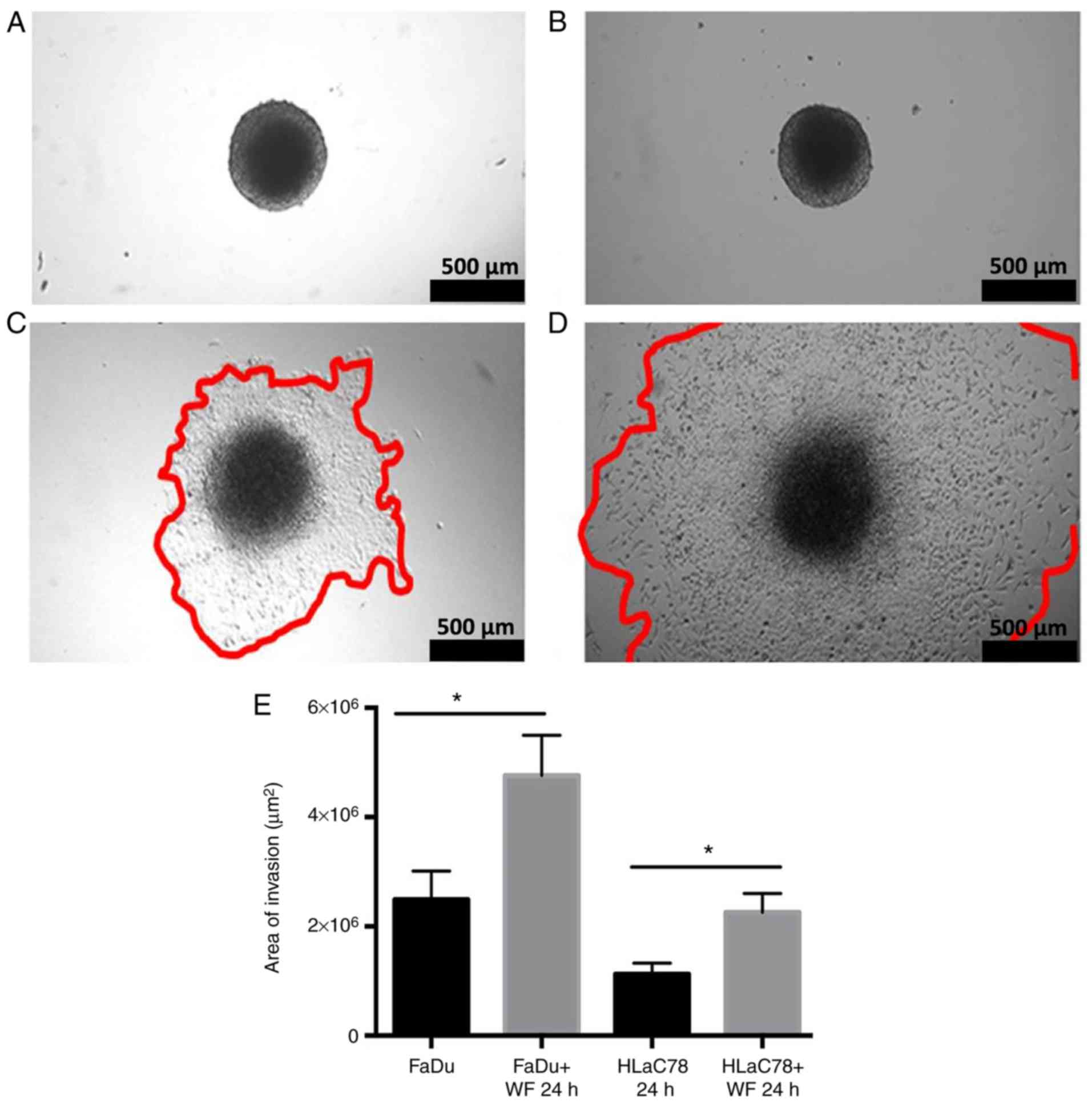
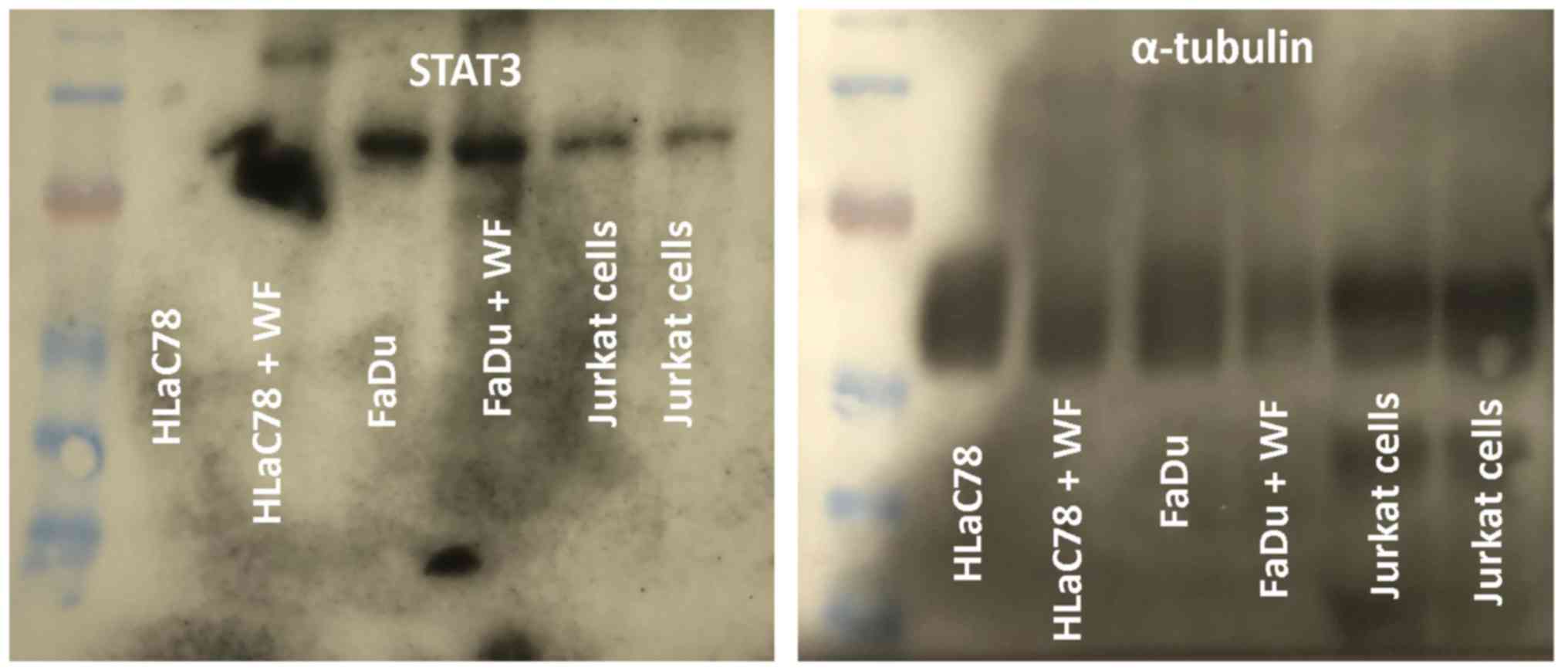
|
1
|
Siegel RL, Miller KD, Fedewa SA, Ahnen DJ,
Meester RGS, Barzi A and Jemal A: Colorectal cancer statistics,
2017. CA Cancer J Clin. 67:177–193. 2017. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
2
|
Wynn TA and Vannella KM: Macrophages in
tissue repair, regeneration, and fibrosis. Immunity. 44:450–462.
2016. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
3
|
Wynn TA: Cellular and molecular mechanisms
of fibrosis. J Pathol. 214:199–210. 2008. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
4
|
Valeta-Magara A, Hatami R, Axelrod D,
Roses DF, Guth A, Formenti SC and Schneider RJ: Pro-oncogenic
cytokines and growth factors are differentially expressed in the
post-surgical wound fluid from malignant compared to benign breast
lesions. SpringerPlus. 4:4832015. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
5
|
Cutting KF: Wound exudate: Composition and
functions. Br J Community Nurs. 8 (Suppl 9):S4–S9. 2003. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
6
|
Abramovitch R, Marikovsky M, Meir G and
Neeman M: Stimulation of tumour growth by wound-derived growth
factors. Br J Cancer. 79:1392–1398. 1999. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
7
|
Scherzed A, Hackenberg S, Froelich K,
Radeloff A, Technau A, Kessler M, Hagen R, Rak K, Koehler C and
Kleinsasser N: The effect of wound fluid on adipose-derived stem
cells in vitro: A study in human cell materials. Tissue Eng Part C
Methods. 17:809–817. 2011. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
8
|
Zhang Y, Ma Q, Liu T, Guan G, Zhang K,
Chen J, Jia N, Yan S, Chen G, Liu S, et al: Interleukin-6
suppression reduces tumour self-seeding by circulating tumour cells
in a human osteosarcoma nude mouse model. Oncotarget. 7:446–458.
2016.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
9
|
Ara T, Song L, Shimada H, Keshelava N,
Russell HV, Metelitsa LS, Groshen SG, Seeger RC and DeClerck YA:
Interleukin-6 in the bone marrow microenvironment promotes the
growth and survival of neuroblastoma cells. Cancer Res. 69:329–337.
2009. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
10
|
Ogata A, Chauhan D, Teoh G, Treon SP,
Urashima M, Schlossman RL and Anderson KC: IL-6 triggers cell
growth via the Ras-dependent mitogen-activated protein kinase
cascade. J Immunol. 159:2212–2221. 1997.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
11
|
Ataie-Kachoie P, Pourgholami MH and Morris
DL: Inhibition of the IL-6 signaling pathway: A strategy to combat
chronic inflammatory diseases and cancer. Cytokine Growth Factor
Rev. 24:163–173. 2013. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
12
|
Suchi K, Fujiwara H, Okamura S, Okamura H,
Umehara S, Todo M, Furutani A, Yoneda M, Shiozaki A, Kubota T, et
al: Overexpression of Interleukin-6 suppresses cisplatin-induced
cytotoxicity in esophageal squamous cell carcinoma cells.
Anticancer Res. 31:67–75. 2011.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
13
|
Sierra A: Metastases and their
microenvironments: Linking pathogenesis and therapy. Drug Resist
Updat. 8:247–257. 2005. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
14
|
Abroun S, Saki N, Ahmadvand M, Asghari F,
Salari F and Rahim F: STATs: An οld σtory, υet μesmerizing. Cell J.
17:395–411. 2015.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
15
|
Klemm JD, Schreiber SL and Crabtree GR:
Dimerization as a regulatory mechanism in signal transduction. Annu
Rev Immunol. 16:569–592. 1998. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
16
|
Banerjee K and Resat H: Constitutive
activation of STAT3 in breast cancer cells: A review. Int J Cancer.
138:2570–2578. 2016. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
17
|
Berishaj M, Gao SP, Ahmed S, Leslie K,
Al-Ahmadie H, Gerald WL, Bornmann W and Bromberg JF: Stat3 is
tyrosine-phosphorylated through the interleukin-6/glycoprotein
130/janus kinase pathway in breast cancer. Breast Cancer Res.
9:R322007. View
Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
18
|
Rangan SR: A new human cell line (FaDu)
from a hypopharyngeal carcinoma. Cancer. 29:117–121. 1972.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
19
|
Zenner HP, Lehner W and Herrmann IF:
Establishment of carcinoma cell lines from larynx and submandibular
gland. Arch Otorhinolaryngol. 225:269–277. 1979. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
20
|
Mosmann T: Rapid colorimetric assay for
cellular growth and survival: Application to proliferation and
cytotoxicity assays. J Immunol Methods. 65:55–63. 1983. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
21
|
Scherzed A, Hackenberg S, Froelich K,
Kessler M, Koehler C, Hagen R, Radeloff A, Friehs G and Kleinsasser
N: BMSC enhance the survival of paclitaxel treated squamous cell
carcinoma cells in vitro. Cancer Biol Ther. 11:349–357. 2011.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
22
|
Scherzad A, Steber M, Gehrke T, Rak K,
Froelich K, Schendzielorz P, Hagen R, Kleinsasser N and Hackenberg
S: Human mesenchymal stem cells enhance cancer cell proliferation
via IL-6 secretion and activation of ERK1/2. Int J Oncol.
47:391–397. 2015. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
23
|
Lowry OH, Rosebrough NJ, Farr AL and
Randall RJ: Protein measurement with the Folin phenol reagent. J
Biol Chem. 193:265–275. 1951.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
24
|
Scholzen T and Gerdes J: The Ki-67
protein: From the known and the unknown. J Cell Physiol.
182:311–322. 2000. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
25
|
Loetscher P, Seitz M, Clark-Lewis I,
Baggiolini M and Moser B: Monocyte chemotactic proteins MCP-1,
MCP-2, and MCP-3 are major attractants for human CD4+
and CD8+ T lymphocytes. FASEB J. 8:1055–1060. 1994.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
26
|
Gonzalez AC, Costa TF, Andrade ZA and
Medrado AR: Wound healing - A literature review. An Bras Dermatol.
91:614–620. 2016. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
27
|
Guo S and Dipietro LA: Factors affecting
wound healing. J Dent Res. 89:219–229. 2010. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
28
|
Ho J, Walsh C, Yue D, Dardik A and Cheema
U: Current advancements and strategies in tissue engineering for
wound healing: A comprehensive review. Adv Wound Care. 6:191–209.
2017. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
29
|
Lee DE, Ayoub N and Agrawal DK:
Mesenchymal stem cells and cutaneous wound healing: Novel methods
to increase cell delivery and therapeutic efficacy. Stem Cell Res
Ther. 7:372016. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
30
|
Barrientos S, Brem H, Stojadinovic O and
Tomic-Canic M: Clinical application of growth factors and cytokines
in wound healing. Wound Repair Regen. 22:569–578. 2014. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
31
|
Heldin CH: Targeting the PDGF signaling
pathway in tumor treatment. Cell Commun Signal. 11:972013.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
32
|
Alieva M, van Rheenen J and Broekman ML:
Potential impact of invasive surgical procedures on primary tumor
growth and metastasis. Clin Exp Metastasis. 35:319–331. 2018.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
33
|
Wang B, Hendricks DT, Wamunyokoli F and
Parker MI: A growth-related oncogene/CXC chemokine receptor 2
autocrine loop contributes to cellular proliferation in esophageal
cancer. Cancer Res. 66:3071–3077. 2006. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
34
|
Lian S, Zhai X, Wang X, Zhu H, Zhang S,
Wang W, Wang Z and Huang J: Elevated expression of growth-regulated
oncogene-alpha in tumor and stromal cells predicts unfavorable
prognosis in pancreatic cancer. Medicine. 95:e43282016. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
35
|
Chaubey N and Ghosh SS: Overexpression of
granulocyte macrophage colony stimulating factor in breast cancer
cells leads towards drug sensitization. Appl Biochem Biotechnol.
175:1948–1959. 2015. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
36
|
Mitsuyama K, Sata M and Rose-John S:
Interleukin-6 trans-signaling in inflammatory bowel disease.
Cytokine Growth Factor Rev. 17:451–461. 2006. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
37
|
Gallo O, Gori AM, Attanasio M, Martini F,
Paola G, Storchi OF and Abbate R: Acute-phase proteins and
interleukin 6 serum level in head and neck cancer. Arch Otolaryngol
Head Neck Surg. 118:1366–1367. 1992. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
38
|
Chen Z, Malhotra PS, Thomas GR, Ondrey FG,
Duffey DC, Smith CW, Enamorado I, Yeh NT, Kroog GS, Rudy S, et al:
Expression of proinflammatory and proangiogenic cytokines in
patients with head and neck cancer. Clin Cancer Res. 5:1369–1379.
1999.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
39
|
Ihle JN: The stat family in cytokine
signaling. Curr Opin Cell Biol. 13:211–217. 2001. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
40
|
Heinrich PC, Behrmann I, Haan S, Hermanns
HM, Muller-Newen G and Schaper F: Principles of interleukin
(IL)-6-type cytokine signalling and its regulation. Biochem J.
374:1–20. 2003. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
41
|
Wang Y, van Boxel-Dezaire AH, Cheon H,
Yang J and Stark GR: STAT3 activation in response to IL-6 is
prolonged by the binding of IL-6 receptor to EGF receptor. Proc
Natl Acad Sci USA. 110:16975–16980. 2013. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
42
|
Yan JF, Huang WJ, Zhao JF, Fu HY, Zhang
GY, Huang XJ and Lv BD: The platelet-derived growth factor
receptor/STAT3 signaling pathway regulates the phenotypic
transition of corpus cavernosum smooth muscle in rats. PLoS One.
12:e01721912017. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
43
|
Simon AR, Takahashi S, Severgnini M,
Fanburg BL and Cochran BH: Role of the JAK-STAT pathway in
PDGF-stimulated proliferation of human airway smooth muscle cells.
Am J Physiol Lung Cell Mol Physiol. 282:L1296–L1304. 2002.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
44
|
Ishida Y, Kimura A, Kuninaka Y, Inui M,
Matsushima K, Mukaida N and Kondo T: Pivotal role of the CCL5/CCR5
interaction for recruitment of endothelial progenitor cells in
mouse wound healing. J Clin Invest. 122:711–721. 2012. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
45
|
Karnoub AE, Dash AB, Vo AP, Sullivan A,
Brooks MW, Bell GW, Richardson AL, Polyak K, Tubo R and Weinberg
RA: Mesenchymal stem cells within tumour stroma promote breast
cancer metastasis. Nature. 449:557–563. 2007. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
46
|
Waters JH, Miller LR, Clack S and Kim JV:
Cause of metabolic acidosis in prolonged surgery. Crit Care Med.
27:2142–2146. 1999. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
47
|
Corbet C and Feron O: Emerging roles of
lipid metabolism in cancer progression. Curr Opin Clin Nutr Metab
Care. 20:254–260. 2017. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
48
|
Menard JA, Christianson HC, Kucharzewska
P, Bourseau- Guilmain E, Svensson KJ, Lindqvist E, Indira Chandran
V, Kjellén L, Welinder C, Bengzon J, et al: Metastasis stimulation
by hypoxia and acidosis-induced extracellular lipid uptake is
mediated by proteoglycan-dependent endocytosis. Cancer Res.
76:4828–4840. 2016. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
49
|
Wang D, Hu K, Gao N, Zhang H, Jiang Y, Liu
C, Wang S and Zhao Z: High throughput screening of cytokines,
chemokines and matrix metalloproteinases in wound fluid induced by
mammary surgery. Oncotarget. 6:29296–29310. 2015.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
50
|
Licitra L, Perrone F, Tamborini E, Bertola
L, Ghirelli C, Negri T, Orsenigo M, Filipazzi P, Pastore E,
Pompilio M, et al: Role of EGFR family receptors in proliferation
of squamous carcinoma cells induced by wound healing fluids of head
and neck cancer patients. Ann Oncol. 22:1886–1893. 2011. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
51
|
Zimmermann M, Zouhair A, Azria D and
Ozsahin M: The epidermal growth factor receptor (EGFR) in head and
neck cancer: Its role and treatment implications. Radiat Oncol.
1:112006. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
52
|
Sano D, Gule MK, Rosenthal DI, Bell D,
Yates J, El-Naggar AK and Myers JN: Early postoperative epidermal
growth factor receptor inhibition: Safety and effectiveness in
inhibiting microscopic residual of oral squamous cell carcinoma in
vivo. Head Neck. 35:321–328. 2013. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
53
|
Gordon CR, Rojavin Y, Patel M, Zins JE,
Grana G, Kann B, Simons R and Atabek U: A review on bevacizumab and
surgical wound healing: An important warning to all surgeons. Ann
Plastic Surg. 62:707–709. 2009. View Article : Google Scholar
|