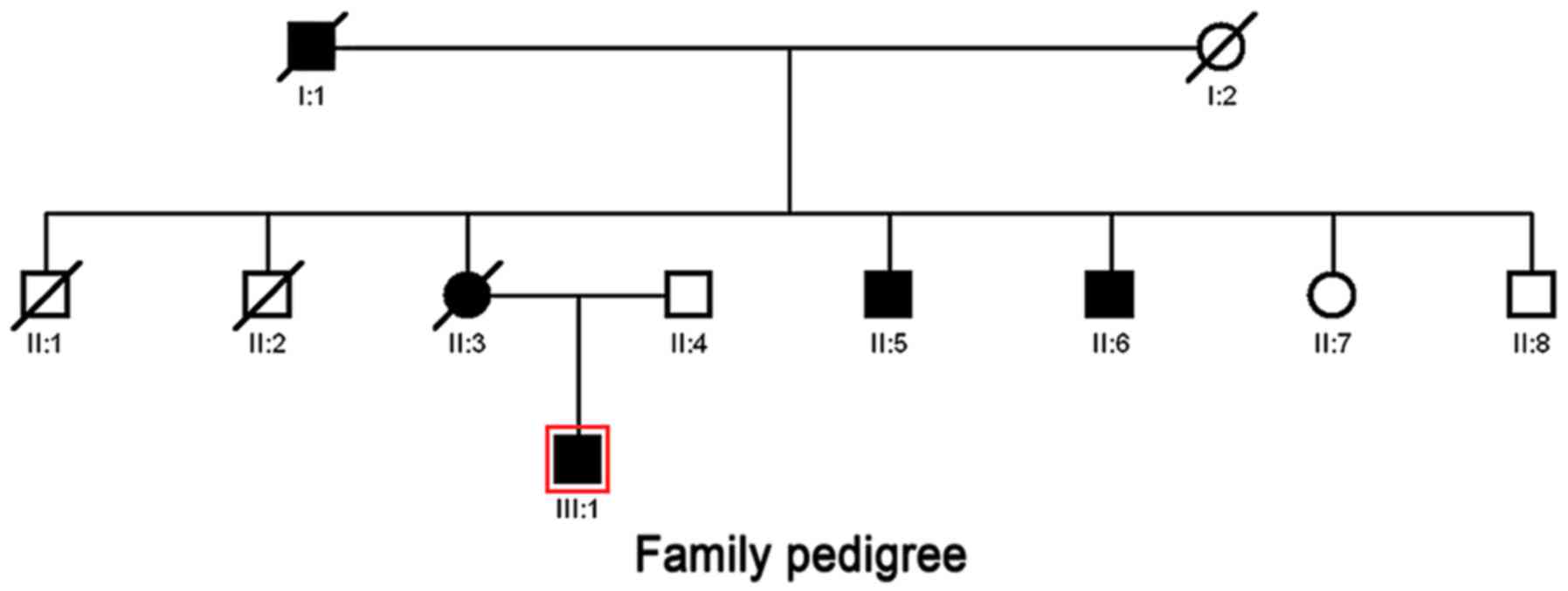
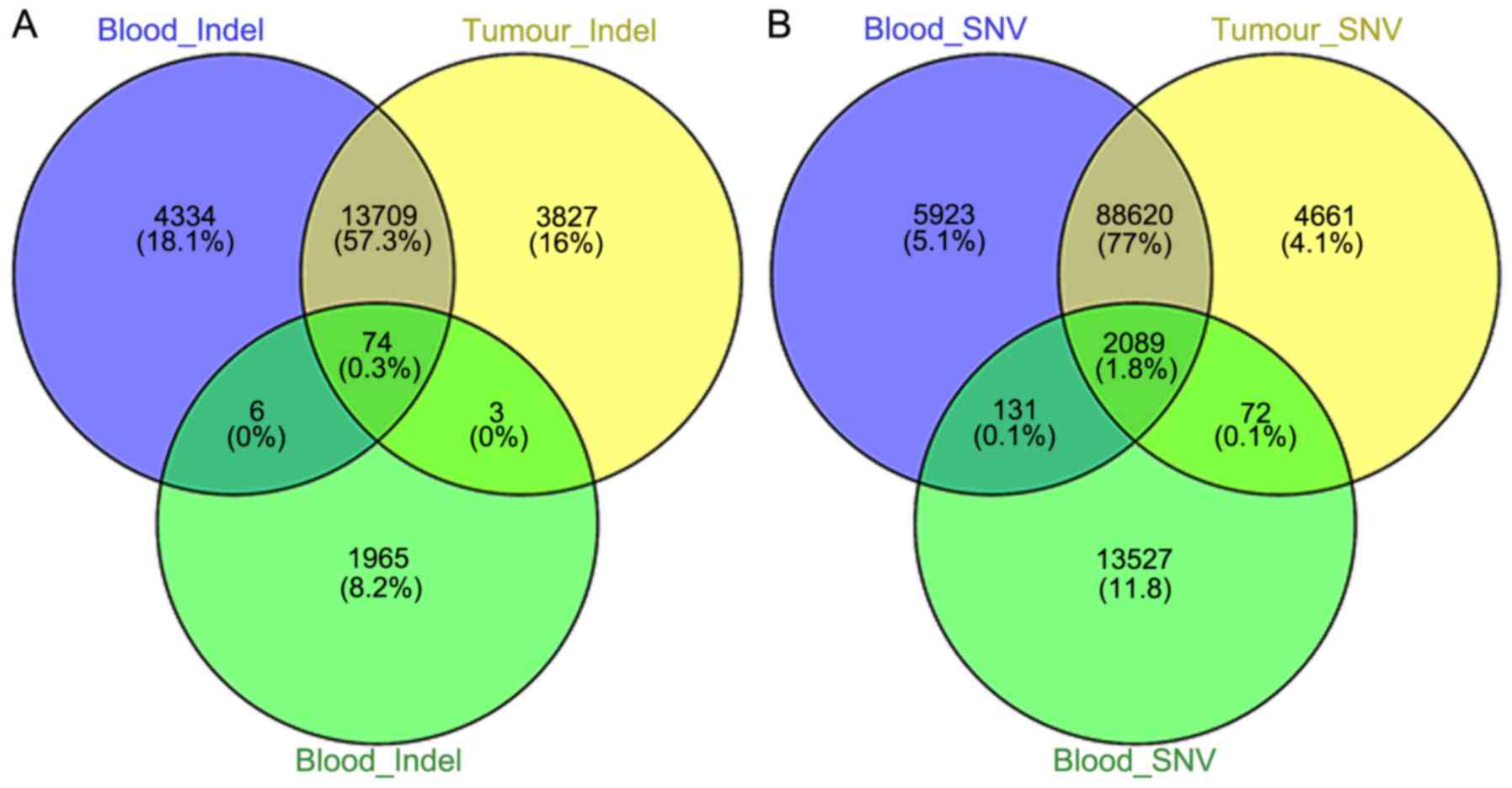
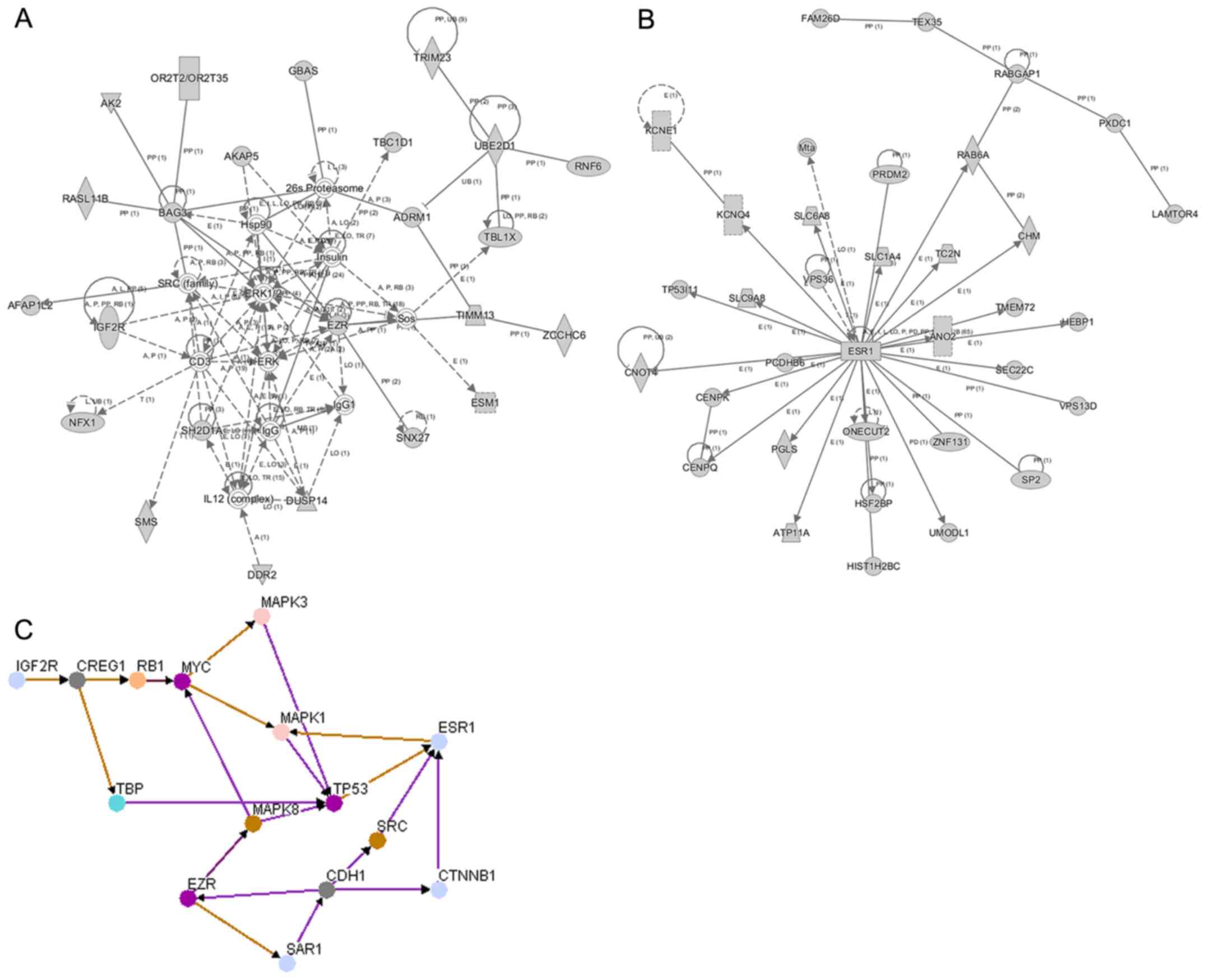
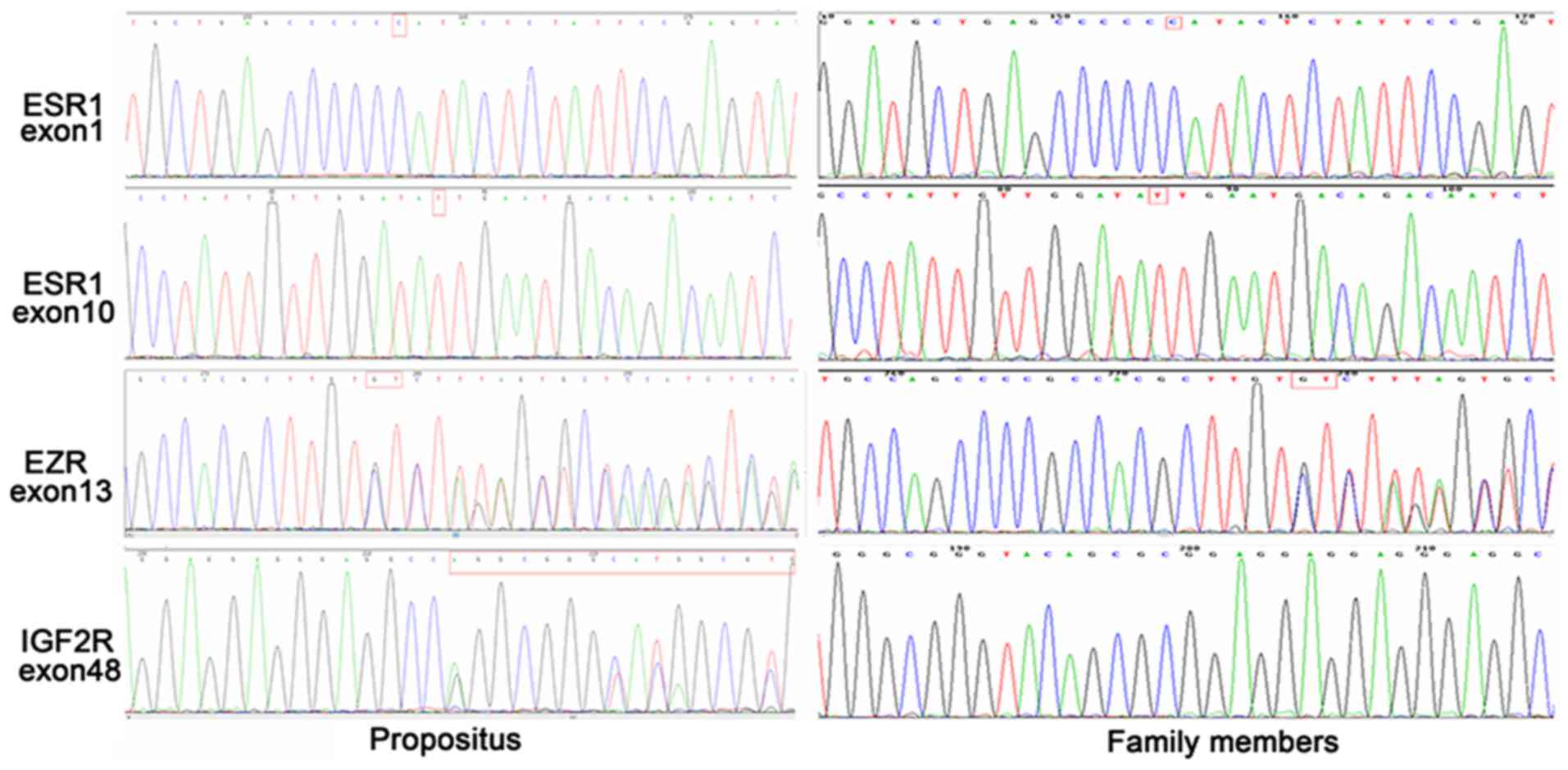
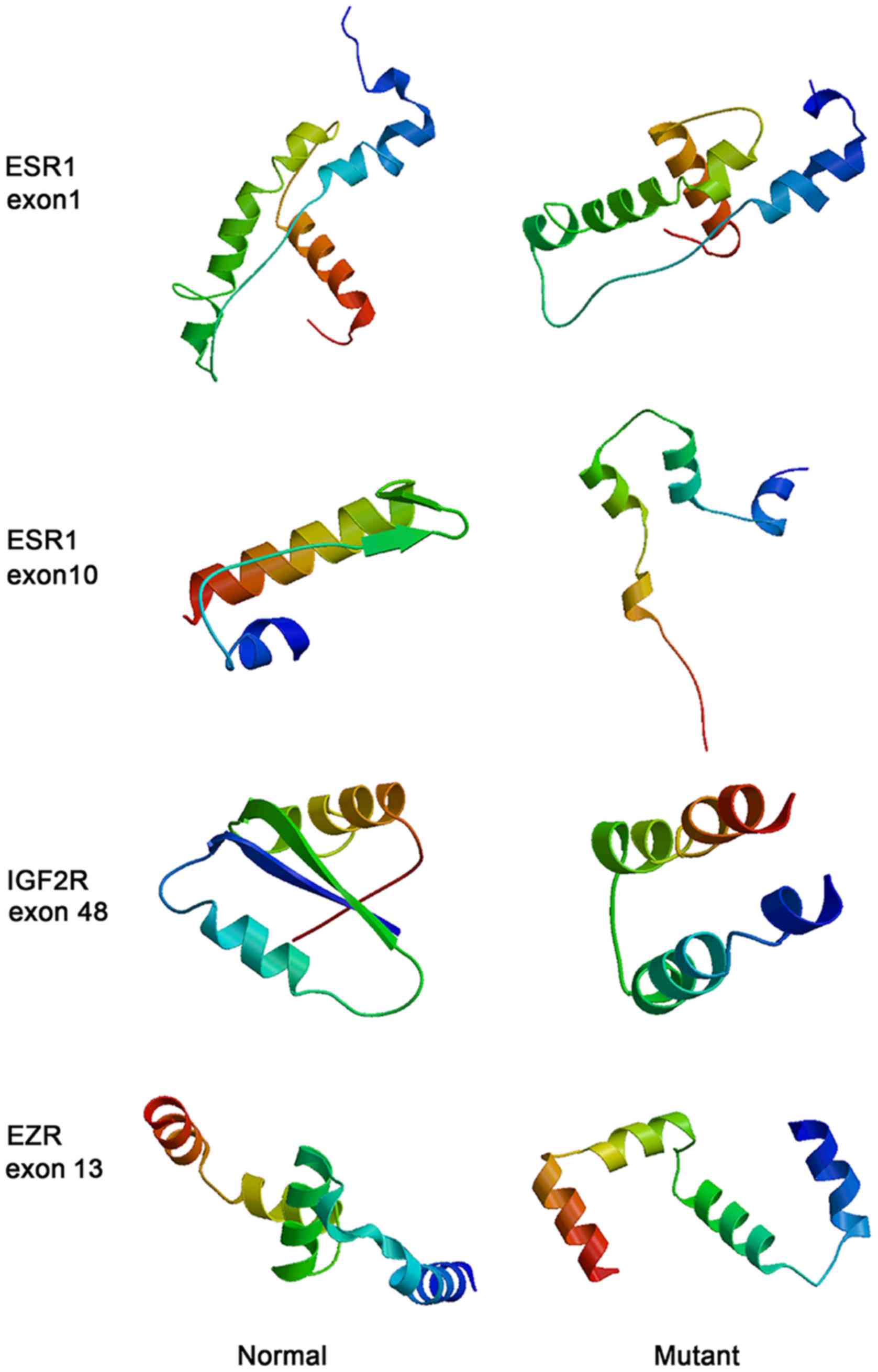
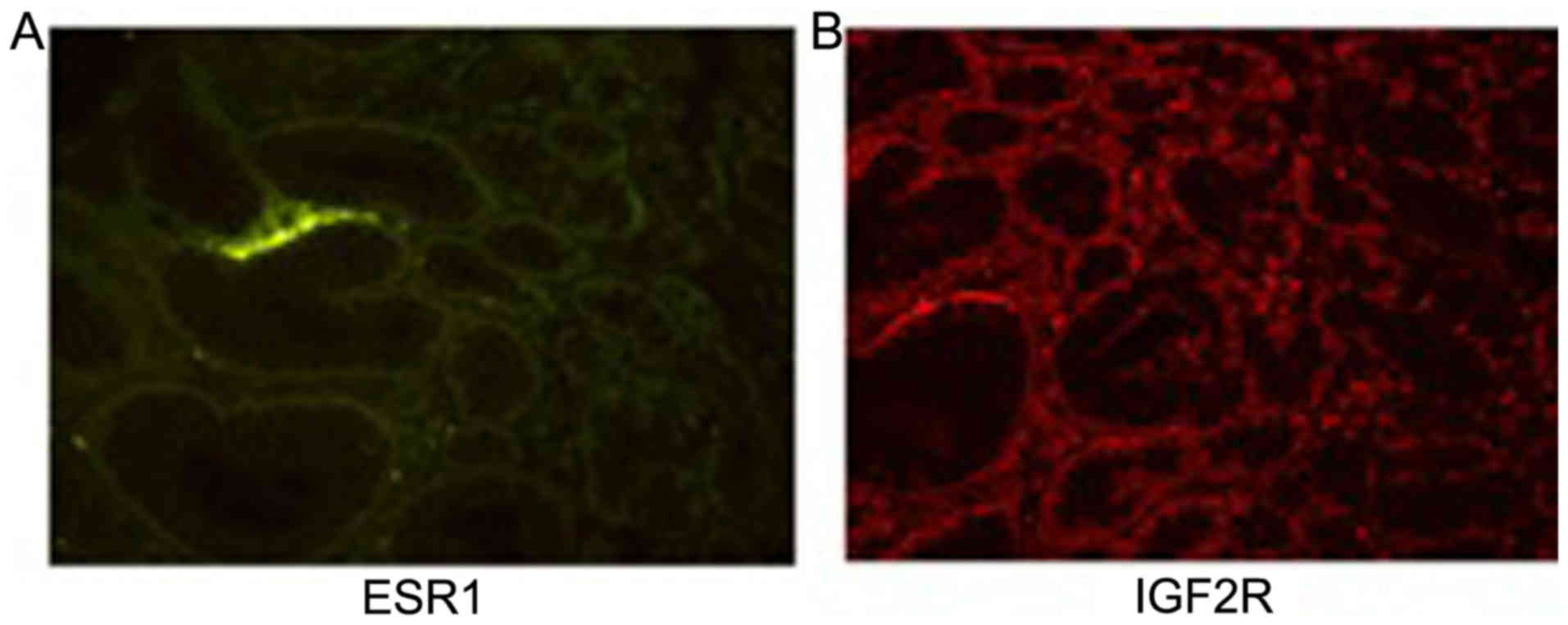
|
1
|
Rugge M, Fassan M and Graham DY:
Epidemiology of Gastric Cancer. Springer International Publishing;
pp. 23–34. 2015, PubMed/NCBI
|
|
2
|
Yaghoobi M, Bijarchi R and Narod SA:
Family history and the risk of gastric cancer. Br J Cancer.
102:237–242. 2010. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
3
|
Vogelaar IP, van der Post RS, Bisseling
TM, van Krieken JHJ, Ligtenberg MJ and Hoogerbrugge N: Familial
gastric cancer: Detection of a hereditary cause helps to understand
its etiology. Hered Cancer Clin Pract. 10:182012. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
4
|
Caldas C, Carneiro F, Lynch HT, Yokota J,
Wiesner GL, Powell SM, Lewis FR, Huntsman DG, Pharoah PD, Jankowski
JA, et al: Familial gastric cancer: Overview and guidelines for
management. J Med Genet. 36:873–880. 1999.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
5
|
Carneiro F: Hereditary gastric cancer.
Pathologe. 33 Suppl 2:S231–S234. 2012. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
6
|
Oliveira C, Pinheiro H, Figueiredo J,
Seruca R and Carneiro F: Familial gastric cancer: Genetic
susceptibility, pathology, and implications for management. Lancet
Oncol. 16:e60–e70. 2015. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
7
|
Nagarajan N, Bertrand D, Hillmer AM, Zang
ZJ, Yao F, Jacques PÉ, Teo AS, Cutcutache I, Zhang Z, Lee WH, et
al: Whole-genome reconstruction and mutational signatures in
gastric cancer. Genome Biol. 13:R1152012. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
8
|
Suleiman SH, Koko ME, Nasir WH, Elfateh O,
Elgizouli UK, Abdallah MO, Alfarouk KO, Hussain A, Faisal S,
Ibrahim FM, et al: Exome sequencing of a colorectal cancer family
reveals shared mutation pattern and predisposition circuitry along
tumor pathways. Front Genet. 6:2882015. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
9
|
Sommer S and Fuqua SA: Estrogen receptor
and breast cancer. Semin Cancer Biol. 11:339–352. 2001. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
10
|
Schaffer BS, Lin MF, Byrd JC, Park JH and
MacDonald RG: Opposing roles for the insulin-like growth factor
(IGF)-II and mannose 6-phosphate (Man-6-P) binding activities of
the IGF-II/Man-6-P receptor in the growth of prostate cancer cells.
Endocrinology. 144:955–966. 2003. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
11
|
Vaheri A, Carpén O, Heiska L, Helander TS,
Jääskeläinen J, Majander-Nordenswan P, Sainio M, Timonen T and
Turunen O: The ezrin protein family: Membrane-cytoskeleton
interactions and disease associations. Curr Opin Cell Biol.
9:659–666. 1997. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
12
|
Krämer A, Green J, Pollard J Jr and
Tugendreich S: Causal analysis approaches in Ingenuity Pathway
Analysis. Bioinformatics. 30:523–530. 2014. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
13
|
Breitkreutz BJ, Stark C and Tyers M:
Osprey: A network visualization system. Genome Biol. 4:R222003.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
14
|
Gasteiger E, Gattiker A, Hoogland C,
Ivanyi I, Appel RD and Bairoch A: ExPASy: The proteomics server for
in-depth protein knowledge and analysis. Nucleic Acids Res.
31:3784–3788. 2003. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
15
|
Pirooznia M, Nagarajan V and Deng Y:
GeneVenn - A web application for comparing gene lists using Venn
diagrams. Bioinformation. 1:420–422. 2007. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
16
|
Bernini M, Barbi S, Roviello F, Scarpa A,
Moore P, Pedrazzani C, Beghelli S, Marrelli D and de Manzoni G:
Family history of gastric cancer: A correlation between
epidemiologic findings and clinical data. Gastric Cancer. 9:9–13.
2006. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
17
|
Filipe MI, Potet F, Bogomoletz WV, Dawson
PA, Fabiani B, Chauveinc P, Fenzy A, Gazzard B, Goldfain D and
Zeegen R: Incomplete sulphomucin-secreting intestinal metaplasia
for gastric cancer. Preliminary data from a prospective study from
three centres. Gut. 26:1319–1326. 1985. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
18
|
Cassaro M, Rugge M, Gutierrez O, Leandro
G, Graham DY and Genta RM: Topographic patterns of intestinal
metaplasia and gastric cancer. Am J Gastroenterol. 95:1431–1438.
2000. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
19
|
Ghosh A, Hartge P, Purdue MP, Chanock SJ,
Amundadottir L, Wang Z, Wentzensen N, Chatterjee N and Wacholder S:
Assessing disease risk in genome-wide association studies using
family history. Epidemiology. 23:616–622. 2012. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
20
|
Cavalli V, Vilbois F, Corti M, Marcote MJ,
Tamura K, Karin M, Arkinstall S and Gruenberg J: The stress-induced
MAP kinase p38 regulates endocytic trafficking via the GDI: Rab5
complex. Mol Cell. 7:421–432. 2001. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
21
|
Junttila MR, Li SP and Westermarck J:
Phosphatase-mediated crosstalk between MAPK signaling pathways in
the regulation of cell survival. FASEB J. 22:954–965. 2008.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
22
|
Reddy KB, Nabha SM and Atanaskova N: Role
of MAP kinase in tumor progression and invasion. Cancer Metastasis
Rev. 22:395–403. 2003. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
23
|
Dhillon AS, Hagan S, Rath O and Kolch W:
MAP kinase signalling pathways in cancer. Oncogene. 26:3279–3290.
2007. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
24
|
Chimento A, Sirianni R, Casaburi I,
Ruggiero C, Maggiolini M, Andò S and Pezzi V: 17β-Estradiol
activates GPER- and ESR1-dependent pathways inducing apoptosis in
GC-2 cells, a mouse spermatocyte-derived cell line. Mol Cell
Endocrinol. 355:49–59. 2012. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
25
|
Buchanan CM, Phillips AR and Cooper GJ: A
novel two-chain IGF-II-derived peptide from purified β-cell
granules. Growth Horm IGF Res. 20:360–366. 2010. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
26
|
Khanna C, Wan X, Bose S, Cassaday R, Olomu
O, Mendoza A, Yeung C, Gorlick R, Hewitt SM and Helman LJ: The
membrane-cytoskeleton linker ezrin is necessary for osteosarcoma
metastasis. Nat Med. 10:182–186. 2004. View
Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
27
|
Roberts PJ and Der CJ: Targeting the
Raf-MEK-ERK mitogen-activated protein kinase cascade for the
treatment of cancer. Oncogene. 26:3291–3310. 2007. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
28
|
Robinson DR, Wu YM, Vats P, Su F, Lonigro
RJ, Cao X, Kalyana - Sundaram S, Wang R, Ning Y, Hodges L, et al:
Activating ESR1 mutations in hormone-resistant metastatic breast
cancer. Nat Genet. 45:1446–1451. 2013. View
Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
29
|
Toy W, Shen Y, Won H, Green B, Sakr RA,
Will M, Li Z, Gala K, Fanning S, King TA, et al: ESR1
ligand-binding domain mutations in hormone-resistant breast cancer.
Nat Genet. 45:1439–1445. 2013. View
Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
30
|
Schiavon G, Hrebien S, Garcia-Murillas I,
Cutts RJ, Pearson A, Tarazona N, Fenwick K, Kozarewa I,
Lopez-Knowles E, Ribas R, et al: Analysis of ESR1 mutation
in circulating tumor DNA demonstrates evolution during therapy for
metastatic breast cancer. Sci Transl Med. 7:313ra1822015.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
31
|
Woo IS, Park MJ, Choi SW, Kim SJ, Lee MA,
Kang JH, Hong YS and Lee KS: Loss of estrogen receptor-alpha
expression is associated with hypermethylation near its ATG start
codon in gastric cancer cell lines. Oncol Rep. 11:617–622.
2004.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
32
|
Kong FM, Anscher MS, Washington MK,
Killian JK and Jirtle RL: M6P/IGF2R is mutated in squamous
cell carcinoma of the lung. Oncogene. 19:1572–1578. 2000.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
33
|
Oka Y, Waterland RA, Killian JK, Nolan CM,
Jang HS, Tohara K, Sakaguchi S, Yao T, Iwashita A, Yata Y, et al:
M6P/IGF2R tumor suppressor gene mutated in hepatocellular
carcinomas in Japan. Hepatology. 35:1153–1163. 2002. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
34
|
Yamada T, De Souza AT, Finkelstein S and
Jirtle RL: Loss of the gene encoding mannose
6-phosphate/insulin-like growth factor II receptor is an early
event in liver carcinogenesis. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA.
94:10351–10355. 1997. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
35
|
De Souza AT, Hankins GR, Washington MK,
Orton TC and Jirtle RL: M6P/IGF2R gene is mutated in human
hepatocellular carcinomas with loss of heterozygosity. Nat Genet.
11:447–449. 1995. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
36
|
Hankins GR, De Souza AT, Bentley RC, Patel
MR, Marks JR, Iglehart JD and Jirtle RL: M6P/IGF2 receptor: A
candidate breast tumor suppressor gene. Oncogene. 12:2003–2009.
1996.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
37
|
Yu H and Rohan T: Role of the insulin-like
growth factor family in cancer development and progression. J Natl
Cancer Inst. 92:1472–1489. 2000. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
38
|
Mäkitie T, Carpén O, Vaheri A and Kivelä
T: Ezrin as a prognostic indicator and its relationship to tumor
characteristics in uveal malignant melanoma. Invest Ophthalmol Vis
Sci. 42:2442–2449. 2001.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
39
|
Hirota WK, Zuckerman MJ, Adler DG, Davila
RE, Egan J, Leighton JA, Qureshi WA, Rajan E, Fanelli R,
Wheeler-Harbaugh J, et al: Standards of Practice Committee,
American Society for Gastrointestinal Endoscopy: ASGE guideline:
The role of endoscopy in the surveillance of premalignant
conditions of the upper GI tract. Gastrointest Endosc. 63:570–580.
2006. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|