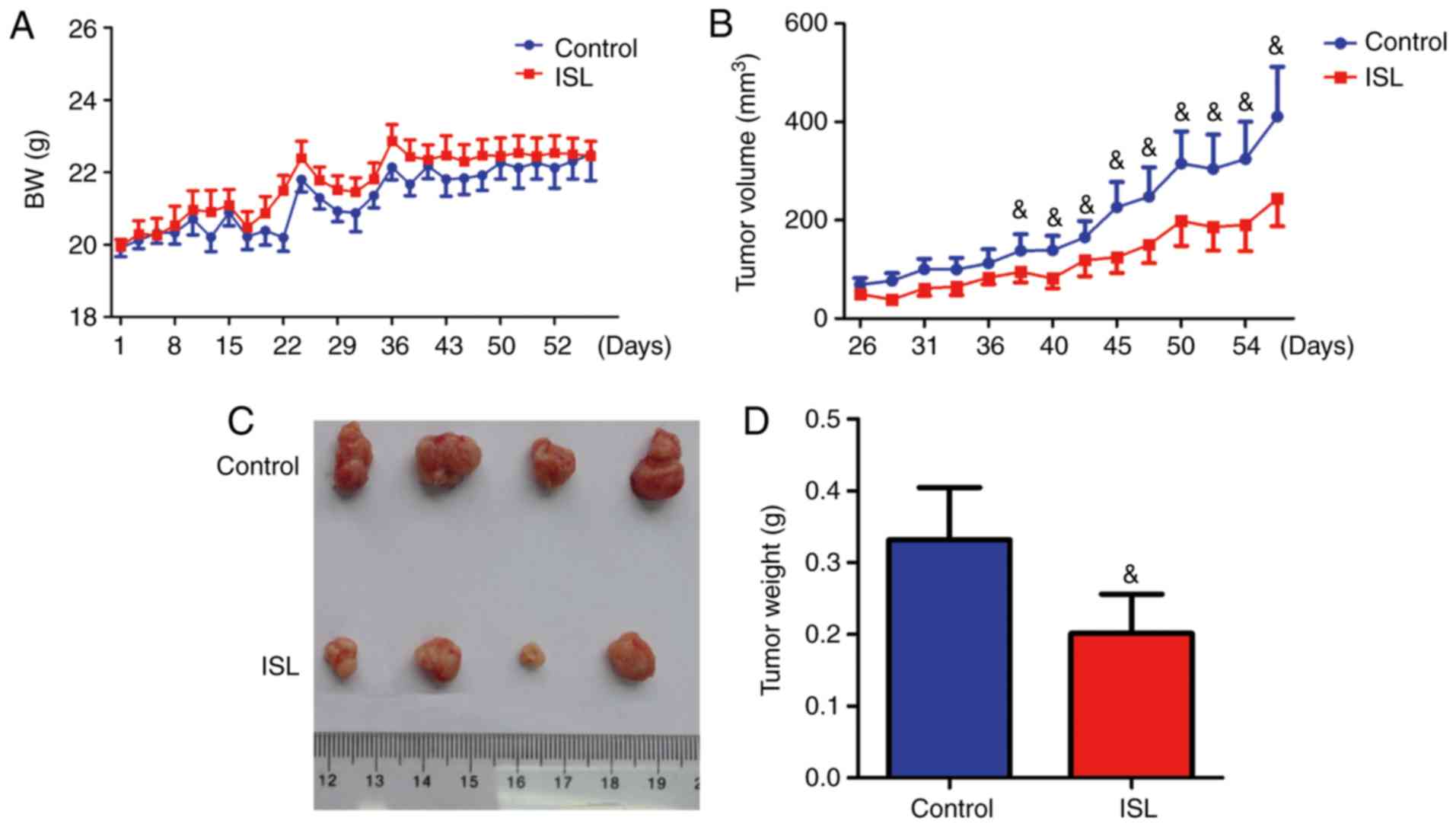
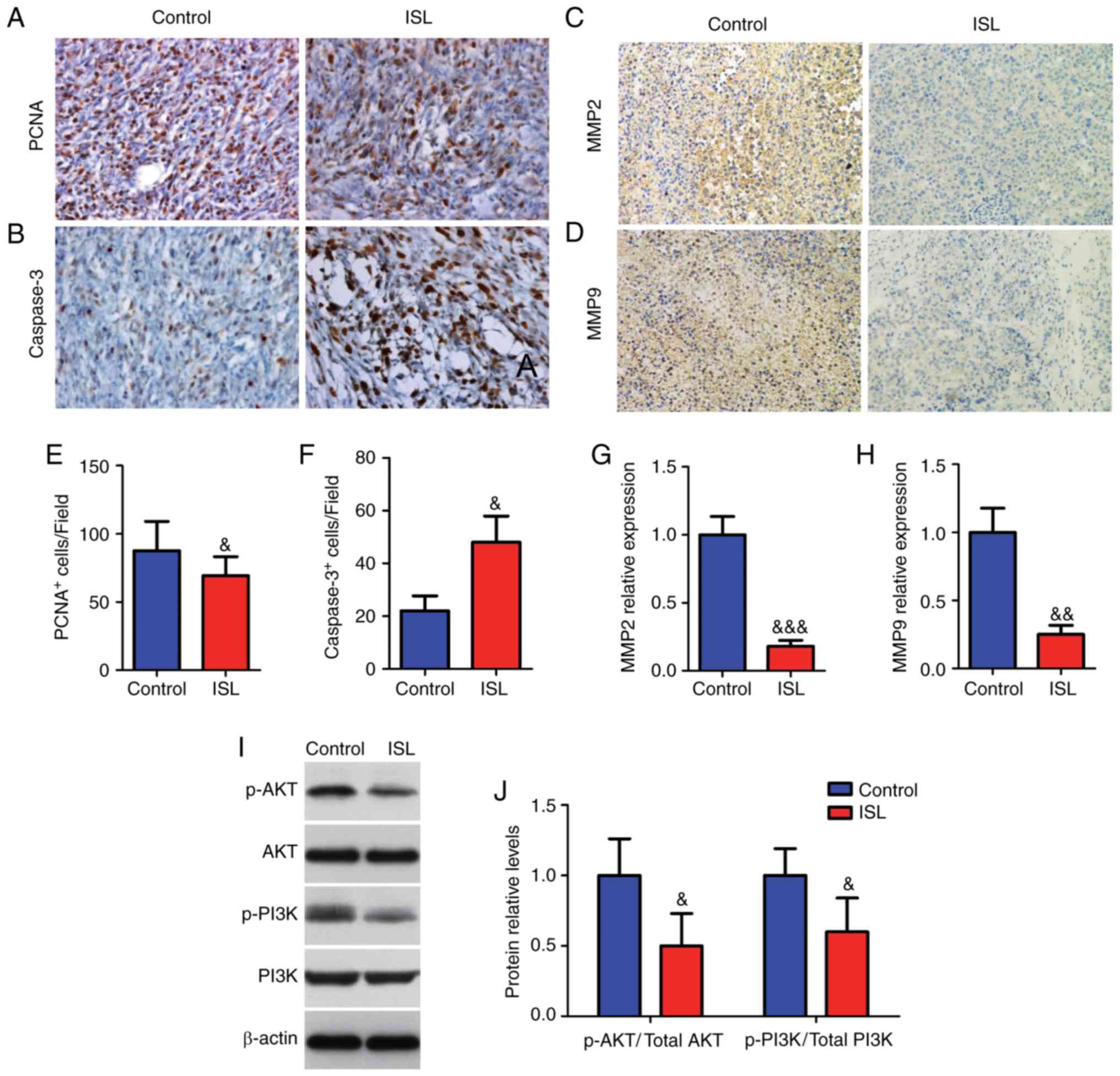
|
1
|
Zambo I and Vesely K: WHO classification
of tumours of soft tissue and bone 2013: The main changes compared
to the 3rd edition. Cesk Patol. 50:64–70. 2014.(In Czech).
PubMed/NCBI
|
|
2
|
Bernthal NM, Federman N, Eilber FR, Nelson
SD, Eckardt JJ, Eilber FC and Tap WD: Long-term results (>25
years) of a randomized, prospective clinical trial evaluating
chemotherapy in patients with high-grade, operable osteosarcoma.
Cancer. 118:5888–5893. 2012. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
3
|
Eilber FR and Rosen G: Adjuvant
chemotherapy for osteosarcoma. Semin Oncol. 16:312–322.
1989.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
4
|
Chin YW, Jung HA, Liu Y, Su BN, Castoro
JA, Keller WJ, Pereira MA and Kinghorn AD: Anti-oxidant
constituents of the roots and stolons of licorice (Glycyrrhiza
glabra). J Agric Food Chem. 55:4691–4697. 2007. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
5
|
Peng F, Du Q, Peng C, Wang N, Tang H, Xie
X, Shen J and Chen J: A review: The pharmacology of
isoliquiritigenin. Phytother Res. 29:969–977. 2015. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
6
|
Asl MN and Hosseinzadeh H: Review of
pharmacological effects of Glycyrrhiza sp. and its bioactive
compounds. Phytother Res. 22:709–724. 2008. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
7
|
Lin Y, Sun H, Dang Y and Li Z:
Isoliquiritigenin inhibits the proliferation and induces the
differentiation of human glioma stem cells. Oncol Rep. 39:687–694.
2018.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
8
|
Chen HY, Huang TC, Shieh TM, Wu CH, Lin LC
and Hsia SM: Isoliquiritigenin induces autophagy and inhibits
ovarian cancer cell growth. Int J Mol Sci. 18(pii): E20252017.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
9
|
Hsu YL, Kuo PL, Lin LT and Lin CC:
Isoliquiritigenin inhibits cell proliferation and induces apoptosis
in human hepatoma cells. Planta Med. 71:130–134. 2005. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
10
|
Wang Z, Wang N, Han S, Wang D, Mo S, Yu L,
Huang H, Tsui K, Shen J and Chen J: Dietary compound
isoliquiritigenin inhibits breast cancer neoangiogenesis via
VEGF/VEGFR-2 signaling pathway. PLoS One. 8:e685662013. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
11
|
Jung JI, Chung E, Seon MR, Shin HK, Kim
EJ, Lim SS, Chung WY, Park KK and Park JH: Isoliquiritigenin (ISL)
inhibits ErbB3 signaling in prostate cancer cells. Biofactors.
28:159–168. 2006. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
12
|
Li Y, Zhao H, Wang Y, Zheng H, Yu W, Chai
H, Zhang J, Falck JR, Guo AM, Yue J, et al: Isoliquiritigenin
induces growth inhibition and apoptosis through downregulating
arachidonic acid metabolic network and the deactivation of PI3K/Akt
in human breast cancer. Toxicol Appl Pharmacol. 272:37–48. 2013.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
13
|
Wang KL, Hsia SM, Chan CJ, Chang FY, Huang
CY, Bau DT and Wang PS: Inhibitory effects of isoliquiritigenin on
the migration and invasion of human breast cancer cells. Expert
Opin Ther Targets. 17:337–349. 2013. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
14
|
Zhu J, Sun Y, Lu Y, Jiang X, Ma B, Yu L,
Zhang J, Dong X and Zhang Q: Glaucocalyxin A exerts anticancer
effect on osteosarcoma by inhibiting GLI1 nuclear translocation via
regulating PI3K/Akt pathway. Cell Death Dis. 9:7082018. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
15
|
Angulo P, Kaushik G, Subramaniam D,
Dandawate P, Neville K, Chastain K and Anant S: Natural compounds
targeting major cell signaling pathways: A novel paradigm for
osteosarcoma therapy. J Hematol Oncol. 10:102017. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
16
|
Zhang J, Yu XH, Yan YG, Wang C and Wang
WJ: PI3K/Akt signaling in osteosarcoma. Clin Chim Acta.
444:182–192. 2015. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
17
|
Wu CH, Chen HY, Wang CW, Shieh TM, Huang
TC, Lin LC, Wang KL and Hsia SM: Isoliquiritigenin induces
apoptosis and autophagy and inhibits endometrial cancer growth in
mice. Oncotarget. 7:73432–73447. 2016.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
18
|
Livak KJ and Schmittgen TD: Analysis of
relative gene expression data using real-time quantitative PCR and
the 2−ΔΔCT method. Methods. 25:402–408. 2001. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
19
|
Ingham M and Schwartz GK: Cell-cycle
therapeutics come of age. J Clin Oncol. 35:2949–2959. 2017.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
20
|
Akin S, Babacan T, Sarici F and Altundag
K: A novel targeted therapy in breast cancer: Cyclin dependent
kinase inhibitors. J Buon. 19:42–46. 2014.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
21
|
Wang Y, Ma J, Yan X, Chen X, Si L, Liu Y,
Han J, Hao W and Zheng Q: Isoliquiritigenin inhibits proliferation
and induces apoptosis via alleviating hypoxia and reducing
glycolysis in mouse melanoma B16F10 cells. Recent Pat Anticancer
Drug Discov. 11:215–227. 2016. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
22
|
Zhang X, Yeung ED, Wang J, Panzhinskiy EE,
Tong C, Li W and Li J: Isoliquiritigenin, a natural anti-oxidant,
selectively inhibits the proliferation of prostate cancer cells.
Clin Exp Pharmacol Physiol. 37:841–847. 2010.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
23
|
Maggiolini M, Statti G, Vivacqua A,
Gabriele S, Rago V, Loizzo M, Menichini F and Amdò S: Estrogenic
and antiproliferative activities of isoliquiritigenin in MCF7
breast cancer cells. J Steroid Biochem Mol Biol. 82:315–322. 2002.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
24
|
Li ZX, Li J, Li Y, You K, Xu H and Wang J:
Novel insights into the apoptosis mechanism of DNA topoisomerase I
inhibitor isoliquiritigenin on HCC tumor cell. Biochem Biophys Res
Commun. 464:548–553. 2015. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
25
|
Jung SK, Lee MH, Lim DY, Kim JE, Singh P,
Lee SY, Jeong CH, Lim TG, Chen H, Chi YI, et al: Isoliquiritigenin
induces apoptosis and inhibits xenograft tumor growth of human lung
cancer cells by targeting both wild type and L858R/T790M mutant
EGFR. J Biol Chem. 289:35839–35848. 2014. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
26
|
Hirchaud F, Hermetet F, Ablise M,
Fauconnet S, Vuitton DA, Prétet JL and Mougin C: Isoliquiritigenin
induces caspase-dependent apoptosis via downregulation of HPV16 E6
expression in cervical cancer Ca Ski cells. Planta Med.
79:1628–1635. 2013. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
27
|
Chen G, Hu X, Zhang W, Xu N, Wang FQ, Jia
J, Zhang WF, Sun ZJ and Zhao YF: Mammalian target of rapamycin
regulates isoliquiritigenin-induced autophagic and apoptotic cell
death in adenoid cystic carcinoma cells. Apoptosis. 17:90–101.
2012. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
28
|
Yuan X, Zhang B, Gan L, Wang ZH, Yu BC,
Liu LL, Zheng QS and Wang ZP: Involvement of the
mitochondrion-dependent and the endoplasmic reticulum
stress-signaling pathways in isoliquiritigenin-induced apoptosis of
HeLa cell. Biomed Environ Sci. 26:268–276. 2013.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
29
|
Jung JI, Lim SS, Choi HJ, Cho HJ, Shin HK,
Kim EJ, Chung WY, Park KK and Park JH: Isoliquiritigenin induces
apoptosis by depolarizing mitochondrial membranes in prostate
cancer cells. J Nutr Biochem. 17:689–696. 2006. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
30
|
Yang HH, Zhang C, Lai SH, Zeng CC, Liu YJ
and Wang XZ: Isoliquiritigenin induces cytotoxicity in PC-12 cells
in vitro. Appl Biochem Biotechnol. 183:1173–1190. 2017. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
31
|
Kale J, Osterlund EJ and Andrews DW: BCL-2
family proteins: Changing partners in the dance towards death. Cell
Death Differ. 25:65–80. 2018. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
32
|
Maes ME, Schlamp CL and Nickells RW: BAX
to basics: How the BCL2 gene family controls the death of
retinal ganglion cells. Prog Retin Eye Res. 57:1–25. 2017.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
33
|
Strasser A and Vaux DL: Viewing BCL2 and
cell death control from an evolutionary perspective. Cell Death
Differ. 25:13–20. 2018. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
34
|
Hsu YL, Kuo PL and Lin CC:
Isoliquiritigenin induces apoptosis and cell cycle arrest through
p53-dependent pathway in Hep G2 cells. Life Sci. 77:279–292. 2005.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
35
|
Kwon GT, Cho HJ, Chung WY, Park KK, Moon A
and Park JH: Isoliquiritigenin inhibits migration and invasion of
prostate cancer cells: Possible mediation by decreased JNK/AP-1
signaling. J Nutr Biochem. 20:663–676. 2009. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
36
|
Chien MH, Lin CW, Cheng CW, Wen YC and
Yang SF: Matrix metalloproteinase-2 as a target for head and neck
cancer therapy. Expert Opin Ther Targets. 17:203–216. 2013.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
37
|
Kessenbrock K, Plaks V and Werb Z: Matrix
metalloproteinases: Regulators of the tumor microenvironment. Cell.
141:52–67. 2010. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
38
|
Yang JS, Lin CW, Su SC and Yang SF:
Pharmacodynamic considerations in the use of matrix
metalloproteinase inhibitors in cancer treatment. Expert Opin Drug
Metab Toxicol. 12:191–200. 2016. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
39
|
Lan H, Hong W, Fan P, Qian D, Zhu J and
Bai B: Quercetin inhibits cell migration and invasion in human
osteosarcoma cells. Cell Physiol Biochem. 43:553–567. 2017.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
40
|
Kunz P, Sahr H, Lehner B, Fischer C,
Seebach E and Fellenberg J: Elevated ratio of MMP2/MMP9 activity is
associated with poor response to chemotherapy in osteosarcoma. BMC
Cancer. 16:2232016. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
41
|
Yang Z, Zeng B, Pan Y, Huang P and Wang C:
Autophagy participates in isoliquiritigenin-induced melanin
degradation in human epidermal keratinocytes through PI3K/AKT/mTOR
signaling. Biomed Pharmacother. 97:248–254. 2018. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
42
|
Chen T, Deng S and Lin R: The inhibitory
effect of Isoliquiritigenin on the proliferation of human arterial
smooth muscle cell. BMC Pharmacol Toxicol. 18:572017. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|