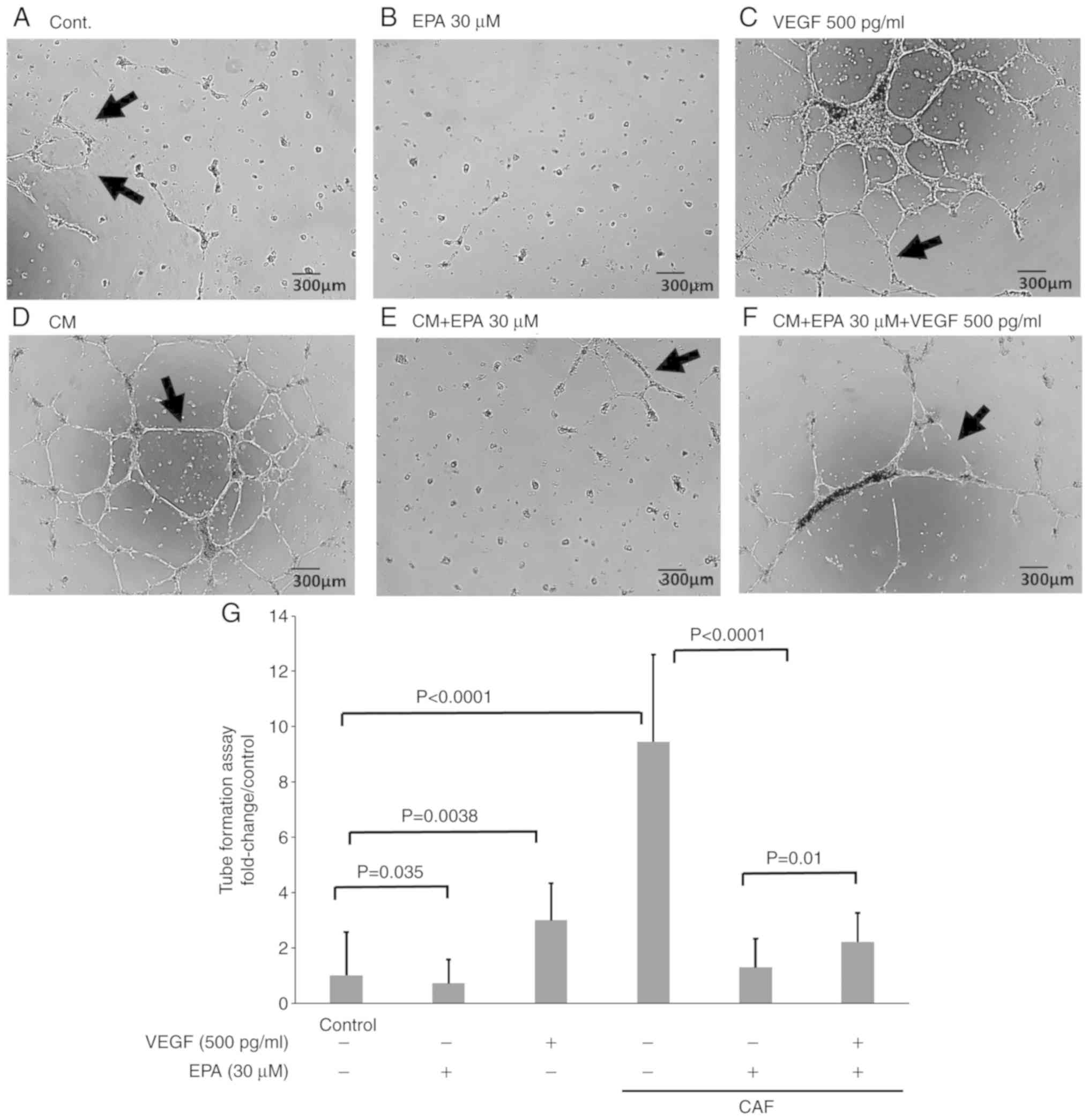
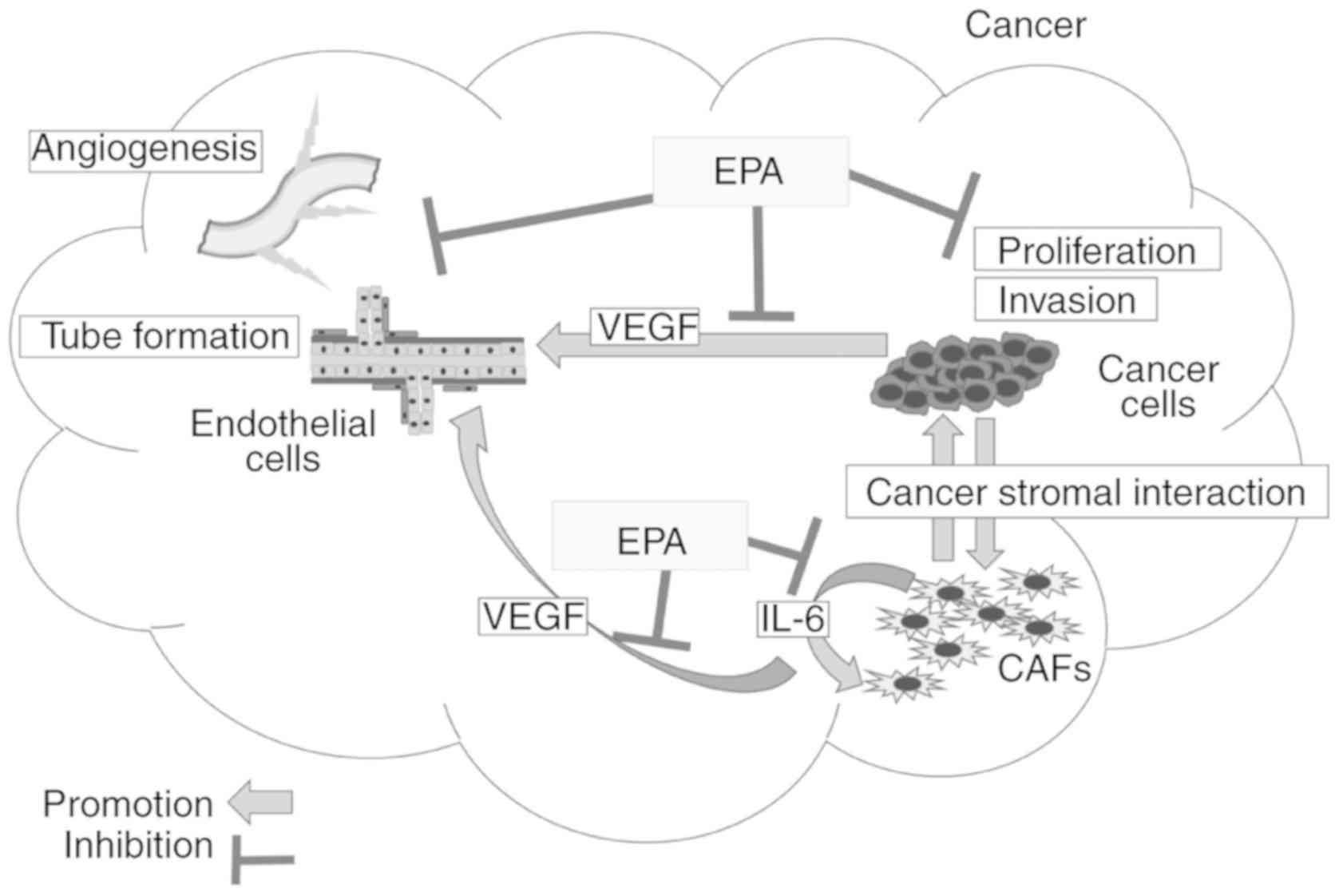
|
1
|
Shiga K, Hara M, Nagasaki T, Sato T,
Takahashi H and Takeyama H: Cancer-associated fibroblasts: Their
characteristics and their roles in tumor growth. Cancers (Basel).
7:2443–2458. 2015. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
2
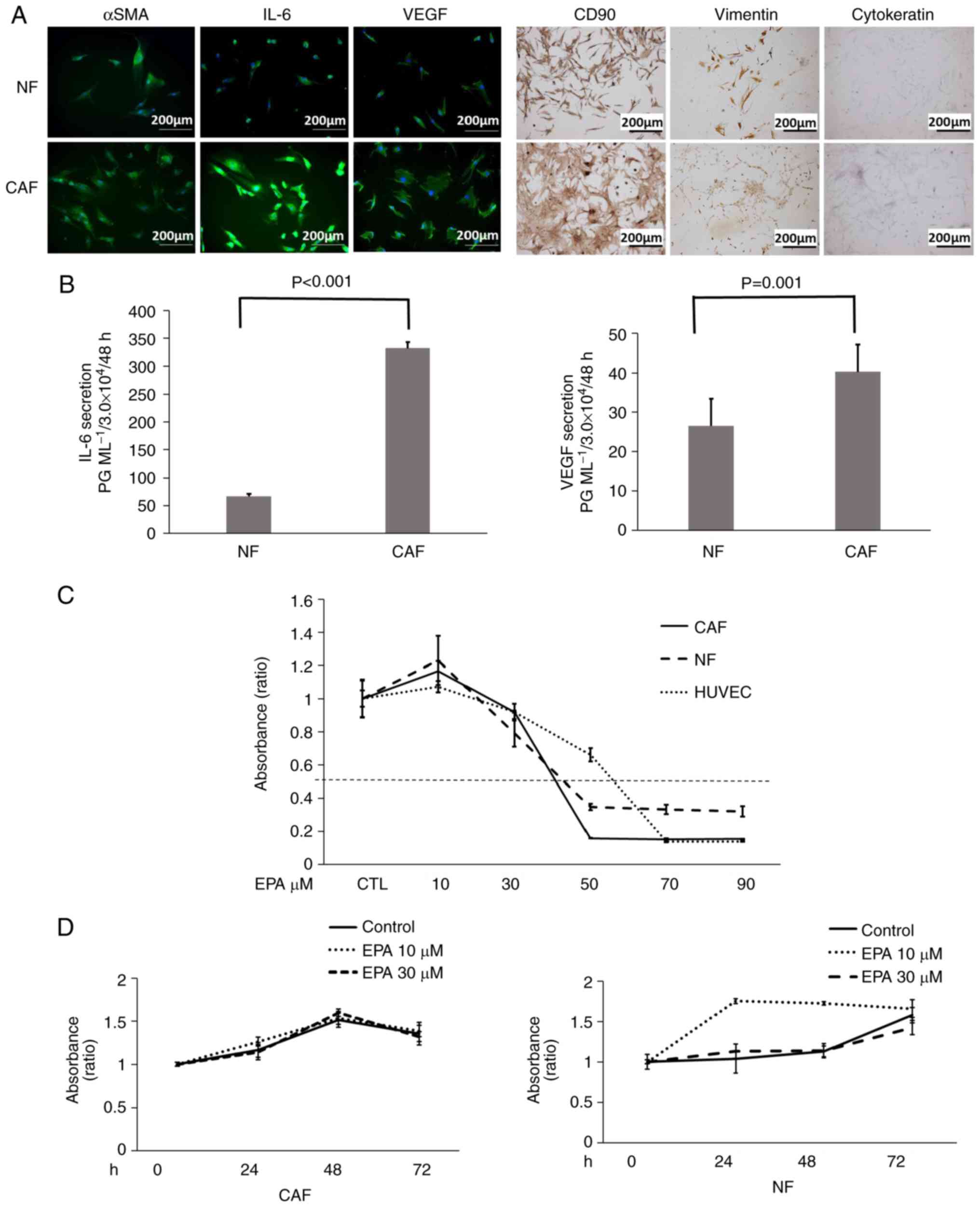
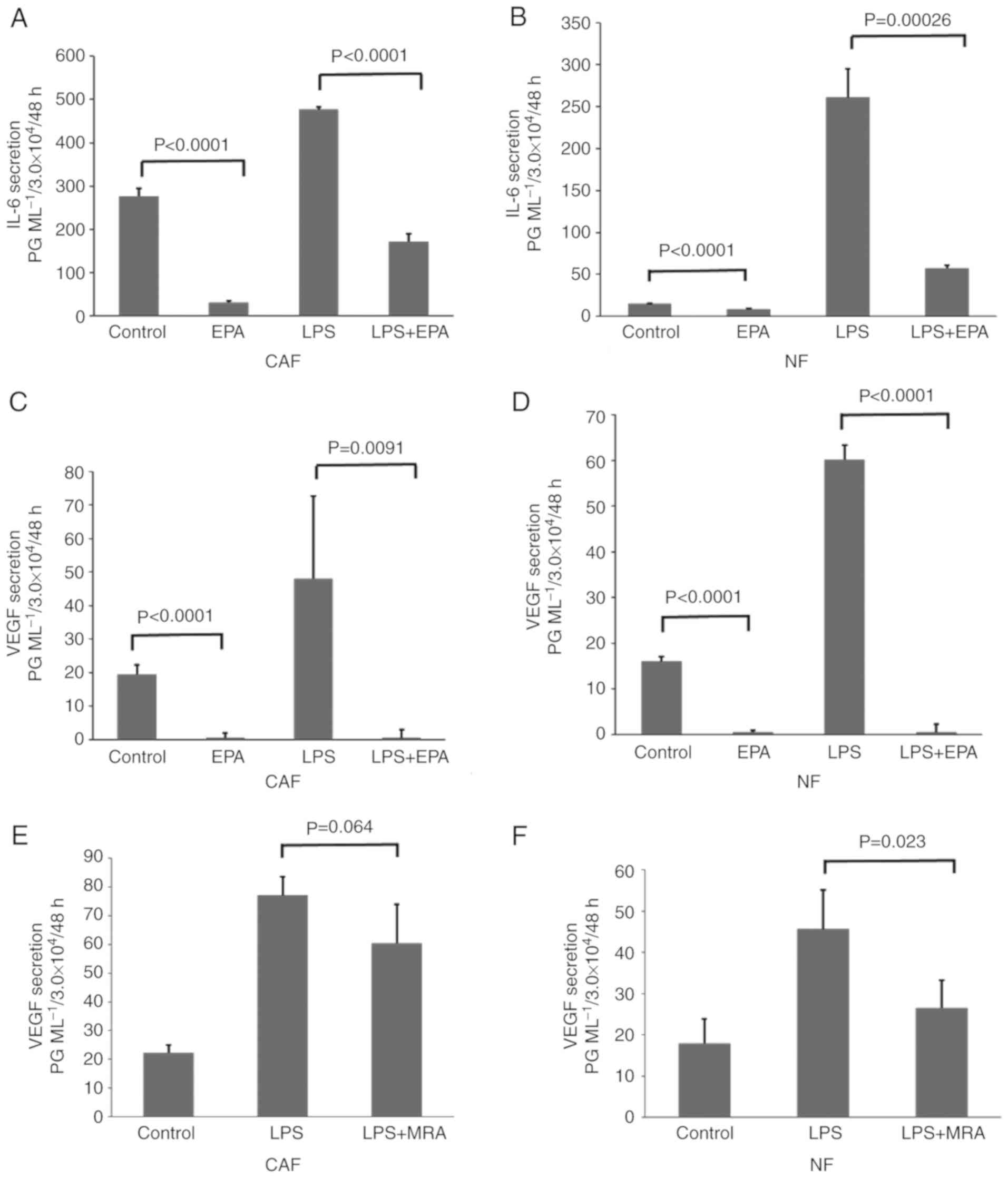
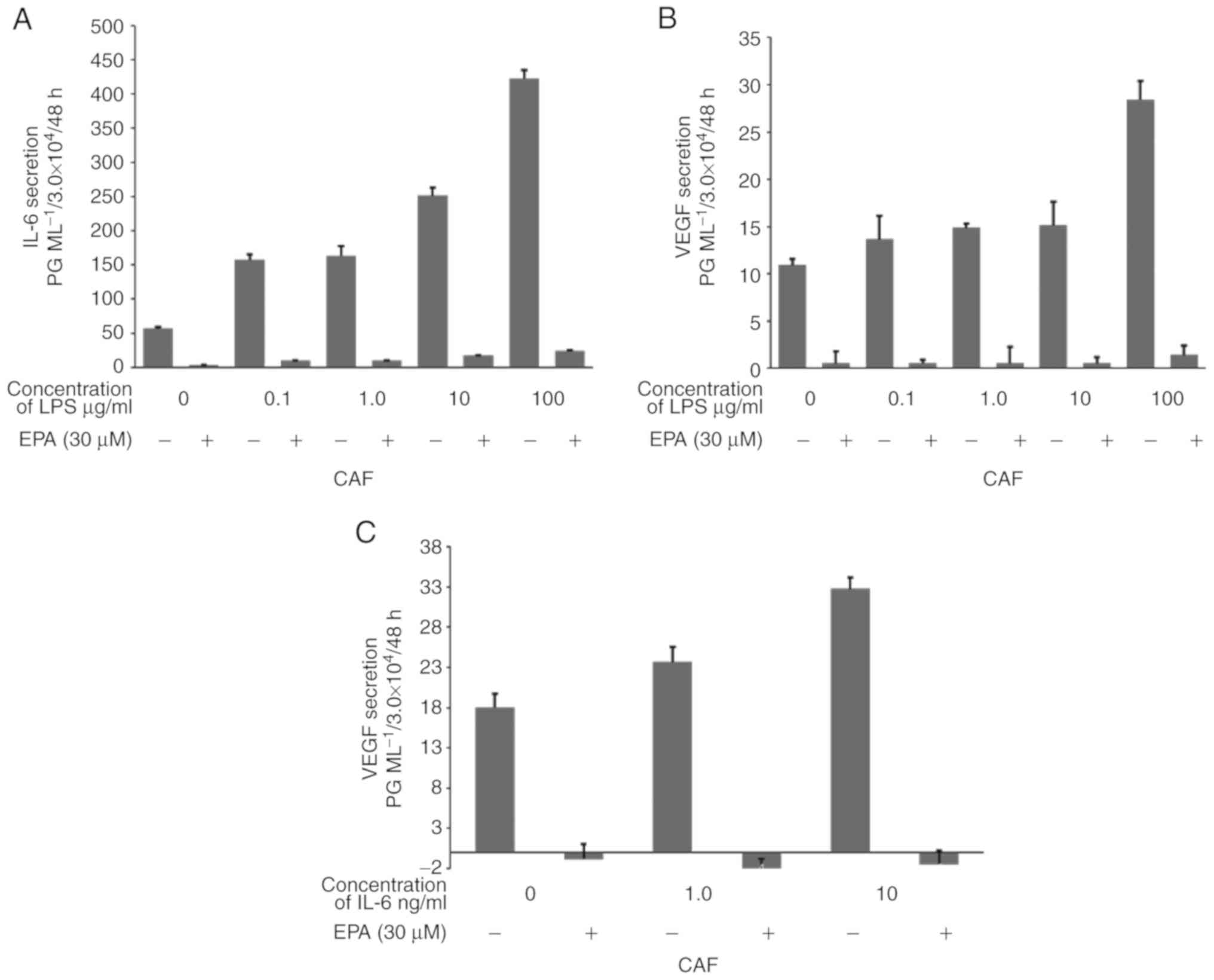
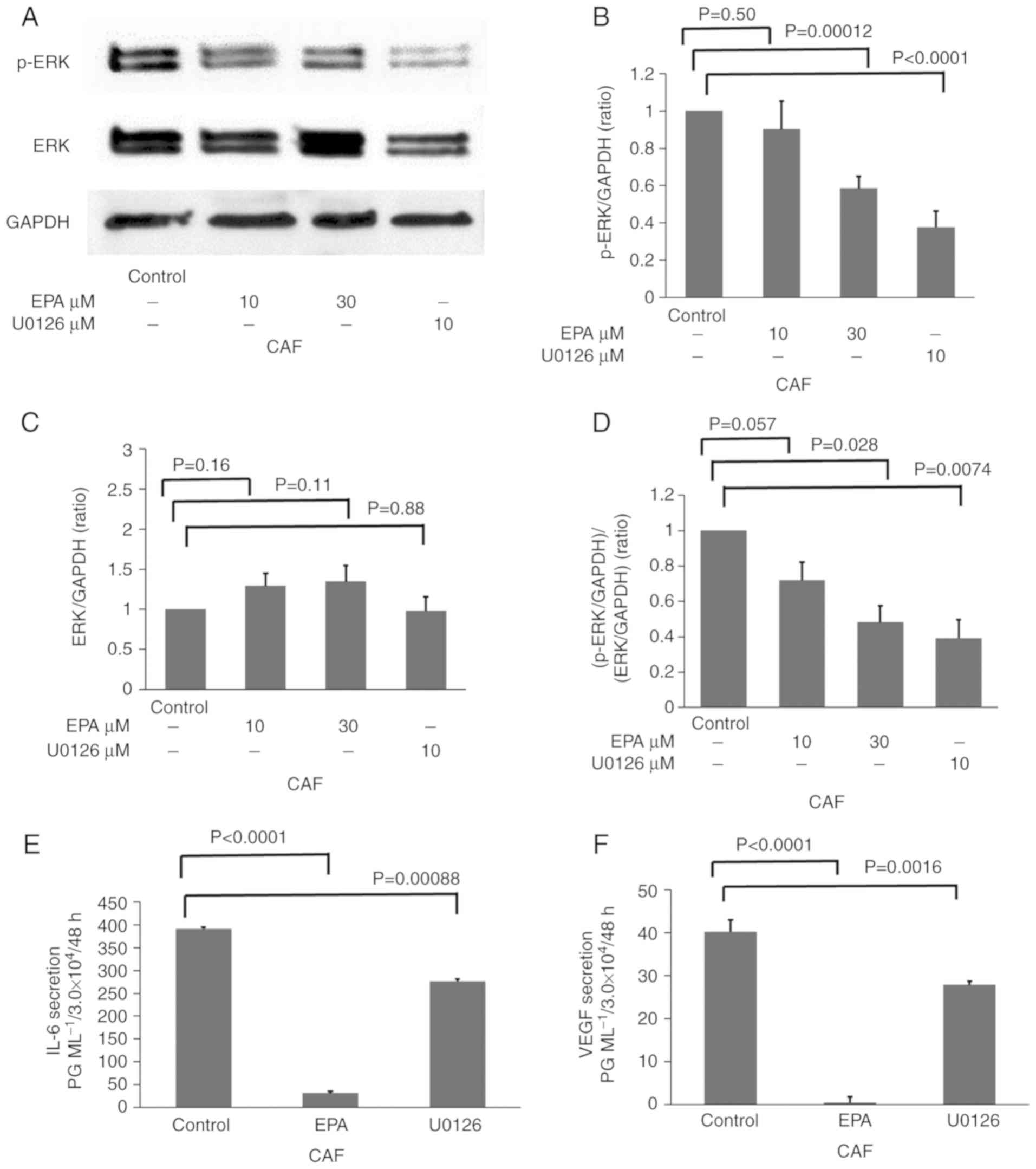
|
Wu MH, Hong HC, Hong TM, Chiang WF, Jin YT
and Chen YL: Targeting galectin-1 in carcinoma-associated
fibroblasts inhibits oral squamous cell carcinoma metastasis by
downregulating MCP-1/CCL2 expression. Clin Cancer Res.
17:1306–1316. 2011. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
3
|
Zhang Y, Tang H, Cai J, Zhang T, Guo J,
Feng D and Wang Z: Ovarian cancer-associated fibroblasts contribute
to epithelial ovarian carcinoma metastasis by promoting
angiogenesis, lymphangiogenesis and tumor cell invasion. Cancer
Lett. 303:47–55. 2011. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
4
|
Rosen LS: Clinical experience with
angiogenesis signaling inhibitors: Focus on vascular endothelial
growth factor (VEGF) blockers. Cancer Control. 9 (Suppl 2):S36–S44.
2002. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
5
|
Procaccio L, Damuzzo V, Di Sarra F, Russi
A, Todino F, Dadduzio V, Bergamo F, Prete AA, Lonardi S, Prenen H,
et al: Safety and tolerability of anti-angiogenic protein kinase
inhibitors and vascular-disrupting agents in cancer: Focus on
gastrointestinal malignancies. Drug Saf. 42:159–179. 2019.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
6
|
Cavaco A, Rezaei M, Niland S and Eble JA:
Collateral damage intended-cancer-associated fibroblasts and
vasculature are potential targets in cancer therapy. Int J Mol Sci.
18:E23552017. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
7
|
Jung JG and Le A: Targeting metabolic
cross talk between cancer cells and cancer-associated fibroblasts.
Adv Exp Med Biol. 1063:167–178. 2018. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
8
|
Melzer C, von der Ohe J, Lehnert H,
Ungefroren H and Hass R: Cancer stem cell niche models and
contribution by mesenchymal stroma/stem cells. Mol Cancer.
16:282017. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
9
|
Ramamonjisoa N and Ackerstaff E:
Characterization of the tumor microenvironment and tumor-stroma
interaction by non-invasive preclinical imaging. Front Oncol.
7:32017. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
10
|
Nagasaki T, Hara M, Nakanishi H, Takahashi
H, Sato M and Takeyama H: Interleukin-6 released by colon
cancer-associated fibroblasts is critical for tumour angiogenesis:
Anti-interleukin-6 receptor antibody suppressed angiogenesis and
inhibited tumour-stroma interaction. Br J Cancer. 110:469–478.
2014. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
11
|
Kubota H, Matsumoto H, Higashida M,
Murakami H, Nakashima H, Oka Y, Okumura H, Yamamura M, Nakamura M
and Hirai T: Eicosapentaenoic acid modifies cytokine activity and
inhibits cell proliferation in an oesophageal cancer cell line.
Anticancer Res. 33:4319–4324. 2013.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
12
|
Adam O: Dietary fatty acids and immune
reactions in synovial tissue. Eur J Med Res. 8:381–387.
2003.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
13
|
Pappalardo G, Almeida A and Ravasco P:
Eicosapentaenoic acid in cancer improves body composition and
modulates metabolism. Nutrition. 31:549–555. 2015. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
14
|
Serini S and Calviello G: Modulation of
Ras/ERK and phosphoinositide signaling by long-chain n-3 PUFA in
breast cancer and their potential complementary role in combination
with targeted drugs. Nutrients. 9:E1852017. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
15
|
Liu Z, Hopkins MM, Zhang Z, Quisenberry
CB, Fix LC, Galvan BM and Meier KE: Omega-3 fatty acids and other
FFA4 agonists inhibit growth factor signaling in human prostate
cancer cells. J Pharmacol Exp Ther. 352:380–394. 2015. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
16
|
Liang P, Henning SM, Schokrpur S, Wu L,
Doan N, Said J, Grogan T, Elashoff D, Cohen P and Aronson WJ:
Effect of dietary Omega-3 fatty acids on tumor-associated
macrophages and prostate cancer progression. Prostate.
76:1293–1302. 2016. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
17
|
Cao W, Ma Z, Rasenick MM, Yeh S and Yu J:
N-3 poly-unsaturated fatty acids shift estrogen signaling to
inhibit human breast cancer cell growth. PLoS One. 7:e528382012.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
18
|
Han L, Zhang Y, Meng M, Cheng D and Wang
C: Eicosapentaenoic acid induced SKOV-3 cell apoptosis through
ERK1/2-mTOR- NF-kappaB pathways. Anticancer Drugs. 27:635–642.
2016. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
19
|
Eltweri AM, Howells LM, Thomas AL,
Dennison AR and Bowrey DJ: Effects of Omegaven®, EPA,
DHA and oxaliplatin on oesophageal adenocarcinoma cell lines
growth, cytokine and cell signal biomarkers expression. Lipids
Health Dis. 17:192018. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
20
|
Calviello G, Di Nicuolo F, Gragnoli S,
Piccioni E, Serini S, Maggiano N, Tringali G, Navarra P, Ranelletti
FO and Palozza P: n-3 PUFAs reduce VEGF expression in human colon
cancer cells modulating the COX-2/PGE2 induced ERK-1 and −2 and
HIF-1alpha induction pathway. Carcinogenesis. 25:2303–2310. 2004.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
21
|
Morin C, Rodriguez E, Blier PU and Fortin
S: Potential application of eicosapentaenoic acid monoacylglyceride
in the management of colorectal cancer. Mar Drugs. 15:E2832017.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
22
|
Mueller L, Goumas FA, Himpel S, Brilloff
S, Rogiers X and Broering DC: Imatinib mesylate inhibits
proliferation and modulates cytokine expression of human
cancer-associated stromal fibroblasts from colorectal metastases.
Cancer Lett. 250:329–338. 2007. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
23
|
Maeda Y, Takahashi H, Nakai N, Yanagita T,
Ando N, Okubo T, Saito K, Shiga K, Hirokawa T, Hara M, et al:
Apigenin induces apoptosis by suppressing Bcl-xl and Mcl-1
simultaneously via signal transducer and activator of transcription
3 signaling in colon cancer. Int J Oncol. Mar 7–2018.(Epub ahead of
print). doi: 10.3892/ijo.2018.4308. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
24
|
Matsuo Y, Campbell PM, Brekken RA, Sung B,
Ouellette MM, Fleming JB, Aggarwal BB, Der CJ and Guha S: K-Ras
promotes angiogenesis mediated by immortalized human pancreatic
epithelial cells through mitogen-activated protein kinase signaling
pathways. Mol Cancer Res. 7:799–808. 2009. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
25
|
Nakagawa H, Liyanarachchi S, Davuluri RV,
Auer H, Martin EW Jr, de la Chapelle A and Frankel WL: Role of
cancer-associated stromal fibroblasts in metastatic colon cancer to
the liver and their expression profiles. Oncogene. 23:7366–7377.
2004. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
26
|
Leung DW, Cachianes G, Kuang WJ, Goeddel
DV and Ferrara N: Vascular endothelial growth factor is a secreted
angiogenic mitogen. Science. 246:1306–1309. 1989. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
27
|
Li CC, Hou YC, Yeh CL and Yeh SL: Effects
of eicosapentaenoic acid and docosahexaenoic acid on prostate
cancer cell migration and invasion induced by tumor-associated
macrophages. PLoS One. 9:e996302014. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
28
|
Hopkins MM, Zhang Z, Liu Z and Meier KE:
Eicosopentaneoic acid and other free fatty acid receptor agonists
inhibit lysophosphatidic acid- and epidermal growth factor-induced
proliferation of human breast cancer cells. J Clin Med. 5:E162016.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
29
|
Denys A, Hichami A and Khan NA:
Eicosapentaenoic acid and docosahexaenoic acid modulate MAP kinase
(ERK1/ERK2) signaling in human T cells. J Lipid Res. 42:2015–2020.
2001.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
30
|
Szymczak M, Murray M and Petrovic N:
Modulation of angiogenesis by omega-3 polyunsaturated fatty acids
is mediated by cyclooxygenases. Blood. 111:3514–3521. 2008.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
31
|
Greten FR, Eckmann L, Greten TF, Park JM,
Li ZW, Egan LJ, Kagnoff MF and Karin M: IKKbeta links inflammation
and tumorigenesis in a mouse model of colitis-associated cancer.
Cell. 118:285–296. 2004. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
32
|
Grivennikov S, Karin E, Terzic J, Mucida
D, Yu GY, Vallabhapurapu S, Scheller J, Rose-John S, Cheroutre H,
Eckmann L and Karin M: IL-6 and Stat3 are required for survival of
intestinal epithelial cells and development of colitis-associated
cancer. Cancer Cell. 15:103–113. 2009. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
33
|
Mocellin MC, Camargo CQ, Nunes EA, Fiates
GMR and Trindade EBSM: A systematic review and meta-analysis of the
n-3 polyunsaturated fatty acids effects on inflammatory markers in
colorectal cancer. Clin Nutr. 35:359–369. 2016. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
34
|
Jung YD, Nakano K, Liu W, Gallick GE and
Ellis LM: Extracellular signal-regulated kinase activation is
required for up-regulation of vascular endothelial growth factor by
serum starvation in human colon carcinoma cells. Cancer Res.
59:4804–4807. 1999.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
35
|
Kojima Y, Acar A, Eaton EN, Mellody KT,
Scheel C, Ben-Porath I, Onder TT, Wang ZC, Richardson AL, Weinberg
RA and Orimo A: Autocrine TGF-beta and stromal cell-derived
factor-1 (SDF-1) signaling drives the evolution of tumor-promoting
mammary stromal myofibroblasts. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA.
107:20009–20014. 2010. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
36
|
Tomiyama K, Murase N, Stolz DB, Toyokawa
H, O'Donnell DR, Smith DM, Dudas JR, Rubin JP and Marra KG:
Characterization of transplanted green fluorescent protein+ bone
marrow cells into adipose tissue. Stem Cells. 26:330–338. 2008.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
37
|
Ishii G, Sangai T, Oda T, Aoyagi Y, Hasebe
T, Kanomata N, Endoh Y, Okumura C, Okuhara Y, Magae J, et al:
Bone-marrow-derived myofibroblasts contribute to the cancer-induced
stromal reaction. Biochem Biophys Res Commun. 309:232–240. 2003.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
38
|
Iwano M, Plieth D, Danoff TM, Xue C, Okada
H and Neilson EG: Evidence that fibroblasts derive from epithelium
during tissue fibrosis. J Clin Invest. 110:341–350. 2002.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
39
|
Powell DW, Adegboyega PA, Di Mari JF and
Mifflin RC: Epithelial cells and their neighbors I. Role of
intestinal myofibroblasts in development, repair, and cancer. Am J
Physiol Gastrointest Liver Physiol. 289:G2–G7. 2005. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
40
|
Worthley DL, Giraud AS and Wang TC:
Stromal fibroblasts in digestive cancer. Cancer Microenviron.
3:117–125. 2010. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
41
|
Paland N, Kamer I, Kogan-Sakin I, Madar S,
Goldfinger N and Rotter V: Differential influence of normal and
cancer-associated fibroblasts on the growth of human epithelial
cells in an in vitro cocultivation model of prostate cancer. Mol
Cancer Res. 7:1212–1223. 2009. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
42
|
Fuyuhiro Y, Yashiro M, Noda S, Kashiwagi
S, Matsuoka J, Doi Y, Kato Y, Hasegawa T, Sawada T and Hirakawa K:
Upregulation of cancer-associated myofibroblasts by TGF-beta from
scirrhous gastric carcinoma cells. Br J Cancer. 105:996–1001. 2011.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
43
|
Higashino N, Koma YI, Hosono M, Takase N,
Okamoto M, Kodaira H, Nishio M, Shigeoka M, Kakeji Y and Yokozaki
H: Fibroblast activation protein-positive fibroblasts promote tumor
progression through secretion of CCL2 and interleukin-6 in
esophageal squamous cell carcinoma. Lab Invest. Jan 25–2019.(Epub
ahead of print). doi: 10.1038/s41374-018-0185-6. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
44
|
Ebbing EA, van der Zalm AP, Steins A,
Creemers A, Hermsen S, Rentenaar R, Klein M, Waasdorp C, Hooijer
GKJ, Meijer SL, et al: Stromal-derived interleukin 6 drives
epithelial-to-mesenchymal transition and therapy resistance in
esophageal adenocarcinoma. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA. 116:2237–2242.
2019. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|