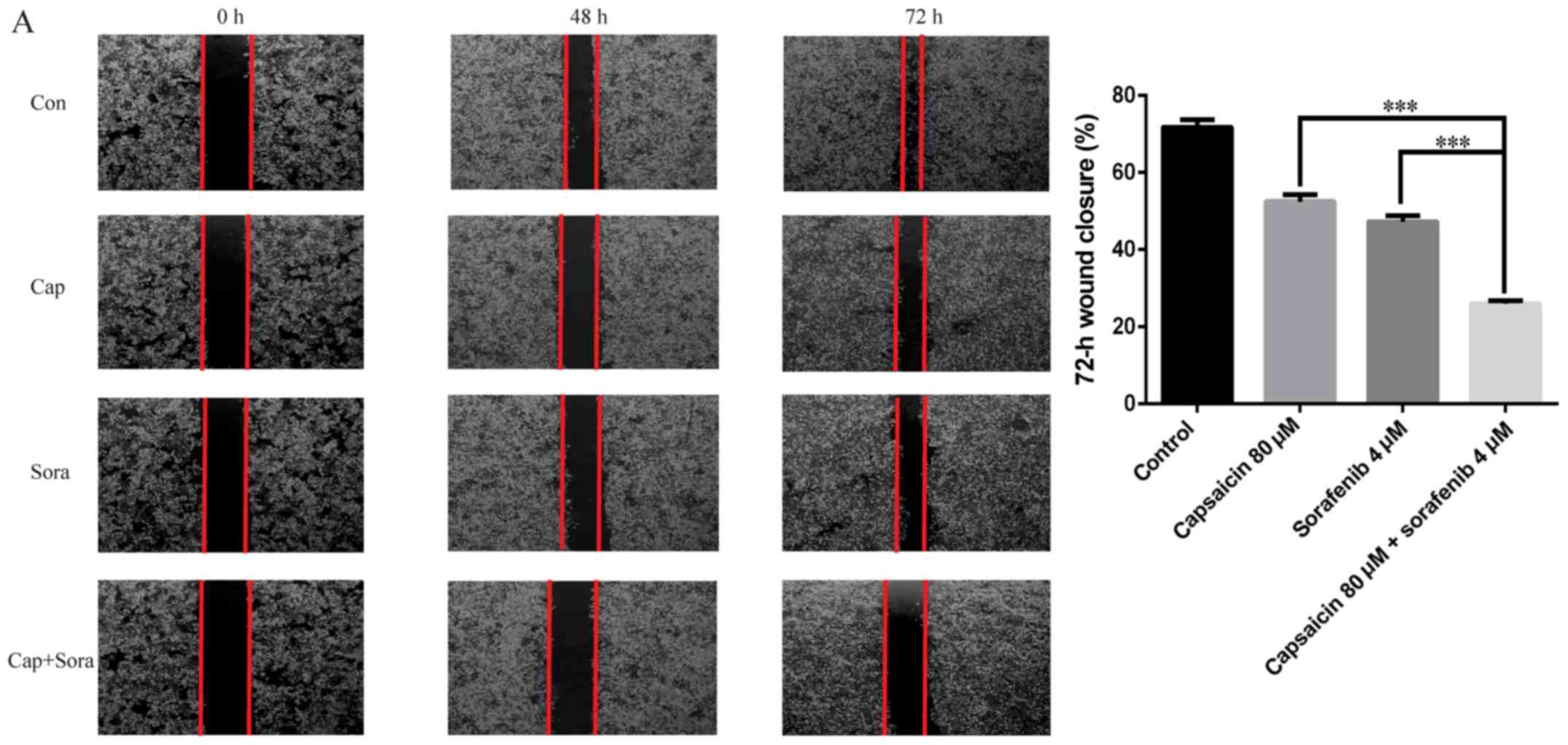
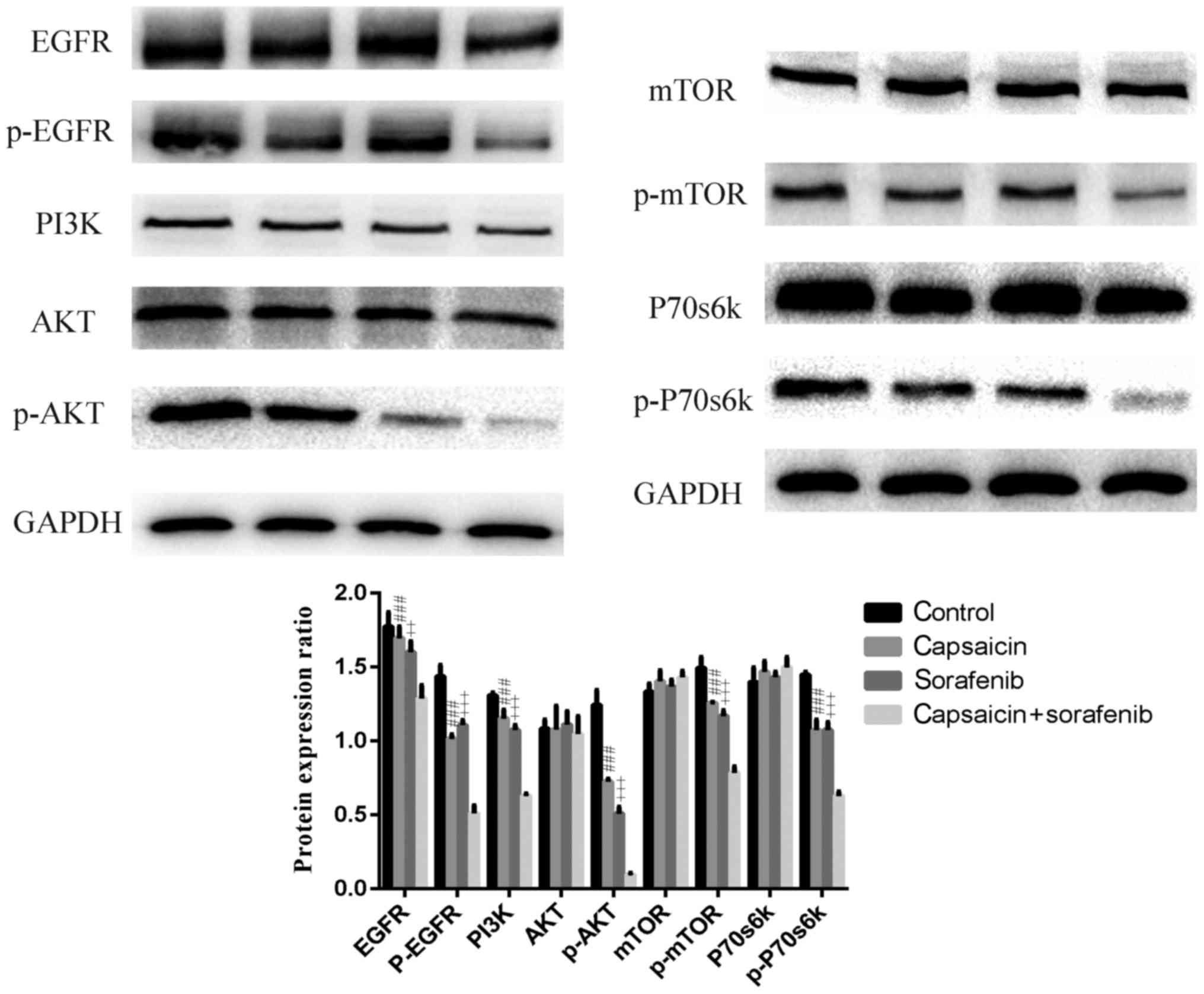
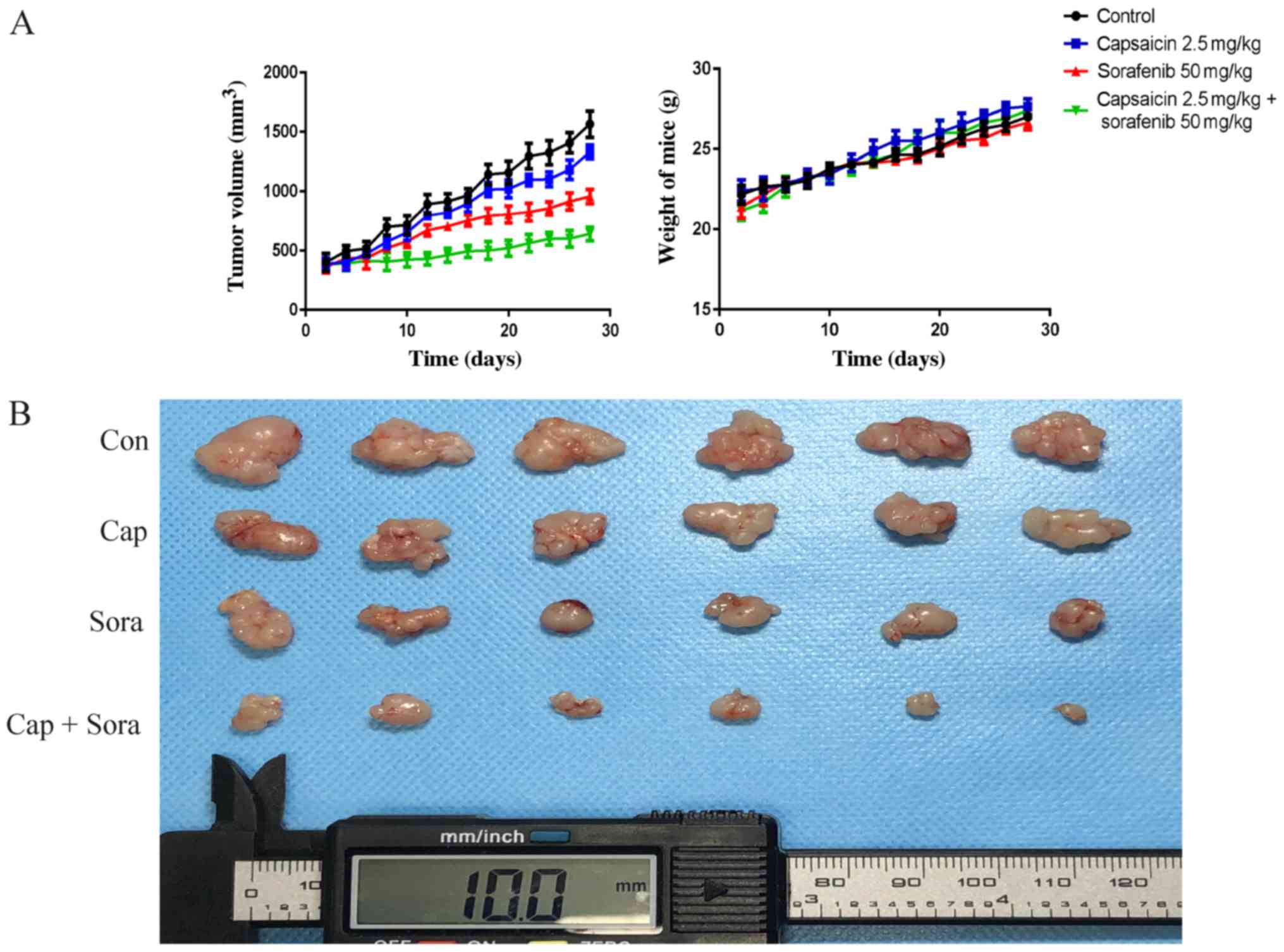
|
1
|
Laursen L: A preventable cancer. Nature.
516 Suppl:S2–S3. 2014. View
Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
2
|
Gomaa AI, Khan SA, Toledano MB, Waked I
and Taylor-Robinson SD: Hepatocellular carcinoma: Epidemiology,
risk factors and pathogenesis. World J Gastroenterol. 14:4300–4308.
2008. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
3
|
Xie B, Wang DH and Spechler SJ: Sorafenib
for treatment of hepatocellular carcinoma: A systematic review. Dig
Dis Sci. 57:1122–1129. 2012. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
4
|
Colombo M and Sangiovanni A: Treatment of
hepatocellular carcinoma: Beyond international guidelines. Liver
Int. 35 Suppl 1:S129–S138. 2015. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
5
|
Llovet JM and Hernandez-Gea V:
Hepatocellular carcinoma: Reasons for phase III failure and novel
perspectives on trial design. Clin Cancer Res. 20:2072–2079. 2014.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
6
|
Osaki M, Oshimura M and Ito H: PI3K-Akt
pathway: Its functions and alterations in human cancer. Apoptosis.
9:667–676. 2004. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
7
|
Wang H and Chen L: Tumor microenviroment
and hepatocellular carcinoma metastasis. J Gastroenterol Hepatol.
28 Suppl 1:S43–S48. 2013. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
8
|
Gao JJ, Shi ZY, Xia JF, Inagaki Y and Tang
W: Sorafenib-based combined molecule targeting in treatment of
hepatocellular carcinoma. World J Gastroenterol. 21:12059–12070.
2015. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
9
|
Sricharoen P, Lamaiphan N, Patthawaro P,
Limchoowong N, Techawongstien S and Chanthai S: Phytochemicals in
Capsicum oleoresin from different varieties of hot chilli peppers
with their antidiabetic and antioxidant activities due to some
phenolic compounds. Ultrason Sonochem. 38:629–639. 2017. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
10
|
Diaz-Laviada I and Rodriguez-Henche N: The
potential antitumor effects of capsaicin. Prog Drug Res
Fortschritte der Arzneimittelforschung Progres Des Recherches
Pharm. 68:181–208. 2014.
|
|
11
|
Nazıroğlu M, Çiğ B, Blum W, Vizler C,
Buhala A, Marton A, Katona R, Jósvay K, Schwaller B, Oláh Z and
Pecze L: Targeting breast cancer cells by MRS1477, a positive
allosteric modulator of TRPV1 channels. PLoS One. 12:e01799502017.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
12
|
Lee JY, Lee SY, Kim GG, Hur MG, Yang SD,
Park JH and Kim SW: Development of
68Ga-SCN-DOTA-Capsaicin as an imaging agent targeting
apoptosis and cell cycle arrest in breast cancer. Cancer Biother
Radiopharm. 32:169–175. 2017. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
13
|
Yoshitani SI, Tanaka T, Kohno H and
Takashima S: Chemoprevention of azoxymethane-induced rat colon
carcinogenesis by dietary capsaicin and rotenone. Int J Oncol.
19:929–939. 2001.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
14
|
Kim YM, Hwang JT, Kwak DW, Lee YK and Park
OJ: Involvement of AMPK signaling cascade in capsaicin-induced
apoptosis of HT-29 colon cancer cells. Ann N Y Acad Sci.
1095:496–503. 2007. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
15
|
Lin YT, Wang HC, Hsu YC, Cho CL, Yang MY
and Chien CY: Capsaicin induces autophagy and apoptosis in human
nasopharyngeal carcinoma cells by downregulating the PI3K/AKT/mTOR
pathway. Int J Mol Sci. 18:E13432017. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
16
|
Wu CC, Lin JP, Yang JS, Chou ST, Chen SC,
Lin YT, Lin HL and Chung JG: Capsaicin induced cell cycle arrest
and apoptosis in human esophagus epidermoid carcinoma CE 81T/VGH
cells through the elevation of intracellular reactive oxygen
species and Ca2+ productions and caspase-3 activation. Mutat Res.
601:71–82. 2006. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
17
|
Huang SP, Chen JC, Wu CC, Chen CT, Tang
NY, Ho YT, Lo C, Lin JP, Chung JG and Lin JG: Capsaicin-induced
apoptosis in human hepatoma HepG2 cells. Anticancer Res.
29:165–174. 2009.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
18
|
Chen X, Tan M, Xie Z, Feng B, Zhao Z, Yang
K, Hu C, Liao N, Wang T, Chen D, et al: Inhibiting
ROS-STAT3-dependent autophagy enhanced capsaicin-induced apoptosis
in human hepatocellular carcinoma cells. Free Radic Res.
50:744–755. 2016. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
19
|
Lee JH, Kim C, Baek SH, Ko JH, Lee SG,
Yang WM, Um JY, Sethi G and Ahn KS: Capsazepine inhibits JAK/STAT3
signaling, tumor growth, and cell survival in prostate cancer.
Oncotarget. 8:17700–17711. 2017.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
20
|
Xin M and Deng X: Nicotine inactivation of
the proapoptotic function of Bax through phosphorylation. J Biol
Chem. 280:10781–10789. 2005. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
21
|
Yu X, Long YC and Shen HM: Differential
regulatory functions of three classes of phosphatidylinositol and
phosphoinositide 3-kinases in autophagy. Autophagy. 11:1711–1728.
2015. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
22
|
Choudhari SK, Chaudhary M, Bagde S,
Gadbail AR and Joshi V: Nitric oxide and cancer: A review. World J
Surg Oncol. 11:1182013. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
23
|
Qian Y, Corum L, Meng Q, Blenis J, Zheng
JZ, Shi X, Flynn DC and Jiang BH: PI3K induced actin filament
remodeling through Akt and p70S6K1: Implication of essential role
in cell migration. Am J Physiol Cell Physiol. 286:C153–C163. 2004.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
24
|
Kim D, Kim S, Koh H, Yoon SO, Chung AS,
Cho KS and Chung J: Akt/PKB promotes cancer cell invasion via
increased motility and metalloproteinase production. FASEB J.
15:1953–1962. 2001. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
25
|
Grille SJ, Bellacosa A, Upson J,
Klein-Szanto AJ, van Roy F, Lee-Kwon W, Donowitz M, Tsichlis PN and
Larue L: The protein kinase Akt induces epithelial mesenchymal
transition and promotes enhanced motility and invasiveness of
squamous cell carcinoma lines. Cancer Res. 63:2172–2178.
2003.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
26
|
Nicholson RI, Gee JM and Harper ME: EGFR
and cancer prognosis. Eur J Cancer. 37 Suppl 4:S9–S15. 2001.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
27
|
Kannangai R, Sahin F and Torbenson MS:
EGFR is phosphorylated at Ty845 in hepatocellular carcinoma. Mod
Pathol. 19:1456–1461. 2006. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
28
|
O'Reilly KE, Rojo F, She QB, Solit D,
Mills GB, Smith D, Lane H, Hofmann F, Hicklin DJ, Ludwig DL, et al:
mTOR inhibition induces upstream receptor tyrosine kinase signaling
and activates Akt. Cancer Res. 66:1500–1508. 2006. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
29
|
Cheng GZ, Park S, Shu S, He L, Kong W,
Zhang W, Yuan Z, Wang LH and Cheng JQ: Advances of AKT pathway in
human oncogenesis and as a target for anti-cancer drug discovery.
Curr Cancer Drug Targets. 8:2–6. 2008. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
30
|
Hwang YP, Yun HJ, Choi JH, Han EH, Kim HG,
Song GY, Kwon KI, Jeong TC and Jeong HG: Suppression of EGF-induced
tumor cell migration and matrix metalloproteinase-9 expression by
capsaicin via the inhibition of EGFR-mediated FAK/Akt, PKC/Raf/ERK,
p38 MAPK, and AP-1 signaling. Mol Nutr Food Res. 55:594–605. 2011.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
31
|
Zhang CZ, Wang XD, Wang HW, Cai Y and Chao
LQ: Sorafenib inhibits liver cancer growth by decreasing mTOR, AKT,
and PI3K expression. J BUON. 20:218–222. 2015.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
32
|
Cui SX, Shi WN, Song ZY, Wang SQ, Yu XF,
Gao ZH and Qu XJ: Des-gamma-carboxy prothrombin antagonizes the
effects of Sorafenib on human hepatocellular carcinoma through
activation of the Raf/MEK/ERK and PI3K/Akt/mTOR signaling pathways.
Oncotarget. 7:36767–36782. 2016. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
33
|
Jiang S, Wang Q, Feng M, Li J, Guan Z, An
D, Dong M, Peng Y, Kuerban K and Ye L: C2-ceramide enhances
sorafenib-induced caspase-dependent apoptosis via PI3K/AKT/mTOR and
Erk signaling pathways in HCC cells. Appl Microbiol Biotechnol.
101:1535–1546. 2017. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
34
|
Lee DH, Szczepanski MJ and Lee YJ:
Magnolol induces apoptosis via inhibiting the EGFR/PI3K/Akt
signaling pathway in human prostate cancer cells. J Cell Biochem.
106:1113–1122. 2009. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
35
|
Zhang L, Wang F, Jiang Y, Xu S, Lu F, Wang
W and Sun X and Sun X: Migration of retinal pigment epithelial
cells is EGFR/PI3K/AKT dependent. Front Biosci (Schol Ed).
5:661–671. 2013. View
Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
36
|
He C and Klionsky DJ: Regulation
mechanisms and signaling pathways of autophagy. Ann Rev Genet.
43:67–93. 2009. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
37
|
Jacinto E, Facchinetti V, Liu D, Soto N,
Wei S, Jung SY, Huang Q, Qin J and Su B: SIN1/MIP1 maintains
rictor-mTOR complex integrity and regulates Akt phosphorylation and
substrate specificity. Cell. 127:125–137. 2006. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
38
|
Li TT, Zhu D, Mou T, Guo Z, Pu JL, Chen
QS, Wei XF and Wu ZJ: IL-37 induces autophagy in hepatocellular
carcinoma cells by inhibiting the PI3K/AKT/mTOR pathway. Mol
Immunol. 87:132–140. 2017. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
39
|
Wang SS, Chen YH, Chen N, Wang LJ, Chen
DX, Weng HL, Dooley S and Ding HG: Hydrogen sulfide promotes
autophagy of hepatocellular carcinoma cells through the
PI3K/Akt/mTOR signaling pathway. Cell Death Dis. 8:e26882017.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|