|
1
|
Cho KR and Shih Ie M: Ovarian cancer. Annu
Rev Pathol. 4:287–313. 2009. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
2
|
Kurman RJ and Shih Ie M: The origin and
pathogenesis of epithelial ovarian cancer: A proposed unifying
theory. Am J Surg Pathol. 34:433–443. 2010. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
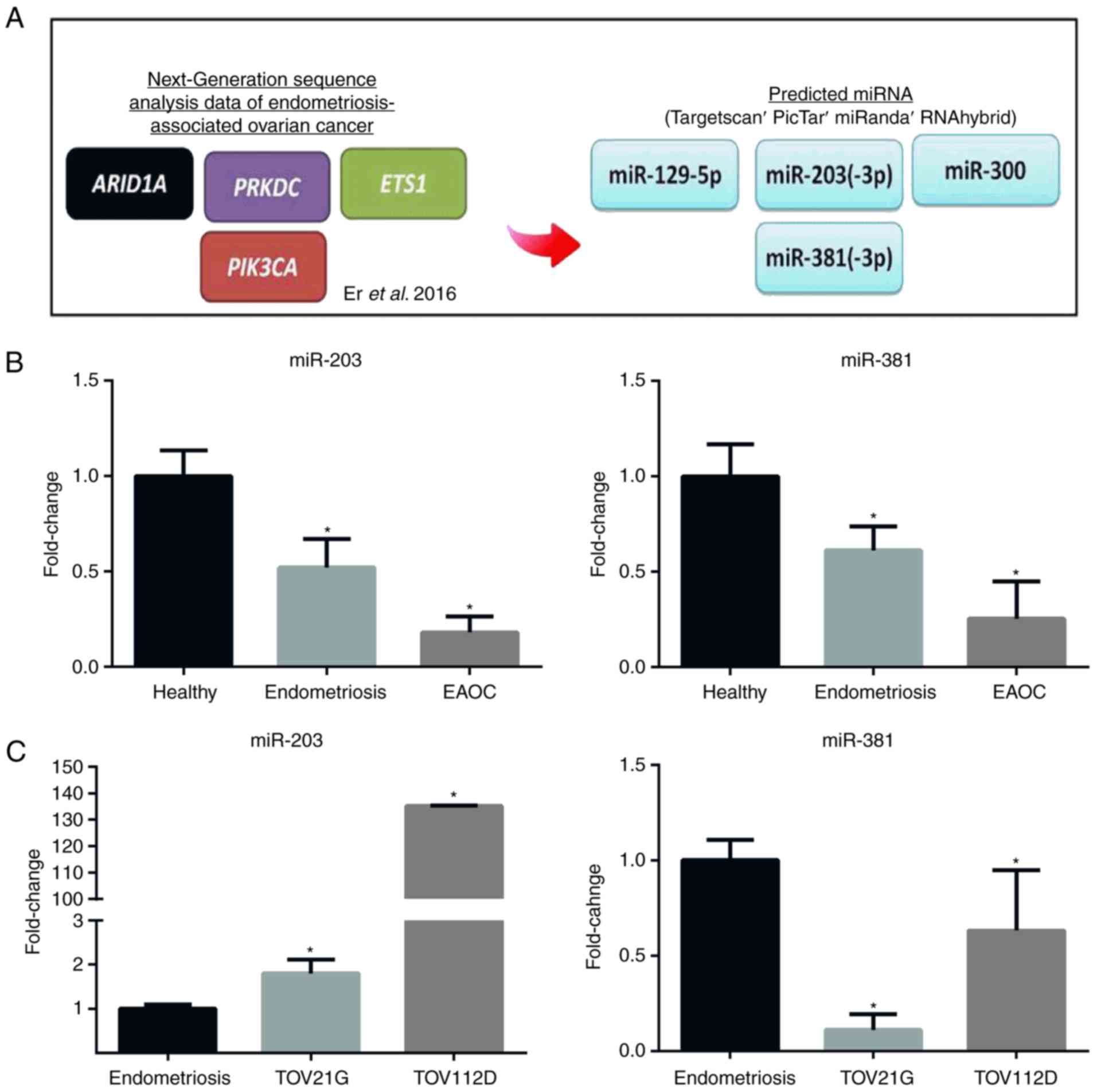
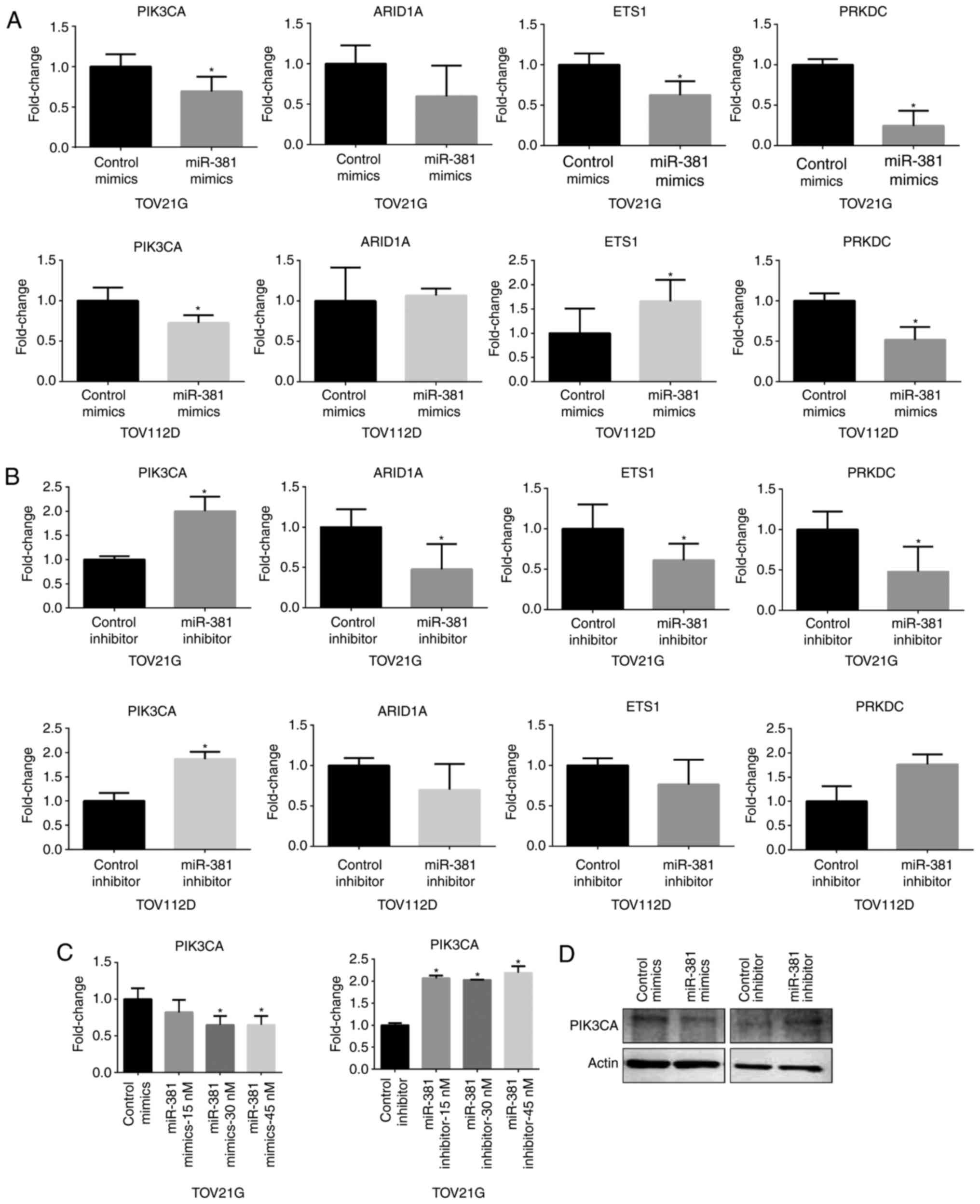
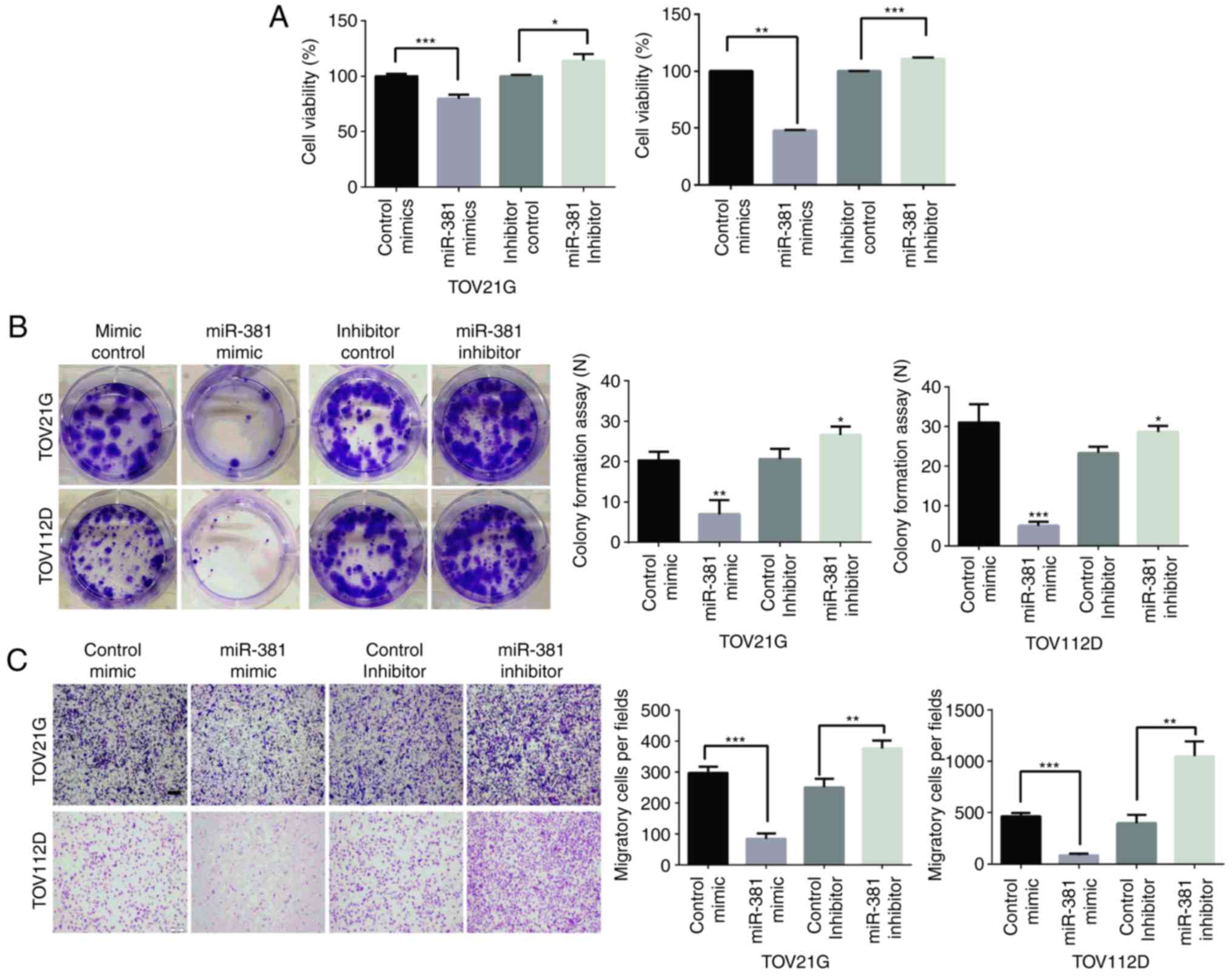
|
3
|
Koshiyama M, Matsumura N and Konishi I:
Recent concepts of ovarian carcinogenesis: Type I and type II.
Biomed Res Int. 2014:9342612014. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
4
|
Shen H and Laird PW: Interplay between the
cancer genome and epigenome. Cell. 153:38–55. 2013. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
5
|
Berdasco M and Esteller M: Aberrant
epigenetic landscape in cancer: How cellular identity goes awry.
Dev Cell. 19:698–711. 2010. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
6
|
Shih IeM and Kurman RJ: Ovarian
tumorigenesis: A proposed model based on morphological and
molecular genetic analysis. Am J Pathol. 164:1511–1518. 2004.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
7
|
Jones S, Wang TL, Shih IeM, Mao TL,
Nakayama K, Roden R, Glas R, Slamon D, Diaz LA Jr, Vogelstein B, et
al: Frequent mutations of chromatin remodeling gene ARID1A in
ovarian clear cell carcinoma. Science. 330:228–231. 2010.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
8
|
Campbell IG, Russell SE, Choong DY,
Montgomery KG, Ciavarella ML, Hooi CS, Cristiano BE, Pearson RB and
Phillips WA: Mutation of the PIK3CA gene in ovarian and breast
cancer. Cancer Res. 64:7678–7681. 2004. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
9
|
Wiegand KC, Shah SP, Al-Agha OM, Zhao Y,
Tse K, Zeng T, Senz J, McConechy MK, Anglesio MS, Kalloger SE, et
al: ARID1A mutations in endometriosis-associated ovarian
carcinomas. N Engl J Med. 363:1532–1543. 2010. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
10
|
Ahmed AA, Etemadmoghadam D, Temple J,
Lynch AG, Riad M, Sharma R, Stewart C, Fereday S, Caldas C, Defazio
A, et al: Driver mutations in TP53 are ubiquitous in high grade
serous carcinoma of the ovary. J Pathol. 221:49–56. 2010.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
11
|
Bartel DP: MicroRNAs: Genomics,
biogenesis, mechanism, and function. Cell. 116:281–297. 2004.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
12
|
Calin GA and Croce CM: MicroRNA signatures
in human cancers. Nat Rev Cancer. 6:857–866. 2006. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
13
|
Er TK, Su YF, Wu CC, Chen CC, Wang J,
Hsieh TH, Herreros-Villanueva M, Chen WT, Chen YT, Liu TC, et al:
Targeted next-generation sequencing for molecular diagnosis of
endometriosis-associated ovarian cancer. J Mol Med. 94:835–847.
2016. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
14
|
Kao AP, Wang KH, Chang CC, Lee JN, Long
CY, Chen HS, Tsai CF, Hsieh TH and Tsai EM: Comparative study of
human eutopic and ectopic endometrial mesenchymal stem cells and
the development of an in vivo endometriotic invasion model. Fertil
Steril. 95:1308–1315.e1. 2011. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
15
|
Ryan IP, Schriock ED and Taylor RN:
Isolation, characterization, and comparison of human endometrial
and endometriosis cells in vitro. J Clin Endocrinol Metab.
78:642–649. 1994. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
16
|
Revised American Society for Reproductive
Medicine classification of endometriosis: 1996. Fertil Steril.
67:817–821. 1997. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
17
|
Prat J: FIGO Committee on Gynecologic
Oncology: FIGO's staging classification for cancer of the ovary,
fallopian tube, and peritoneum: Abridged republication. J Gynecol
Oncol. 26:87–89. 2015. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
18
|
Livak KJ and Schmittgen TD: Analysis of
relative gene expression data using real-time quantitative PCR and
the 2−ΔΔCT method. Methods. 25:402–408. 2001. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
19
|
Farre D, Roset R, Huerta M, Adsuara JE,
Roselló L, Albà MM and Messeguer X: Identification of patterns in
biological sequences at the ALGGEN server: PROMO and MALGEN.
Nucleic Acids Res. 31:3651–3653. 2003. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
20
|
Lewis BP, Burge CB and Bartel DP:
Conserved seed pairing, often flanked by adenosines, indicates that
thousands of human genes are microRNA targets. Cell. 120:15–20.
2005. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
21
|
Franken NA, Rodermond HM, Stap J, Haveman
J and van Bree C: Clonogenic assay of cells in vitro. Nat Protoc.
1:2315–2319. 2006. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
22
|
Li H, Zeng J and Shen K: PI3K/AKT/mTOR
signaling pathway as a therapeutic target for ovarian cancer. Arch
Gynecol Obstet. 290:1067–1078. 2014. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
23
|
Ferrara N and Kerbel RS: Angiogenesis as a
therapeutic target. Nature. 438:967–974. 2005. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
24
|
Nakayama I, Shibazaki M, Yashima-Abo A,
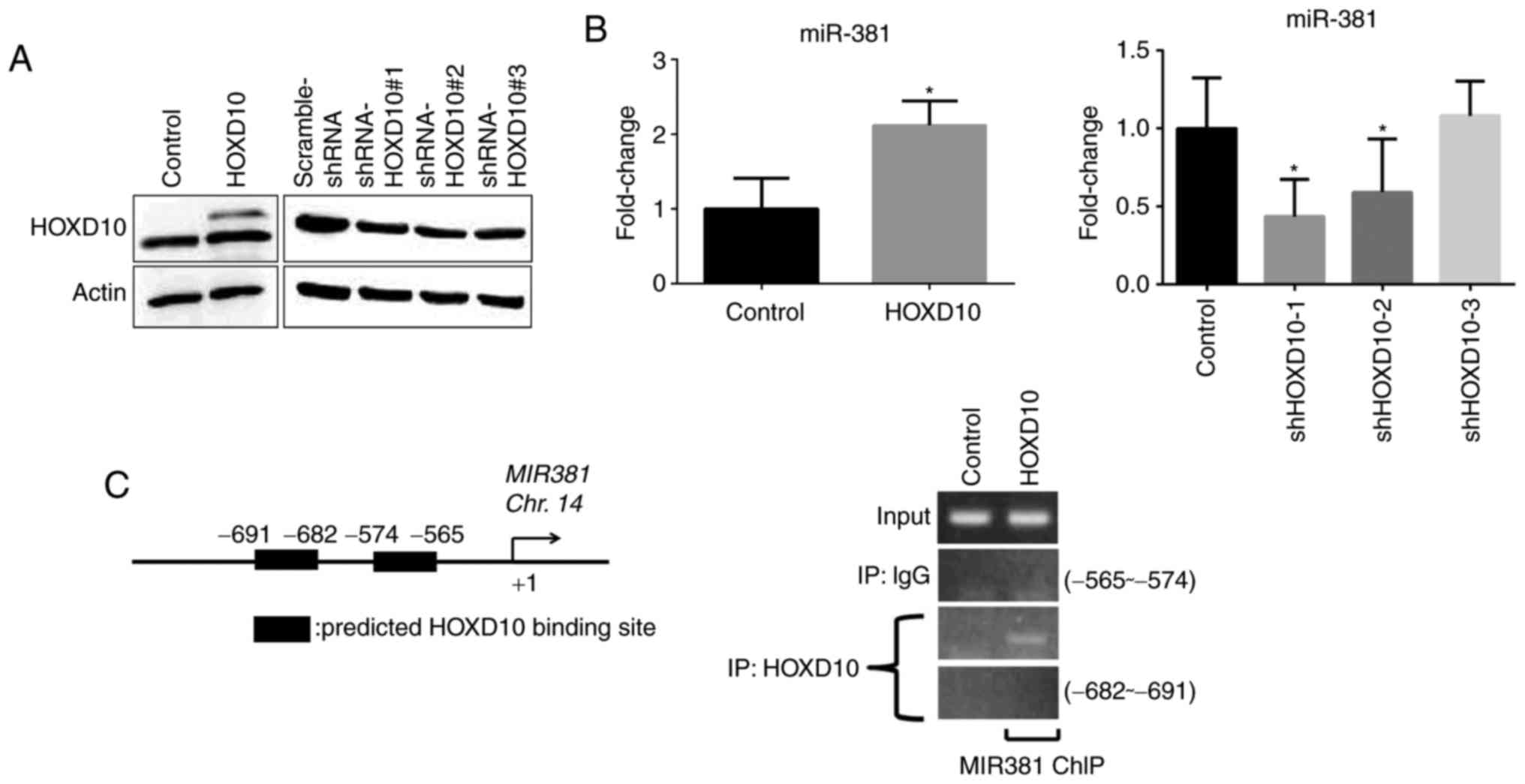
Miura F, Sugiyama T, Masuda T and Maesawa C: Loss of HOXD10
expression induced by upregulation of miR-10b accelerates the
migration and invasion activities of ovarian cancer cells. Int J
Oncol. 43:63–71. 2013. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
25
|
Chen X, Ba Y, Ma L, Cai X, Yin Y, Wang K,
Guo J, Zhang Y, Chen J, Guo X, et al: Characterization of microRNAs
in serum: A novel class of biomarkers for diagnosis of cancer and
other diseases. Cell Res. 18:997–1006. 2008. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
26
|
Ambros V: The functions of animal
microRNAs. Nature. 431:350–355. 2004. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
27
|
Iorio MV, Visone R, Di Leva G, Donati V,
Petrocca F, Casalini P, Taccioli C, Volinia S, Liu CG, Alder H, et
al: MicroRNA signatures in human ovarian cancer. Cancer Res.
67:8699–8707. 2007. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
28
|
Dahiya N and Morin PJ: MicroRNAs in
ovarian carcinomas. Endocr Relat Cancer. 17:F77–F89. 2010.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
29
|
Mateescu B, Batista L, Cardon M, Gruosso
T, de Feraudy Y, Mariani O, Nicolas A, Meyniel JP, Cottu P,
Sastre-Garau X and Mechta-Grigoriou F: miR-141 and miR-200a act on
ovarian tumorigenesis by controlling oxidative stress response. Nat
Med. 17:1627–1635. 2011. View
Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
30
|
He X, Wei Y, Wang Y, Liu L, Wang W and Li
N: MiR-381 functions as a tumor suppressor in colorectal cancer by
targeting Twist1. Onco Targets Ther. 9:1231–1239. 2016.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
31
|
Xue Y, Xu W, Zhao W, Wang W, Zhang D and
Wu P: miR-381 inhibited breast cancer cells proliferation,
epithelial-to-mesenchymal transition and metastasis by targeting
CXCR4. Biomed Pharmacother. 86:426–433. 2017. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
32
|
Xia B, Li H, Yang S, Liu T and Lou G:
MiR-381 inhibits epithelial ovarian cancer malignancy via YY1
suppression. Tumour Biol. 37:9157–9167. 2016. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
33
|
Xu Y, Ohms SJ, Li Z, Wang Q, Gong G, Hu Y,
Mao Z, Shannon MF and Fan JY: Changes in the expression of miR-381
and miR-495 are inversely associated with the expression of the
MDR1 gene and development of multi-drug resistance. PLoS One.
8:e820622013. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
34
|
Boren T, Xiong Y, Hakam A, Wenham R, Apte
S, Chan G, Kamath SG, Chen DT, Dressman H and Lancaster JM:
MicroRNAs and their target messenger RNAs associated with ovarian
cancer response to chemotherapy. Gynecol Oncol. 113:249–255. 2009.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
35
|
Lee S, Choi EJ, Jin C and Kim DH:
Activation of PI3K/Akt pathway by PTEN reduction and PIK3CA mRNA
amplification contributes to cisplatin resistance in an ovarian
cancer cell line. Gynecol Oncol. 97:26–34. 2005. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
36
|
Mitsuuchi Y, Johnson SW, Selvakumaran M,
Williams SJ, Hamilton TC and Testa JR: The phosphatidylinositol
3-kinase/AKT signal transduction pathway plays a critical role in
the expression of p21WAF1/CIP1/SDI1 induced by cisplatin
and paclitaxel. Cancer Res. 60:5390–5394. 2000.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
37
|
Astanehe A, Arenillas D, Wasserman WW,
Leung PC, Dunn SE, Davies BR, Mills GB and Auersperg N: Mechanisms
underlying p53 regulation of PIK3CA transcription in ovarian
surface epithelium and in ovarian cancer. J Cell Sci. 121:664–674.
2008. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
38
|
Carrio M, Arderiu G, Myers C and Boudreau
NJ: Homeobox D10 induces phenotypic reversion of breast tumor cells
in a three-dimensional culture model. Cancer Res. 65:7177–7185.
2005. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
39
|
Xiao H, Li H, Yu G, Xiao W, Hu J, Tang K,
Zeng J, He W, Zeng G, Ye Z and Xu H: MicroRNA-10b promotes
migration and invasion through KLF4 and HOXD10 in human bladder
cancer. Oncol Rep. 31:1832–1838. 2014. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
40
|
Yang H, Zhou J, Mi J, Ma K, Fan Y, Ning J,
Wang C, Wei X, Zhao H and Li E: HOXD10 acts as a tumor-suppressive
factor via inhibition of the RHOC/AKT/MAPK pathway in human
cholangiocellular carcinoma. Oncol Rep. 34:1681–1691. 2015.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
41
|
Reddy SD, Ohshiro K, Rayala SK and Kumar
R: MicroRNA-7, a homeobox D10 target, inhibits p21-activated kinase
1 and regulates its functions. Cancer Res. 68:8195–8200. 2008.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
42
|
Myers C, Charboneau A, Cheung I, Hanks D
and Boudreau N: Sustained expression of homeobox D10 inhibits
angiogenesis. Am J Pathol. 161:2099–2109. 2002. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
43
|
Ma L, Teruya-Feldstein J and Weinberg RA:
Tumour invasion and metastasis initiated by microRNA-10b in breast
cancer. Nature. 449:682–688. 2007. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|