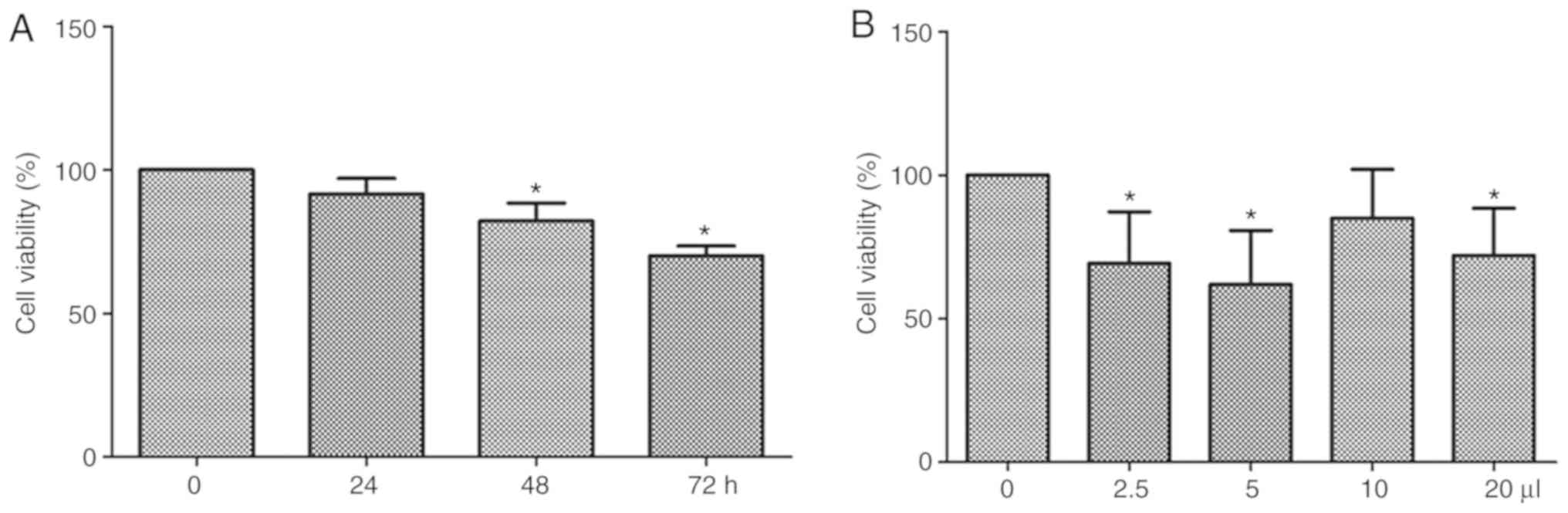
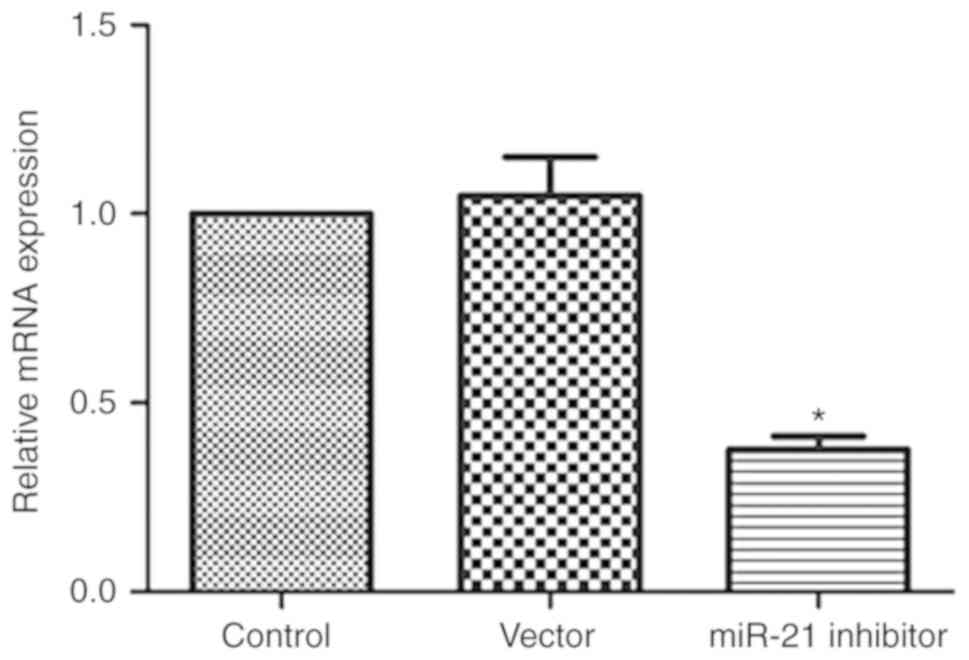
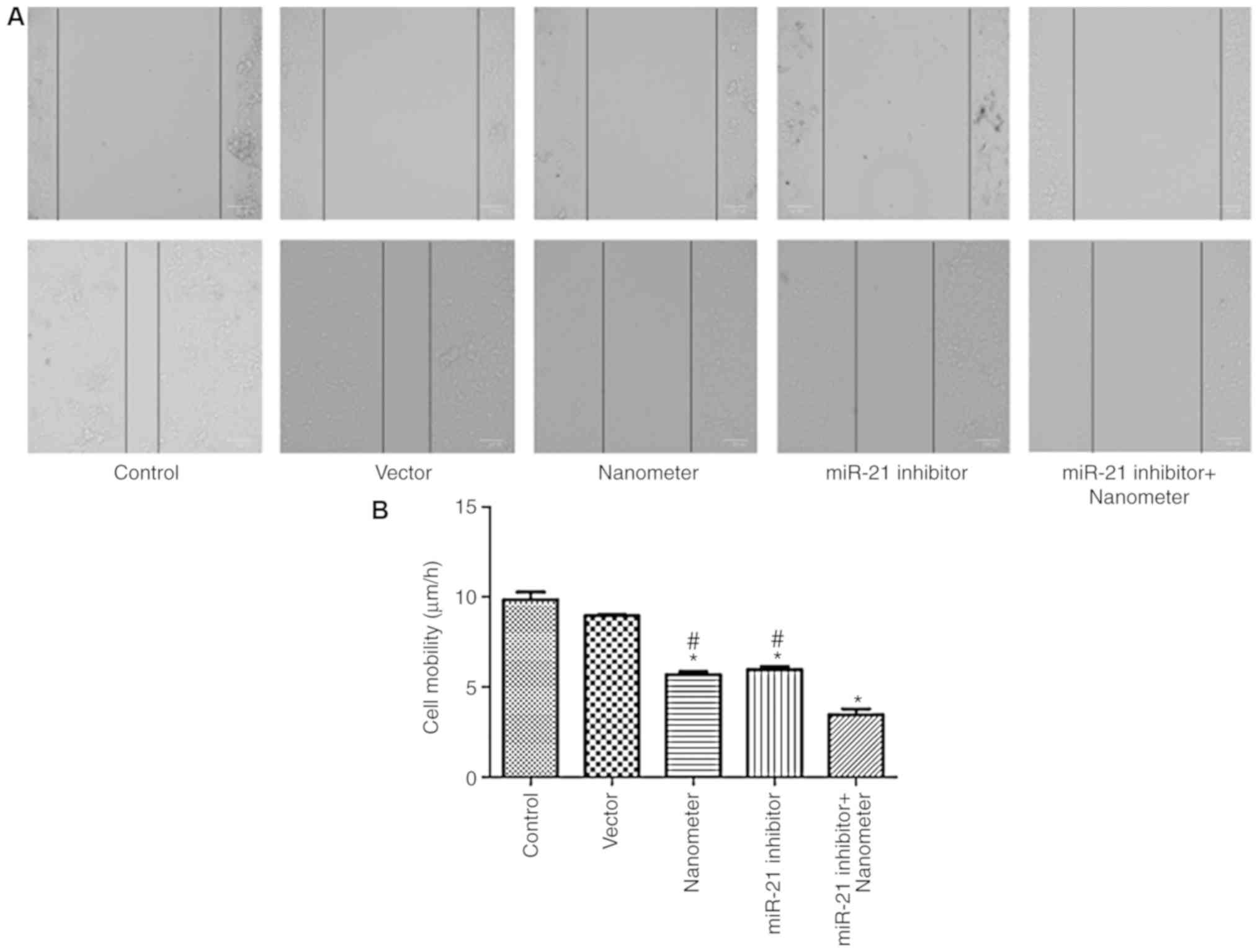
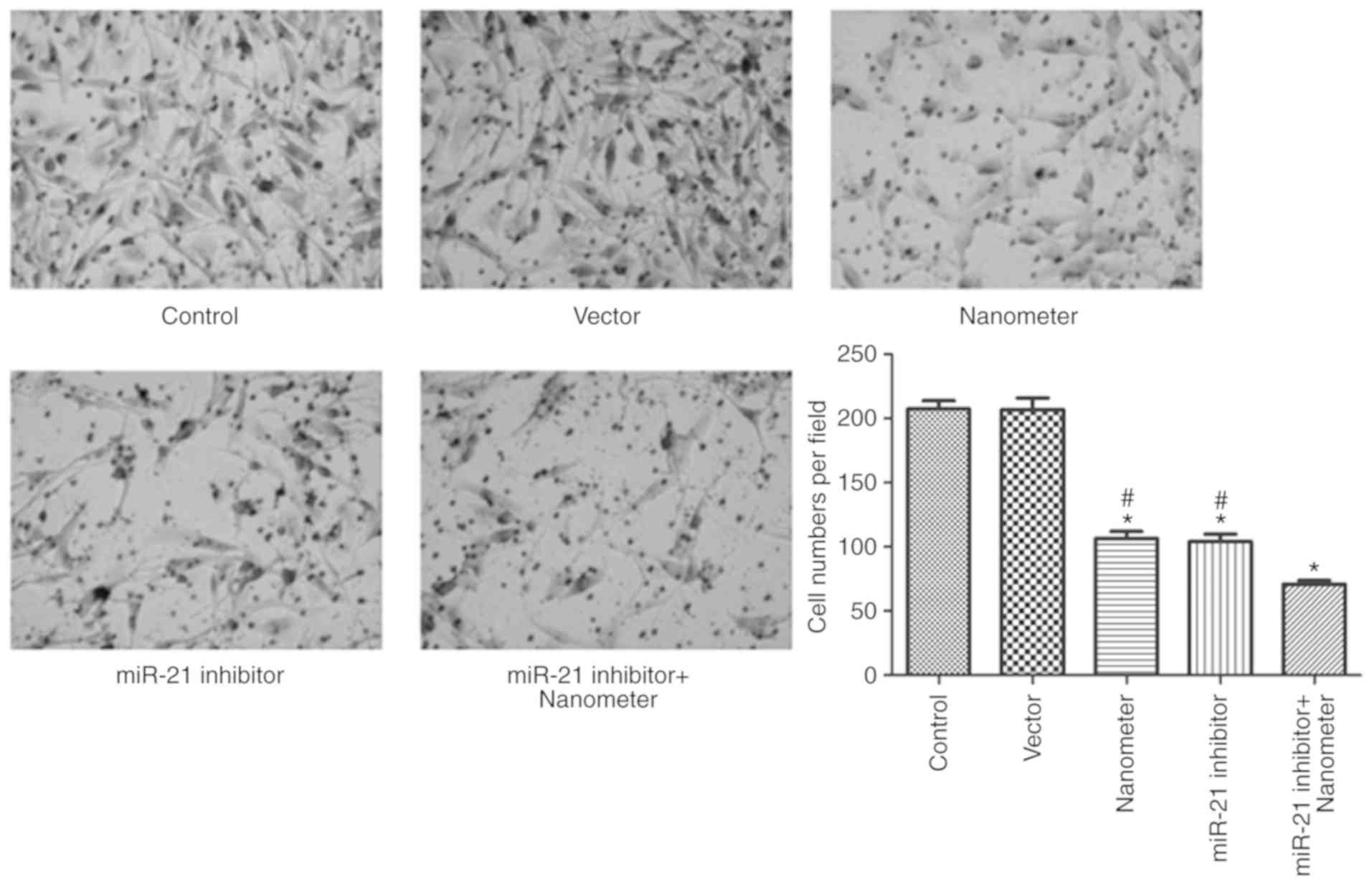
|
1
|
Gopalani SV, Janitz AE and Campbell JE:
Trends in cervical cancer incidence and mortality in Oklahoma and
the United States, 1999–2013. Cancer Epidemiol. 56:140–145. 2018.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
2
|
Gunda D, Kido I, Kilonzo S, Nkandala I,
Igenge J and Mpondo B: Prevalence and associated factors of
incidentally diagnosed prostatic carcinoma among patients Who had
transurethral prostatectomy in Tanzania: A retrospective study.
Ethiop J Health Sci. 28:11–18. 2018. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
3
|
Lv Y, Song Y, Ni C, Wang S, Chen Z, Shi X,
Jiang Q, Cao C and Zuo Y: Overexpression of lymphocyte antigen 6
complex, locus E in gastric cancer promotes cancer cell growth and
metastasis. Cell Physiol Biochem. 45:1219–1229. 2018. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
4
|
Hasan S, Taha R and Omri HE: Current
opinions on chemoresistance: An overview. Bioinformation. 14:80–85.
2018. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
5
|
Wu X, Xing X, Dowlut D, Zeng Y, Liu J and
Liu X: Integrating phosphoproteomics into kinase-targeted cancer
therapies in precision medicine. J Proteomics. 191:68–79. 2019.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
6
|
Jindal AB, Bachhav SS and Devarajan PV: In
situ hybrid nano drug delivery system (IHN-DDS) of antiretroviral
drug for simultaneous targeting to multiple viral reservoirs: An in
vivo proof of concept. Int J Pharm. 521:196–203. 2017. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
7
|
Ma X, Gong N, Zhong L, Sun J and Liang XJ:
Future of nanotherapeutics: Targeting the cellular sub-organelles.
Biomaterials. 97:10–21. 2016. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
8
|
Ying M, Chen G and Lu W: recent advances
and strategies in tumor vasculature targeted nano-drug delivery
systems. Curr Pharm Des. 21:3066–3075. 2015. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
9
|
Garg T, Bhandari S, Rath G and Goyal AK:
Current strategies for targeted delivery of bio-active drug
molecules in the treatment of brain tumor. J Drug Target.
23:865–887. 2015. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
10
|
Huang Y, Liu W, Gao F, Fang X and Chen Y:
c(RGDyK)-decorated Pluronic micelles for enhanced doxorubicin and
paclitaxel delivery to brain glioma. Int J Nanomedicine.
11:1629–1641. 2016.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
11
|
Chen Y, Zhang W, Huang Y, Gao F, Sha X and
Fang X: Pluronic-based functional polymeric mixed micelles for
co-delivery of doxorubicin and paclitaxel to multidrug resistant
tumor. Int J Pharm. 488:44–58. 2015. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
12
|
Yang Z, Luo X, Zhang X, Liu J and Jiang Q:
Targeted delivery of 10-hydroxycamptothecin to human breast cancers
by cyclic RGD-modified lipid-polymer hybrid nanoparticles. Biomed
Mater. 8:0250122013. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
13
|
Bohme D and Beck-Sickinger AG: Drug
delivery and release systems for targeted tumor therapy. J Pept
Sci. 21:186–200. 2015. View
Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
14
|
Ooi CY, Carter DR, Liu B, Mayoh C, Beckers
A, Lalwani A, Nagy Z, De Brouwer S, Decaesteker B, Hung TT, et al:
Network modeling of microRNA-mRNA interactions in neuroblastoma
tumorigenesis identifies miR-204 as a direct inhibitor of MYCN.
Cancer Res. 78:3122–3134. 2018.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
15
|
Li M, Zhang F, Su Y, Zhou J and Wang W:
Nanoparticles designed to regulate tumor microenvironment for
cancer therapy. Life Sci. 201:37–44. 2018. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
16
|
Nogales-Cadenas R, Cai Y, Lin JR, Zhang Q,
Zhang W, Montagna C and Zhang ZD: MicroRNA expression and gene
regulation drive breast cancer progression and metastasis in PyMT
mice. Breast Cancer Res. 18:752016. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
17
|
Ghosal S, Saha S, Das S, Sen R, Goswami S,
Jana SS and Chakrabarti J: miRepress: Modelling gene expression
regulation by microRNA with non-conventional binding sites. Sci
Rep. 6:223342016. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
18
|
Wandler A, Riber-Hansen R, Hager H,
Hamilton-Dutoit SJ, Schmidt H, Nielsen BS, Stougaard M and
Steiniche T: Quantification of microRNA-21 and microRNA-125b in
melanoma tissue. Melanoma Res. 27:417–428. 2017. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
19
|
Hermansen SK, Dahlrot RH, Nielsen BS,
Hansen S and Kristensen BW: MiR-21 expression in the tumor cell
compartment holds unfavorable prognostic value in gliomas. J
Neurooncol. 111:71–81. 2013. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
20
|
Guo L, Ding W and Zheng LM: The
C(RgdyK)-conjugated Fe3O4 nanoparticles with high drug load for
dual-targeting integrin alpha(v)beta3-expressing cancer cells. J
Nanosci Nanotechnol. 14:4858–4864. 2014. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
21
|
Livak KJ and Schmittgen TD: Analysis of
relative gene expression data using real-time quantitative PCR and
the 2(-Delta Delta C(T)) method. Methods. 25:402–408. 2001.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
22
|
Yamamoto A: Recent therapeutic strategies
for metastatic melanoma: Introduction to invited articles. Int J
Clin Oncol. Apr 6–2018.(Epub ahead of print). View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
23
|
Kim IK, Lane AM, Jain P, Awh C and
Gragoudas ES: Ranibizumab for the prevention of radiation
complications in patients treated with proton beam irradiation for
choroidal melanoma. Trans Am Ophthalmol Soc. 114:T22016.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
24
|
Mohamed AA, Richards CJ, Boyle K and Faust
G: Severe inflammatory ileitis resulting in ileal perforation in
association with combination immune checkpoint blockade for
metastatic malignant melanoma. BMJ Case Rep. 2018(pii): bcr
2018-224913 2018.
|
|
25
|
Neto OV, Raymundo S, Franzoi MA, do Carmo
Artmann A, Tegner M, Müller VV, Hahn RZ, Alves GV, Schwartsmann G,
Linden R and Antunes MV: DPD functional tests in plasma, fresh
saliva and dried saliva samples as predictors of 5-fluorouracil
exposure and occurrence of drug-related severe toxicity. Clin
Biochem. 56:18–25. 2018. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
26
|
Lin C, Zhang X, Chen H, Bian Z, Zhang G,
Riaz MK, Tyagi D, Lin G, Zhang Y, Wang J, et al: Dual-ligand
modified liposomes provide effective local targeted delivery of
lung-cancer drug by antibody and tumor lineage-homing
cell-penetrating peptide. Drug Deliv. 25:256–266. 2018. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
27
|
Ke X, Lin W, Li X, Wang H, Xiao X and Guo
Z: Synergistic dual-modified liposome improves targeting and
therapeutic efficacy of bone metastasis from breast cancer. Drug
Deliv. 24:1680–1689. 2017. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
28
|
Belhadj Z, Zhan C, Ying M, Wei X, Xie C,
Yan Z and Lu W: Multifunctional targeted liposomal drug delivery
for efficient glioblastoma treatment. Oncotarget. 8:66889–66900.
2017. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
29
|
Zhang HL, Si LB, Zeng A, Long F, Qi Z,
Zhao R and Bai M: MicroRNA-21 antisense oligonucleotide improves
the sensitivity of A375 human melanoma cell to Cisplatin: An in
vitro study. J Cell Biochem. 119:3129–3141. 2018. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
30
|
Lin KY, Chen CM, Lu CY, Cheng CY and Wu
YH: Regulation of miR-21 expression in human melanoma via
UV-ray-induced melanin pigmentation. Environ Toxicol. 32:2064–2069.
2017. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
31
|
Cifdaloz M, Osterloh L, Graña O,
Riveiro-Falkenbach E, Ximénez-Embún P, Muñoz J, Tejedo C, Calvo TG,
Karras P, Olmeda D, et al: Systems analysis identifies
melanoma-enriched pro-oncogenic networks controlled by the RNA
binding protein CELF1. Nat Commun. 8:22492017. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
32
|
Juliano RL, Ming X, Nakagawa O, Xu R and
Yoo H: Integrin targeted delivery of gene therapeutics.
Theranostics. 1:211–219. 2011. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
33
|
Jiang X, Sha X, Xin H, Chen L, Gao X, Wang
X, Law K, Gu J, Chen Y, Jiang Y, et al: Self-aggregated pegylated
poly (trimethylene carbonate) nanoparticles decorated with c(RGDyK)
peptide for targeted paclitaxel delivery to integrin-rich tumors.
Biomaterials. 32:9457–9469. 2011. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
34
|
Qiu L, Hu Q, Cheng L, Li L, Tian C, Chen
W, Chen Q, Hu W, Xu L, Yang J, et al: cRGDyK modified pH responsive
nanoparticles for specific intracellular delivery of doxorubicin.
Acta Biomater. 30:285–298. 2016. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
35
|
Chen Y, Zhang W, Huang Y, Gao F and Fang
X: In vivo biodistribution and anti-tumor efficacy evaluation of
doxorubicin and paclitaxel-loaded pluronic micelles decorated with
c(RGDyK) peptide. PLoS One. 11:e01499522016. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
36
|
Ribas J and Lupold SE: The transcriptional
regulation of miR-21, its multiple transcripts, and their
implication in prostate cancer. Cell Cycle. 9:923–929. 2010.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
37
|
Wang Q and Zhang L, Yuan X, Ou Y, Zhu X,
Cheng Z, Zhang P, Wu X, Meng Y and Zhang L: The relationship
between the Bcl-2/Bax proteins and the mitochondria-mediated
apoptosis pathway in the differentiation of adipose-derived stromal
cells into neurons. PLoS One. 11:e01633272016. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
38
|
Fan Y, Yang F, Cao X, Chen C, Zhang X,
Zhang X, Lin W, Wang X and Liang C: Gab1 regulates SDF-1-induced
progression via inhibition of apoptosis pathway induced by
PI3K/AKT/Bcl-2/BAX pathway in human chondrosarcoma. Tumour Biol.
37:1141–1149. 2016. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
39
|
Ou X, Lu Y, Liao L, Li D, Liu L, Liu H and
Xu H: Nitidine chloride induces apoptosis in human hepatocellular
carcinoma cells through a pathway involving p53, p21, Bax and
Bcl-2. Oncol Rep. 33:1264–1274. 2015. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
40
|
Dolka I, Król M and Sapierzyński R:
Evaluation of apoptosis-associated protein (Bcl-2, Bax, cleaved
caspase-3 and p53) expression in canine mammary tumors: An
immunohistochemical and prognostic study. Res Vet Sci. 105:124–133.
2016. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
41
|
Li C, Shen J, Wei X, Xie C and Lu W:
Targeted delivery of a novel palmitylated D-peptide for
antiglioblastoma molecular therapy. J Drug Target. 20:264–271.
2012. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
42
|
Li G, Song YZ, Huang ZJ, Chen K, Chen DW
and Deng YH: Novel, nano-sized, liposome-encapsulated
polyamidoamine dendrimer derivatives facilitate tumour targeting by
overcoming the polyethylene glycol dilemma and integrin saturation
obstacle. J Drug Target. 25:734–746. 2017. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|