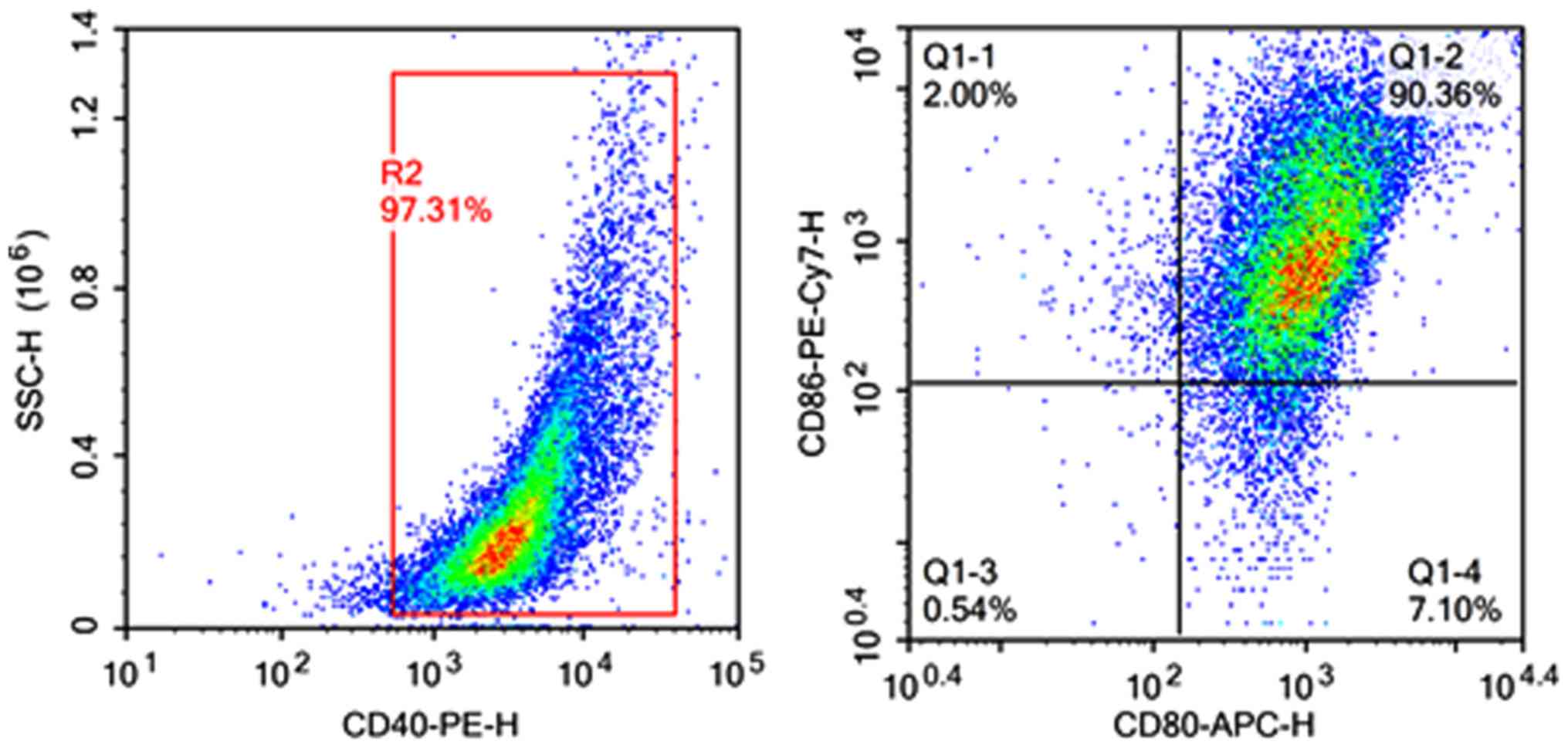
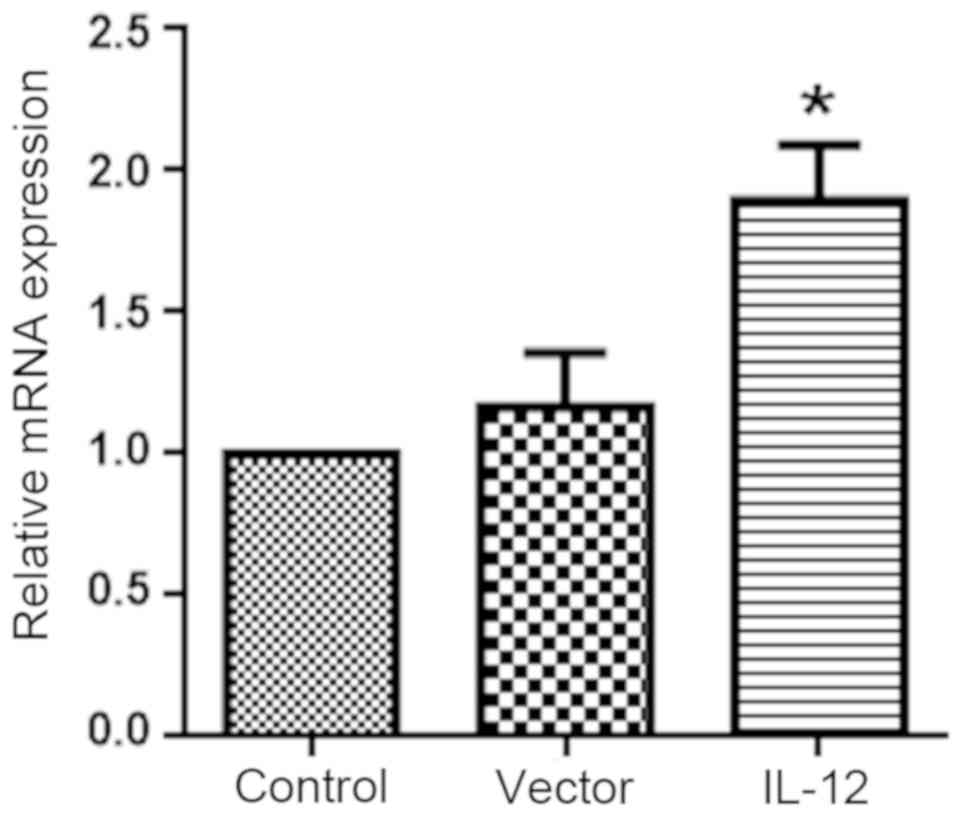
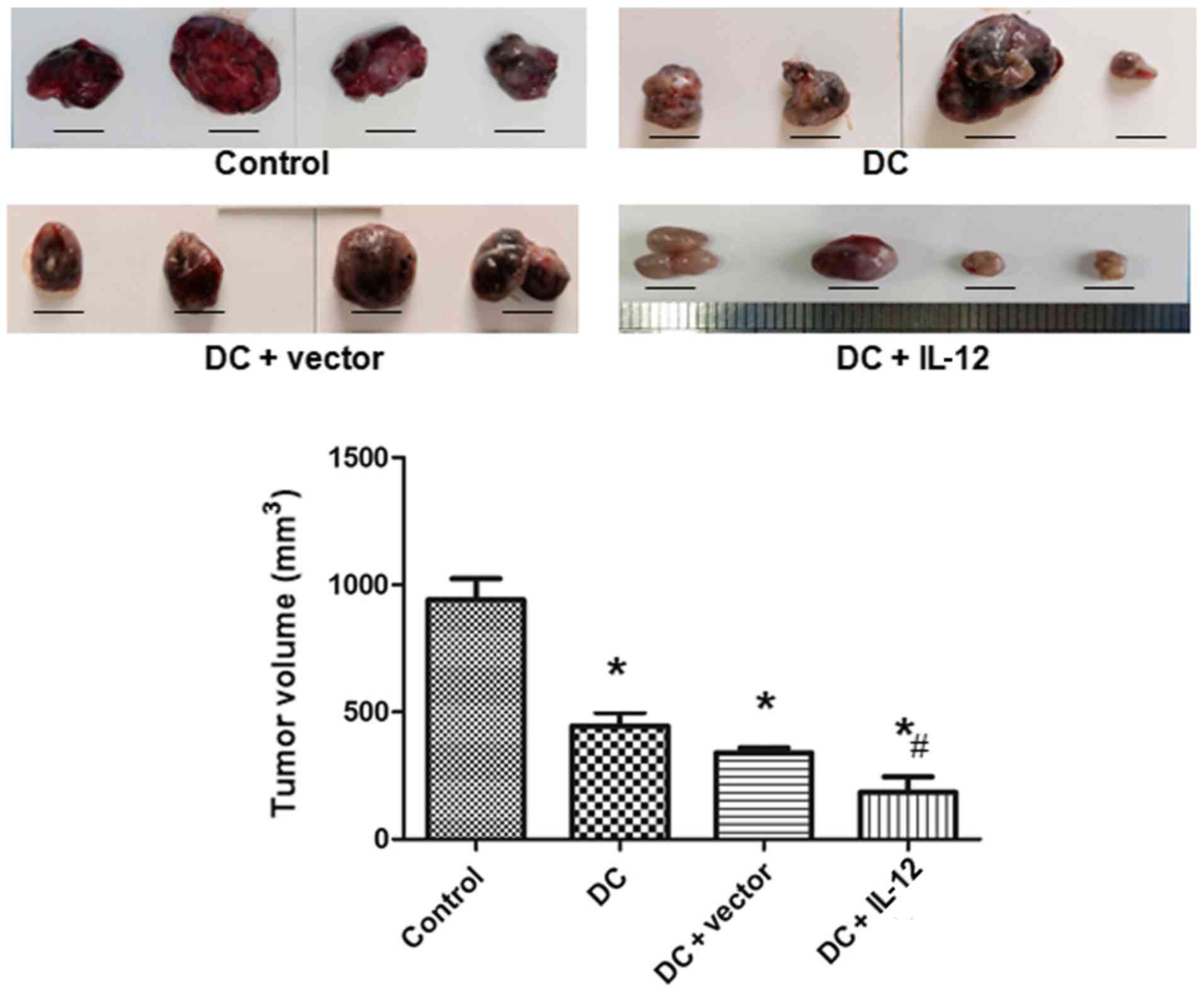
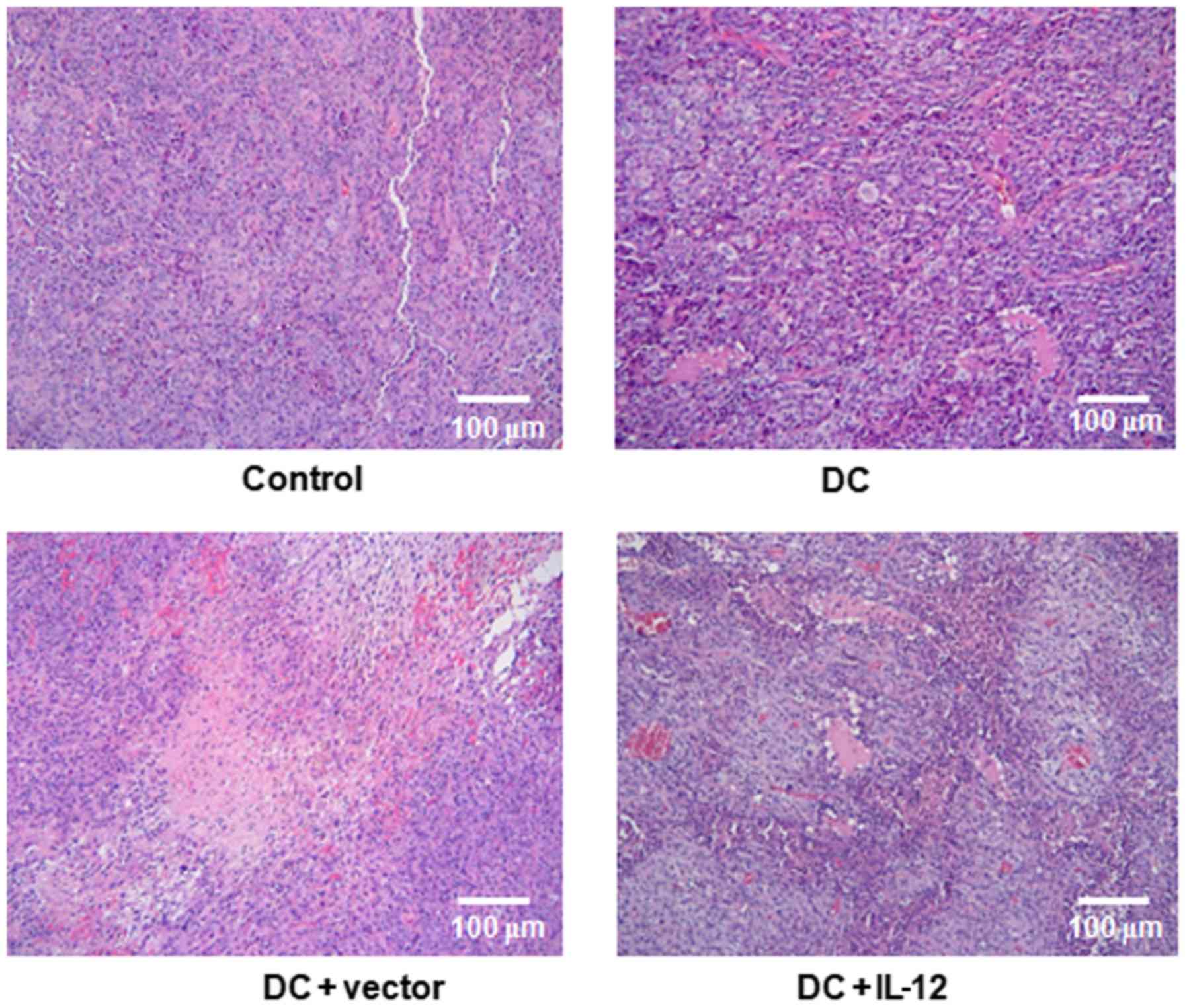
|
1
|
Thomson CH, Cassell O, Peach H, Holloway
S, Garioch J and Moncrieff M: Neuropathic pain and quality of life
after wide local excision and sentinel lymph node biopsy for
melanoma: A multicentre study. Melanoma Res. 27:121–125. 2017.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
2
|
de Vries IJ, Lesterhuis WJ, Barentsz JO,
Verdijk P, van Krieken JH, Boerman OC, Oyen WJ, Bonenkamp JJ,
Boezeman JB, Adema GJ, et al: Magnetic resonance tracking of
dendritic cells in melanoma patients for monitoring of cellular
therapy. Nat Biotechnol. 23:1407–1413. 2005. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
3
|
Cheng Y, Ma XL, Wei YQ and Wei XW:
Potential roles and targeted therapy of the CXCLs/CXCR2 axis in
cancer and inflammatory diseases. Biochim Biophys Acta Rev Cancer.
1871:289–312. 2019. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
4
|
Barry RJ, Tallouzi MO, Bucknall N, Mathers
JM, Murray PI, Calvert MJ, Moore DJ and Denniston AK: Anti-tumour
necrosis factor biological therapies for the treatment of uveitic
macular oedema (UMO) for non-infectious uveitis. Cochrane Database
Syst Rev. 12:CD0125772018.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
5
|
Mandalà M and Rutkowski P: Rational
combination of cancer immunotherapy in melanoma. Virchows Arch.
474:433–447. 2019. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
6
|
Summerfield A and McCullough KC: Dendritic
cells in innate and adaptive immune responses against influenza
virus. Viruses. 1:1022–1034. 2009. View
Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
7
|
Mellman I: Dendritic cells: Master
regulators of the immune response. Cancer Immunol Res. 1:145–149.
2013. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
8
|
Liu J, Cao S, Kim S, Chung EY, Homma Y,
Guan X, Jimenez V and Ma X: Interleukin-12: An update on its
immunological activities, signaling and regulation of gene
expression. Curr Immunol Rev. 1:119–137. 2005. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
9
|
Lasek W, Zagożdżon R and Jakobisiak M:
Interleukin-12: Still a promising candidate for tumor
immunotherapy? Cancer Immunol Immunother. 63:419–435. 2014.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
10
|
Tagawa T, Albanese M, Bouvet M, Moosmann
A, Mautner J, Heissmeyer V, Zielinski C, Lutter D, Hoser J,
Hastreiter M, et al: Epstein-Barr viral miRNAs inhibit antiviral
CD4+ T cell responses targeting IL-12 and peptide
processing. J Exp Med. 213:2065–2080. 2016. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
11
|
Cemazar M, Ambrozic Avgustin J, Pavlin D,
Sersa G, Poli A, Krhac Levacic A, Tesic N, Lampreht Tratar U, Rak M
and Tozon N: Efficacy and safety of electrochemotherapy combined
with peritumoral IL-12 gene electrotransfer of canine mast cell
tumours. Vet Comp Oncol. 15:641–654. 2017. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
12
|
Komai-Koma M, Wang E, Kurowska-Stolarska
M, Li D, McSharry C and Xu D: Interleukin-33 promoting Th1
lymphocyte differentiation dependents on IL-12. Immunobiol.
221:412–417. 2016. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
13
|
Lu X: Impact of IL-12 in cancer. Curr
Cancer Drug Target. 17:682–697. 2017. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
14
|
Li L, Jiang Y, Lao S, Yang B, Yu S, Zhang
Y and Wu C: Mycobacterium tuberculosis-Specific
IL-21+IFN-γ+CD4+ T cells are
regulated by IL-12. PLoS One. 11:e01473562016. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
15
|
Feng C, Feng M, Jiao R, Liu D, Jin Y, Zhao
X and Xiao R: Effect of Dezocine on IL-12 and IL-10 secretion and
lymphocyte activation by culturing dendritic cells from human
umbilical cord blood. Europ J Pharmacol. 796:110–114. 2017.
View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
16
|
Thada S, Ponnana M, Sivangala R, Joshi L,
Alasandagutti M, Ansari MS, Schumann RR, Valluri V and Gaddam S:
Polymorphisms of IFN-γ (+874A/T) and IL-12 (+1188A/C) in
tuberculosis patients and their household contacts in Hyderabad,
India. Hum Immunol. 77:559–565. 2016. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
17
|
Naito S, von Eschenbach AC, Giavazzi R and
Fidler IJ: Growth and metastasis of tumor cells isolated from a
human renal cell carcinoma implanted into different organs of nude
mice. Cancer Res. 46:4109–4115. 1986.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
18
|
Livak KJ and Schmittgen TD: Analysis of
relative gene expression data using real-time quantitative PCR and
the 2(-Delta Delta C(T)) method. Methods. 25:402–408. 2001.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
19
|
Ribas A, Hamid O, Daud A, Hodi FS, Wolchok
JD, Kefford R, Joshua AM, Patnaik A, Hwu WJ, Weber JS, et al:
Association of pembrolizumab with tumor response and survival among
patients with advanced melanoma. JAMA. 315:1600–1609. 2016.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
20
|
See P, Dutertre CA, Chen J, Günther P,
McGovern N, Irac SE, Gunawan M, Beyer M, Händler K, Duan K, et al:
Mapping the human DC lineage through the integration of
high-dimensional techniques. Science. 356:eaag30092017. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
21
|
Bhattacharya P, Thiruppathi M, Elshabrawy
HA, Alharshawi K, Kumar P and Prabhakar BS: GM-CSF: An immune
modulatory cytokine that can suppress autoimmunity. Cytokine.
75:261–271. 2015. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
22
|
Deng J, Li Y, Pennati A, Yuan S, Wu JH,
Waller EK and Galipeau J: GM-CSF and IL-4 fusion cytokine induces B
cell-dependent hematopoietic regeneration. Mol Ther. 25:416–426.
2017. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
23
|
Lutz MB, Suri RM, Niimi M, Ogilvie AL,
Kukutsch NA, Rössner S, Schuler G and Austyn JM: Immature dendritic
cells generated with low doses of GM-CSF in the absence of IL-4 are
maturation resistant and prolong allograft survival in vivo. Eur J
Immunol. 30:1813–1822. 2000. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
24
|
Fukao T, Tanabe M, Terauchi Y, Ota T,
Matsuda S, Asano T, Kadowaki T, Takeuchi T and Koyasu S:
PI3K-mediated negative feedback regulation of IL-12 production in
DCs. Nat Immunol. 3:875–881. 2002. View
Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
25
|
Kamensek U, Cemazar M, Lampreht Tratar U,
Ursic K and Sersa G: Antitumor in situ vaccination effect of TNFα
and IL-12 plasmid DNA electrotransfer in a murine melanoma model.
Cancer Immunol Immunother. 67:785–795. 2018. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
26
|
Oliveira Brito PK, Goncalves TE, Fernandes
FF, Miguel CB, Rodrigues WF, Lazo Chica JE, Roque-Barreira MC and
da Silva TA: Systemic effects in naïve mice injected with
immunomodulatory lectin ArtinM. PLoS One. 12:e01871512017.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
27
|
Sonabend AM, Velicu S, Ulasov IV, Han Y,
Tyler B, Brem H, Matar MM, Fewell JG, Anwer K and Lesniak MS: A
safety and efficacy study of local delivery of interleukin-12
transgene by PPC polymer in a model of experimental glioma.
Anticancer Drugs. 19:133–142. 2008. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
28
|
Kobiyama K, Temizoz B, Kanuma T, Ozasa K,
Momota M, Yamamoto T, Aoshi T, Kuroda E and Ishii KJ:
Species-dependent role of type I IFNs and IL-12 in the CTL response
induced by humanized CpG complexed with β-glucan. Eur J Immunol.
46:1142–1151. 2016. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
29
|
Yoshimoto T, Yasuda K, Tanaka H, Nakahira
M, Imai Y, Fujimori Y and Nakanishi K: Basophils contribute to
T(H)2-IgE responses in vivo via IL-4 production and presentation of
peptide-MHC class II complexes to CD4+ T cells. Nat
Immunol. 10:706–712. 2009. View
Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
30
|
Yeap WH, Wong KL, Shimasaki N, Teo EC,
Quek JK, Yong HX, Diong CP, Bertoletti A, Linn YC and Wong SC: CD16
is indispensable for antibody-dependent cellular cytotoxicity by
human monocytes. Sci Rep. 6:343102016. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
31
|
Helmy A, Guilfoyle MR, Carpenter KLH,
Pickard JD, Menon DK and Hutchinson PJ: Recombinant human
interleukin-1 receptor antagonist promotes M1 microglia biased
cytokines and chemokines following human traumatic brain injury. J
Cereb Blood Flow Metab. 36:1434–1448. 2016. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
32
|
Lee HL, Park MH, Song JK, Jung YY, Kim Y,
Kim KB, Hwang DY, Yoon do Y, Song MJ, Han SB and Hong JT: Tumor
growth suppressive effect of IL-4 through p21-mediated activation
of STAT6 in IL-4Rα overexpressed melanoma models. Oncotarget.
7:23425–23438. 2016.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
33
|
Sznol M: Betting on immunotherapy for
melanoma. Curr Oncol Rep. 11:397–404. 2009. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|