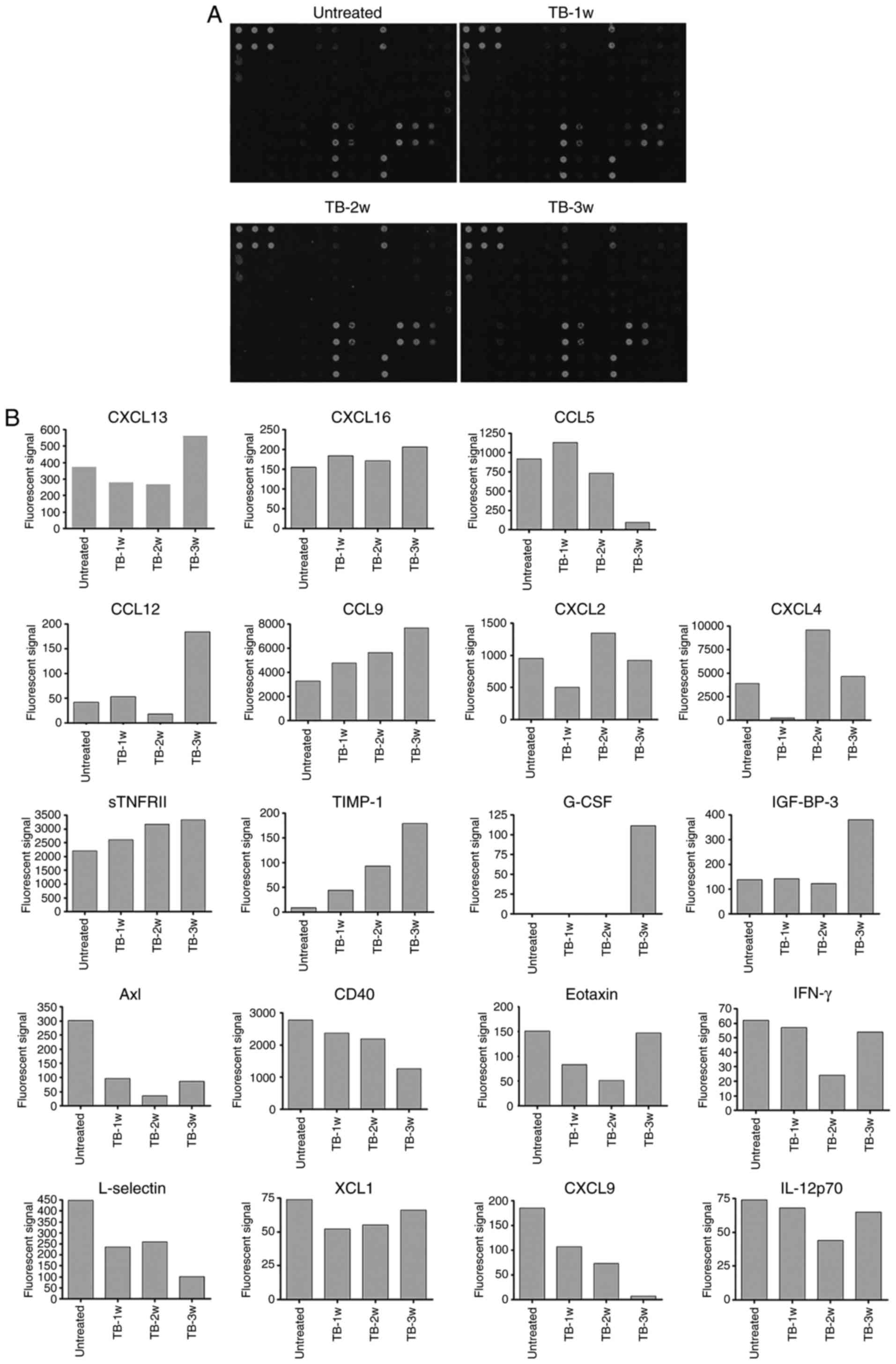
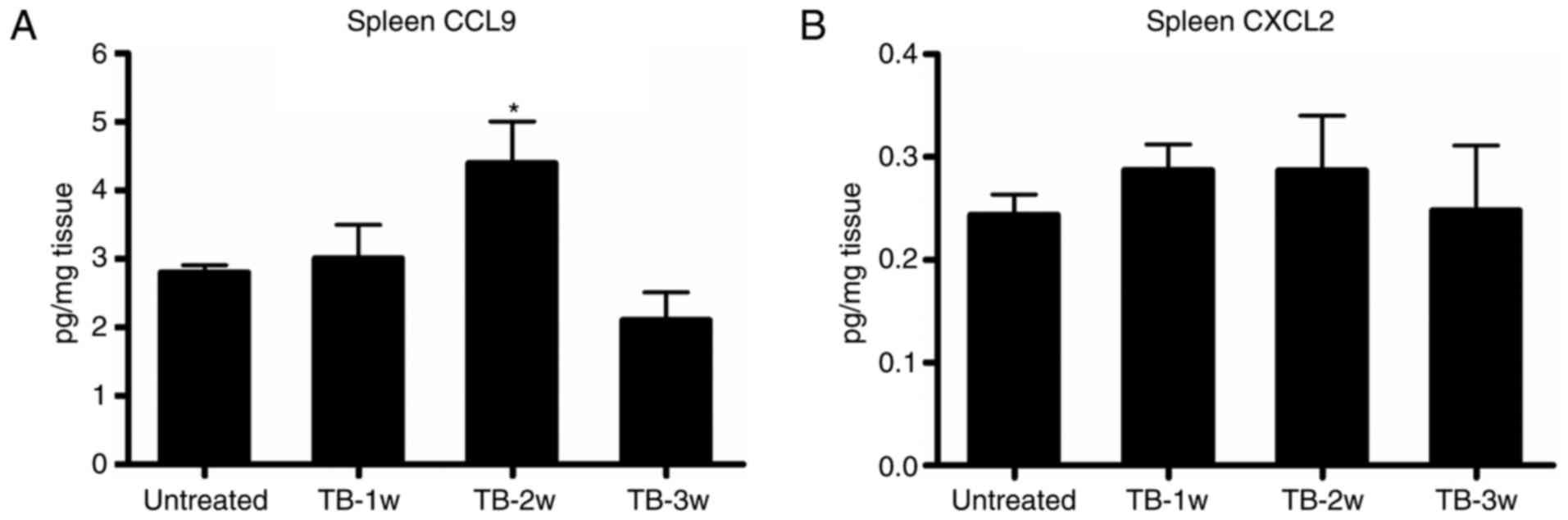
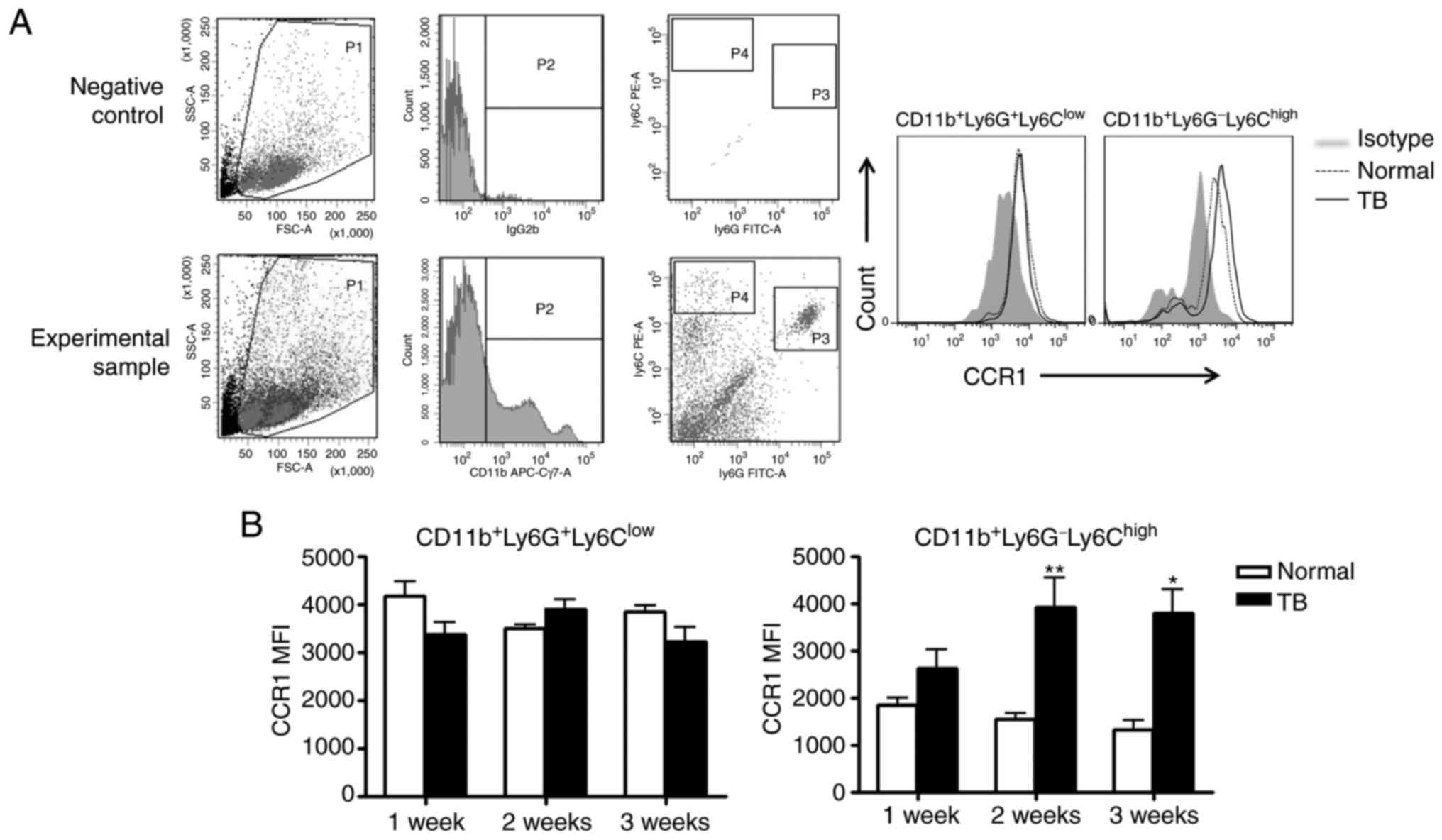
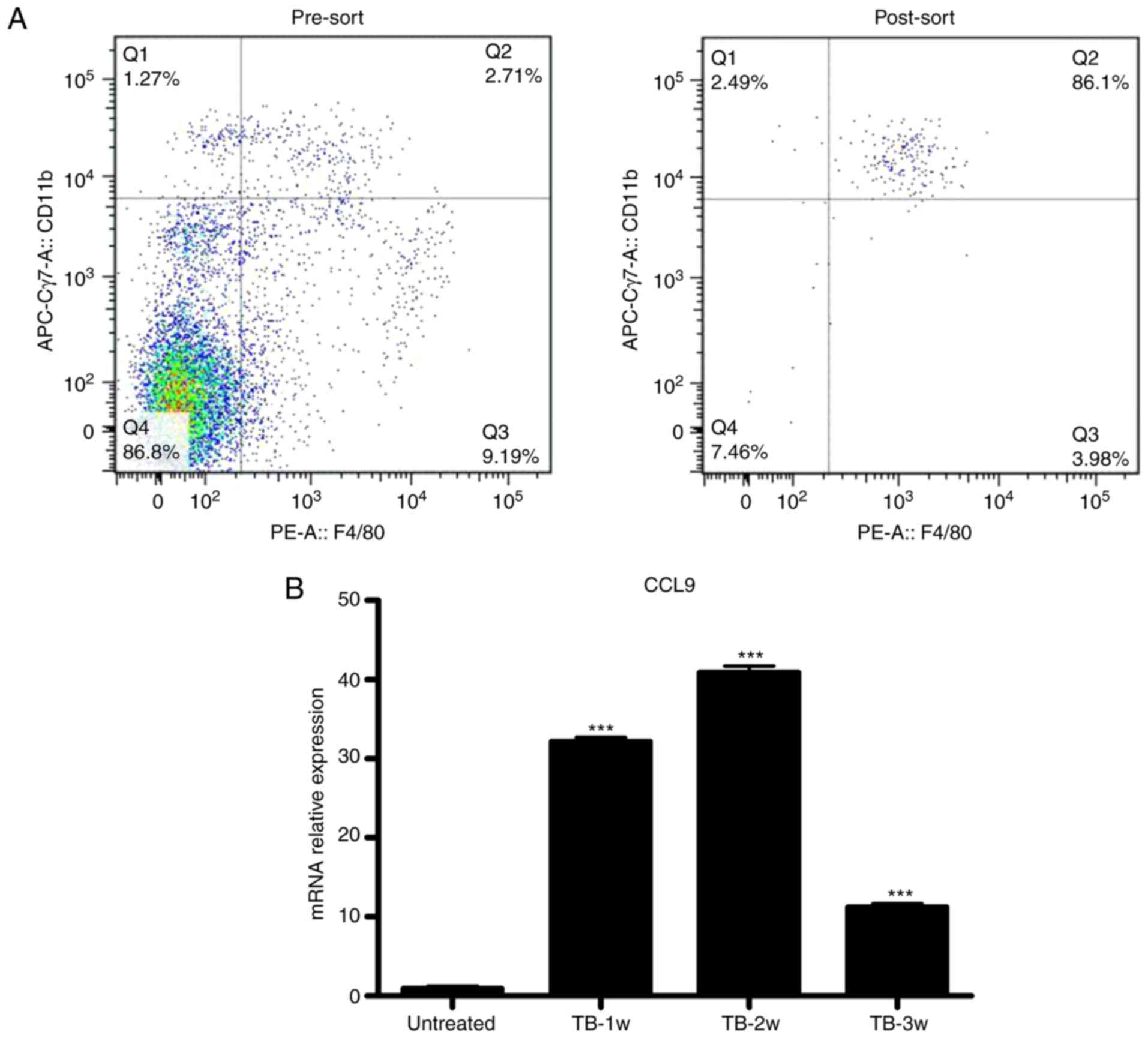
|
1
|
Talmadge JE and Gabrilovich DI: History of
myeloid-derived suppressor cells. Nat Rev Cancer. 13:739–752. 2013.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
2
|
Schrader J: The role of MDSCs in
hepatocellular carcinoma-in vivo veritas? J Hepatol. 59:921–923.
2013. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
3
|
Kumar V, Patel S, Tcyganov E and
Gabrilovich DI: The nature of myeloid-derived suppressor cells in
the tumor microenvironment. Trends Immunol. 37:208–220. 2016.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
4
|
Arina A and Bronte V: Myeloid-derived
suppressor cell impact on endogenous and adoptively transferred T
cells. Curr Opin Immunol. 33:120–125. 2015. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
5
|
Pan PY, Ma G, Weber KJ, Ozao-Choy J, Wang
G, Yin B, Divino CM and Chen SH: Immune stimulatory receptor CD40
is required for T-cell suppression and T regulatory cell activation
mediated by myeloid-derived suppressor cells in cancer. Cancer Res.
70:99–108. 2010. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
6
|
Gabrilovich DI: Myeloid-derived suppressor
cells. Cancer Immunol Res. 5:3–8. 2017. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
7
|
Pardoll DM: Distinct mechanisms of tumor
resistance to NK killing: Of mice and men. Immunity. 42:605–606.
2015. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
8
|
You TG, Wang HS, Yang JH, Qian QJ, Fan RF
and Wu MC: Transfection of IL-2 and/or IL-12 genes into spleen in
treatment of rat liver cancer. World J Gastroenterol. 10:2190–2194.
2004. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
9
|
Imai S, Nio Y, Shiraishi T, Tsubono M,
Morimoto H, Tseng CC, Kawabata K, Masai Y and Tobe T: Effects of
splenectomy on pulmonary metastasis and growth of SC42 carcinoma
transplanted into mouse liver. J Surg Oncol. 47:178–187. 1991.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
10
|
Zusman I, Kossoy G and Ben-Hur H: T cell
kinetics and apoptosis in immune organs and mammary tumors of rats
treated with cyclophosphamide and soluble tumor-associated
antigens. In Vivo. 16:567–576. 2002.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
11
|
Cortez-Retamozo V, Etzrodt M, Newton A,
Rauch PJ, Chudnovskiy A, Berger C, Ryan RJ, Iwamoto Y, Marinelli B,
Gorbatov R, et al: Origins of tumor-associated macrophages and
neutrophils. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA. 109:2491–2496. 2012.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
12
|
Li B, Zhang S, Huang N, Chen H, Wang P, Li
J, Pu Y, Yang J and Li Z: Dynamics of the spleen and its
significance in a murine H22 orthotopic hepatoma model. Exp Biol
Med. 241:863–872. 2016. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
13
|
Levy L, Mishalian I, Bayuch R, Zolotarov
L, Michaeli J and Fridlender ZG: Splenectomy inhibits non-small
cell lung cancer growth by modulating anti-tumor adaptive and
innate immune response. Oncoimmunology. 4:e9984692015. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
14
|
Serafini P, Carbley R, Noonan KA, Tan G,
Bronte V and Borrello I: High-dose granulocyte-macrophage
colony-stimulating factor-producing vaccines impair the immune
response through the recruitment of myeloid suppressor cells.
Cancer Res. 64:6337–6343. 2004. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
15
|
Waight JD, Hu Q, Miller A, Liu S and
Abrams SI: Tumor-derived G-CSF facilitates neoplastic growth
through a granulocytic myeloid-derived suppressor cell-dependent
mechanism. PLoS One. 6:e276902011. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
16
|
Markiewski MM, DeAngelis RA, Benencia F,
Ricklin-Lichtsteiner SK, Koutoulaki A, Gerard C, Coukos G and
Lambris JD: Modulation of the antitumor immune response by
complement. Nat Immunol. 9:1225–1235. 2008. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
17
|
Shields JD, Kourtis IC, Tomei AA, Roberts
JM and Swartz MA: Induction of lymphoidlike stroma and immune
escape by tumors that express the chemokine CCL21. Science.
328:749–752. 2010. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
18
|
Yu F, Shi Y, Wang J, Li J, Fan D and Ai W:
Deficiency of Kruppel-like factor KLF4 in mammary tumor cells
inhibits tumor growth and pulmonary metastasis and is accompanied
by compromised recruitment of myeloid-derived suppressor cells. Int
J Cancer. 133:2872–2883. 2013.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
19
|
Zhou Y and Guo F: A selective
sphingosine-1-phosphate receptor 1 agonist SEW-2871 aggravates
gastric cancer by recruiting myeloid-derived suppressor cells. J
Biochem. 163:77–83. 2018. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
20
|
Chang AL, Miska J, Wainwright DA, Dey M,
Rivetta CV, Yu D, Kanojia D, Pituch KC, Qiao J, Pytel P, et al:
CCL2 produced by the glioma microenvironment is essential for the
recruitment of regulatory T cells and myeloid-derived suppressor
cells. Cancer Res. 76:5671–5682. 2016. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
21
|
Blattner C, Fleming V, Weber R, Himmelhan
B, Altevogt P, Gebhardt C, Schulze TJ, Razon H, Hawila E, Wildbaum
G, et al: CCR5+ myeloid-derived suppressor cells are
enriched and activated in melanoma lesions. Cancer Res. 78:157–167.
2018. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
22
|
Yamamoto T, Kawada K, Itatani Y, Inamoto
S, Okamura R, Iwamoto M, Miyamoto E, Chen-Yoshikawa TF, Hirai H,
Hasegawa S, et al: Loss of SMAD4 promotes lung metastasis of
colorectal cancer by accumulation of CCR1+
tumor-associated neutrophils through CCL15-CCR1 axis. Clin Cancer
Res. 23:833–844. 2017. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
23
|
Long X, Ye Y, Zhang L, Liu P, Yu W, Wei F,
Ren X and Yu J: I L-8, a novel messenger to cross-link inflammation
and tumor EMT via autocrine and paracrine pathways (Review). Int J
Oncol. 48:5–12. 2016. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
24
|
Kapanadze T, Gamrekelashvili J, Ma C, Chan
C, Zhao F, Hewitt S, Zender L, Kapoor V, Felsher DW, Manns MP, et
al: Regulation of accumulation and function of myeloid derived
suppressor cells in different murine models of hepatocellular
carcinoma. J Hepatol. 59:1007–1013. 2013. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
25
|
Bunt SK, Yang L, Sinha P, Clements VK,
Leips J and Ostrand-Rosenberg S: Reduced inflammation in the tumor
microenvironment delays the accumulation of myeloid-derived
suppressor cells and limits tumor progression. Cancer Res.
67:10019–10026. 2007. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
26
|
Sinha P, Clements VK, Fulton AM and
Ostrand-Rosenberg S: Prostaglandin E2 promotes tumor progression by
inducing myeloid-derived suppressor cells. Cancer Res.
67:4507–4513. 2007. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
27
|
Eisenblaetter M, Flores-Borja F, Lee JJ,
Wefers C, Smith H, Hueting R, Cooper MS, Blower PJ, Patel D,
Rodriguez-Justo M, et al: Visualization of tumor-immune
interaction-target-specific imaging of S100A8/A9 reveals
pre-metastatic niche establishment. Theranostics. 7:2392–2401.
2017. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
28
|
Ba H, Li B, Li X, Li C, Feng A, Zhu Y,
Wang J, Li Z and Yin B: Transmembrane tumor necrosis factor-α
promotes the recruitment of MDSCs to tumor tissue by upregulating
CXCR4 expression via TNFR2. Int Immunopharmacol. 44:143–152. 2017.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
29
|
Ugel S, Peranzoni E, Desantis G, Chioda M,
Walter S, Weinschenk T, Ochando JC, Cabrelle A, Mandruzzato S and
Bronte V: Immune tolerance to tumor antigens occurs in a
specialized environment of the spleen. Cell Rep. 2:628–639. 2012.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
30
|
Schmittgen TD and Livak KJ: Analyzing
real-time PCR data by the comparative C(T) method. Nat Protoc.
3:1101–1108. 2008. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
31
|
Xu P, He H, Gu Y, Wang Y, Sun Z, Yang L
and Miao C: Surgical trauma contributes to progression of colon
cancer by downregulating CXCL4 and recruiting MDSCs. Exp Cell Res.
370:692–698. 2018. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
32
|
Vandercappellen J, Van Damme J and Struyf
S: The role of the CXC chemokines platelet factor-4 (CXCL4/PF-4)
and its variant (CXCL4L1/PF-4var) in inflammation, angiogenesis and
cancer. Cytokine Growth Factor Rev. 22:1–18. 2011. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
33
|
Wang Z and Huang H: Platelet factor-4
(CXCL4/PF-4): An angiostatic chemokine for cancer therapy. Cancer
Lett. 331:147–153. 2013. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
34
|
Youn BS, Jang IK, Broxmeyer HE, Cooper S,
Jenkins NA, Gilbert DJ, Copeland NG, Elick TA, Fraser MJ Jr and
Kwon BS: A novel chemokine, macrophage inflammatory protein-related
protein-2, inhibits colony formation of bone marrow myeloid
progenitors. J Immunol. 155:2661–2667. 1995.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
35
|
Clark CE, Hingorani SR, Mick R, Combs C,
Tuveson DA and Vonderheide RH: Dynamics of the immune reaction to
pancreatic cancer from inception to invasion. Cancer Res.
67:9518–9527. 2007. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
36
|
Younos IH, Dafferner AJ, Gulen D, Britton
HC and Talmadge JE: Tumor regulation of myeloid-derived suppressor
cell proliferation and trafficking. Int Immunopharmacol.
13:245–256. 2012. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
37
|
Sawanobori Y, Ueha S, Kurachi M, Shimaoka
T, Talmadge JE, Abe J, Shono Y, Kitabatake M, Kakimi K, Mukaida N,
et al: Chemokine-mediated rapid turnover of myeloid-derived
suppressor cells in tumor-bearing mice. Blood. 111:5457–5466. 2008.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
38
|
Lean JM, Murphy C, Fuller K and Chambers
TJ: CC L9/MIP-1gamma and its receptor CCR1 are the major chemokine
ligand/receptor species expressed by osteoclasts. J Cell Biochem.
87:386–393. 2002. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
39
|
Yan HH, Jiang J, Pang Y, Achyut BR,
Lizardo M, Liang X, Hunter K, Khanna C, Hollander C and Yang L:
CCL9 induced by TGFβ signaling in myeloid cells enhances tumor cell
survival in the premetastatic organ. Cancer Res. 75:5283–5298.
2015. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
40
|
Kitamura T, Fujishita T, Loetscher P,
Revesz L, Hashida H, Kizaka-Kondoh S, Aoki M and Taketo MM:
Inactivation of chemokine (C-C motif) receptor 1 (CCR1) suppresses
colon cancer liver metastasis by blocking accumulation of immature
myeloid cells in a mouse model. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA.
107:13063–13068. 2010. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
41
|
Fujimi S, Lapchak PH, Zang Y, MacConmara
MP, Maung AA, Delisle AJ, Mannick JA and Lederer JA: Murine
dendritic cell antigen-presenting cell function is not altered by
burn injury. J Leukoc Biol. 85:862–870. 2009. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
42
|
Gatto D, Wood K, Caminschi I,
Murphy-Durland D, Schofield P, Christ D, Karupiah G and Brink R:
The chemotactic receptor EBI2 regulates the homeostasis,
localization and immunological function of splenic dendritic cells.
Nat Immunol. 14:446–453. 2013. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
43
|
Zhang S, Li ZF, Pan D, Huang C, Zhou R and
Liu ZW: Changes of splenic macrophage during the process of liver
cancer induced by diethylnitrosamine in rats. Chin Med J.
122:3043–3047. 2009.PubMed/NCBI
|