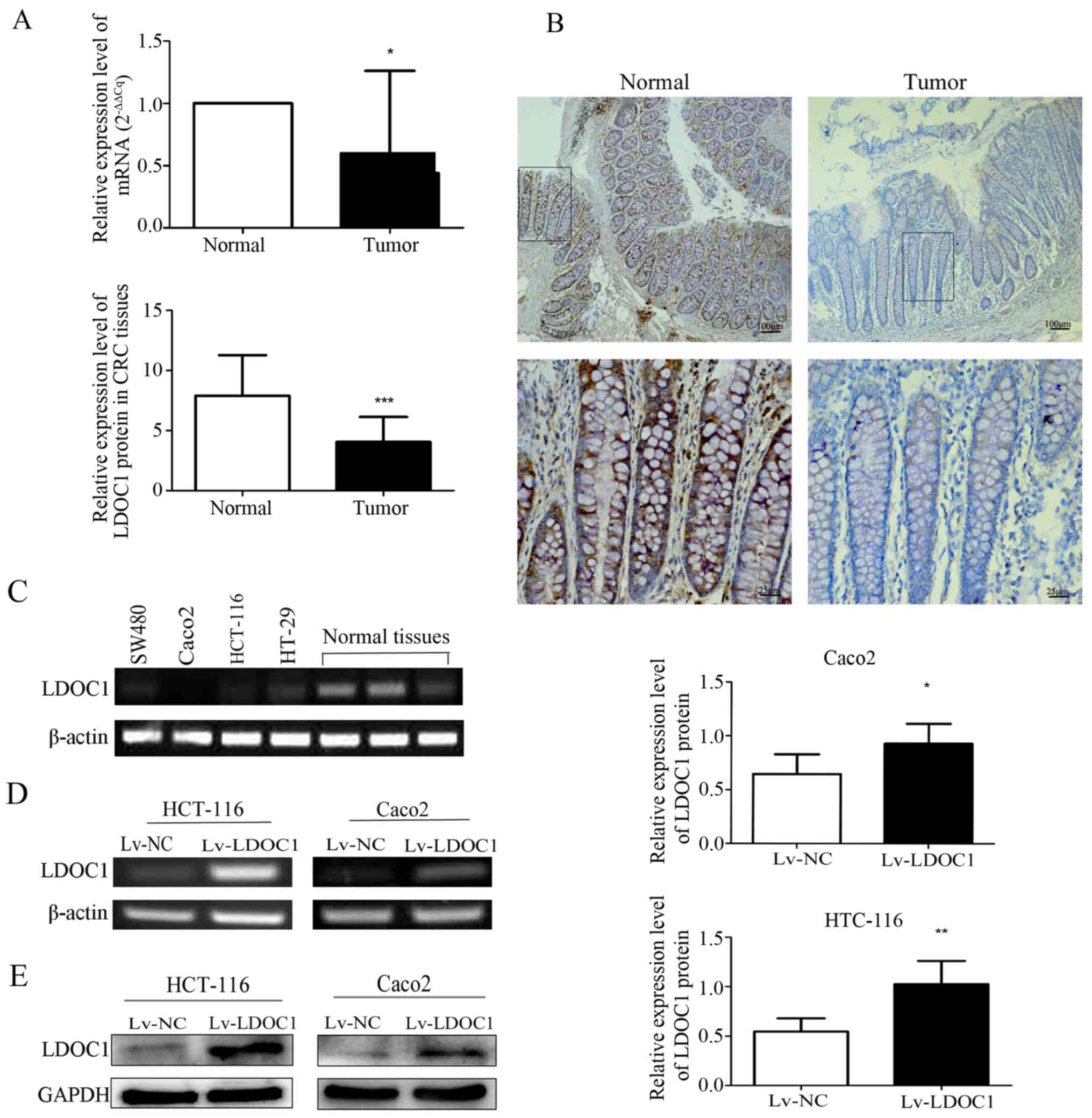
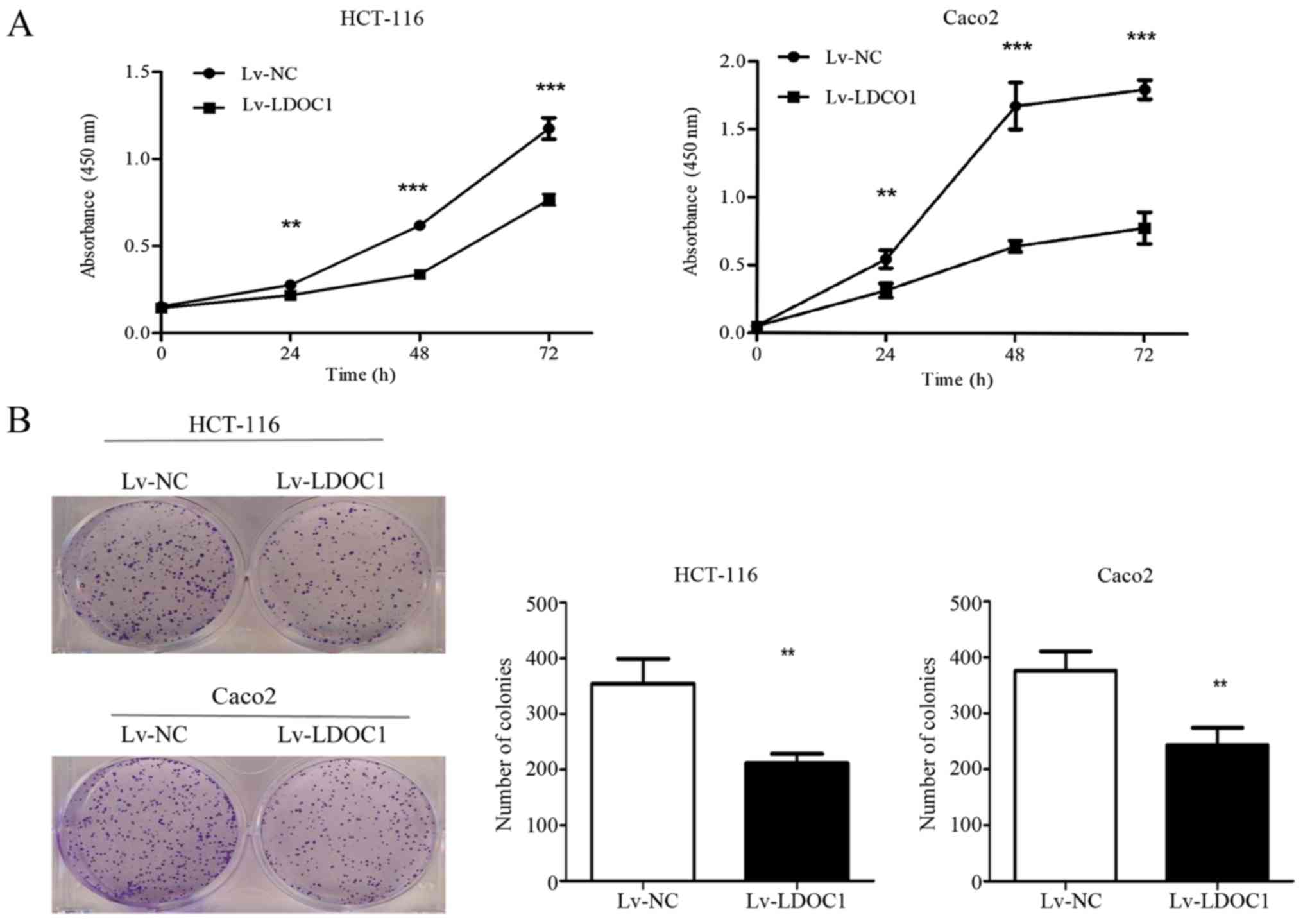
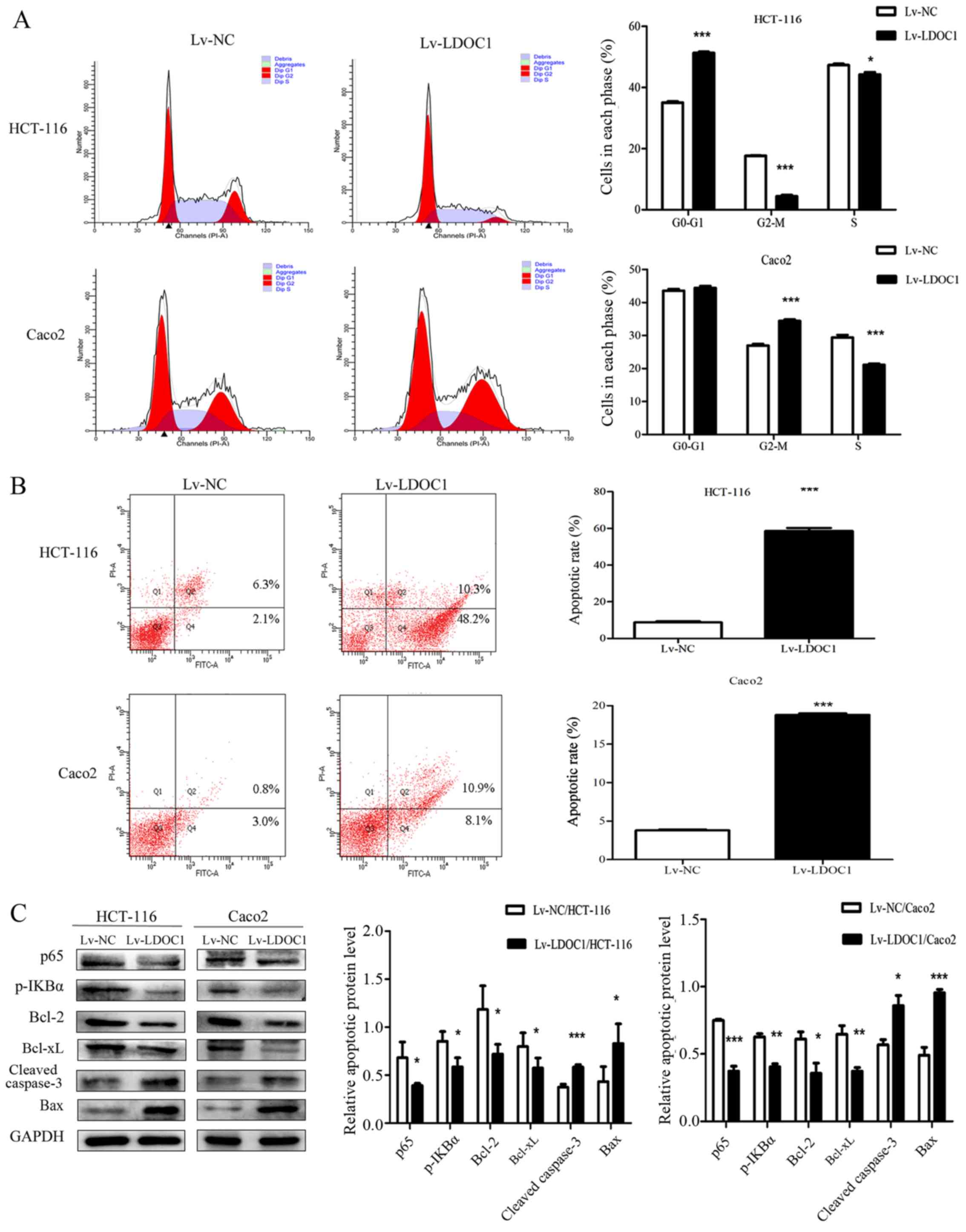
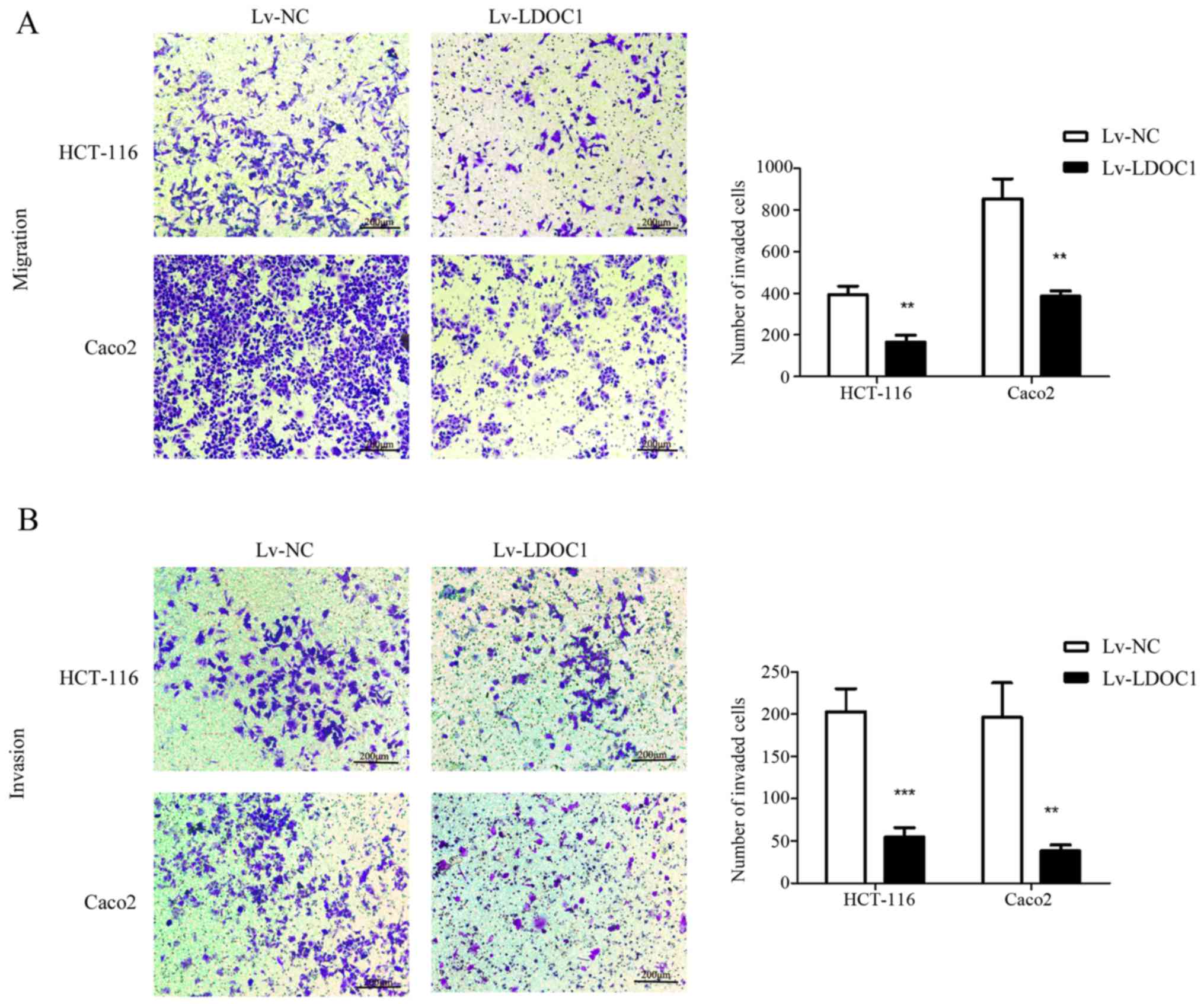
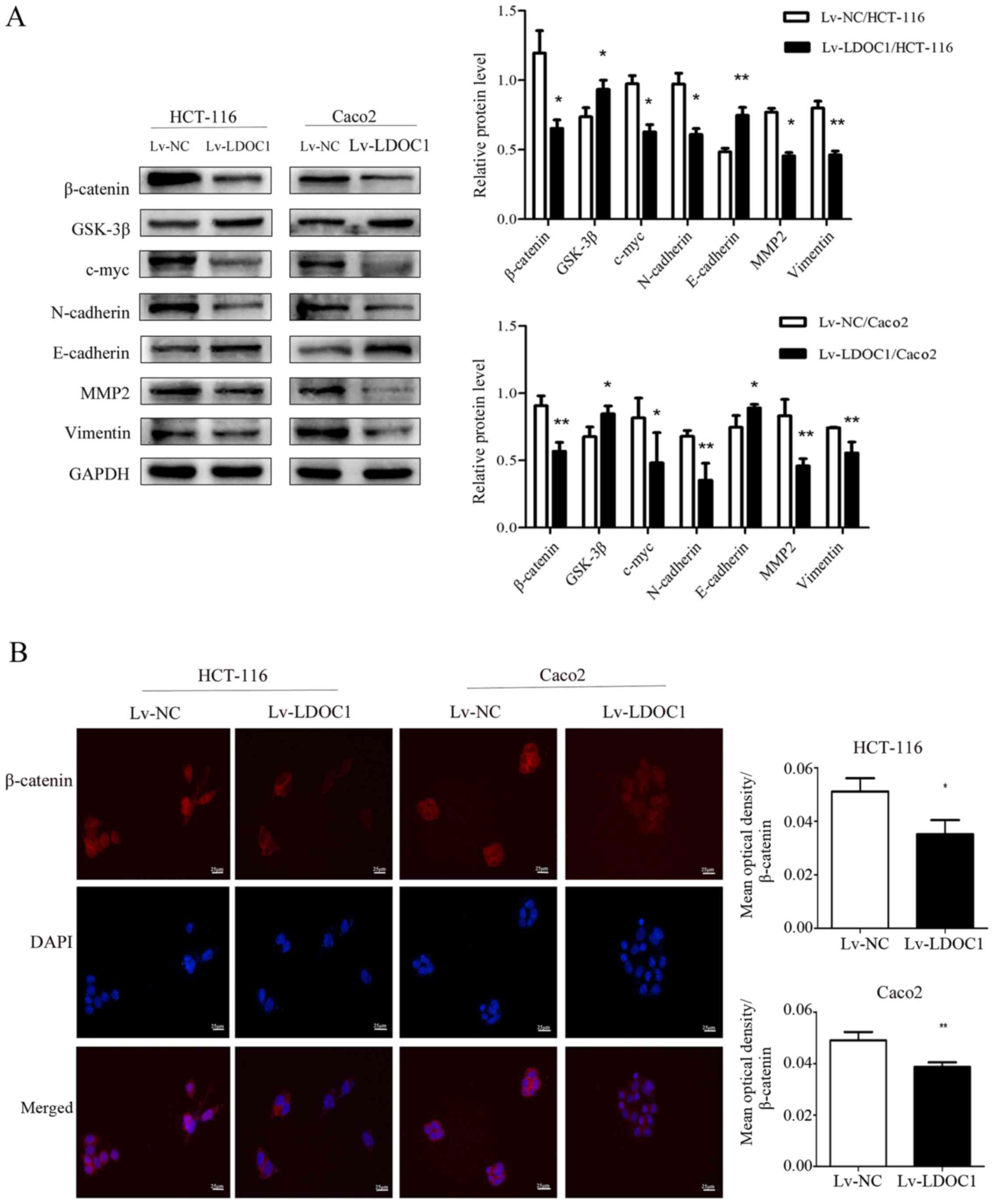
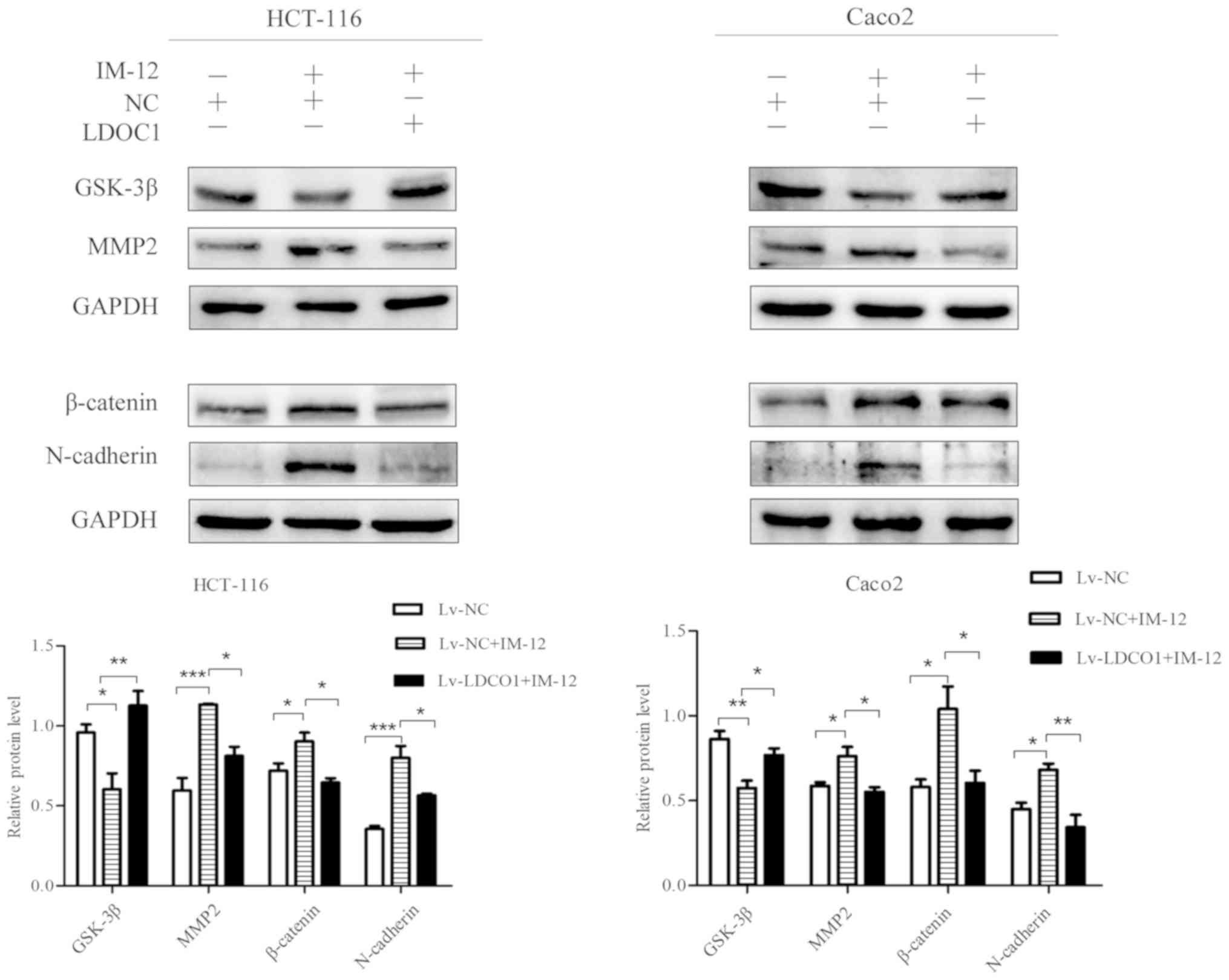
|
1
|
Torre LA, Bray F, Siegel RL, Ferlay J,
Lortet-Tieulent J and Jemal A: Global cancer statistics, 2012. CA
Cancer J Clin. 65:87–108. 2015. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
2
|
Siegel RL, Miller KD, Fedewa SA, Ahnen DJ,
Meester RG, Barzi A and Jemal A: Colorectal cancer statistics,
2017. CA Cancer J Clin. 67:177–193. 2017. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
3
|
Bray F, Ferlay J, Soerjomataram I, Siegel
RL, Torre LA and Jemal A: Global cancer statistics 2018: GLOBOCAN
estimates of incidence and mortality worldwide for 36 cancers in
185 countries. CA Cancer J Clin. 68:394–424. 2018. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
4
|
Luo Y, Tsuchiya KD, Il Park D, Fausel R,
Kanngurn S, Welcsh P, Dzieciatkowski S, Wang J and Grady WM: RET is
a potential tumor suppressor gene in colorectal cancer. Oncogene.
32:2037–2047. 2013. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
5
|
Nagasaki K, Manabe T, Hanzawa H, Maass N,
Tsukada T and Yamaguchi K: Identification of a novel gene, LDOC1,
down-regulated in cancer cell lines. Cancer Lett. 140:227–234.
1999. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
6
|
Zhao S, Wang Q, Li Z, Ma X, Wu L, Ji H and
Qin G: LDOC1 inhibits proliferation and promotes apoptosis by
repressing NF-κB activation in papillary thyroid carcinoma. J Exp
Clin Cancer Res. 34:1462015. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
7
|
Lee CH, Pan KL, Tang YC, Tsai MH, Cheng
AJ, Shen MY, Cheng YM, Huang TT and Lin P: LDOC1 silenced by
cigarette exposure and involved in oral neoplastic transformation.
Oncotarget. 6:25188–25201. 2015.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
8
|
Riordan JD and Dupuy AJ: Domesticated
transposable element gene products in human cancer. Mob Genet
Elements. 3:e266932013. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
9
|
Camões MJ, Paulo P, Ribeiro FR,
Barros-Silva JD, Almeida M, Costa VL, Cerveira N, Skotheim RI,
Lothe RA, Henrique R, et al: Potential downstream target genes of
aberrant ETS transcription factors are differentially affected in
Ewing's sarcoma and prostate carcinoma. PLoS One. 7:e498192012.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
10
|
Inoue M, Takahashi K, Niide O, Shibata M,
Fukuzawa M and Ra C: LDOC1, a novel MZF-1-interacting protein,
induces apoptosis. FEBS Lett. 579:604–608. 2005. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
11
|
Griesinger AM, Witt DA, Grob ST, Georgio
Westover SR, Donson AM, Sanford B, Mulcahy Levy JM, Wong R, Moreira
DC, DeSisto JA, et al: NF-κB upregulation through epigenetic
silencing of LDOC1 drives tumor biology and specific
immunophenotype in Group A ependymoma. Neuro Oncol. 19:1350–1360.
2017. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
12
|
Thoompumkal IJ, Rehna K, Anbarasu K and
Mahalingam S: Leucine zipper down-regulated in cancer-1 (LDOC1)
interacts with guanine nucleotide binding protein-like 3-like
(GNL3L) to modulate nuclear factor-kappa B (NF-κB) signaling during
cell proliferation. Cell Cycle. 15:3251–3267. 2016. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
13
|
Nagasaki K, Schem C, von Kaisenberg C,
Biallek M, Rösel F, Jonat W and Maass N: Leucine-zipper protein,
LDOC1, inhibits NF-kappaB activation and sensitizes pancreatic
cancer cells to apoptosis. Int J Cancer. 105:454–458. 2003.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
14
|
Buchholtz ML, Brüning A, Mylonas I and
Jückstock J: Epigenetic silencing of the LDOC1 tumor suppressor
gene in ovarian cancer cells. Arch Gynecol Obstet. 290:149–154.
2014. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
15
|
Buchholtz ML, Jückstock J, Weber E,
Mylonas I, Dian D and Brüning A: Loss of LDOC1 expression by
promoter methylation in cervical cancer cells. Cancer Invest.
31:571–577. 2013. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
16
|
Yong BC, Lu JC, Xie XB, Su Q, Tan PX, Tang
QL, Wang J, Huang G, Han J, Xu HW, et al: LDOC1 regulates Wnt5a
expression and osteosarcoma cell metastasis and is correlated with
the survival of osteosarcoma patients. Tumour Biol. Feb
1–2017.(Epub ahead of print). doi.org/10.1177/1010428317691188.
PubMed/NCBI
|
|
17
|
Chen X, Jia C, Jia C, Jin X and Gu X:
MicroRNA-374a inhibits aggressive tumor biological behavior in
bladder carcinoma by suppressing Wnt/β-catenin signaling. Cell
Physiol Biochem. 48:815–826. 2018. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
18
|
Park HW, Kim YC, Yu B, Moroishi T, Mo JS,
Plouffe SW, Meng Z, Lin KC, Yu FX, Alexander CM, et al: Alternative
Wnt signaling activates YAP/TAZ. Cell. 162:780–794. 2015.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
19
|
Zhang LZ, Huang LY, Huang AL, Liu JX and
Yang F: CRIP1 promotes cell migration, invasion and
epithelial-mesenchymal transition of cervical cancer by activating
the Wnt/β catenin signaling pathway. Life Sci. 207:420–427. 2018.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
20
|
Yu R, Cai L, Chi Y, Ding X and Wu X:
miR-377 targets CUL4A and regulates metastatic capability in
ovarian cancer. Int J Mol Med. 41:3147–3156. 2018.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
21
|
Ling DJ, Chen ZS, Zhang YD, Liao QD, Feng
JX, Zhang XY and Shi TS: MicroRNA-145 inhibits lung cancer cell
metastasis. Mol Med Rep. 11:3108–3114. 2015. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
22
|
Wang YP, Guo PT, Zhu Z, Zhang H, Xu Y,
Chen YZ, Liu F and Ma SP: Pleomorphic adenoma gene like-2 induces
epithelial-mesenchymal transition via Wnt/β-catenin signaling
pathway in human colorectal adenocarcinoma. Oncol Rep.
37:1961–1970. 2017. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
23
|
Tang X, Zha L, Li H, Liao G, Huang Z, Peng
X and Wang Z: Upregulation of GNL3 expression promotes colon cancer
cell proliferation, migration, invasion and epithelial-mesenchymal
transition via the Wnt/β-catenin signaling pathway. Oncol Rep.
38:2023–2032. 2017. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
24
|
Kim HJ, Moon SJ, Kim SH, Heo K and Kim JH:
DBC1 regulates Wnt/β-catenin-mediated expression of MACC1, a key
regulator of cancer progression, in colon cancer. Cell Death Dis.
9:8312018. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
25
|
Livak KJ and Schmittgen TD: Analysis of
relative gene expression data using real-time quantitative PCR and
the 2(-Delta Delta C(T)) method. Methods. 25:402–408. 2001.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
26
|
Tao Y, Tao T, Gross N, Peng X, Li Y, Huang
Z, Liu L, Li G, Chen X and Yang J: Combined effect of IL-12Rβ2 and
IL-23R expression on prognosis of patients with laryngeal cancer.
Cell Physiol Biochem. 50:1041–1054. 2018. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
27
|
Chen J: The cell-cycle arrest and
apoptotic functions of p53 in tumor initiation and progression.
Cold Spring Harb Perspect Med. 6:a0261042016. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
28
|
Patil M, Pabla N and Dong Z: Checkpoint
kinase 1 in DNA damage response and cell cycle regulation. Cell Mol
Life Sci. 70:4009–4021. 2013. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
29
|
Wang X, Zhu Y, Sun C, Wang T, Shen Y, Cai
W, Sun J, Chi L, Wang H, Song N, et al: Feedback activation of
basic fibroblast growth factor signaling via the Wnt/β-catenin
pathway in skin fibroblasts. Front Pharmacol. 8:322017.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
30
|
Cai T, Sun D, Duan Y, Wen P, Dai C, Yang J
and He W: WNT/β-catenin signaling promotes VSMCs to osteogenic
transdifferentiation and calcification through directly modulating
Runx2 gene expression. Exp Cell Res. 345:206–217. 2016. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
31
|
Johnson IT and Belshaw NJ: Environment,
diet and CpG island methylation: Epigenetic signals in
gastrointestinal neoplasia. Food Chem Toxicol. 46:1346–1359. 2008.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
32
|
Hayden MS and Ghosh S: Regulation of NF-κB
by TNF family cytokines. Semin Immunol. 26:253–266. 2014.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
33
|
Yu L, Li L, Medeiros LJ and Young KH:
NF-κB signaling pathway and its potential as a target for therapy
in lymphoid neoplasms. Blood Rev. 31:77–92. 2017. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
34
|
Shukla S, Shankar E, Fu P, MacLennan GT
and Gupta S: Suppression of NF-κB and NF-κB-regulated gene
expression by apigenin through IκBα and IKK pathway in TRAMP mice.
PLoS One. 10:e01387102015. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
35
|
Prasad S, Ravindran J and Aggarwal BB:
NF-kappaB and cancer: How intimate is this relationship. Mol Cell
Biochem. 336:25–37. 2010. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
36
|
Brentnall M, Rodriguez-Menocal L, De
Guevara RL, Cepero E and Boise LH: Caspase-9, caspase-3 and
caspase-7 have distinct roles during intrinsic apoptosis. BMC Cell
Biol. 14:322013. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
37
|
Dai G, Zheng D, Wang Q, Yang J, Liu G,
Song Q, Sun X, Tao C, Hu Q, Gao T, et al: Baicalein inhibits
progression of osteosarcoma cells through inactivation of the
Wnt/β-catenin signaling pathway. Oncotarget. 8:86098–86116. 2017.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
38
|
Kwon YJ, Baek HS, Ye DJ, Shin S, Kim D and
Chun YJ: CYP1B1 enhances cell proliferation and metastasis through
induction of EMT and activation of Wnt/β-catenin signaling via Sp1
upregulation. PLoS One. 11:e01515982016. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
39
|
Lee JM, Dedhar S, Kalluri R and Thompson
EW: The epithelial-mesenchymal transition: New insights in
signaling, development, and disease. J Cell Biol. 172:973–981.
2006. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|