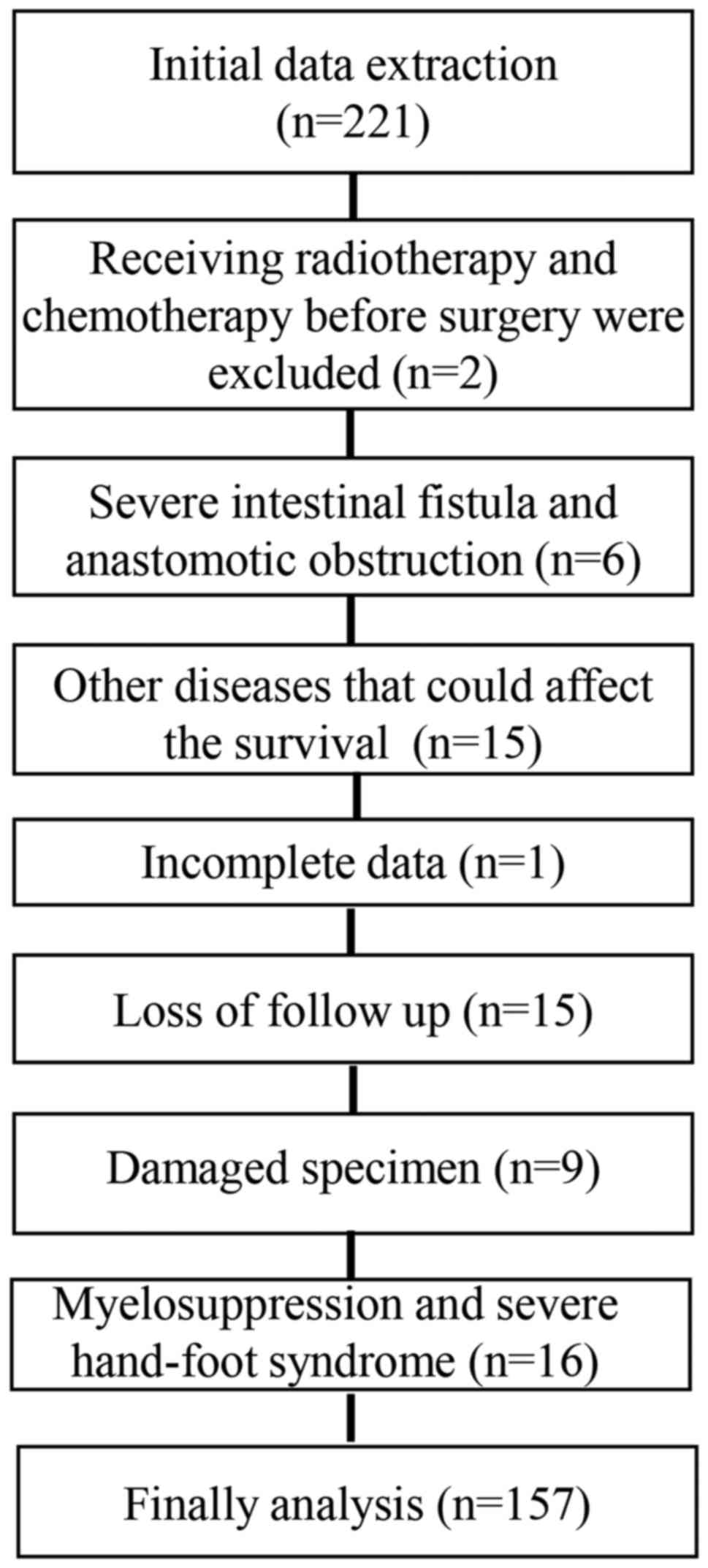
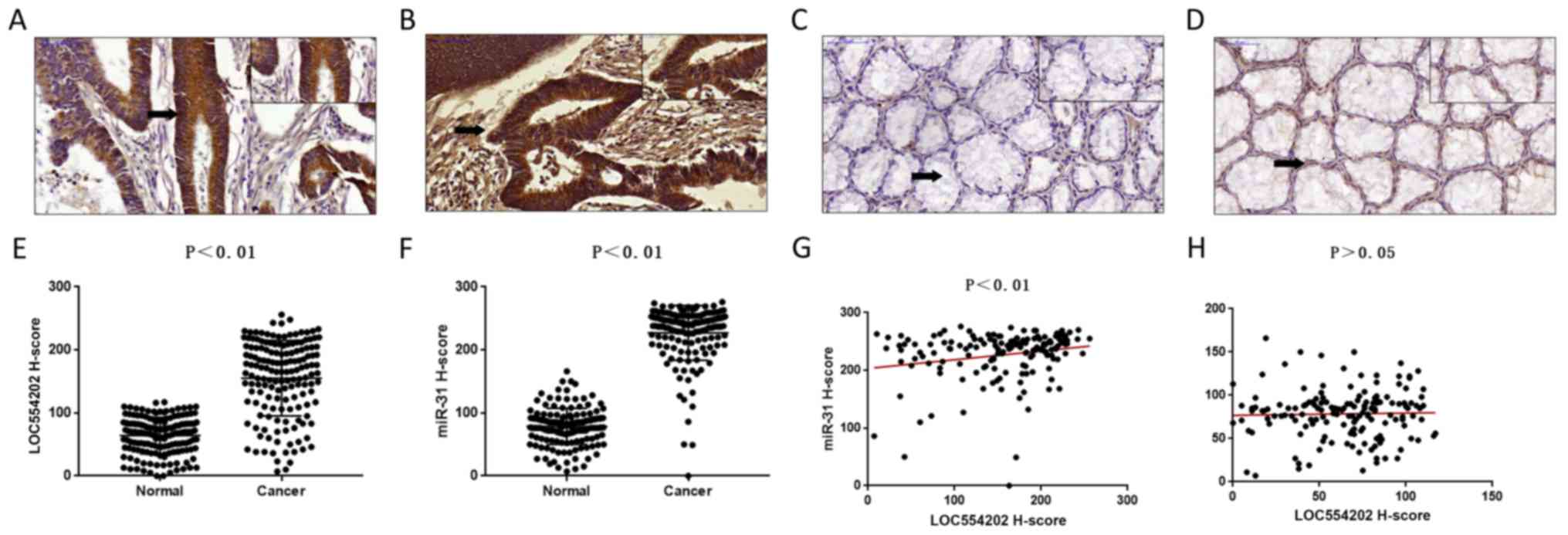
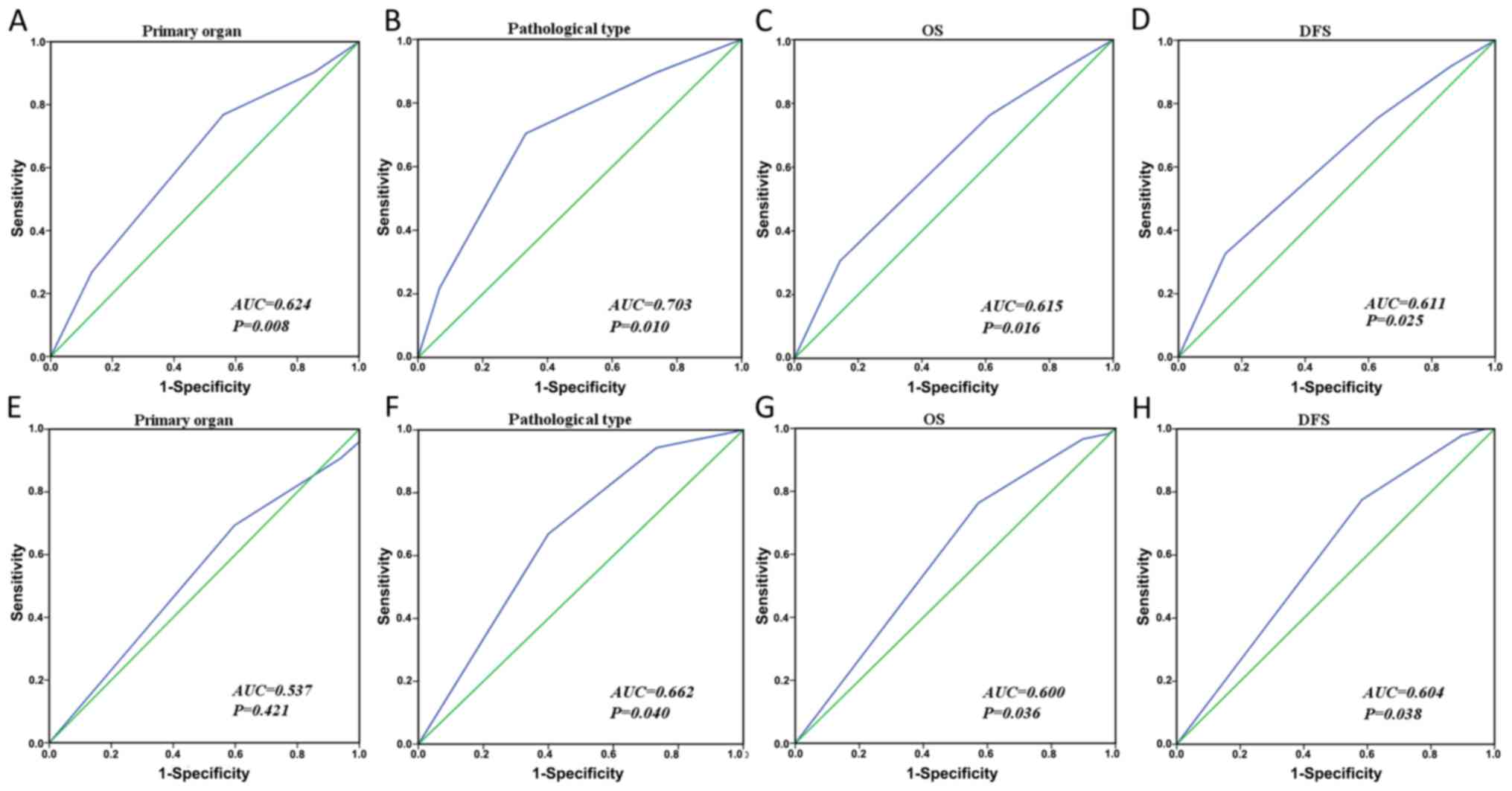
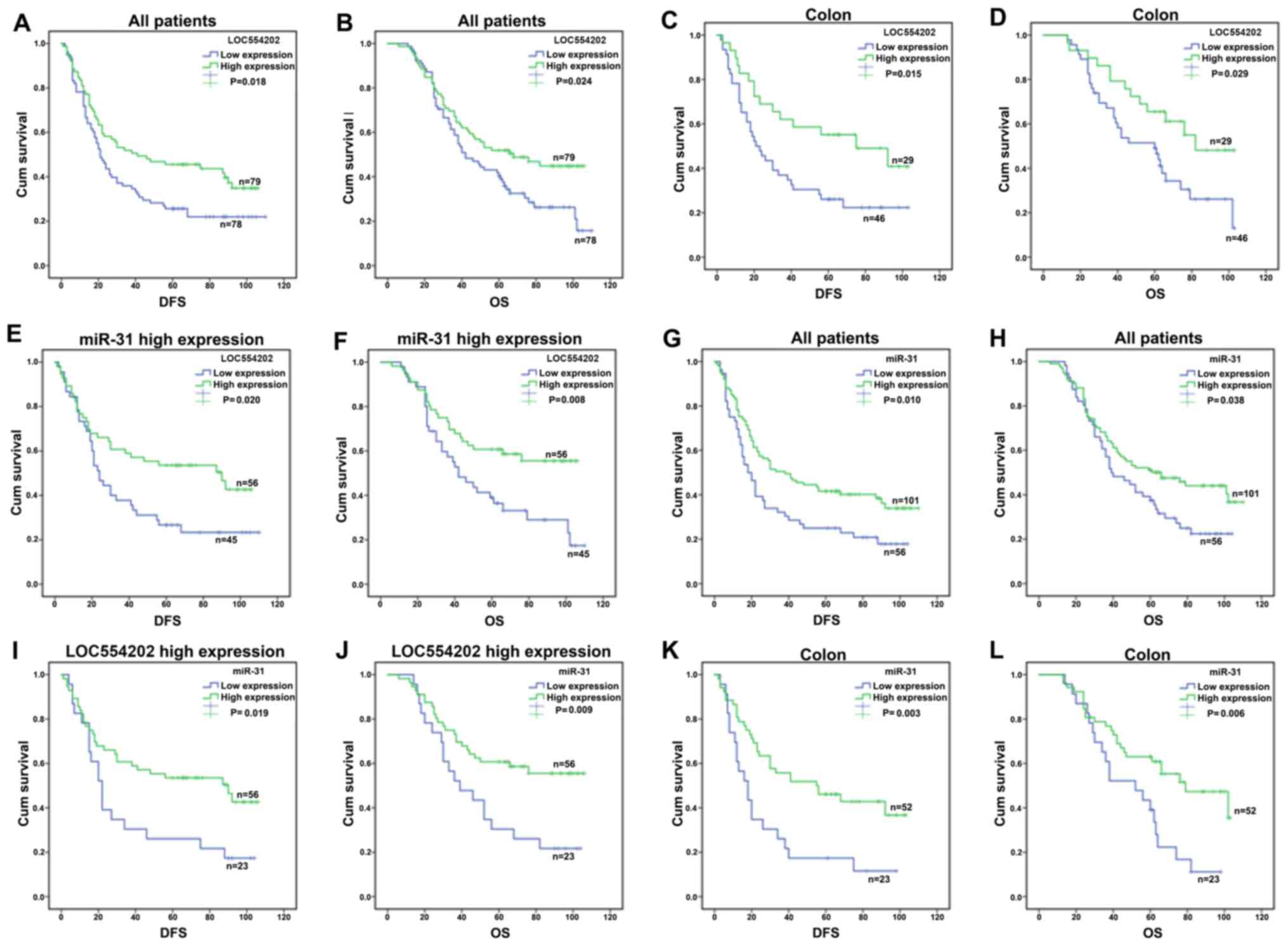
|
1
|
Ferlay J, Shin HR, Bray F, Forman D,
Mathers C and Parkin DM: Estimates of worldwide burden of cancer in
2008: GLOBOCAN 2008. Int J Cancer. 127:2893–2917. 2010. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
2
|
Siegel R, Naishadham D and Jemal A: Cancer
statistics, 2013. CA Cancer J Clin. 63:11–30. 2013. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
3
|
Siegel R, Desantis C and Jemal A:
Colorectal cancer statistics, 2014. CA Cancer J Clin. 64:104–117.
2014. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
4
|
Chen W, Zheng R, Zeng H, Zhang S and He J:
Annual report on status of cancer in China, 2011. Chin J Cancer
Res. 27:2–12. 2015. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
5
|
Augoff K, McCue B, Plow EF and
Sossey-Alaoui K: miR-31 and its host gene lncRNA LOC554202 are
regulated by promoter hypermethylation in triple-negative breast
cancer. Mol Cancer. 11:52012. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
6
|
He L, Thomson JM, Hemann MT,
Hernando-Monge E, Mu D, Goodson S, Powers S, Cordon-Cardo C, Lowe
SW, Hannon GJ, et al: A microRNA polycistron as a potential human
oncogene. Nature. 435:828–833. 2005. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
7
|
Esquela-Kerscher A and Slack FJ:
Oncomirs-microRNAs with a role in cancer. Nat Rev Cancer.
6:259–269. 2006. View
Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
8
|
Slaby O, Svoboda M, Fabian P, Smerdova T,
Knoflickova D, Bednarikova M, Nenutil R and Vyzula R: Altered
expression of miR-21, miR-31, miR-143 and miR-145 is related to
clinicopathologic features of colorectal cancer. Oncology.
72:397–402. 2007. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
9
|
Nosho K, Igarashi H, Nojima M, Ito M,
Maruyama R, Yoshii S, Naito T, Sukawa Y, Mikami M, Sumioka W, et
al: Association of microRNA-31 with BRAF mutation, colorectal
cancer survival and serrated pathway. Carcinogenesis. 35:776–783.
2014. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
10
|
Corcoran DL, Pandit KV, Gordon B,
Bhattacharjee A, Kaminski N and Benos PV: Features of mammalian
microRNA promoters emerge from polymerase II chromatin
immunoprecipitation data. PLoS One. 4:e52792009. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
11
|
Spizzo R, Almeida MI, Colombatti A and
Calin GA: Long non-coding RNAs and cancer: A new frontier of
translational research? Oncogene. 31:4577–4587. 2012. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
12
|
Yao Y, Li J and Wang L: Large intervening
non-coding RNA HOTAIR is an indicator of poor prognosis and a
therapeutic target in human cancers. Int J Mol Sci. 15:18985–18999.
2014. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
13
|
Luo M, Li Z, Wang W, Zeng Y, Liu Z and Qiu
J: Long non-coding RNA H19 increases bladder cancer metastasis by
associating with EZH2 and inhibiting E-cadherin expression. Cancer
Lett. 333:213–221. 2013. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
14
|
Zhao XL, Zhao ZH, Xu WC, Hou JQ and Du XY:
Increased expression of SPRY4-IT1 predicts poor prognosis and
promotes tumor growth and metastasis in bladder cancer. Int J Clin
Exp Pathol. 8:1954–1960. 2015.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
15
|
Tazawa H, Tsuchiya N, Izumiya M and
Nakagama H: Tumor-suppressive miR-34a induces senescence-like
growth arrest through modulation of the E2F pathway in human colon
cancer cells. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA. 104:15472–14477. 2007.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
16
|
Xi Y, Shalgi R, Fodstad O, Pilpel Y and Ju
J: Differentially regulated micro-RNAs and actively translated
messenger RNA transcripts by tumor suppressor p53 in colon cancer.
Clin Cancer Res. 12:2014–2024. 2006. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
17
|
Bandres E, Cubedo E, Agirre X, Malumbres
R, Zarate R, Ramirez N, Abajo A, Navarro A, Moreno I, Monzó M, et
al: Identification by real-time PCR of 13 mature microRNAs
differentially expressed in colorectal cancer and non-tumoral
tissues. Mol Cancer. 5:292006. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
18
|
Baskerville S and Bartel DP: Microarray
profiling of microRNAs reveals frequent coexpression with
neighboring miRNAs and host genes. RNA. 11:241–247. 2005.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
19
|
Shi Y, Lu J, Zhou J, Tan X, He Y, Ding J,
Tian Y, Wang L and Wang K: Long non-coding RNA Loc554202 regulates
proliferation and migration in breast cancer cells. Biochem Biophys
Res Commun. 446:448–453. 2014. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
20
|
Schee K, Boye K, Abrahamsen TW, Fodstad O
and Flatmark K: Clinical relevance of microRNA miR-21, miR-31,
miR-92a, miR-101, miR-106a and miR-145 in colorectal cancer. BMC
Cancer. 12:5052012. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
21
|
Yang L, Wei H and Xiao HJ: Long non-coding
RNA Loc554202 expression as a prognostic factor in patients with
colorectal cancer. Eur Rev Med Pharmacol Sci. 20:4243–4247.
2016.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
22
|
Xi S, Yang M, Tao Y, Xu H, Shan J,
Inchauste S, Zhang M, Mercedes L, Hong JA, Rao M, et al: Cigarette
smoke induces C/EBP-β-mediated activation of miR-31 in normal human
respiratory epithelia and lung cancer cells. PLoS One.
5:e137642010. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
23
|
Yang MH, Yu J, Chen N, Wang XY, Liu XY,
Wang S and Ding YQ: Elevated microRNA-31 expression regulates
colorectal cancer progression by repressing its target gene SATB2.
PLoS One. 8:e853532013. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
24
|
Dindo D, Demartines N and Clavien PA:
Classification of surgical complications: A new proposal with
evaluation in a cohort of 6336 patients and results of a survey.
Ann Surg. 240:205–213. 2004. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
25
|
Wang F, Flanagan J, Su N, Wang LC, Bui S,
Nielson A, Wu X, Vo HT, Ma XJ and Luo Y: RNAscope: A novel in situ
RNA analysis platform for formalin-fixed, paraffin-embedded
tissues. J Mol Diagn. 14:22–29. 2012. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
26
|
Yeo W, Chan SL, Mo FK, Chu CM, Hui JW,
Tong JH, Chan AW, Koh J, Hui EP, Loong H, et al: Phase I/II study
of temsirolimus for patients with unresectable Hepatocellular
Carcinoma (HCC)- a correlative study to explore potential
biomarkers for response. BMC Cancer. 15:3952015. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
27
|
Azim HA Jr, Peccatori FA, Brohee S,
Branstetter D, Loi S, Viale G, Piccart M, Dougall WC, Pruneri G and
Sotiriou C: RANK-ligand (RANKL) expression in young breast cancer
patients and during pregnancy. Breast Cancer Res. 17:242015.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
28
|
Li SC, Tang P and Lin WC: Intronic
microRNA: discovery and biological implications. DNA Cell Biol.
26:195–207. 2007. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
29
|
Chen Y and Gorski DH: Regulation of
angiogenesis through a microRNA (miR-130a) that down-regulates
antiangiogenic homeobox genes GAX and HOXA5. Blood. 111:1217–1226.
2008. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
30
|
Yi R, Pasolli HA, Landthaler M, Hafner M,
Ojo T, Sheridan R, Sander C, O'Carroll D, Stoffel M, Tuschl T, et
al: DGCR8-dependent microRNA biogenesis is essential for skin
development. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA. 106:498–502. 2009. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
31
|
Ozsolak F, Poling LL, Wang Z, Liu H, Liu
XS, Roeder RG, Zhang X, Song JS and Fisher DE: Chromatin structure
analyses identify miRNA promoters. Genes Dev. 22:3172–3183. 2008.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
32
|
Ding J, Lu B, Wang J, Wang J, Shi Y, Lian
Y, Zhu Y, Wang J, Fan Y, Wang Z, et al: Long non-coding RNA
Loc554202 induces apoptosis in colorectal cancer cells via the
caspase cleavage cascades. J Exp Clin Cancer Res. 34:1002015.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
33
|
Luo LJ, Yang F, Ding JJ, Yan DL, Wang DD,
Yang SJ, Ding L, Li J, Chen D, Ma R, et al: MiR-31 inhibits
migration and invasion by targeting SATB2 in triple negative breast
cancer. Gene. 594:47–58. 2016. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
34
|
Wang H, Zhang X, Liu Y, Ni Z, Lin Y, Duan
Z, Shi Y, Wang G and Li F: Downregulated miR-31 level associates
with poor prognosis of gastric cancer and its restoration
suppresses tumor cell malignant phenotypes by inhibiting E2F2.
Oncotarget. 7:36577–36589. 2016.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
35
|
Du Z, Niu S, Xu X and Xu Q:
MicroRNA31-NDRG3 regulation axes are essential for hepatocellular
carcinoma survival and drug resistance. Cancer Biomark. 19:221–230.
2017. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
36
|
Wang CJ, Zhou ZG, Wang L, Yang L, Zhou B,
Gu J, Chen HY and Sun XF: Clinicopathological significance of
microRNA-31, −143 and −145 expression in colorectal cancer. Dis
Markers. 26:27–34. 2009. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
37
|
Sun Y, Jin L, Liu JH, Sui YX, Han LL and
Shen XL: Interfering EZH2 expression reverses the cisplatin
resistance in human ovarian cancer by inhibiting autophagy. Cancer
Biother Radiopharm. 31:246–252. 2016. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
38
|
Zhou W, Wang J, Man WY, Zhang QW and Xu
WG: siRNA silencing EZH2 reverses cisplatin-resistance of human
non-small cell lung and gastric cancer cells. Asian Pac J Cancer
Prev. 16:2425–2430. 2015. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
39
|
Hu S, Yu L, Li Z, Shen Y, Wang J and Cai
J: Overexpression of EZH2 contributes to acquired cisplatin
resistance in ovarian cancer cells in vitro and in vivo. Cancer
Biol Ther. 10:788–795. 2010. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
40
|
Li M, Chen W, Zhang H, Zhang Y, Ke F, Wu
X, Zhang Y, Weng M, Liu Y and Gong W: MiR-31 regulates the
cisplatin resistance by targeting Src in gallbladder cancer.
Oncotarget. 7:83060–83070. 2016.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
41
|
Ayiomamitis GD, Notas G, Zaravinos A,
Zizi-Sermpetzoglou A, Georgiadou M, Sfakianaki O and Kouroumallis
E: Differences in telomerase activity between colon and rectal
cancer. Can J Surg. 57:199–208. 2014. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
42
|
Wen L, Cheng F, Zhou Y and Yin C: MiR-26a
enhances the sensitivity of gastric cancer cells to cisplatin by
targeting NRAS and E2F2. Saudi J Gastroenterol. 21:313–319. 2015.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
43
|
Liu H, Li W, Yu X, Gao F, Duan Z, Ma X,
Tan S, Yuan Y, Liu L, Wang J, et al: : EZH2-mediated Puma gene
repression regulates non-small cell lung cancer cell proliferation
and cisplatin-induced apoptosis. Oncotarget. 7:56338–56354.
2016.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
44
|
Cai L, Wang Z and Liu D: Interference with
endogenous EZH2 reverses the chemotherapy drug resistance in
cervical cancer cells partly by up-regulating Dicer expression.
Tumour Biol. 37:6359–6369. 2016. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
45
|
Zhang Q, Padi SK, Tindall DJ and Guo B:
Polycomb protein EZH2 suppresses apoptosis by silencing the
proapoptotic miR-31. Cell Death Dis. 5:e14862014. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
46
|
Ito M, Mitsuhashi K, Igarashi H, Nosho K,
Naito T, Yoshii S, Takahashi H, Fujita M, Sukawa Y, Yamamoto E, et
al: : MicroRNA-31 expression in relation to BRAF mutation, CpG
island methylation and colorectal continuum in serrated lesions.
Int J Cancer. 135:2507–2515. 2014. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
47
|
Zhong Z, Dong Z, Yang L, Chen X and Gong
Z: MicroRNA-31-5p modulates cell cycle by targeting human mutL
homolog 1 in human cancer cells. Tumour Biol. 34:1959–1965. 2013.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
48
|
Godnic I, Zorc M, Jevsinek Skok D, Calin
GA, Horvat S, Dovc P, Kovac M and Kunej T: Genome-wide and
species-wide in silico screening for intragenic MicroRNAs in human,
mouse and chicken. PLoS One. 8:e651652013. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
49
|
Daniunaite K, Dubikaityte M, Gibas P,
Bakavicius A, Rimantas Lazutka J, Ulys A, Jankevicius F and
Jarmalaite S: Clinical significance of miRNA host gene promoter
methylation in prostate cancer. Hum Mol Genet. 26:2451–2461. 2017.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
50
|
Machal J, Novak J, Hezova R, Zlamal F,
Vasku A, Slaby O and Bienertova-Vasku J: Polymorphism in miR-31 and
miR-584 binding site in the angiotensinogen gene differentially
influences body fat distribution in both sexes. Genes Nutr.
10:4882015. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
51
|
Chen Z, Xu L, Ye X, Shen S, Li Z, Niu X
and Lu S: Polymorphisms of microRNA sequences or binding sites and
lung cancer: A meta-analysis and systematic review. PLoS One.
8:e610082013. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
52
|
Tateishi Y, Okudela K, Mitsui H, Umeda S,
Suzuki T, Kojima Y, Watanabe K, Kawano N, Endo I and Ohashi K: The
potential role of microRNA-31 expression in early colorectal
cancer. Pathol Int. 65:513–518. 2015. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
53
|
Carames C, Cristobal I, Moreno V, Marin
JP, Gonzalez-Alonso P, Torrejon B, Minguez P, Leon A, Martín JI,
Hernández R, et al: MicroRNA-31 Emerges as a predictive biomarker
of pathological response and outcome in locally advanced rectal
cancer. Int J Mol Sci. 17(pii): E8782016. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
54
|
Yang X, Xu X, Zhu J, Zhang S, Wu Y, Wu Y,
Zhao K, Xing C, Cao J, Zhu H, et al: miR-31 affects colorectal
cancer cells by inhibiting autophagy in cancer-associated
fibroblasts. Oncotarget. 7:79617–79628. 2016. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
55
|
Liu Z, Bai J, Zhang L, Lou F, Ke F, Cai W
and Wang H: Conditional knockout of microRNA-31 promotes the
development of colitis associated cancer. Biochem Biophys Res
Commun. 490:62–68. 2017. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
56
|
Tian Y, Ma X, Lv C, Sheng X, Li X, Zhao R,
Song Y, Andl T, Plikus MV, Sun J, et al: Stress responsive miR-31
is a major modulator of mouse intestinal stem cells during
regeneration and tumorigenesis. Elife. 6(pii):
e295382017.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
57
|
Wang YN, Chen ZH and Chen WC: Novel
circulating microRNAs expression profile in colon cancer: A pilot
study. Eur J Med Res. 22:512017. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
58
|
Jo P, Azizian A, Salendo J, Kramer F,
Bernhardt M, Wolff HA, Gruber J, Grade M, Beißbarth T, Ghadimi BM
and Gaedcke J: Changes of microrna levels in plasma of patients
with rectal cancer during chemoradiotherapy. Int J Mol Sci.
18(pii): E11402017. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
59
|
Ma X, Qi S, Duan Z, Liao H, Yang B, Wang
W, Tan J, Li Q and Xia X: Long non-coding RNA LOC554202 modulates
chordoma cell proliferation and invasion by recruiting EZH2 and
regulating miR-31 expression. Cell Prolif. 50:2017. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
60
|
Chen T, Yao LQ, Shi Q, Ren Z, Ye LC, Xu
JM, Zhou PH and Zhong YS: MicroRNA-31 contributes to colorectal
cancer development by targeting factor inhibiting HIF-1alpha
(FIH-1). Cancer Biol Ther. 15:516–523. 2014. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|