|
1
|
Nelson HD, Zakher B, Cantor A, Fu R,
Griffin J, O'Meara ES, Buist DS, Kerlikowske K, van Ravesteyn NT,
Trentham-Dietz A, et al: Risk factors for breast cancer for women
aged 40 to 49 years: A systematic review and meta-analysis. Ann
Intern Med. 156:635–648. 2012. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
2
|
Porter PL: Global trends in breast cancer
incidence and mortality. Salud Publica Mex. 51 (Suppl 2):S141–S146.
2009. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
3
|
McGuire KP, Eisen S, Rodriguez A, Meade T,
Cox CE and Khakpour N: Factors associated with improved outcome
after surgery in metastatic breast cancer patients. Am J Surg.
198:511–515. 2009. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
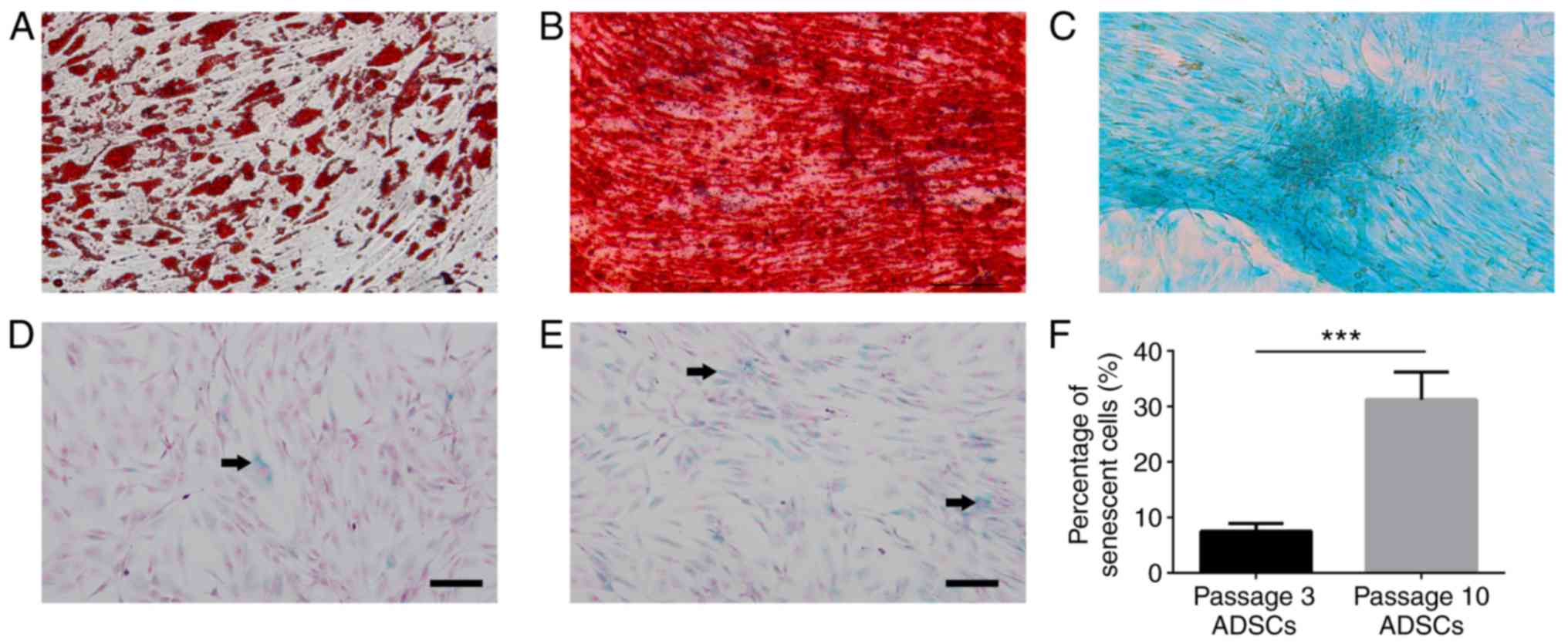
|
|
4
|
Munhoz AM, Montag E, Filassi JR and
Gemperli R: Current approaches to managing partial breast defects:
The role of conservative breast surgery reconstruction. Anticancer
Res. 34:1099–1114. 2014.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
5
|
Longaker MT, Aston SJ, Baker DC and
Rohrich RJ: Fat Transfer in 2014: What we do not know. Plast
Reconstr Surg. 133:1305–1307. 2014.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
6
|
Eto H, Kato H, Suga H, Aoi N, Doi K, Kuno
S and Yoshimura K: The Fate of Adipocytes after nonvascularized fat
grafting. Plast Reconstr Surg. 129:1081–1092. 2012. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
7
|
Chung MT, Paik KJ, Atashroo DA, Hyun JS,
McArdle A, Senarath-Yapa K, Zielins ER, Tevlin R, Duldulao C, Hu
MS, et al: Studies in fat grafting: Part I. Effects of injection
technique on in vitro fat viability and in vivo volume retention.
Plast Reconstr Surg. 134:29–38. 2014. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
8
|
Atashroo D, Raphel J, Chung MT, Paik KJ,
Parisi-Amon A, McArdle A, Senarath-Yapa K, Zielins ER, Tevlin R,
Duldulao C, et al: Studies in fat grafting: Part II. Effects of
injection mechanics on material properties of fat. Plast Reconstr
Surg. 134:39–46. 2014. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
9
|
Dong Z, Peng Z, Chang Q, Zhan W, Zeng Z,
Zhang S and Lu F: The angiogenic and adipogenic modes of adipose
tissue after free fat grafting. Plast Reconstr Surg. 135:556e–567e.
2015. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
10
|
Bellei B, Migliano E, Tedesco M, Caputo S,
Papaccio F, Lopez G and Picardo M: Adipose tissue-derived
extracellular fraction characterization: Biological and clinical
considerations in regenerative medicine. Stem Cell Res Ther.
9:2072018. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
11
|
Yoshimura K, Shigeura T, Matsumoto D, Sato
T, Takaki Y, Aiba-Kojima E, Sato K, Inoue K, Nagase T, Koshima I,
et al: Characterization of freshly isolated and cultured cells
derived from the fatty and fluid portions of liposuction aspirates.
J Cell Physiol. 208:64–76. 2006. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
12
|
Pearl RA, Leedham SJ and Pacifico MD: The
safety of autologous fat transfer in breast cancer: Lessons from
stem cell biology. J Plast Reconstr Aesthet Surg. 65:283–288. 2012.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
13
|
Wang Y, Lehuédé C, Laurent V, Dirat B,
Dauvillier S, Bochet L, Le Gonidec S, Escourrou G, Valet P and
Muller C: Adipose tissue and breast epithelial cells: A dangerous
dynamic duo in breast cancer. Cancer Lett. 324:142–151. 2012.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
14
|
Kolle SF, Fischer-Nielsen A, Mathiasen AB,
Elberg JJ, Oliveri RS, Glovinski PV, Kastrup J, Kirchhoff M,
Rasmussen BS, Talman ML, et al: Enrichment of autologous fat grafts
with ex-vivo expanded adipose tissue-derived stem cells for graft
survival: A randomised placebo-controlled trial. Lancet.
382:1113–1120. 2013. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
15
|
Doi K, Ogata F, Eto H, Kato H, Kuno S,
Kinoshita K, Kanayama K, Feng J, Manabe I and Yoshimura K:
Differential contributions of graft-derived and host-derived cells
in tissue regeneration/remodeling after fat grafting. Plast
Reconstr Surg. 135:1607–1617. 2015. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
16
|
Suga H, Eto H, Aoi N, Kato H, Araki J, Doi
K, Higashino T and Yoshimura K: Adipose tissue remodeling under
ischemia: Death of adipocytes and activation of stem/progenitor
cells. Plast Reconstr Surg. 126:1911–1923. 2010. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
17
|
Kuhbier JW, Bucan V, Reimers K, Strauss S,
Lazaridis A, Jahn S, Radtke C and Vogt PM: Observed changes in the
morphology and phenotype of breast cancer cells in direct
co-culture with adipose-derived stem cells. Plast Reconstr Surg.
134:414–423. 2014. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
18
|
Kamat P, Schweizer R, Kaenel P, Salemi S,
Calcagni M, Giovanoli P, Gorantla VS, Eberli D, Andres AC and Plock
JA: Human adipose-derived mesenchymal stromal cells may promote
breast cancer progression and metastatic spread. Plast Reconstr
Surg. 136:76–84. 2015. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
19
|
Kucerova L, Skolekova S, Matuskova M,
Bohac M and Kozovska Z: Altered features and increased
chemosensitivity of human breast cancer cells mediated by adipose
tissue-derived mesenchymal stromal cells. Bmc Cancer. 13:5352013.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
20
|
Zhang Y, Daquinag A, Traktuev DO,
Amaya-Manzanares F, Simmons PJ, March KL, Pasqualini R, Arap W and
Kolonin MG: White adipose tissue cells are recruited by
experimental tumors and promote cancer progression in mouse models.
Cancer Res. 69:5259–5266. 2009. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
21
|
Eterno V, Zambelli A, Pavesi L, Villani L,
Zanini V, Petrolo G, Manera S, Tuscano A and Amato A:
Adipose-derived mesenchymal stem cells (ASCs) may favour breast
cancer recurrence via HGF/c-Met signaling. Oncotarget. 5:613–633.
2014. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
22
|
Alessio N, Bohn W, Rauchberger V, Rizzolio
F, Cipollaro M, Rosemann M, Irmler M, Beckers J, Giordano A and
Galderisi U: Silencing of RB1 but not of RB2/P130 induces cellular
senescence and impairs the differentiation potential of human
mesenchymal stem cells. Cell Mol Life Sci. 70:1637–1651. 2013.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
23
|
Gary RK and Kindell SM: Quantitative assay
of senescence-associated beta-galactosidase activity in mammalian
cell extracts. Anal Biochem. 343:329–334. 2005. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
24
|
Livak KJ and Schmittgen TD: Analysis of
relative gene expression data using real-time quantitative PCR and
the 2−ΔΔCT method. Methods. 25:402–408. 2001. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
25
|
Wang W, Zhong W, Yuan J, Yan C, Hu S, Tong
Y, Mao Y, Hu T, Zhang B and Song G: Involvement of
Wnt/β-catenin signaling in the mesenchymal stem cells
promote metastatic growth and chemoresistance of
cholangiocarcinoma. Oncotarget. 6:42276–42289. 2015.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
26
|
Zhou M, Liu S, Jiang Y, Ma H, Shi M, Wang
Q, Zhong W, Liao W and Xing MM: Doxorubicin-loaded single wall
nanotube thermo-sensitive hydrogel for gastric cancer
chemo-photothermal therapy. Adv Funct Mater. 25:4730–4739. 2015.
View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
27
|
Naito S, von Eschenbach AC, Giavazzi R and
Fidler IJ: Growth and metastasis of tumor cells isolated from a
human renal cell carcinoma implanted into different organs of nude
mice. Cancer Res. 46:4109–4115. 1986.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
28
|
Choi JS, Kim BS, Kim JY, Kim JD, Choi YC,
Yang HJ, Park K, Lee HY and Cho YW: Decellularized extracellular
matrix derived from human adipose tissue as a potential scaffold
for allograft tissue engineering. J Biomed Mater Res A. 97:292–299.
2011. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
29
|
Rhee K, Lee J and Eom Y: Mesenchymal stem
cell-mediated effects of tumor support or suppression. Int J Mol
Sci. 16:30015–30033. 2015. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
30
|
Waked K, Colle J, Doornaert M, Cocquyt V
and Blondeel P: Systematic review: The oncological safety of
adipose fat transfer after breast cancer surgery. Breast.
31:128–136. 2017. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
31
|
Massa M, Gasparini S, Baldelli I,
Scarabelli L, Santi P, Quarto R and Repaci E: Interaction between
breast cancer cells and adipose tissue cells derived from fat
grafting. Aesthet Surg J. 36:358–363. 2016. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
32
|
Ito S, Kai Y, Masuda T, Tanaka F,
Matsumoto T, Kamohara Y, Hayakawa H, Ueo H, Iwaguro H, Hedrick MH,
et al: Long-term outcome of adipose-derived regenerative
cell-enriched autologous fat transplantation for reconstruction
after breast-conserving surgery for Japanese women with breast
cancer. Surg Today. 47:1500–1511. 2017. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
33
|
Bielli A, Scioli MG, Gentile P,
Agostinelli S, Tarquini C, Cervelli V and Orlandi A: Adult
adipose-derived stem cells and breast cancer: A controversial
relationship. Springerplus. 3:1–10. 2014. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
34
|
Ponte AL, Marais E, Gallay N, Langonne A,
Delorme B, Herault O, Charbord P and Domenech J: The in vitro
migration capacity of human bone marrow mesenchymal stem cells:
Comparison of chemokine and growth factor chemotactic activities.
Stem Cells. 25:1737–1745. 2007. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
35
|
Spaeth E, Klopp A, Dembinski J, Andreeff M
and Marini F: Inflammation and tumor microenvironments: Defining
the migratory itinerary of mesenchymal stem cells. Gene Ther.
15:730–738. 2008. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
36
|
Lejmi E, Perriraz N, Clément S, Morel P,
Baertschiger R, Christofilopoulos P, Meier R, Bosco D, Bühler LH
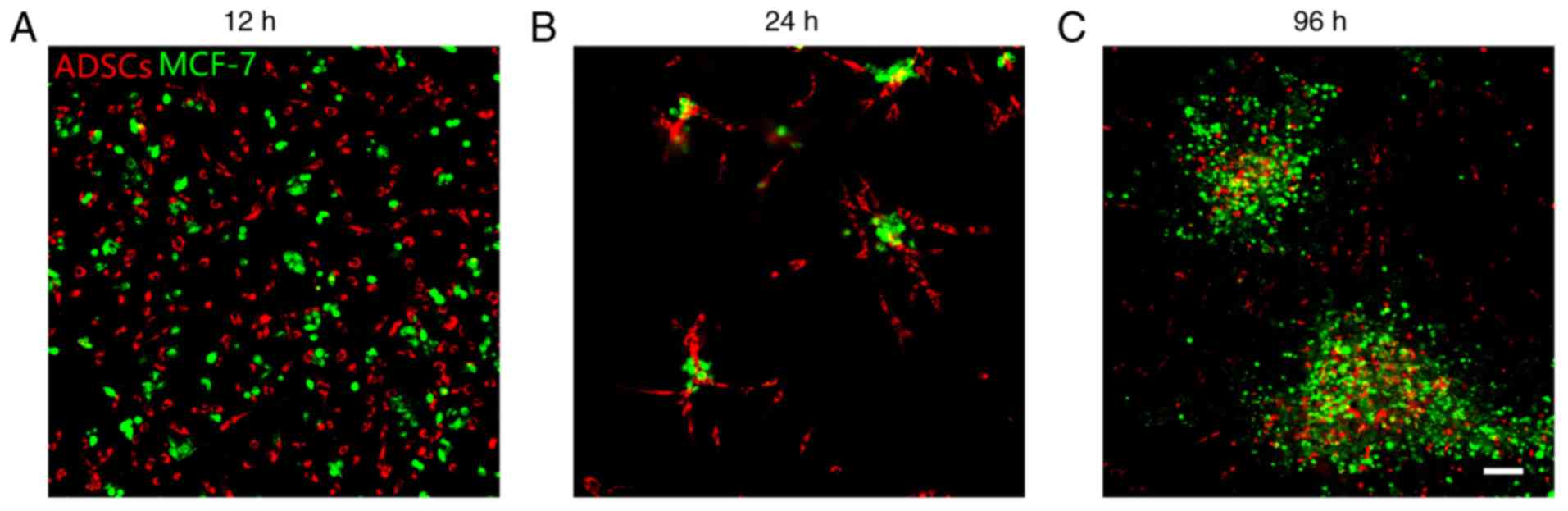
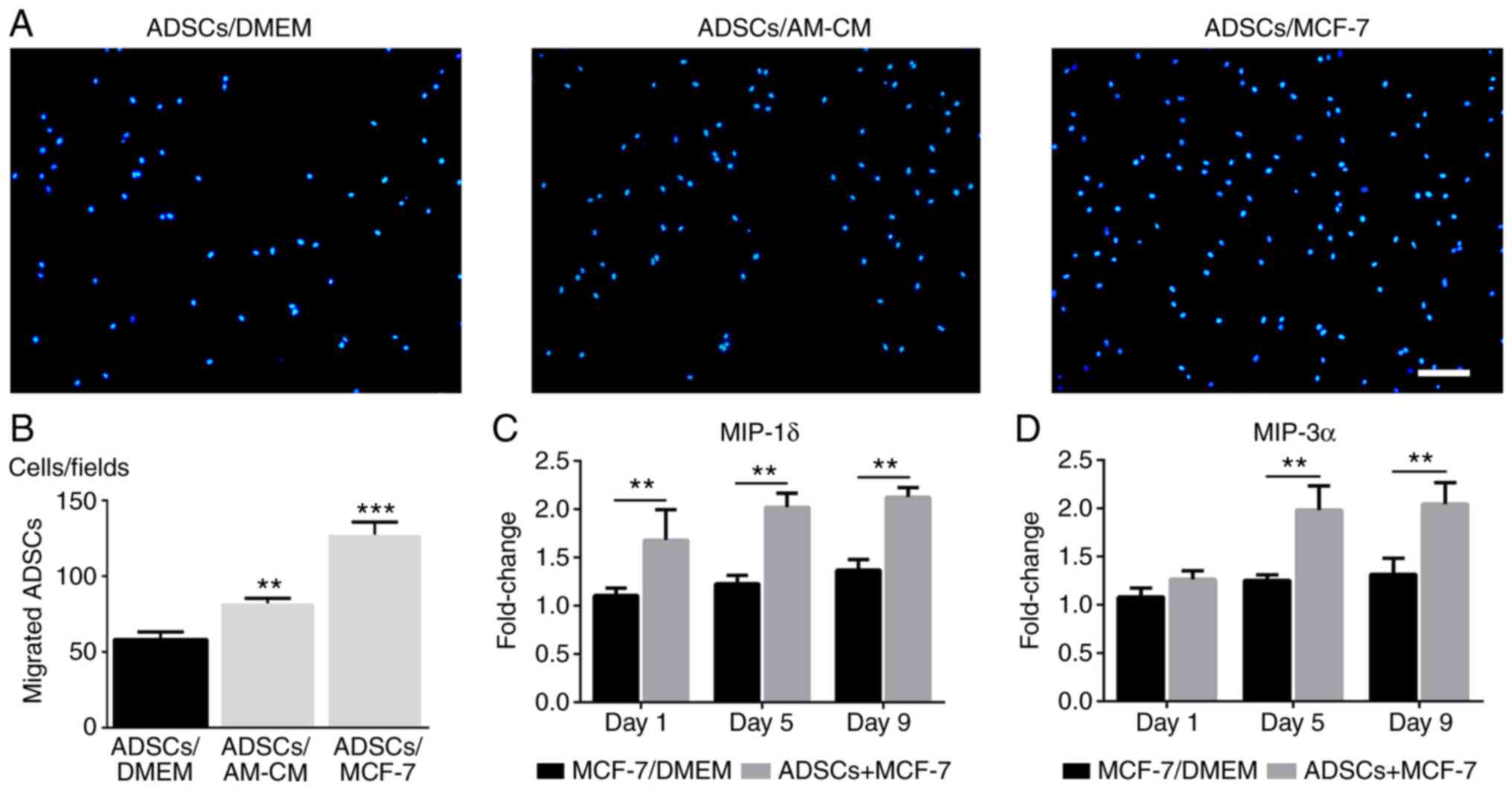
and Gonelle-Gispert C: Inflammatory chemokines MIP-1δ and MIP-3α
are involved in the migration of multipotent mesenchymal stromal
cells induced by hepatoma cells. Stem Cells Dev. 24:1223–1235.
2015. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
37
|
Chamberlain G, Smith H, Rainger GE and
Middleton J: Mesenchymal stem cells exhibit firm adhesion,
crawling, spreading and transmigration across aortic endothelial
cells: Effects of chemokines and shear. PLoS One. 6:e256632011.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
38
|
Wang H, Cao F, De A, Cao Y, Contag C,
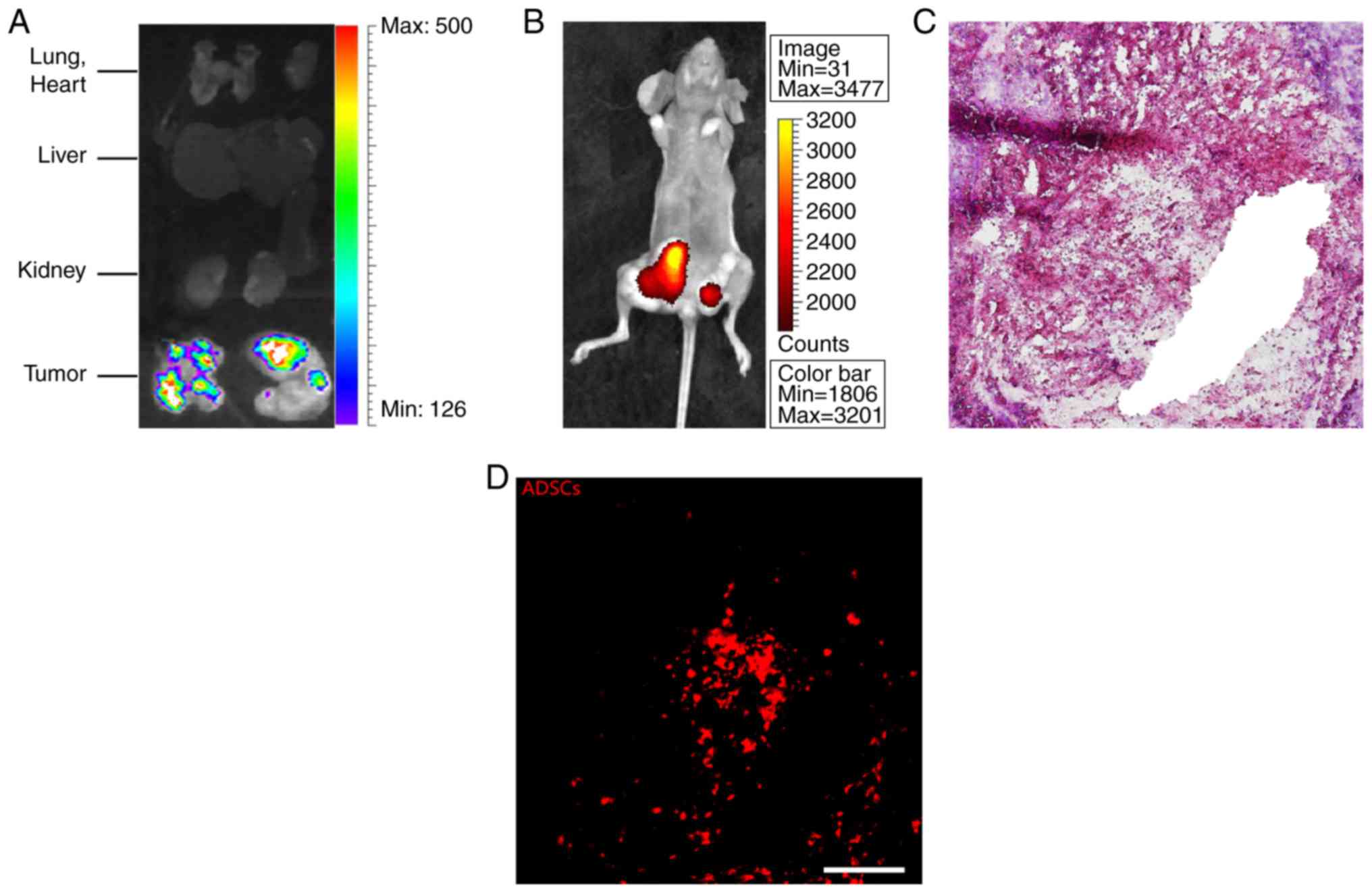
Gambhir SS, Wu JC and Chen X: Trafficking mesenchymal stem cell
engraftment and differentiation in tumor-bearing mice by
bioluminescence imaging. Stem Cells. 27:1548–1558. 2009. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
39
|
Menon LG, Picinich S, Koneru R, Gao H, Lin
SY, Koneru M, Mayer-Kuckuk P, Glod J and Banerjee D: Differential
gene expression associated with migration of mesenchymal stem cells
to conditioned medium from tumor cells or bone marrow cells. Stem
Cells. 25:520–528. 2007. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
40
|
Ho IA, Chan KY, Ng WH, Guo CM, Hui KM,
Cheang P and Lam PY: Matrix metalloproteinase 1 is necessary for
the migration of human bone marrow-derived mesenchymal stem cells
toward human glioma. Stem Cells. 27:1366–1375. 2009. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
41
|
Egea V, von Baumgarten L, Schichor C,
Berninger B, Popp T, Neth P, Goldbrunner R, Kienast Y, Winkler F,
Jochum M, et al: TNF-α respecifies human mesenchymal
stem cells to a neural fate and promotes migration toward
experimental glioma. Cell Death Differ. 18:853–863. 2011.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
42
|
Dwyer RM, Potter-Beirne SM, Harrington KA,
Lowery AJ, Hennessy E, Murphy JM, Barry FP, O'Brien T and Kerin MJ:
Monocyte chemotactic protein-1 secreted by primary breast tumors
stimulates migration of mesenchymal stem cells. Clin Cancer Res.
13:5020–5027. 2007. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
43
|
Lazennec G and Richmond A: Chemokines and
chemokine receptors: New insights into cancer-related inflammation.
Trends Mol Med. 16:133–144. 2010. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
44
|
Balkwill F: Cancer and the chemokine
network. Nat Rev Cancer. 4:540–550. 2004. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
45
|
Zernecke A, Weber KS, Erwig LP, Kluth DC,
Schroppel B, Rees AJ and Weber C: Combinatorial model of chemokine
involvement in glomerular monocyte recruitment: Role of CXC
chemokine receptor 2 in infiltration during nephrotoxic nephritis.
J Immunol. 166:5755–5762. 2001. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
46
|
Ali S and Lazennec G: Chemokines: Novel
targets for breast cancer metastasis. Cancer Metastasis Rev.
26:401–420. 2007. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
47
|
Zlotnik A, Burkhardt AM and Homey B:
Homeostatic chemokine receptors and organ-specific metastasis. Nat
Rev Immunol. 11:597–606. 2011. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
48
|
Escobar P, Bouclier C, Serret J, Bieche I,
Brigitte M, Caicedo A, Sanchez E, Vacher S, Vignais ML, Bourin P,
et al: IL-1β produced by aggressive breast cancer cells
is one of the factors that dictate their interactions with
mesenchymal stem cells through chemokine production. Oncotarget.
6:29034–29047. 2015. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
49
|
Griffith JW, Sokol CL and Luster AD:
Chemokines and chemokine receptors: Positioning cells for host
defense and immunity. Annu Rev Immunol. 32:659–702. 2014.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
50
|
Li Y, Wu J, Zhang W, Zhang N and Guo H:
Identification of serum CCL15 in hepatocellular carcinoma. Br J
Cancer. 108:99–106. 2013. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
51
|
Cao L, Zhou Y, Zhai B, Liao J, Xu W, Zhang
R, Li J, Zhang Y, Chen L, Qian H, et al: Sphere-forming cell
subpopulations with cancer stem cell properties in human hepatoma
cell lines. BMC Gastroenterol. 11:712011. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
52
|
Weiswald L, Bellet D and Dangles-Marie V:
Spherical cancer models in tumor biology. Neoplasia. 17:1–15. 2015.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
53
|
Pastrana E, Silva-Vargas V and Doetsch F:
Eyes wide open: A critical review of sphere-formation as an assay
for stem cells. Cell Stem Cell. 8:486–498. 2011. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
54
|
Ponti D, Costa A, Zaffaroni N, Pratesi G,
Petrangolini G, Coradini D, Pilotti S, Pierotti MA and Daidone MG:
Isolation and in vitro propagation of tumorigenic breast cancer
cells with stem/progenitor cell properties. Cancer Res.
65:5506–5511. 2005. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
55
|
Liu A, Yu X and Liu S: Pluripotency
transcription factors and cancer stem cells: Small genes make a big
difference. Chin J Cancer. 32:483–487. 2013.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
56
|
Santini R, Pietrobono S, Pandolfi S,
Montagnani V, D'Amico M, Penachioni JY, Vinci MC, Borgognoni L and
Stecca B: SOX2 regulates self-renewal and tumorigenicity of human
melanoma-initiating cells. Oncogene. 33:4697–4708. 2014. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
57
|
Turhan AG, Lemoine FM, Debert C, Bonnet
ML, Baillou C, Picard F, Macintyre EA and Varet B: Highly purified
primitive hematopoietic stem cells are PML-RARA negative and
generate nonclonal progenitors in acute promyelocytic leukemia.
Blood. 85:2154–2161. 1995.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
58
|
Holyoake TL, Jiang X, Drummond MW, Eaves
AC and Eaves CJ: Elucidating critical mechanisms of deregulated
stem cell turnover in the chronic phase of chronic myeloid
leukemia. Leukemia. 16:549–558. 2002. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
59
|
Marsden CG, Wright MJ, Pochampally R and
Rowan BG: Breast tumor-initiating cells isolated from patient core
biopsies for study of hormone action. Methods Mol Biol.
590:363–375. 2009. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
60
|
Ricci-Vitiani L, Lombardi DG, Pilozzi E,
Biffoni M, Todaro M, Peschle C and De Maria R: Identification and
expansion of human colon-cancer-initiating cells. Nature.
445:111–115. 2007. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
61
|
Mani SA, Guo W, Liao MJ, Eaton EN, Ayyanan
A, Zhou AY, Brooks M, Reinhard F, Zhang CC, Shipitsin M, et al: The
epithelial-mesenchymal transition generates cells with properties
of stem cells. Cell. 133:704–715. 2008. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
62
|
Thiery JP and Sleeman JP: Complex networks
orchestrate epithelial-mesenchymal transitions. Nat Rev Mol Cell
Biol. 7:131–142. 2006. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
63
|
Kalluri R and Weinberg RA: The basics of
epithelial-mesenchymal transition. J Clin Invest. 119:1420–1428.
2009. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
64
|
Vega SL, Kwon MY and Burdick JA: Recent
advances in hydrogels for cartilage tissue engineering. Eur Cell
Mater. 33:59–75. 2017. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
65
|
Kondiah PJ, Choonara YE, Kondiah PP,
Marimuthu T, Kumar P, du Toit LC and Pillay V: A review of
injectable polymeric hydrogel systems for application in bone
tissue engineering. Molecules. 21(pii): E15802016. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
66
|
Zuk PA, Zhu M, Mizuno H, Huang J, Futrell
JW, Katz AJ, Benhaim P, Lorenz HP and Hedrick MH: Multilineage
cells from human adipose tissue: Implications for cell-based
therapies. Tissue Eng. 7:211–228. 2001. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|