res.
30:662011. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
18
|
Song MQ, Zhu JS, Chen JL, Wang L, Da W,
Zhu L and Zhang WP: Synergistic effect of oxymatrine and
angiogenesis inhibitor NM-3 on modulating apoptosis in human
gastric cancer cells. World J Gastroenterol. 13:1788–1793. 2007.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
19
|
Zou J, Ran ZH, Xu Q and Xiao SD:
Experimental study of the killing effects of oxymatrine on human
colon cancer cell line SW1116. Chin J Dig Dis. 6:15–20. 2005.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
20
|
Zhang Y, Piao B, Zhang Y, Hua B, Hou W, Xu
W, Qi X, Zhu X, Pei Y and Lin H: Oxymatrine diminishes the side
population and inhibits the expression of β-catenin in MCF-7 breast
cancer cells. Med Oncol. 28 (Suppl 1):S99–S107. 2011. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
21
|
Inghirami G, Chiarle R, Simmons WJ, Piva
R, Schlessinger K and Levy DE: New and old functions of STAT3: A
pivotal target for individualized treatment of cancer. Cell cycle.
4:1131–1133. 2005. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
22
|
Ulrich TA, de Juan Pardo EM and Kumar S:
The mechanical rigidity of the extracellular matrix regulates the
structure, motility, and proliferation of glioma cells. Cancer Res.
69:4167–4174. 2009. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
23
|
Tu Y, Gao X, Li G, Fu H, Cui D, Liu H, Jin
W and Zhang Y: MicroRNA-218 inhibits glioma invasion, migration,
proliferation, and cancer stem-like cell self-renewal by targeting
the polycomb group gene Bmi1. Cancer Res. 73:6046–6055. 2013.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
24
|
Schlegel J, Merdes A, Stumm G, Albert FK,
Forsting M, Hynes N and Kiessling M: Amplification of the
epidermal-growth-factor-receptor gene correlates with different
growth behaviour in human glioblastoma. Int J Cancer. 56:72–77.
1994. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
25
|
Goncharova EA, Goncharov DA, Damera G,
Tliba O, Amrani Y, Panettieri RA Jr and Krymskaya VP: Signal
transducer and activator of transcription 3 is required for
abnormal proliferation and survival of TSC2-deficient cells:
Relevance to pulmonary lymphangioleiomyomatosis. Mol Pharmacol.
76:766–777. 2009. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
26
|
Zhou J, Wulfkuhle J, Zhang H, Gu P, Yang
Y, Deng J, Margolick JB, Liotta LA, Petricoin E III and Zhang Y:
Activation of the PTEN/mTOR/STAT3 pathway in breast cancer
stem-like cells is required for viability and maintenance. Proc
Natl Acad Sci USA. 104:16158–16163. 2007. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
27
|
Massagué J: G1 cell-cycle control and
cancer. Nature. 432:298–306. 2004. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
28
|
Kastan MB and Bartek J: Cell-cycle
checkpoints and cancer. Nature. 432:316–323. 2004. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
29
|
Ye X, Guo Y, Zhang Q, Chen W, Hua X, Liu
W, Yang Y and Chen G: βKlotho suppresses tumor growth in
hepatocellular carcinoma by regulating Akt/GSK-3β/cyclin D1
signaling pathway. PLoS One. 8:e556152013. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
30
|
Lu M, Gong X, Lu Y, Guo J, Wang C and Pan
Y: Molecular cloning and functional characterization of a
cell-permeable superoxide dismutase targeted to lung adenocarcinoma
cells. Inhibition cell proliferation through the Akt/p27kip1
pathway. J Biol Chem. 281:13620–13627. 2006.
|
|
31
|
Zhao W, Zhou SF, Zhang ZP, Xu GP, Li XB
and Yan JL: Gambogic acid inhibits the growth of osteosarcoma cells
in vitro by inducing apoptosis and cell cycle arrest. Oncol Rep.
25:1289–1295. 2011.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
32
|
Pal HC, Sharma S, Strickland LR, Agarwal
J, Athar M, Elmets CA and Afaq F: Delphinidin reduces cell
proliferation and induces apoptosis of non-small-cell lung cancer
cells by targeting EGFR/VEGFR2 signaling pathways. PLoS One.
8:e772702013. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
33
|
Guo B, Zhang T, Su J, Wang K and Li X:
Oxymatrine targets EGFRp-Tyr845 and inhibits
EGFR-related signaling pathways to suppress the proliferation and
invasion of gastric cancer cells. Cancer Chemother Pharmacol.
75:353–363. 2015. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
34
|
Burlacu A: Regulation of apoptosis by
Bcl-2 family proteins. J Cell Mol Med. 7:249–257. 2003. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
35
|
Stennicke HR and Salvesen GS: Properties
of the caspases. Biochim Biophys Acta. 1387:17–31. 1998. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
36
|
Budihardjo I, Oliver H, Lutter M, Luo X
and Wang X: Biochemical pathways of caspase activation during
apoptosis. Annu Rev Cell Dev Biol. 15:269–290. 1999. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
37
|
Morozevich GE, Kozlova NI, Ushakova NA,
Preobrazhenskaya ME and Berman AE: Integrin α5β1 simultaneously
controls EGFR-dependent proliferation and Akt-dependent
pro-survival signaling in epidermoid carcinoma cells. Aging.
4:368–374. 2012. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
38
|
Zhang C, Li C, Chen S, Li Z, Jia X, Wang
K, Bao J, Liang Y, Wang X, Chen M, et al: Berberine protects
against 6-OHDA-induced neurotoxicity in PC12 cells and zebrafish
through hormetic mechanisms involving PI3K/AKT/Bcl-2 and Nrf2/HO-1
pathways. Redox Biol. 11:1–11. 2017. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
39
|
Giese A, Bjerkvig R, Berens ME and
Westphal M: Cost of migration: Invasion of malignant gliomas and
implications for treatment. J Clin Oncol. 21:1624–1636. 2003.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
40
|
Louis DN, Pomeroy SL and Cairncross JG:
Focus on central nervous system neoplasia. Cancer Cell. 1:125–128.
2002. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
41
|
Paw I, Carpenter RC, Watabe K, Debinski W
and Lo HW: Mechanisms regulating glioma invasion. Cancer Lett.
362:1–7. 2015. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
42
|
Wang X, Liu C, Wang J, Fan Y, Wang Z and
Wang Y: Oxymatrine inhibits the migration of human colorectal
carcinoma RKO cells via inhibition of PAI-1 and the TGF-β1/Smad
signaling pathway. Oncol Rep. 37:747–753. 2017. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
43
|
Liu F, Wang B, Wang J, Ling X, Li Q, Meng
W and Ma J: Oxymatrine inhibits proliferation and migration while
inducing apoptosis in human glioblastoma cells. Biomed Res Int.
2016:17841612016. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|