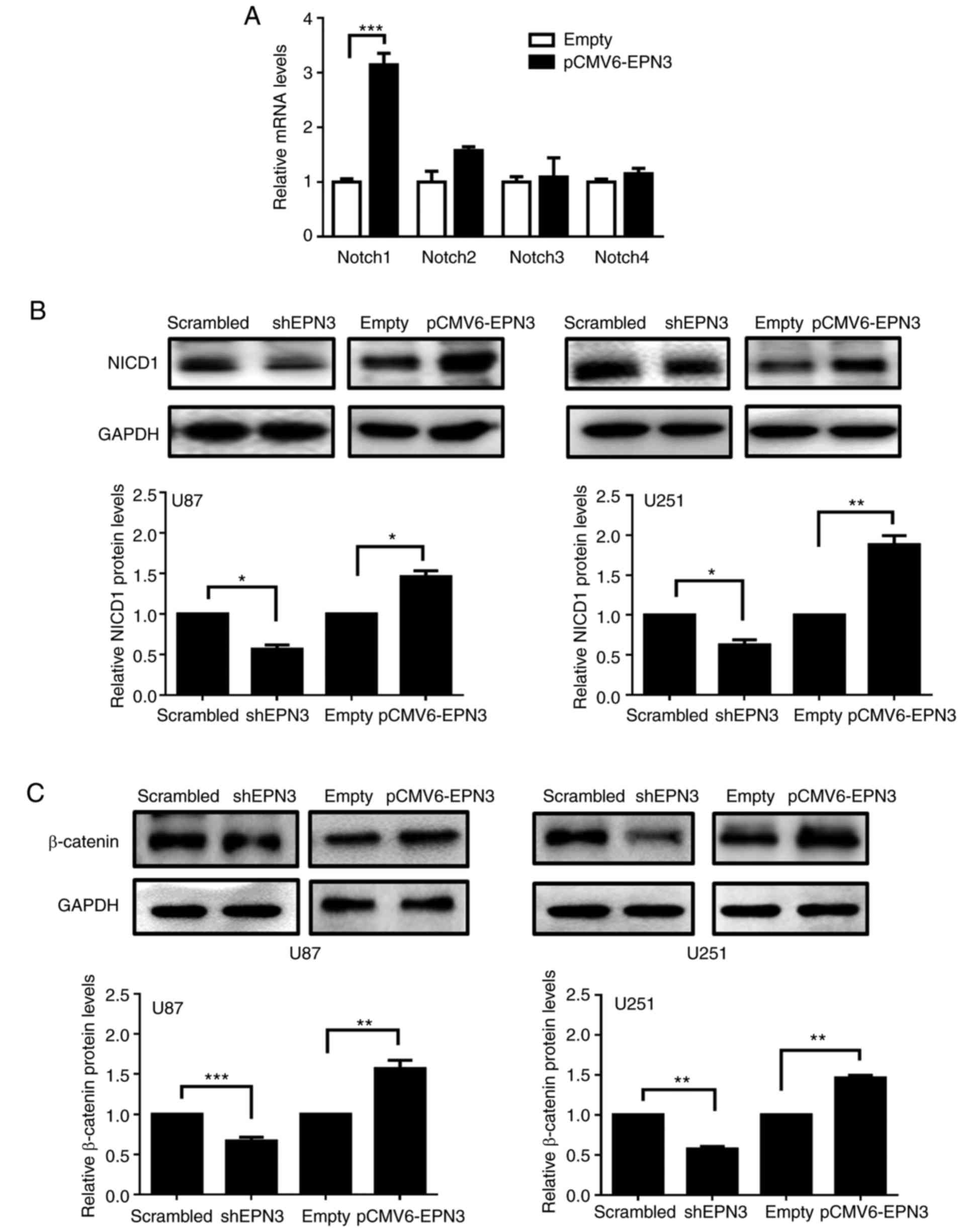
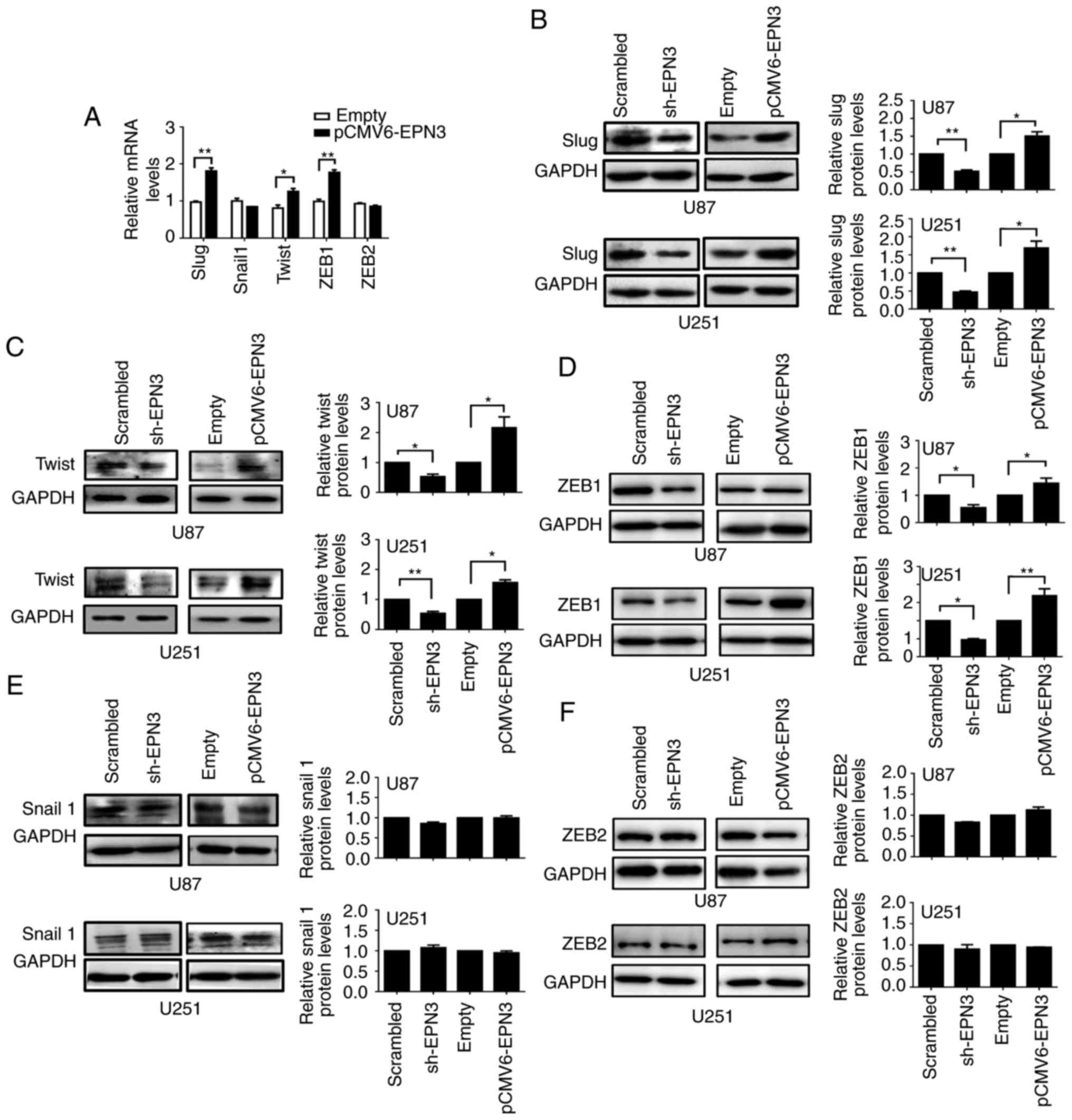
|
1
|
Khan MN, Sharma AM, Pitz M, Loewen SK,
Quon H, Poulin A and Essig M: High-grade glioma management and
response assessment-recent advances and current challenges. Curr
Oncol. 23:e383–e391. 2016. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
2
|
Majchrzak-Celińska A, Paluszczak J,
Szalata M, Barciszewska AM, Nowak S, Kleszcz R, Sherba A and
Baer-Dubowska W: The methylation of a panel of genes differentiates
low-grade from high-grade gliomas. Tumor Biol. 36:3831–3841. 2015.
View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
3
|
Cloughesy TF, Cavenee WK and Mischel PS:
Glioblastoma: From molecular pathology to targeted treatment. Ann
Rev Pathol. 9:12014. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
4
|
Olar A and Aldape KD: Using the molecular
classification of glioblastoma to inform personalized treatment. J
Pathol. 232:165–177. 2014. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
5
|
Montgomery RM, Lde Queiroz S and Rogerio
F: EGFR, p53, IDH-1 and MDM2 immunohistochemical analysis in
glioblastoma: Therapeutic and prognostic correlation. Arq
Neuropsiquiatr. 73:561–568. 2015. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
6
|
Furnari FB, Fenton T, Bachoo RM, Mukasa A,
Stommel JM, Stegh A, Hahn WC, Ligon KL, Louis DN, Brennan C, et al:
Malignant astrocytic glioma: Genetics, biology, and paths to
treatment. Genes Dev. 21:2683–2710. 2007. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
7
|
Stupp R, Mason WP, van den Bent MJ, Weller
M, Fisher B, Taphoorn MJ, Belanger K, Brandes AA, Marosi C, Bogdahn
U, et al: Radiotherapy plus concomitant and adjuvant temozolomide
for glioblastoma. N Engl J Med. 352:987–996. 2005. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
8
|
Louis DN, Ohgaki H, Wiestler OD, Cavenee
WK, Burger PC, Jouvet A, Scheithauer BW and Kleihues P: The 2007
WHO classification of tumours of the central nervous system. Acta
Neuropathol. 114:97–109. 2007. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
9
|
Xie X, Cho B and Fischer JA: Drosophila
Epsin's role in Notch ligand cells requires three Epsin protein
functions: The lipid binding function of the ENTH domain, a single
Ubiquitin interaction motif, and a subset of the C-terminal protein
binding modules. Dev Biol. 363:399–412. 2012. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
10
|
Chen H, Fre S, Slepnev VI, Capua MR, Takei
K, Butler MH, Di Fiore PP and De Camilli P: Epsin is an
EH-domain-binding protein implicated in clathrin-mediated
endocytosis. Nature. 394:793–797. 1998. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
11
|
Tessneer KL, Cai X, Pasula S, Dong Y, Liu
X, Chang B, McManus J, Hahn S, Yu L and Chen H: Epsin family of
endocytic adaptor proteins as oncogenic regulators of cancer
progression. J Can Res Updates. 2:144–150. 2013.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
12
|
Rosenthal JA, Chen H, Slepnev VI,
Pellegrini L, Salcini AE, Di Fiore PP and De Camilli P: The epsins
define a family of proteins that interact with components of the
clathrin coat and contain a new protein module. J Biol Chem.
274:33959–33965. 1999. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
13
|
Ko G, Paradise S, Chen H, Graham M, Vecchi
M, Bianchi F, Cremona O, Di Fiore PP and De Camilli P: Selective
high-level expression of epsin 3 in gastric parietal cells, where
it is localized at endocytic sites of apical canaliculi. Proc Natl
Acad Sci USA. 107:215112010. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
14
|
Spradling KD, McDaniel AE, Lohi J and
Pilcher BK: Epsin 3 is a novel extracellular matrix-induced
transcript specific to wounded epithelia. J Biol Chem.
276:29257–29267. 2001. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
15
|
Bache KG, Slagsvold T and Stenmark H:
Defective downregulation of receptor tyrosine kinases in cancer.
EMBO J. 23:2707–2712. 2014. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
16
|
Mcmahon HT and Boucrot E: Molecular
mechanism and physiological functions of clathrin-mediated
endocytosis. Nat Rev Mol Cell Biol. 12:517–533. 2011. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
17
|
Chang B, Tessneer KL, McManus J, Liu X,
Hahn S, Pasula S, Wu H, Song H, Chen Y, Cai X, et al: Epsin is
required for Dishevelled stability and Wnt signalling activation in
colon cancer development. Nat Commun. 6:63802015. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
18
|
Purow BW, Haque RM, Noel MW, Su Q, Burdick
MJ, Lee J, Sundaresan T, Pastorino S, Park JK, Mikolaenko I, et al:
Expression of Notch-1 and its ligands, Delta-like-1 and Jagged-1,
is critical for glioma cell survival and proliferation. Cancer Res.
65:2353–2363. 2005. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
19
|
Wang J, Wakeman TP, Lathia JD, Hjelmeland
AB, Wang XF, White RR, Rich JN and Sullenger BA: Notch promotes
radioresistance of glioma stem cells. Stem Cells. 28:17–28.
2010.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
20
|
Korkaya H and Wicha MS: HER-2, notch, and
breast cancer stem cells: Targeting an axis of evil. Clin Cancer
Res. 15:1845–1847. 2009. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
21
|
Benedito R, Roca C, Sörensen I, Adams S,
Gossler A, Fruttiger M and Adams RH: The Notch ligands Dll4 and
Jagged1 have opposing effects on angiogenesis. Cell. 137:1124–1135.
2009. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
22
|
Kopan R and Ilagan MX: The canonical Notch
signaling pathway: Unfolding the activation mechanism. Cell.
137:216–233. 2009. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
23
|
Blitzer JT and Nusse R: A critical role
for endocytosis in Wnt signaling. BMC Cell Biol. 7:282006.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
24
|
Yamamoto H, Komekado H and Kikuchi A:
Caveolin is necessary for Wnt-3a-dependent internalization of LRP6
and accumulation of beta-catenin. Dev Cell. 11:213–223. 2006.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
25
|
Gonzalez DM and Medici D: Signaling
mechanisms of the epithelial-mesenchymal transition. Sci Signal.
7:re82014. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
26
|
Zavadil J, Cermak L, Soto-Nieves N and
Böttinger EP: Integration of TGF-beta/Smad and Jagged1/Notch
signalling in epithelial-to-mesenchymal transition. EMBO J.
23:1155–1165. 2004. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
27
|
Kahlert UD, Maciaczyk D, Doostkam S, Orr
BA, Simons B, Bogiel T, Reithmeier T, Prinz M, Schubert J,
Niedermann G, et al: Activation of canonical WNT/β-catenin
signaling enhances in vitro motility of glioblastoma cells by
activation of ZEB1 and other activators of
epithelial-to-mesenchymal transition. Cancer Lett. 325:42–53. 2012.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
28
|
Prieto-García E, Díaz-García CV,
García-Ruiz I and Agulló-Ortuño MT: Epithelial-to-mesenchymal
transition in tumor progression. Med Oncol. 34:1222017. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
29
|
Kalluri R and Weinberg RA: The basics of
epithelial-mesenchymal transition. J Clin Invest. 119:1420–1428.
2009. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
30
|
Livak KJ and Schmittgen TD: Analysis of
relative gene expression data using real-time quantitative PCR and
the 2−ΔΔCT method. Methods. 25:402–408. 2001.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
31
|
Allen M, Bjerke M, Edlund H, Nelander S
and Westermark B: Origin of the U87MG glioma cell line: Good news
and bad news. Sci Transl Med. 8:354re32016. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
32
|
Yang J and Weinberg RA:
Epithelial-mesenchymal transition: At the crossroads of development
and tumor metastasis. Dev Cell. 14:818–829. 2008. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
33
|
Xu R, Shimizu F, Hovinga K, Beal K, Karimi
S, Droms L, Peck KK, Gutin P, Iorgulescu JB, Kaley T, et al:
Molecular and clinical effects of Notch inhibition in glioma
patients: A phase 0/I trial. Clin Cancer Res. 22:4786–4796. 2016.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
34
|
Cheng W, Zhang C, Ren X, Jiang Y, Han S,
Liu Y, Cai J, Li M, Wang K, Liu Y, et al: Bioinformatic analyses
reveal a distinct Notch activation induced by STAT3 phosphorylation
in the mesenchymal subtype of glioblastoma. J Neurosurg.
126:249–259. 2017. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
35
|
Chen H, Ko G, Zatti A, Di Giacomo G, Liu
L, Raiteri E, Perucco E, Collesi C, Min W, Zeiss C, et al:
Embryonic arrest at midgestation and disruption of Notch signaling
produced by the absence of both epsin 1 and epsin 2 in mice. Proc
Natl Acad Sci USA. 106:13838–13843. 2009. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
36
|
Overstreet E, Fitch E and Fischer JA: Fat
facets and Liquid facets promote Delta endocytosis and Delta
signaling in the signaling cells. Development. 131:5355–5366. 2004.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
37
|
Wang W and Struhl G: Drosophila
Epsin mediates a select endocytic pathway that DSL ligands must
enter to activate Notch. Development. 131:5367–5380. 2004.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
38
|
Leong KG, Niessen K, Kulic I, Raouf A,
Eaves C, Pollet I and Karsan A: Jagged1-mediated Notch activation
induces epithelial-to-mesenchymal transition through Slug-induced
repression of E-cadherin. J Exp Med. 204:2935–2948. 2007.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
39
|
Pasula S, Cai X, Dong Y, Messa M, McManus
J, Chang B, Liu X, Zhu H, Mansat RS, Yoon SJ, et al: Endothelial
epsin deficiency decreases tumor growth by enhancing VEGF
signaling. J Clin Invest. 122:4424–4438. 2012. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
40
|
Tessneer KL, Pasula S, Cai X, Dong Y, Liu
X, Yu L, Hahn S, McManus J, Chen Y, Chang B and Chen H: Endocytic
adaptor protein epsin is elevated in prostate cancer and required
for cancer progression. ISRN Oncol. 2013:4205972013.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
41
|
Coon BG, Burgner J, Camonis JH and Aguilar
RC: The epsin family of endocytic adaptors promotes fibrosarcoma
migration and invasion. J Biol Chem. 285:33073–33081. 2010.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
42
|
Hellwig B, Madjar K, Edlund K, Marchan R,
Cadenas C, Heimes AS, Almstedt K, Lebrecht A, Sicking I, Battista
MJ, et al: Epsin family member 3 and ribosome-related genes are
associated with late metastasis in estrogen receptor-positive
breast cancer and long-term survival in non-small cell lung cancer
using a genome-wide identification and validation strategy. PLoS
One. 11:e01675852016. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
43
|
Nagano T, Nakano M, Nakashima A, Onishi K,
Yamao S, Enari M, Kikkawa U and Kamada S: Identification of
cellular senescence-specific genes by comparative transcriptomics.
Sci Rep. 6:317582016. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
44
|
Mori J, Tanikawa C, Ohnishi N, Funauchi Y,
Toyoshima O, Ueda K and Matsuda K: Epsin 3, a novel p53 target,
regulates the apoptotic pathway and gastric carcinogenesis1.
Neoplasia. 19:185–195. 2017. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
45
|
Howe CL and Mobley WC: Signaling endosome
hypothesis: A cellular mechanism for long distance communication. J
Neurobiol. 58:207–216. 2004. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
46
|
Vanlandingham PA, Fore TR, Chastain LR,
Royer SM, Bao H, Reist NE and Zhang B: Epsin 1 promotes synaptic
growth by enhancing BMP signal levels in motoneuron nuclei. PLoS
One. 8:e659972013. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
47
|
Nusse R: Wnt signaling and stem cell
control. Cell Res. 18:523–527. 2008. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
48
|
Ayyanan A, Civenni G, Ciarloni L, Morel C,
Mueller N, Lefort K, Mandinova A, Raffoul W, Fiche M, Dotto GP and
Brisken C: Increased Wnt signaling triggers oncogenic conversion of
human breast epithelial cells by a Notch-dependent mechanism. Proc
Natl Acad Sci USA. 103:3799–3804. 2006. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
49
|
Wang Z, Li Y, Kong D, Banerjee S, Ahmad A,
Azmi AS, Ali S, Abbruzzese JL, Gallick GE and Sarkar FH:
Acquisition of epithelial-mesenchymal transition phenotype of
gemcitabine-resistant pancreatic cancer cells is linked with
activation of Notch signaling pathway. Cancer Res. 69:2400–2407.
2009. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
50
|
Kim HA, Koo BK, Cho JH, Kim YY, Seong J,
Chang HJ, Oh YM, Stange DE, Park JG, Hwang D and Kong YY: Notch1
counteracts WNT/β-catenin signaling through chromatin modification
in colorectal cancer. J Clin Invest. 122:3248–3259. 2012.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
51
|
Kohn KW, Zeeberg BM, Reinhold WC and
Pommier Y: Gene expression correlations in human cancer cell lines
define molecular interaction networks for epithelial phenotype.
PLoS One. 9:e992692014. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|