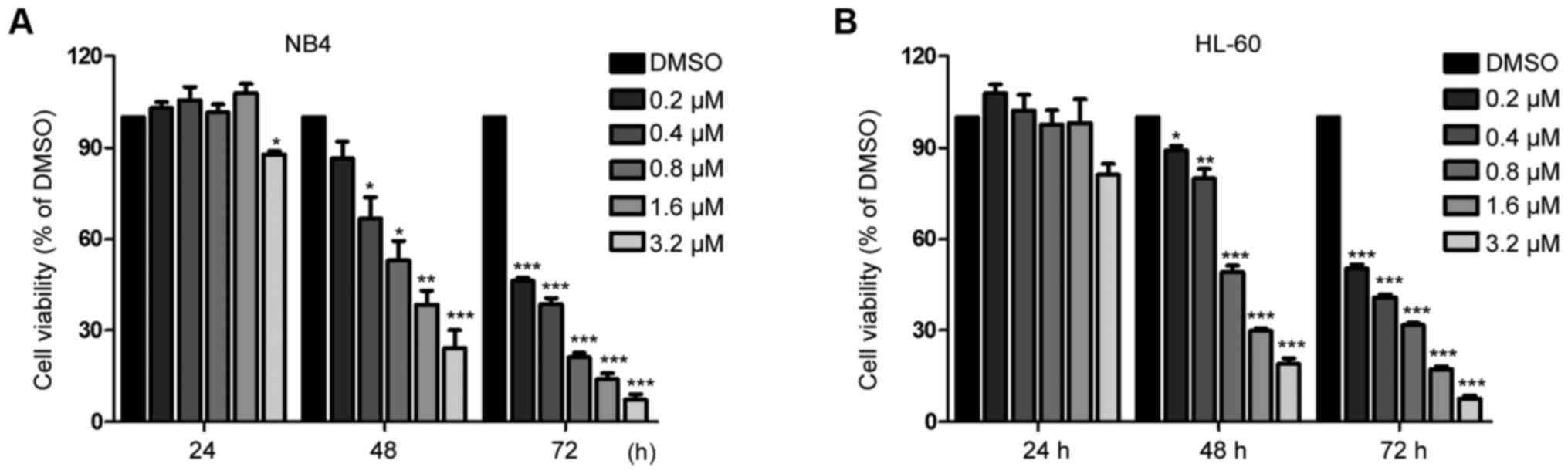
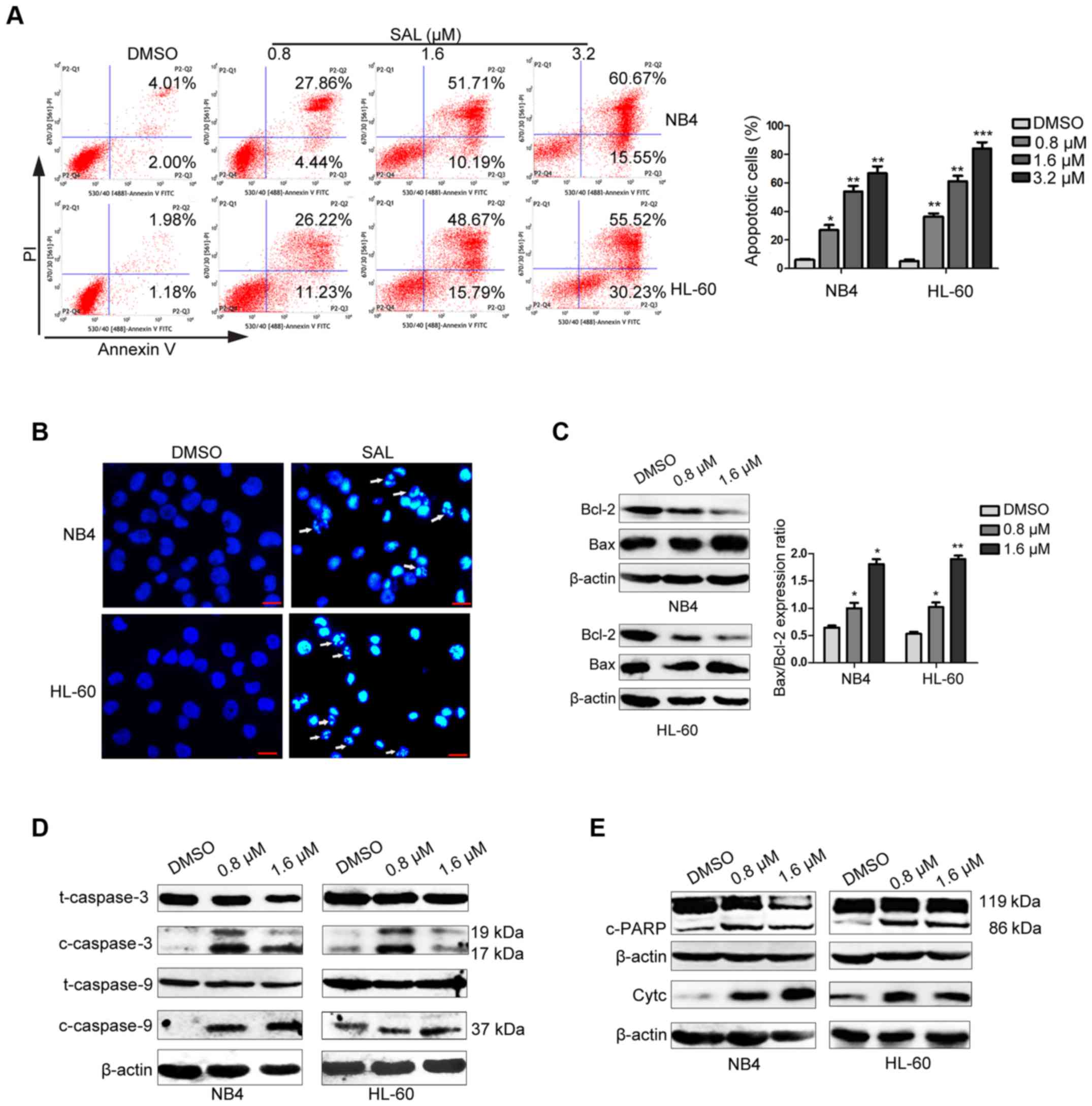
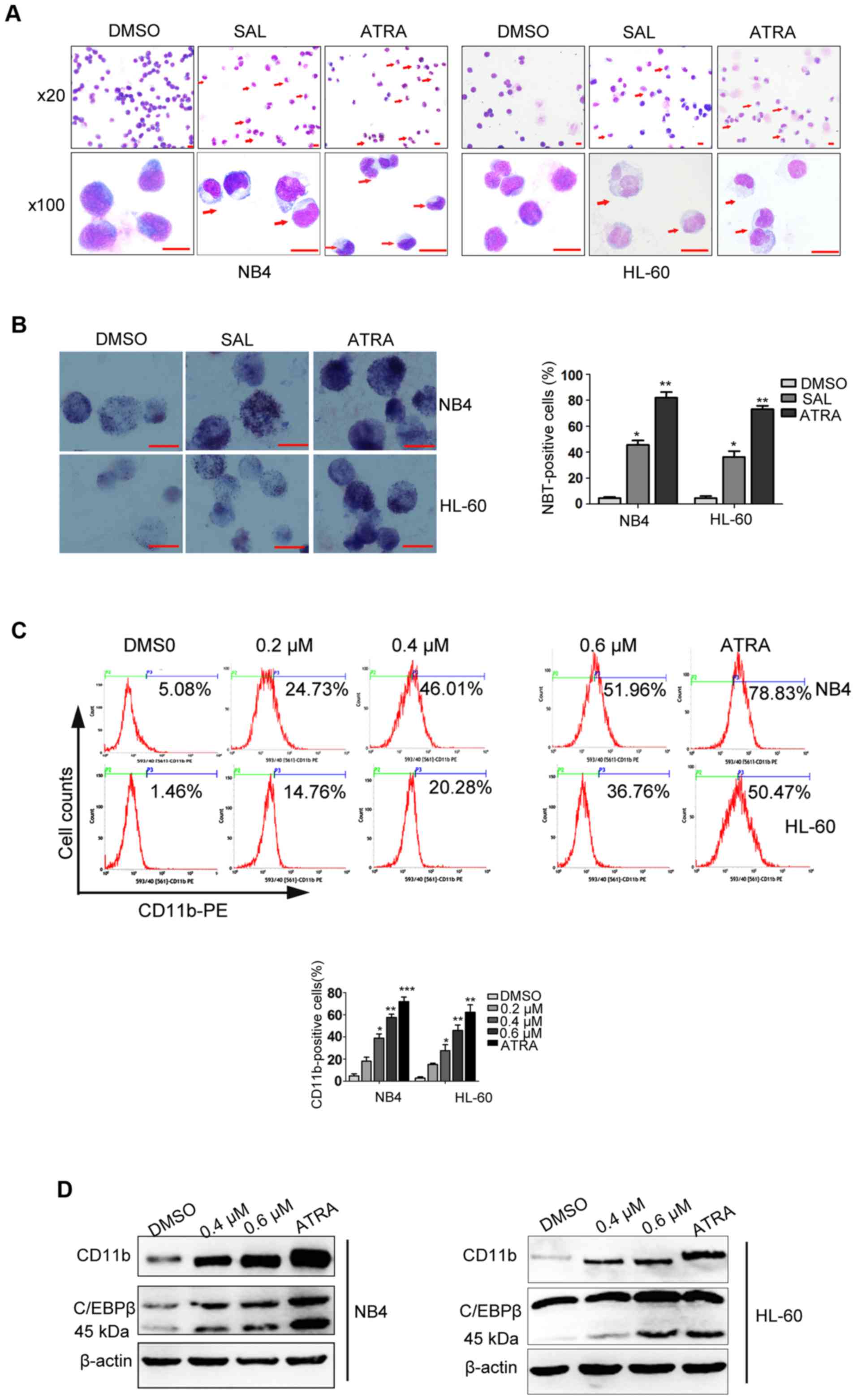
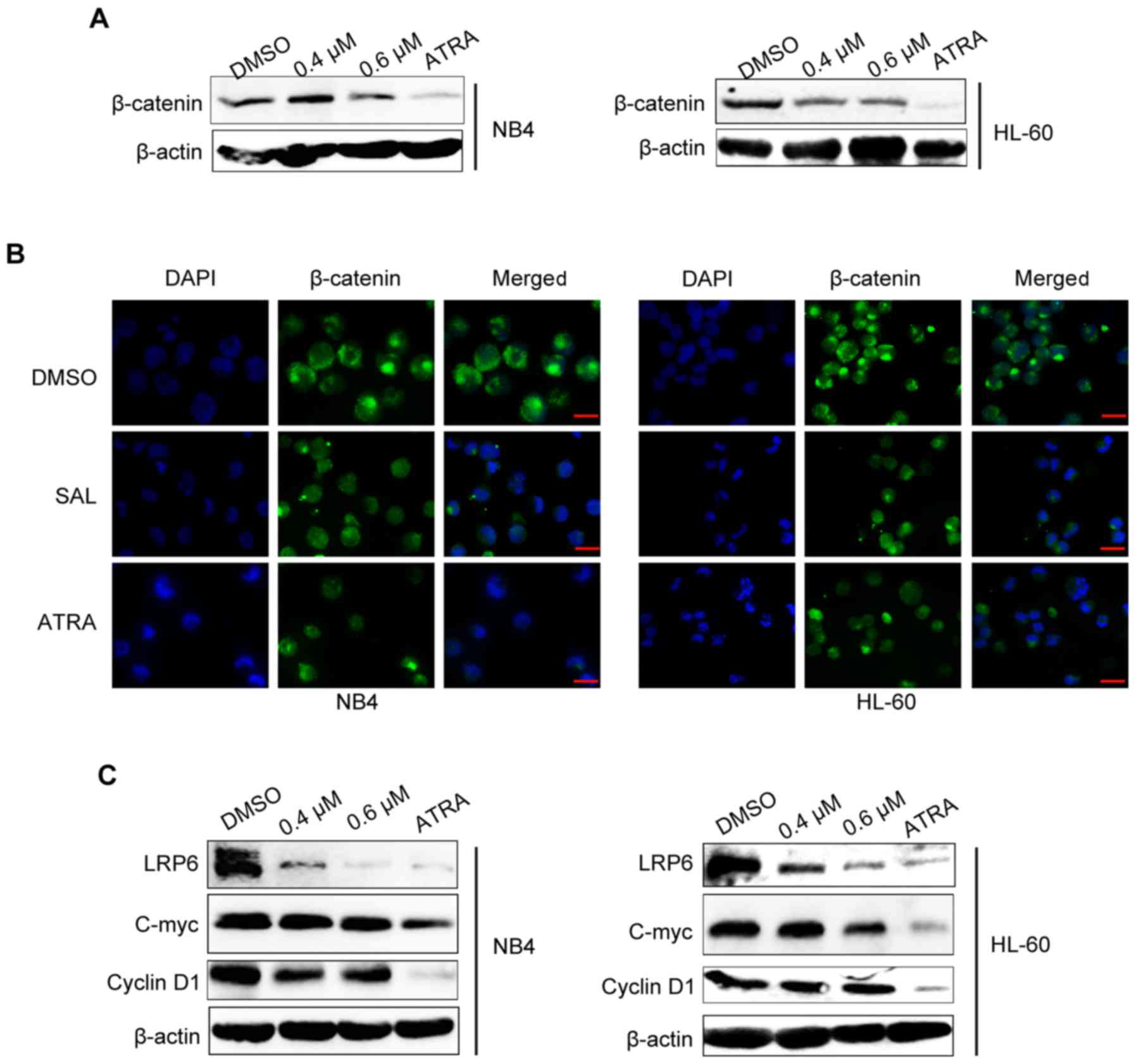
|
1
|
Lafage-Pochitaloff M, Alcalay M, Brunel V,
Longo L, Sainty D, Simonetti J, Birg F and Pelicci PG: Acute
promyelocytic leukemia cases with nonreciprocal PML/RARa or
RARa/PML fusion genes. Blood. 85:1169–1174. 1995.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
2
|
Rodeghiero F and Castaman G: The
pathophysiology and treatment of hemorrhagic syndrome of acute
promyelocytic leukemia. Leukemia. 8 (Suppl 2):S20–S26.
1994.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
3
|
Wang ZY and Chen Z: Acute promyelocytic
leukemia: From highly fatal to highly curable. Blood.
111:2505–2515. 2008. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
4
|
Wang ZY: Mechanism of action of all-trans
retinoic acid and arsenic trioxide in the treatment of acute
promyelocytic leukemia. Gan To Kagaku Ryoho. 29 (Suppl 1):214–218.
2002.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
5
|
Tallman MS: Treatment of relapsed or
refractory acute promyelocytic leukemia. Best Pract Res Clin
Haematol. 20:57–65. 2007. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
6
|
Tomita A, Kiyoi H and Naoe T: Mechanisms
of action and resistance to all-trans retinoic acid (ATRA) and
arsenic trioxide (As2O 3) in acute promyelocytic leukemia. Int J
Hematol. 97:717–725. 2013. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
7
|
Sanz MA and Montesinos P: How we prevent
and treat differentiation syndrome in patients with acute
promyelocytic leukemia. Blood. 123:2777–2782. 2014. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
8
|
Butaye P, Devriese LA and Haesebrouck F:
Antimicrobial growth promoters used in animal feed: Effects of less
well known antibiotics on gram-positive bacteria. Clin Microbiol
Rev. 16:175–188. 2003. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
9
|
Gupta PB, Onder TT, Jiang G, Tao K,
Kuperwasser C, Weinberg RA and Lander ES: Identification of
selective inhibitors of cancer stem cells by high-throughput
screening. Cell. 138:645–659. 2009. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
10
|
Xiao Z, Sperl B, Ullrich A and Knyazev P:
Metformin and salinomycin as the best combination for the
eradication of NSCLC monolayer cells and their alveospheres (cancer
stem cells) irrespective of EGFR, KRAS, EML4/ALK and LKB1 status.
Oncotarget. 5:12877–12890. 2014. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
11
|
Li T, Liu X, Shen Q, Yang W, Huo Z, Liu Q,
Jiao H and Chen J: Salinomycin exerts anti-angiogenic and
anti-tumorigenic activities by inhibiting vascular endothelial
growth factor receptor 2-mediated angiogenesis. Oncotarget.
7:26580–26592. 2016.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
12
|
Mirkheshti N, Park S, Jiang S, Cropper J,
Werner SL, Song CS and Chatterjee B: Dual targeting of androgen
receptor and mTORC1 by salinomycin in prostate cancer. Oncotarget.
7:62240–62254. 2016. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
13
|
Xipell E, Gonzalez-Huarriz M, Martinez de
Irujo JJ, García-Garzón A, Lang FF, Jiang H, Fueyo J, Gomez-Manzano
C and Alonso MM: Salinomycin induced ROS results in abortive
autophagy and leads to regulated necrosis in glioblastoma.
Oncotarget. 7:30626–30641. 2016. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
14
|
Lu D, Choi MY, Yu J, Castro JE, Kipps TJ
and Carson DA: Salinomycin inhibits Wnt signaling and selectively
induces apoptosis in chronic lymphocytic leukemia cells. Proc Natl
Acad Sci USA. 108:13253–13257. 2011. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
15
|
Niwa AM, D Epiro GF, Marques LA, Semprebon
SC, Sartori D, Ribeiro LR and Mantovani MS: Salinomycin efficiency
assessment in non-tumor (HB4a) and tumor (MCF-7) human breast
cells. Naunyn Schmiedebergs Arch Pharmacol. 389:557–571. 2016.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
16
|
Roulston GD, Burt CL, Kettyle LM, Matchett
KB, Keenan HL, Mulgrew NM, Ramsey JM, Dougan C, McKiernan J,
Grishagin IV, et al: Low-dose salinomycin induces anti-leukemic
responses in AML and MLL. Oncotarget. 7:73448–73461. 2016.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
17
|
Singh A and Settleman J: EMT, cancer stem
cells and drug resistance: An emerging axis of evil in the war on
cancer. Oncogene. 29:4741–4751. 2010. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
18
|
Mao J, Fan S, Ma W, Fan P, Wang B, Zhang
J, Wang H, Tang B, Zhang Q, Yu X, et al: Roles of Wnt/β-catenin
signaling in the gastric cancer stem cells proliferation and
salinomycin treatment. Cell Death Dis. 5:e10392014. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
19
|
Lee HG, Shin SJ and Chung HW: Salinomycin
reduces stemness and induces apoptosis on human ovarian cancer stem
cell. J Gynecol Oncol. 28:e142017. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
20
|
Fuchs D, Daniel V, Sadeghi M, Opelz G and
Naujokat C: Salinomycin overcomes ABC transporter-mediated
multidrug and apoptosis resistance in human leukemia stem cell-like
KG-1a cells. Biochem Biophys Res Commun. 394:1098–1104. 2010.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
21
|
Zou ZZ, Nie PP, Li YW, Hou BX, Rui-Li, Shi
XP, Ma ZK, Han BW and Luo XY: Synergistic induction of apoptosis by
salinomycin and gefitinib through lysosomal and mitochondrial
dependent pathway overcomes gefitinib resistance in colorectal
cancer. Oncotarget. 8:22414–22432. 2017.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
22
|
Hermawan A, Wagner E and Roidl A:
Consecutive salinomycin treatment reduces doxorubicin resistance of
breast tumor cells by diminishing drug efflux pump expression and
activity. Oncol Rep. 35:1732–1740. 2016. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
23
|
Li R, Dong T, Hu C, Lu J, Dai J and Liu P:
Salinomycin repressed the epithelial-mesenchymal transition of
epithelial ovarian cancer cells via downregulating Wnt/β-catenin
pathway. Onco Targets Ther. 10:1317–1325. 2017. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
24
|
Clevers H: Wnt/beta-catenin signaling in
development and disease. Cell. 127:469–480. 2006. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
25
|
Simon M, Grandage VL, Linch DC and Khwaja
A: Constitutive activation of the Wnt/beta-catenin signalling
pathway in acute myeloid leukaemia. Oncogene. 24:2410–2420. 2005.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
26
|
Luis TC, Ichii M, Brugman MH, Kincade P
and Staal FJ: Wnt signaling strength regulates normal hematopoiesis
and its deregulation is involved in leukemia development. Leukemia.
26:414–421. 2012. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
27
|
Zang S, Liu N, Wang H, Wald DN, Shao N,
Zhang J, Ma D, Ji C and Tse W: Wnt signaling is involved in
6-benzylthioinosine-induced AML cell differentiation. BMC Cancer.
14:8862014. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
28
|
Sheng Y, Ju W, Huang Y, Li J, Ozer H, Qiao
X and Qian Z: Activation of wnt/β-catenin signaling blocks
monocyte-macrophage differentiation through antagonizing
PU.1-targeted gene transcription. Leukemia. 30:2106–2109. 2016.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
29
|
Gandillet A, Park S, Lassailly F,
Griessinger E, Vargaftig J, Filby A, Lister TA and Bonnet D:
Heterogeneous sensitivity of human acute myeloid leukemia to
β-catenin down-modulation. Leukemia. 25:770–780. 2011. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
30
|
Lee SC, Kim OH, Lee SK and Kim SJ: IWR-1
inhibits epithelial-mesenchymal transition of colorectal cancer
cells through suppressing Wnt/β-catenin signaling as well as
survivin expression. Oncotarget. 6:27146–27159. 2015.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
31
|
McCubrey JA, Steelman LS, Bertrand FE,
Davis NM, Abrams SL, Montalto G, D'Assoro AB, Libra M, Nicoletti F,
Maestro R, et al: Multifaceted roles of GSK-3 and Wnt/β-catenin in
hematopoiesis and leukemogenesis: Opportunities for therapeutic
intervention. Leukemia. 28:15–33. 2014. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
32
|
Xu G and Shi Y: Apoptosis signaling
pathways and lymphocyte homeostasis. Cell Res. 17:759–771. 2007.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
33
|
Chen Y, Liu ZH, Xia J, Li XP, Li KQ, Xiong
W, Li J and Chen DL: 20(S)-ginsenoside Rh2 inhibits the
proliferation and induces the apoptosis of KG-1a cells through the
Wnt/β-catenin signaling pathway. Oncol Rep. 36:137–146. 2016.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
34
|
Staal FJ, Famili F, Garcia Perez L and
Pike-Overzet K: Aberrant Wnt Signaling in Leukemia. Cancers
(Basel). 8:82016. View Article : Google Scholar :
|
|
35
|
King TD, Suto MJ and Li Y: The
Wnt/β-catenin signaling pathway: A potential therapeutic target in
the treatment of triple negative breast cancer. J Cell Biochem.
113:13–18. 2012. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
36
|
Ahmadzadeh A, Norozi F, Shahrabi S,
Shahjahani M and Saki N: Wnt/β-catenin signaling in bone marrow
niche. Cell Tissue Res. 363:321–335. 2016. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
37
|
Lu W and Li Y: Salinomycin suppresses LRP6
expression and inhibits both Wnt/β-catenin and mTORC1 signaling in
breast and prostate cancer cells. J Cell Biochem. 115:1799–1807.
2014. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
38
|
Chen B, Dodge ME, Tang W, Lu J, Ma Z, Fan
CW, Wei S, Hao W, Kilgore J, Williams NS, et al: Small
molecule-mediated disruption of Wnt-dependent signaling in tissue
regeneration and cancer. Nat Chem Biol. 5:100–107. 2009. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
39
|
Kühn K, Cott C, Bohler S, Aigal S, Zheng
S, Villringer S, Imberty A, Claudinon J and Römer W: The interplay
of autophagy and β-Catenin signaling regulates differentiation in
acute myeloid leukemia. Cell Death Discov. 1:150312015. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
40
|
Orfali N, O'Donovan TR, Nyhan MJ,
Britschgi A, Tschan MP, Cahill MR, Mongan NP, Gudas LJ and McKenna
SL: Induction of autophagy is a key component of all-trans-retinoic
acid-induced differentiation in leukemia cells and a potential
target for pharmacologic modulation. Exp Hematol. 43:781–793. 2015.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
41
|
Wang Z, Cao L, Kang R, Yang M, Liu L, Zhao
Y, Yu Y, Xie M, Yin X, Livesey KM, et al: Autophagy regulates
myeloid cell differentiation by p62/SQSTM1-mediated degradation of
PML-RARα oncoprotein. Autophagy. 7:401–411. 2011. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
42
|
Ignatz-Hoover JJ, Wang H, Moreton SA,
Chakrabarti A, Agarwal MK, Sun K, Gupta K and Wald DN: The role of
TLR8 signaling in acute myeloid leukemia differentiation. Leukemia.
29:918–926. 2015. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|