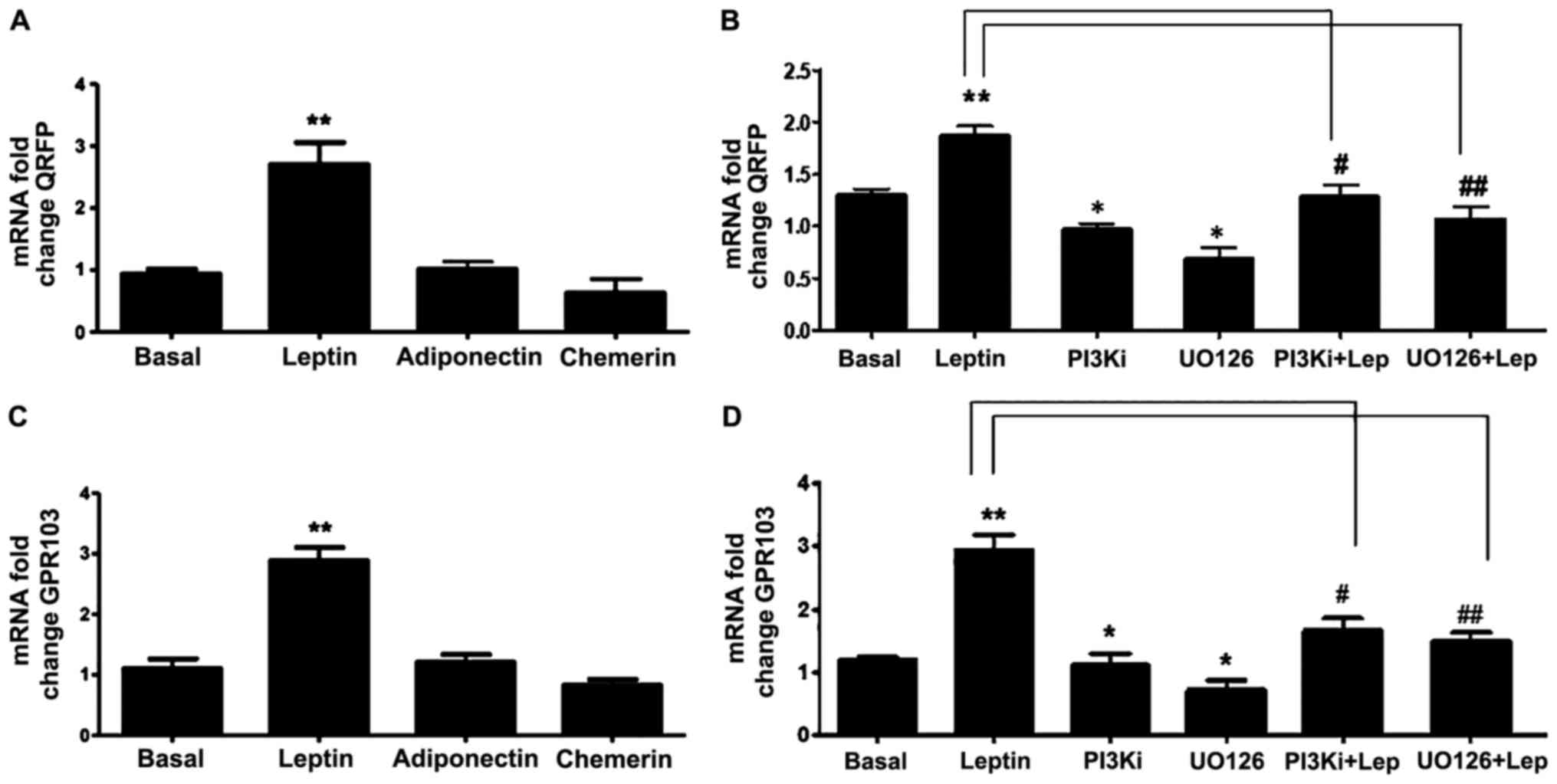
|
1
|
Findeisen M, Rathmann D and Beck-Sickinger
AG: RFamide peptides: Structure, function, mechanisms and
pharmaceutical potential. Pharmaceuticals. 4:1248–1280. 2011.
View Article : Google Scholar :
|
|
2
|
Ukena K, Vaudry H, Leprince J and Tsutsui
K: Molecular evolution and functional characterization of the
orexigenic peptide 26RFa and its receptor in vertebrates. Cell
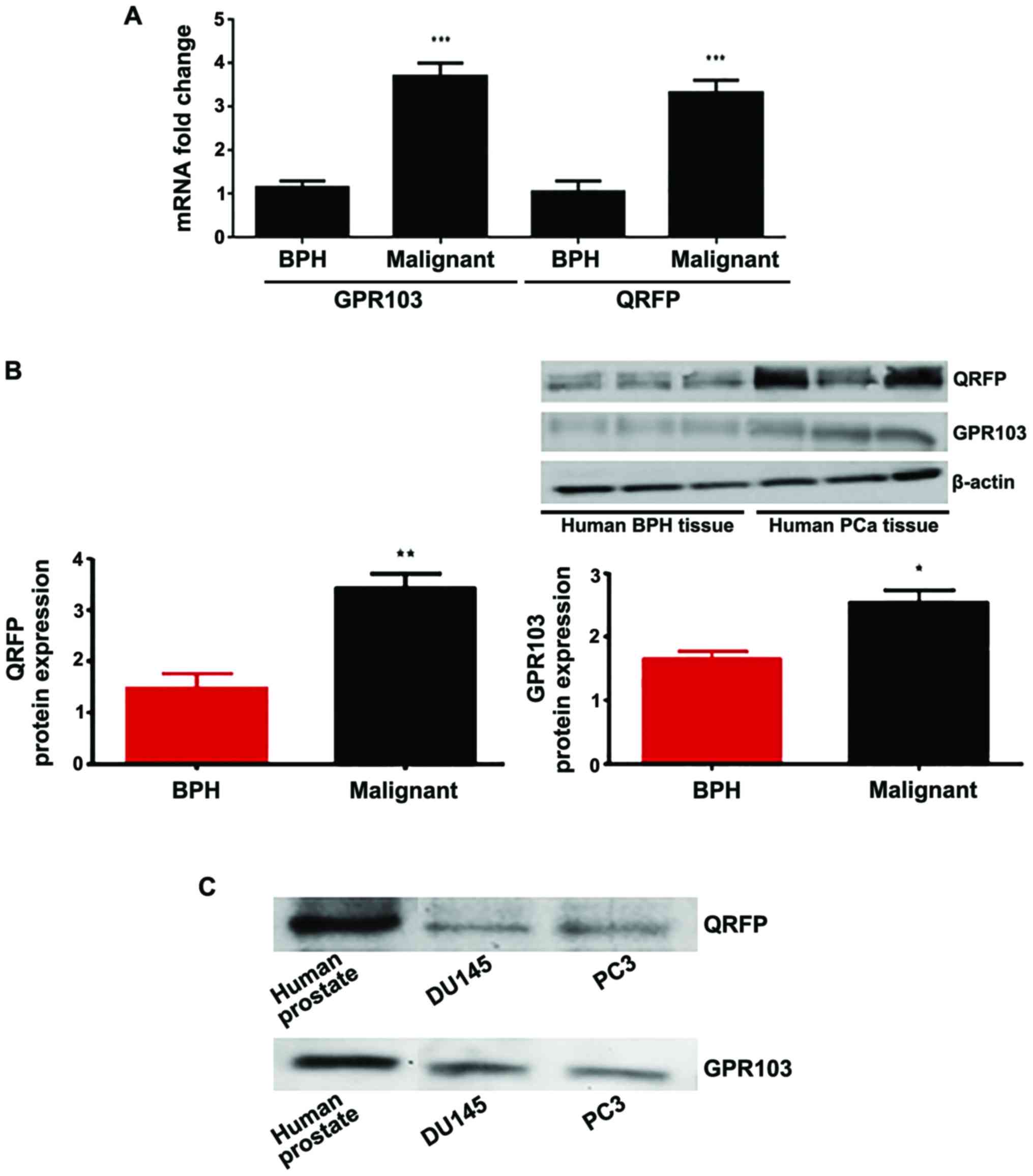
Tissue Res. 343:475–81. 2011. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
3
|
Sandvik GK, Hodne K, Haug TM, Okubo K and
Weltzien FA: RFamide peptides in early vertebrate development.
Front Endocrinol. 5:2032014. View Article : Google Scholar
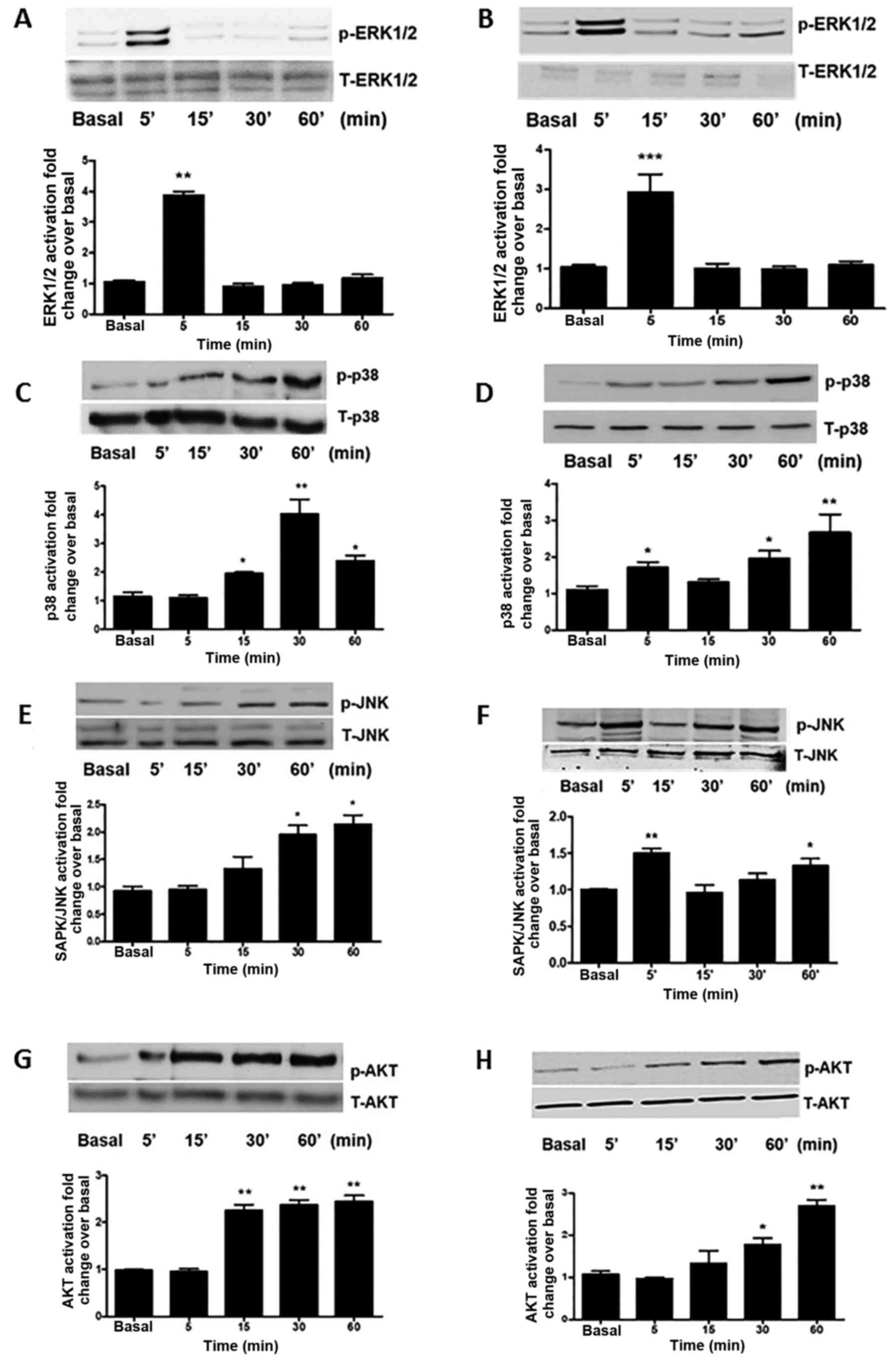
|
|
4
|
Chartrel N, Dujardin C, Anouar Y, Leprince
J, Decker A, Clerens S, Do-Régo JC, Vandesande F, Llorens-Cortes C,
Costentin J, et al: Identification of 26RFa, a hypothalamic
neuropeptide of the RFamide peptide family with orexigenic
activity. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA. 100:15247–52. 2003. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
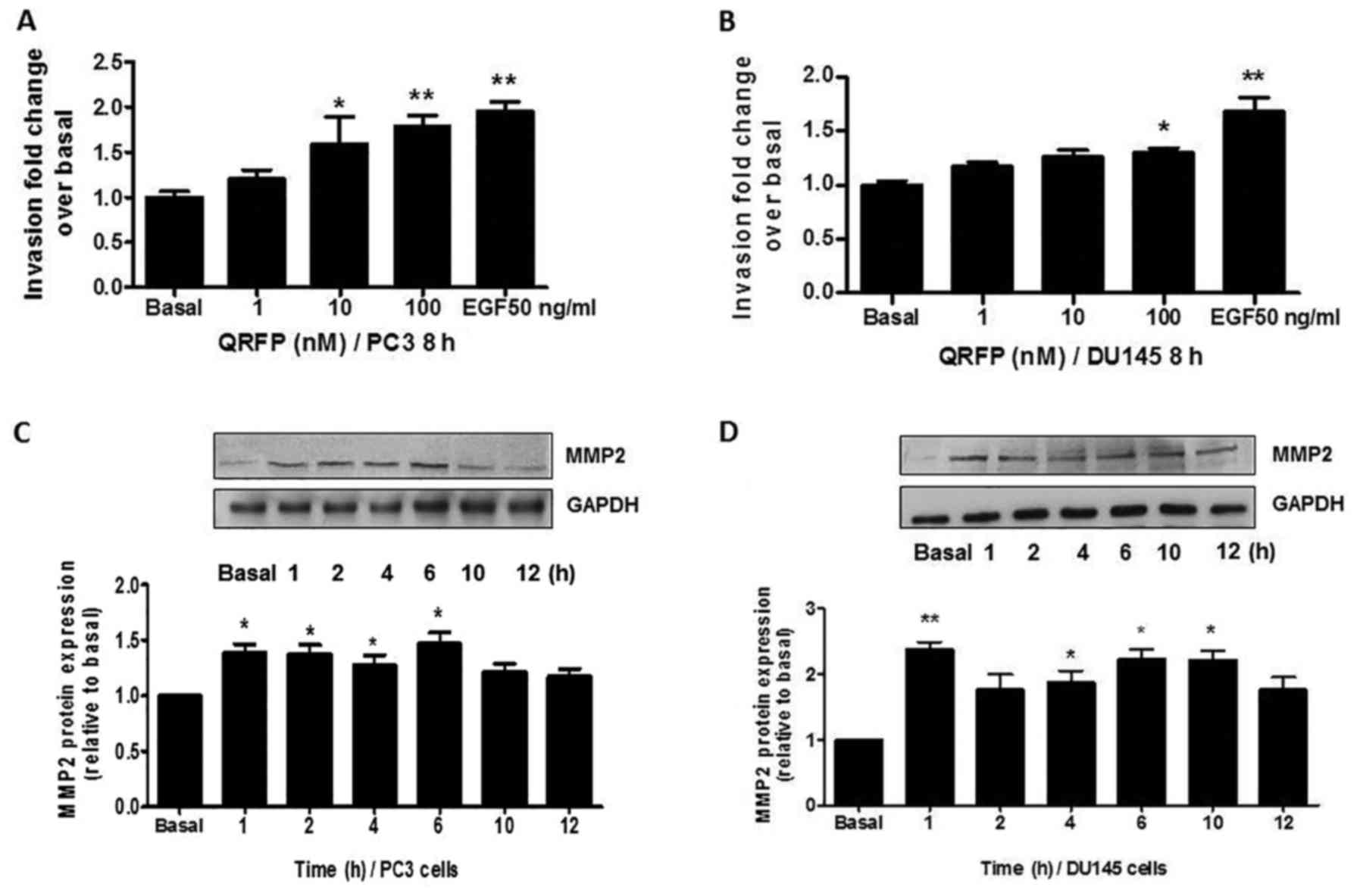
5
|
Bruzzone F, Lectez B, Tollemer H, Leprince
J, Dujardin C, Rachidi W, Chatenet D, Baroncini M, Beauvillain JC,
Vallarino M, et al: Anatomical distribution and biochemical
characterization of the novel RFamide peptide 26RFa in the human
hypothalamus and spinal cord. J Neurochem. 99:616–627. 2006.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
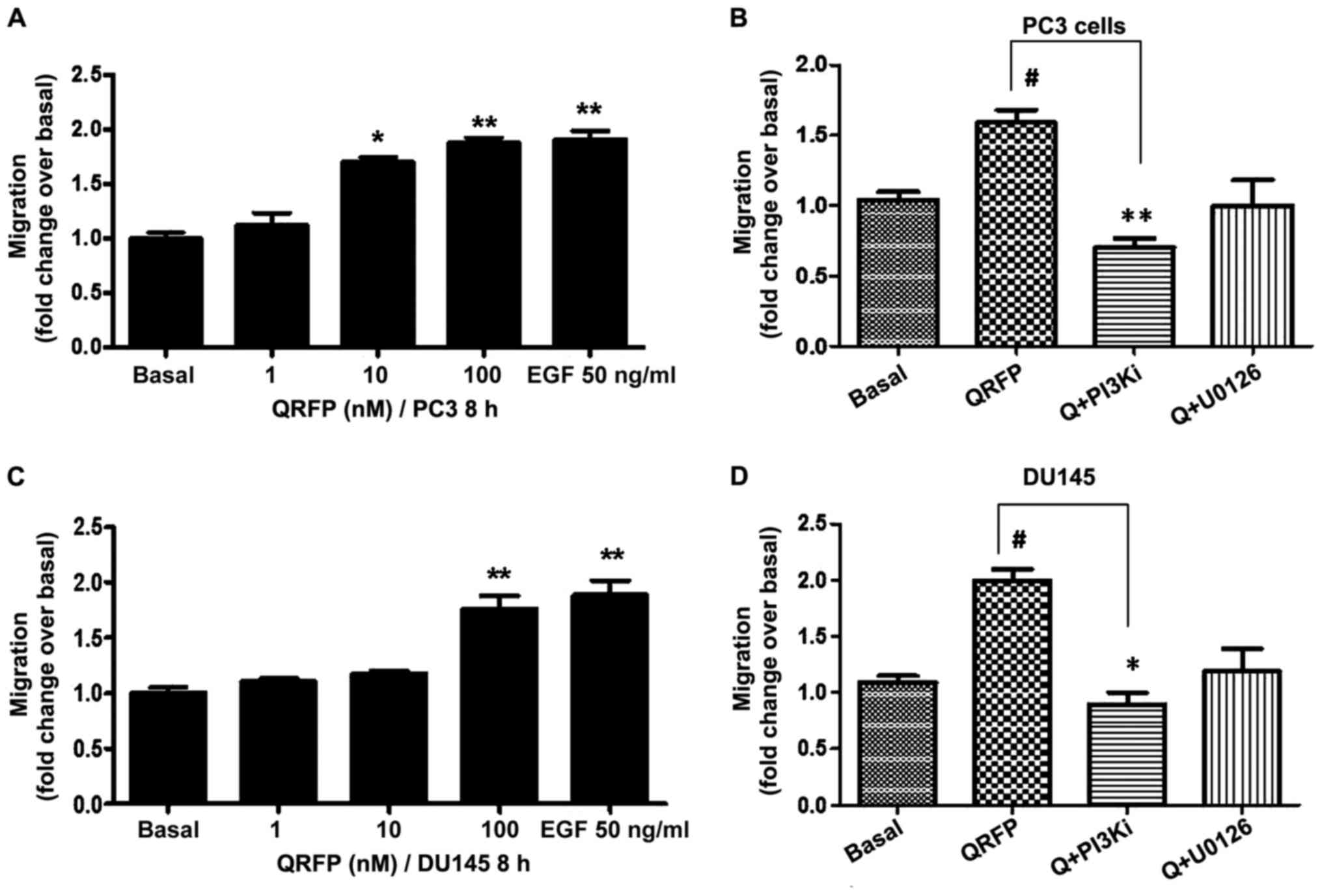
|
|
6
|
Takayasu S, Sakurai T, Iwasaki S,
Teranishi H, Yamanaka A, Williams SC, Iguchi H, Kawasawa YI, Ikeda
Y, Sakakibara I, et al: A neuropeptide ligand of the G
protein-coupled receptor GPR103 regulates feeding, behavioral
arousal, and blood pressure in mice. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA.
103:7438–7443. 2006. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
7
|
Leprince J, Bagnol D, Bureau R, Fukusumi
S, Granata R, Hinuma S, Larhammar D, Primeaux S, Sopkova-de
Oliveiras, Santos J, Tsutsui K, et al: The Arg-Phe-amide peptide
26RFa/glutamine RF-amide peptide and its receptor: IUPHAR Review
24. Br J Pharmacol. 174:3573–3607. 2017. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
8
|
Jiang Y, Luo L, Gustafson EL, Yadav D,
Laverty M, Murgolo N, Vassileva G, Zeng M, Laz TM, Behan J, et al:
Identification and characterization of a novel RF-amide peptide
ligand for orphan G-protein-coupled receptor SP9155. J Biol Chem.
278:27652–27657. 2003. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
9
|
Fukusumi S, Yoshida H, Fujii R, Maruyama
M, Komatsu H, Habata Y, Shintani Y, Hinuma S and Fujino M: A new
peptidic ligand and its receptor regulating adrenal function in
rats. J Biol Chem. 278:46387–46395. 2003. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
10
|
Baribault H, Danao J, Gupte J, Yang L, Sun
B, Richards W and Tian H: The G-protein-coupled receptor GPR103
regulates bone formation. Mol Cell Biol. 26:709–717. 2006.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
11
|
Moriya R, Sano H, Umeda T, Ito M,
Takahashi Y, Matsuda M, Ishihara A, Kanatani A and Iwaasa H:
RFamide peptide QRFP43 causes obesity with hyperphagia and reduced
thermogenesis in mice. Endocrinology. 147:2916–2922. 2006.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
12
|
Navarro VM, Fernández-Fernández R,
Nogueiras R, Vigo E, Tovar S, Chartrel N, Le Marec O, Leprince J,
Aguilar E, Pinilla L, et al: Novel role of 26RFa, a hypothalamic
RFamide orexigenic peptide, as putative regulator of the
gonadotropic axis. J Physiol. 573:237–249. 2006. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
13
|
Patel SR, Murphy KG, Thompson EL,
Patterson M, Curtis AE, Ghatei MA and Bloom SR: Pyroglutamylated
RFamide peptide 43 stimulates the hypothalamic-pituitary-gonadal
axis via gonadotropin-releasing hormone in rats. Endocrinology.
149:4747–4754. 2008. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
14
|
Alonzeau J, Alexandre D, Jeandel L, Courel
M, Hautot C, El Yamani FZ, Gobet F, Leprince J, Magoul R, Amarti A,
et al: The neuropeptide 26RFa is expressed in human prostate cancer
and stimulates the neuroendocrine differentiation and the migration
of androgeno-independent prostate cancer cells. Eur J Cancer.
49:511–519. 2013. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
15
|
Ørsted DD, Bojesen SE, Nielsen SF and
Nordestgaard BG: Association of clinical benign prostate
hyperplasia with prostate cancer incidence and mortality revisited:
A nationwide cohort study of 3,009,258 men. Eur Urol. 60:691–698.
2011. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
16
|
Ervik M, Lam F, Ferlay J, Mery L,
Soerjomataram I and Bray F: Cancer Today. Lyon, France:
International Agency for Research on Cancer. Cancer Today 2016.
http://gco.iarc.fr/todayJanuary
22–2018
|
|
17
|
Ferlay J, Soerjomataram I, Dikshit R, Eser
S, Mathers C, Rebelo M, Parkin DM, Forman D and Bray F: Cancer
incidence and mortality worldwide: Sources, methods and major
patterns in GLOBOCAN 2012. Int J Cancer. 136:E359–E386. 2015.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
18
|
Center MM, Jemal A, Lortet-Tieulent J,
Ward E, Ferlay J, Brawlt O and Bray F: International variation in
prostate cancer incidence and mortality rates. Eur Urol.
61:1079–1092. 2012. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
19
|
Nelson EC, Cambio AJ, Yang JC, Ok JH, Lara
PN Jr and Evans CP: Clinical implications of neuroendocrine
differentiation in prostate cancer. Prostate Cancer Prostatic Dis.
10:6–14. 2007. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
20
|
Foster HA, Davies J, Pink RC, Turkcigdem
S, Goumenou A, Carter DR, Saunders NJ, Thomas P and Karteris E: The
human myometrium differentially expresses mTOR signalling
components before and during pregnancy: Evidence for regulation by
progesterone. J Steroid Biochem Mol Biol. 139:166–172. 2014.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
21
|
Johnson TR, Khandrika L, Kumar B, Venezia
S, Koul S, Chandhoke R, Maroni P, Donohue R, Meacham RB and Koul
HK: Focal adhesion kinase controls aggressive phenotype of
androgen-independent prostate cancer. Mol Cancer Res. 6:1639–1648.
2008. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
22
|
Chen Y, Xin X, Li J, Xu J, Yu X, Li T, Mo
Z and Hu Y: RTK/ERK pathway under natural selection associated with
prostate cancer. PLoS One. 8:e782542013. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
23
|
Li WH, Qiu Y, Zhang HQ, Tian XX and Fang
WG: P2Y2 receptor and EGFR cooperate to promote prostate cancer
cell invasion via ERK1/2 pathway. PLoS One. 10:e01331652015.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
24
|
Ghosh PM, Malik SN, Bedolla RG, Wang Y,
Mikhailova M, Prihoda TJ, Troyer DA and Kreisberg JI: Signal
transduction pathways in androgen-dependent and -independent
prostate cancer cell proliferation. Endocr Relat Cancer.
12:119–134. 2005. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
25
|
McCubrey JA, Steelman LS, Abrams SL,
Bertrand FE, Ludwig DE, Bäsecke J, Libra M, Stivala F, Milella M,
Tafuri A, et al: Targeting survival cascades induced by activation
of Ras/Raf/MEK/ERK, PI3K/PTEN/Akt/mTOR and Jak/STAT pathways for
effective leukemia therapy. Leukemia. 22:708–722. 2008. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
26
|
Tibbles LA and Woodgett JR: The
stress-activated protein kinase pathways. Cell Mol Life Sci.
55:1230–1254. 1999. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
27
|
Ricote M, García-Tuñón I, Fraile B,
Fernández C, Aller P, Paniagua R and Royuela M: P38 MAPK protects
against TNF-alpha-provoked apoptosis in LNCaP prostatic cancer
cells. Apoptosis. 11:1969–1975. 2006. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
28
|
Koul HK, Pal M and Koul S: Role of p38 MAP
Kinase signal transduction in solid tumors. Genes Cancer.
4:342–359. 2013. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
29
|
Lotan TL, Lyon M, Huo D, Taxy JB, Brendler
C, Foster BA, Stadler W and Rinker-Schaeffer CW: Up-regulation of
MKK4, MKK6 and MKK7 during prostate cancer progression: An
important role for SAPK signalling in prostatic neoplasia. J
Pathol. 212:386–394. 2007. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
30
|
Magi-Galluzzi C, Mishra R, Fiorentino M,
Montironi R, Yao H, Capodieci P, Wishnow K, Kaplan I, Stork PJ and
Loda M: Mitogen-activated protein kinase phosphatase 1 is
overexpressed in prostate cancers and is inversely related to
apoptosis. Lab Invest. 76:37–51. 1997.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
31
|
Boldt S, Weidle UH and Kolch W: The role
of MAPK pathways in the action of chemotherapeutic drugs.
Carcinogenesis. 23:1831–1838. 2002. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
32
|
Xia Z, Dickens M, Raingeaud J, Davis RJ
and Greenberg ME: Opposing effects of ERK and JNK-p38 MAP kinases
on apoptosis. Science. 270:1326–1331. 1995. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
33
|
Xu L, Chen S and Bergan RC: MAPKAPK2 and
HSP27 are downstream effectors of p38 MAP kinase-mediated matrix
metalloproteinase type 2 activation and cell invasion in human
prostate cancer. Oncogene. 25:2987–2998. 2006. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
34
|
Chen L, He HY, Li HM, Zheng J, Heng WJ,
You JF and Fang WG: ERK1/2 and p38 pathways are required for P2Y
receptor-mediated prostate cancer invasion. Cancer Lett.
215:239–247. 2004. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
35
|
Gururajan M, Chui R, Karuppannan AK, Ke J,
Jennings CD and Bondada S: c-Jun N-terminal kinase (JNK) is
required for survival and proliferation of B-lymphoma cells. Blood.
106:1382–1391. 2005. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
36
|
Shimada K, Nakamura M, Ishida E, Kishi M,
Yonehara S and Konishi N: c-Jun NH2-terminal kinase-dependent Fas
activation contributes to etoposide-induced apoptosis in
p53-mutated prostate cancer cells. Prostate. 55:265–280. 2003.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
37
|
Rodríguez-Berriguete G, Fraile B,
Martínez-Onsurbe P, Olmedilla G, Paniagua R and Royuela M: MAP
kinases and prostate cancer. J Signal Transduct. 2012:1691702012.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
38
|
Davis RJ: Signal transduction by the JNK
group of MAP kinases. Cell. 103:239–252. 2000. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
39
|
Sui X, Kong N, Ye L, Han W, Zhou J, Zhang
Q, He C and Pan H: p38 and JNK MAPK pathways control the balance of
apoptosis and autophagy in response to chemotherapeutic agents.
Cancer Lett. 344:174–179. 2014. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
40
|
Guo J, Zhu T, Chen L, Nishioka T, Tsuji T,
Xiao ZX and Chen CY: Differential sensitization of different
prostate cancer cells to apoptosis. Genes Cancer. 1:836–846. 2010.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
41
|
Shukla S, Maclennan GT, Hartman DJ, Fu P,
Resnick MI and Gupta S: Activation of PI3K-Akt signaling pathway
promotes prostate cancer cell invasion. Int J Cancer.
121:1424–1432. 2007. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
42
|
Toren P and Zoubeidi A: Targeting the
PI3K/Akt pathway in prostate cancer: Challenges and opportunities
(Review). Int J Oncol. 45:1793–1801. 2014. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
43
|
Gan Y, Shi C, Inge L, Hibner M, Balducci J
and Huang Y: Differential roles of ERK and Akt pathways in
regulation of EGFR-mediated signaling and motility in prostate
cancer cells. Oncogene. 29:4947–4958. 2010. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
44
|
Yao Huang and Yongchang Chang: Epidermal
Growth Factor Receptor (EGFR) Phosphorylation, Signaling and
Trafficking in Prostate Cancer. Prostate Cancer-From Bench to
Bedside. Dr. Philippe E. Spiess (ed). InTech. doi: 10.5772/27021.
2011.
|
|
45
|
Ding G, Fang J, Tong S, Qu L, Jiang H,
Ding Q and Liu J: Over-expression of lipocalin 2 promotes cell
migration and invasion through activating ERK signalling to
increase SLUG expression in prostate cancer. Prostate. 75:957–968.
2015. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
46
|
Ljujic M, Mijatovic S, Bulatovic MZ, Mojic
M, Maksimovic-Ivanic D, Radojkovic D and Topic A:
Alpha-1-antitrypsin antagonizes cisplatin-induced cytotoxicity in
prostate cancer (PC3) and melanoma cancer (A375) cell lines. Pathol
Oncol Res. 23:335–343. 2017. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
47
|
Rybak AP, Ingram AJ and Tang D:
Propagation of human prostate cancer stem-like cells occurs through
EGFR-mediated ERK activation. PLoS One. 8:e617162013. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
48
|
Xiao LJ, Lin P, Lin F, Liu X, Qin W, Zou
HF, Guo L, Liu W, Wang SJ and Yu XG: ADAM17 targets MMP-2 and MMP-9
via EGFR-MEK-ERK pathway activation to promote prostate cancer cell
invasion. Int J Oncol. 40:1714–1724. 2012.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
49
|
Moulik S, Pal S, Biswas J and Chatterjee
A: Role of ERK in modulating MMP 2 and MMP 9 with respect to tumour
invasiveness in human cancer cell line MCF-7 and MDA-MB-231.
Journal of Tumor. 2:87–98. 2014.
|
|
50
|
Yang JL, Lin JH, Weng SW, Chen JC, Yang
JS, Amagaya S, Funayana S, Wood WG, Kuo CL and Chung JG: Crude
extract of Euphorbia formosana inhibits the migration and invasion
of DU145 human prostate cancer cells: The role of matrix
metalloproteinase-2/9 inhibition via the MAPK signaling pathway.
Mol Med Rep. 7:1403–1408. 2013. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
51
|
Huang X, Chen S, Xu L, Liu Y, Deb DK,
Platanias LC and Bergan RC: Genistein inhibits p38 map kinase
activation, matrix metalloproteinase type 2, and cell invasion in
human prostate epithelial cells. Cancer Res. 65:3470–3478. 2005.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
52
|
Oguic R, Mozetič V, Cini Tešar E, Fučkar
Čupić D, Mustać E and Dorđević G: Matrix metalloproteinases 2 and 9
immunoexpression in prostate carcinoma at the positive margin of
radical prostatectomy specimens. Patholog Res Int 2014.
2621952014.
|
|
53
|
Trudel D, Fradet Y, Meyer F, Harel F and
Têtu B: Significance of MMP-2 expression in prostate cancer: An
immunohistochemical study. Cancer Res. 63:8511–8515.
2003.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
54
|
Kyrou I, Randeva HS and Weickert MO:
Clinical Problems Caused by Obesity. De Groot LJ, Chrousos G,
Dungan K, Feingold KR, Grossman A, Hershman JM, Koch C, Korbonits
M, McLachlan R, New M, Purnell J, Rebar R, Singer F and Vinik A:
South Dartmouth (MA): MDText.com, Inc.; 2014, Available on Endotext
[Internet].
|
|
55
|
Kyrou I, Mattu HS, Chatha K and Randeva
HS; Chapter 7-Fat Hormones, Adipokines, . Schisler JC, Lang CH and
Willis MS: Endocrinology of the Heart in Health and Disease.
Academic Press. 2017. pp. 167–205. 2017
|
|
56
|
Alshaker H, Sacco K, Alfraidi A, Muhammad
A, Winkler M and Pchejetski D: Leptin signalling, obesity and
prostate cancer: Molecular and clinical perspective on the old
dilemma. Oncotarget. 6:35556–35563. 2015. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
57
|
Baillargeon J and Rose DP: Obesity,
adipokines, and prostate cancer (Review). Int J Oncol. 28:737–745.
2006.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
58
|
Szyszka M, Tyczewska M, Milecka P, Jopek
K, Celichowski P, Malendowicz LK and Rucinski M: Effects of leptin
on leptin receptor isoform expression and proliferative activity in
human normal prostate and prostate cancer cell lines. Oncol Rep.
39:182–192. 2018.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
59
|
Hoda MR, Theil G, Mohammed N, Fischer K
and Fornara P: The adipocyte-derived hormone leptin has
proliferative actions on androgen-resistant prostate cancer cells
linking obesity to advanced stages of prostate cancer. J Oncol.
280386:2012.
|
|
60
|
Onuma M, Bub JD, Rummel TL and Iwamoto Y:
Prostate cancer cell-adipocyte interaction: Leptin mediates
androgen-independent prostate cancer cell proliferation through
c-Jun NH2-terminal kinase. J Biol Chem. 278:42660–42667. 2003.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
61
|
Miyazaki T, Bub JD and Iwamoto Y: c-Jun
NH2-terminal kinase mediates leptin-stimulated
androgen-independent prostate cancer cell proliferation via signal
transducer and activator of transcription 3 and Akt. Biochim
Biophys Acta. 1782:593–604. 2008. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|