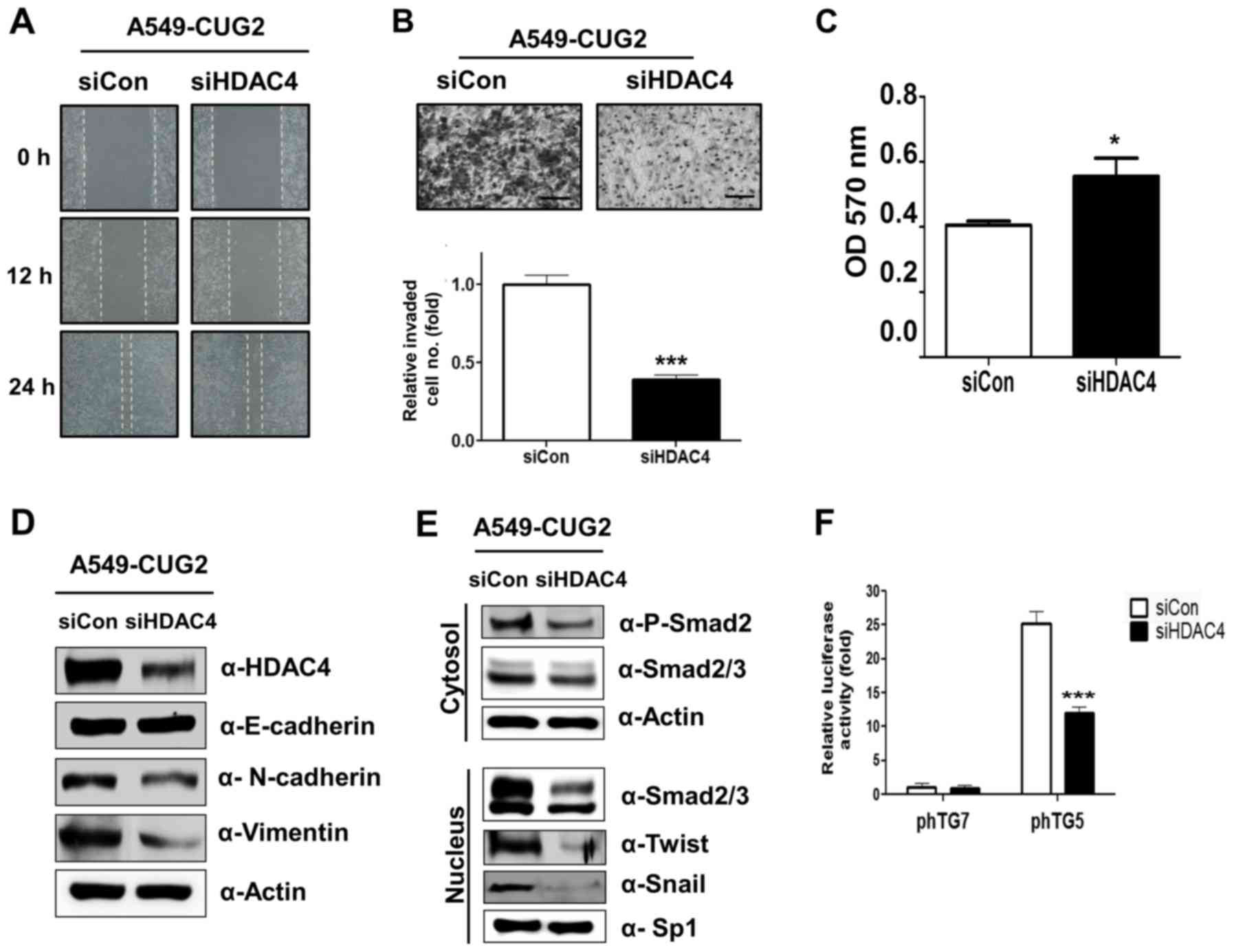
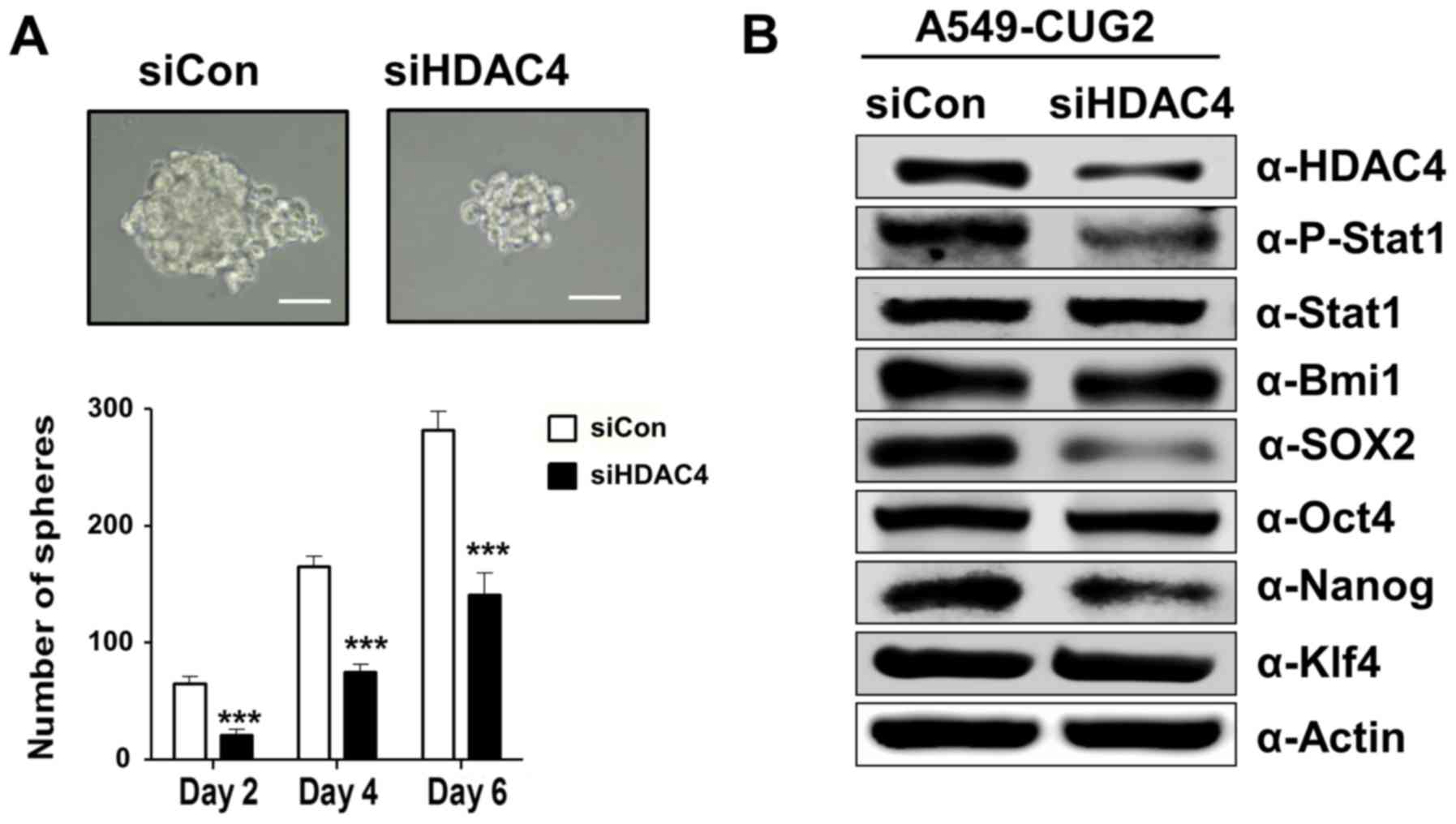
|
1
|
Lee S, Gang J, Jeon SB, Choo SH, Lee B,
Kim YG, Lee YS, Jung J, Song SY and Koh SS: Molecular cloning and
functional analysis of a novel oncogene, cancer-upregulated gene 2
(CUG2). Biochem Biophys Res Commun. 360:633–639. 2007.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
2
|
Hori T, Amano M, Suzuki A, Backer CB,
Welburn JP, Dong Y, McEwen BF, Shang WH, Suzuki E, Okawa K, et al:
CCAN makes multiple contacts with centromeric DNA to provide
distinct pathways to the outer kinetochore. Cell. 135:1039–1052.
2008. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
3
|
Kim H, Lee M and Lee S, Park B, Koh W, Lee
DJ, Lim DS and Lee S: Cancer-upregulated gene 2 (CUG2), a new
component of centromere complex, is required for kinetochore
function. Mol Cells. 27:697–701. 2009. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
4
|
Park EH, Park EH, Cho IR, Srisuttee R, Min
HJ, Oh MJ, Jeong YJ, Jhun BH, Johnston RN, Lee S, et al: CUG2, a
novel oncogene confers reoviral replication through Ras and p38
signaling pathway. Cancer Gene Ther. 17:307–314. 2010. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
5
|
McEntee G, Kyula JN, Mansfield D, Smith H,
Wilkinson M, Gregory C, Roulstone V, Coffey M and Harrington KJ:
Enhanced cytotoxicity of reovirus and radiotherapy in melanoma
cells is mediated through increased viral replication and
mitochondrial apoptotic signalling. Oncotarget. 7:48517–48532.
2016. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
6
|
Sborov DW, Nuovo GJ, Stiff A, Mace T,
Lesinski GB, Benson DM Jr, Efebera YA, Rosko AE, Pichiorri F,
Grever MR, et al: A phase I trial of single-agent reolysin in
patients with relapsed multiple myeloma. Clin Cancer Res.
20:5946–5955. 2014. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
7
|
Malilas W, Koh SS, Srisuttee R, Boonying
W, Cho IR, Jeong CS, Johnston RN and Chung YH: Cancer upregulated
gene 2, a novel oncogene, confers resistance to oncolytic vesicular
stomatitis virus through STAT1-OASL2 signaling. Cancer Gene Ther.
20:125–132. 2013. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
8
|
Malilas W, Koh SS, Kim S, Srisuttee R, Cho
IR, Moon J, Yoo HS, Oh S, Johnston RN and Chung YH: Cancer
upregulated gene 2, a novel oncogene, enhances migration and drug
resistance of colon cancer cells via STAT1 activation. Int J Oncol.
43:1111–1116. 2013. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
9
|
Kaowinn S, Kim J, Lee J, Shin DH, Kang CD,
Kim DK, Lee S, Kang MK, Koh SS, Kim SJ, et al: Cancer upregulated
gene 2 induces epithelial-mesenchymal transition of human lung
cancer cells via TGF-βeta signaling. Oncotarget. 8:5092–5110. 2017.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
10
|
Chin YE, Kitagawa M, Kuida K, Flavell RA
and Fu XY: Activation of the STAT signaling pathway can cause
expression of caspase 1 and apoptosis. Mol Cell Biol. 17:5328–5337.
1997. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
11
|
Kumar A, Commane M, Flickinger TW, Horvath
CM and Stark GR: Defective TNF-alpha-induced apoptosis in
STAT1-null cells due to low constitutive levels of caspases.
Science. 278:1630–1632. 1997. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
12
|
Chin YE, Kitagawa M, Su WC, You ZH,
Iwamoto Y and Fu XY: Cell growth arrest and induction of
cyclin-dependent kinase inhibitor p21WAF1/CIP1 mediated
by STAT1. Science. 272:719–722. 1996. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
13
|
Townsend PA, Scarabelli TM, Davidson SM,
Knight RA, Latchman DS and Stephanou A: STAT-1 interacts with p53
to enhance DNA damage-induced apoptosis. J Biol Chem.
279:5811–5820. 2004. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
14
|
Khodarev NN, Beckett M, Labay E, Darga T,
Roizman B and Weichselbaum RR: STAT1 is overexpressed in tumors
selected for radioresistance and confers protection from radiation
in transduced sensitive cells. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA.
101:1714–1719. 2004. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
15
|
Weichselbaum RR, Ishwaran H, Yoon T,
Nuyten DS, Baker SW, Khodarev N, Su AW, Shaikh AY, Roach P, Kreike
B, et al: An interferon-related gene signature for DNA damage
resistance is a predictive marker for chemotherapy and radiation
for breast cancer. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA. 105:18490–18495. 2008.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
16
|
Fryknas M, Dhar S, Oberg F, Rickardson L,
Rydaker M, Goransson H, Gustafsson M, Pettersson U, Nygren P,
Larsson R and Isaksson A: STAT1 signaling is associated with
acquired crossresistance to doxorubicin and radiation in myeloma
cell lines. Int J Cancer. 120:189–195. 2007. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
17
|
Roberts D, Schick J, Conway S, Biade S,
Laub PB, Stevenson JP, Hamilton TC, O'Dwyer PJ and Johnson SW:
Identification of genes associated with platinum drug sensitivity
and resistance in human ovarian cancer cells. Br J Cancer.
92:1149–1158. 2005. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
18
|
Yang XJ and Seto E: HATs and HDACs: From
structure, function and regulation to novel strategies for therapy
and prevention. Oncogene. 26:5310–5318. 2007. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
19
|
Geng H, Harvey CT, Pittsenbarger J, Liu Q,
Beer TM, Xue C and Qian DZ: HDAC4 protein regulates HIF1α protein
lysine acetylation and cancer cell response to hypoxia. J Biol
Chem. 286:38095–38102. 2011. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
20
|
Mihaylova MM, Vasquez DS, Ravnskjaer K,
Denechaud PD, Yu RT, Alvarez JG, Downes M, Evans RM, Montminy M and
Shaw RJ: Class IIa histone deacetylases are hormone-activated
regulators of FOXO and mammalian glucose homeostasis. Cell.
145:607–621. 2011. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
21
|
Stronach EA, Alfraidi A, Rama N, Datler C,
Studd JB, Agarwal R, Guney TG, Gourley C, Hennessy BT, Mills GB, et
al: HDAC4-regulated STAT1 activation mediates platinum resistance
in ovarian cancer. Cancer Res. 71:4412–4422. 2011. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
22
|
Giaginis C, Alexandrou P, Delladetsima I,
Giannopoulou I, Patsouris E and Theocharis S: Clinical significance
of histone deacetylase (HDAC)-1, HDAC-2, HDAC-4, and HDAC-6
expression in human malignant and benign thyroid lesions. Tumour
Biol. 35:61–71. 2014. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
23
|
Wilson AJ, Byun DS, Nasser S, Murray LB,
Ayyanar K, Arango D, Figueroa M, Melnick A, Kao GD, Augenlicht LH
and Mariadason JM: HDAC4 promotes growth of colon cancer cells via
repression of p21. Mol Biol Cell. 19:4062–4075. 2008. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
24
|
Shen YF, Wei AM, Kou Q, Zhu QY and Zhang
L: Histone deacetylase 4 increases progressive epithelial ovarian
cancer cells via repression of p21 on fibrillar collagen matrices.
Oncol Rep. 35:948–954. 2016. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
25
|
Kang ZH, Wang CY, Zhang WL, Zhang JT, Yuan
CH, Zhao PW, Lin YY, Hong S, Li CY and Wang L: Histone deacetylase
HDAC4 promotes gastric cancer SGC-7901 cells progression via p21
repression. PLoS One. 9:e988942014. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
26
|
Kim SJ, Glick A, Sporn MB and Roberts AB:
Characterization of the promoter region of the human transforming
growth factor-beta 1 gene. J Biol Chem. 264:402–408.
1989.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
27
|
Zhang Y, Wang W, Wang Y, Huang X, Zhang Z,
Chen B, Xie W, Li S, Shen S and Peng B: NEK2 promotes
hepatocellular carcinoma migration and invasion through modulation
of the epithelial-mesenchymal transition. Oncol Rep. 39:1023–1033.
2018.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
28
|
Kramer OH and Heinzel T:
Phosphorylation-acetylation switch in the regulation of STAT1
signaling. Mol Cell Endocrinol. 315:40–48. 2010. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
29
|
Jechlinger M, Sommer A, Moriggl R, Seither
P, Kraut N, Capodiecci P, Donovan M, Cordon-Cardo C, Beug H and
Grunert S: Autocrine PDGFR signaling promotes mammary cancer
metastasis. J Clin Invest. 116:1561–1570. 2006. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
30
|
Seshacharyulu P, Ponnusamy MP, Rachagani
S, Lakshmanan I, Haridas D, Yan Y, Ganti AK and Batra SK: Targeting
EGF-receptor(s)-STAT1 axis attenuates tumor growth and metastasis
through downregulation of MUC4 mucin in human pancreatic cancer.
Oncotarget. 6:5164–5181. 2015. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
31
|
Suyama K, Onishi H, Imaizumi A, Shinkai K,
Umebayashi M, Kubo M, Mizuuchi Y, Oda Y, Tanaka M, Nakamura M, et
al: CD24 suppresses malignant phenotype by downregulation of SHH
transcription through STAT1 inhibition in breast cancer cells.
Cancer Lett. 374:44–53. 2016. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
32
|
Zeng LS, Yang XZ, Wen YF, Mail SJ, Wang
MH, Zhang MY, Zheng XF and Wang HY: Overexpressed HDAC4 is
associated with poor survival and promotes tumor progression in
esophageal carcinoma. Aging. 8:1236–1249. 2016. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
33
|
Kikuchi S, Suzuki R, Ohguchi H, Yoshida Y,
Lu D, Cottini F, Jakubikova J, Bianchi G, Harada T, Gorgun G, et
al: Class IIa HDAC inhibition enhances ER stress-mediated cell
death in multiple myeloma. Leukemia. 29:1918–1927. 2015. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
34
|
Marek L, Hamacher A, Hansen FK, Kuna K,
Gohlke H, Kassack MU and Kurz T: Histone deacetylase (HDAC)
inhibitors with a novel connecting unit linker region reveal a
selectivity profile for HDAC4 and HDAC5 with improved activity
against chemoresistant cancer cells. J Med Chem. 56:427–436. 2013.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
35
|
Kaowinn S, Jun SW, Kim CS, Shin DM, Hwang
YH, Kim K, Shin B, Kaewpiboon C, Jeong HH, Koh SS, et al: Increased
EGFR expression induced by a novel oncogene, CUG2, confers
resistance to doxorubicin through Stat1-HDAC4 signaling. Cell
Oncol. 40:549–561. 2017. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
36
|
Kramer OH, Knauer SK, Greiner G, Jandt E,
Reichardt S, Gührs KH, Stauber RH, Böhmer FD and Heinzel T: A
phosphorylation-acetylation switch regulates STAT1 signaling. Genes
Dev. 23:223–235. 2009. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
37
|
Ginter T, Bier C, Knauer SK, Sughra K,
Hildebrand D, Munz T, Liebe T, Heller R, Henke A, Stauber RH, et
al: Histone deacetylase inhibitors block IFNγ-induced STAT1
phosphorylation. Cell Signal. 24:1453–1460. 2012. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|