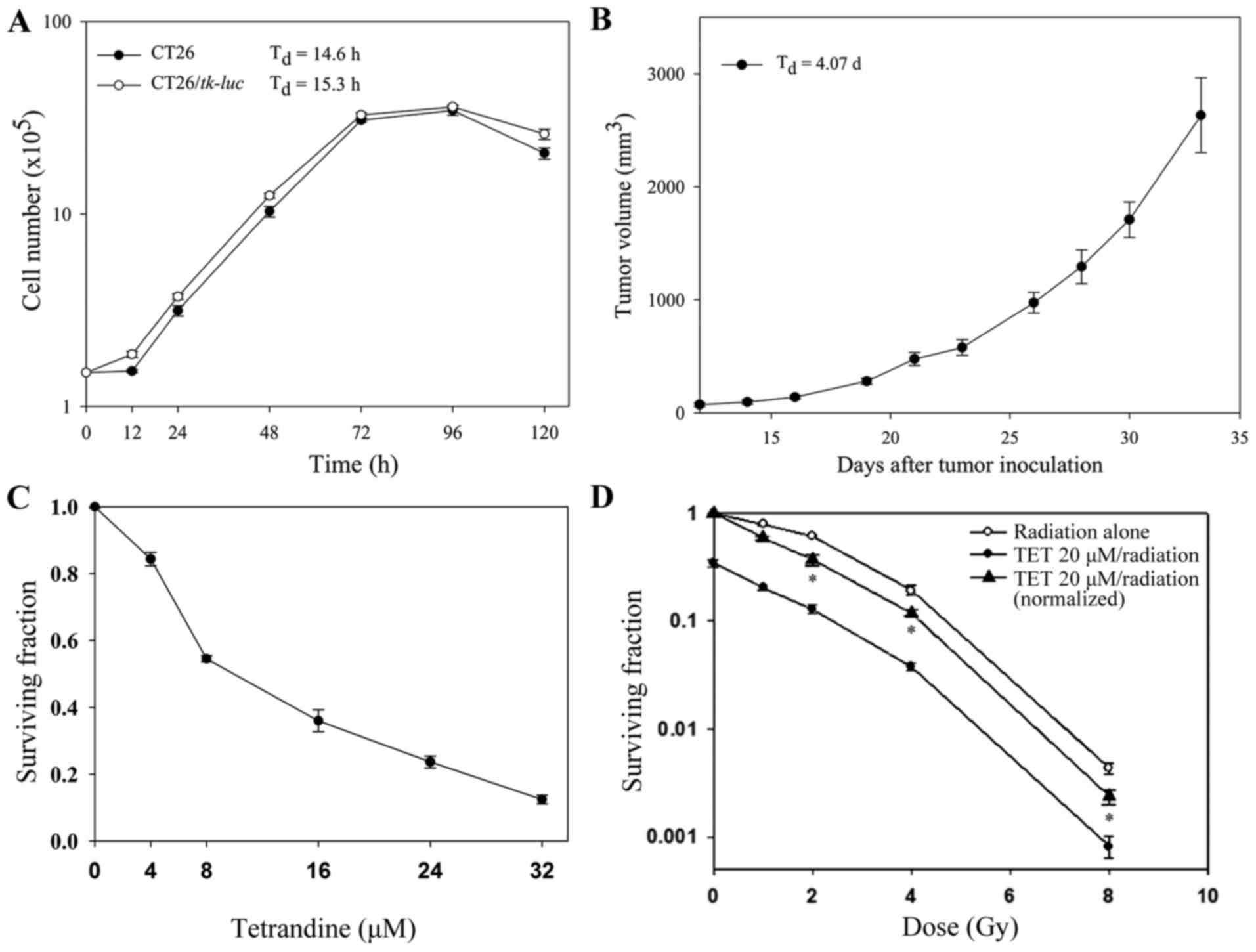
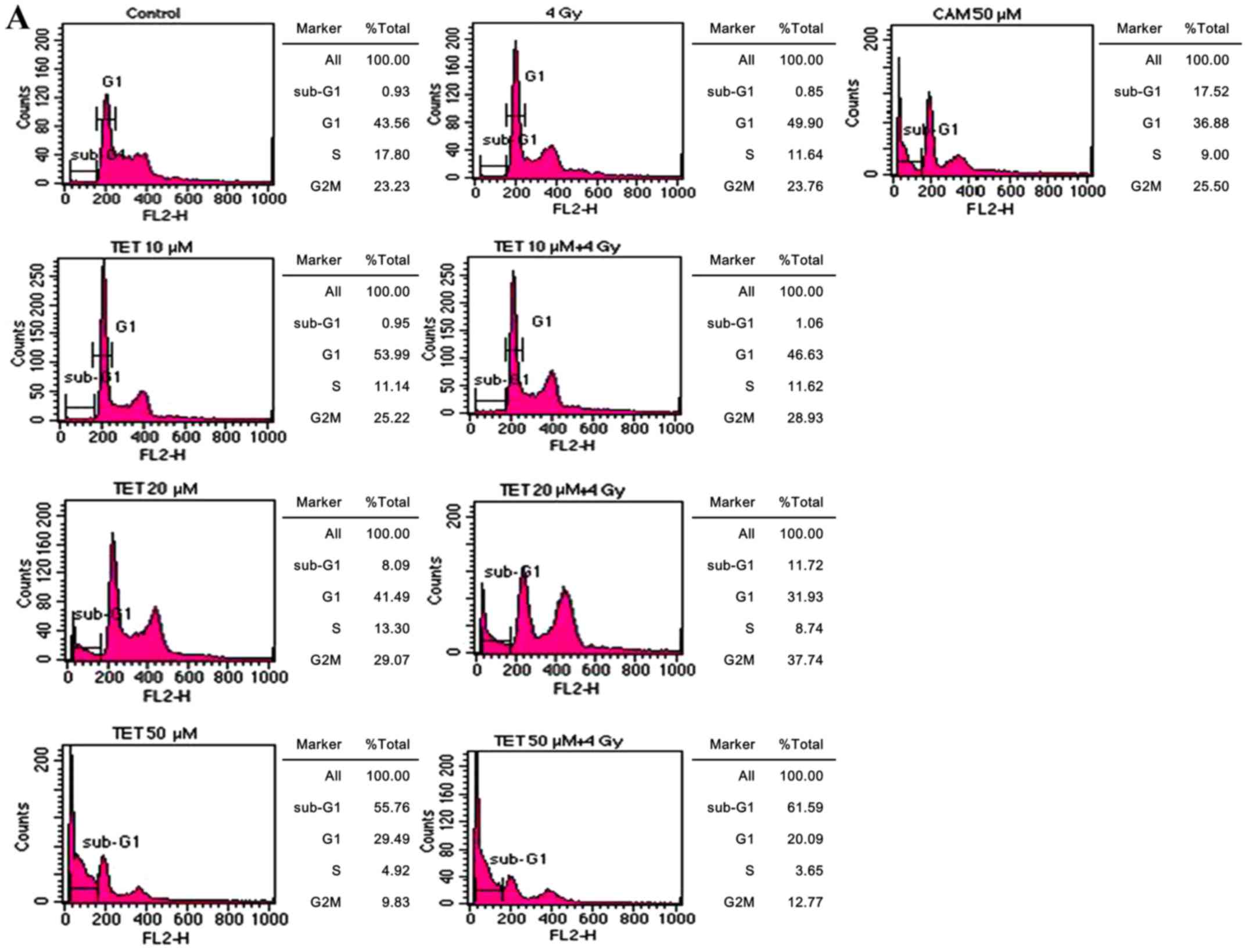
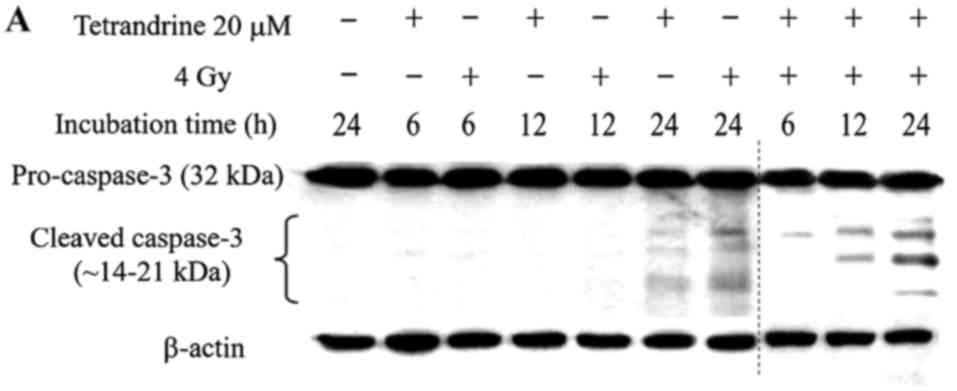
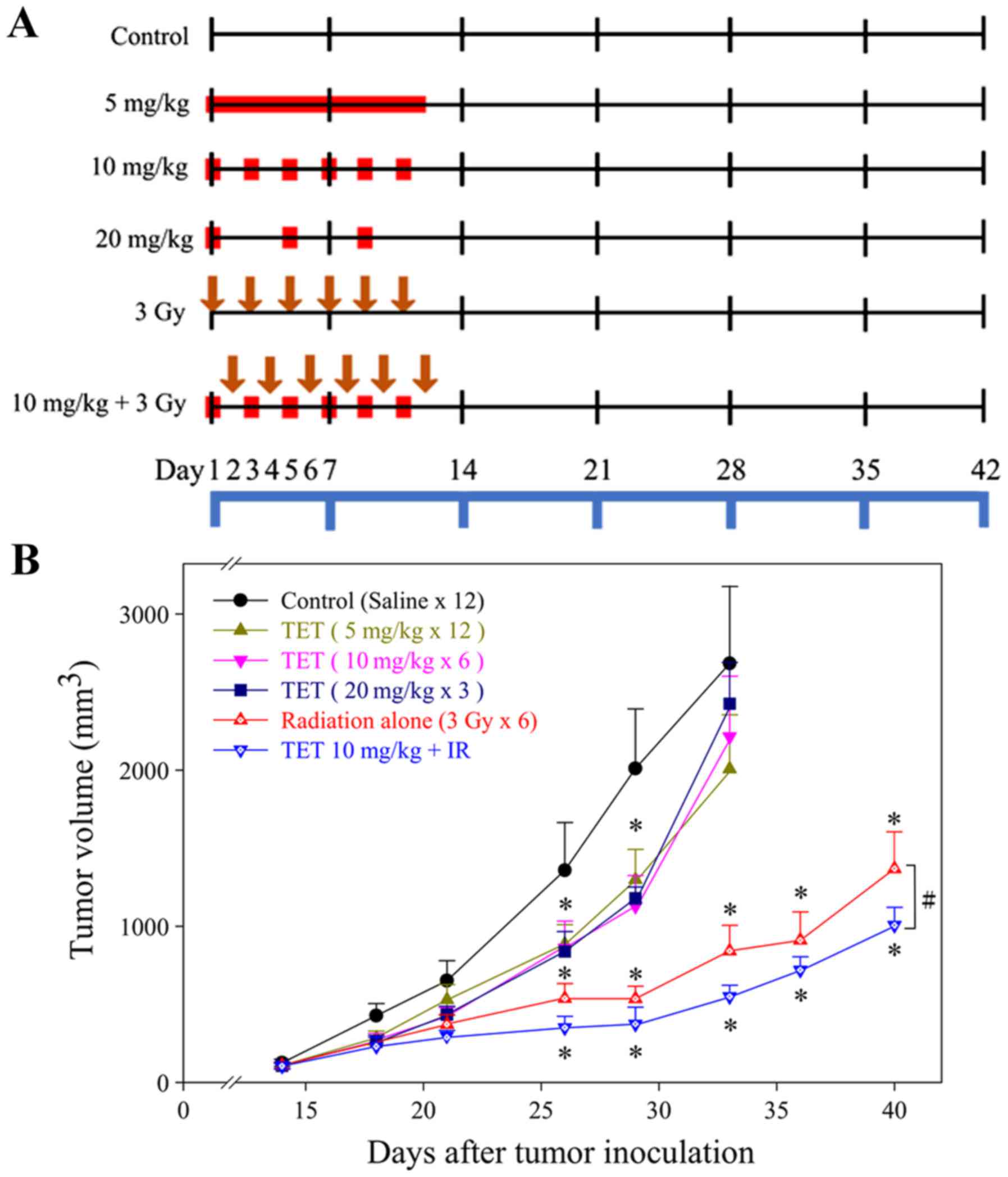
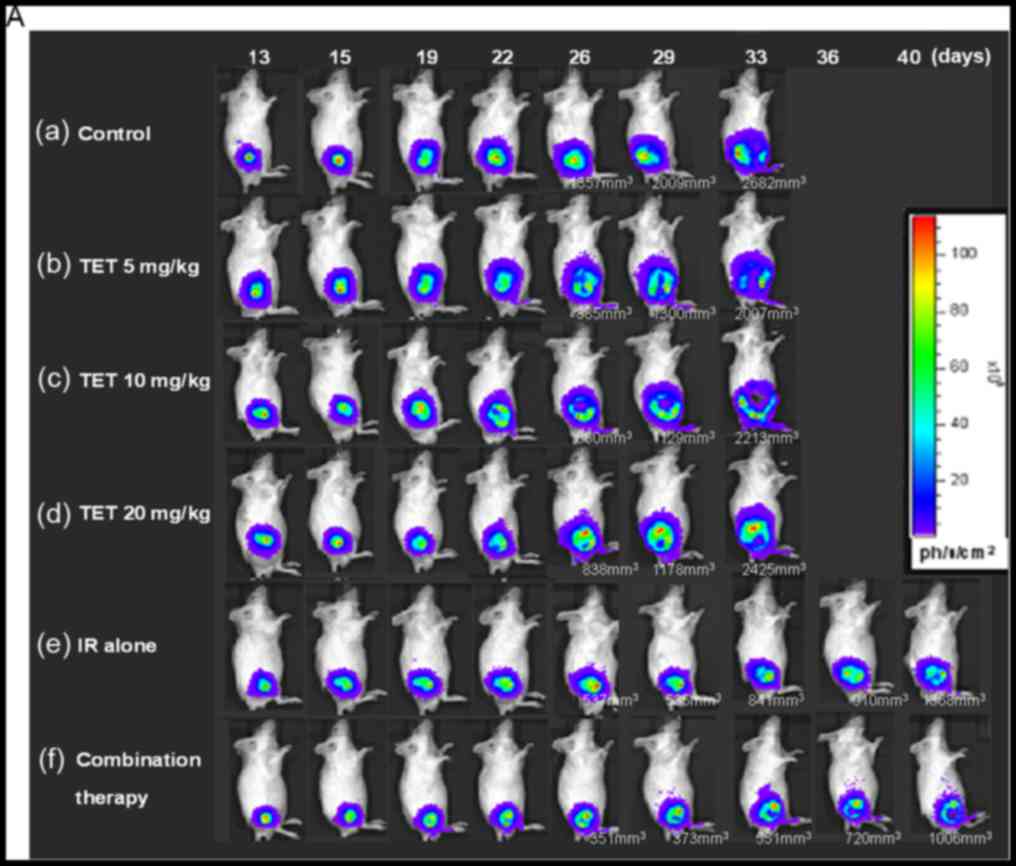
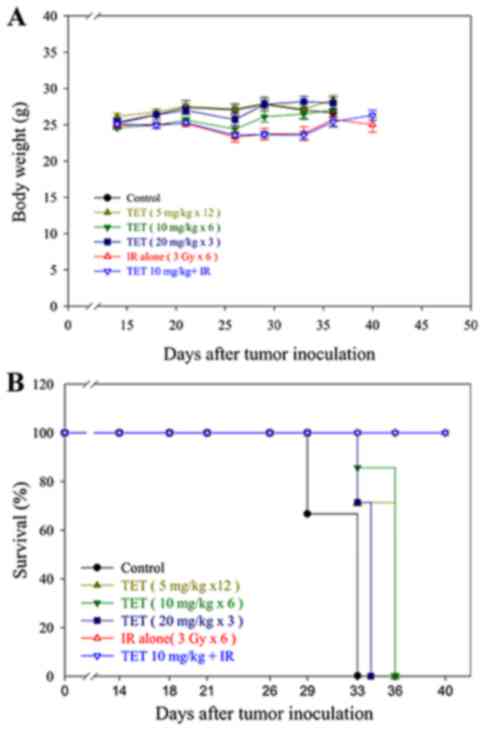
|
1
|
Siegel RL, Miller KD and Jemal A: Cancer
statistics, 2015. CA Cancer J Clin. 65:5–29. 2015. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
2
|
Sebag-Montefiore D, Stephens RJ, Steele R,
Monson J, Grieve R, Khanna S, Quirke P, Couture J, de Metz C, Myint
AS, et al: Preoperative radiotherapy versus selective postoperative
chemoradiotherapy in patients with rectal cancer (MRC CR07 and
NCIC-CTG C016): A multicentre, randomised trial. Lancet.
373:811–820. 2009. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
3
|
Lin JK, Lee LK, Chen WS, Lin TC, Jiang JK,
Yang SH, Wang HS, Chang SC, Lan YT, Lin CC, et al: Concurrent
chemoradiotherapy followed by metastasectomy converts to survival
benefitin stage IV rectum cancer. J Gastrointest Surg.
16:1888–1896. 2012. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
4
|
Abbasakoor F, Vaizey CJ and Boulos PB:
Improving the morbidity of anorectal injury from pelvic
radiotherapy. Colorectal Dis. 8:2–10. 2006. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
5
|
Chen YJ: Potential role of tetrandrine in
cancer therapy. Acta Pharmacol Sin. 23:1102–1106. 2002.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
6
|
Lai JH: Immunomodulatory effects and
mechanisms of plant alkaloid tetrandrine in autoimmune diseases.
Acta Pharmacol Sin. 23:1093–1101. 2002.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
7
|
Wang H, Liu T, Li L, Wang Q, Yu C, Liu X
and Li W: Tetrandrine is a potent autophagy agonist via activated
intracellular reactive oxygen species. Cell Biosci. 5:42015.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
8
|
Liu T, Liu X and Li W: Tetrandrine, a
Chinese plant-derived alkaloid, is a potential candidate for cancer
chemotherapy. Oncotarget. 7:40800–40815. 2016.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
9
|
Wong VK, Zeng W, Chen J, Yao XJ, Leung EL,
Wang QQ, Chiu P, Ko BCB and Law BYK: Tetrandrine, an activator of
autophagy, induces autophagic cell death via PKC-α inhibitionand
mTOR-dependent mechnisms. Front Pharmacol. 8:3512017. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
10
|
Lai YL, Chen YJ, Wu TY, Wang SY, Chang KH,
Chung CH and Chen ML: Induction of apoptosis in human leukemic U937
cells by tetrandrine. Anticancer Drugs. 9:77–81. 1998. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
11
|
Lee JH, Kang GH, Kim KC, Kim KM, Park DI,
Choi BT, Kang HS, Lee YT and Choi YH: Tetrandrine-induced cell
cycle arrest and apoptosis in A549 human lung carcinoma cells. Int
J Oncol. 21:1239–1244. 2002.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
12
|
Yoo SM, Oh SH, Lee SJ, Lee BW, Ko WG, Moon
CK and Lee BH: Inhibition of proliferation and induction of
apoptosis by tetrandrine in HepG2 cells. J Ethnopharmacol.
81:225–229. 2002. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
13
|
Chen Y, Chen JC and Tseng SH: Effects of
tetrandrine plus radiation on neuroblastoma cells. Anticancer Res.
29:3163–3171. 2009.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
14
|
Wu K, Zhou M, Wu QX, Yuan SX, Wang DX, Jin
JL, Huang J, Yang JQ, Sun WJ, Wan LH and He BC: The role of IGFBP-5
in mediating the anti-proliferation effect of tetrandrine in human
colon cancer cells. Int J Oncol. 46:1205–1213. 2015. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
15
|
Chang KH, Chen ML, Chen HC, Huang YW, Wu
TY and Chen YJ: Enhancement of radiosensitivity in human
glioblastoma U138MG cells by tetrandrine. Neoplasma. 46:196–200.
1999.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
16
|
Gupta S: Molecular steps of death receptor
and mitochondrial pathways of apoptosis. Life Sci. 69:2957–2964.
2001. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
17
|
Salvesen GS: Caspase 8: Igniting the death
machine. Structure. 7:R225–R229. 1999. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
18
|
Stennicke HR, Jürgensmeier JM, Shin H,
Deveraux Q, Wolf BB, Yang X, Zhou Q, Ellerby HM, Ellerby LM,
Bredesen D, et al: Pro-caspase-3 is a major physiologic target of
caspase-8. J Biol Chem. 273:27084–27090. 1998. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
19
|
Haimovitz-Friedman A, Kan CC, Ehleiter D,
Persaud RS, McLoughlin M, Fuks Z and Kolesnick RN: Ionizing
radiation acts on cellular membranes to generate ceramide and
initiate apoptosis. J Exp Med. 180:525–535. 1994. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
20
|
Yu J, Liu F, Sun M, Sun Z and Sun S:
Enhancement of radiosensitivity and the potential mechanism on
human esophageal carcinoma cells by tetrandrine. Cancer Biother
Radiopharm. 26:437–442. 2011. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
21
|
Chang YF, Lin YY, Wang HE, Liu RS, Pang F
and Hwang JJ: Monitoring of tumor growth and metastasis potential
in MDA-MB-435s/tk-luc human breast cancer xenografts. Nucl Instrum
Meth A. 571:155–159. 2007. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
22
|
Chen CC, Hwang JJ, Ting G, Tseng YL, Wang
SJ and Peng JW: Monitoring and quantitative assessment of tumor
burden using in vivo bioluminescence imaging. Nucl Instrum Meth A.
571:437–441. 2007. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
23
|
Jänicke RU, Sprengart ML, Wati MR and
Porter AG: Caspase-3 is required for DNA fragmentation and
morphological changes associated with apoptosis. J Biol Chem.
273:9357–9360. 1998. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
24
|
Burgos JS, Rosol M, Moats RA, Khankaldyyan
V, Kohn DB, Nelson MD Jr and Laug WE: Time course of bioluminescent
signal in orthotopic and heterotopic brain tumors in nude mice.
Biotechniques. 34:1184–1188. 2003.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
25
|
Cividalli A, Ceciarelli F, Livdi E,
Altavista P, Cruciani G, Marchetti P and Danesi DT:
Radiosensitization by oxaliplatin in a mouse adenocarcinoma:
Influence of treatment schedule. Int J Radiat Oncol Biol Phys.
52:1092–1098. 2002. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
26
|
Heckelsmiller K, Rall K, Beck S, Schlamp
A, Seiderer J, Jahrsdörfer B, Krug A, Rothenfusser S, Endres S and
Hartmann G: Peritumoral CpG DNA elicits a coordinated response of
CD8 T cells and innate effectors to cure established tumors in a
murine colon carcinoma model. J Immunol. 169:3892–3899. 2002.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
27
|
Jang BC, Lim KJ, Paik JH, Cho JW, Baek WK,
Suh MH, Park JB, Kwon TK, Park JW, Kim SP, et al:
Tetrandrine-induced apoptosis is mediated by activation of caspases
and PKC-δ in U937 cells. Biochem Pharmacol. 67:1819–1829. 2004.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
28
|
Kuo PL and Lin CC: Tetrandrine-induced
cell cycle arrest and apoptosis in Hep G2 cells. Life Sci.
73:2432522003. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
29
|
Ng LT, Chiang LC, Lin YT and Lin CC:
Antiproliferative and apoptotic effects of tetrandrine on different
human hepatoma cell lines. Am J Chin Med. 34:125–135. 2006.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
30
|
Sun X, Xu R, Deng Y, Cheng H, Ma J, Ji J
and Zhou Y: Effects of Tetrandrine on apoptosis and
radiosensitivity of nasopharyngeal carcinoma cell line CNE. Acta
Biochim Biophys Sin. 39:869–878. 2007. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
31
|
Hsu FT, Chang B, Chen JC, Chiang IT, Liu
YC, Kwang WK and Hwang JJ: Synergistic effect of sorafenib and
radiation on human oral carcinoma in vivo. Sci Rep. 5:153912015.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
32
|
Wu CJ, Wang YH, Lin CJ, Chen HH and Chen
YJ: Tetrandrine down-regulaties ERK/NF-κB signaling and inhibits
activtion of mesangial cells. Toxicol in vitro. 25:1834–1840. 2011.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
33
|
Chen S, Liu W, Wang K, Fan Y, Chen J, Ma
J, Wang X, He D, Zeng J and Li L: Tetrandrine inhibits migration
and invasion of human renal cell carcinoma by regulating
Akt/NF-κB/MMP-9 signaling. PLoS One. 12:e01737252017. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|